Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Selective Sorbent for the Extraction of Zearalenone in Edible Vegetable Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Oil Samples
2.3. Extraction and Clean-Up Using MIP-SPE
2.4. Liquid–Liquid Extraction Procedure
2.5. QuEChERS Extraction Procedure
2.6. HPLC-FLD Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analytical Parameters of the HPLC Method
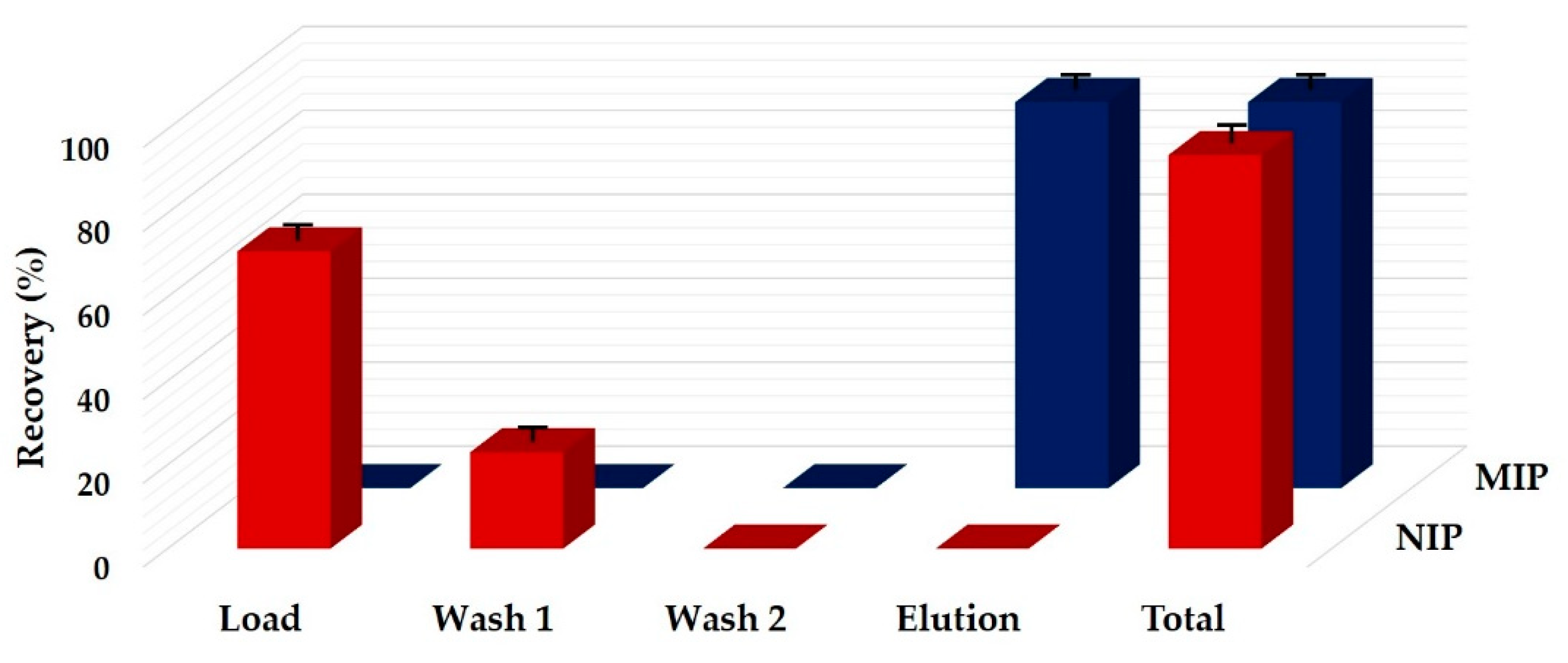
3.2. Evaluation of MIP-SPE Procedure for the Selective Extraction of Zearalenone
3.3. Validation of the MIP-SPE Procedure
3.4. Application of MIP-SPE in Commercial Edible Oils
3.5. Application of MIP-SPE in Maize Oil Samples at Various Stages of the Refining Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gromadzka, K.; Waskiewicz, A.; Chełkowski, J.; Golinski, P. Zearalenone and its metabolites: Occurrence, detection, toxicity, and guidelines. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, T.; Reijula, K.; Johnsson, T.; Hemminki, K.; Hintikka, E.L.; Lindroos, O.; Kalso, S.; Koukila-Kahkola, P.; Mussalo-Rauhamaa, H.; Haahtela, T. Mycotoxins in crude building materials from water damaged buildings. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Varzakas, T. Advances in occurrence, importance, and mycotoxin control strategies: Prevention and detoxification in foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.; Reddy, K.R.N. Challenges and issues concerning mycotoxins contamination in oil seeds and their edible oils: Updates from last decade. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldars-García, L.; Ramos, A.J.; Sanchis, V.; Marín, S. Modeling postharvest mycotoxins in foods: Recent research. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 11, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Rai, V.R.; Karim, A.A. Mycotoxins-Present status and future concerns. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Manez, M.; Hernandez, E. Influence of water activity and temperature on the production of zearalenone in corn by three Fusarium species. Int J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumy, J.L.; Bailly, J.D.; Burgat, V.; Guerre, P. Zearalenone: Properties and experimental toxicity. Revue de Méd Vét. 2001, 152, 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Lioi, M.B.; Santoro, A.; Barbieri, R.; Salzano, S.; Ursini, M.V. Ochratoxin and zearalenone: A comparative study on genotoxic effects and cell death induced in bovine lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 2004, 557, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, K.; Chekir, L.; Creppy, E.E.; Ellouz, F.; Bacha, H. Zearalenone induces modifications in haematological and biochemical parameters in rats. Toxicon 1996, 34, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berek, L.; Petri, I.B.; Mesterhazy, A.; Teren, J.; Molnar, J. Effects of mycotoxins on human immune functions in vitro. Toxicol. In Vitro 2001, 15, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Molto, J.C.; Manes, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations, and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zöllner, P.; Jodlbauer, J.; Lindner, W. Determination of zearalenone in grains by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after solid-phase extraction with RP-18 columns or immunoaffinity columns. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 858, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenberger, M.; Muller, H.M.; Rufle, M.; Drochner, W. Natural occurrence of 16 Fusarium toxins in edible oil marketed in Germany. Food Control 2008, 19, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappenstein, O.; St. Klaffke, H.; Mehlitz, I.; Tiebach, R.; Weber, R.; Lepschy, J.; Wittkowski, R. Determination of zearalenone in edible oils with SEC and LC-ESI-MS/MS. Mycotoxin Res. 2005, 21, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific opinion on the risks for public health related to the presence of zearalenone in food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1126/2007 of 28 September 2007, Official Journal of the European Union.
- Bozkurt, S.S.; Işık, G. Ionic liquid based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for preconcentration of zearalenone and its determination in beer and cereal samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, S.S.; Weiz, W.; Heinze, J.; Marten, S.; Prinz, C.; Zimathies, A.; Garbe, A.; Koch, M. Automated solid-phase extraction coupled on-line with HPLC-FLD for the quantification of zearalenone in edible oil. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3489–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Reyes, D.; Gómez-Martinez, L.; Cueva-Rolón, R. Zearalenone contamination in corn for human consumption in the state of Tlaxcala, Mexico. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempelaki, I.E.; Sakkas, V.A.; Albanis, T.A. The development of a sensitive and rapid liquid-phase microextraction method followed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for the determination of zearalenone residues in beer samples. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urraca, J.L.; Marazuela, M.D.; Merino, E.R.; Orellana, G.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Molecularly imprinted polymers with a streamlined mimic for zearalenone analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.Y.; Shyu, C.L.; Liao, C.W.; Lee, R.J.; Lee, M.R.; Vickroy, T.W.; Chou, C.C. Liquid chromatography incorporating ultraviolet and electrochemical analyses for dual detection of zeranol and zearalenone metabolites in mouldy grains. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto-Figueira, P.; Camacho, I.; Câmara, J.S. Exploring the potentialities of an improved ultrasound-assisted quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe-based extraction technique combined with ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for determination of zearalenone in cereals. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1408, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Núñez, O.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Martins, C.P.; Lucci, P. New trends in fast liquid chromatography for food and environmental analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1228, 298–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Present and future prospective. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucci, P.; Núñez, O.; Galceran, M.T. Solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of natural and synthetic estrogens from aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4828–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, A.; Bottaro, C.S. A critical review of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of organic pollutants in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A. 2020, 1614, 460603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucci, P.; Derrien, D.; Alix, F.; Perollier, C.; Bayoudh, S. Molecularly imprinted polymer solid phase extraction for detection of zearalenone in cereal sample extracts. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 672, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucci, P.; Núñez, O. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction in food analysis. In New Trends in Sample Preparation Techniques; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor mimics for selective cell recognition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5574–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhotská, I.; Gajdošová, B.; Solich, P.; Šatínský, D. Molecularly imprinted vs. reversed-phase extraction for the determination of zearalenone: A method development and critical comparison of sample clean-up efficiency achieved in an on-line coupled SPE chromatography system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3265–3273. [Google Scholar]
- Radi, A.-E.; Eissa, A.; Wahdan, T. Molecularly imprinted impedimetric sensor for determination of mycotoxin zearalenone. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Liao, S.; Chen, G. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the identification of zearalenone in grains. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4725–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucci, P.; Bertoz, V.; Pacetti, D.; Moret, S.; Conte, L. Effect of the refining process on total hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and tocopherol contents of olive oil. Foods 2020, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pano-Farias, N.S.; Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; Muñiz-Valencia, R.; Gonzalez, J. Validation and assessment of matrix effect and uncertainty of a gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry method for pesticides in papaya and avocado samples. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmili, K.; Jinap, S.; Sukor, R. Development, optimization, and validation of QuEChERS based liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of multimycotoxin in vegetable oil. Food Control 2016, 70, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 401/2006 of 23 February 2006, Official Journal of the European Union.
- Siegel, D.; Andrae, K.; Proske, M.; Kochan, C.; Koch, M.; Weber, M. Dynamic covalent hydrazine chemistry as a selective extraction and cleanup technique for the quantification of the Fusarium mycotoxin zearalenone in edible oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2206–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, H. Removal of mycotoxins during food processing. In Mycotoxins and phycotoxins. Bioactive Molecules; Natori, S., Hashimoto, K., Ueno, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 10, pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar]




| Spike (µg/kg) | Recovery (%) | Main (%) | sr (µg/kg) | RSDr (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||||
| 20 | 71 | 74 | 71 | 72 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| 100 | 95 | 94 | 92 | 93 | 1.3 | 1.4 |
| 200 | 91 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| 300 | 93 | 90 | 90 | 91 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Procedure | Recovery (%) | Main (%) | sr (µg/kg) | RSDr (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||||
| MIP-SPE | 91 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| LLE | 68 | 69 | 58 | 65 | 4.9 | 7.5 |
| QuEChERS | 70 | 65 | 62 | 65 | 3.2 | 5.1 |
| Type of Oil | Sample | Level of ZON (µg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Maize oil | 1 | 12.5 ± 1 |
| 2 | 27.1 ± 2 | |
| 3 | 22.6 ± 1 | |
| 4 | 20.1 ± 1 | |
| 5 | - | |
| 6 | 51.1 ± 2 | |
| 7 | 23.8 ± 1 | |
| Soybean oil | 1 | - |
| 2 | 12.7 ± 0 | |
| 3 | - | |
| Rice oil | 1 | 5.7 ± 0 |
| Sample | Level of ZON (µg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Crude | 73.9 ± 3 |
| Neutralized | 52.8 ± 1 |
| Bleached | 57.7 ± 2 |
| Refined | 29.3 ± 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucci, P.; David, S.; Conchione, C.; Milani, A.; Moret, S.; Pacetti, D.; Conte, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Selective Sorbent for the Extraction of Zearalenone in Edible Vegetable Oils. Foods 2020, 9, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101439
Lucci P, David S, Conchione C, Milani A, Moret S, Pacetti D, Conte L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Selective Sorbent for the Extraction of Zearalenone in Edible Vegetable Oils. Foods. 2020; 9(10):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101439
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucci, Paolo, Stefano David, Chiara Conchione, Andrea Milani, Sabrina Moret, Deborah Pacetti, and Lanfranco Conte. 2020. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Selective Sorbent for the Extraction of Zearalenone in Edible Vegetable Oils" Foods 9, no. 10: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101439
APA StyleLucci, P., David, S., Conchione, C., Milani, A., Moret, S., Pacetti, D., & Conte, L. (2020). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Selective Sorbent for the Extraction of Zearalenone in Edible Vegetable Oils. Foods, 9(10), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101439






