Genetic Damage to Human Lymphocytes Induced by Contaminated Water in Populations Surrounding Lake Chapala and the Santiago River, Jalisco, México
Highlights
- The potent genotoxicity of the Santiago River is due to the incorporation of industrial waste from industries located in the river basin.
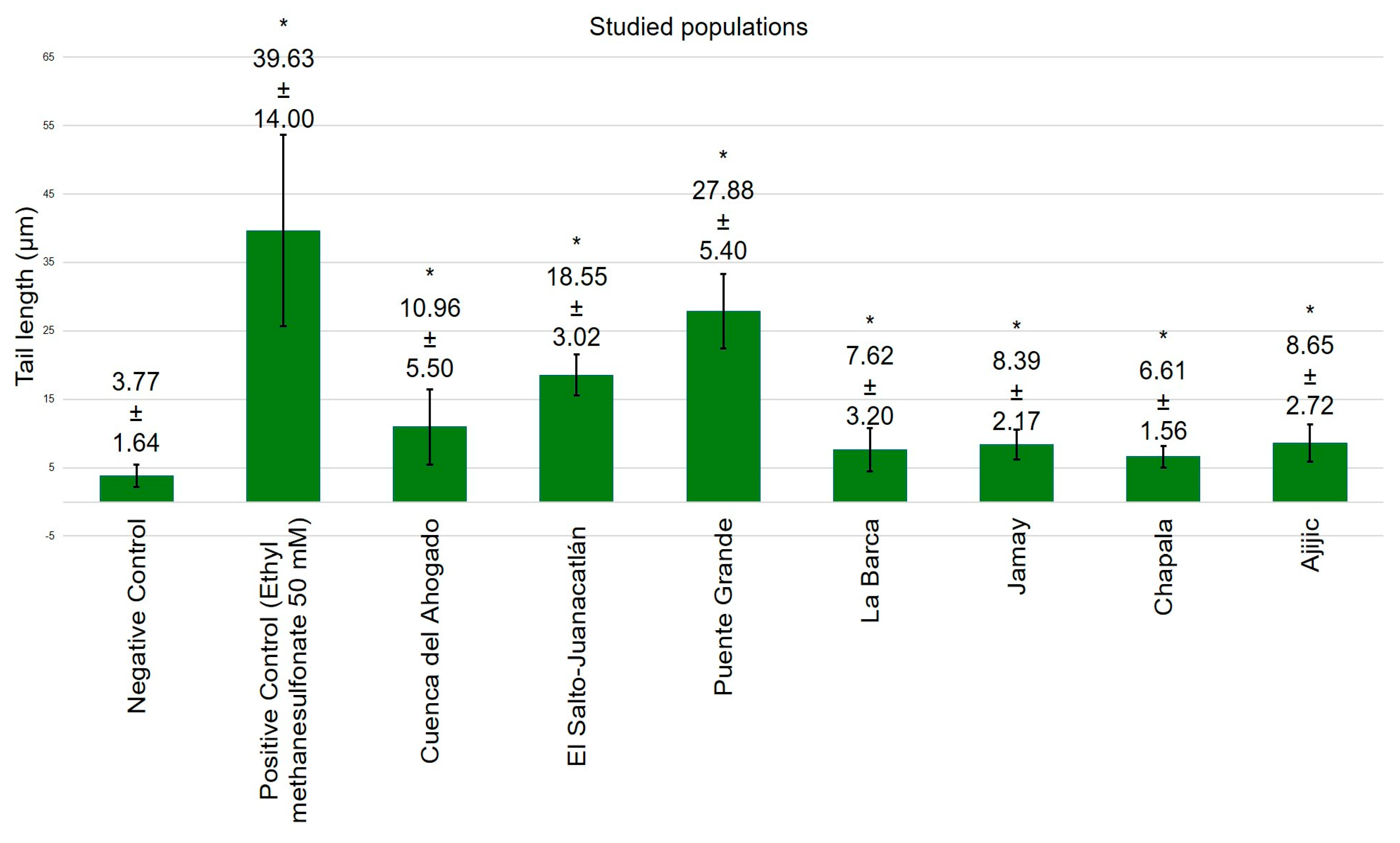
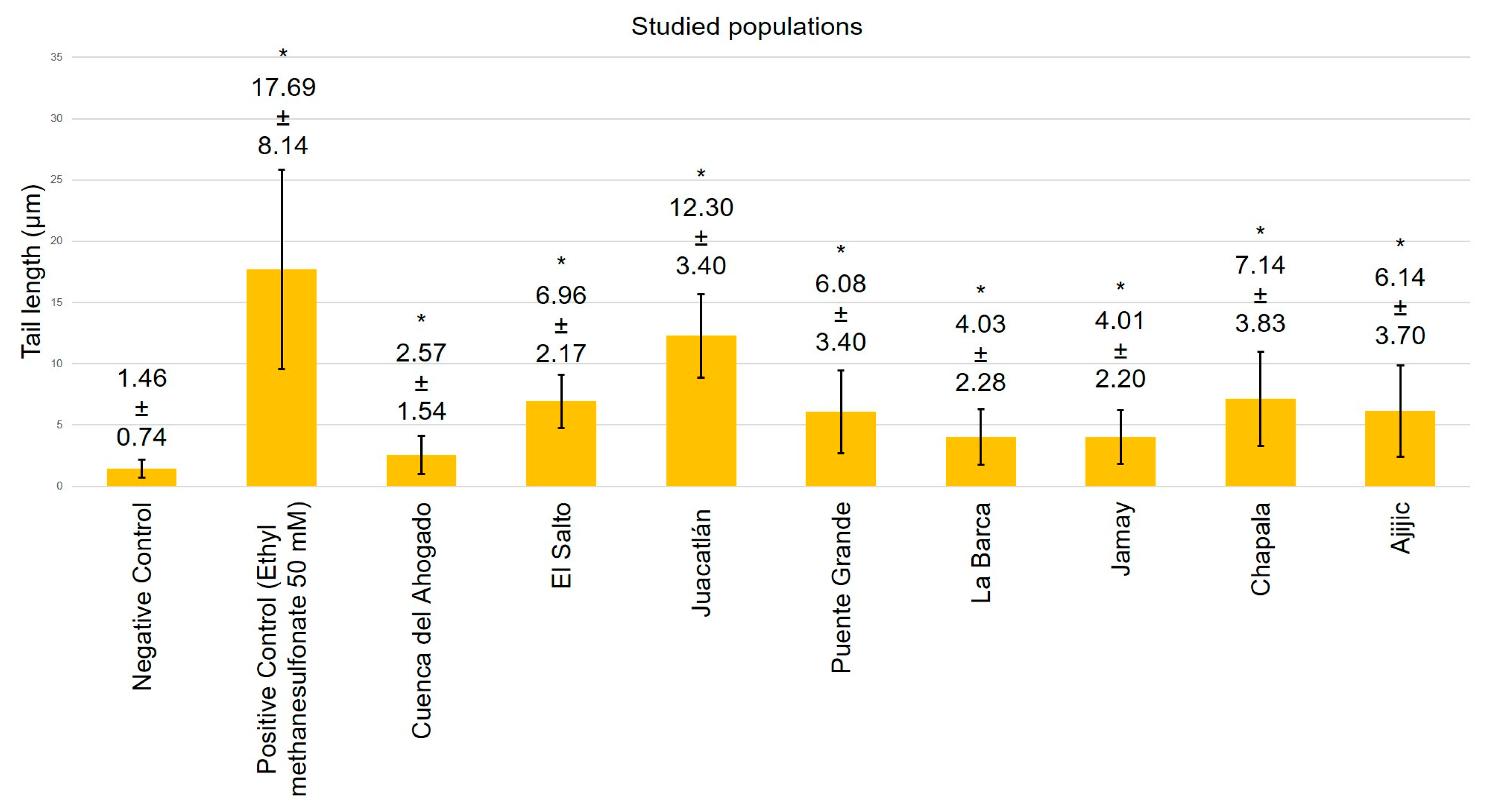
- Residents surrounding the Santiago River exhibit significant genetic damage compared to those near Lake Chapala.
- The genetic damage observed in residents and the genotoxicity of the Santiago River waters confirm the increase in cancer cases reported by residents.
- There is a high risk of increasing cases of cancer and other diseases due to the excessive and shameful pollution of the Santiago River.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents Used
2.2. Collection of Water Samples
2.3. Collection of Human Blood Cells
2.4. Assessment of the Genotoxic Potential of Water Samples
2.5. Assessment of Genetic Damage to Blood Cells in Individuals Exposed to Contaminated Waters
2.6. Alkaline Comet Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
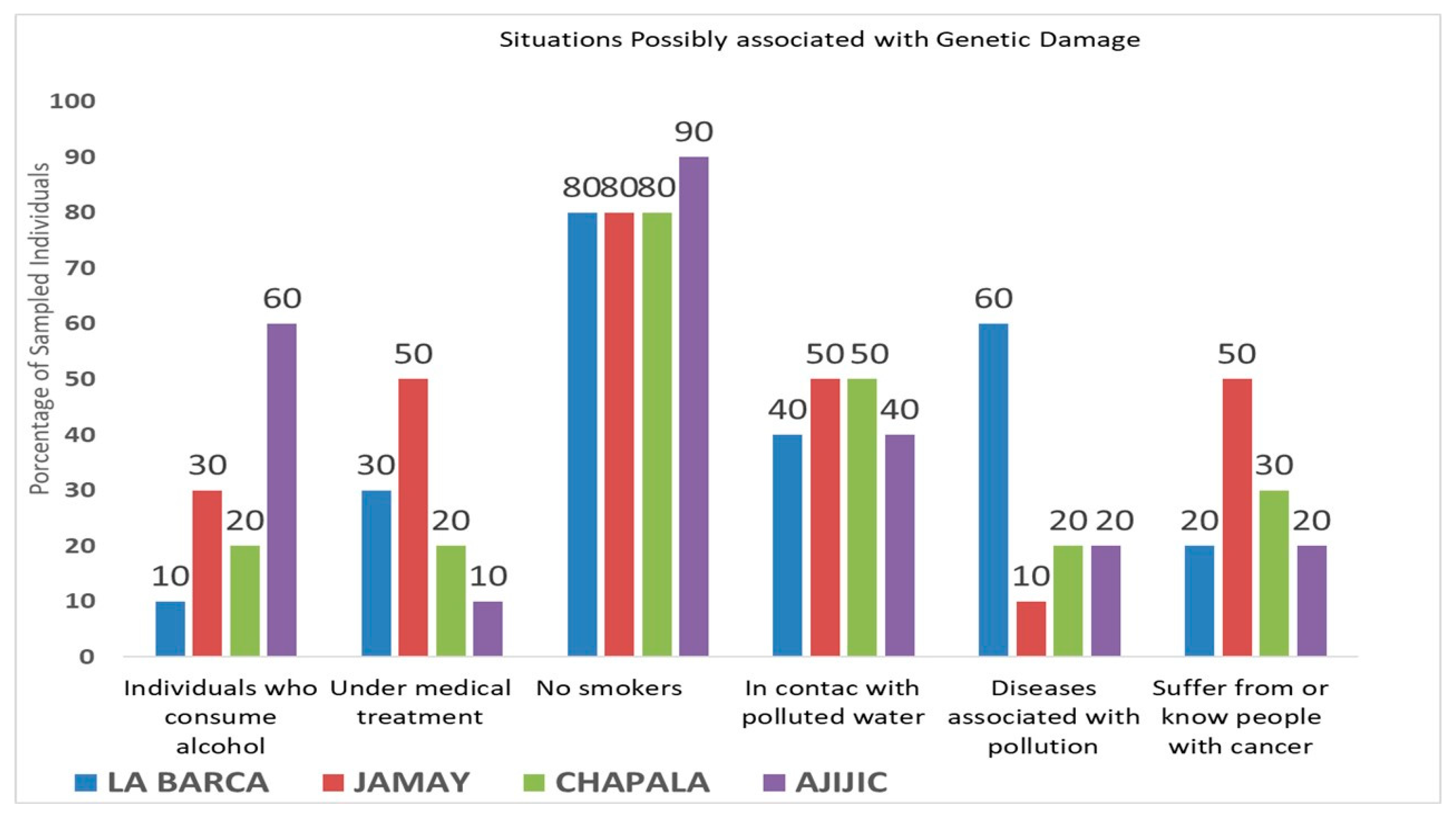
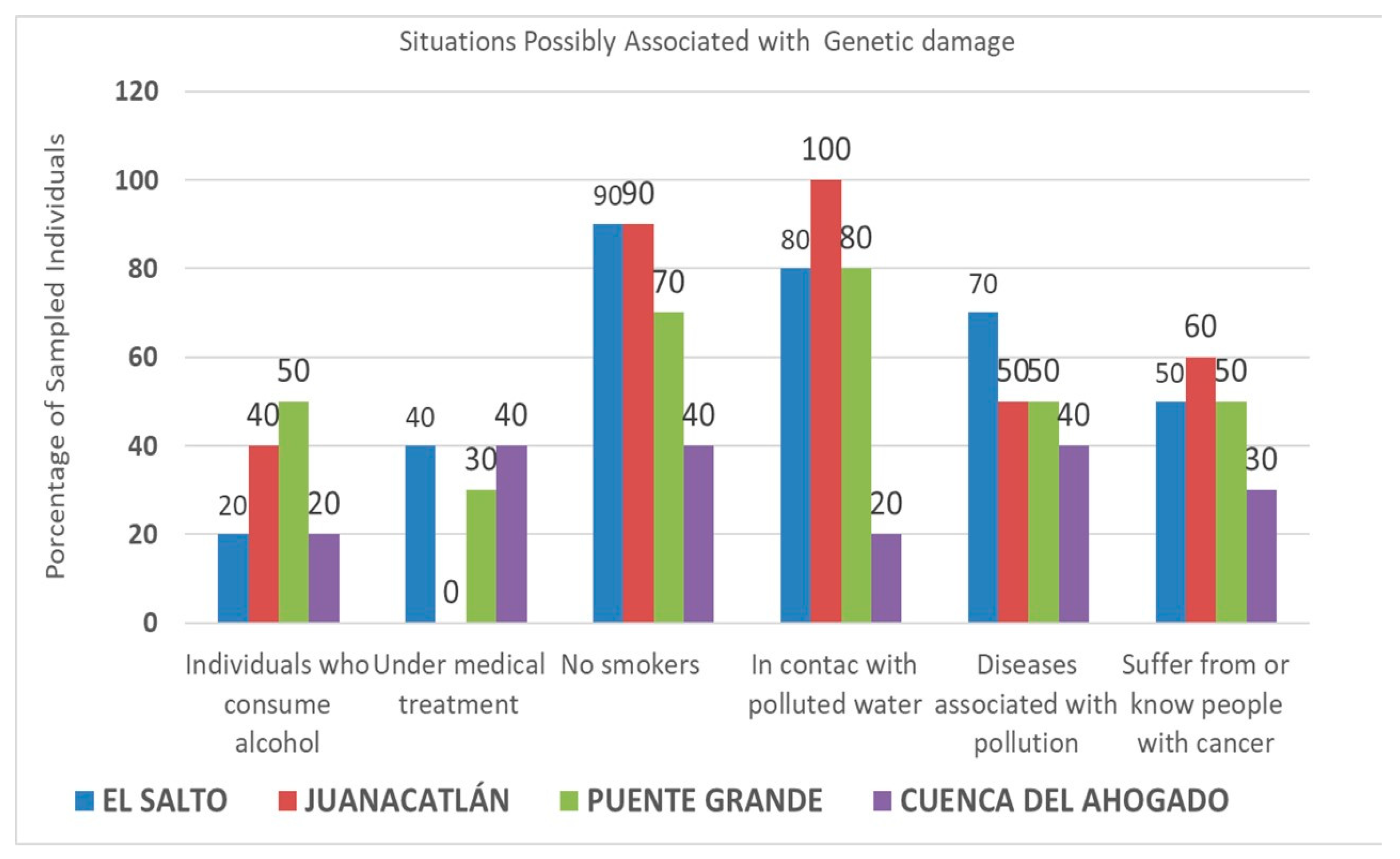
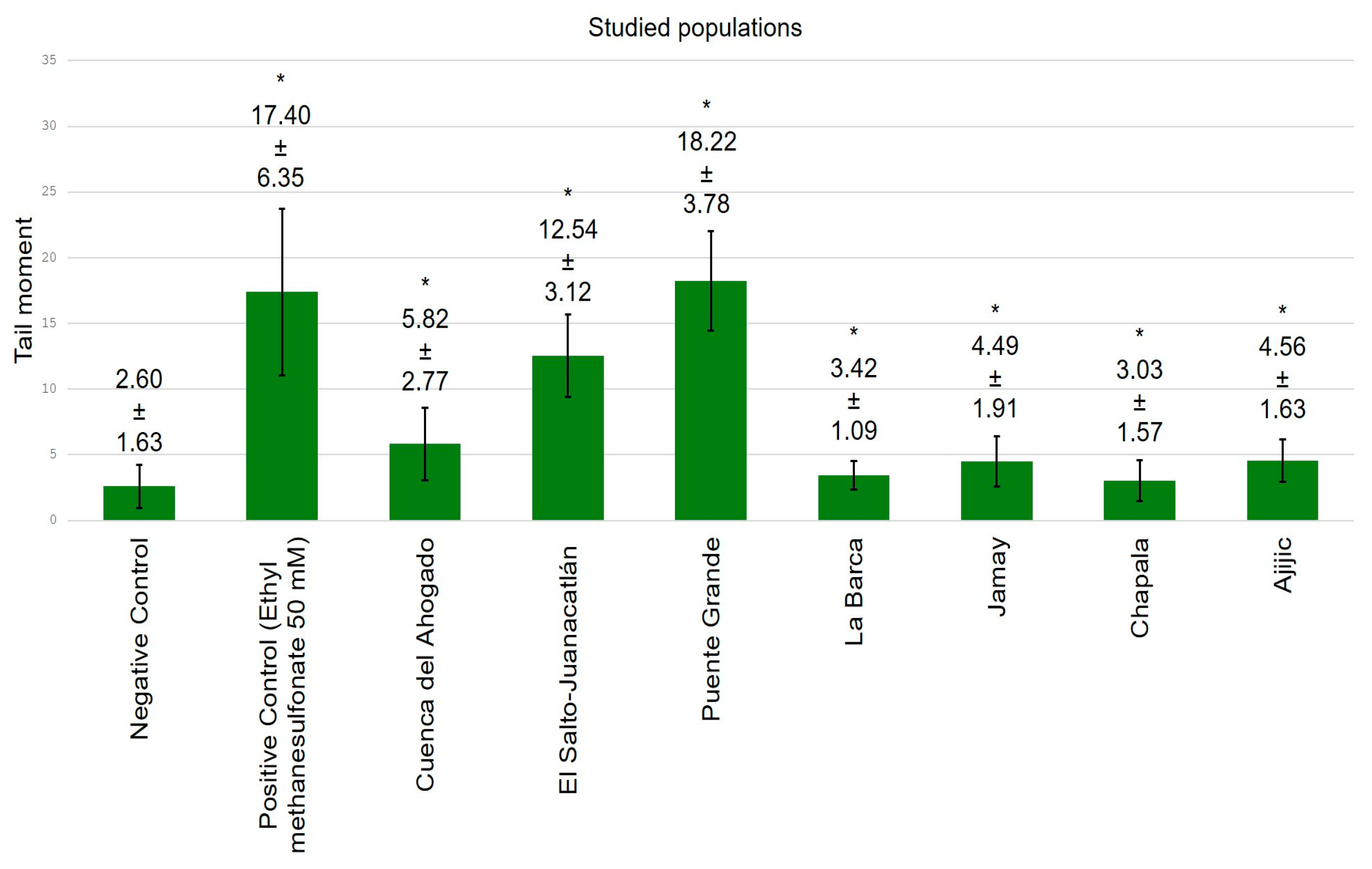
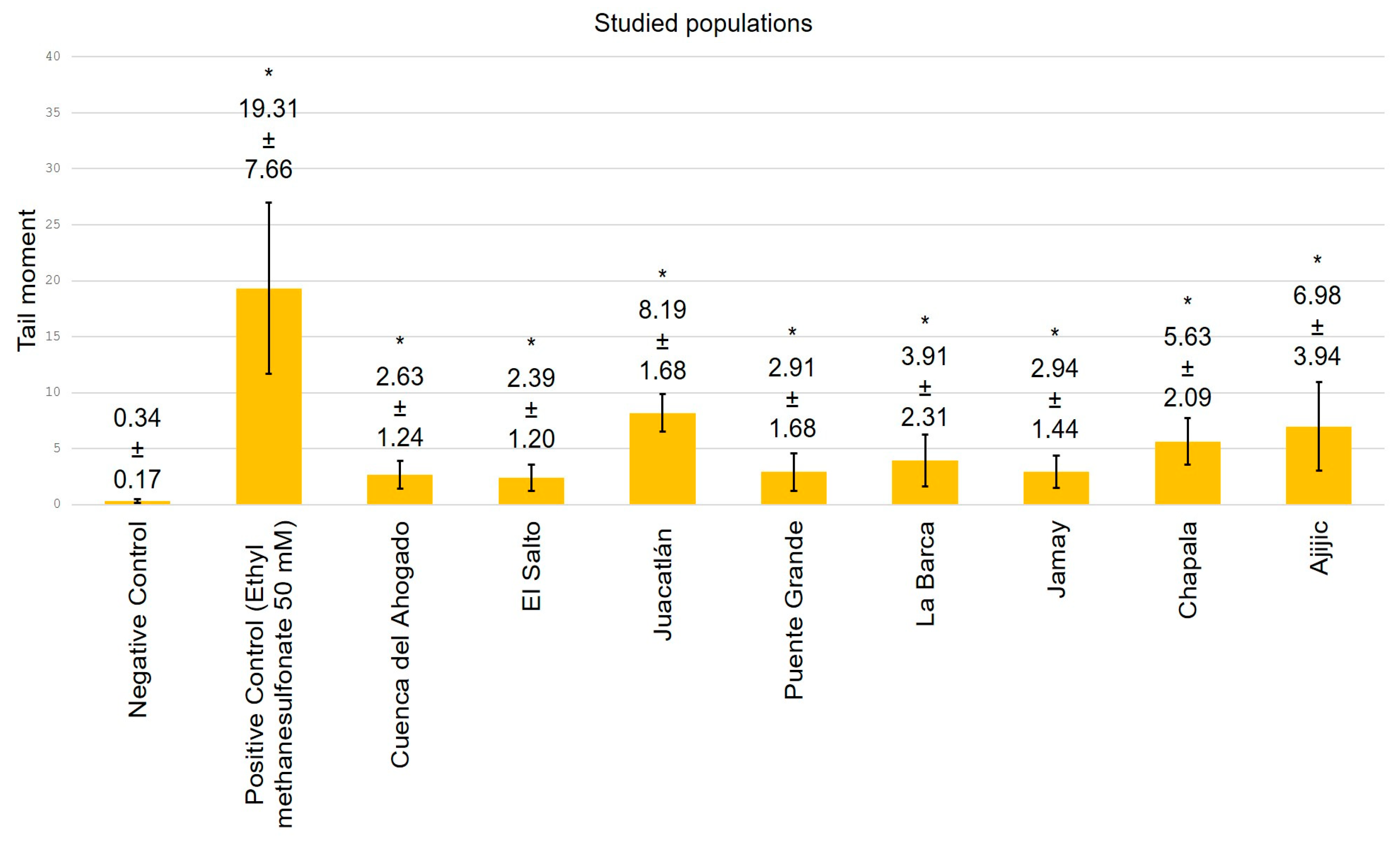
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrera, A.; Bolay, J.C.; García, C.; Hostettler, S.; Gerritsen, P.; Mejía, R.; Ortiz, C.; Sanchez, R.M.; Pedrazzini, Y.; Poschet, L.; et al. JACS Central America and the Caribbean. Key challenges of sustainable development and research priorities: Social practices as driving forces of change. In Research for Mitigating Syndromes of Global Change. A Transdisciplinary Appraisal of Selected Regions of the World to Prepare Development Oriented Research Partnerships; NCCR North-South/CDE—University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 293–328. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/41939316_JACS_Central_America_and_the_Caribbean_Key_Challenges_of_Sustainable_development_and_research_priorities_Social_Practices_as_driving_forces_for_change#fullTextFileContent (accessed on 2 April 2021).
- Cotler-Ávalos, H. Las Cuencas Hidrográficas de México: Diagnóstico y Priorización; Pluralia Ediciones e Impresiones: Coyoacán, Mexico, 2010; Available online: https://agua.org.mx/biblioteca/las-cuencas-hidrograficas-de-mexico-diagnostico-y-priorizacion/ (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- McCulligh, C.; Tetreault, D. La gestión del agua en la Zona Metropolitana de Guadalajara. El modelo dominante versus las alternativas de la sociedad civil organizada. In Proceedings of the Seminario Taller Agua, Ciudad Y Cambio Climático, Guadalajara, Mexico, 8–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Ayala, E.; Arguello-Pérez, M.A.; Tintos-Gómez, A.; Pérez-Rodríguez, R.Y.; Díaz-Gómez, J.A.; Borja-Gómez, I.; Salomé-Baylón, J. Review of the biomonitoring of persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic substances in aquatic ecosystems of Mexico: 2001–2016. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 48, 705–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oregel-Zamudio, E.; Alvarez-Bernal, D.; Franco-Hernandez, M.O.; Buelna-Osben, H.R.; Mora, M. Bioaccumulation of PCBs and PBDEs in fish from a tropical Lake Chapala, Mexico. Toxics 2021, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V.; Zamora-Perez, A.L.; Rojas-Ramírez, J.P.; Rocha-Muñoz, A.D. Buccal micronucleus cytome assay of populations under chronic heavy metal and other metal exposure along the Santiago River, Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Sánchez, H.U.; Fajardo-Montiel, A.L. Assessment of water quality, ecological and health risks of inland water bodies in Mexico: A case study of Lake Chapala. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2024, 23, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavaş, T.; Könen, S. Detection of cytogenetic and DNA damage in peripheral erythrocytes of goldfish (Carassius auratus) exposed to a glyphosate formulation using the micronucleus test and the comet assay. Mutagenesis 2007, 22, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Moya, C.; Reynoso-Silva, M. Use of comet assay in human lymphocytes as a molecular biomarker for simultaneous monitoring of genetic damage and genotoxicity in residents who lived nearby the Santiago River, Mexico, in 2012. Glob. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 1, 004–008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.M.; Hernández, E. Impactos de la contaminación del Río Santiago en el bienestar de los habitantes de El Salto, Jalisco. Espac. Abierto 2009, 18, 709–729. [Google Scholar]
- Beringola, M.L.B. Genotoxicidad de Las Aguas del Río Tajo. Doctoral Dissertation, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 1997. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/tesis?codigo=16265 (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Baršienė, J.; Dedonytė, V.; Rybakovas, A.; Broeg, K.; Forlin, L.; Gercken, J.; Balk, L. Environmental mutagenesis in different zones of the Baltic Sea. Acta Zool. Litu. 2005, 15, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishwajit, N.; Bhaskar, D.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Arup, P.; Sad, A.; Hossain, M.A.; Priyanka, M.; Dutta, R.N.; Dutta, S.; Chakraborti, D. Groundwater arsenic contamination in the Sahibganj district of Jharkhand state, India in the middle Ganga plain and adverse health effects. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2008, 90, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, K.; Saravana Devi, S.; Hengstler, J.G.; Hermes, M.; Kumar, K.; Dutta, D.; Chakrabarti, T. Genotoxicity of sludges, wastewater and effluents from three different industries. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.R.; Dong, H.W.; Tang, X.L.; Sun, X.R.; Han, X.H.; Chen, B.Q.; Yang, B.F. Genotoxicity of water from the Songhua River, China, in 1994–1995 and 2002–2003: Potential risks for human health. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.R.; Crittenden, P.D.; Dauvalter, V.A.; Jones, V.; Kuhry, P.; Loskutova, O. Multiple indicators of human impacts on the environment in the Pechora Basin, north-eastern European Russia. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenstein, A. The consequences of industrialization: Evidence from water pollution and digestive cancers in China. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2012, 94, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiani, S.; Gertler, P.; Schargrodsky, E. Water for life: The impact of the privatization of water services on child mortality. J. Political Econ. 2005, 113, 83–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Villegas, M.M.; Ramírez-Hernández, B.C.; Torres-Morán, M.; Álvarez-Moya, C.; Zarazúa-Villaseñor, P.; Velasco-Ramírez, A.P. Presence of arsenic and potentially toxic metals (Cd, Cr, Pb) in water and soil of the NE shore of Chapala Lake, Mexico, and its genotoxic effect in the edible chayote fruit (Sechium edule (Jacq.) Sw.). Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 85, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Madera, R.J.; Salazar-Flores, J.; Peregrina-Lucano, A.A.; Mendoza-Michel, J.; Ceja-Gálvez, H.R.; Rojas-Bravo, D.; Reyna-Villela, M.Z.; Torres-Sánchez, E.D. Pesticide contamination in drinking and surface water in the Cienega, Jalisco, México. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, A.; Soetan, M.; Adefabi, A. Assessment of heavy metal concentrations in imported marine fish species consumed in Ogun state, Nigeria. Aceh J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 9, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes Rubio, P.Y.; Aguilar Castro, N.; Ávila Domínguez, R.; Macbani Olvera, P.; Raygoza Anaya, M.; Garnica Guerrero, B.; Vázquez, J.R.; Ruvalcaba-Ledezma, J.C. Contaminación del río Santiago: Un problema epidemiológico ambiental persistente de salud pública en Jalisco, México. J. Negat. No Posit. Results 2021, 6, 1222–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, B. The Lerma-Chapala Basin. The Water of Discord. Gestión Política Pública 2006, 15, 369–391. [Google Scholar]
- Un Salto de Vida. Available online: https://unsaltodevida.wordpress.com/2015/06/29/contaminacion-provoca-cancer-r-insuficiencia-renal/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Rizo-Decelis, L.D.; Andreo, B. Water quality assessment of the Santiago River and attenuation capacity of pollutants downstream Guadalajara City, Mexico. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.; Bajpayee, M.; Parmar, D. Comet assay: A reliable tool for the assessment of DNA damage in different models. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2009, 25, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.; Koppen, G.; Valdiglesias, V.; Dusinska, M.; Kruszewski, M.; Møller, P. The comet assay as a tool for human biomonitoring studies: The ComNet project. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2014, 759, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekaert, C.; Rast, C.; Ferrier, V.; Bispo, A.; Jourdain, M.J.; Vasseur, P. Use of in vitro (Ames and Mutatox tests) and in vivo (Amphibian Micronucleus test) assays to assess the genotoxicity of leachates from a contaminated soil. Org. Geochem. 1999, 30, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEA Jalisco. Resultados del monitoreo Río Santiago, Río Zula y Arroyo del Ahogado de Junio de 2013. Available online: http://www.ceajalisco.gob.mx/notas/documentos/2013/monitoreo_jun2013.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Zarazúa, G.; Ávila-Pérez, P.; Tejeda, S.; Valdivia-Barrientos, M.; Zepeda-Gómez, C.; Macedo-Miranda, G. Evaluación de los metales pesados Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn y Pb en sombrerillo de agua (Hydrocotyle ranunculoides) del curso alto del río Lerma, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2013, 29, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, A.A.; Silva, M.R.; Moya, C.Á. Compuestos organo-persistentes y daño genético en núcleos hepáticos de Goodea atripinnis del Lago de Chapala. Sci.-Cucba 2011, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- de Anda, J.; Shear, H.; Lugo-Melchor, O.Y.; Padilla-Tovar, L.E.; Bravo, S.D.; Olvera-Vargas, L.A. Use of the pesticide toxicity index to determine potential ecological risk in the Santiago-Guadalajara River Basin, Mexico. Water 2024, 16, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Waheed, I.; Akash, M.S.H. Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Jornada. Available online: https://www.jornada.com.mx/2024/11/10/estados/021n1est (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- CEA Jalisco. Available online: https://www.ceajalisco.gob.mx/contenido/chapala/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- McCulligh, C.; Páez, J.C.; Moya, G. Mártires del Río Santiago, Informe Sobre Violaciones al Derecho a la Salud ya un Medio Ambiente Sano en Juanacatlán y El Salto, Jalisco, México; Instituto Mexicano para el Desarrollo Comunitario, AC: Guadalajara, México, 2007; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11117/5338 (accessed on 2 June 2019).
- Lee, E.; Oh, E.; Lee, J.; Sul, D.; Lee, J. Use of the tail moment of the lymphocytes to evaluate DNA damage in human biomonitoring studies. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 81, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobierno de Jalisco. Available online: https://transparencia.info.jalisco.gob.mx/sites/default/files/Mapa%20topogr%C3%A1fico%20Juanacatl%C3%A1n.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- LaJornada, 25 March 2013. Available online: https://www.jornada.com.mx/2013/03/25/politica/002n1pol#:~:text=En%20el%20camino%20de%20Ocotl%C3%A1n,Mexicano%20para%20el%20Desarrollo%20Comunitario (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- Tice, R.R.; Agurell, E.; Anderson, D.; Burlinson, B.; Hartmann, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Sasaki, Y.F. Single cell gel/comet assay: Guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, P.L.; Banáth, J.P. The comet assay: A method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Lara, K.; Galar-Martínez, M.; García-Medina, S.; Hernández-Díaz, M.; Cano-Viveros, S.; García-Medina, A.L.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Parra-Ortega, I.; Morales-Balcázar, I.; Hernández-Rosas, N.A.; et al. Human health risk assessment by exposure to contaminants from an urban reservoir: A pilot study in the Madin Dam (México). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reynoso-Silva, M.; Alvarez-Moya, C.; Guzmán-Rubio, F.M.; Velázquez-Cruz, D.G.; Moreno-Del Río, D.; Ramírez-Hernández, B.C.; Barrientos-Ramírez, L.; Vargas-Radillo, J.d.J.; Gutiérrez-Martínez, P.B.; Ruíz-López, M.A. Genetic Damage to Human Lymphocytes Induced by Contaminated Water in Populations Surrounding Lake Chapala and the Santiago River, Jalisco, México. Toxics 2025, 13, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100887
Reynoso-Silva M, Alvarez-Moya C, Guzmán-Rubio FM, Velázquez-Cruz DG, Moreno-Del Río D, Ramírez-Hernández BC, Barrientos-Ramírez L, Vargas-Radillo JdJ, Gutiérrez-Martínez PB, Ruíz-López MA. Genetic Damage to Human Lymphocytes Induced by Contaminated Water in Populations Surrounding Lake Chapala and the Santiago River, Jalisco, México. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100887
Chicago/Turabian StyleReynoso-Silva, Mónica, Carlos Alvarez-Moya, Fernando Manuel Guzmán-Rubio, Daniela Guadalupe Velázquez-Cruz, Daniel Moreno-Del Río, Blanca Catalina Ramírez-Hernández, Lucía Barrientos-Ramírez, José de Jesús Vargas-Radillo, Paulina Beatriz Gutiérrez-Martínez, and Mario Alberto Ruíz-López. 2025. "Genetic Damage to Human Lymphocytes Induced by Contaminated Water in Populations Surrounding Lake Chapala and the Santiago River, Jalisco, México" Toxics 13, no. 10: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100887
APA StyleReynoso-Silva, M., Alvarez-Moya, C., Guzmán-Rubio, F. M., Velázquez-Cruz, D. G., Moreno-Del Río, D., Ramírez-Hernández, B. C., Barrientos-Ramírez, L., Vargas-Radillo, J. d. J., Gutiérrez-Martínez, P. B., & Ruíz-López, M. A. (2025). Genetic Damage to Human Lymphocytes Induced by Contaminated Water in Populations Surrounding Lake Chapala and the Santiago River, Jalisco, México. Toxics, 13(10), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100887








