Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover in the City of Tyumen (Western Siberia, Russia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
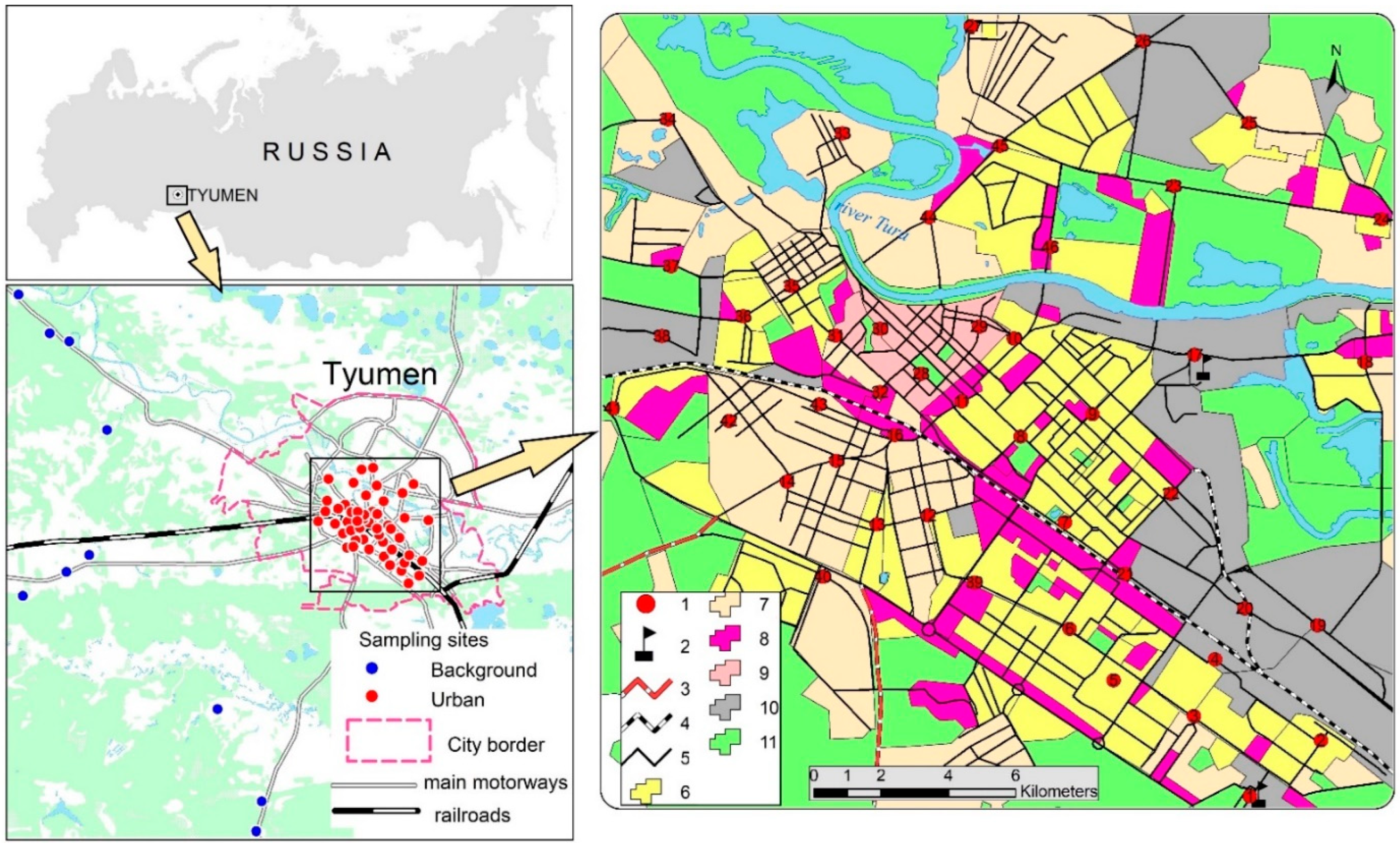
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
- (1)
- the historical center with buildings that have existed since the 17th century and are now used by social and administrative organizations;
- (2)
- low-rise residential areas that have existed since the 19th century;
- (3)
- high-rise residential areas that have been constructed within a period from the 1950s to the present time and that now house the major part of the Tyumen population;
- (4)
- business and public facilities areas;
- (5)
- industrial zones;
- (6)
- transport zones affected by road traffic (located between main roads and buildings of various usage).
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analyses
2.3. Calculations and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Physico-Chemical Properties of Snow
3.2. PAH Content
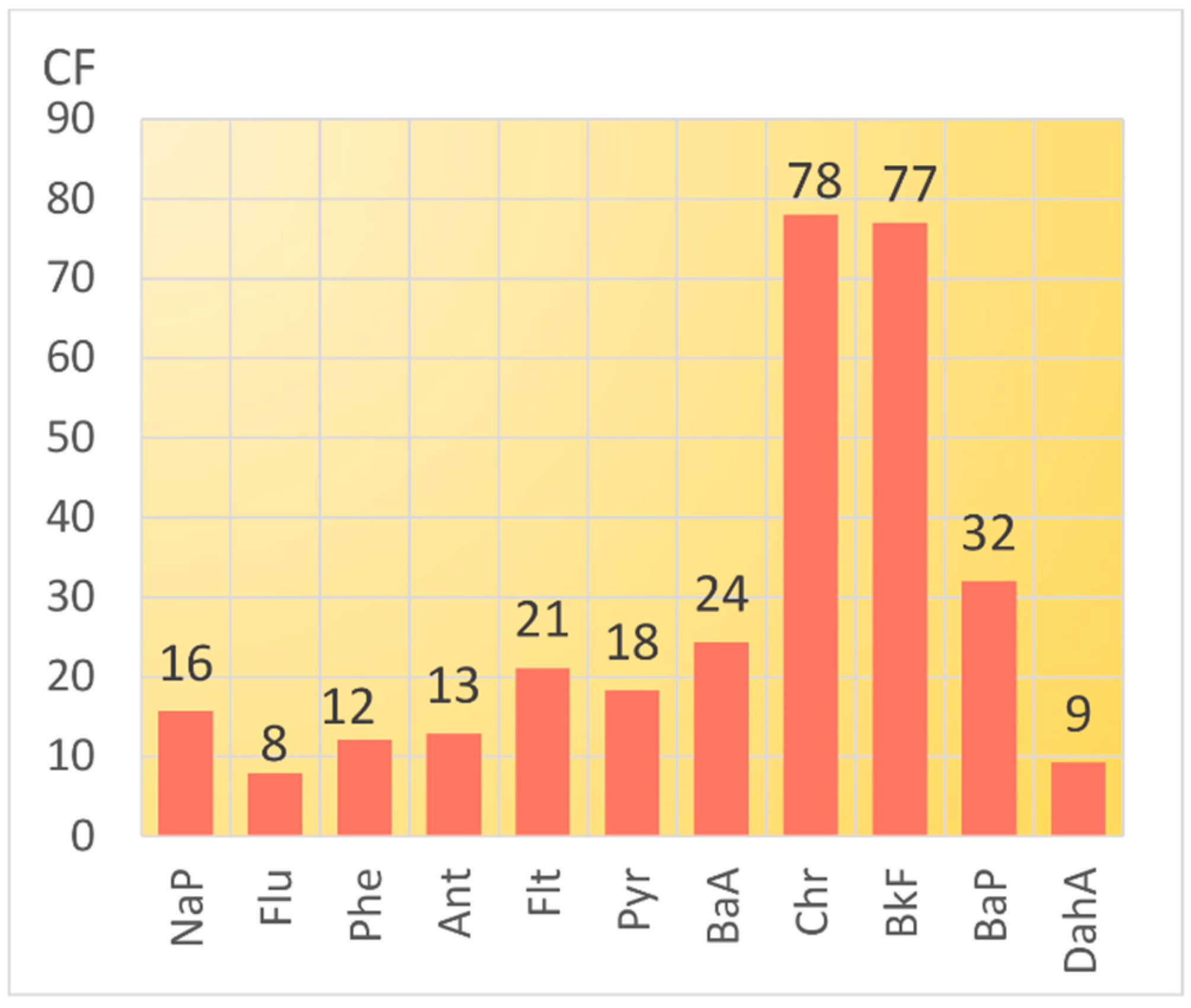
3.3. Source Identification
3.4. Spatial Distribution and Land-Use Effects
3.5. Contamination Levels and Comparison with Other Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, D.; Ghosh, S.K.; Raha, S. Impacts of photochemical ageing on the half-lives and diagnostic ratio of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons intrinsic to PM2.5 collected from ‘realworld’ like combustion events of wood and rice straw burnin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Nakajima, F.; Furumai, H. Size-and density-distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road dust. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offenberg, J.H.; Baker, J.E. Precipitation scavenging of polychlorinated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons along an urban to over-water transect. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3763–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. The distribution variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons between fresh snow and seasonal snowpack in campus in Changchun City, Northeast China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; McBean, E.A. PAH deposition to snow surface. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2001, 8, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.O.; Field, R.A.; Goldstone, M.E.; Kirk, P.W.; Lester, J.N.; Perry, R. A review of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Sources, fate and behavior. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 60, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Drooge, B.L.; Fernández, P.; Grimalt, J.O.; Stuchlík, E.; García, C.J.T.; Cuevas, E. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in remote European and Atlantic sites located above the boundary mixing layer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Zhang, J.; Xing, X.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Zheng, J.; Yao, R.; Cao, J. Seasonal variation and health risk assessment of atmospheric PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a classic agglomeration industrial city, central China. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syso, A.I.; Artamonova, V.S.; Sidorova, M.Y.; Ermolov, Y.V.; Cherevko, A.S. Pollution of the atmosphere, snow and soil cover of Novosibirsk. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2005, 18, 593–599. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kosheleva, N.E.; Kasimov, N.S.; Vlasov, D.V.; Nikiforova, E.M. Critical loads of benzo (a) pyrene on urban soils. Doklady Earth Sci. 2017, 472, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimov, N.S.; Kosheleva, N.E.; Nikiforova, E.M.; Vlasov, D.V. Benzo [a] pyrene in urban environments of eastern Moscow: Pollution levels and critical loads. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavgorodnyaya, Y.A.; Chikidova, A.L.; Biryukov, M.V.; Demin, V.V. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particulate depositions and urban soils of Moscow, Russia. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3155–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanchenko, N.I.; Belykh, L.I.; Slutsky, S.L.; Lanko, A.V. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in solid residue and volatile organic compounds in snow cover filtrate of Bratsk. Bull. Tomsk. Polytech. Univ. Geo Assets Eng. 2016, 327, 52–58. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zhurba, O.M.; Alekseyenko, A.N.; Shayakhmetov, S.F.; Merinov, A.V. Study of polycyclic aromatic and petroleum hydrocarbons in a snow cover in an urbanized territory. Gig. I Sanit. 2019, 98, 1037–1042. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.E.; Morozov, S.V.; Raputa, V.F.; Kokovkin, V.V.; Khvostov, I.V. Investigation of aerosol precipitation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the sphere of influence of Barnaul. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 19, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Levshina, S. Distribution and characteristic of PAHs in snow of the urban and reserve areas of southern Far East Russia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotel’nikova, I.M.; Kuimova, N.G.; Pavlova, L.M.; Sergeyeva, A.G.; Shumilova, L.P. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in snow cover solid like indicators of urban atmosphere pollution. Izv. Samar. Nauchnogo Tsentra Ross. Akad. Nauk. 2011, 13, 1341–1346. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kozhevnikov, A.Y.; Falev, D.I.; Sypalov, S.A.; Kozhevnikova, I.S.; Kosyakov, D.S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the snow cover of the northern city agglomeration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilevich, M.I.; Beznosikov, V.A.; Gabov, D.N. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the snow cover of the background territories of the taiga zone of the European northeast of Russia. Environ. Geosci. 2014, 4, 337–343. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zavgorodnyaya, Y.A.; Popovicheva, O.B.; Kobelev, V.O.; Starodymova, D.P.; Shevchenko, V.P.; Kasimov, N.S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the snowpack of Yamal-Nenetz Autonomous region as indicators of anthropogenic source influence. Arct. Antarct. Res. 2021, 67, 261–279. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guseynov, A.N.; Mogutova, L.M.; Goubareva, N.N.; Moskovchenko, D.V. Content of Oil Products and 3.4-Benzpyrene in Soils of Tyumen. Ecol. Ind. Russ. 2000, 7, 31–32. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinova, E.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; Antonenko, E.; Konstantinov, A. Levels, sources, and toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban topsoils of an intensively developing Western Siberian city. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinova, E.; Minkina, T.; Konstantinov, A.; Sushkova, S.; Antonenko, E.; Kurasova, A.; Loiko, S. Pollution status and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban street dust of Tyumen city, Russia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 44, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, M.; Rykowska, I.; Wolski, R.; Andrzejewski, L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their Derivatives (O-PAHs, N-PAHs, OH-PAHs): Determination in Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM)–a Review. Environ. Process 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeman, M.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Cass, G.R. Size and composition distribution of fine particulate matter emitted from motor vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lei, Y.D.; Wania, F.; Shoeib, M.; Harner, T. Regressing gas/particle partitioning data for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3558–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reference Book on the USSR Climate. Tyumen and Omsk Regions. Series 2. Issue 17; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1998; 702p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Krest’yannikova, E.V.; Kozlova, V.V.; Larina, N.S.; Larin, S.I. Chemical and environmental assessment of lead pollution in the atmosphere of the city of Tyumen. Izv. Samar. Nauchnogo Tsentra Ross. Akad. Nauk. 2015, 17, 679–684. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Germanova, T.V.; Kernozhitskaya, A.F. On the issue of environmental assessment of the transport system in urbanized territories (on the example of Tyumen City). Izv. Samar. Nauchnogo Tsentra Ross. Akad. Nauk. 2014, 16, 1713–1716. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Weather Archive in Tyumen. Weather Schedule. Available online: https://rp5.ru/Weather_archive_in_Tyumen (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- US EPA (2007). Method 3550c:Ultrasonic Extraction. Revision 3. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3550c.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- US EPA (1996). Method 3630c:Silica Gel Cleanup. Revision 3. 1996. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3630c.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, T.; Schmid, P.; Schlatter, C. The use of toxic equivalency factors in assessing occupational and environmental health risk associated with exposure to airborne mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemosphere 1996, 32, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.M.; Ivatt, P.D.; Evans, M.J.; Kroll, J.H.; Hrdina, A.I.H.; Kohale, I.N.; Selin, N.E. Global cancer risk from unregulated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. GeoHealth 2021, 5, e2021GH000401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, P.; Maîtrea, A.; Persoons, R.; Bicout, D.J. Lung cancer risk assessment for workers exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in various industries. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 32, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaustov, A.; Redina, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover of Moscow (Case Study of the RUDN University Campus). Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2021, 41, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Sharma, K.; Brassard, B.W.; Hazewinkel, R. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Deposition in the Snowpack of the Athabasca Oil Sands Region of Alberta, Canada. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilevich, M.I.; Beznosikov, V.A.; Kondratenok, B.M. Chemical composition of snow cover in the taiga zone of the Komi Republic. Water Resour. 2011, 38, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovchenko, D.V.; Babushkin, A.G. Peculiarities of formation of chemical composition of snow waters (on example of Khanty-Mansi autonomous district). Earth Cryosphere 2012, 16, 71–81. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, V.P.; Lisitsyn, A.P.; Stein, R.; Goryunova, N.V.; Klyuvitkin, A.A.; Kravchishina, M.D.; Krivs, M.; Novigatsky, A.N.; Sokolov, V.T.; Filippov, A.S.; et al. Distribution and composition of particulate matter in the Arctic snow. Probl. Arct. Antarct. 2007, 75, 106–118. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kasimov, N.S.; Kosheleva, N.E.; Vlasov, D.V.; Terskaya, E.V. Geochemistry of snow cover in the Eastern District of Moscow. Mosc. Univ. Bull. Ser. 5 Geogr. 2012, 4, 14–25. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Huang, P.; Chen, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Urumqi, China: Distribution, source contributions, and potential health risks. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 5639–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Hou, S.; Niu, H.; Tian, K.; Liu, X.; Wu, F. Status, sources, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of Xi’an, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18947–18959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, N.; Wu, X.; Pu, J.; He, J.; Zhang, C. Sources and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of different glaciers over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, L.; Grimalt, J.O.; Fernández, P.; Lopez, J.F.; Nickus, U.; Thies, H. Persistent organic pollutant accumulation in seasonal snow along an altitudinal gradient in the Tyrolean Alps. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 12638–12650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorshkov, A.G.; Marinayte, I.I.; Obolkin, V.A.; Baram, G.I.; Khodzher, T.V. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the snow cover of the southern shore of Lake Baikal. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 1998, 11, 913–918. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zhidkin, A.P.; Gennadiev, A.N.; Koshovskii, T.S. Input and behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in arable, fallow, and forest soils of the taiga zone (Tver oblast). Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, P.Q.; Taniguchi, T.; Nabeshima, Y.; Bandow, H.; Trung, N.Q.; Takenaka, N. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons concentrations simultaneously obtained in gas, rainwater and particles. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, N.T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH’s) in the terrestrial environment–a review. J. Environ. Qual. 1983, 12, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, K.; Toor, G.S.; Chirenje, T.; Ma, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of different land uses in Miami, Florida. Soil Sediment Contam. 2010, 19, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsibart, A.S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in pyrogenic soils of conservation territories («Khakassky» nature reserve). Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2012, 2, 50–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tsibart, A.S.; Gennadiev, A.N. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils: Sources, behavior, and indication significance (a review). Eurasian Soil Sci. 2013, 46, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fingas, M.; Shu, Y.Y.; Sigouin, L.; Landriault, M.; Lambert, P.; Mullin, J. Quantitative characterization of PAHs in burn residue and soot samples and differentiation of pyrogenic PAHs from petrogenic PAHs− The 1994 mobile burn study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, N.; Muresan, B.; Hedde, M.; François, D. PAH dynamics in roadside environments: Influence on the consistency of diagnostic ratio values and ecosystem contamination assessments. Sci Total Environ. 2015, 538, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soclo, H.H.; Garrigues, P.H.; Ewald, M. Origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marine sediments: Case studies in Cotonou (Benin) and Aquitaine (France) areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muel, B.; Saguem, S. Determination of 23 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particulate matter of the Paris area and photolysis by sunlight. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1985, 19, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, B.A., Jr.; Bryner, N.P.; Wise, S.A.; Mulholland, G.H.; Lao, R.C.; Fingas, M.F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions from combustion of crude oil on water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, E.M.; Kosheleva, N.E. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils (Moscow, Eastern District). Eurasian Soil Sc. 2011, 44, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisler, R. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Hazards to Fish, Wildlife, and Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review; U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Laurel, MD, USA, 1987; p. 55.
- Konan, B.R.; Yoboue, V.; Adiaffi, B.; Diaby, M.; Oga, Y.M.S.; Bakayoko, A.; Gnamien, S.; Keita, S.; Bahino, J.; Ossohou, M. Source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rainwater and effect on the health of the population: The case of the District of Abidjan in the South of Ivory Coast. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, A.G.; Mikhailova, T.A.; Berezhnaya, N.S.; Vereshchagin, A.L. Pine needles as a biomonitor for estimation of the regional-scale distribution of organic pollutants. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2006, 408, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chao, S.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Fan, X. Urbanization-related changes in soil PAHs and potential health risks of emission sources in a township in Southern Jiangsu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Crittenden, J.C. Assessing the combined risks of PAHs and metals in urban soils by urbanization indicators. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickiforova, E.M.; Kozin, I.S.; Tsird, K. Contamination of urban soils with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to the effect of heating. Eurasian Soil Sci. 1993, 34, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chikidova, A.L. Politsiklicheskiye Aromaticheskiye Uglevodorody v Ekosistemakh g. Moskvy (na Primere Vostochnogo Administrativnogo Okruga). [Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ecosystems of Moscow (by the Example of the Eastern Administrative District)]. Ph.D. Dissertation, Faculty of Soil Science, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, 2017; 141p. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Bayraktar, H.; Paloluoğlu, C.; Turalioğlu, F.S.; Gaga, E.O. A multipoint (49 points) study of dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Erzurum, Turkey by using surrogated snow surface samplers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12400–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodygin, E.D.; Chukov, S.N.; Beznosikov, V.A.; Gabov, D.N. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils of Vasilievsky Island (St. Petersburg). Eurasian Soil Sci. 2008, 41, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.G.; Cheng, J.P.; Jiao, F.; Duo, K.X.; Rong, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, W.H. Distribution, sources, and potential risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in drinking water resources from Henan Province in middle of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 146, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Nie, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Occurrence and Toxicological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Resources of Southern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozhitkov, R.Y. The content of suspended particles PM2.5 and PM10 in the surface layer of the atmosphere of Tyumen in June 2020. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2020, 33, 913–917. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Laboratory melting of late-winter urban snow samples: The magnitude and dynamics of releases of heavy metals and PAHs. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hough, R.; Fu, Q.; An, L.; Shen, Z.; Li, Y.-F.; Liu, D.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fresh snow in the city of Harbin in northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilevich, M.I.; Gabov, D.N.; Beznosikov, V.A.; Kondratenok, B.M. Organic matter in snow cover in the influence zone of emissions from a pulp-and-paper mill. Water Resour. 2009, 36, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | Tyumen (n = 46) | Background Area (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|
| Snow depth, cm | 17–38 26 | 30–58 41 |
| Snow density, g cm −3 | 0.16–0.30 0.21 | 0.14–0.23 0.18 |
| TDS, mg L−1 | 11.9–564.0 68.1 | 6.4–18.3 9.5 |
| pH | 5.9–8.1 6.3 | 4.2–5.5 4.7 |
| Particulate matter content, mg L−1 | 9.4–121 37.1 | 4.1–10.9 7.5 |
| Deposition flux values, mg m −2 day −1 | 5.4–94.3 20 | 2.4–8.3 5.5 |
| PAH Compounds | Background Area (n = 8) | Tyumen (n = 46) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | Min-Max | Mean | Median | Min-Max | |
| Naphthalene (NaP) | 1.36 | 0.80 | nd–4.4 | 21.3 | 11.7 | 3.29–47.3 |
| Fluorene (Flu) | 0.18 | 0.18 | nd–0.4 | 1.4 | 0.86 | 0.08–11.8 |
| Phenanthrene (Phe) | 2.19 | 2.20 | 1.55–3.25 | 26.4 | 14.0 | 4.69–198.5 |
| Anthracene (Ant) | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.05–0.3 | 1.93 | 0.84 | 0.18–29.4 |
| Fluoranthene (Flt) | 0.90 | 1.00 | nd–1.8 | 19.0 | 9.1 | 2.38–214.1 |
| Pyrene (Pyr) | 0.89 | 0.93 | nd–2.4 | 16.4 | 7.8 | 0.92–211.3 |
| Benzo(a)anthracene (BaA) | 0.094 | 0.05 | nd–0.3 | 2.2 | 1.6 | nd–18.12 |
| Chrysene (Chr) | 0.11 | 0.00 | nd–0.55 | 8.8 | 3.9 | nd–201.6 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene (BbF) | nd | 0.00 | nd | 6.7 | 5.2 | nd–62.57 |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene (BkF) | 0.03 | 0.00 | nd–0.1 | 2.4 | 1.6 | nd–20.7 |
| Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) | 0.11 | 0.08 | nd–0.35 | 3.6 | 2.7 | nd–22.6 |
| Dibenzo(ah)anthracene (DahA) | 0.13 | 0.00 | nd–1.05 | 1.2 | 0.00 | nd–15.3 |
| Benzo(ghi)perylene (BghiP) | nd | 0.00 | nd | 5.5 | 2.55 | nd–46.7 |
| Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene (IcdP) | nd | 0.00 | nd | 5.9 | 0.00 | nd–41.8 |
| ∑14 PAHs | 6.2 | 5.7 | 1.7–10.9 | 123 | 78.3 | 17.8–1019 |
| ∑LMW PAHs | 4.78 | 4.5 | 1.7–8.15 | 70.1 | 36.0 | 13.3–575.2 |
| ∑HMW PAHs | 1.38 | 1.2 | nd–3.5 | 52.7 | 30.7 | 3.8–443.7 |
| Land-Use Areas | Diagnostic Ratio | M | SD | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical center | LMW/HMW | 1.9 | 1.5 | 4.0 |
| Flt/Pyr | 1.3 | 0.3 | 1.7 | |
| Low-rise residential areas | LMW/HMW | 1.3 | 0.4 | 1.7 |
| Flt/Pyr | 1.4 | 0.3 | 1.7 | |
| High-rise residential areas | LMW/HMW | 2.7 | 1.6 | 4.6 |
| Flt/Pyr | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.8 | |
| Business and public facilities areas | LMW/HMW | 1.6 | 0.7 | 2.5 |
| Flt/Pyr | 1.9 | 0.9 | 3.3 | |
| Industrial zone | LMW/HMW | 1.9 | 0.8 | 2.7 |
| Flt/Pyr | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.8 | |
| Transport zone | LMW/HMW | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.6 |
| Flt/Pyr | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.9 |
| Land-Use Areas | BaPeq Values, Mean ± SD (Max) | Isomers Determining Toxicity × |
|---|---|---|
| Historical center | 6.0 ± 3.6 (11.1) | BaP55 DahA22 BbF8 |
| Low-rise residential areas | 6.2 ± 5.0 (14.5) | BaP42 DahA37 BbF9 |
| High-rise residential areas | 5.4 ± 7.7 (23.1) | DahA41 BaP34 IcdP13 BbF5 |
| Business and public facilities areas | 4.8 ± 3.7 (15.4) | BaP65 BbF10 IcdP10 |
| Industrial areas | 4.1 ± 3.2 (9.9) | BaP55 DahA22 BbF8 |
| Transport areas | 10.5 ± 7.2 (32.3) | BaP55 DahA13 BbF11 IcdP9 |
| Tyumen in general | 6.8 ± 5.5 (32.3) | BaP53 DahA18 BbF10 IcdP9 |
| City, Country | Concentration, ng L−1 | Deposition, μg m−2 | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tyumen, Russia, ∑14 PAHs (particulate) | 1.7–10.9 (background) 17.8–1018.9 (urban) | 1.0–65.5 | This study |
| Shelekhov, Russia, ∑13 PAHs (total) | 28,600–134,700 | - | [14] |
| Barnaul, Russia, ∑16 PAHs (total) | 179–4575 | - | [15] |
| Khabarovsk, Russia, ∑16 PAHs (total) | 34.8–79.8 (background) 43–695.7 (urban) | - | [16] |
| Erzurum, Turkey, ∑18 PAHs (particulate) | 23,820 | - | [69] |
| Luleå and Umeå, Sweden, ∑16 PAHs (total) | 2,720 (Luleå) 9,640 (Umeå) | - | [74] |
| Harbin, China, ∑16 PAHs (total) | 10,700 (median value) | - | [75] |
| Changchun City, China, ∑16 PAHs (total) | 26,600–36,900 | - | [4] |
| Moscow, Russia, ∑16 PAHs (particulate) | - | 45–57 (residential areas) 140–264 (traffic zone) | [12] |
| Syktyvkar, Russia, ∑13 PAHs (total) | - | 3.5–4.1 background 20.1–76.3 industrial | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moskovchenko, D.; Pozhitkov, R.; Lodygin, E.; Toptygina, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover in the City of Tyumen (Western Siberia, Russia). Toxics 2022, 10, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120743
Moskovchenko D, Pozhitkov R, Lodygin E, Toptygina M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover in the City of Tyumen (Western Siberia, Russia). Toxics. 2022; 10(12):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120743
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoskovchenko, Dmitriy, Roman Pozhitkov, Evgeny Lodygin, and Marina Toptygina. 2022. "Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover in the City of Tyumen (Western Siberia, Russia)" Toxics 10, no. 12: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120743
APA StyleMoskovchenko, D., Pozhitkov, R., Lodygin, E., & Toptygina, M. (2022). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover in the City of Tyumen (Western Siberia, Russia). Toxics, 10(12), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120743







