From Euphoria to Cardiac Stress: Role of Oxidative Stress on the Cardiotoxicity of Methylone and 3,4-DMMC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Experimental Design
2.3. Cell Viability Assessment
2.4. ROS/RNS Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
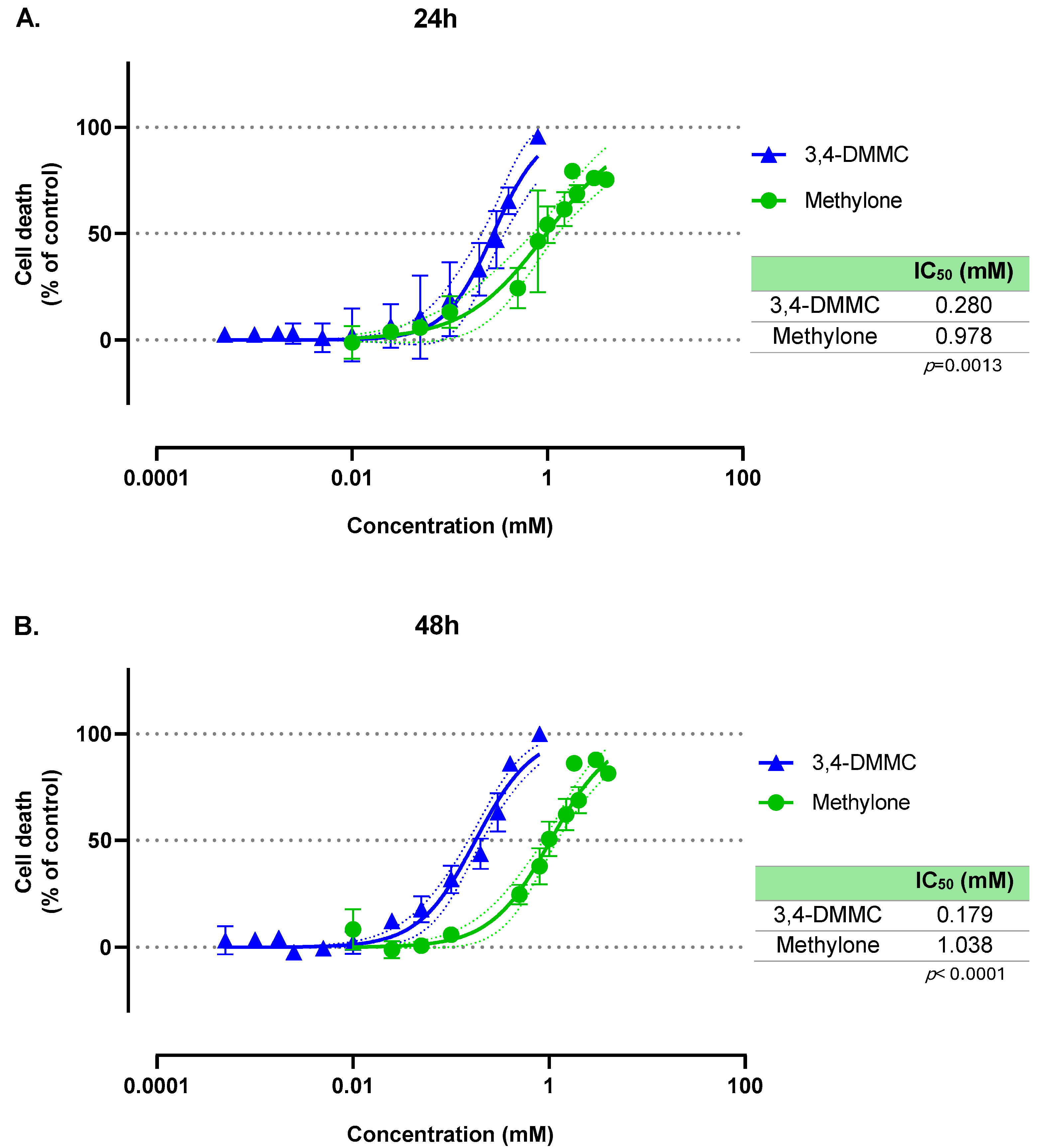
3.1. Methylone and 3,4-DMMC Induce Concentration-Dependent, but Time-Independent, Death of H9c2 Cardiac Cells
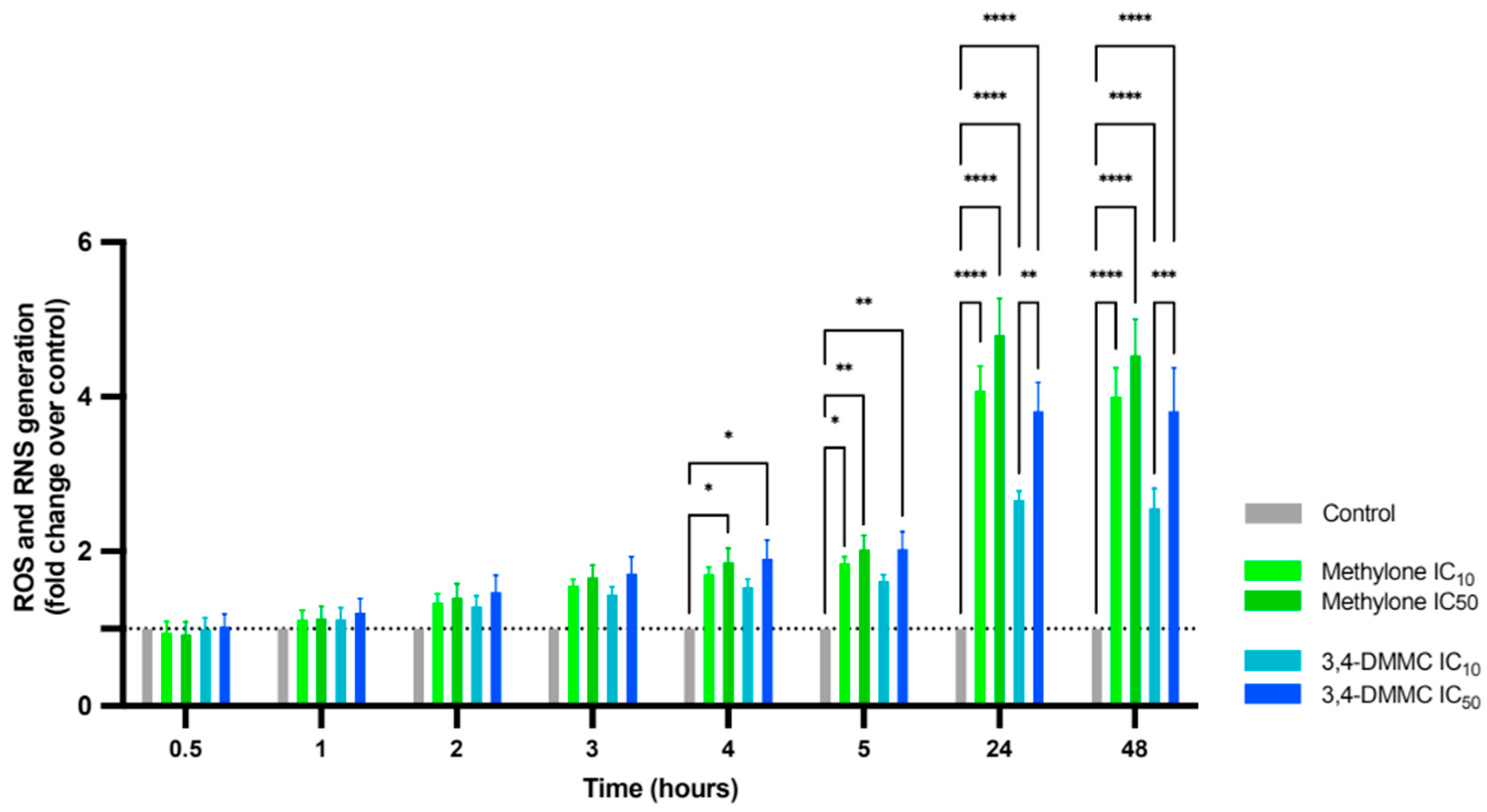
3.2. Methylone and 3,4-DMMC Promote ROS and RNS Generation in H9c2 Cardiac Cells
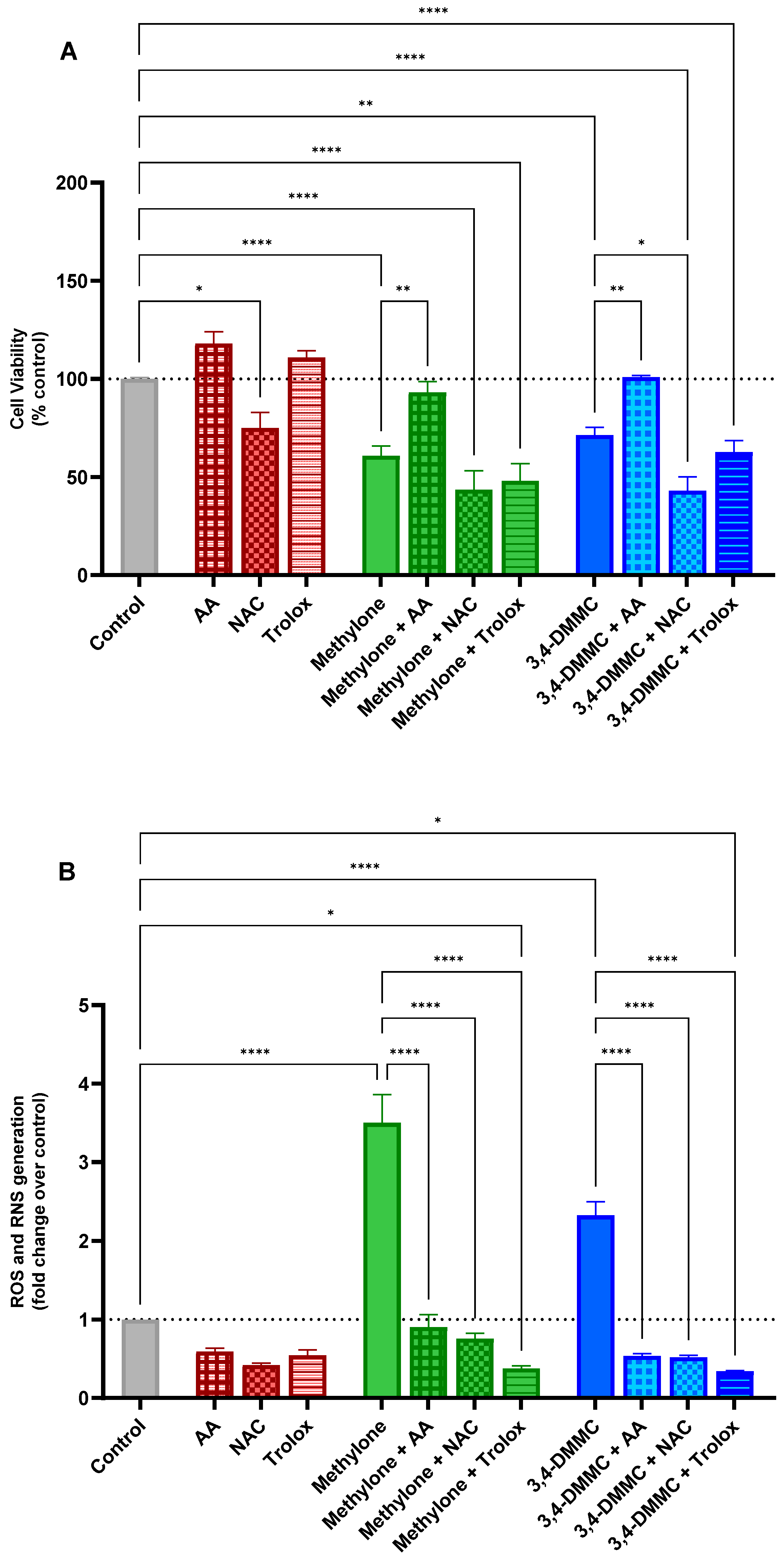
3.3. Ascorbic Acid, but Not NAC or Trolox, Prevents Methylone- and 3,4-DMMC-Induced Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3,4-DMMC | 3,4-Dimethylmethcathinone |
| AA | Ascorbic acid |
| DCFH-DA | 2,7-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EUDA | European Drug Agency |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| IC10/IC40/IC50 | Concentrations inhibiting 10%, 40% or 50% of cell viability, respectively |
| MDMA | 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| MDPV | 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone |
| mPTP | Mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NAC | N-Acetylcysteine |
| NPS | New psychoactive substance |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SCs | Synthetic cathinones |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
References
- Gonçalves, J.L.; Alves, V.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Câmara, J.S. Synthetic cathinones: An evolving class of new psychoactive substances. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.J.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carvalho, F.; Carvalho, M. Khat and synthetic cathinones: A review. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 15–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazdai, L.; Fabbri, M.; Tirri, M.; Corli, G.; Arfè, R.; Marchetti, B.; Bilel, S.; Bergamin, E.; Gaudio, R.M.; Rubini, M.; et al. Epigenetic Studies for Evaluation of NPS Toxicity: Focus on Synthetic Cannabinoids and Cathinones. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUDA (European Union Drugs Agency). European Drug Report 2025: Trends and Developments. 2025. Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2025_en (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Roda, G.; Liberti, V.; Arnoldi, S.; Argo, A.; Rusconi, C.; Suardi, S.; Gambaro, V. Capillary electrophoretic and extraction conditions for the analysis of Catha edulis FORKS active principles. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 228, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.L.; Nelson, K.H.; To, P.; López-Arnau, R.; Xu, P.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.W.; Kuhn, D.M.; Angoa-Perez, M.; et al. Abuse potential and toxicity of the synthetic cathinones (i.e., “Bath salts”). Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 110, 150–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshleman, A.J.; Wolfrum, K.M.; Reed, J.F.; Kim, S.O.; Swanson, T.; Johnson, R.A.; Janowsky, A. Structure-Activity Relationships of Substituted Cathinones, with Transporter Binding, Uptake, and Release. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmler, L.D.; Buser, T.A.; Donzelli, M.; Schramm, Y.; Dieu, L.H.; Huwyler, J.; Chaboz, S.; Hoener, M.C.; Liechti, M.E. Pharmacological characterization of designer cathinones in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmler, L.D.; Rickli, A.; Hoener, M.C.; Liechti, M.E. Monoamine transporter and receptor interaction profiles of a new series of designer cathinones. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesha, K.; Boggs, C.L.; Ripple, M.G.; Allan, C.H.; Levine, B.; Jufer-Phipps, R.; Doyon, S.; Chi, P.; Fowler, D.R. Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (“bath salts”), related death: Case report and review of the literature. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.M.; Hargraves, T.L.; Hair, L.S.; Massucci, C.J.; Frazee, C.C., 3rd; Garg, U.; Pietak, B.R. Three fatal intoxications due to methylone. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 36, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieprzyca, E.; Skowronek, R.; Czekaj, P. Toxicological Analysis of Intoxications with Synthetic Cathinones. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewegen, K.L.; Gresnigt, F.M.J.; Lonkhuyzen, J.J.N.; den Haan, C.; Franssen, E.J.F.; Riezebos, R.K.; Ohana, D.; de Lange, D.W. Cardiotoxicity After Synthetic Cathinone Use; Two Cases, A Case Series and Scoping Review. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2024, 24, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladěnka, P.; Applová, L.; Patočka, J.; Costa, V.M.; Remiao, F.; Pourová, J.; Mladěnka, A.; Karlíčková, J.; Jahodář, L.; Vopršalová, M.; et al. Comprehensive review of cardiovascular toxicity of drugs and related agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1332–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaelli, D.; Manfredi, A.; Zanon, M.; Fattorini, P.; Scopetti, M.; Neri, M.; Frisoni, P.; D’Errico, S. Synthetic Cannabinoids and Cathinones Cardiotoxicity: Facts and Perspectives. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominic, P.; Ahmad, J.; Awwab, H.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Kevil, C.G.; Goeders, N.E.; Murnane, K.S.; Patterson, J.C.; Sandau, K.E.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. Stimulant Drugs of Abuse and Cardiac Arrhythmias. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e010273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwartsen, A.; Hondebrink, L.; Westerink, R.H. Changes in neuronal activity in rat primary cortical cultures induced by illicit drugs and new psychoactive substances (NPS) following prolonged exposure and washout to mimic human exposure scenarios. Neurotoxicology 2019, 74, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naserzadeh, P.; Jokar, F.; Vafaei, F.; Seydi, E.; Pourahmad, J. Toxicity of new synthetic amphetamine drug mephedrone On Rat Heart mitochondria: A warning for its abuse. Xenobiotica 2018, 48, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, D.J.; Capela, J.P.; Feio-Azevedo, R.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.; Bastos Mde, L.; Carvalho, F. Mitochondria: Key players in the neurotoxic effects of amphetamines. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1695–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Carmo, H.; Costa, V.M.; Capela, J.P.; Pontes, H.; Remião, F.; Carvalho, F.; Bastos Mde, L. Toxicity of amphetamines: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1167–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hescheler, J.; Meyer, R.; Plant, S.; Krautwurst, D.; Rosenthal, W.; Schultz, G. Morphological, biochemical, and electrophysiological characterization of a clonal cell (H9c2) line from rat heart. Circ. Res. 1991, 69, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liehr, T.; Kankel, S.; Hardt, K.S.; Buhl, E.M.; Noels, H.; Keller, D.T.; Schröder-Lange, S.K.; Weiskirchen, R. Genetic and Molecular Characterization of H9c2 Rat Myoblast Cell Line. Cells 2025, 14, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, I.; Carvalho, T.; Valente, M.J.; Castro, A.; Araújo, A.M.; Bastos, M.L.; Carvalho, M. The interplay between autophagy and apoptosis mediates toxicity triggered by synthetic cathinones in human kidney cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 331, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.M.; Carvalho, F.; Duarte, J.A.; Bastos Mde, L.; Remião, F. The heart as a target for xenobiotic toxicity: The cardiac susceptibility to oxidative stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 1285–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, J.; Costa, V.M.; Gaspar, H.; Santos, S.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carvalho, F.; Capela, J.P. Structure-cytotoxicity relationship profile of 13 synthetic cathinones in differentiated human SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. Neurotoxicology 2019, 75, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque Bravo, R.; Carmo, H.; Valente, M.J.; Silva, J.P.; Carvalho, F.; Bastos, M.L.; Dias da Silva, D. From street to lab: In vitro hepatotoxicity of buphedrone, butylone and 3,4-DMMC. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 1443–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; He, L.; Lemasters, J.J. Mitochondrial permeability transition: A common pathway to necrosis and apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luethi, D.; Liechti, M.E.; Krähenbühl, S. Mechanisms of hepatocellular toxicity associated with new psychoactive synthetic cathinones. Toxicology 2017, 387, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.J.; Araújo, A.M.; Bastos Mde, L.; Fernandes, E.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Editor’s Highlight: Characterization of Hepatotoxicity Mechanisms Triggered by Designer Cathinone Drugs (β-Keto Amphetamines). Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 153, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka-Kroplewska, K.; Wrońska, A.; Stasiłojć, G.; Kmieć, Z. The Designer Drug 3-Fluoromethcathinone Induces Oxidative Stress and Activates Autophagy in HT22 Neuronal Cells. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 34, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.; Costa, V.M.; Gaspar, H.; Santos, S.; Bastos, M.L.; Carvalho, F.; Capela, J.P. Adverse outcome pathways induced by 3,4-dimethylmethcathinone and 4-methylmethcathinone in differentiated human SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2481–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, M.J.; Amaral, C.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Duarte, J.A.; Bastos, M.L.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Methylone and MDPV activate autophagy in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells: A new insight into the context of β-keto amphetamines-related neurotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3663–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.J.; Bastos, M.L.; Fernandes, E.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Neurotoxicity of β-Keto Amphetamines: Deathly Mechanisms Elicited by Methylone and MDPV in Human Dopaminergic SH-SY5Y Cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hollander, B.; Rozov, S.; Linden, A.M.; Uusi-Oukari, M.; Ojanperä, I.; Korpi, E.R. Long-term cognitive and neurochemical effects of “bath salt” designer drugs methylone and mephedrone. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 103, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Arnau, R.; Martínez-Clemente, J.; Rodrigo, T.; Pubill, D.; Camarasa, J.; Escubedo, E. Neuronal changes and oxidative stress in adolescent rats after repeated exposure to mephedrone. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixidó, E.; Riera-Colomer, C.; Raldúa, D.; Pubill, D.; Escubedo, E.; Barenys, M.; López-Arnau, R. First-Generation Synthetic Cathinones Produce Arrhythmia in Zebrafish Eleutheroembryos: A New Approach Methodology for New Psychoactive Substances Cardiotoxicity Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ascorbic Acid. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Berk, M.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Jaeschke, H.; Marenzi, G.; Richeldi, L.; Wen, F.Q.; Nicoletti, F.; Calverley, P.M.A. The Multifaceted Therapeutic Role of N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) in Disorders Characterized by Oxidative Stress. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1202–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiouvannis, G.; Theodosis-Nobelos, P.; Rekka, E.A. Trolox, Ferulic, Sinapic, and Cinnamic Acid Derivatives of Proline and GABA with Antioxidant and/or Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Lafi, Z.; Abualsoud, B.M.; Al-Najjar, B.O.; Al-Samydai, A.; Oriquat, G.A.; Alshaer, W.; Alqader Ibrahim, A.; Dellinger, A.L. Vitamin C as a Cardioprotective Agent Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e042534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasikumar, S.; Yuvraj, S.; Veilumuthu, P.; Godwin Christopher, J.S.; Anandkumar, P.; Nagarajan, T.; Sureshkumar, S.; Selvam, G.S. Ascorbic acid attenuates cadmium-induced myocardial hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte injury through Nrf2 signaling pathways comparable to resveratrol. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vineetha, R.C.; Binu, P.; Arathi, P.; Nair, R.H. L-ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol attenuate arsenic trioxide-induced toxicity in H9c2 cardiomyocytes by the activation of Nrf2 and Bcl2 transcription factors. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2018, 28, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Slabu, I.; Liehn, E.A.; Rusu, M. Vitamin C in Cardiovascular Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Evidence and Therapeutic Applications. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H. N-acetylcysteine induces apoptosis via the mitochondria-dependent pathway but not via endoplasmic reticulum stress in H9c2 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, K.; Aramaki, T.; Hashiyada, M.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Funayama, M. Quantitative analysis of 3,4-dimethylmethcathinone in blood and urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in a fatal case. Leg. Med. 2014, 16, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.M.; Valente, M.J.; Carvalho, M.; Dias da Silva, D.; Gaspar, H.; Carvalho, F.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. Raising awareness of new psychoactive substances: Chemical analysis and in vitro toxicity screening of ‘legal high’ packages containing synthetic cathinones. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, M.; Bilel, S.; Tirri, M.; Corli, G.; Di Rosa, F.; Gregori, A.; Alkilany, A.M.; Rachid, O.; Roda, E.; De Luca, F.; et al. The synthetic cathinones MDPHP and MDPV: Comparison of the acute effects in mice, in silico ADMET profiles and clinical reports. Neurotoxicology 2024, 103, 230–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chaou, C.H.; Chen, C.K.; Yen, T.H.; Liao, S.C.; Seak, C.J.; Chen, H.Y. Synthetic cathinone poisoning from ingestion of drug-laced “instant coffee packets” in Taiwan. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.S.; Tang, M.H.Y.; Tong, H.F.; Chong, Y.K. N,N-dimethylpentylone poisoning: Clinical manifestations, analytical detection, and metabolic characterization. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 361, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, R.W., Jr.; Galindo, D.G.; Stinson, B.T.; Sulima, A.; Rice, K.C.; Javors, M.A.; Ginsburg, B.C.; Collins, G.T. Cardiovascular and locomotor effects of binary mixtures of common ‘bath salts’ constituents: Studies with methylone, methylenedioxypyrovalerone and caffeine in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 182, 1836–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, M.; Rocha, V.; Araújo, A.M.; Carvalho, M. From Euphoria to Cardiac Stress: Role of Oxidative Stress on the Cardiotoxicity of Methylone and 3,4-DMMC. Toxics 2025, 13, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110998
Moreira M, Rocha V, Araújo AM, Carvalho M. From Euphoria to Cardiac Stress: Role of Oxidative Stress on the Cardiotoxicity of Methylone and 3,4-DMMC. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110998
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Maria, Verónica Rocha, Ana Margarida Araújo, and Márcia Carvalho. 2025. "From Euphoria to Cardiac Stress: Role of Oxidative Stress on the Cardiotoxicity of Methylone and 3,4-DMMC" Toxics 13, no. 11: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110998
APA StyleMoreira, M., Rocha, V., Araújo, A. M., & Carvalho, M. (2025). From Euphoria to Cardiac Stress: Role of Oxidative Stress on the Cardiotoxicity of Methylone and 3,4-DMMC. Toxics, 13(11), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110998










