Anthocyanin-Loaded Double Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Phosphorylated Perilla Seed Protein Isolate–Pectin Complexes and Its Environmental Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of PPSPI–PEC Complexes
2.2.1. Preparation of Perilla Seed Protein Isolate (PSPI)
2.2.2. Preparation of Phosphorylated Perilla Seed Protein Isolate (PPSPI)
2.2.3. Preparation of PPSPI–PEC Complexes
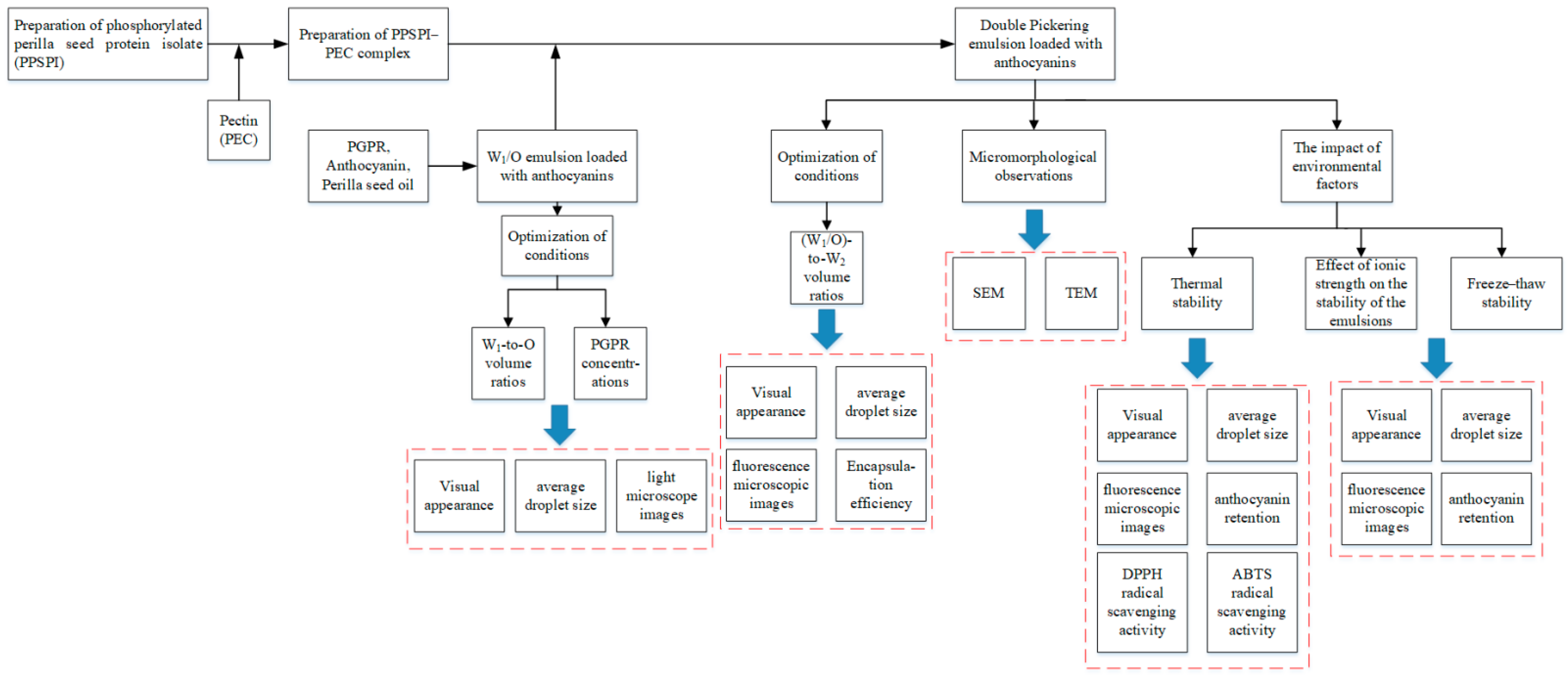
2.3. W1/O/W2 Pickering Emulsions
2.3.1. Preparation of W1/O Emulsions and Optimization of Conditions
2.3.2. Preparation of W1/O/W2 Pickering Emulsions
2.3.3. Observation of the Emulsions’ Microscopic Morphologies
2.3.4. Droplet Size of W1/O Emulsions and W1/O/W2 Pickering Emulsions
2.3.5. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency (EE)
2.3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Environmental Stability
2.4.1. Thermal Stability
2.4.2. Effect of Ionic Strength on the Stability of the Emulsions
2.4.3. Freeze–Thaw Stability
2.4.4. Observation of Emulsions’ Microscopic Morphologies
2.4.5. Emulsion Droplet Size
2.4.6. Anthocyanin Retention
2.4.7. Antioxidant Properties
DPPH
ABTS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
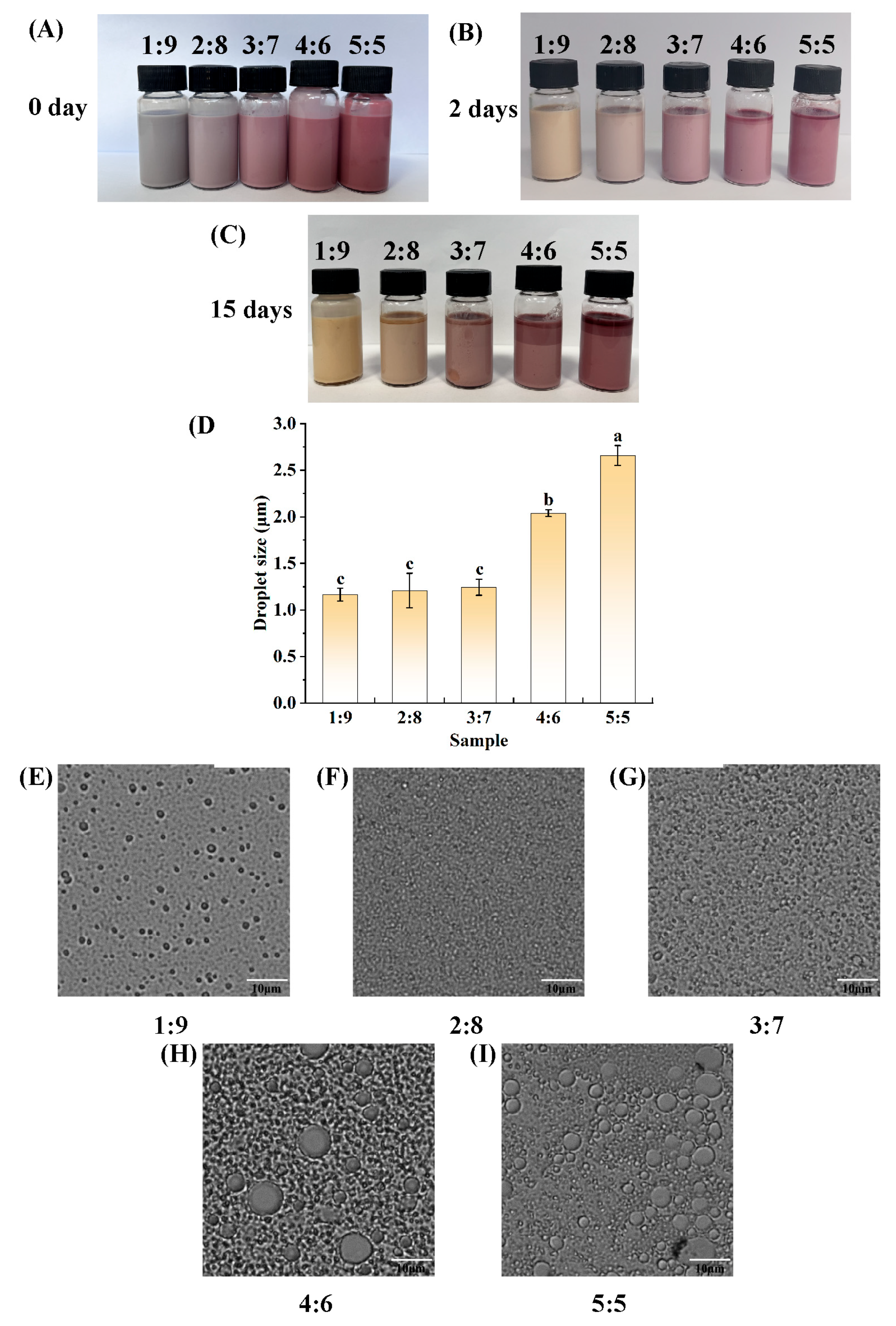
3.1. Determination of W1-to-O Volume Ratio
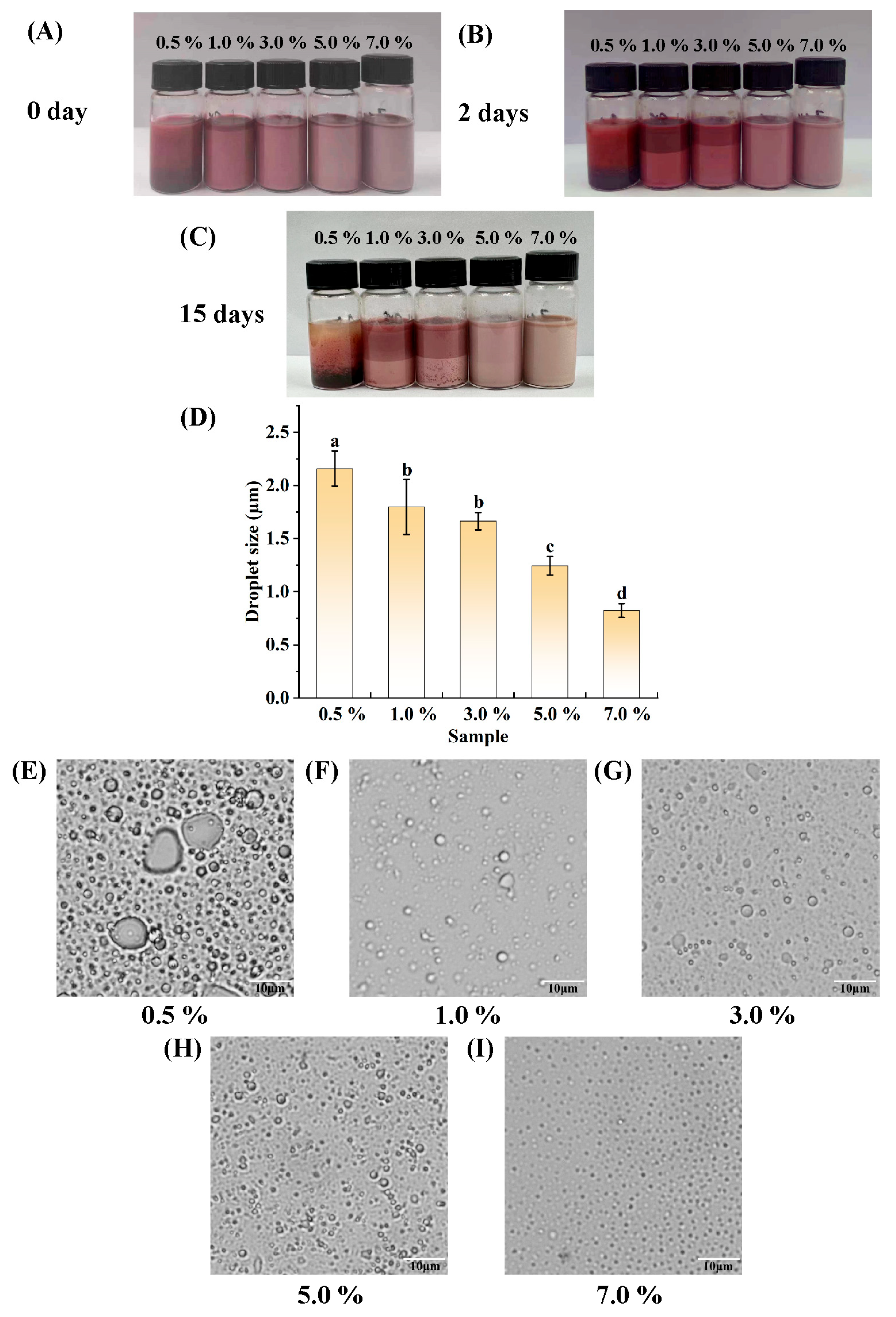
3.2. Determination of the Amount of PGPR
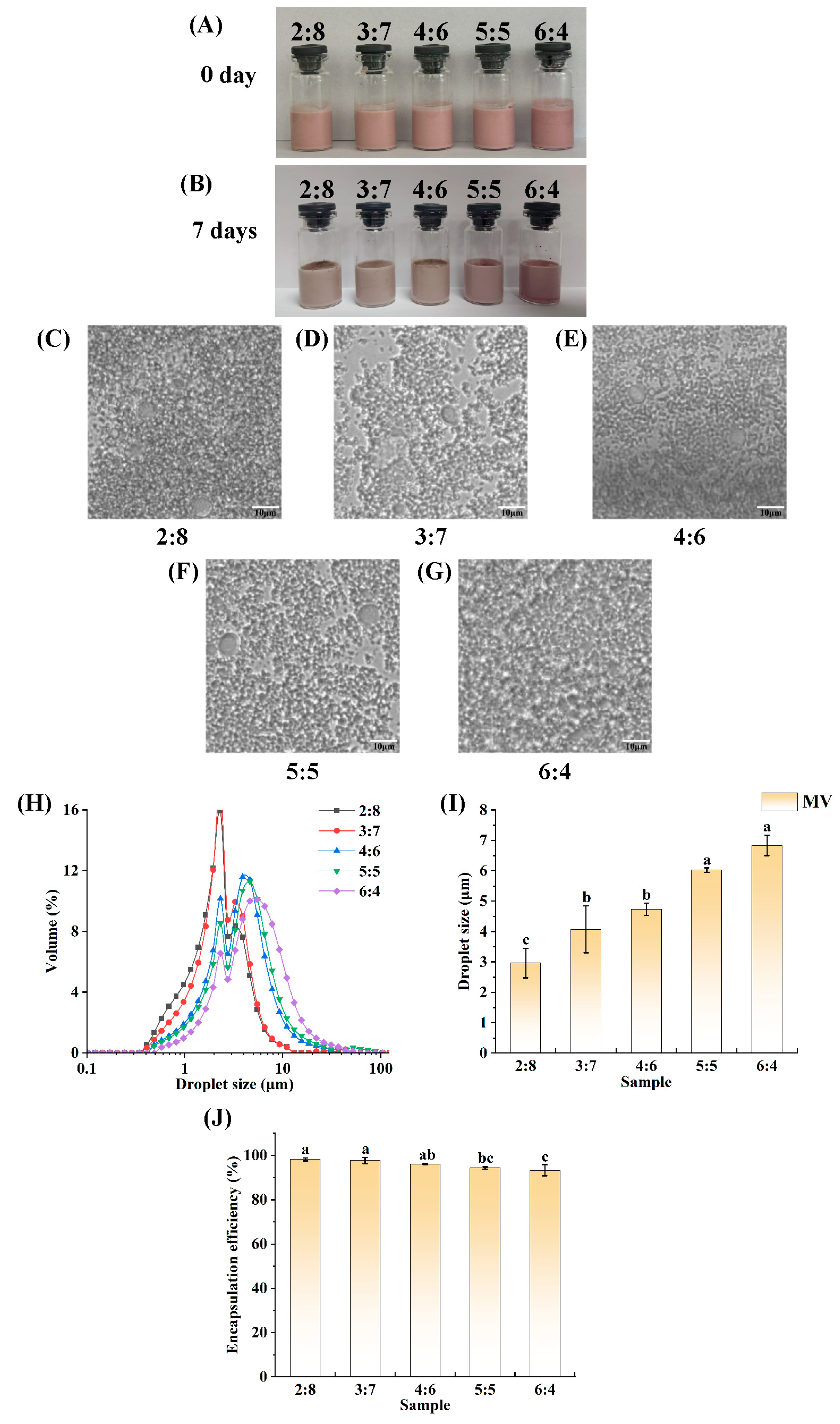
3.3. Determination of the (W1/O)-to-W2 Volume Ratio
3.4. SEM and TEM
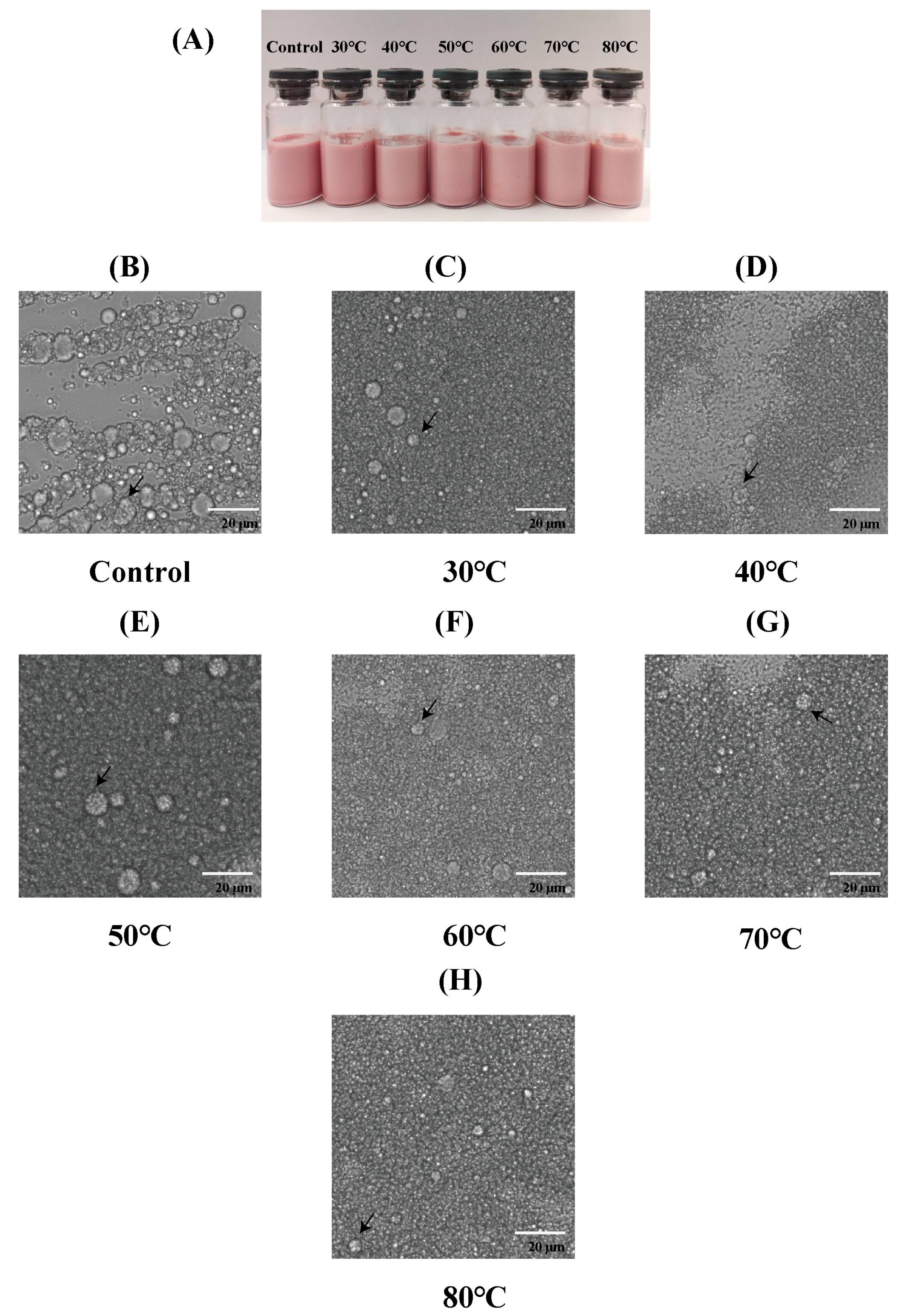
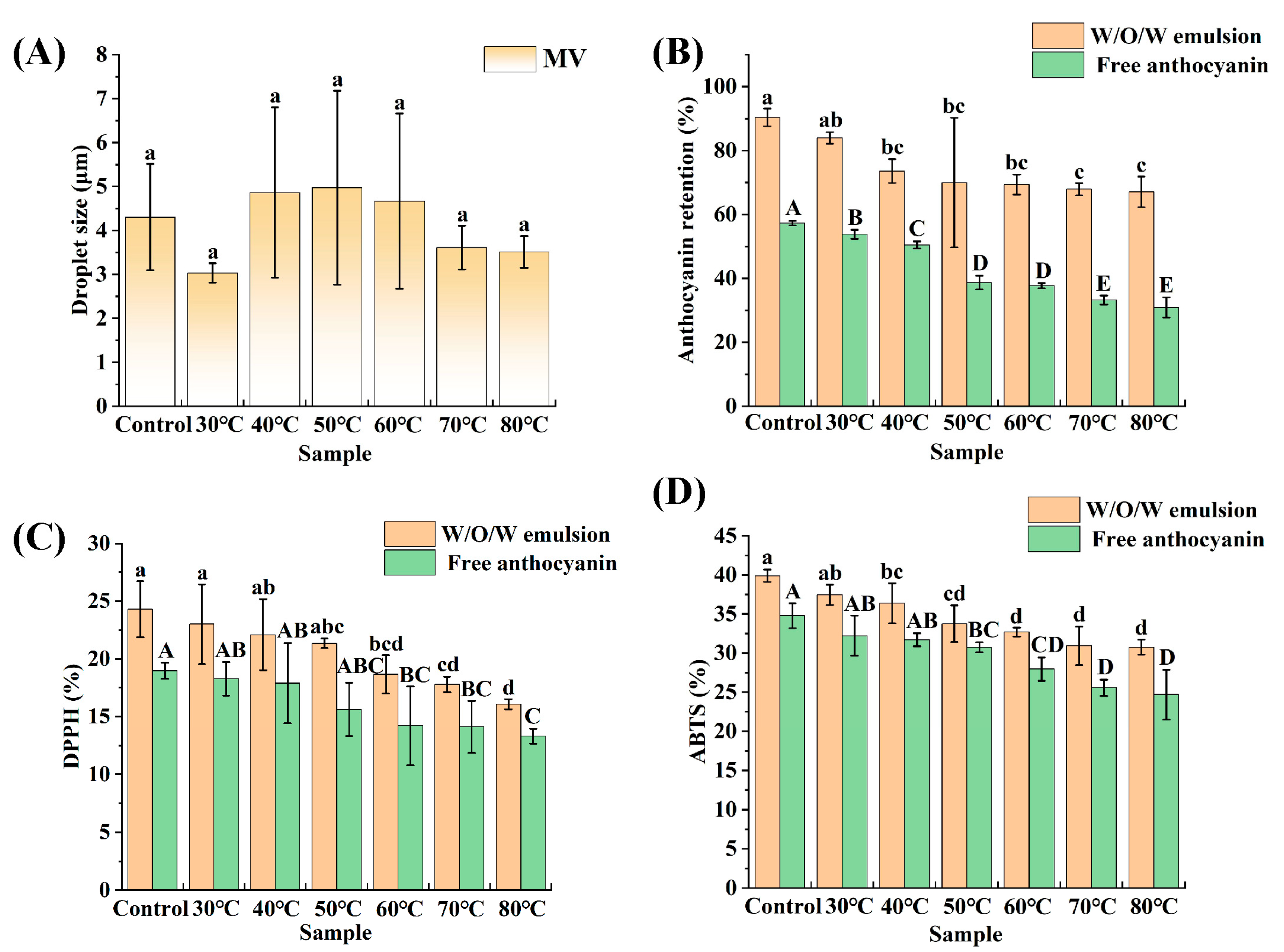
3.5. Thermal Stability
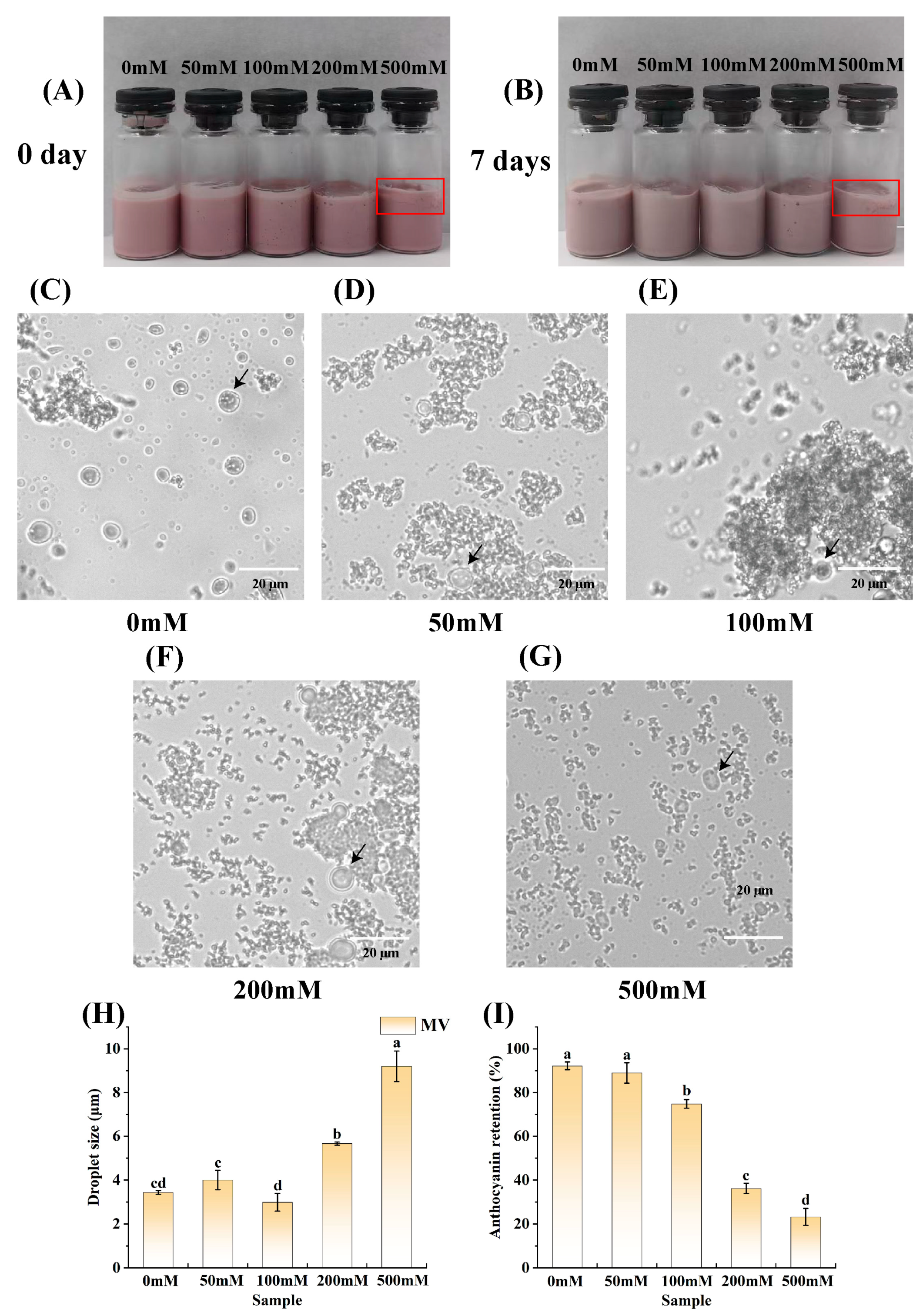
3.6. Effect of Ionic Strength on the Stability of the Emulsions
3.7. Freeze–Thaw Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, S.; Serra, C.A.; Vandamme, T.F.; Yu, W.; Anton, N. Double emulsions prepared by two–step emulsification: History, state-of-the-art and perspective. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, F.; Jafari, S.M.; Ziaiifar, A.M.; Malekjani, N. Stability and release mechanisms of double emulsions loaded with bioactive compounds; a critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, C.C.; Bashir, O.; Amin, T.; Dash, K.K.; Shams, R.; Ramadas, B.K.; Ali, S.M. Pickering emulsion morphology: Stabilization and applications of double emulsions. Food Humanit. 2025, 4, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, F.; Hashemi, H.; Esteghlal, S.; Hosseini, S.M. An Updated Comprehensive Overview of Different Food Applications of W1/O/W2 and O1/W/O2 Double Emulsions. Foods 2024, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Gehlot, R.; Aggarwal, P. New insights into water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsions: Properties, fabrication, instability mechanism, and food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, A.; Erős, I.; Csóka, I. Optimization and development of stable w/o/w cosmetic multiple emulsions by means of the Quality by Design approach. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 38, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, S.; Ramsay, K.; Elvira, K.S. A plug-and-play modular microcapillary platform for the generation of multicompartmental double emulsions using glass or fluorocarbon capillaries. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, H. Thermal field-actuated multifunctional double-emulsion droplet carriers: On-demand migration, core release and released particle focusing. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ma, W.; Li, C.; Pan, J.; Dai, X. Well-designed multihollow magnetic imprinted microspheres based on cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) stabilized Pickering double emulsion polymerization for selective adsorption of bifenthrin. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øye, G.; Simon, S.; Rustad, T.; Paso, K. Trends in food emulsion technology: Pickering, nano-, and double emulsions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 50, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ma, X.; Sun, J.; Bai, W. Fabrication and characterization of anthocyanin-loaded double Pickering emulsions stabilized by β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 655, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, M.; Timgren, A.; Sjöö, M.; Dejmek, P.; Rayner, M. Preparation and encapsulation properties of double Pickering emulsions stabilized by quinoa starch granules. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 423, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Carillo, P.; Pizzolongo, F.; Romano, R.; Sifola, M.I. Chemical Eustress Elicits Tailored Responses and Enhances the Functional Quality of Novel Food Perilla frutescens. Molecules 2019, 24, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, K.; Ji, N.; Yao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, Q.; et al. Perilla Seed Oil and Protein: Composition, Health Benefits, and Potential Applications in Functional Foods. Molecules 2024, 29, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Liceaga, A.M.; Yoon, K.Y. Purification and identification of an antioxidant peptide from perilla seed (Perilla frutescens) meal protein hydrolysate. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.B.; Yoon, Y.K. Biological activity of enzymatic hydrolysates and the membrane ultrafiltration fractions from perilla seed meal protein. Czech J. Food Sci. 2019, 37, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Li, J. High internal phase emulsion gels stabilized by phosphorylated perilla protein isolate for protecting hydrophobic nutrients: Adjusting emulsion performance by incorporating chitosan-protocatechuic acid conjugate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yi, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Properties and Stability of Perilla Seed Protein-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Influence of Protein Concentration, pH, NaCl Concentration and Thermal Treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Xie, K.; Liao, X.; Tan, J. Factors affecting the stability of anthocyanins and strategies for improving their stability: A review. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Benn, A.; Contador, C.A.; Li, M.-W.; Lam, H.-M.; Ah-Hen, K.; Ulloa, P.E.; Ravanal, M.C. Pectin: An overview of sources, extraction and applications in food products, biomedical, pharmaceutical and environmental issues. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, V.; Biswas, D.; Roy, S.; Vaidya, D.; Verma, A.; Gupta, A. Current Advancements in Pectin: Extraction, Properties and Multifunctional Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; Khalifa, I.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Yang, W. Pectin: A review with recent advances in the emerging revolution and multiscale evaluation approaches of its emulsifying characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoollahi, S.; Ariaii, P.; Hosseini, S.E.; Esmaeili, M.; Bagheri, R. Impact of chia seed protein hydrolysate and apple pomace pectin on the properties of egg-free mayonnaise. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Morell, P.; Nicoletti, V.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I. Protein- and polysaccharide-based particles used for Pickering emulsion stabilisation. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Turgeon, S.L. Protein/polysaccharide complexes and coacervates in food systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G.; Du, P.; Li, C. Sanxan–Protein Complex Particles for Stabilization of Pickering Emulsions: Improving Emulsification Properties. Foods 2024, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, J. Emulsion co-stabilized with high methoxyl pectin and myofibrillar protein: Used to enhance the application in emulsified gel. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Shams, R.; Dash, K.K.; Shaikh, A.M.; Kovács, B. Protein-polysaccharide complexes and conjugates: Structural modifications and interactions under diverse treatments. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooshkam, M.; Varidi, M.; Zareie, Z.; Alkobeisi, F. Behavior of protein-polysaccharide conjugate-stabilized food emulsions under various destabilization conditions. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gu, Q.; Hong, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Novel protein-based nanoparticles from perilla oilseed residues as sole Pickering stabilizers for high internal phase emulsions. LWT 2021, 145, 111340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancone, T.; Torrieri, E.; Masi, P.; Michon, C. Protein–polysaccharide interactions: Phase behaviour of pectin–soy flour mixture. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Chen, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, B.; Dou, Z.; Huang, Q. Pectin-stabilized emulsions: Structure-emulsification relationships, covalent and non-covalent modifications, and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 159, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, F.; Zhu, T. Correlationship between self-assembly behavior and emulsion stabilization of pea protein-high methoxyl pectin complexes treated with ultrasound at pH 2. 0. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 2023, 100, 106596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Mayonnaise-like high internal phase Pickering emulsions stabilized by co-assembled phosphorylated perilla protein isolate and chitosan for extrusion 3D printing application. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Muskała, M.; Merecz-Sadowska, A.; Sikora, J.; Picot, L.; Sitarek, P. Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Effects of Anthocyanins in In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanins and Anthocyanidins: A Critical Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S. Grape seed proanthocyanidin-loaded gel-like W/O/W emulsion stabilized by genipin-crosslinked alkaline soluble polysaccharides-whey protein isolate conjugates: Fabrication, stability, and in vitro digestion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, S.; Yin, J.; Chang, F.; Wang, C.; He, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B. Anthocyanin-loaded double Pickering emulsion stabilized by octenylsuccinate quinoa starch: Preparation, stability and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Garcia, E.; Rappolt, M.; Sadeghpour, A.; Simone, E.; Sarkar, A. Fabrication and stability of dual Pickering double emulsions stabilized with food-grade particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hong, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Solubility and emulsifying properties of perilla protein isolate: Improvement by phosphorylation in the presence of sodium tripolyphosphate and sodium trimetaphosphate. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, A.; Güler, Z. Postmortem protein phosphorylation in garlic-treated meat during refrigerated storage: Glycolytic and proteolytic changes. Food Res. Int. 2025, 208, 116236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidi, M.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Ibarz, A. Modified mung bean protein: Optimization of microwave-assisted phosphorylation and its functional and structural characterizations. LWT 2021, 151, 112119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Gong, D.; Li, F. Assembly of perilla seed protein isolate-pectin nanocomplex to deliver curcumin: Properties, characterization, molecular interactions and antioxidant activity. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xue, H. Research on yellowing causes and correction efficacy in a new red-peeled pear variety Hongsumi. J. Fruit Sci. 2022, 39, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lu, X.; Huang, Q. Double emulsion derived from kafirin nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsion: Fabrication, microstructure, stability and in vitro digestion profile. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.S.; Khalid, N.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M.; Kobayashi, I. Formulation and characterization of food grade water-in-oil emulsions encapsulating mixture of essential amino acids. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Qadri, O.S. Anthocyanin and phenolic landscape of Syzygium cumini extracts via green extraction. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Feng, X.; Yang, H.; Shao, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Internal/external aqueous-phase gelation treatment of soybean lipophilic protein W/O/W emulsions: Improvement in microstructure, interfacial properties, physicochemical stability, and digestion characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Gao, Y.; Mao, L. Insights into the thermal responsiveness of W/O emulsions with nanoparticles and oleogels as building blocks. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Decker, E.A.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Physical and chemical stability of β-carotene-enriched nanoemulsions: Influence of pH, ionic strength, temperature, and emulsifier type. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkinali, A.-A.; Matsakidou, A.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Assessing the emulsifying properties of Tenebrio molitor larvae protein preparations: Impact of storage, thermal, and freeze-thaw treatments on o/w emulsion stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Xiang, D.; Li, C. Tea polyphenols encapsulated in W/O/W emulsions with xanthan gum–locust bean gum mixture: Evaluation of their stability and protection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Yuan, Y.; Xiang, J.; Jin, W.; Johnson, J.B.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, D. Green extraction of phenolic compounds from foxtail millet bran by ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction: Optimization, comparison and bioactivities. LWT 2022, 154, 112740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, C.; Celik, S.; Yurdakul, S.; Coteli, E. A new Ag(I)-complex of 5-chloroquinolin-8-ol ligand: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, and DFT investigations, in vitro antioxidant (DPPH and ABTS), α-glucosidase, α-amylase inhibitory activities with protein-binding analysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1325, 141285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Lv, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Fabrication and characterization of blue honeysuckle anthocyanins-loaded nanocomposite films and the application in pork preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, C.A.S.; Taarji, N.; Khalid, N.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M.; Neves, M.A. Formulation and characterization of water-in-oil nanoemulsions loaded with açaí berry anthocyanins: Insights of degradation kinetics and stability evaluation of anthocyanins and nanoemulsions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, X.; Lu, S.; Xu, B.; Bai, C.; Ma, T.; Song, Y. Fabrication of nanocrystal/β-lactoglobulin complexes stabilized W1/O/W2 emulsions: Structure, stabilization mechanism and application for co-encapsulation of curcumin and EGCG. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, T.; Wei, Q.; Jin, Z.; Han, H.; Zhu, H.; Ma, X. Effects of sophorolipids and coconut wax incorporation on the physical, structural, and antibacterial properties of cellulose nanofibers-based Pickering emulsion for cherry tomato preservation. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Physicochemical and digestion properties of fish oil and anthocyanins co-encapsulated W/O/W emulsion reinforced with alginate. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmar, K. Bianco-Peled, Shellac-based nanoparticles provide highly stable Pickering emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 141941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.S.; Upadhyay, A.; Shrivastava, S.; Singh, A.; Saha, S. Architectural influence of polymer brush-modified tri-compartmental anisotropic particles in stabilizing pickering emulsion. Polymer 2025, 324, 128222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, U.; Yeung, C.K.; Zheng, H. Construction of cold-set Mickering emulsion gel using whey protein assembly particles as oil-water interfacial stabilizer and gelling agent: Phase stability, nonlinear rheology, and tribology. J. Dairy Sci. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Chu, H.; Hou, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; He, J. W/O/W emulsions stabilized with whey protein concentrate and pectin: Effects on storage, pasteurization, and gastrointestinal viability of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-J.; Choi, D.; Lee, J.; Jo, Y.-J. Encapsulation of a bioactive peptide in a formulation of W1/O/W2-type double emulsions: Formation and stability. Food Struct. 2020, 25, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Bui, T.H.A.; Dharmadana, D.; Zisu, B.; Chandrapala, J. Ultrasound-assisted formation of double emulsions stabilized by casein-whey protein mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Hu, G.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Changes in the textural and flavor characteristics of egg white emulsion gels induced by lipid and thermal treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 79, 103054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Kulshrestha, R.; Tiwari, S. Cooking Methods and Their Implications in the Preservation of Food Nutrients and Health Benefits. In Traditional Foods: The Reinvented Superfoods; Roy, S., Nisha, P., Chakraborty, R., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, K.K.; Fayaz, U.; Dar, A.H.; Shams, R.; Manzoor, S.; Sundarsingh, A.; Deka, P.; Khan, S.A. A comprehensive review on heat treatments and related impact on the quality and microbial safety of milk and milk-based products. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, R.; Nieuwenhuijse, H. Kinetic modelling of the formation of sulphur-containing flavour components during heat-treatment of milk. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, H. Enhancing emulsification properties of pea protein isolate: Impact of heat treatment and soy hull polysaccharides on conformational modification and stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 140106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Fan, L. Interactions between zein and anthocyanins at different pH: Structural characterization, binding mechanism and stability. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücetepe, M.; Özaslan, Z.T.; Karakuş, M.Ş.; Akalan, M.; Karaaslan, A.; Karaaslan, M.; Başyiğit, B. Unveiling the multifaceted world of anthocyanins: Biosynthesis pathway, natural sources, extraction methods, copigmentation, encapsulation techniques, and future food applications. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, C.; Higaki, N.T.F.; Montrucchio, D.P.; Oliveira, C.F.D.; Gomes, M.L.S.; Miguel, M.D.; Miguel, O.G.; Zanin, S.M.W.; Dias, J.D.F.G. Development of W1/O/W2 emulsion with gallic acid in the internal aqueous phase. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isusi, G.I.S.; Weilandt, M.; Majollari, I.; Karbstein, H.P.; van der Schaaf, U.S. Emulsions stabilised with pectin-based microgels: Investigations into the effect of pH and ionic strength on emulsion stability. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7227–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Lv, W.; Xiao, H. Effect of salt valence and ionic strength on the rheology and 3D printing performance of walnut protein emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 164, 111112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Q.; Lin, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization of the aggregation behavior of sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) myofibrillar proteins mediated by different ionic strengths: Protein structures, gel properties, and emulsion stabilities. LWT 2023, 189, 115483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Han, L.; Liu, H. Stability of electrostatically stabilized Pickering emulsion of silica particles and soy hull polysaccharides: Mechanism of pH and ionic strength. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherze, I.; Knoth, A.; Muschiolik, G. Effect of Emulsification Method on the Properties of Lecithin- and PGPR-Stabilized Water-in-Oil-Emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2006, 27, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzenga, R.; Folmer, B.M.; Hughes, E. Design of Double Emulsions by Osmotic Pressure Tailoring. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3574–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Guo, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, N. Study on the structure, stability characterization, and oxidative stability of a conjugated stabilized walnut oil emulsion using walnut protein isolate and gum Arabic. LWT 2024, 210, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Yin, F.; Zhu, C.; Liu, H.; Ru, A.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K. Yield twice the result with half the effort: Effect of ionic strength on quality of myofibrillar protein micro-gel pickering emulsion mediated by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. LWT 2025, 215, 117195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Utilizing carboxymethyl cellulose to assist soy protein isolate in the formation of emulsion to deliver β-carotene: Exploring the correlation between interfacial behavior and emulsion stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 303, 140650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, B.; Rafiq, S.; Fayaz, I.; Makroo, H.A. Food and Dairy Freezing and Cooling Techniques. In Engineering Solutions for Sustainable Food and Dairy Production: Innovations and Techniques in Food Processing and Dairy Engineering; Deka, S.C., Nickhil, C., Haghi, A.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Zhong, R.; Xiao, J.; Rogers, M.A.; Cao, Y.; Lan, Y. Interfacial crystallized oleogel emulsion with improved freeze-thaw stability and tribological properties: Influence of cooling rate. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, B.; Bian, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Song, Z.; Zhang, N. High freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsion stabilized by SPI-maltose particles and its effect on frozen dough. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Kong, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Huang, Q. Collaborative stabilizing effect of trehalose and myofibrillar protein on high internal phase emulsions: Improved freeze-thaw stability and 3D printability. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Chi, Y.; Chi, Y. Preparation of high internal phase emulsions based on high-temperature glycation-modified egg white protein: Structural characteristics, stability, and β-carotene bioavailability under multi-parameter regulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Anthocyanin-Loaded Double Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Phosphorylated Perilla Seed Protein Isolate–Pectin Complexes and Its Environmental Stability. Foods 2025, 14, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091650
Chen Z, Yang J, Guo H, Zhang X, Zhang W. Anthocyanin-Loaded Double Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Phosphorylated Perilla Seed Protein Isolate–Pectin Complexes and Its Environmental Stability. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091650
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhao, Jun Yang, Hao Guo, Xiuling Zhang, and Wentao Zhang. 2025. "Anthocyanin-Loaded Double Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Phosphorylated Perilla Seed Protein Isolate–Pectin Complexes and Its Environmental Stability" Foods 14, no. 9: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091650
APA StyleChen, Z., Yang, J., Guo, H., Zhang, X., & Zhang, W. (2025). Anthocyanin-Loaded Double Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Phosphorylated Perilla Seed Protein Isolate–Pectin Complexes and Its Environmental Stability. Foods, 14(9), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091650




