Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Biocides in Chao Lake and Its Tributaries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
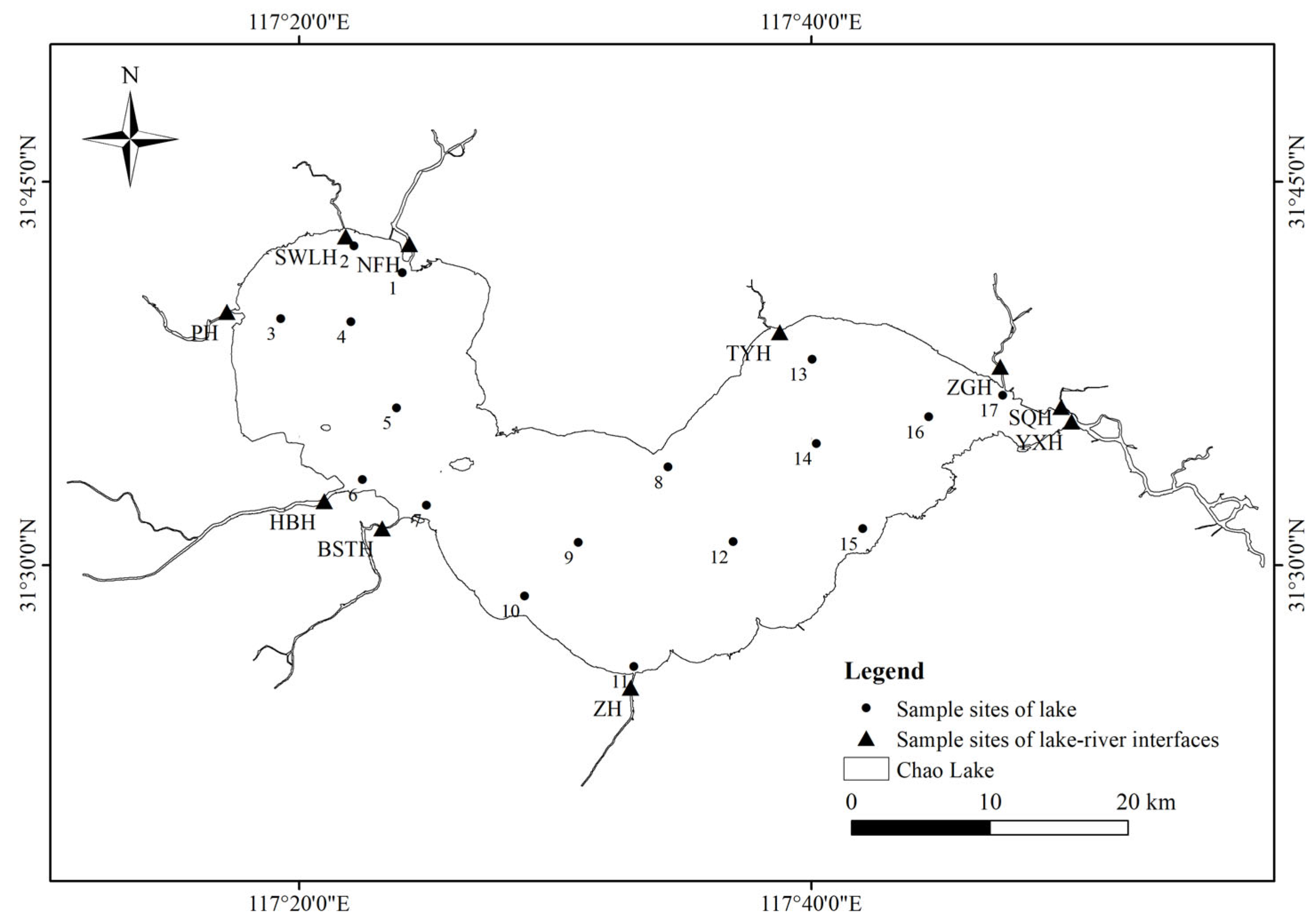
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Extraction
2.4. Instrumental Analysis and Quality Control
2.5. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.6. Human Health Risk Assessment
3. Results
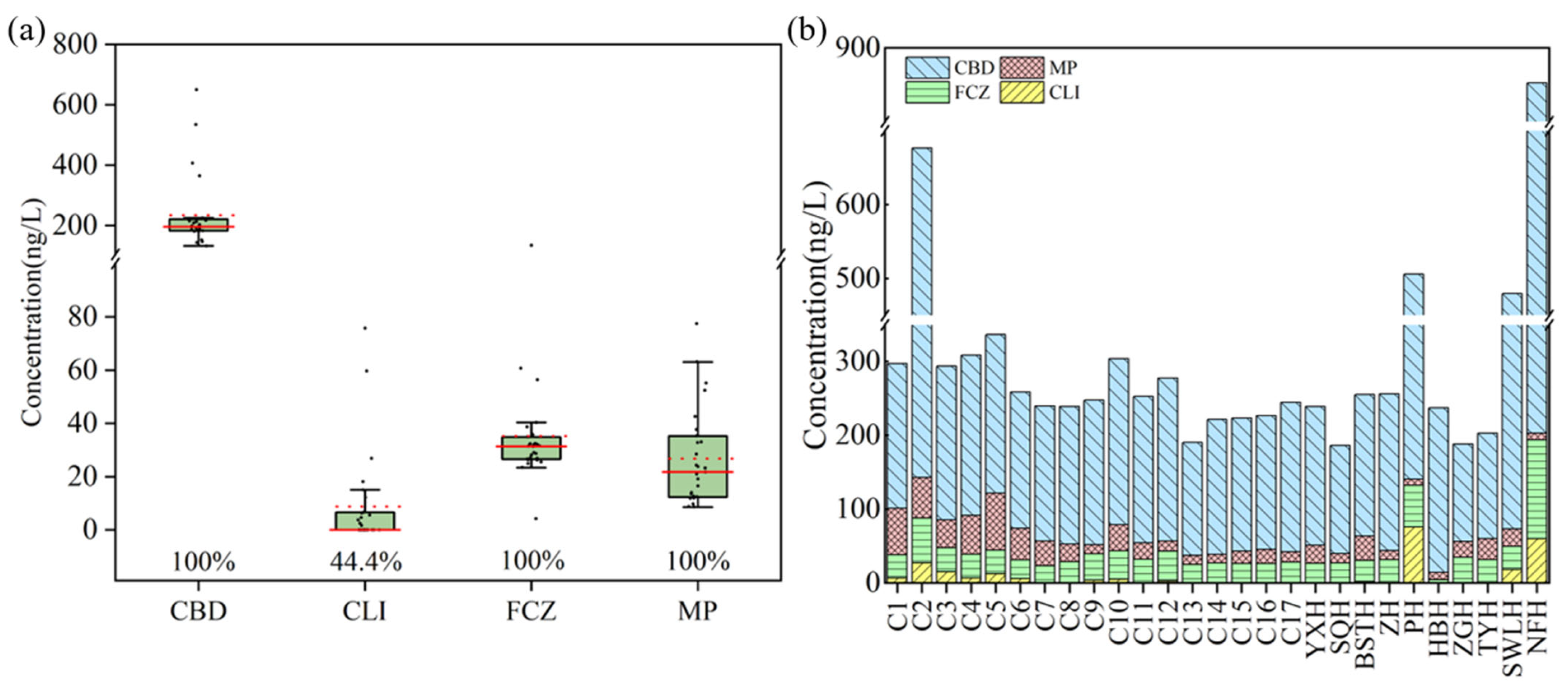
3.1. Concentrations of Biocides in Chao Lake
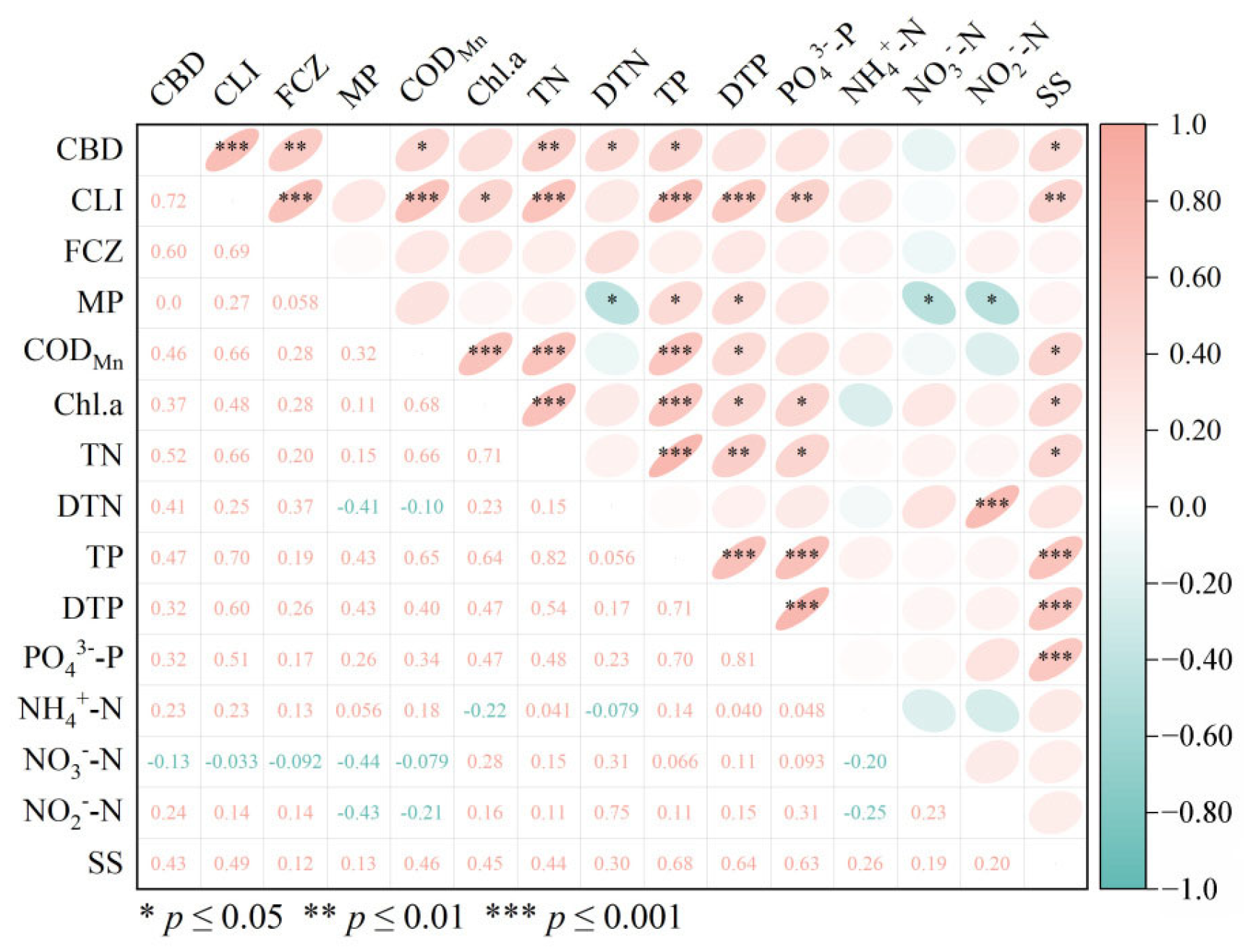
3.2. Correlations Between Biocides and Environmental Variables
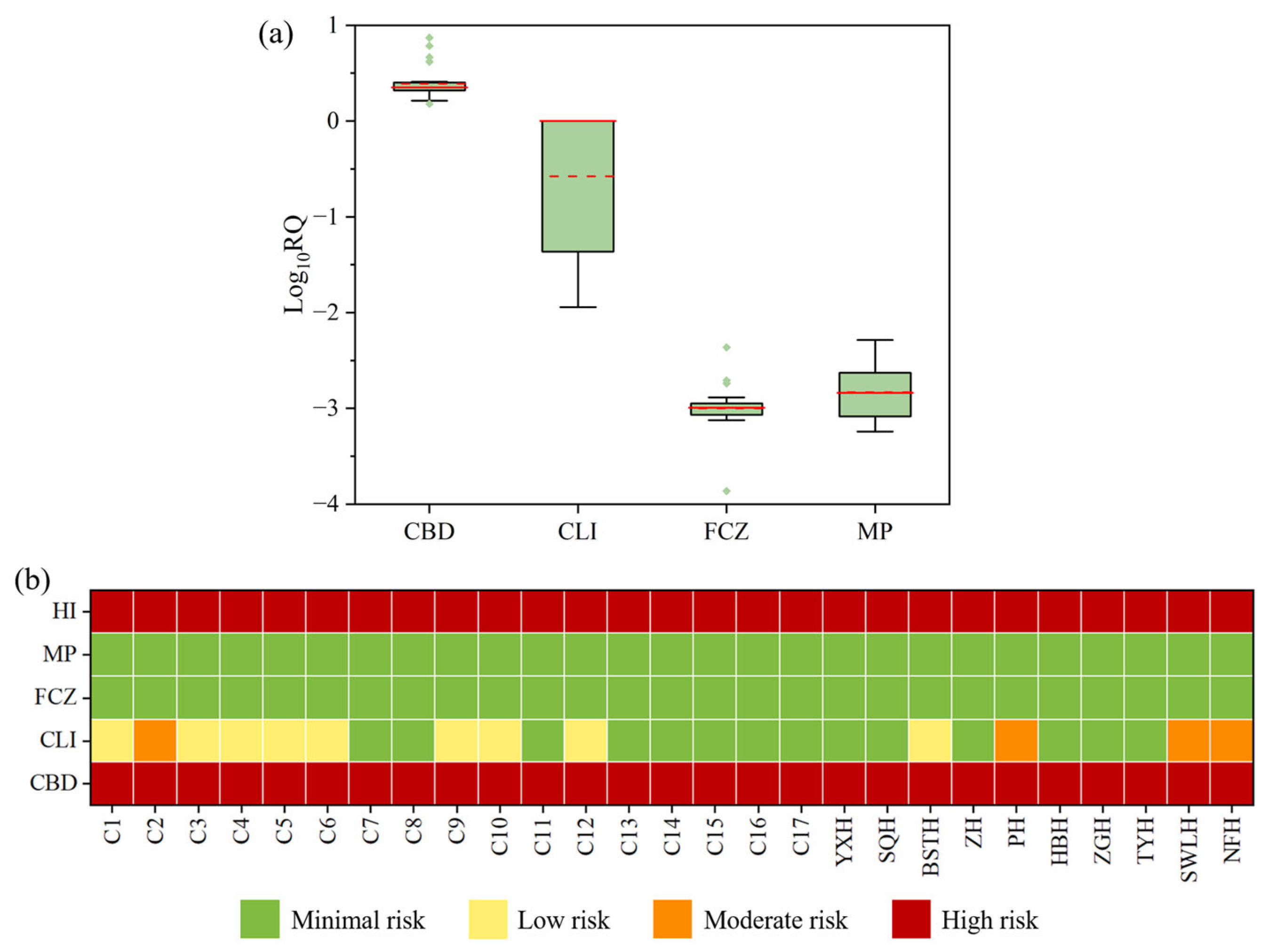
3.3. Assessment of Potential Ecological Risk
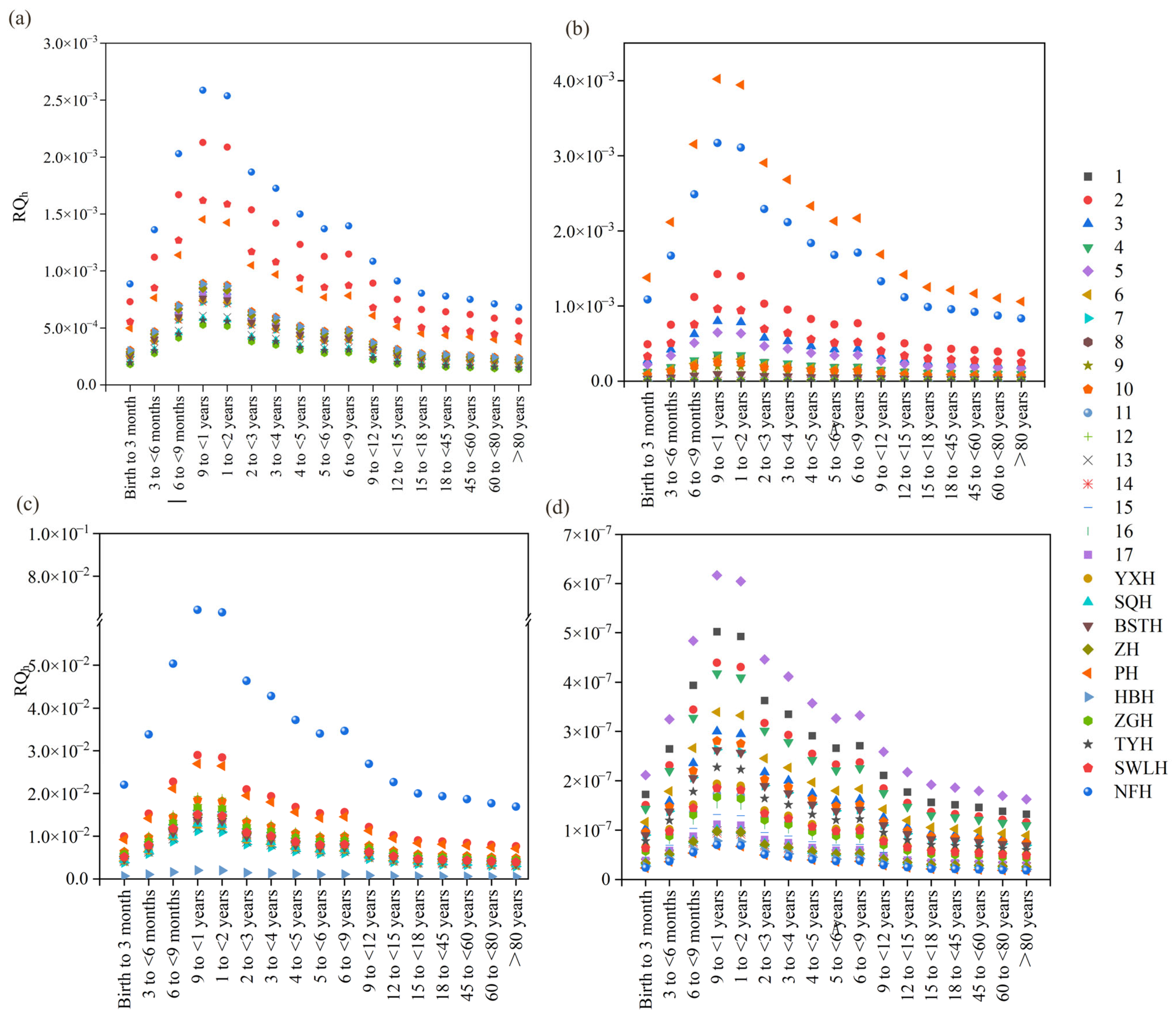
3.4. Assessment of Potential Human Health Risk
4. Discussion
4.1. Pollution Levels of Biocides in Chao Lake
4.2. Distribution Characteristics and Sources of Biocides
4.3. Risks and Management of Biocides
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBD | Carbendazim |
| CLI | Climbazole |
| MP | Methylparaben |
| FCZ | Fluconazole |
| TBD | Thiabendazole |
| CTZ | Clotrimazole |
| MCZ | Miconazole |
| RQ | Risk quotient |
| PNEC | Predicted no-effect concentrations |
| NOEC | No-observed effect concentration value |
| LC50 | Median lethal concentration |
| EC50 | Median effective concentration |
| AF | Assessment factor |
| HI | Hazard index |
| RQh | Risk quotient for human health |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| DTN | Dissolved total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| YXH | Yuxi River |
| SQH | Shuangqiao River |
| BSTH | Baishitian River |
| ZH | Zhao River |
| HBH | Hangbu River |
| ZGH | Zhegao River |
| TYH | Tongyang River |
| NFH | Nanfei River |
| PH | Pai River |
| SWLH | Shiwuli River |
References
- EC (European Commission) Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (Biocidal Products Directive (BPD) 98/8/EC). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/1998/8/oj/eng (accessed on 17 October 2025).
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Lai, H.-J.; Chen, F.; Su, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-S.; Peng, F.-Q.; Zhao, J.-L. Determination of biocides in different environmental matrices by use of ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 3175–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, B.R.; Tang, L.J. Carbendazim residues in vegetables in China between 2014 and 2016 and a chronic carbendazim exposure risk assessment. Food Control 2018, 91, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Ho, L.; Li, S.; Doherty, J.; Lee, J.; Clark, J.M.; He, L. Efficacy of Household and Commercial Washing Agents in Removing the Pesticide Thiabendazole Residues from Fruits. Foods 2025, 14, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, E.; Wick, A.; Ternes, T.A.; Coors, A. Ecotoxicity of climbazole, a fungicide contained in antidandruff shampoo. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, K.W.; Coakley, A.J.; Jezequel, S.G.; Tarbit, M.H. The Disposition and Metabolism of [14C] Fluconazole in Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1991, 19, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letzel, M.; Metzner, G.; Letzel, T. Exposure assessment of the pharmaceutical diclofenac based on long-term measurements of the aquatic input. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC (European Commission). Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2020/1161. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2020, 257, 35. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dec_impl/2020/1161/oj (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Azeredo, D.B.C.; Sousa Anselmo, D.d.; Falcão Veríssimo, A.C.; Souza, L.L.d.; Lisboa, P.C.; Soares, P.; Santos-Silva, A.P.; Graceli, J.B.; Carvalho, D.P.d.; Magliano, D.A.; et al. Endocrine-disrupting chemical, methylparaben, in environmentally relevant exposure promotes hazardous effects on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2025, 598, 112444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerta, Y.T.; Guimarães, P.S.; Martins, S.E.; Martins, C.d.M.G. Toxicity of methylparaben to green microalgae species and derivation of a predicted no effect concentration (PNEC) in freshwater ecosystems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. Scrutinizing pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 392A–399A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Granger, C.; Dong, H.; Mao, Y.; Duan, S.; Li, J.; Qiang, Z. Occurrences of 29 pesticides in the Huangpu River, China: Highest ecological risk identified in Shanghai metropolitan area. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, X.; Huang, R.; Xu, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, A.; et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of azole fungicides during the urban water cycle: A year-long study along the Yangtze River, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 141, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, S.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Sultana, T.; Amé, M.V.; Menone, M.L. Pesticides in Surface Waters in Argentina Monitored Using Polar Organic Chemical Integrative Samplers. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 104, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tran, T.M.; Nguyen, V.T.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Kannan, K. Neonicotinoids, fipronil, chlorpyrifos, carbendazim, chlorotriazines, chlorophenoxy herbicides, bentazon, and selected pesticide transformation products in surface water and drinking water from northern Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, S.-S.; Chen, J.; Peng, F.-J.; Lai, H.-J.; Pan, C.-G. Triclosan as a surrogate for household biocides: An investigation into biocides in aquatic environments of a highly urbanized region. Water Res. 2014, 58, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montone, C.M.; Giannelli Moneta, B.; Aita, S.E.; Aulenta, F.; Cavaliere, C.; Cerrato, A.; Fazi, S.; Laganà, A.; Paolini, V.; Petracchini, F.; et al. Untargeted analysis of contaminants in river water samples: Comparison between two different sorbents for solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry determination. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.-F.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Ying, G.-G. Biocides in the Yangtze River of China: Spatiotemporal distribution, mass load and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Li, H.; Luo, Z.; Lin, H.; Yang, Z. Occurrence, distribution, and environmental risk of four categories of personal care products in the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27524–27534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.A.; Davies, P.J.; McRae, C. The occurrence of methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl parabens in the urban rivers and stormwaters of Sydney, Australia. Environ. Sci. Wat. Res. 2016, 2, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Guo, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, M. Carbendazim: Ecological risks, toxicities, degradation pathways and potential risks to human health. Chemosphere 2023, 314, 137723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchika, G.K.; Naik, B.K.; Ramana, G.V.V.; Nirupama, R.; Ranjani, T.S.; Venkaiah, K.; Reddy, M.H.; Sainath, S.B.; Pradeepkiran, J.A. Transcriptomic profile in carbendazim-induced developmental defects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos/larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 280, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.R.; Cardoso, D.N.; Cruz, A.; Lourenço, J.; Mendo, S.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of a binary combination of triclosan and carbendazim to Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Z.; Zhao, G.; Feng, W.B.; Yang, C.J.; Jiang, Y. Fluconazole induces cardiovascular toxicity in zebrafish by promoting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and disruption of key developmental genes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2025, 408, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xia, W.; Li, Y.; et al. Parabens exposure in early pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihama, Y.; Yoshinaga, J.; Iida, A.; Konishi, S.; Imai, H.; Yoneyama, M.; Nakajima, D.; Shiraishi, H. Association between paraben exposure and menstrual cycle in female university students in Japan. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 63, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasmahapatra, A.K.; Chatterjee, J.; Tchounwou, P.B. A systematic review of the toxic potential of parabens in fish. Front. Toxicol. 2024, 6, 1399467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Yan, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Li, Z.C.; Pang, Y. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the surface water and fishes in Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75907–75920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.L.; Yang, C.; He, W.; He, Q.S.; Li, Y.L.; Kang, L.; Liu, W.X.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Xing, B. Bias and association of sediment organic matter source apportionment indicators: A case study in a eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Geng, D.; Wei, C.; Ji, H.; Xu, H. Distribution of arsenic between the particulate and aqueous phases in surface water from three freshwater lakes in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7452–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, H.; Dong, H.; Ma, B.; Sun, H.; Pan, T.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, R.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of organic micropollutants in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China: A case study of water diversion. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-X.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Qin, N.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, B.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Jorgensen, S.E.; et al. Aquatic biota as potential biological indicators of the contamination, bioaccumulation and health risks caused by organochlorine pesticides in a large, shallow Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-r.; Meng, W.; Jin, X.-c.; Zheng, B.-h.; Zhang, L.; Xi, H.-y. Ecological security problems of the major key lakes in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3825–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hong, P.; Ruan, Y.; Lin, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, S.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Surveillance in Bufo gargarizans from Inlet Watersheds of Chaohu Lake, China: Tissue Distribution and Bioaccumulation Potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13148–13160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Xu, S.-D.; Liu, T.; Wu, L.-L.; Liu, S.-T.; Liu, G.; Sun, J.; Luo, Y.-X.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; et al. Risk prioritization and experimental validation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in Chaohu Lake: Based on nontarget and target analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.-R.; Zhang, X.-T.; Zhao, L.-L.; Peng, S.-C.; Wang, J.-Z.; Chen, Y.-H. Variations in the concentration, inventory, source, and ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Lake Chaohu. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Arif, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, S. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Chaohu Lake and its tributaries in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Tu, Q. Lake Eutrophication Survey Specifications; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- EC (European Commission). Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment. 2003. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC23785 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Ma, J.; Zheng, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, S. Differential Sensitivity of Two Green Algae, Scenedesmus obliqnus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa, to 12 Pesticides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 52, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H. Comparative toxicities of 10 widely used biocides in three freshwater invertebrate species. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 35, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, A.L.; Stedman, D.B.; Ball, J.; Hillegass, J.M.; Flood, A.; Zhang, C.X.; Panzica-Kelly, J.; Cao, J.; Coburn, A.; Enright, B.P.; et al. Inter-laboratory assessment of a harmonized zebrafish developmental toxicology assay—Progress report on phase I. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assress, H.A.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Occurrence and risk assessment of azole antifungal drugs in water and wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Yang, B.; Lai, H.-J.; Liu, Y.-S.; Pan, C.-G.; Peng, F.-Q. Photodegradation of the azole fungicide fluconazole in aqueous solution under UV-254: Kinetics, mechanistic investigations and toxicity evaluation. Water Res. 2014, 52, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbins, L.L.; Usenko, S.; Brain, R.A.; Brooks, B.W. Probabilistic ecological hazard assessment of parabens using Daphnia magna and Pimephales promelas. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 28, 2744–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Tamura, I.; Hirata, Y.; Kato, J.; Kagota, K.; Katsuki, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Kagami, Y.; Tatarazako, N. Aquatic toxicity and ecological risk assessment of seven parabens: Individual and additive approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Jia, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, S.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Y. Individual and synergistic toxic effects of carbendazim and chlorpyrifos on zebrafish embryonic development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.-J.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, N.-N.; Xu, R.; Wei, L.-N.; Xu, X.-R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Xing, P.; Li, H.; et al. Nationwide occurrence and prioritization of tire additives and their transformation products in lake sediments of China. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Mo, L.; Zhuang, X.; Qin, R.; Cai, F.; Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J. Residual and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in Water and Sediments of Typical Drinking Water Sources in Hainan Province. Asian J. Environ. 2022, 17, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X. Exposure Factors Handbook of Chinese Population; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X. Highlight of Chinese Children’s Exposure Factors Handbook; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- PPDB. Carbendazim (Ref: BAS 346F). Available online: https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/116.htm (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Schönrath, I.; Schmidtkunz, C.; Küpper, K.; Weber, T.; Leng, G.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Exposure of young German adults to the anti-dandruff agent climbazole from 2002 to 2022: Analysis of specific biomarkers in urinary samples. Chemosphere 2024, 367, 143611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaluations of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Available online: https://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/Home/Chemical/3206 (accessed on 17 October 2025).
- Wang, T.; Zhong, M.; Lu, M.; Xu, D.; Xue, Y.; Huang, J.; Blaney, L.; Yu, G. Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution, and risk assessment of current-use pesticides in surface water: A case study near Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.S.; Liu, Y.S.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Price, O.R.; Ying, G.G. Ecological risks of home and personal care products in the riverine environment of a rural region in South China without domestic wastewater treatment facilities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, A.; Martínez-Piernas, A.B.; Moreno-González, D.; Gilbert-López, B.; Molina-Díaz, A.; García-Reyes, J.F. Occurrence and risk assessment of pesticides and their transformation products related to olive groves in surface waters of the Guadalquivir river basin. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yang, G.; Yun, X.; Luo, T.; Guo, H.; Pan, L.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Carbendazim residue in plant-based foods in China: Consecutive surveys from 2011 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 17, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Helm, P.; Paterson, G.; Kaltenecker, G.; Murray, C.; Nowierski, M.; Sultana, T. Pesticides related to land use in watersheds of the Great Lakes basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, M.; Lu, W.; Xue, L.; Lin, X.; Liu, E. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of PPCPs in water and sediments of Longgang River in Shenzhen City, south China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 189, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Peng, X. Chiral profiling of azole antifungals in municipal wastewater and recipient rivers of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8890–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juksu, K.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Yao, L.; Sarin, C.; Sreesai, S.; Klomjek, P.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence, fate and risk assessment of biocides in wastewater treatment plants and aquatic environments in Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.M.; Pham, P.T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Bui, M.Q.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Vu, N.D.; Kannan, K.; Tran, T.M. A survey of parabens in aquatic environments in Hanoi, Vietnam and its implications for human exposure and ecological risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46767–46777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Czarczyńska-Goślińska, B.; Grześkowiak, T. Determination of Parabens in Polish River and Lake Water as a Function of Season. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.S.; Henriques, J.F.; Almeida, A.R.; Machado, A.L.; Koba, O.; Giang, P.T.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Domingues, I. Carbendazim exposure induces developmental, biochemical and behavioural disturbance in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; An, X.; Cai, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, C. Carbendazim has the potential to induce oxidative stress, apoptosis, immunotoxicity and endocrine disruption during zebrafish larvae development. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, N.; Kumar, V.; Datta, S.; Wani, A.B.; Singh, D.; Singh, K.; Singh, J. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of the fungicide carbendazim. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.R.; Silva, P.V.; Soares, A.R.; González-Alcaraz, M.N.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; Roelofs, D.; Moura, G.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Daphnia magna Multigeneration Exposure to Carbendazim: Gene Transcription Responses. Toxics 2023, 11, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Ye, P.; Yang, B.; Shi, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ying, G. Biodegradation of typical azole fungicides in activated sludge under aerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulandaivelu, J.; Choi, P.M.; Shrestha, S.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Sharma, K.; Yuan, Z.; Mueller, J.F.; Wang, C.; et al. Assessing the removal of organic micropollutants from wastewater by discharging drinking water sludge to sewers. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, M.; Buerge, I.J.; Hauser, A.; Müller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Azole fungicides: Occurrence and fate in wastewater and surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rivera, A.A.; Hu, T.; Aardema, M.J.; Nash, J.F. Evaluation of the genotoxicity of the imidazole antifungal climbazole: Comparison to published results for other azole compounds. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2009, 672, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.G.; Taylor, S.L.; Greenberg, N.A.; Burdock, G.A. Evaluation of the health aspects of methyl paraben: A review of the published literature. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 1335–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boberg, J.; Taxvig, C.; Christiansen, S.; Hass, U. Possible endocrine disrupting effects of parabens and their metabolites. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, L. Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Biocides in Chao Lake and Its Tributaries. Toxics 2025, 13, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13111001
Ji L, Jiang L, Wang S, Hu X, Chen K, Wu Q, Zhou L. Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Biocides in Chao Lake and Its Tributaries. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13111001
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Longxiao, Lei Jiang, Shengxing Wang, Xiaozhen Hu, Kaining Chen, Qinglong Wu, and Lijun Zhou. 2025. "Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Biocides in Chao Lake and Its Tributaries" Toxics 13, no. 11: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13111001
APA StyleJi, L., Jiang, L., Wang, S., Hu, X., Chen, K., Wu, Q., & Zhou, L. (2025). Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Biocides in Chao Lake and Its Tributaries. Toxics, 13(11), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13111001






