Ambient Benzo[a]pyrene’s Effect on Kinetic Modulation of Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation: A Tentative Association between Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.; Kim, W.-H.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Park, H.-Y. Air Pollution and Central Nervous System Disease: A Review of the Impact of Fine Particulate Matter on Neurological Disorders. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 575330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahad, O.; Lelieveld, J.; Birklein, F.; Lieb, K.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Ambient Air Pollution Increases the Risk of Cerebrovascular and Neuropsychiatric Disorders through Induction of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmeyer, S.; D’Angiulli, A. How air pollution alters brain development: The role of neuroinflammation. Transl. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Cole, T.B.; Dao, K.; Chang, Y.-C.; Coburn, J.; Garrick, J.M. Effects of air pollution on the nervous system and its possible role in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 210, 107523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, G.; Danti, S.; Carlesi, C.; Borin, G. Danger in the Air: Air Pollution and Cognitive Dysfunction. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dementiasr. 2018, 33, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusinkveld, H.J.; Wahle, T.; Campbell, A.; Westerink, R.H.S.; Tran, L.; Johnston, H.; Stone, V.; Cassee, F.R.; Schins, R.P.F. Neurodegenerative and neurological disorders by small inhaled particles. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Klunk, W.E. Imaging beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the aging human brain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 1469–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Xin, R.; Sun, Y. Genetic and environmental factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and promising therapeutic intervention via fecal microbiota transplantation. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Sohn, J.; Noh, J.; Jang, H.; Kim, W.; Cho, S.-K.; Seo, H.; Seo, G.; Lee, S.-K.; Noh, Y.; et al. Association between exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and brain cortical thinning: The Environmental Pollution-Induced Neurological EFfects (EPINEF) study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianelle, V.; Colombi, C.; Caserini, S.; Ozgen, S.; Galante, S.; Marongiu, A.; Lanzani, G. Benzo(a)pyrene air concentrations and emission inventory in Lombardy region, Italy. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiberová, M.; Vlasáková, L.; Vlček, O.; Šmejdířová, J.; Horálek, J.; Bieser, J. Benzo[a]pyrene in the Ambient Air in the Czech Republic: Emission Sources, Current and Long-Term Monitoring Analysis and Human Exposure. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Ding, X.; He, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhu, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Shen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, X.; et al. Nationwide increase of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ultrafine particles during winter over China revealed by size-segregated measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14581–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leikauf, G.D.; Kim, S.-H.; Jang, A.-S. Mechanisms of ultrafine particle-induced respiratory health effects. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liu, Y.; Jing, G.; Li, K.; Zhao, Y.; Sha, B.; Wang, Q.; Wu, D. Rapid and efficient crossing blood-brain barrier: Hydrophobic drug delivery system based on propionylated amylose helix nanoclusters. Biomaterials 2017, 113, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirnkor, V.A.; Ngozi, V.E.; Ajero, C.M.; Charity, L.K.; Ngozi, O.S.; Ebere, E.C.; Emeka, A.C. Biomonitoring of concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in blood and urine of children at playgrounds within Owerri, Imo State, Nigeria. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2019, 34, e2019011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Li, M. Benzo[a]pyrene-induced neurobehavioral function and neurotransmitter alterations in coke oven workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2009, 67, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Whiten, D.R.; Ruggeri, F.S.; Hughes, C.; Rodrigues, M.; Sideris, D.I.; Taylor, C.G.; Aprile, F.A.; Muyldermans, S.; Knowles, T.P.J.; et al. Soluble aggregates present in cerebrospinal fluid change in size and mechanism of toxicity during Alzheimer’s disease progression. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Sideris, D.; Danial, J.S.H.; Emin, D.; Ruggeri, F.S.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lobanova, E.; Dakin, H.; De, S.; Miller, A.; et al. Soluble amyloid beta-containing aggregates are present throughout the brain at early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barage, S.H.; Sonawane, K.D. Amyloid cascade hypothesis: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropeptides 2015, 52, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J. A beta oligomers—A decade of discovery. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölttä, M.; Hansson, O.; Andreasson, U.; Hertze, J.; Minthon, L.; Nägga, K.; Andreasen, N.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Evaluating Amyloid-β Oligomers in Cerebrospinal Fluid as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, M.K.; Cappai, R.; Pham, C.L.L.; Ciccotosto, G.D. Membrane-bound tetramer and trimer Aβ oligomeric species correlate with toxicity towards cultured neurons. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Beta-Amyloid: The key peptide in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauk, A. Why is the amyloid beta peptide of Alzheimer’s disease neurotoxic? Dalton Trans. 2008, 10, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, K.P. Bioinorganic Chemistry of Alzheimer’s Disease. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5193–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaumbekova, S.; Torkmahalleh, M.A.; Sakaguchi, N.; Umezawa, M.; Shah, D. Effect of ambient polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nicotine on the structure of Aβ42 protein. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, C.; Sholts, S.B.; Österlund, N.; Luo, J.; Jarvet, J.; Roos, P.M.; Ilag, L.; Gräslund, A.; Wärmländer, S.K. Alzheimer’s disease and cigarette smoke components: Effects of nicotine, PAHs, and Cd(II), Cr(III), Pb(II), Pb(IV) ions on amyloid-β peptide aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Z. Chronic exposure to low benzo[a]pyrene level causes neurodegenerative disease-like syndromes in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 167, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wang, C.; Xi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Z. Early-Life Benzo[a]Pyrene Exposure Causes Neurodegenerative Syndromes in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and the Mechanism Involved. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 157, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tu, D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.-M.; Zhou, H. Benzo(a)pyrene exposure induced neuronal loss, plaque deposition, and cognitive decline in APP/PS1 mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Pall, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. Gromacs: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laprtops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerben, S.; Lemkul, J.; Brown, A.M.; Bevan, D. Comparing atomistic molecular mechanics force fields for a difficult target: A case study on the Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 32, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malde, A.K.; Zuo, L.; Breeze, M.; Stroet, M.; Poger, D.; Nair, P.C.; Oostenbrink, C.; Mark, A.E. An Automated Force Field Topology Builder (ATB) and Repository: Version 1.0. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 4026–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.; Fraaije, J.G. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Bevan, D.R. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Amyloid β -Peptide (1-42): Tetramer Formation and Membrane Interactions. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östersund, N.; Kulkarni, Y.S.; Misiaszek, A.D.; Wallin, C.; Krüger, D.M.; Liao, Q.; Mashayekhy Rad, F.; Jarvet, J.; Strodel, B.; Wärmländer, S.K.; et al. Amyloid-β Peptide Interactions with Amphiphilic Surfactants: Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Effects. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhanu, W.M.; Hansmann, U.H.E. Structure and Dynamics of Amyloid-β Segmental Polymorphisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokar, S.; Erfani, M.; Bavi, O.; Khazaei, S.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Hajiramezanali, M.; Beiki, D.; Shamloo, A. Design of peptide-based inhibitor agent against amyloid-β aggregation: Molecular docking, synthesis and in vitro evaluation. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 102, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, G.; Lionello, C.; Stojceski, F. Highlighting the effect of amyloid beta assemblies on the mechanical properties and conformational stability of cell membrane. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2020, 100, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Samantray, S.; Anteghini, M.; Khaled, M.; Strodel, B. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the amyloid-β peptide revealed by Markov state models based on MD data in agreement with experiment. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 6652–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.F.; Xu, T.H.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.R.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Amyloid beta: Structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1205–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.T.; Derreumaux, P.; Vu, V.V.; Nam, P.C.; Ngo, S.T. C-Terminal Plays as the Possible Nucleation of the Self-Aggregation of the S-Shape Aβ. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11066–11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Krupa, P.; Hai, N.M.; Linh, H.Q.; Li, M.S. Structure and Physicochemical Properties of the Aβ42 Tetramer: Multiscale Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 7253–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatafta, H.; Khaled, M.; Owen, M.C.; Sayyed-Ahmad, A.; Strodel, B. Amyloid-β peptide dimers undergo a random coil to β-sheet transition in the aqueous phase but not at the neuronal membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106210118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, J.F.; Loomes, K.M.; Konarkowska, B.; Cooper, G.J.S. Suppression by polycyclic compounds of the conversion of human amylin into insoluble amyloid. Biochem. J. 2003, 374 Pt 3, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Tang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Qing, G.; Sun, T. Protein/Peptide Aggregation and Amyloidosis on Biointerfaces. Materials 2016, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
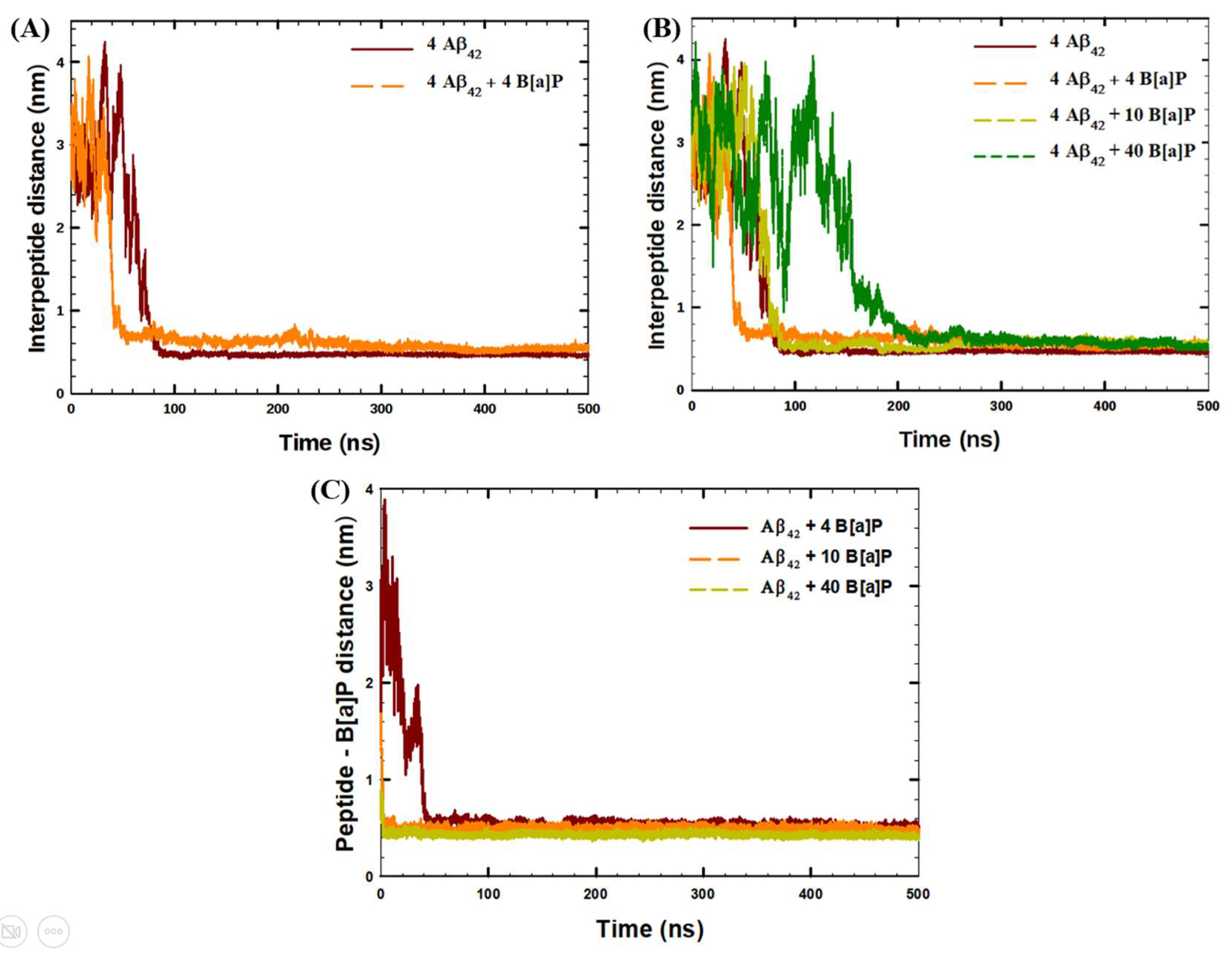
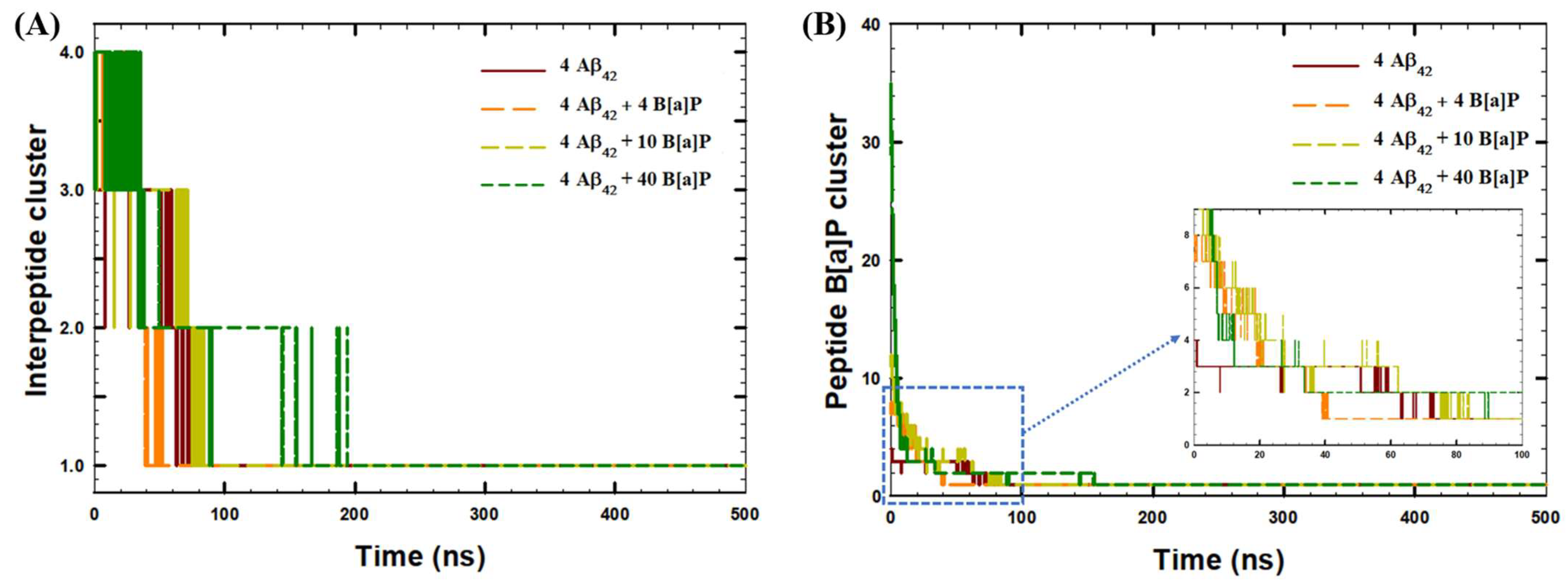


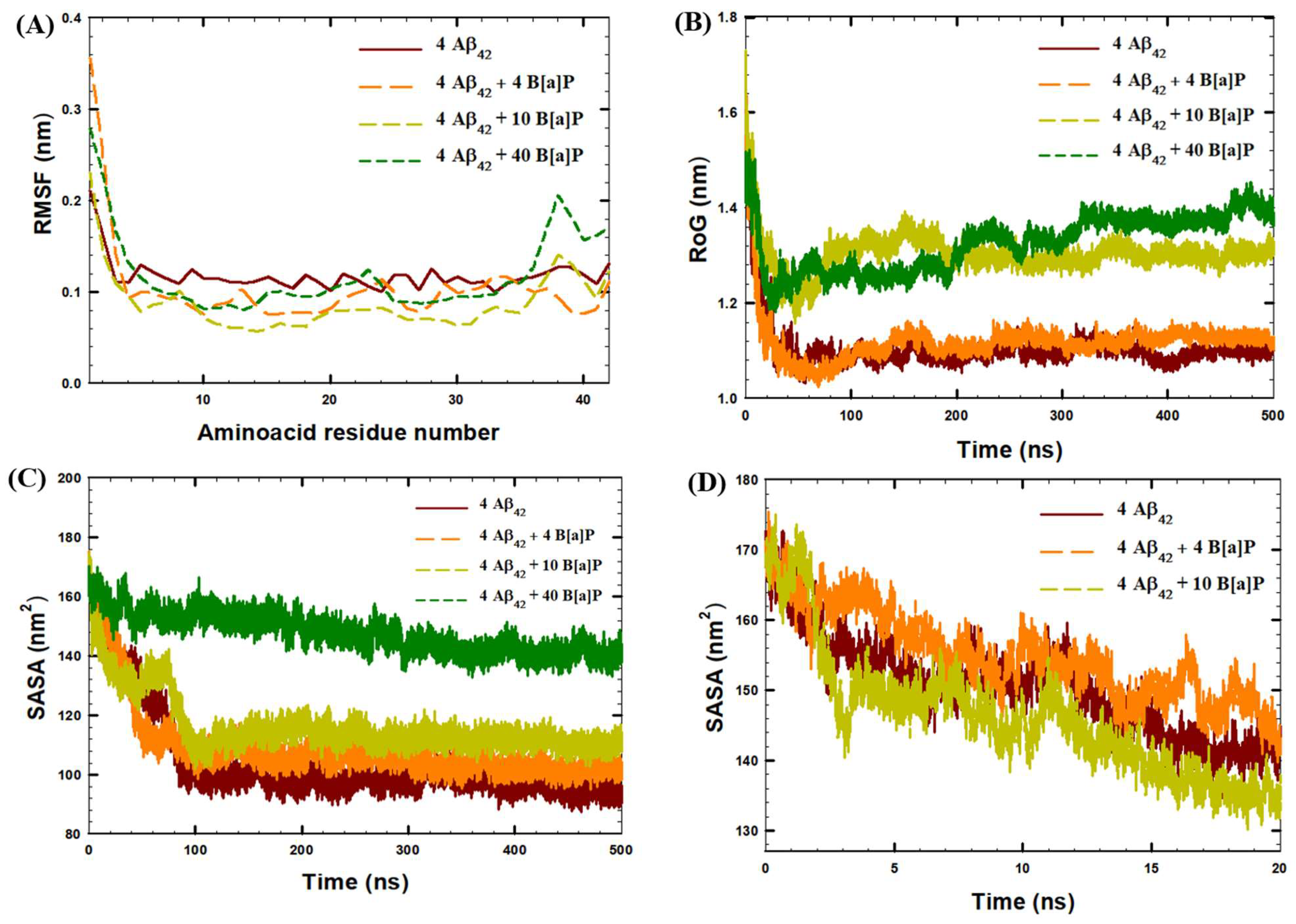
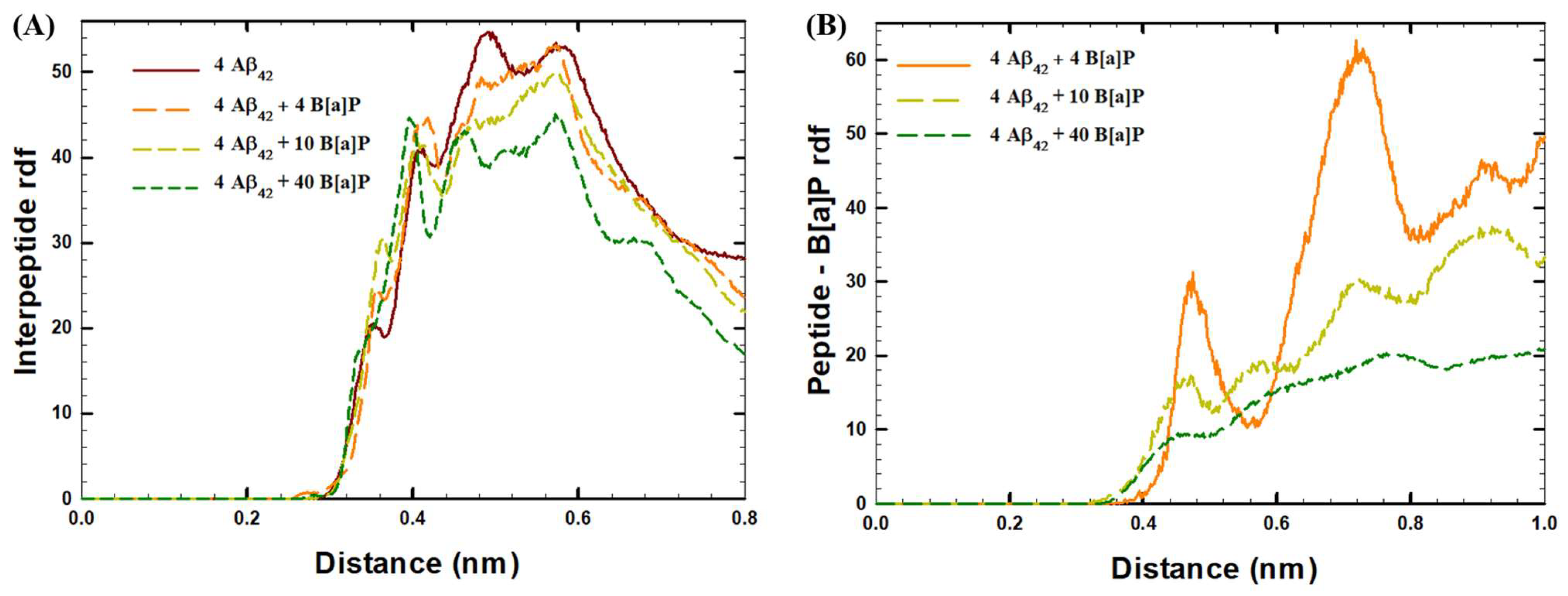
| System | Aβ42 | B[a]P | B[a]P Concentration | H2O | Na+ | Cl− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Aβ42 | 4 | 0 | 0 mM | 42,296 | 128 | 120 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 4 B[a]P | 4 | 4 | 5.00 mM | 42,270 | 128 | 120 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 10 B[a]P | 4 | 10 | 12.5 mM | 42,179 | 128 | 120 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 40 B[a]P | 4 | 40 | 50.0 mM | 41,798 | 128 | 120 |
| SASA0 ns (nm2) | SASA500 ns (nm2) | SASAmin (nm2) | H-Bonds (Last 30 ns) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Aβ42 | 171.6 | 94.60 | 87.30 | 115 ± 5 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 4 B[a]P | 169.0 | 102.7 | 95.10 | 119 ± 5 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 10 B[a]P | 169.6 | 110.0 | 101.5 | 113 ± 5 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 40 B[a]P | 166.5 | 139.2 | 132.7 | 109 ± 5 |
| System | Peptide–Peptide (kJ/mol) | Peptide–B[a]P (kJ/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coul–SR | LJ–SR | Coul–LR | LJ–LR | Coul–SR | LJ–SR | |
| 4 Aβ42 | −44,048 ± 26 | −3712 ± 11 | 27,804 ± 8 | −38.5 ± 3.4 | - | - |
| 4 Aβ42 + 4 B[a]P | −44,333 ± 10 | −3577 ± 7 | 28,052 ± 12 | −44.1 ± 1.9 | −49.2 ± 2.2 | −423 ± 2 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 10 B[a]P | −43,963 ± 40 | −3536 ± 9 | 28,042 ± 7 | −7.9 ± 3 | −60.6 ± 2.8 | −762 ± 16 |
| 4 Aβ42 + 40 B[a]P | −43,945 ± 22 | −3016 ± 7 | 28,043 ± 6 | 9.8 ± 3 | −191.7 ± 3 | −2020 ± 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaumbekova, S.; Torkmahalleh, M.A.; Shah, D. Ambient Benzo[a]pyrene’s Effect on Kinetic Modulation of Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation: A Tentative Association between Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Alzheimer’s Disease. Toxics 2022, 10, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120786
Kaumbekova S, Torkmahalleh MA, Shah D. Ambient Benzo[a]pyrene’s Effect on Kinetic Modulation of Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation: A Tentative Association between Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Alzheimer’s Disease. Toxics. 2022; 10(12):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120786
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaumbekova, Samal, Mehdi Amouei Torkmahalleh, and Dhawal Shah. 2022. "Ambient Benzo[a]pyrene’s Effect on Kinetic Modulation of Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation: A Tentative Association between Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Alzheimer’s Disease" Toxics 10, no. 12: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120786
APA StyleKaumbekova, S., Torkmahalleh, M. A., & Shah, D. (2022). Ambient Benzo[a]pyrene’s Effect on Kinetic Modulation of Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation: A Tentative Association between Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Alzheimer’s Disease. Toxics, 10(12), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120786








