Quantification of Cheese Yield Reduction in Manufacturing Parmigiano Reggiano from Milk with Non-Compliant Somatic Cells Count
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parmigiano Reggiano Cheesemaking Process
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition and Physico-Chemical Properties of Vat Milk
3.2. Cheese Yield and Cheesemaking Losses of Vat Milk
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Maréchal, C.; Thiéry, R.; Vautor, E.; Le Loir, Y. Mastitis impact on technological properties of milk and quality of milk products—A review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2011, 91, 247–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004, Laying Down Specific Hygiene Rules for on the Hygiene of Foodstuffs, Web Site. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2004:139:0055:0205:en:PDF (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Ali, A.E.; Andrews, A.T.; Cheeseman, G.C. Influence of elevated somatic cell count on casein distribution and cheese-making. J. Dairy Res. 1980, 47, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbano, D.M.; Rasmussen, R.R.; Lynch, J.M. Influence of milk somatic cell count and milk age on cheese yield. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klei, L.; Yun, J.; Sapru, A.; Lynch, J.; Barbano, D.M.; Sears, P.; Galton, D. Effects of milk somatic cell count on Cottage cheese yield and quality. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, A.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P.; Malacarne, M. Characteristics of raw milk produced by free-stall or tie-stall cattle herds in the Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese production area. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardy and Emilia Romagna Experimental Zootechnical Institute (IZSLER) Web Site. Available online: https://www.izsler.it/pls/izs_bs/v3_s2ew_consultazione.mostra_pagina?id_pagina=524 (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Summer, A.; Lora, I.; Formaggioni, P.; Gottardo, F. Impact of heat stress on milk and meat production. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Regulation (EC) No 510/2006 of 20 March 2006 on the Protection of Geographical Indications and Designations of Origin for agricultural Products and Foodstuffs, Web Site. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006R0510&from=en (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Summer, A.; Formaggioni, P.; Franceschi, P.; Di Frangia, F.; Righi, F.; Malacarne, M. Cheese as functional food: The example of Parmigiano Reggiano and Grana Padano. Food Tech. Biotech. 2017, 55, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, P.; Summer, A.; Sandri, S.; Formaggioni, P.; Malacarne, M.; Mariani, P. Effects of the full cream milk somatic cell content on the characteristics of vat milk in the manufacture of Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese. Vet. Res. Commun. 2009, 33 (Suppl. 1), 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, A.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P.; Malacarne, M. Influence of milk somatic cell content on Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese yield. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF Standard. Milk, Enumeration of Somatic Cells, Part 2: Guidance on the Operation of Fluoro-Opto-Electronic Counters; 148-2/ISO13366-2; International Dairy Federation Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IDF Standard. Milk and Liquid Milk Products, Guidelines for the Application of Mid- Infrared Spectrometry; 141/ISO9622; International Dairy Federation Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- IDF Standard. Milk, Determination of Fat Content, Acido-Butyrometric (Gerber Method); 238-2/ISO19662-2; International Dairy Federation Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists [AOAC]. Nitrogen (total) in milk, method no. 991.20. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; Horowitz, W., Ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists [AOAC]. Noncasein nitrogen content of milk, method no. 998.05. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; Horowitz, W., Ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists [AOAC]. Nonprotein nitrogen in whole milk, method no. 991.21. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; Horowitz, W., Ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Malacarne, M.; Criscione, A.; Franceschi, P.; Tumino, S.; Bordonaro, S.; Di Frangia, F.; Marletta, D.; Summer, A. Distribution of Ca, P and Mg and casein micelle mineralisation in donkey milk from the second to ninth month of lactation. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 66, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, M.; Criscione, A.; Franceschi, P.; Bordonaro, S.; Formaggioni, P.; Marletta, D.; Summer, A. New insights into chemical and mineral composition of donkey milk throughout nine months of lactation. Animals 2019, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shook, G.E.; Schutz, M.M. Selection on somatic cell score to improve resistance to mastitis in the United States. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF Standard. Cheese and Processed Cheese, Determination of the Total Solids Content (Reference Method); 4/ISO5534; International Dairy Federation Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Formaggioni, P.; Summer, A.; Malacarne, M.; Franceschi, P.; Mucchetti, G. Italian and Italian-style hard cooked cheeses: Predictive formulas for Parmigiano-Reggiano 24 h cheese yield. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 51, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, M.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P.; Sandri, S.; Mariani, P.; Summer, A. Influence of micellar calcium and phosphorus on rennet coagulation properties of cows milk. J. Dairy Res. 2014, 81, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summer, A.; Franceschi, P.; Malacarne, M.; Formaggioni, P.; Tosi, F.; Tedeschi, G.; Mariani, P. Influence of somatic cell count on mineral content and salt equilibria of milk. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8 (Suppl. 2), 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urech, E.; Puhan, Z.; Schällibaum, M. Changes in milk protein fraction as affected by subclinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, J.; O’Brien, B.; Meany, W.; Kelly, A.L. Heterogeneity of proteolytic enzyme activities in milk samples of different somatic cell count. J. Dairy Res. 2003, 70, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shennan, D.B.; Peaker, M. Transport of milk constituents by the mammary gland. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 925–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, I.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F. Association between somatic cell count of milk and cheese-yielding capacity. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazal, G.; Vianna, P.C.B.; Santos, M.V.; Gigante, M.L. Effect of somatic cell count on Prato cheese composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, P.; Malacarne, M.; Formaggioni, P.; Stocco, G.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Summer, A. Effect of season and cheese-factory on cheese-making efficiency in Parmigiano Reggiano cheese manufacture. Foods 2019, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleminger, G.; Ragones, H.; Merin, U.; Silanikove, N.; Leitner, G. Chemical and structural characterization of bacterially-derived casein peptides that impair milk clotting. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretto, D.; De Marchi, M.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M. Effect of milk composition and coagulation traits on Grana Padano cheese yield under field conditions. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier-Metz, I.; Coulon, J.B.; Pradel, P. Relationship between milk fat and protein contents and cheese yield. Anim. Res. 2001, 50, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Unit of Measure | LCC 1 n 2 = 10 | HCC 1 n 2 = 10 | SE 3 | p4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude protein | g/100 g | 3.30 | 3.16 | 0.06 | NS |
| Casein | g/100 g | 2.57 | 2.43 | 0.05 | * |
| Casein number | % | 77.80 | 77.03 | 0.31 | * |
| NPN × 6.38 | g/100 g | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.01 | NS |
| True protein | g/100 g | 3.13 | 3.00 | 0.06 | NS |
| Fat | g/100 g | 2.75 | 2.68 | 0.05 | NS |
| Fat to casein ratio | Value | 1.07 | 1.10 | 0.01 | NS |
| Calcium | mg/100 g | 114.75 | 114.17 | 1.54 | NS |
| Phosphorus | mg/100 g | 92.46 | 88.37 | 1.32 | * |
| Magnesium | mg/100 g | 11.12 | 10.70 | 0.25 | NS |
| Chloride | mg/100 g | 104.12 | 111.88 | 2.72 | * |
| Titratable acidity | °SH/50 mL | 3.34 | 3.16 | 0.04 | * |
| pH | Value | 6.71 | 6.77 | 0.02 | * |
| Somatic cell count | 103 cells/mL | 146 | 259 | 5 | ** |
| Parameter | Unit of Measure | LCC 1 n 2 = 10 | HCC 1 n 2 = 10 | SE 3 | p4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheese yield: | |||||
| Actual cheese yield at 24 months | kg/100 kg | 7.39 | 6.74 | 0.18 | * |
| Dry yield at 24 months | kg/100 kg | 5.19 | 4.74 | 0.20 | * |
| Cheese characteristics: | |||||
| Moisture | g/100 g | 29.84 | 29.78 | 0.28 | NS |
| Estimated cheesemaking losses: | |||||
| Protein | % | 26.59 | 26.92 | 0.28 | NS |
| Casein | % | 5.65 | 5.13 | 0.22 | NS |
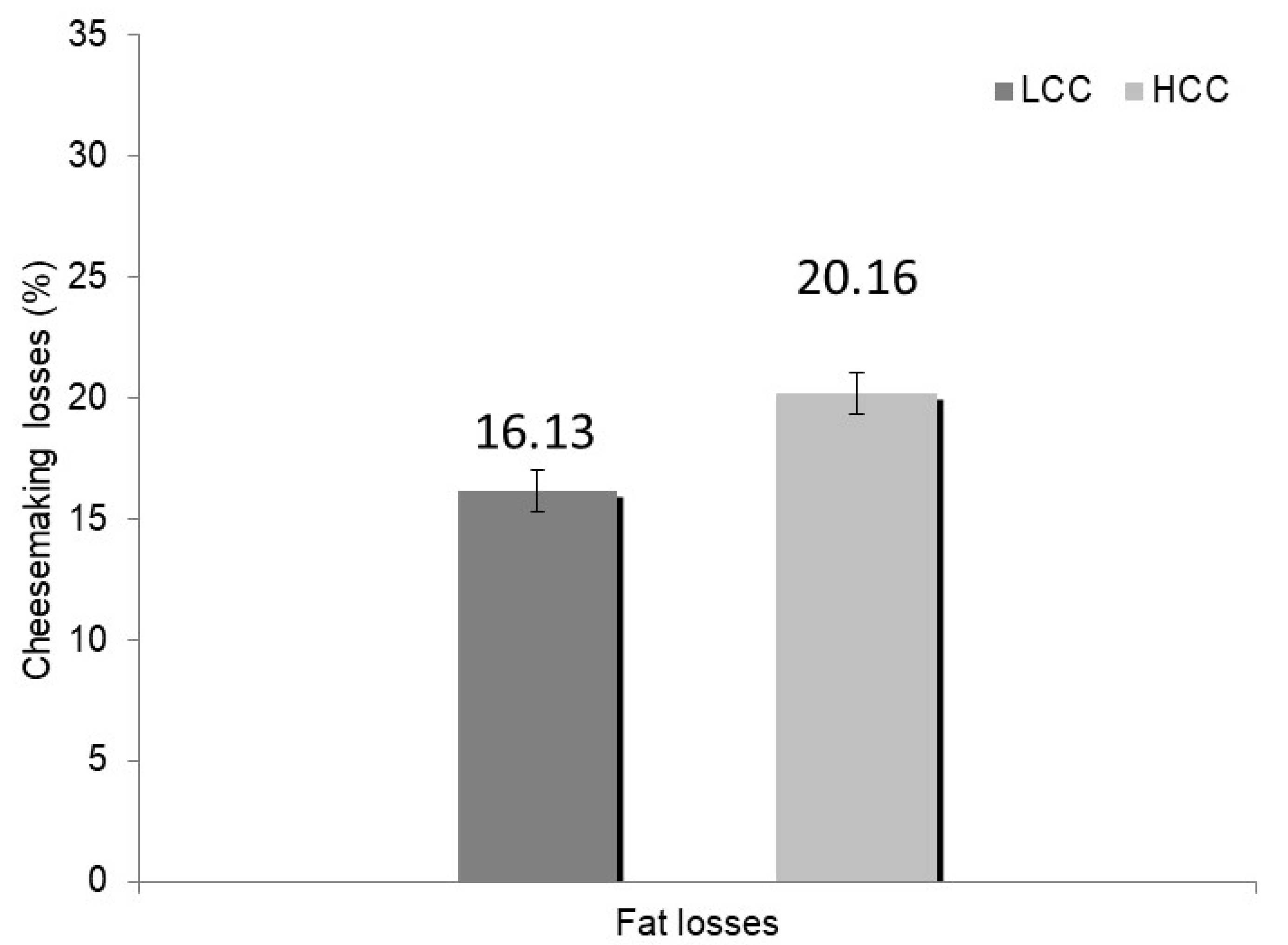
| Fat | % | 16.13 | 20.16 | 0.87 | ** |
| Phosphorus | % | 49.86 | 50.28 | 0.87 | NS |
| Calcium | % | 33.86 | 34.71 | 0.51 | NS |
| Magnesium | % | 76.92 | 77.36 | 1.69 | NS |
| Cheese Yield 1 | Protein Losses | Fat Losses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p2 | r | p2 | r | p2 | |
| Somatic cells 3 | −0.57 | * | 0.06 | NS | 0.34 | NS |
| Crude protein | 0.68 | * | 0.03 | NS | −0.58 | ** |
| Casein | 0.69 | * | −0.20 | NS | −0.64 | ** |
| Fat | 0.60 | * | −0.09 | NS | −0.34 | NS |
| Fat to casein ratio | −0.18 | NS | 0.15 | NS | 0.46 | * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franceschi, P.; Faccia, M.; Malacarne, M.; Formaggioni, P.; Summer, A. Quantification of Cheese Yield Reduction in Manufacturing Parmigiano Reggiano from Milk with Non-Compliant Somatic Cells Count. Foods 2020, 9, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9020212
Franceschi P, Faccia M, Malacarne M, Formaggioni P, Summer A. Quantification of Cheese Yield Reduction in Manufacturing Parmigiano Reggiano from Milk with Non-Compliant Somatic Cells Count. Foods. 2020; 9(2):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9020212
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranceschi, Piero, Michele Faccia, Massimo Malacarne, Paolo Formaggioni, and Andrea Summer. 2020. "Quantification of Cheese Yield Reduction in Manufacturing Parmigiano Reggiano from Milk with Non-Compliant Somatic Cells Count" Foods 9, no. 2: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9020212
APA StyleFranceschi, P., Faccia, M., Malacarne, M., Formaggioni, P., & Summer, A. (2020). Quantification of Cheese Yield Reduction in Manufacturing Parmigiano Reggiano from Milk with Non-Compliant Somatic Cells Count. Foods, 9(2), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9020212









