Acute and Transgenerational Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Daphnia magna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
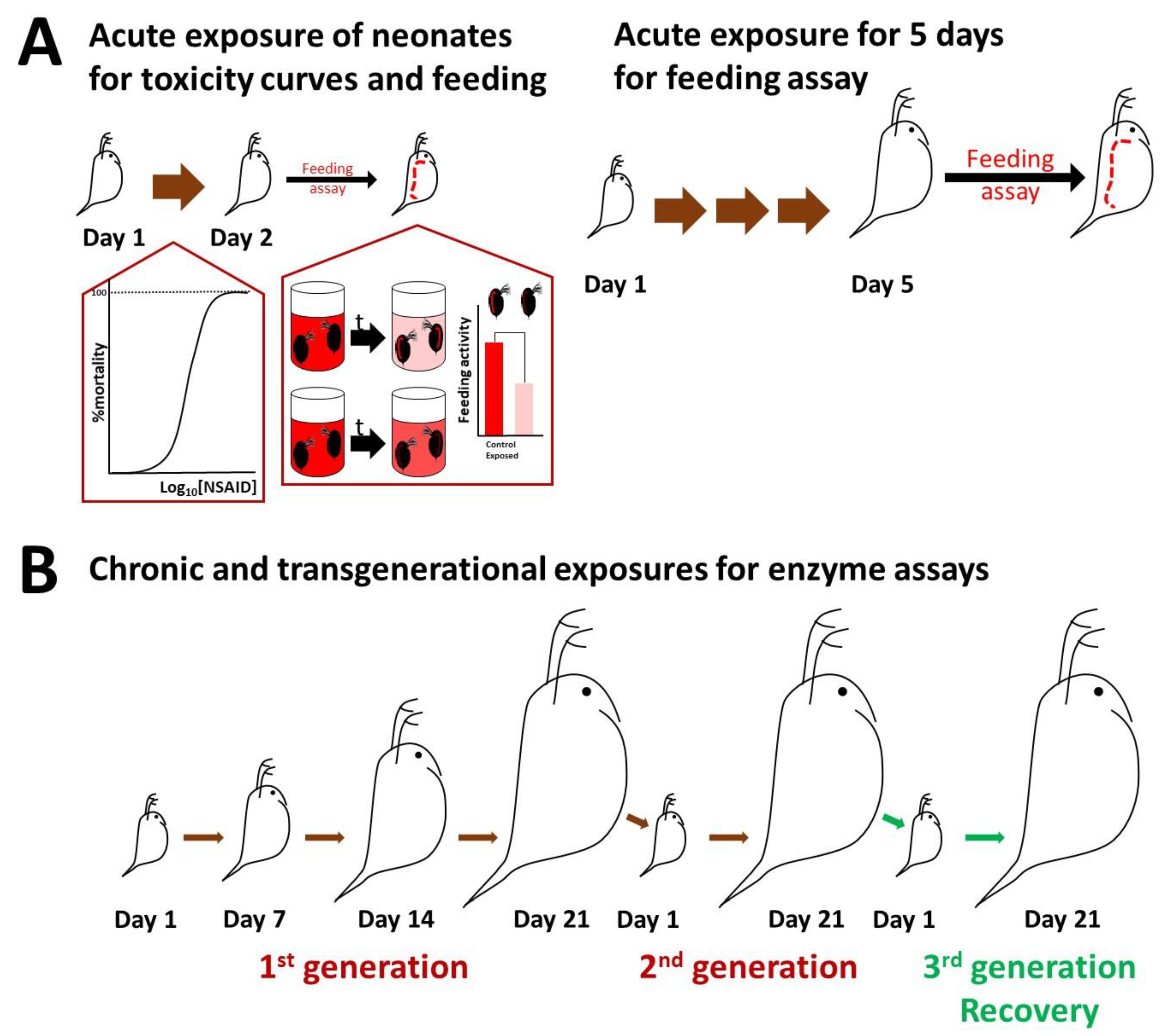
2.2. Culturing of Daphnids and Acute Toxicity
2.3. Feeding Assay and Imaging
2.4. Biochemical Assays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of NSAIDs and Their Mixture
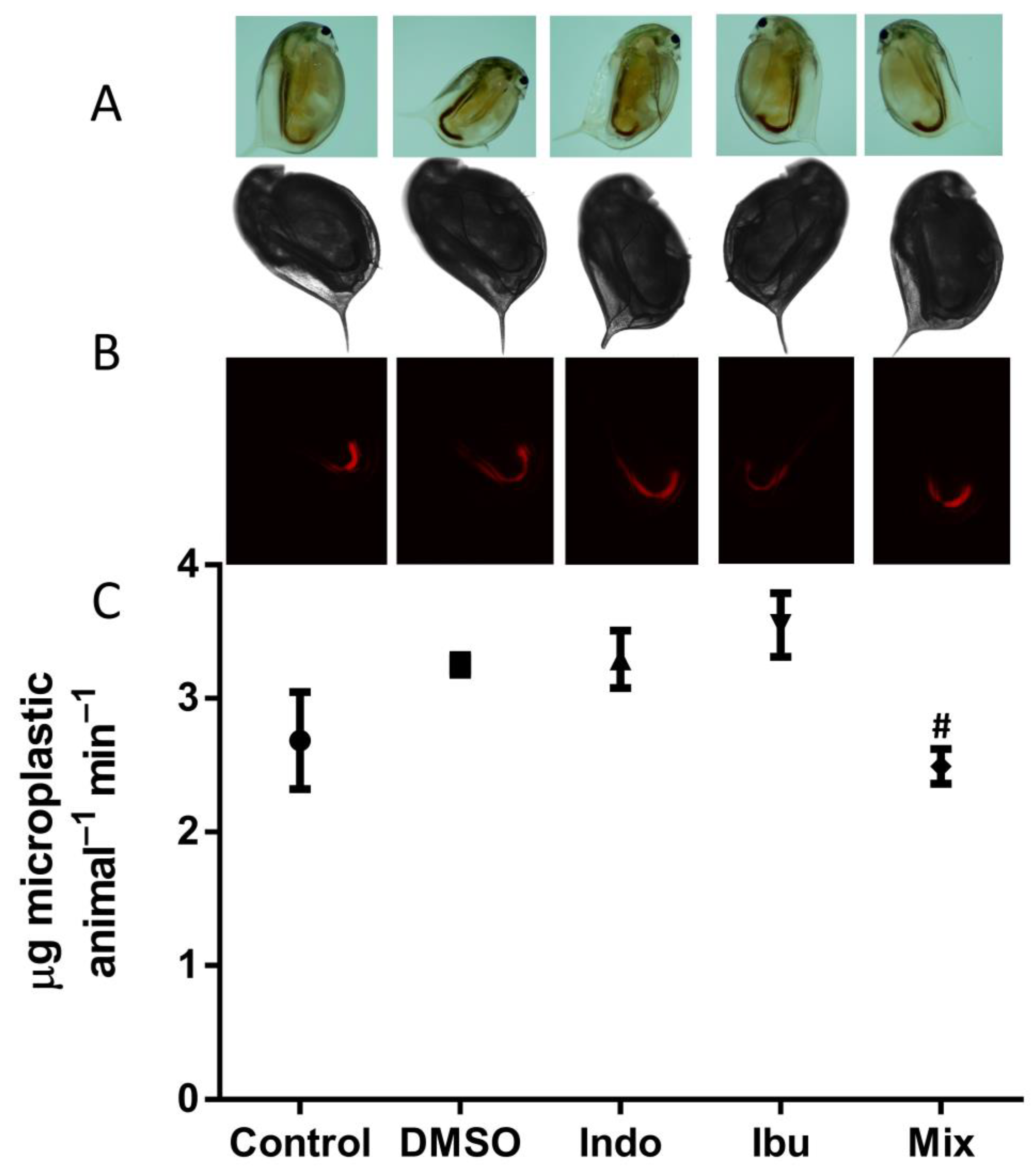
3.2. Feeding Assay and Imaging
3.3. Enzymatic Activity following Chronic and Transgenerational Exposure of Daphnids to NSAIDs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, M.E.; Ulvi, A. Monitoring the release of anti-inflammatory and analgesic pharmaceuticals in the receiving environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 36887–36902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.P.; Almeida, C.M.R. Pharmaceutical Compounds in Aquatic Environments-Occurrence, Fate and Bioremediation Prospective. Toxics 2021, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, S.; Petre, J.; Lucaciu, I.; Stoica, C.; Nita-Lazar, M. Risk screening of pharmaceutical compounds in Romanian aquatic environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Ishibashi, H.; Yamauchi, R.; Ichikawa, N.; Takao, Y.; Hirano, M.; Koga, M.; Arizono, K. Acute toxicity of pharmaceutical and personal care products on freshwater crustacean (Thamnocephalus platyurus) and fish (Oryzias latipes). J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 34, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieno, N.M.; Tuhkanen, T.; Kronberg, L. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in effluents from a sewage treatment plant and in the recipient water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8220–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, C.; Singer, H.P.; Oellers, S.; Müller, S.R. Occurrence and fate of carbamazepine, clofibric acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen in surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Raffaele, M.; Nicklas, P. Pharmaceuticals in STP effluents and their solar photodegradation in aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M. Toxicity of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, diclofenac, ibuprofen and naproxen towards freshwater invertebrates: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiacka, K.; Michnowska, A.; Maculewicz, J.; Caban, M.; Smolarz, K. Toxic effects of NSAIDs in non-target species: A review from the perspective of the aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 273, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S. The Pharmacology of Indomethacin. Headache 2016, 56, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, P.; Xu, B.; Chu, W.; Pan, Y. Detection, transformation, and toxicity of indole-derivative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during chlorine disinfection. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.; Kim, C.Y. Development of an alternative zebrafish model for drug-induced intestinal toxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudłak, B.; Wieczerzak, M.; Namieśnik, J. Determination of Toxicological Parameters of Selected Bioactive Organic Chemicals Using the Ostracodtoxkit FTM. Chem. Didact. Ecol. Metrol. 2018, 23, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsik, P.; Rezek, J.; Zidkova, M.; Kramulova, B.; Tauchen, J.; Vanek, T. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the watercourses of Elbe basin in Czech Republic. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines—22nd List; 2021 (WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Gonzalez, F.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. NSAIDs: Learning new tricks from old drugs. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushra, R.; Aslam, N. An overview of clinical pharmacology of Ibuprofen. Oman Med. J. 2010, 25, 155–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiuk, M.; Pijanowska, J.; Markowska, M.; Bednarska, A. Morphological deformation of Daphnia magna embryos caused by prolonged exposure to ibuprofen. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, L.H.; Callaghan, A.; Hooper, H.L.; Connon, R.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Maund, S.J.; Sibly, R.M. Chronic toxicity of ibuprofen to Daphnia magna: Effects on life history traits and population dynamics. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 172, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Nawaz Khan, K.; Saif Ur Rehman, M.; Mustafa, G.; Faizan Nazar, M.; Sun, Q.; Iqbal, J.; Mulla, S.I.; Yu, C.-P. Ecological risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in the receiving environment of pharmaceutical wastewater in Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmoreland, C.; Bender, H.J.; Doe, J.E.; Jacobs, M.N.; Kass, G.E.N.; Madia, F.; Mahony, C.; Manou, I.; Maxwell, G.; Prieto, P.; et al. Use of New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) in regulatory decisions for chemical safety: Report from an EPAA Deep Dive Workshop. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2022, 135, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.I.; Hanazato, T. Commentary on effects of anthropogenic and natural organic chemicals on development, swimming behavior, and reproduction of Daphnia, a key member of aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103 (Suppl. S4), 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.R.; Pfrender, M.E.; Eads, B.D.; Klaper, R.; Callaghan, A.; Sibly, R.M.; Colson, I.; Jansen, B.; Gilbert, D.; Colbourne, J.K. Daphnia as an emerging model for toxicological genomics. In Advances in Experimental Biology; Hogstrand, C., Kille, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 165–328. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. Daphnia: Development of a Model Organism in Ecology and Evolution. Excell. Ecol. 2011, 21, 1–275. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Olivan, L.M.; Galar-Martinez, M.; Garcia-Medina, S.; Valdes-Alanis, A.; Islas-Flores, H.; Neri-Cruz, N. Genotoxic response and oxidative stress induced by diclofenac, ibuprofen and naproxen in Daphnia magna. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 37, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalaki, A.; McGivern, A.R.; Poschet, G.; Büttner, M.; Altenburger, R.; Grintzalis, K. The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids—Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution. Toxics 2022, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Choi, K.; Kim, J.; Ji, K.; Kim, S.; Ahn, B.; Yun, J.; Choi, K.; Khim, J.S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Endocrine disruption and consequences of chronic exposure to ibuprofen in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) and freshwater cladocerans Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, K.; Engelmann, B.; Altenburger, R.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; Grintzalis, K. Molecular Responses of Daphnids to Chronic Exposures to Pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, L.-H.; Sibly, R.M.; Connon, R.; Hooper, H.L.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Maund, S.J.; Hill, C.J.; Bouetard, A.; Callaghan, A. Systems biology meets stress ecology: Linking molecular and organismal stress responses in Daphnia magna. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpali, V.; Belavgeni, A.; Dailianis, S. Investigation of toxic effects of imidazolium ionic liquids, [bmim][BF4] and [omim][BF4], on marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis with or without the presence of conventional solvents, such as acetone. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpali, V.; Dailianis, S. Toxicity of two imidazolium ionic liquids, [bmim][BF4] and [omim][BF4], to standard aquatic test organisms: Role of acetone in the induced toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 117, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Dai, W.; Panagiotidis, K.; Belavgeni, A.; Viant, M.R. Miniaturising acute toxicity and feeding rate measurements in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudry, R.; Hornstein, S.; Fehr-Bigger, M.; Guyer, S. TCH-024 Long-Term Stability of Indomethacin 0.2 mg/ml Ready-To-Use Solution For Intravenous Use. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. Sci. Pract. 2013, 20, A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.E.; Gray, S.; Schmidt, B. Stability of reconstituted indomethacin sodium trihydrate in original vials and polypropylene syringes. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. AJHP Off. J. Am. Soc. Health-Syst. Pharm. 1998, 55, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volonté, M.a.G.; Valora, P.D.; Cingolani, A.; Ferrara, M. Stability of ibuprofen in injection solutions. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2005, 62, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.E.; Choudhury, J.; Law, S.; Iazzetta, J. Stability of Ibuprofen solutions in normal saline or 5% dextrose in water. Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2011, 64, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, T.; Brown, S. Monitoring Commercial Ibuprofen Potency Changes Over 1 Year When Stored in a Household Setting. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 36, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toński, M.; Dołżonek, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Białk-Bielińska, A. Hydrolytic stability of selected pharmaceuticals and their transformation products. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, K.; Worthington, V. Worthington Enzyme Manual. Available online: https://www.worthington-biochem.com/index/manual.html (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Tang, S.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chang, G.G. Metal-catalyzed oxidation and cleavage of octopus glutathione transferase by the Cu(II)-ascorbate system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 21, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warholm, M.; Guthenberg, C.; Mannervik, B.; Pacifici, G.M.; Rane, A. Glutathione S-transferases in human fetal liver. Acta Chem. Scandinavica. Ser. B Org. Chem. Biochem. 1981, 35, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Georgiou, C.D.; Schneider, Y.J. An accurate and sensitive Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250-based assay for protein determination. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 480, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltemsah, Y.S.; Bohn, T. Acute and chronic effects of polystyrene microplastics on juvenile and adult Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Huang, B.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, B.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z. Mechanisms underlying the acute toxicity of fullerene to Daphnia magna: Energy acquisition restriction and oxidative stress. Water Res. 2017, 123, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Protein Oxidation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 899, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Ganjayi, M.S.; Oruganti, L.; Hari, B.; Meriga, B. Glutathione S-transferases Detoxify Endogenous and Exogenous Toxic Agents-Minireview. J. Dairy Vet. Anim. Res. 2017, 5, 00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhano, V.; Zeumer, R.; Monteiro, M.S.; Knopf, B.; Meisterjahn, B.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S.; Schlechtriem, C.; Lopes, I. Effects of wastewater-spiked nanoparticles of silver and titanium dioxide on survival, growth, reproduction and biochemical markers of Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Heckmann, L.H.; Callaghan, A.; Sibly, R.M. Reproduction recovery of the crustacean Daphnia magna after chronic exposure to ibuprofen. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.; Ji, K.; Kho, Y.; Kim, P.; Lee, J.; Ryu, J.; Choi, K. Chronic toxicity and endocrine disruption of naproxen in freshwater waterfleas and fish, and steroidogenic alteration using H295R cell assay. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Doval, J.C.; Kukkonen, J.V.; Rodrigo, P.; Munoz, I. Effects of indomethacin and propranolol on Chironomus riparius and Physella (Costatella) acuta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoskova, M.; Dobsikova, R.; Stancova, V.; Zivna, D.; Blahova, J.; Marsalek, P.; Zelníckova, L.; Bartos, M.; di Tocco, F.C.; Faggio, C. Evaluation of ibuprofen toxicity for zebrafish (Danio rerio) targeting on selected biomarkers of oxidative stress. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2013, 34 (Suppl. S2), 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, J.L. Effects of ibuprofen, diclofenac and paracetamol on hatch and motor behavior in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2017, 182, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, M.; Bebianno, M.J. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) ibuprofen distresses antioxidant defense system in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis gills. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, M.; Bebianno, M.J. Does non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) ibuprofen induce antioxidant stress and endocrine disruption in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombini, C.; Kazakova, J.; Montilla-Lopez, A.; Fernandez-Cisnal, R.; Hampel, M.; Fernandez-Torres, R.; Bello-Lopez, M.A.; Abril, N.; Blasco, J. Assessment of pharmaceutical mixture (ibuprofen, ciprofloxacin and flumequine) effects to the crayfish Procambarus clarkii: A multilevel analysis (biochemical, transcriptional and proteomic approaches). Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombini, C.; Hampel, M.; Blasco, J. Assessing the effect of human pharmaceuticals (carbamazepine, diclofenac and ibuprofen) on the marine clam Ruditapes philippinarum: An integrative and multibiomarker approach. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Martinez, G.V.; DelValls, A.T.; Laura Martin-Diaz, M. Yes, caffeine, ibuprofen, carbamazepine, novobiocin and tamoxifen have an effect on Corbicula fluminea (Muller, 1774). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Lorenz, C.; Pflugmacher, S.; Nutzmann, G.; Kloas, W.; Wiegand, C. Exposure to human pharmaceuticals Carbamazepine, Ibuprofen and Bezafibrate causes molecular effects in Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.H.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Hong, N.-H.; Sekhon, S.S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Min, J. Acute and chronic toxicity assessment and the gene expression of Dhb, Vtg, Arnt, CYP4, and CYP314 in Daphnia magna exposed to pharmaceuticals. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2015, 11, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, C.; Alanon, P.; Gutierrez-Alonso, S.; Riva, M.C.; Fernandez, C.; Tarazona, J.V. A Daphnia magna feeding bioassay as a cost effective and ecological relevant sublethal toxicity test for Environmental Risk Assessment of toxic effluents. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, J.L.; Pfenning-Butterworth, A.C.; Vetter, R.E.; Cressler, C.E. A high-throughput method to quantify feeding rates in aquatic organisms: A case study with Daphnia. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 6239–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yan, S.-w.; Li, R.-z.; Hu, Y.-w.; Chang, X.-X. Lethal/sublethal responses of Daphnia magna to acute norfloxacin contamination and changes in phytoplankton-zooplankton interactions induced by this antibiotic. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, M.V.; Rodríguez, J.A.; García-Hortigüela, P.; Fernández, A.; Beltrán, E.M.; Torrijos, M.; Fernández, C. Sublethal and chronic effects of reclaimed water on aquatic organisms. Looking for relationships between physico-chemical characterisation and toxic effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.-H.; Xin, Y.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y. Humic acid alleviates the toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastic particles to Daphnia Magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkimin, G.D.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Barata, C.; Nunes, B. Evaluation of ketoprofen toxicity in two freshwater species: Effects on biochemical, physiological and population endpoints. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoom, M.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Dong, H.; Yang, H. Bioconcentration, behavioral, and biochemical effects of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5704–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Nie, X.; Pan, B.; Ku, P.; Bao, S. Gene response of CYP360A, CYP314, and GST and whole-organism changes in Daphnia magna exposed to ibuprofen. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 179, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, Â.; Solé, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Freitas, R. Anti-inflammatory drugs in the marine environment: Bioconcentration, metabolism and sub-lethal effects in marine bivalves. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiner, N.; Radersma, R.; Vasquez, L.; Ringner, M.; Nystedt, B.; Raine, A.; Tobi, E.W.; Heijmans, B.T.; Uller, T. Environmentally induced DNA methylation is inherited across generations in an aquatic keystone species. iScience 2022, 25, 104303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, M.; Li, X.; Abdallah, M.A.; Stubbings, W.; Yan, N.; Barnard, M.; Guo, L.H.; Colbourne, J.K.; Orsini, L. Daphnia as a Sentinel Species for Environmental Health Protection: A Perspective on Biomonitoring and Bioremediation of Chemical Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14237–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
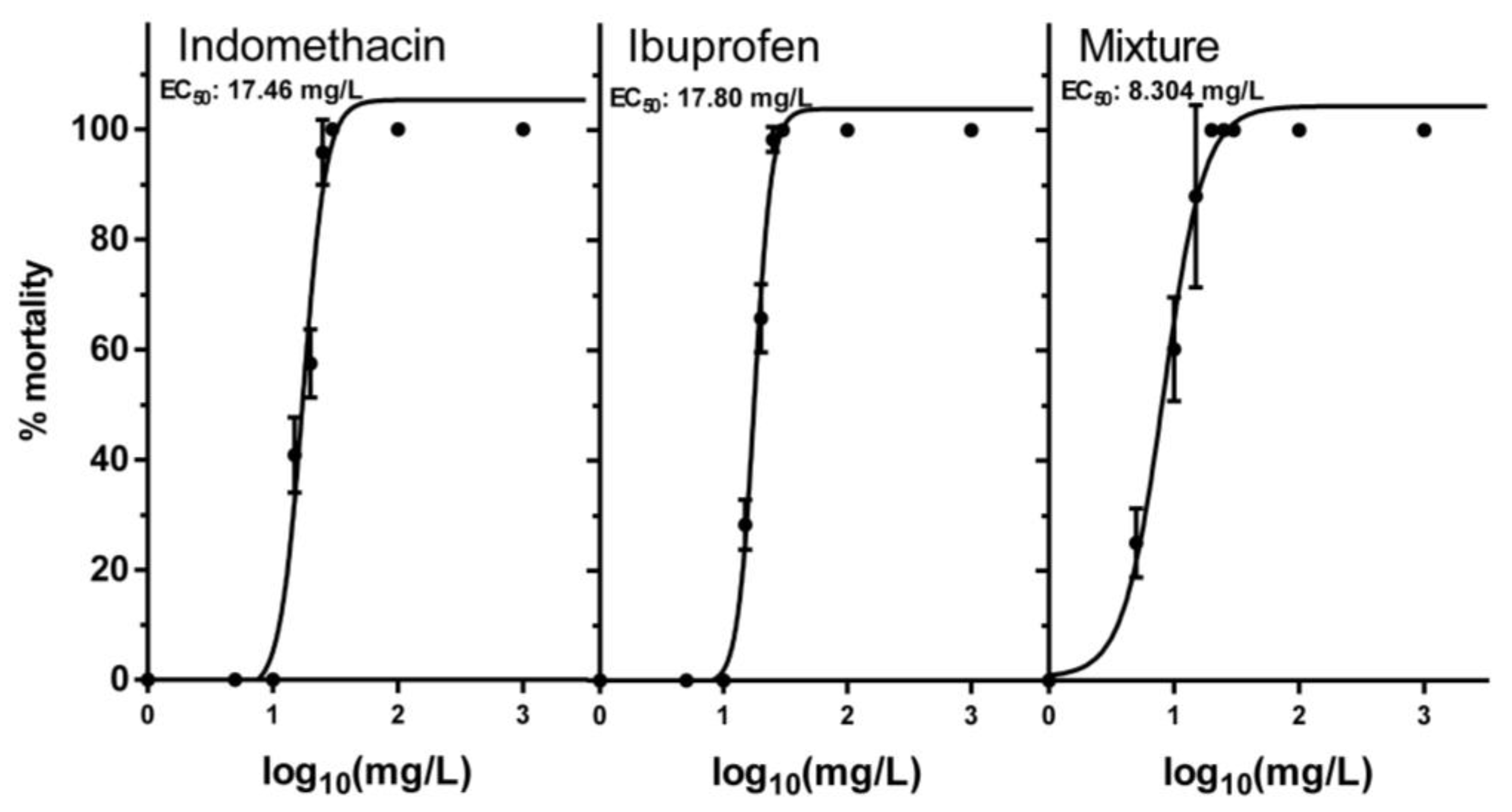

| Chemical | EC50 | (Min–Max) | Hill Slope | EC1 | EC5 | EC10 | EC20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indomethacin | 17.46 | 16.38–18.61 | 4.731 | 6.61 | 9.37 | 10.97 | 13.02 |
| Ibuprofen | 17.80 | 17.30–18.31 | 6.341 | 8.62 | 11.19 | 12.59 | 14.3 |
| Mixture 1:1 | 8.304 | 7.48–9.21 | 2.696 | 1.51 | 2.78 | 3.67 | 4.97 |
| Age (Days) | Control | DMSO | Indomethacin | Ibuprofen | Mixture | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | ALP | 5.45 ± 0.34 | 7.16 ± 0.4 * | 6.22 ± 0.21 #* (−13%) | 6.55 ± 0.26 * | 7.25 ± 0.34 * |
| ACP | 5.61 ± 0.44 | 7.74 ± 1.15 | 6.82 ± 0.51 * | 8.14 ± 0.33 * | 9.07 ± 0.72 * | |
| β-gal | 1.66 ± 0.18 | 1.51 ± 0.04 | 0.91 ± 0.14 #* (−40%) | 1.26 ± 0.06 #* (−17%) | 1.41 ± 0.03 # (−7%) | |
| LIP | 131.01 ± 19.67 | 137.72 ± 2.71 | 72.94 ± 11.09 #* (−47%) | 123.76 ± 2.26 # (−10%) | 93.14 ± 6.58 # (−32%) | |
| PEP | 24.57 ± 1.04 | 23.62 ± 2.53 | 27.26 ± 5.01 | 29.54 ± 7.34 | 21.73 ± 4.54 | |
| GST | 91.2 ± 3 | 97.6 ± 12.3 | 107.9 ± 11.6 | 95.6 ± 10 | 76.7 ± 12.7 | |
| 14 | ALP | 2.61 ± 0.02 | 3.24 ± 0.35 | 3.05 ± 0.29 | 2.63 ± 0.14 | 3.13 ± 0.16 * |
| ACP | 4.57 ± 0.28 | 5.35 ± 0.91 | 6.02 ± 0.71 | 4.55 ± 0.2 | 4.39 ± 0.19 | |
| β-gal | 2.08 ± 0.08 | 2.46 ± 0.19 | 2.23 ± 0.39 | 2.08 ± 0.75 | 1.77 ± 0.16 # (−28%) | |
| LIP | 159.59 ± 16.43 | 141.47 ± 8.09 | 193.84 ± 25.81 | 148.12 ± 37.62 | 140.13 ± 10.69 | |
| PEP | 1.99 ± 0.1 | 2.32 ± 0.29 | 1.94 ± 0.06 | 1.93 ± 0.27 | 1.9 ± 0.12 | |
| GST | 132.3 ± 2.7 | 162.1 ± 12.4 * | 144.7 ± 5.4 * | 151.7 ± 11.7 | 151.3 ± 19.2 | |
| 21 | ALP | 5.32 ± 0.37 | 4.86 ± 0.2 | 5.05 ± 0.17 | 4.89 ± 0.37 | 4.69 ± 0.18 * |
| ACP | 2.96 ± 0.07 | 3.17 ± 0.09 * | 2.84 ± 0.13 # (−10%) | 3.09 ± 0.04 | 2.87 ± 0.11 # (−9%) | |
| β-gal | 6.04 ± 0.31 | 5.36 ± 0.24 * | 5.93 ± 0.19 # (+11%) | 5.13 ± 0.25 * | 5.05 ± 0.29 * | |
| LIP | 95.93 ± 5.85 | 81.04 ± 7.29 * | 90.86 ± 0.42 | 78.43 ± 4.27 * | 77.29 ± 7.29 * | |
| PEP | 11.41 ± 0.6 | 9.35 ± 0.43 * | 10.82 ± 0.6 # (+16%) | 10.52 ± 1.39 | 9.75 ± 0.59 * | |
| GST | 44.2 ± 3.4 | 54.2 ± 3.7 * | 52.3 ± 1.5 * | 67.6 ± 4.4 #* (+25%) | 67.7 ± 5.8 #* (+25%) | |
| 21 2nd generation | ALP | 3.3 ± 0.26 | 3.64 ± 0.19 | 3.8 ± 0.18 * | 3.27 ± 0.15 # (−10%) | 3.09 ± 0.16 # (−15%) |
| ACP | 3.09 ± 0.09 | 2.75 ± 0.16 * | 2.67 ± 0.15 * | 2.78 ± 0.21 | 3.29 ± 0.19 # (+20%) | |
| β-gal | 4.48 ± 0.24 | 4.76 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.23 | 3.93 ± 0.22 #* (−17%) | 3.8 ± 0.09 #* (−20%) | |
| LIP | 70.46 ± 3.87 | 66.3 ± 5.65 | 56.41 ± 3.09 #* (−15%) | 47.53 ± 1.66 #* (−28%) | 56.53 ± 4.31 #* (−15%) | |
| PEP | 7.43 ± 0.6 | 7.89 ± 0.56 | 6.81 ± 0.26 # (−14%) | 7.15 ± 0.13 | 6.44 ± 0.33 # (−18%) | |
| GST | 98.4 ± 4.2 | 104.3 ± 0.6 | 94.6 ± 2.9 # (−9%) | 123.5 ± 2.1 #* (+18%) | 111 ± 5.8 * | |
| 21 3rd generation recovery | ALP | 4.83 ± 0.36 | 4.2 ± 0.11 * | 4.16 ± 0.24 * | 4.55 ± 0.44 | 4.32 ± 0.28 |
| ACP | 3.42 ± 0.28 | 2.83 ± 0.08 * | 3.21 ± 0.28 | 3.24 ± 0.47 | 3.06 ± 0.14 | |
| β-gal | 6 ± 0.54 | 4.75 ± 0.17 * | 5.03 ± 0.44 * | 4.54 ± 0.24 * | 4.97 ± 0.36 * | |
| LIP | 55.14 ± 1.79 | 53.39 ± 2.08 | 51.19 ± 2.04 * | 53.32 ± 6.51 | 53.56 ± 3.73 | |
| PEP | 6.21 ± 0.45 | 4.47 ± 0.27 * | 5.33 ± 0.49 | 4.61 ± 0.35 * | 5.18 ± 0.41 #* (+16%) | |
| GST | 124.4 ± 11.8 | 130.3 ± 3.5 | 154.7 ± 4.2 #* (+19%) | 138.3 ± 3.5 # (+6%) | 141.8 ± 9.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalaki, A.; Grintzalis, K. Acute and Transgenerational Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Daphnia magna. Toxics 2023, 11, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040320
Michalaki A, Grintzalis K. Acute and Transgenerational Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Daphnia magna. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040320
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalaki, Anna, and Konstantinos Grintzalis. 2023. "Acute and Transgenerational Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Daphnia magna" Toxics 11, no. 4: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040320
APA StyleMichalaki, A., & Grintzalis, K. (2023). Acute and Transgenerational Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Daphnia magna. Toxics, 11(4), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040320







