Prebiotic Properties of Non-Fructosylated α-Galactooligosaccharides from PEA (Pisum sativum L.) Using Infant Fecal Slurries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Non-Fructosylated α-GOS and β-Galactooligosacharides (GOS) Characterization
2.3. Infant Faecal Samples
2.4. In Vitro Faecal Fermentation
2.5. DNA Extraction
2.6. Microbial Faecal Populations Determined by Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.7. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA) and Lactic Acid Analysis
2.8. PCR-Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis (DGGE) Analysis of Bifidobacteria
2.9. Excision and Sequencing of DGGE Bands
2.10. Carbohydrate Quantification by Gas Chromatography Coupled to Flame-Ionization Detector (GC-FID)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
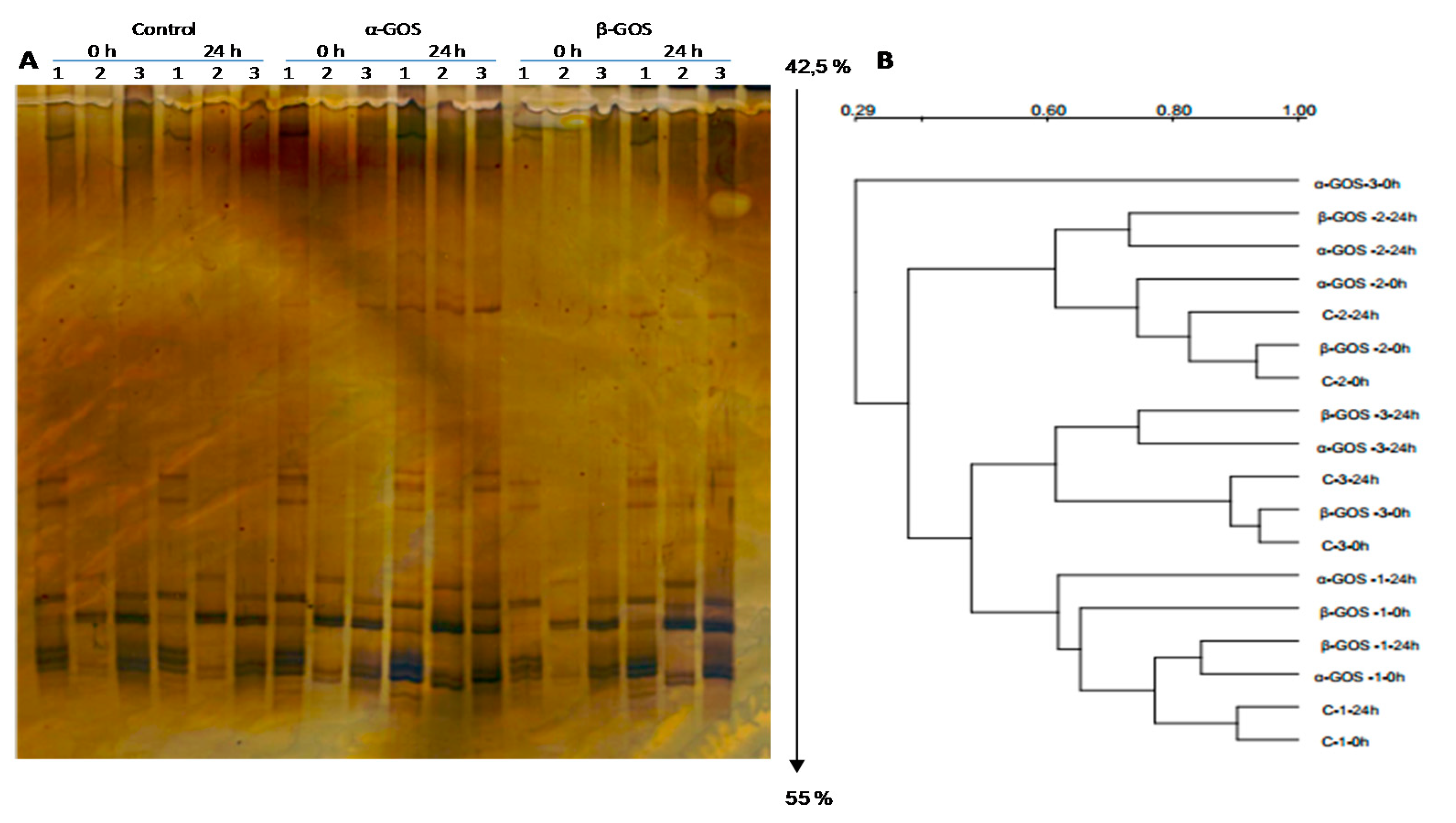
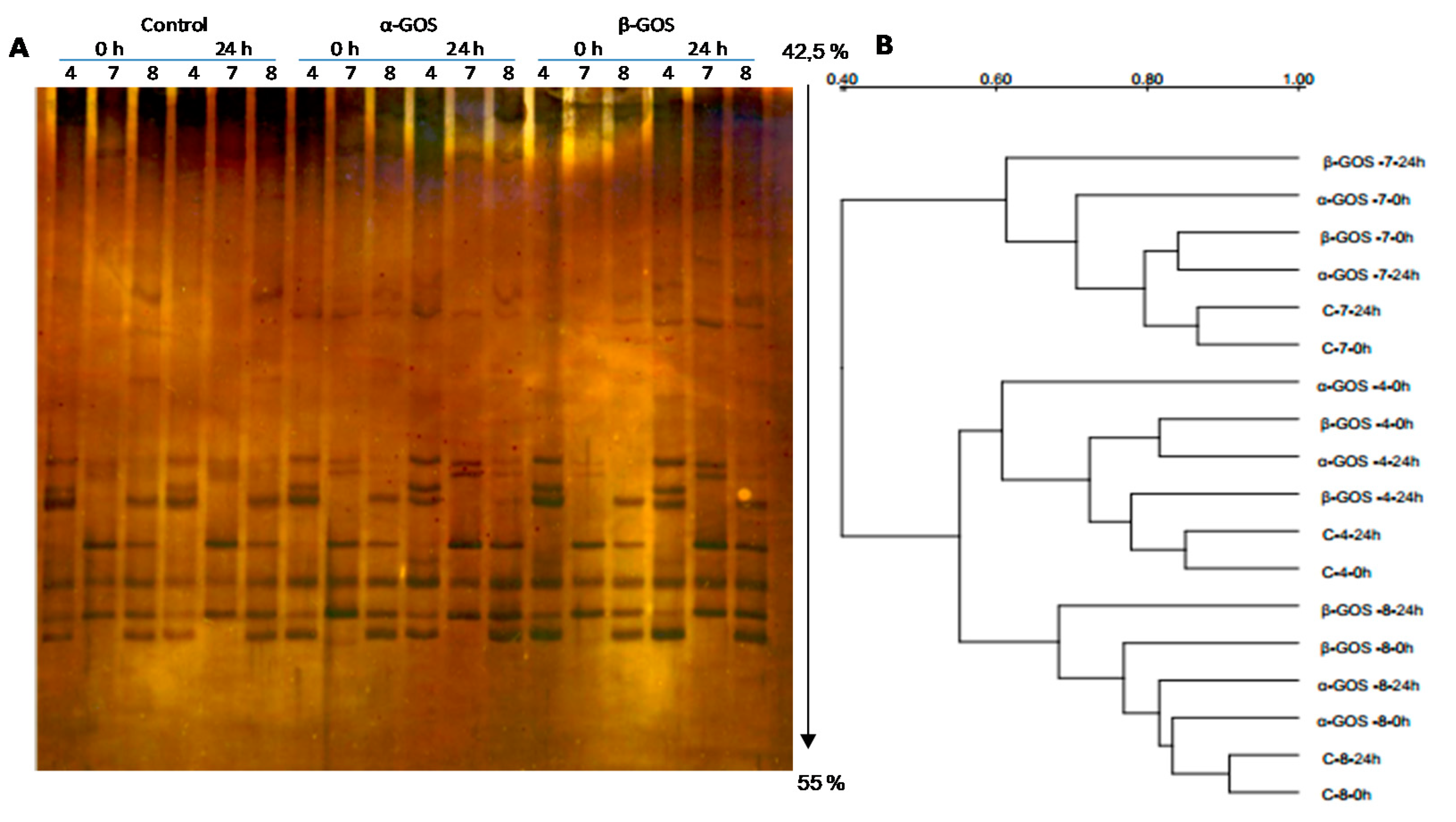
3.1. Microbiota Composition after In Vitro Fermentation of Non-Fructosylated α-GOS and β-GOS with Infant Fecal Samples
3.2. Effect of Non-Fructosylated α-GOS on Bifidobacterial Composition
3.3. Modulation in Bifidobacteria Species Population by Non-Fructosylated α-GOS and β-GOS
3.4. Lactate and Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFA) Concentration
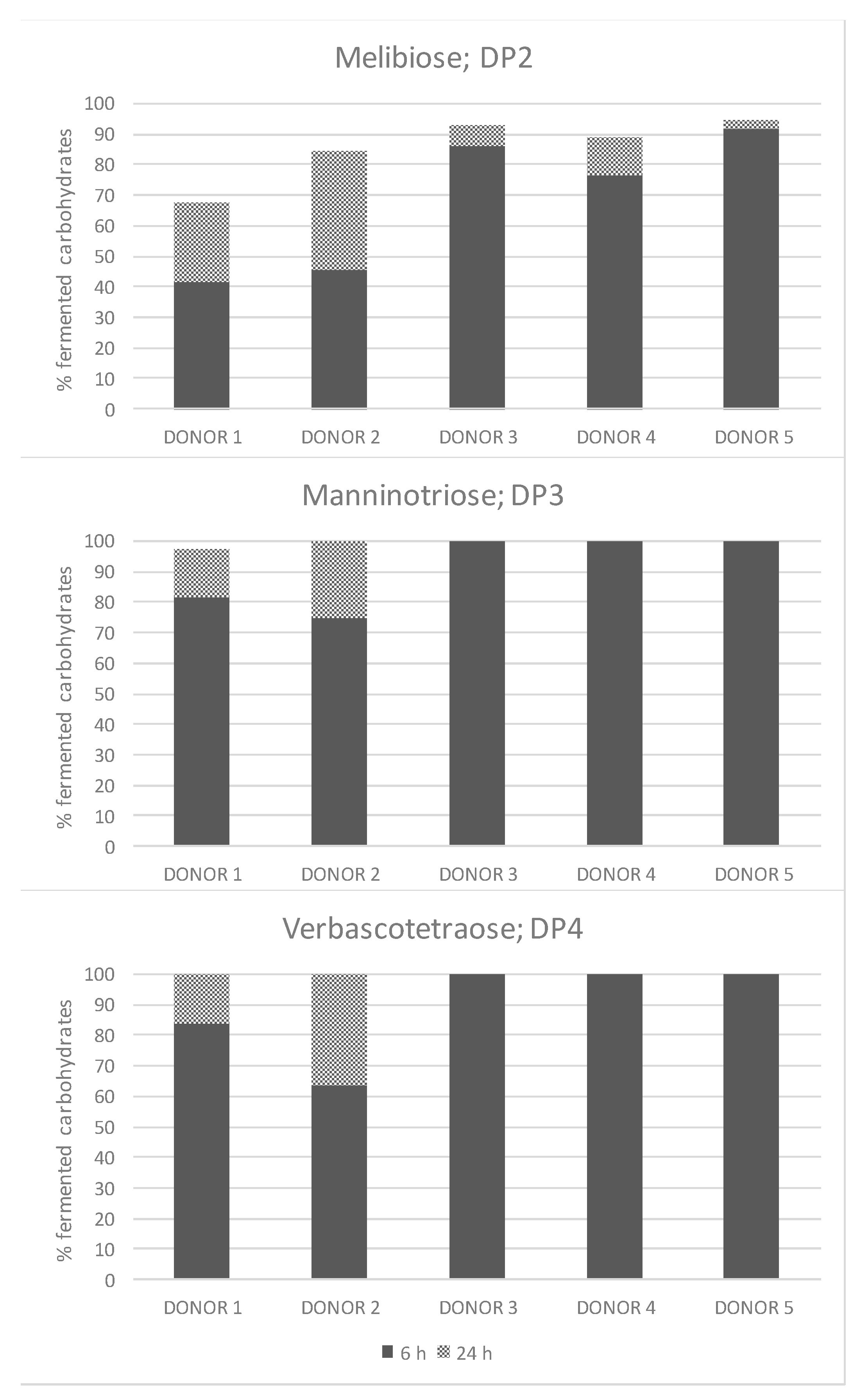
3.5. Consumption of Non-Fructosylated α-GOS Per Donor and Degree of Polymerization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collado, M.C.; Derrien, M.; Isolauri, E.; De Vos, W.M.; Salminen, S. Intestinal integrity and Akkermansia muciniphila, a mucin-degrading member of the intestinal microbiota present in infants, adults, and the elderly. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7767–7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.A.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Kober, O.I.; Juge, N.; Avershina, E.; Rudi, K.; Narbad, A.; Jenmalm, M.C.; et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throught life, with emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26050. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Houghteling, P.D.; Walker, W.A. Mucosal why is initial bacterial colonization of the intestine important to the infant’s and child’s health? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 6, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar]
- Verkhnyatskaya, S.; Ferrari, M.; De Vos, P.; Walvoort, M.T.C. Shaping the infant microbiome with non-digestible carbohydrates. Front. Microbiol. Res. Top. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Cani, P.D.; Verbeke, K.; Reid, G. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, R.; Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Non-digestible carbohydrates in infant formula as substitution for human milk oligosaccharide functions: Effects on microbiota and gut maturation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcobal, A.; Barboza, M.; Froehlich, J.W.; Block, D.E.; German, J.B.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Mills, D.A. Consumption of human milk oligosaccharides by gut-related microbes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5334–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Moyano, S.; Totten, S.M.; Garrido, D.A.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Bruce German, J.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Mills, D.A. Variation in consumption of human milk oligosaccharides by infant gut-associated strains of Bifidobacterium breve. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6040–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Ma, H.; Zeng, W.; Wang, P.G.; Yao, N.; Han, W.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W. Enzymatic production of HMO mimics by the sialylation of galacto-oligosaccharides. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barile, D.; Rastall, R.A. Human milk and related oligosaccharides as prebiotics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswari, H.; Widodo, A.D.; Handayani, F.; Juffrie, M.; Sundjaya, T.; Bindels, J.; Hegar, B. Dosage-related prebiotic effects of inulin in formula-fed infants. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehara, T.; Izumi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Nakazato, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Namba, K.; Takeda, Y. Combinational effects of prebiotic oligosaccharides on bifidobacterial growth and host gene expression in a simplified mixed culture model and neonatal mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalsamy, G.; Mortimer, E.; Greenfield, P.; Bird, A.R.; Young, G.P.; Christophersen, C.T. Resistant starch is actively fermented by infant faecal microbiota and increases microbial diversity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, O.; Olano, A.; Rastall, R.; Moreno, F.J. In Vitro digestibility of dietary carbohydrates: Toward a standardized methodology beyond amylolytic and microbial enzymes. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Ende, W. Multifunctional fructans and raffinose family oligosaccharides. Front. Plant. Sci. 2013, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Myhara, R.M.; Nilsson, K.; Skura, B.J.; Bowmer, E.J.; Cruickshank, P.K. Gas production from melibiose, raffinose and white bean extracts by bacteria of human fecal origin. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 1988, 21, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.N.; Ureta, M.M.; Tymczyszyn, E.E.; Castilho, P.C.; Gomez-Zavaglia, A. Technological aspects of the production of fructo and galacto-oligosaccharides. Enzymatic synthesis and hydrolysis. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetics Products, Nutrition and Allergies). Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to AlphaGOS® and a reduction of post-prandial glycaemic responses pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) N° 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlbaum, S.; Prudence, K.; Kieboom, J.; Heerikhuisen, M.; van den Broek, T.; Schuren, F.H.J.; Steinert, R.E.; Raederstorff, D. In Vitro fermentation of selected prebiotics and their effects on the composition and activity of the adult gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, C.; Zhou, Y.; Thorsrud, B.A.; Morel-Despeisse, F.; Chappuis, E. Safety evaluation of α-galacto-oligosaccharides for use in infant formulas investigated in neonatal piglets. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2017, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, O.; Marín-Manzano, M.C.; Rubio, L.A.; Moreno, F.J.; Sanz, M.L.; Clemente, A. Monomer and linkage type of galacto-oligosaccharides affect their resistance to ileal digestion and prebiotic properties in rats. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleya, S.; Binetti, A.; Salazar, N.; Fernández, N.; Solis, G.; Hernández-Barranco, A.; Margolles, A.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Gueimonde, M. Establisment and development of intestinal microbiota in preterm neonates. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Manzano, M.C.; Abecia, L.; Hernández-Hernández, O.; Sanz, M.L.; Montilla, A.; Olano, A.; Rubio, L.A.; Moreno, F.J.; Clemente, A. Galacto-oligosaccharides derived from lactulose exert a selective stimulation on the growth of Bifidobacterium animalis in the large intestine of growing rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7560–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasco, R.; Fernández de Palencia, P.; Fontecha, J.; Peláez, C.; Requena, T. Competition mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria: Fermentative metabolism and colonization. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E. Ecological Diversity and its Measurements; Princenton University Press: Princenton, NJ, USA, 1988; p. 179. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. Ecological Diversity; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 165. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Biol. Mol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brobst, K.; Lott, C.E. Determination of some components in corn syrup by gas-liquid chromatography of trimethylsilyl derivatives. Cereal Chem. 1966, 43, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, R.; Cela, D.; Swann, J.R.; Vulevic, J.; Gibson, G.R.; Tzortzis, G.; Costabile, A. In Vitro fermentation of β-GOS: Impact of faecal bacterial populations and metabolic activity in autistic and non-autistic children. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borewicz, K.; Suarez-Diez, M.; Hechler, C.; Beijers, R.; de Weerth, C.; Arts, I.; Penders, J.; Thijs, C.; Nauta, A.; Lindner, C.; et al. The effect of prebiotic fortified infant formulas on microbiota composition and dynamics in early life. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispirli, I.; Kaya, Y.; Dertli, E. Bifidogenic effect and In Vitro immunomodulatory roles of melibiose-derived oligosaccharides produced by the acceptor reaction of glucansucrase E81. Proc. Biochem. 2020, 91, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Tanaka, R. Genus- and species-specific PCR primers for the detection and identification of bifidobacterial. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2003, 4, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Turroni, F.; Peano, C.; Pass, D.A.; Foroni, E.; Severgnini, M.; Claesson, M.J.; Kerr, C.; Hourihane, J.; Murray, D.; Fuligni, F. Diversity of Bifidobacteria Within the Infant Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus composition at species level and gut microbiota diversity in infants before 6 weeks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berström, A.; Skoy, T.H.; Bahl, M.I.; Roager, H.M.; Christensen, L.B.; Ejlerskov, K.T.; Molgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. Establishment of intestinal microbiota during early life: A longitudinal, explorative study of a large cohort of Danish infants. App. Environm. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braegger, C.; Chmielewska, A.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Mihatsh, W.; Moreno, L.; Piescik, M.; Puntis, J.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Supplementation of infant formula with probiotics and/or prebiotics: A systematic review and comment by the ESPGHAN committee on nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Walter, J. Towards a more comprehensive concept for prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutkins, R.W.; Krumbeck, J.A.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D.; Fahey, G.; Goh, Y.J.; Hamaker, B.; Martens, E.C.; Mills, D.A.; Rastall, R.A.; et al. Prebiotics: Why definitions matter. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.M.; Martinez, I.; Walter, J.; Goin, C.; Hutkins, R. Barcoded pyrosequencing reveals that consumption of galactooligosaccharides results in a highly specific bifidogenic response in humans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokusaeva, K.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; van Sinderen, D. Carbohydrate metabolism in Bifidobacteria. Genes Nutr. 2011, 6, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kaoutari, A.; Armougom, F.; Gordon, J.I.; Raoult, D.; Henrisat, B. The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ventura, M.; O’Connell-Motherway, M.; Leahy, S.; Moreno-Munoz, J.A.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; van Sinderen, D. From bacterial genome to functionality; case bifidobacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 120, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.; Swanson, K.; Fahey, G.C.; Garleb, K.A. Physiological importance of short-chain fatty acids from undigestible carbohydrate fermentation. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejby, M.; Fredslund, F.; Andersen, J.M.; Žagar, A.V.; Henriksen, J.R.; Andersen, T.L.; Svensson, B.; Slotboom, D.J.; Hachem, M.A. An ATP binding cassette transporter mediates the uptake of α-(1,6)-linked dietary oligosaccharides in Bifidobacterium and correlates with competitive growth on these substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 20220–20231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongaram, T.; Hoeflinger, J.L.; Chow, J.; Miller, M.J. Prebiotic galactooligosaccharides metabolism by probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacterial. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4184–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | % (Dry Matter) |
|---|---|
| Dry matter a | 96.3 |
| Crude proteins a | <0.2 |
| Crude ash a | <0.2 |
| DP1 + Maltose + Sucrose b | <0.2 |
| DP2: Melibiose b | 3.9 |
| DP3: Manninotriose b | 49.2 |
| DP4: Verbascotetraose b | 43.0 |
| Control | α-GOS | β-GOS | p-Values | Pooled SEM | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log10 Copy Number/ Gr Dry Faeces | Bs | 6 h | 24 h | Bs | 6 h | 24 h | Bs | 6 h | 24 h | T | Prebiotics | T * Prebiotics | Bs | |
| All bacteria | 9.78 | 9.83 | 9.75 | 9.77 | 9.79 | 9.79 | 9.89 | 9.77 | 9.83 | 0.871 | 0.316 | 0.600 | <0.001 | 0.027 |
| Bifidobacteria spp. | 7.49 | 7.59 a | 7.68 a | 8.01 | 8.59 b | 8.62 b | 7.61 | 8.18 b | 8.35 b | 0.285 | <0.001 | 0.823 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| Clostridium coccoides/ Eubacterium rectale group | 8.54 | 8.60 | 8.54 | 8.63 | 8.61 | 8.66 | 8.61 | 8.53 | 8.55 | 0.994 | 0.144 | 0.606 | <0.001 | 0.020 |
| Lactobacilli spp. | 5.01 | 4.78 | 4.40 | 5.03 | 4.86 | 5.02 | 5.02 | 4.69 | 4.80 | 0.788 | 0.150 | 0.208 | <0.001 | 0.068 |
| Clostridium leptum subgroup | 7.57 | 7.67 | 7.73 | 7.72 | 7.68 | 7.69 | 8.00 | 7.93 | 7.88 | 0.900 | 0.049 | 0.719 | <0.001 | 0.026 |
| Enterobacteria spp. | 7.81 | 7.85 b | 7.88 b | 8.24 | 8.12 a, b | 8.12 a, b | 7.93 | 7.69 a | 7.70 a | 0817 | <0.001 | 0.967 | <0.001 | 0.028 |
| F. praustnizii | 8.13 | 8.14 | 8.12 | 8.20 | 8.09 | 8.10 | 8.13 | 8.04 | 7.99 | 0.716 | 0.100 | 0.893 | <0.001 | 0.023 |
| Bacteroides | 9.63 | 9.67 | 9.61 | 9.67 | 9.59 | 9.60 | 9.63 | 9.51 | 9.54 | 0.855 | 0.065 | 0.707 | <0,001 | 0.021 |
| Time | Enrichment | Shannon Index | Evenness Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Control | 0 h | 8.33 a | 4.03 | 2.04 a | 0.42 | 0.65 a | 0.13 |
| 24 h | 8.33 a | 4.03 | 2.04 a | 0.42 | 0.65 a | 0.13 | |
| α-GOS | 0 h | 10.83 a | 3.97 | 2.33 a | 0.36 | 0.74 a | 0.11 |
| 24 h | 12.50 a | 4.68 | 2.47 a | 0.36 | 0.78 a | 0.10 | |
| β-GOS | 0 h | 7.50 a | 2.07 | 1.99 a | 0.26 | 0.63 a | 0.08 |
| 24 h | 12.00 b | 3.16 | 2.46 b | 0.24 | 0.78 b | 0.07 | |
| Control | α-GOS | β-GOS | p-Values | Pooled SEM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log10 Copy Number/Gr De Contenido Fecal | 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | Pb | Bs | |
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis | 4.45 | 4.68 | 4.65 | 5.11 | 4.52 | 4.52 | NS | <0.001 | 0.193 |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum | 4.55 | 5.09 b | 4.70 | 4.04 a | 4.57 | 4.27 a | 0.045 | <0.001 | 0.157 |
| Bifidobacterium catenulatum/pseudo-catenulatum | 7.47 | 7.41 a | 7.25 | 7.65 b | 7.44 | 7.74 a, b | 0.068 | <0.001 | 0.094 |
| Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis | 4.96 | 5.12 | 5.22 | 5.40 | 5.17 | 5.48 | NS | <0.001 | 0.117 |
| Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum | 8.25 | 8.26 a | 8.03 | 8.47 b | 8.36 | 8.71 b | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.065 |
| SCFA (mM) | Control | α-GOS | β-GOS | p-Values | Pooled SEM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bs | 6 h | 24 h | Bs | 6 h | 24 h | Bs | 6 h | 24 h | T | Prebiotics | T * Prebiotics | Bs | ||
| Acetate | 14.669 | 21.640 a | 18.908 a | 10.808 | 44.356 b | 45.752 b | 16.587 | 33.463 b | 40.743 b | 0.671 | 0.001 | 0.677 | 0.084 | 2.313 |
| Propionate | 3.163 | 6.491 | 6.116 | 2.915 | 9.130 | 8.522 | 3.971 | 8.196 | 10.072 | 0.839 | 0276 | 0.746 | 0.060 | 0.729 |
| Butyrate | 3.408 | 6.664 | 4.900 | 6.727 | 6.970 | 6.772 | 7.512 | 7.719 | 8.112 | 0.728 | 0714 | 0.831 | 0.044 | 0.746 |
| Iso-butyrate | 0.307 | 0.649 | 0.764 | 0.253 | 0.700 | 0.791 | 0.339 | 0.582 | 0.624 | 0.540 | 0.605 | 0.975 | 0.412 | 0.067 |
| Valerate | 1.174 | 4.228 | 4.788 | 1.139 | 2.216 | 0.607 | 1.197 | 2.102 | 2.249 | 0.779 | 0.059 | 0.678 | 0.000 | 0.531 |
| Iso-valerate | 0.317 | 0.635 | 0.827 | 0.303 | 0.775 | 0.719 | 0.236 | 0.602 | 0.657 | 0.682 | 0.897 | 0.806 | 0.052 | 0.077 |
| Formate | 0.611 | 2.400 a | 2.447 a | 0.523 | 3.651 b | 8.954 b | 0.785 | 4.042 a, b | 3.115 a, b | 0.258 | 0.046 | 0.117 | 0.390 | 0.643 |
| Succinate | 0.265 | 1.022 | 1.022 | 0.428 | 1.065 | 0.975 | 0.354 | 1.018 | 0.969 | 0.899 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.967 | 0.182 |
| Lactate | 0.248 | 0.782 a | 0.500 a | 0.211 | 3.908 b | 1.554 b | 0.343 | 1.353 a, b | 0.559 a, b | 0.028 | 0.009 | 0.225 | 0.015 | 0.250 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marín-Manzano, M.d.C.; Hernandez-Hernandez, O.; Diez-Municio, M.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Moreno, F.J.; Clemente, A. Prebiotic Properties of Non-Fructosylated α-Galactooligosaccharides from PEA (Pisum sativum L.) Using Infant Fecal Slurries. Foods 2020, 9, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070921
Marín-Manzano MdC, Hernandez-Hernandez O, Diez-Municio M, Delgado-Andrade C, Moreno FJ, Clemente A. Prebiotic Properties of Non-Fructosylated α-Galactooligosaccharides from PEA (Pisum sativum L.) Using Infant Fecal Slurries. Foods. 2020; 9(7):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070921
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarín-Manzano, María del Carmen, Oswaldo Hernandez-Hernandez, Marina Diez-Municio, Cristina Delgado-Andrade, Francisco Javier Moreno, and Alfonso Clemente. 2020. "Prebiotic Properties of Non-Fructosylated α-Galactooligosaccharides from PEA (Pisum sativum L.) Using Infant Fecal Slurries" Foods 9, no. 7: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070921
APA StyleMarín-Manzano, M. d. C., Hernandez-Hernandez, O., Diez-Municio, M., Delgado-Andrade, C., Moreno, F. J., & Clemente, A. (2020). Prebiotic Properties of Non-Fructosylated α-Galactooligosaccharides from PEA (Pisum sativum L.) Using Infant Fecal Slurries. Foods, 9(7), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070921






