Comparison of Various Soybean Allergen Levels in Genetically and Non-Genetically Modified Soybeans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Soybean Sample Extraction
2.3. Immunochromatography
2.4. Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
2.5. Antibodies Against the Major Soybean Allergens
2.6. ELISA Using Allergen-Specific Antibodies
2.7. Detection of IgE-Binding Proteins using Patient Sera
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Confirmation of Genetically Modified and Non-Genetically Modified Soybeans
3.2. Comparative Levels of Pollinosis-Related Soybean Allergens (Gly m 4 and Gly m 3) in GM-Soybean and Non-GM Soybean Extracts
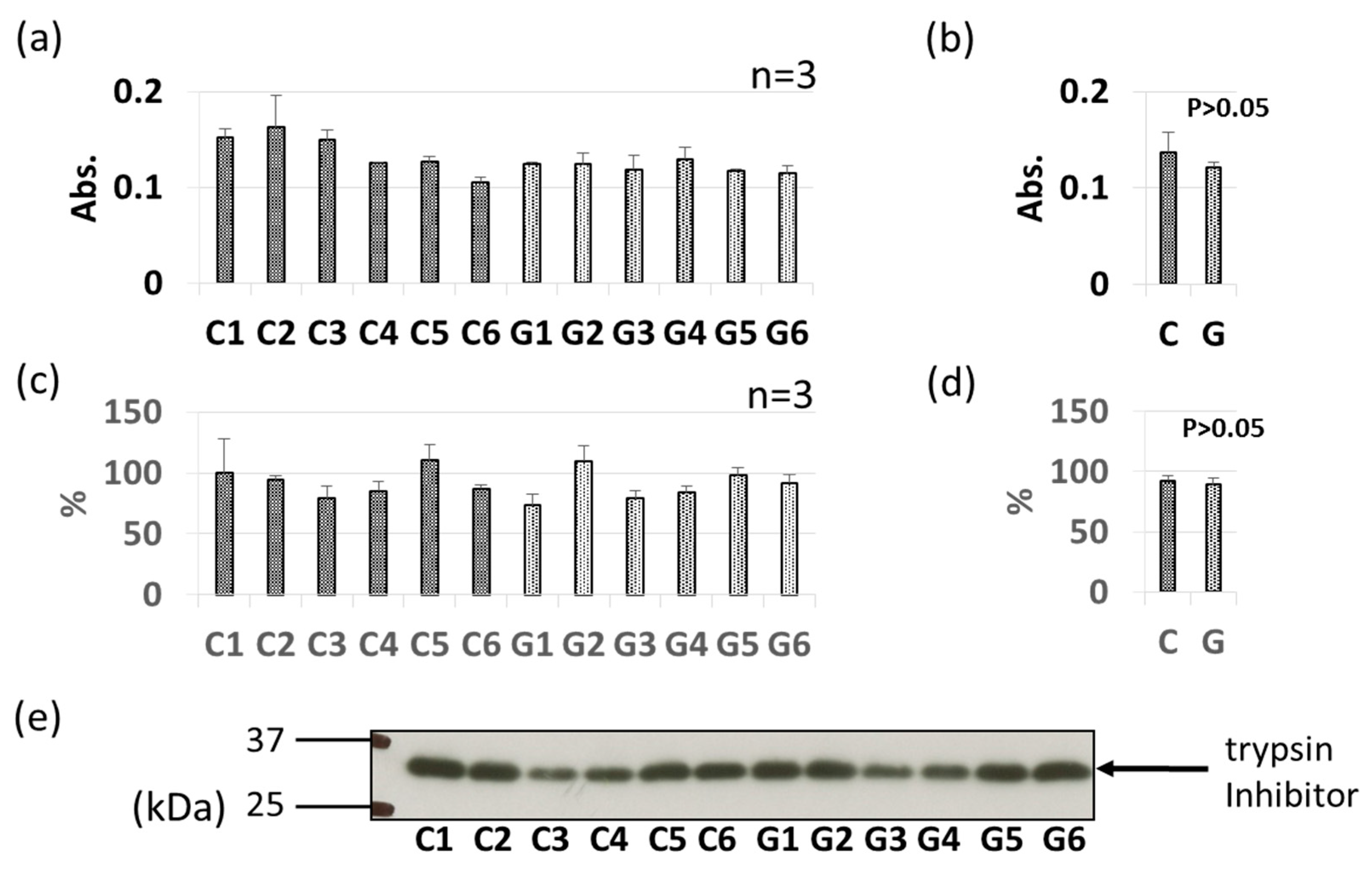
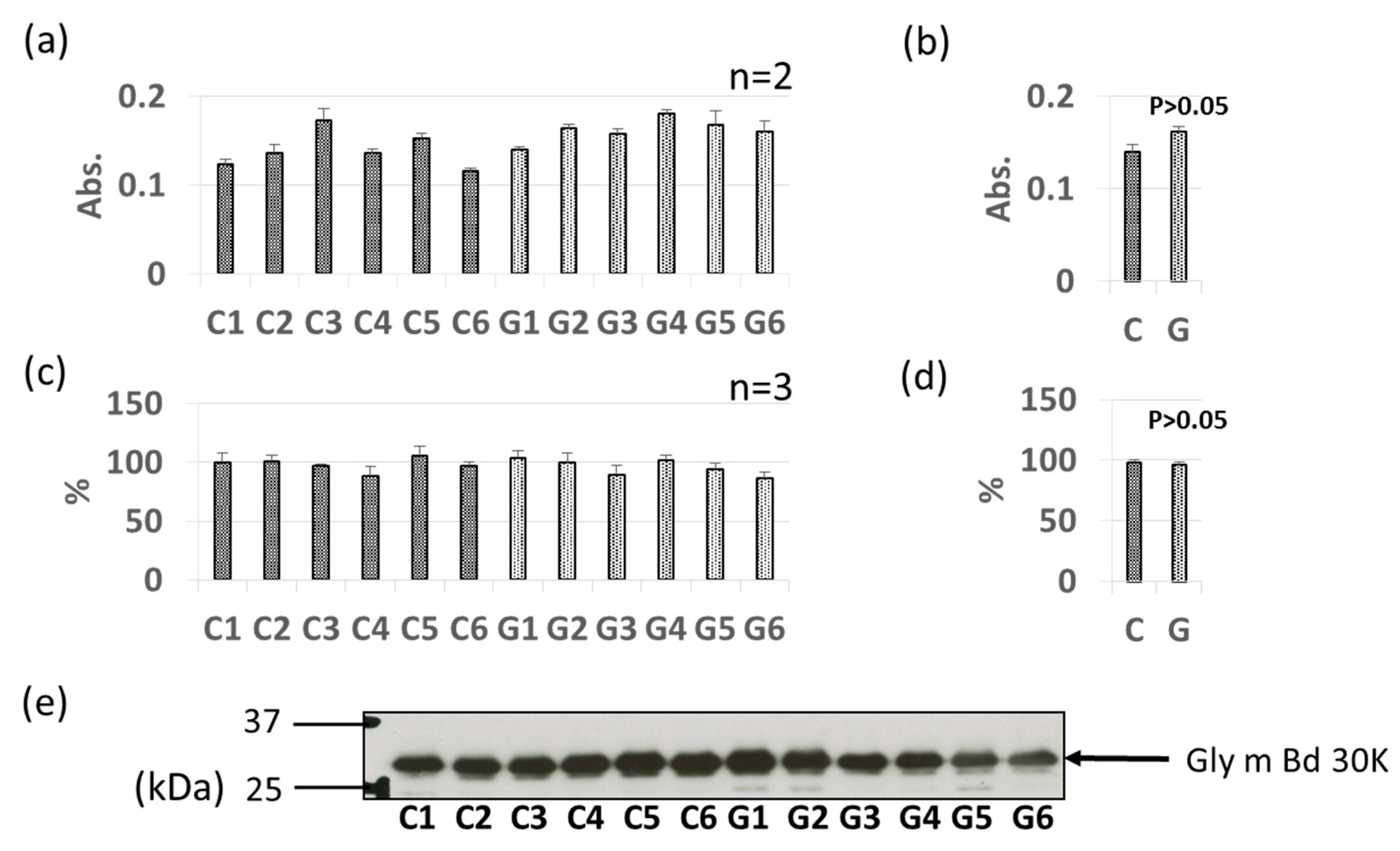
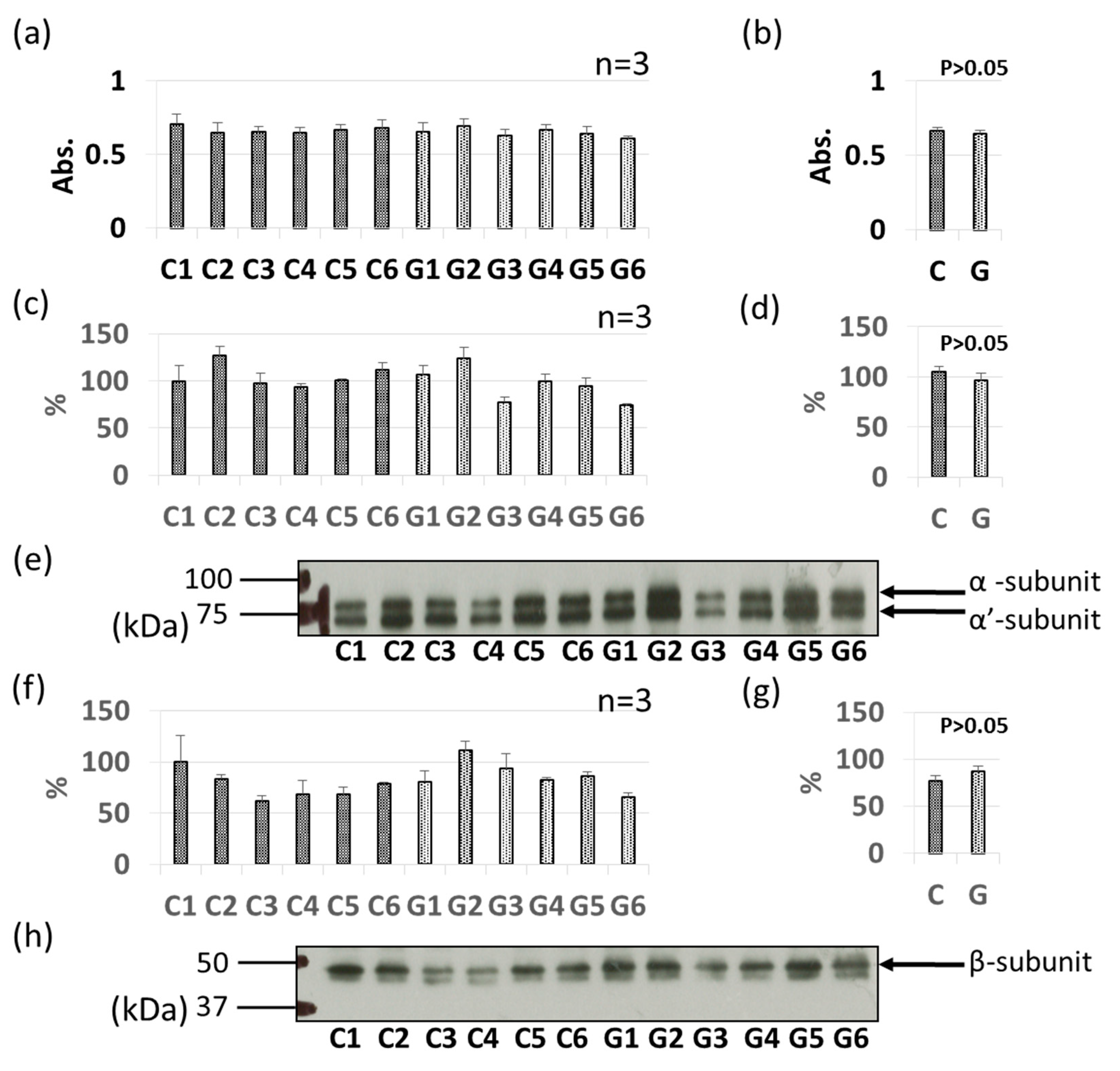
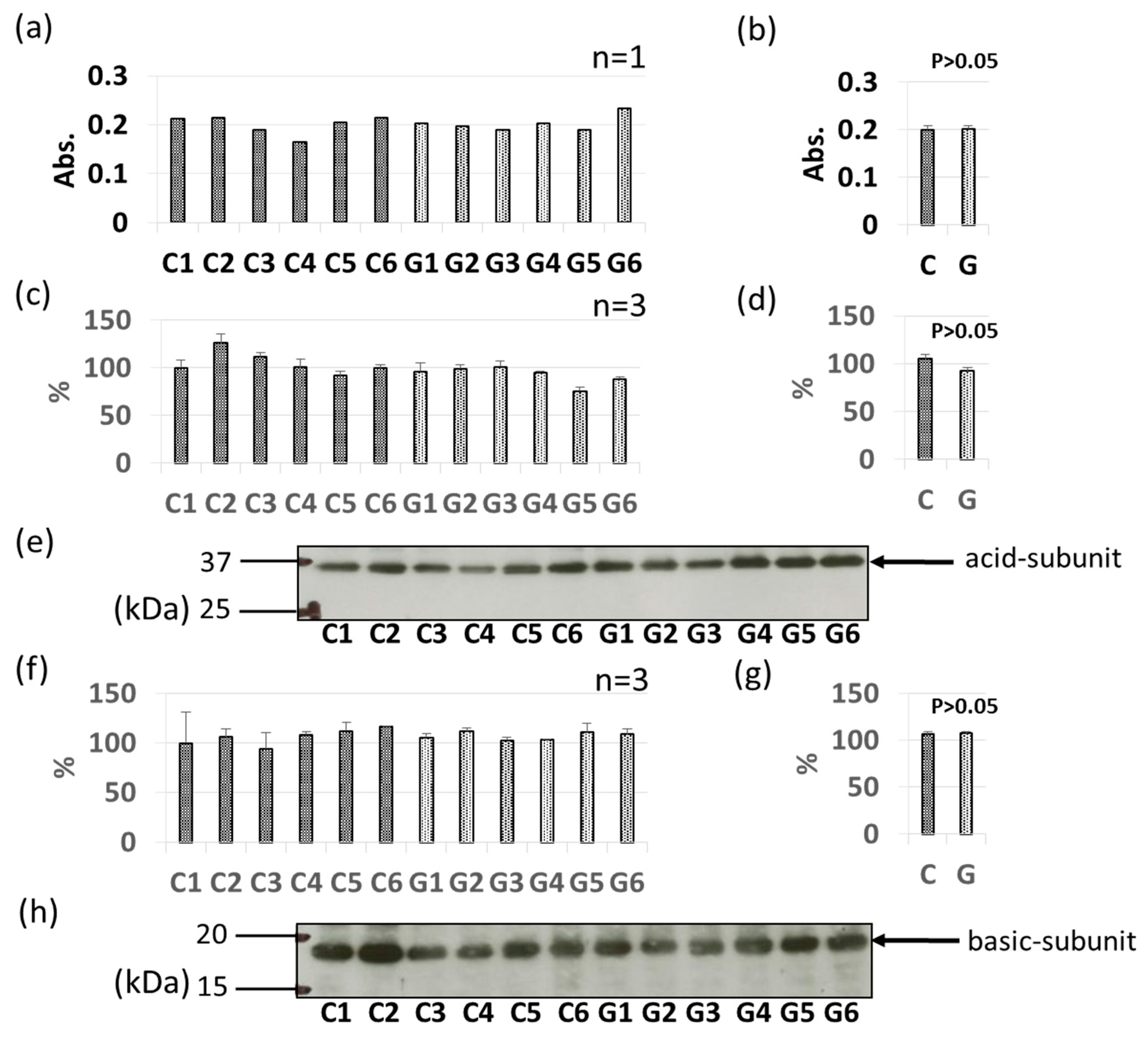
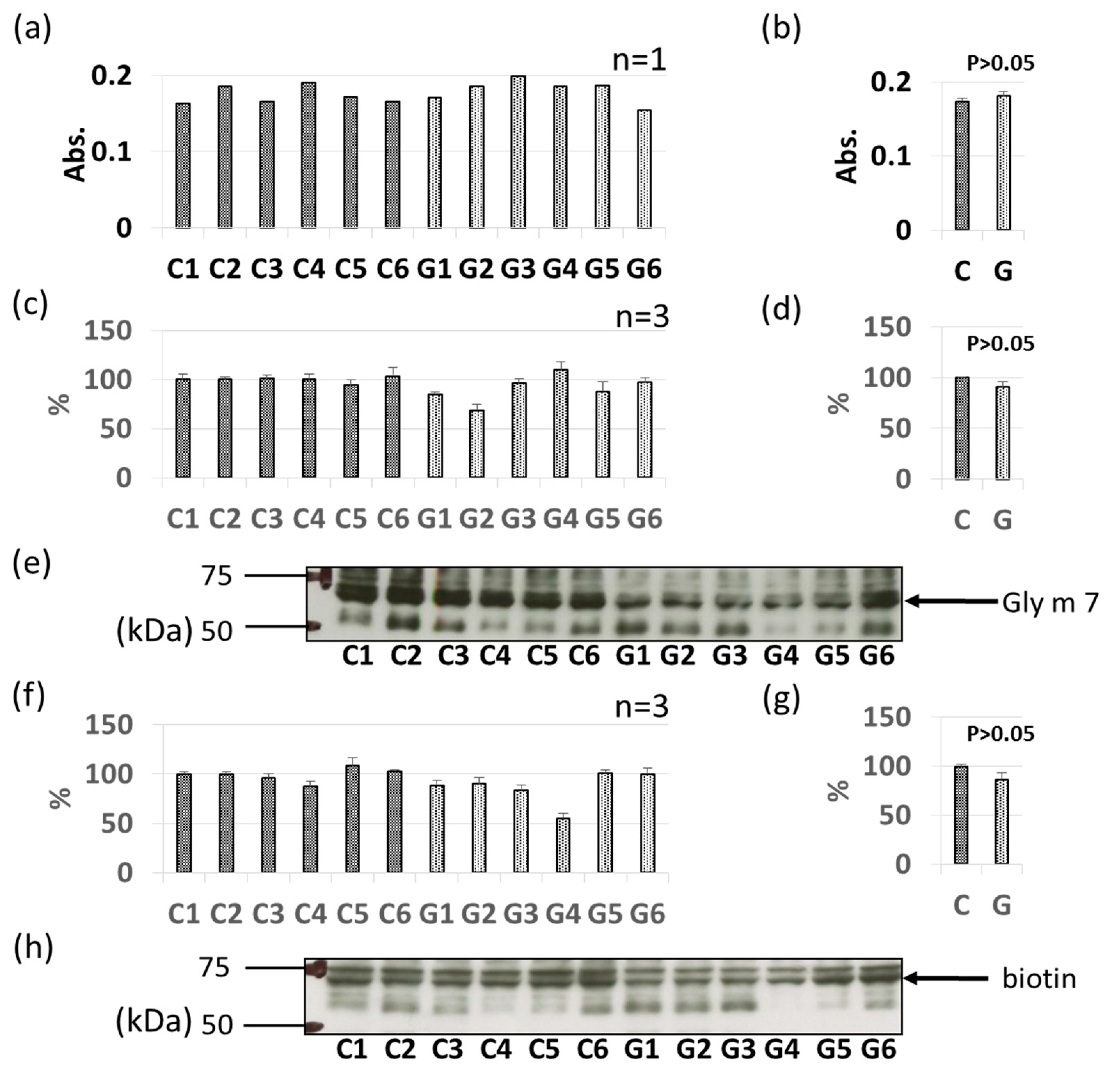
3.3. Comparative Levels of Other Soybean Allergens in GM-Soybean and non-GM Soybean
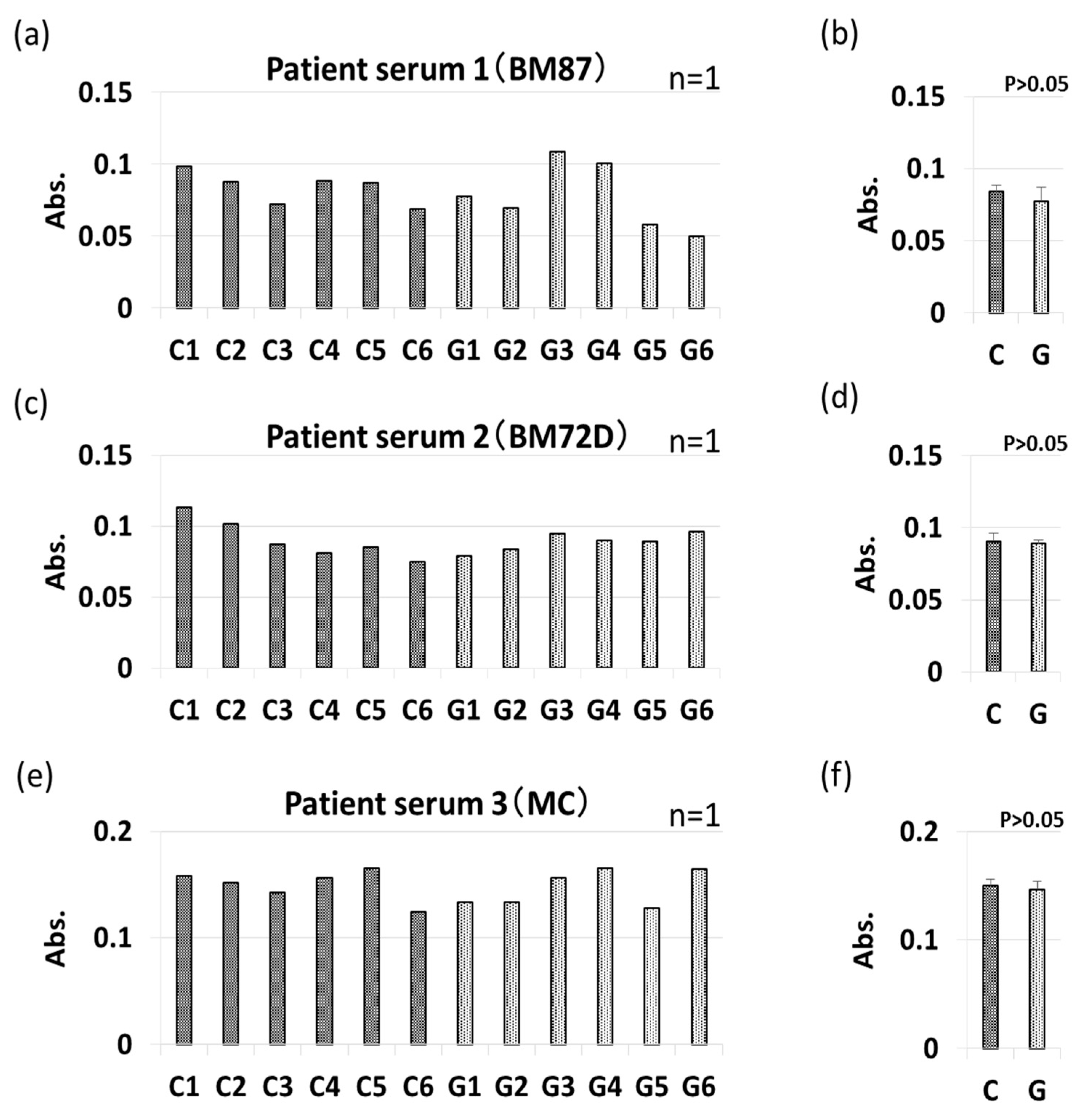
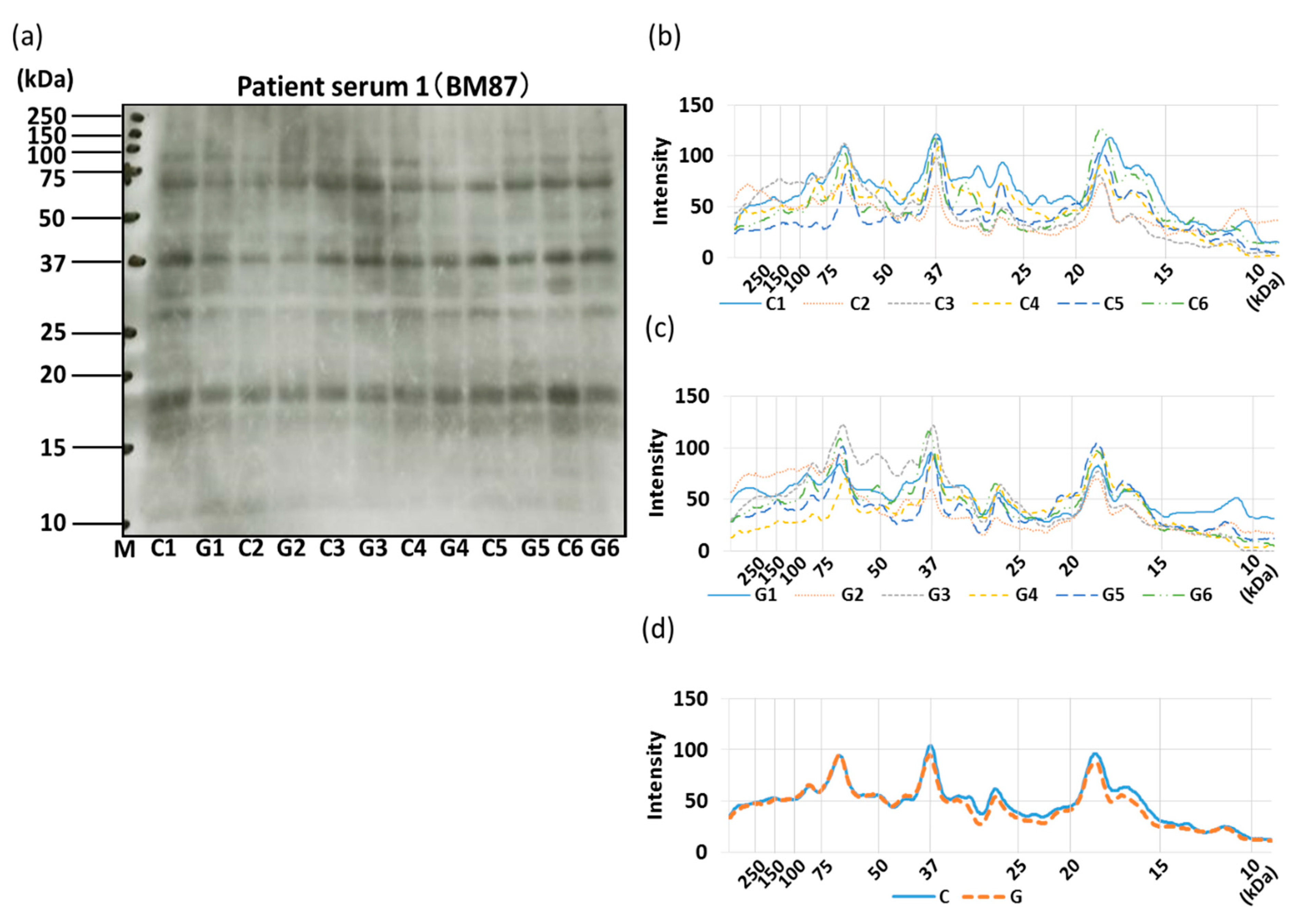
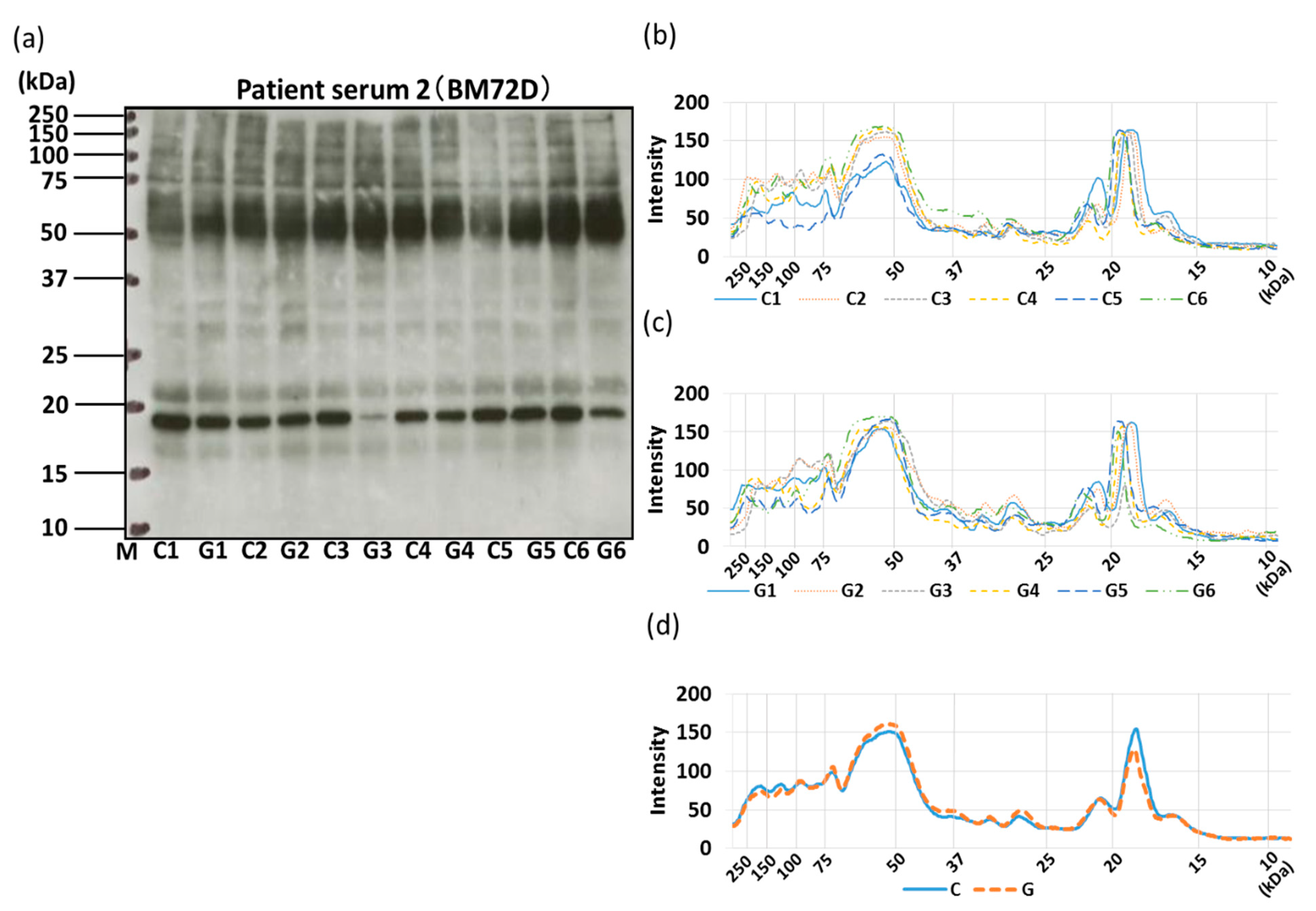
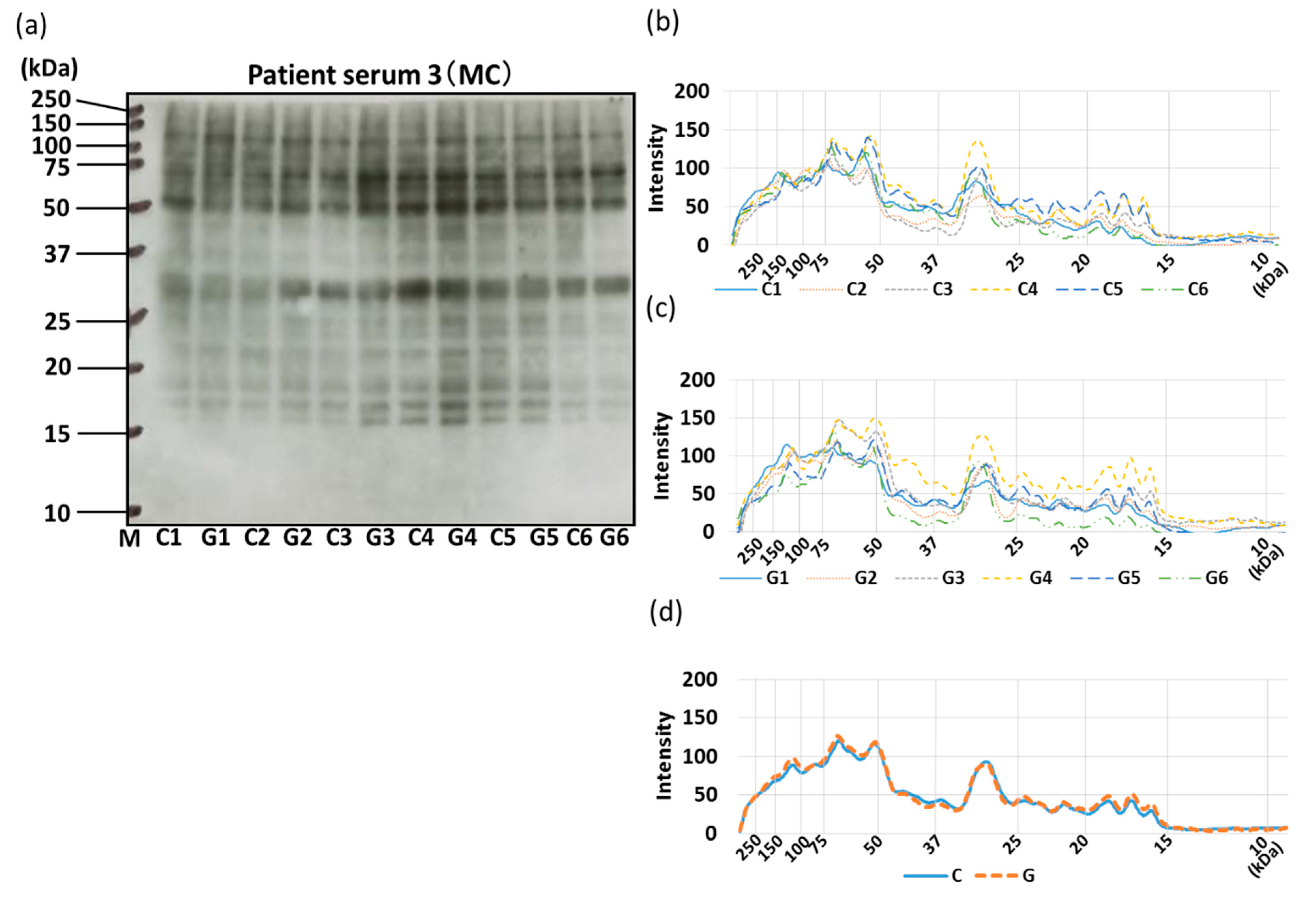
3.4. IgE-ELISA and IgE-Immunoblotting using Patient Serum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chrispeels, M.J. Global production and consumption of genetically engineered crops. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2014, 4, 120–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lua, M.; Jina, Y.; Weber, B.B.; Goodman, R.E. A comparative study of human IgE binding to proteins of a genetically modified (GM) soybean and six non-GM soybeans grown in multiple locations. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichim, M.C. The Romanian experience and perspective on the commercial cultivation of genetically modified crops in Europe. Transgenic Res. 2019, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, M.; Al-Busaidi, K.T.; Trivedi, M.; Tiwari, R.K. Status of research, regulations and challenges for genetically modified crops in India. GM Crops Food 2018, 9, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISAAA. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: Biotech Crop Adoption Surges as Economic Benefits Accumulate in 22 Years; ISAAA: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 100–104. ISBN 978-1-892456-67-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, T.; Samoto, M.; Takahashi, K. Soybean allergens and hypoallergenic soybean products. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2000, 46, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagami, T. Allergies to Cross-Reactive Plant Proteins. Latex-fruit syndrome is comparable with pollen-food allergy syndrome. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 128, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amlot, P.L.; Kemeny, D.M.; Zachary, C.; Parkes, P.; Lessof, M.H. Oral allergy syndrome (OAS): Symptoms of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to foods. Clin. Allergy 1987, 17, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Bando, N.; Tsuji, H.; Nishikawa, K.; Kitamura, K. α-Subunit of β-Conglycinin, an allergenic protein recognized by IgE Antibodies of soybean-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, N.; Sato, S.; Cabanos, C.; Tanaka, A.; Ito, K.; Ebisawa, M. Gly m 5/Gly m 8 fusion component as a potential novel candidate molecule for diagnosing soya bean allergy in Japanese children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzhauser, T.; Wackermann, O.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Scibilia, J.; Perono-Garoffo, L.; Utsumi, S.; Poulsen, L.K.; Vieths, S. Soybean (Glycine max) allergy in Europe: Gly m 5 (β-conglycinin) and Gly m 6 (glycinin) are potential diagnostic markers for severe allergic reactions to soy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riascos, J.J.; Weissinger, S.M.; Weissinger, A.K.; Kulis, M.; Burks, A.W.; Pons, L. The Seed Biotinylated Protein of Soybean (Glycine max): A BoilingResistant New Allergen (Gly m 7) with the Capacity to Induce IgE Mediated Allergic Responses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3890–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Tsuji, H.; Bando, N.; Kitamura, K.; Zhu, Y.L.; Hirano, H.; Nishikawa, K. Identification of the soybean allergenic protein, Gly m Bd 30K, with the soybean seed 34-kDa oil-body-associated protein. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Bando, N.; Tsuji, H.; Okajima, H.; Nishikawa, K.; Sasaoka, K. Investigation of the IgE-binding protein in soybeans by immunoblotting with the sera of the soybean-sensitive patient with atopic dermatitis. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1991, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroz, L.A.; Yang, W.H. Kunitz Soybean Trypsin Inhibitor—A Specific Allergen in Food Anaphylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ying, Y.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y. The characterization of soybean oil body integral oleosin isoforms and the effects of alkaline pH on them. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihs, H.P.; Chen, Z.; Ruëff, F.; Petersen, A.; Rozynek, P.; Heimann, H.; Baur, X. IgE binding of the recombinant allergen soybean profilin (rGly m 3) is mediated by conformational epitopes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagami, A.; Inaba, Y.; Kuno, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tanaka, A.; Sjolander, S.; Saito, H.; Matsunaga, K. Two cases of pollen-food allergy syndrome to soy milk diagnosed by skin prick test, specific serum immunoglobulin E and microarray analysis. J. Dermatol. 2009, 36, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Tabbe, J.; Vogel, L.; Crowell, D.N.; Haustein, U.F.; Vieths, S. Severe oral allergy syndrome and anaphylactic reactions caused by a Bet v 1- related PR-10 protein in soybean, SAM22. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittag, D.; Vieths, S.; Vogel, L.; Becker, W.M.; Rihs, H.P.; Helbling, A.; Wüthrich, B.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K. Soybean allergy in patients allergic to birch pollen: Clinical investigation and molecular characterization of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkner, H.; Neudecker, P.; Mittag, D.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Schweimer, K.; Vieths, S.; Rösch, P. Cross-reactivity of pollen and food allergens: Soybean Gly m 4 is a member of the Bet v 1 superfamily and closely resembles yellow lupine proteins. Biosci. Rep. 2009, 29, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.M.; Ye, Y.M.; Kim, S.H.; Nahm, D.H.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, S.R.; Lee, B.O. Evaluating the Allergic Risk of Genetically Modified Soybean. Yonsei Med. J. 2006, 47, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M.; He, J.; Shen, W. Targeting the middle region of CP4-EPSPS protein for its traceability in highly processed soy-related products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funke, T.; Healy-Fried, M.L.; Han, H.; Alberg, D.G.; Bartlett, P.A.; Schönbrunn, E. Differential Inhibition of Class I and Class II 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate Synthases by Tetrahedral Reaction Intermediate Analogues. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 13344–13351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.J.; Chang, C.Y.; Liao, E.C. Comparison of Allergenicity at Gly m 4 and Gly m Bd 30K of Soybean after Genetic Modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selb, R.; Wal, J.M.; Moreno, F.J.; Lovik, M.; Mills, C.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Fernandez, A. Assessment of endogenous allergenicity of genetically modified plants exemplified by soybean—Where do we stand? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 101, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.E.; Panda, R.; Ariyarathna, H. Evaluation of Endogenous Allergens for the Safety Evaluation of Genetically Engineered Food Crops: Review of Potential Risks, Test Methods, Examples and Relevance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8317–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, L.; Hayder, H.; Mueller, U. Endogenous allergens in the regulatory assessment of genetically engineered crops. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 73, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Mills, E.N.; Lovik, M.; Spoek, A.; Germini, A.; Mikalsen, A.; Wal, J.M. Endogenous allergens and compositional analysis in the allergenicity assessment of genetically modified plants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.; Ariyarathna, H.; Amnuaycheewa, P.; Tetteh, A.; Pramod, S.N.; Taylor, S.L.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Goodman, R.E. Challenges in testing genetically modified crops for potential increases in endogenous allergen expression for safety. Allergy 2013, 68, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO). Guidance on allergenicity assessment of genetically modified plants. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyhse-Andersen, J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: A simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polycrylamide to nitrocellulose. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1984, 10, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; He, P. Determination of beta-conglycinin in soybean and soybean products using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafusa, K.; Murakami, H.; Ueda, T.; Yano, E.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Worm wounding increases levels of pollen-related food allergens in soybean (Glycine max). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, H.B.; Kim, W.S.; Jang, S.; Kerley, M.S. All three subunits of soybean beta-conglycinin are potential food allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, A.; Horikawa, T.; Shimizu, H.; Sarayama, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Sjolander, S.; Tanaka, A.; Moriyama, T. Soybean beta-conglycinin as the main allergen in a patient with food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis by tofu: Food processing alters pepsin resistance. J. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Khan, F.; Song, Q.; Lakshman, S.; Cregan, P.; Scott, R.; Shipe, E.; Garrett, W. Characterization of Soybean Storage and Allergen Proteins Affected by Environmental and Genetic Factors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirce, S.; Fernández-Nieto, M.; Polo, F.; Sastre, J. Soybean trypsin inhibitor is an occupational inhalant allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnuaycheewa, P.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Purification, characterisation, and quantification of the soy allergen profilin (Gly m 3) in soy products. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
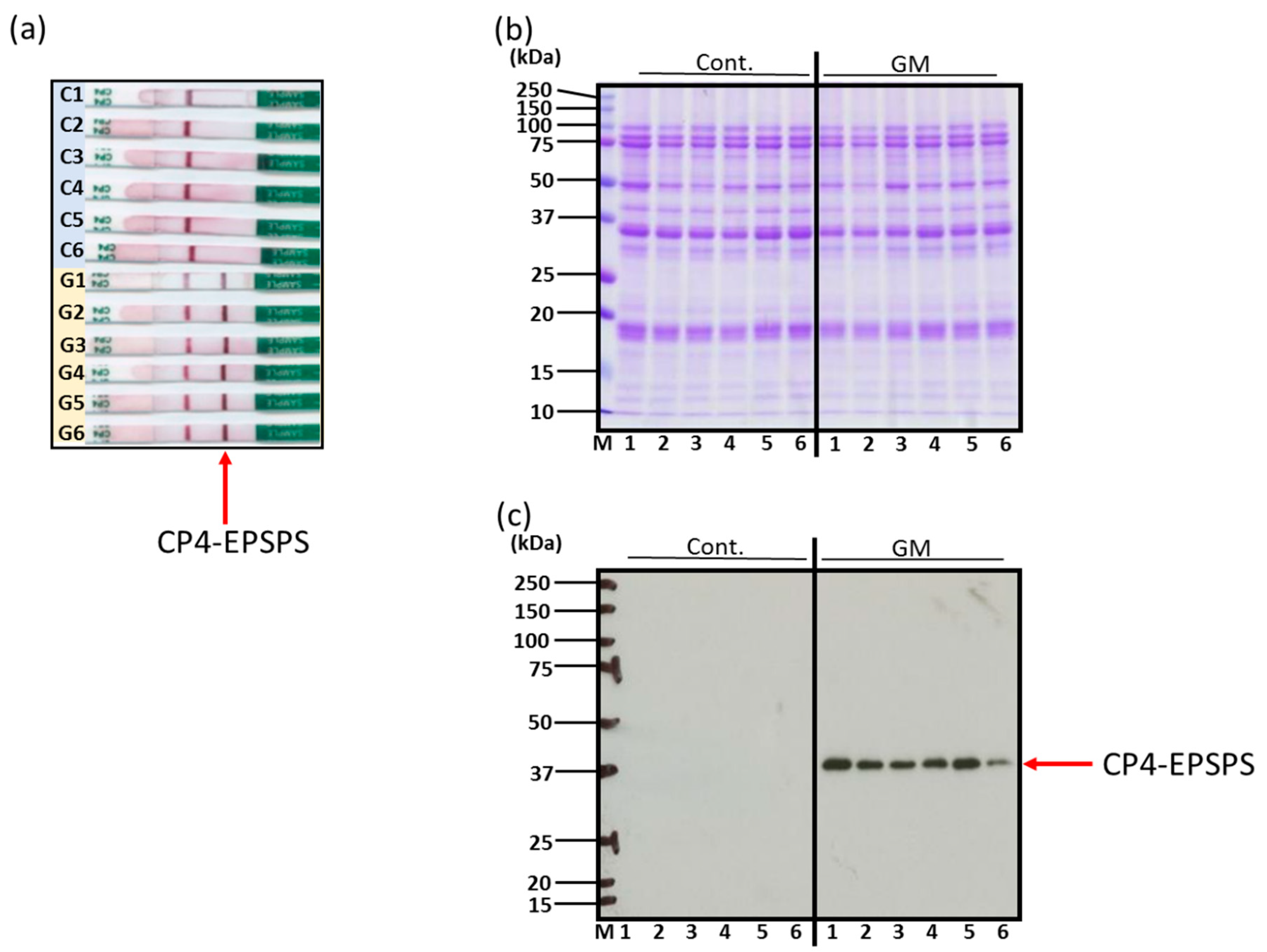
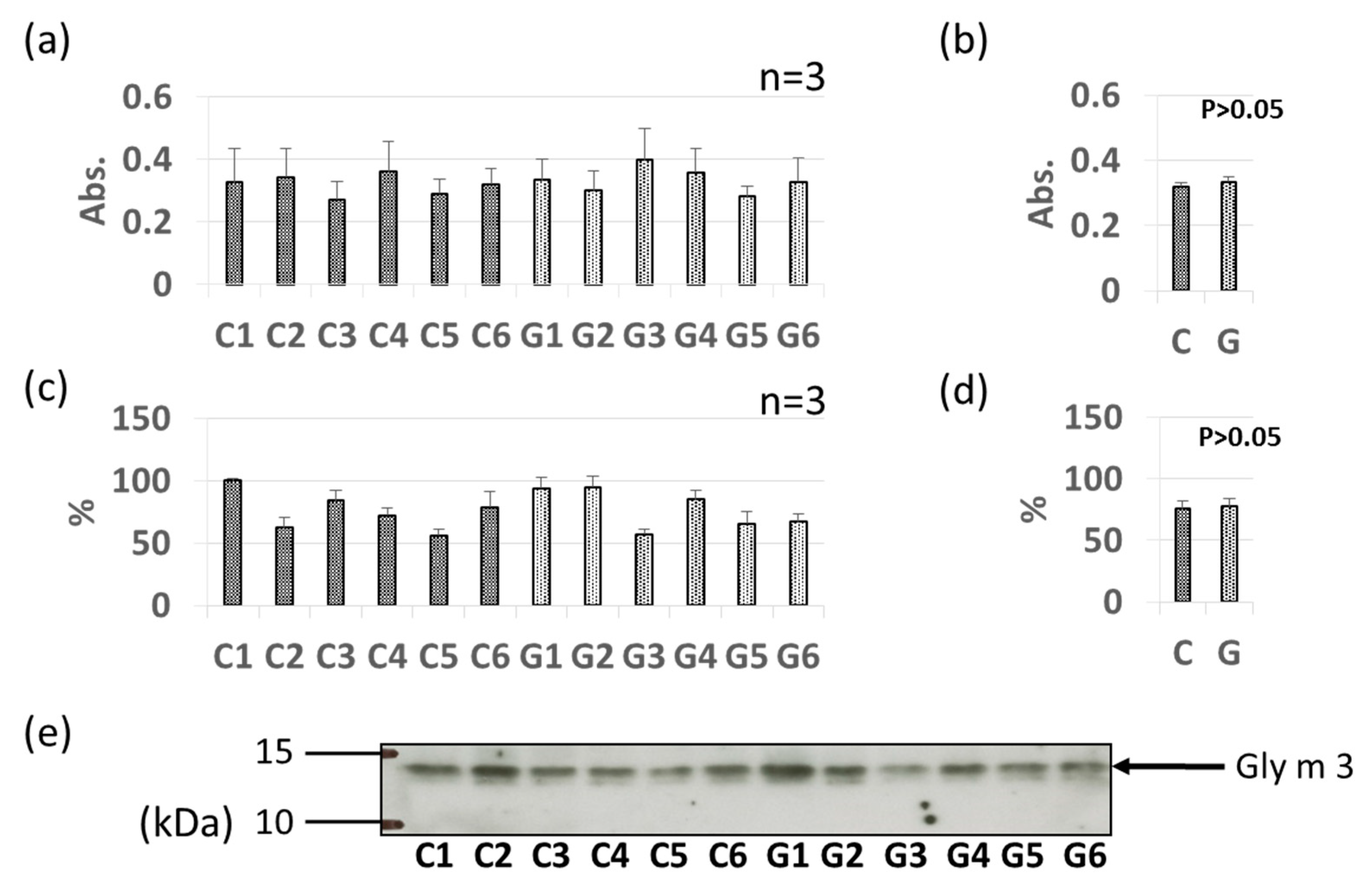
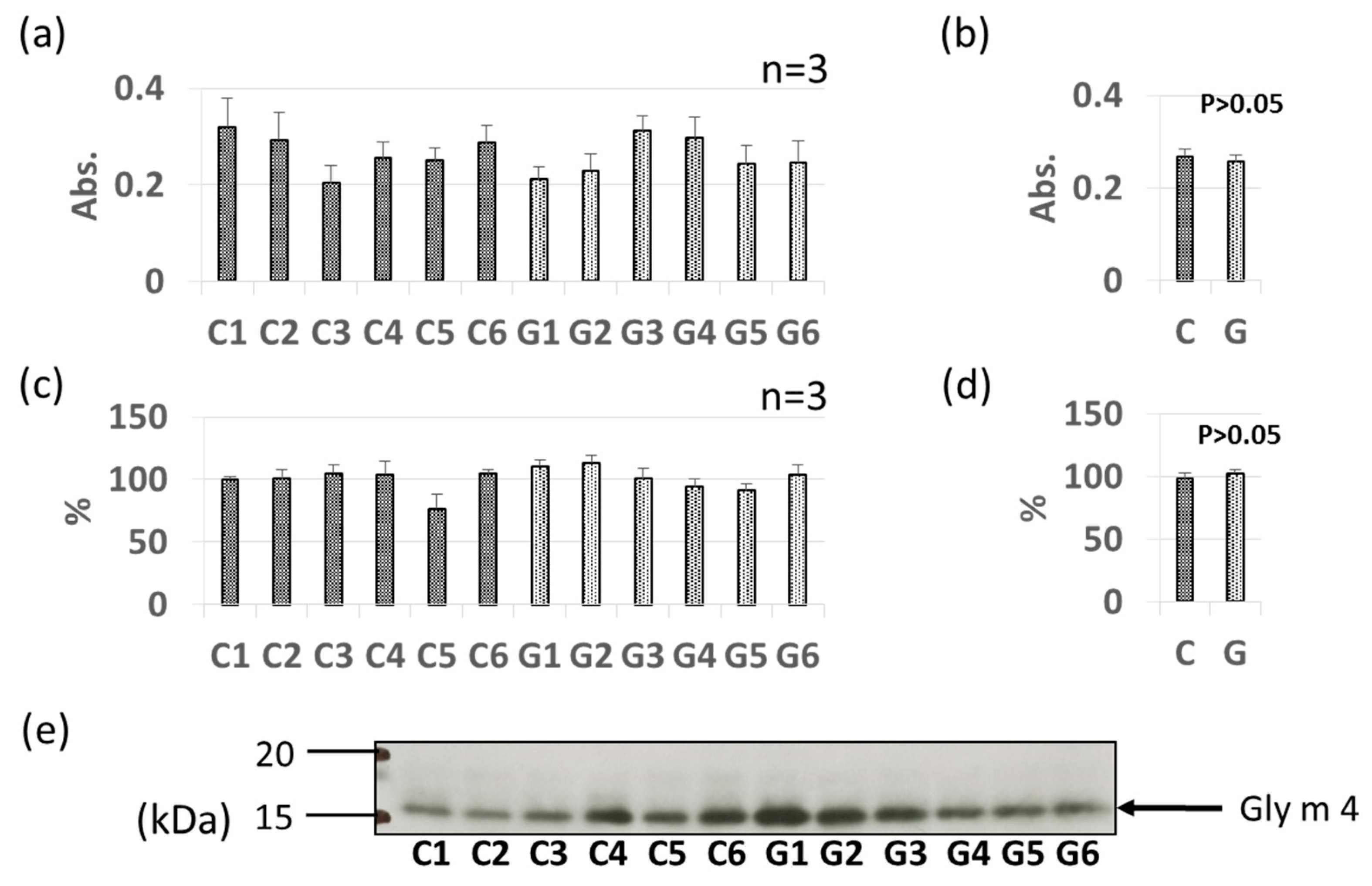
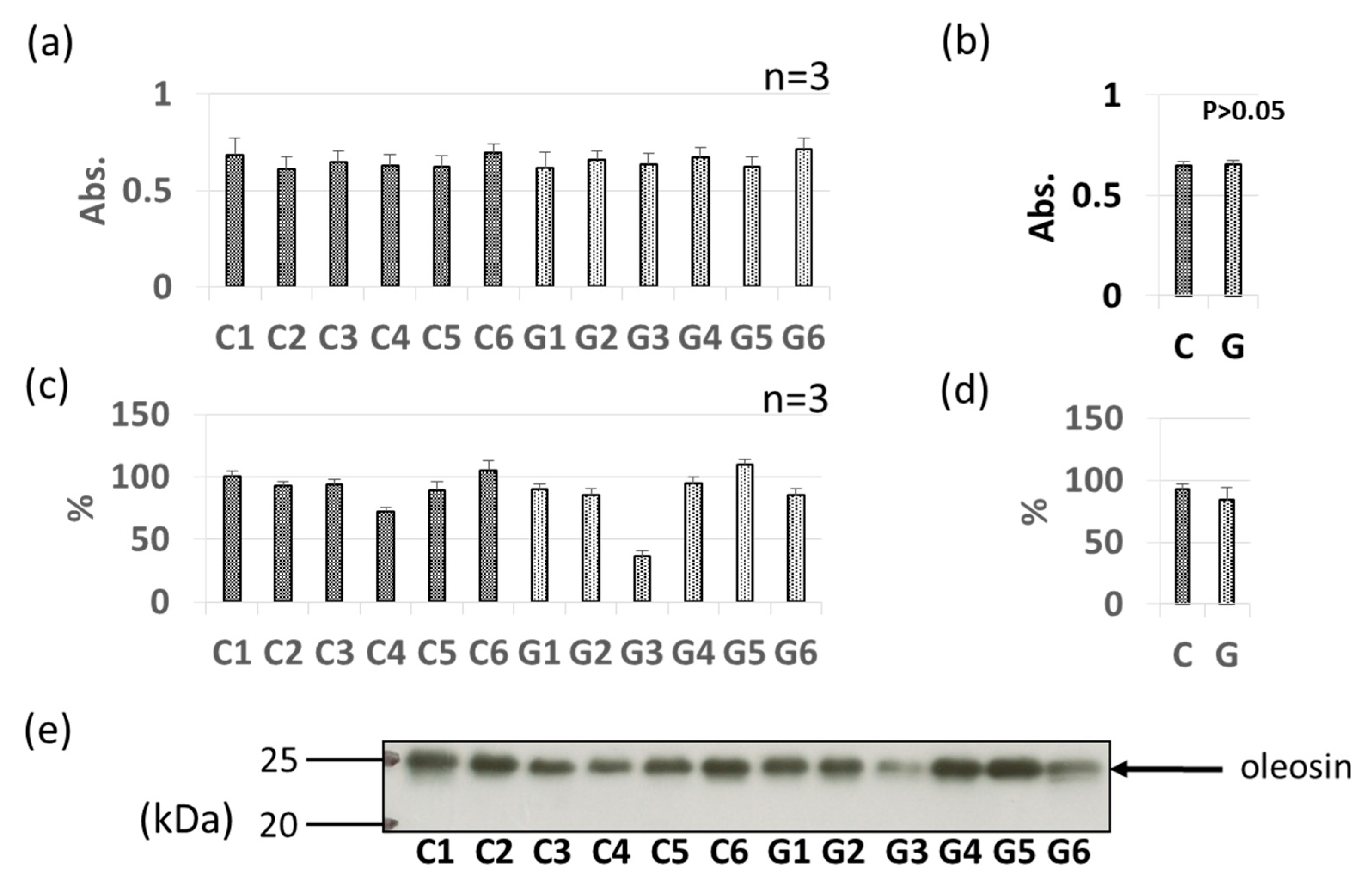
| Allergen Name | Molecular Mass (kDa) | Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean food allergens (class 1 food allergens) | |||
| Gly m 5 (7S globulin) | 72, 68, 50 | Major storage protein, glycoprotein | [9,10] |
| Gly m 6 (11S globulin) | 34, 20 | Major storage protein | [11] |
| Gly m 7 | 76 | Seed-specific biotinylated protein (SBP) | [12] |
| Gly m Bd 30K (P34) | 34 (30) | Homologous to papain | [13,14] |
| Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor | 18 | trypsin inhibitor | [15] |
| Oleosin | 22–24 | Oil body associated protein | [16] |
| Pollen-related soybean allergens (class 2 food allergens) | |||
| Gly m 3 | 14 | Profilin, Bet v 2 homolog | [17,18] |
| Gly m 4 | 17 | PR-10 family, Bet v 1 homolog | [18,19,20,21] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuo, A.; Matsushita, K.; Fukuzumi, A.; Tokumasu, N.; Yano, E.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Comparison of Various Soybean Allergen Levels in Genetically and Non-Genetically Modified Soybeans. Foods 2020, 9, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040522
Matsuo A, Matsushita K, Fukuzumi A, Tokumasu N, Yano E, Zaima N, Moriyama T. Comparison of Various Soybean Allergen Levels in Genetically and Non-Genetically Modified Soybeans. Foods. 2020; 9(4):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040522
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuo, Ayato, Kaho Matsushita, Ayano Fukuzumi, Naoki Tokumasu, Erika Yano, Nobuhiro Zaima, and Tatsuya Moriyama. 2020. "Comparison of Various Soybean Allergen Levels in Genetically and Non-Genetically Modified Soybeans" Foods 9, no. 4: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040522
APA StyleMatsuo, A., Matsushita, K., Fukuzumi, A., Tokumasu, N., Yano, E., Zaima, N., & Moriyama, T. (2020). Comparison of Various Soybean Allergen Levels in Genetically and Non-Genetically Modified Soybeans. Foods, 9(4), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040522






