Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities, and Aromatic Profile of Yogurt Co-Fermented by Weissella cibaria G232 with Traditional Starters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Strains
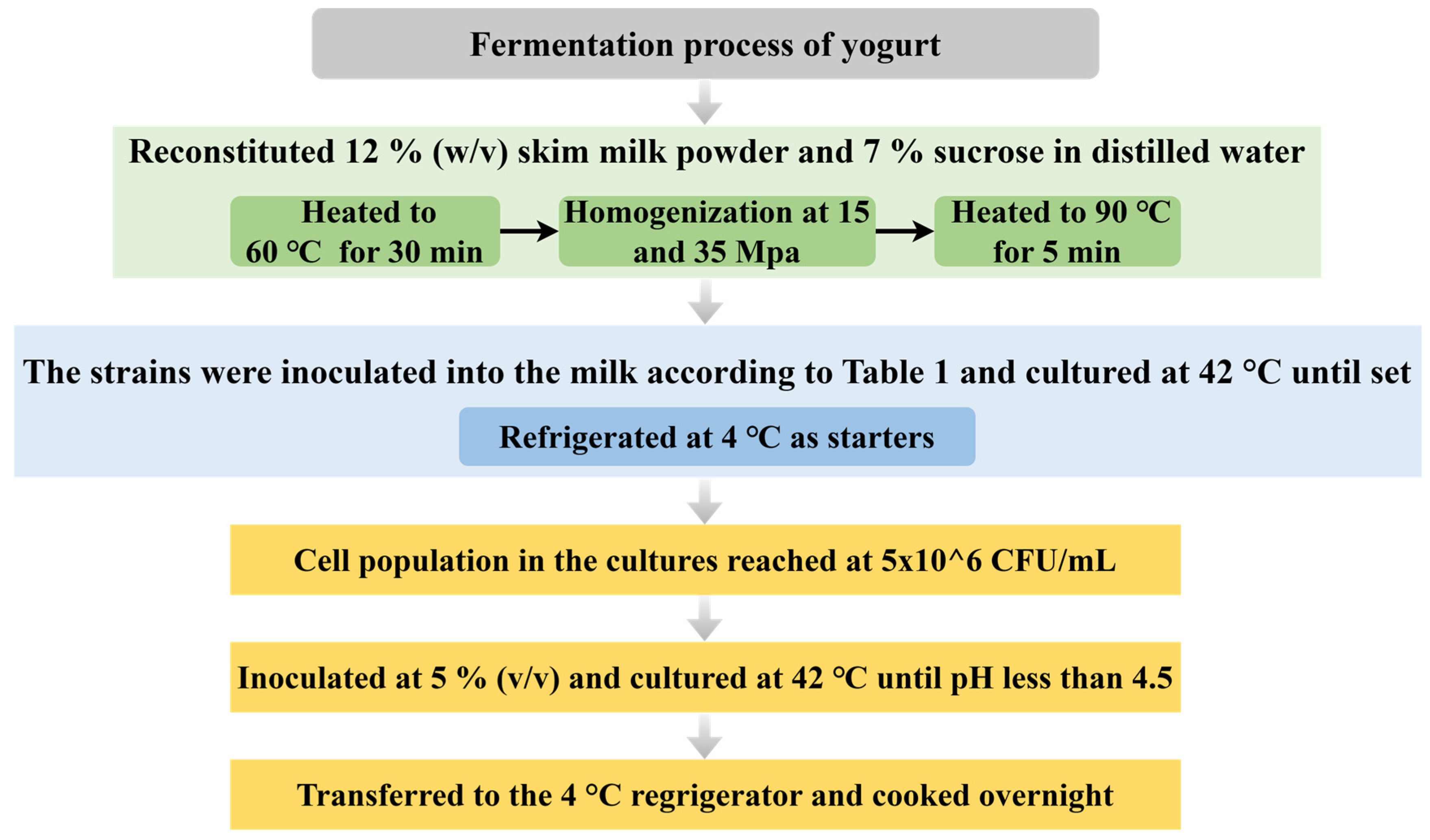
2.2. Yogurt Fermentation
2.3. Physicochemical Characteristics of Yogurt
2.3.1. Determination of pH and Titratable Acidity (TA)
2.3.2. Determination of Viable Counts
2.3.3. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.3.4. Determination of Rheological Property
2.3.5. Texture Analysis
2.4. Determination of Yogurt’s Antioxidant Activity
2.4.1. Determination of ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Ability
2.4.2. Determination of DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Ability
2.4.3. Ferrous Ion Chelating Ability (FRAP)
2.5. Determination of Yogurt’s Sensory Properties by Intelligent Technology
2.5.1. Electronic Nose and Tongue Analysis
2.5.2. GC-IMS Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
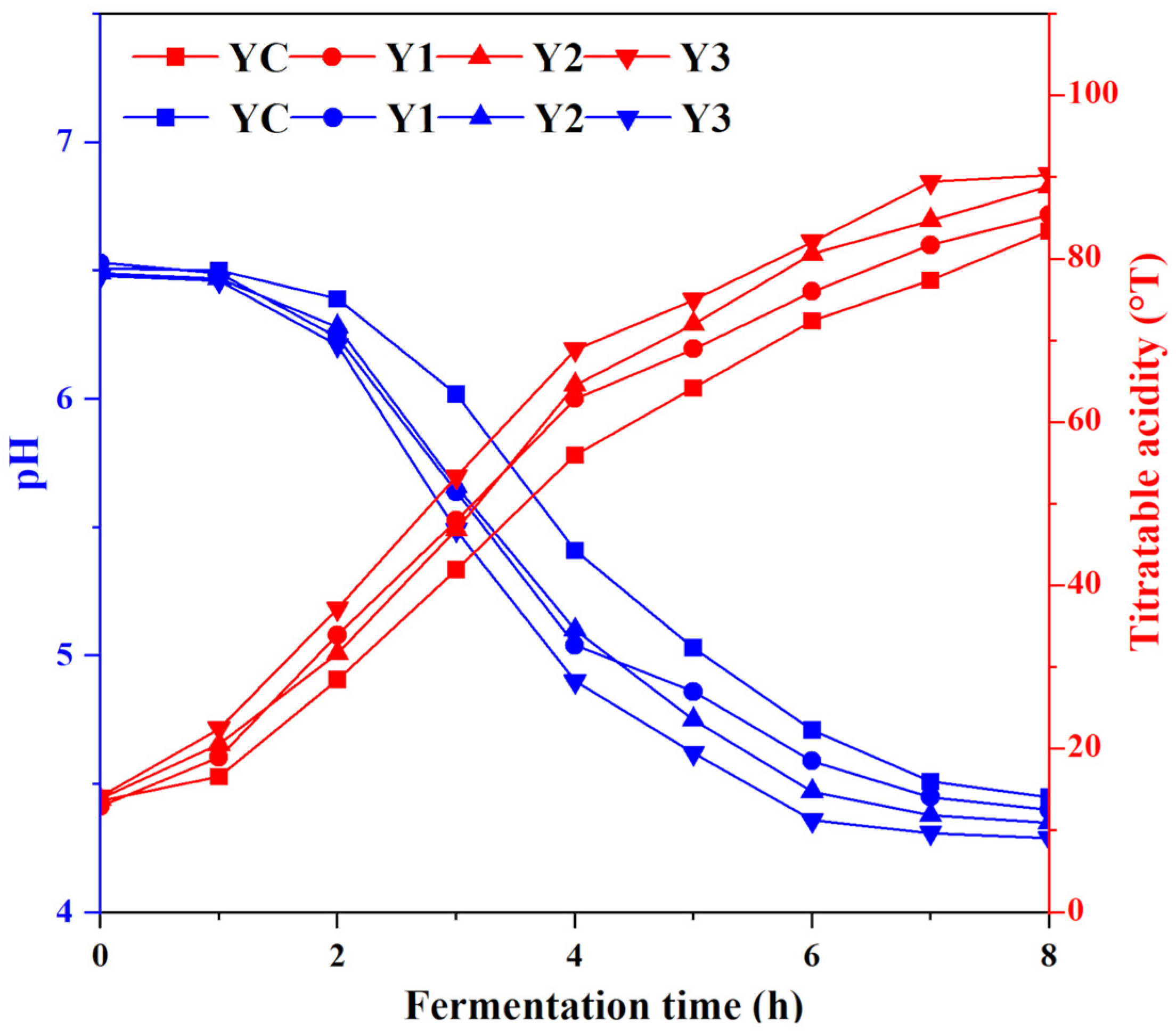
3.1. Changes in Acidity of Yogurt During Fermentation
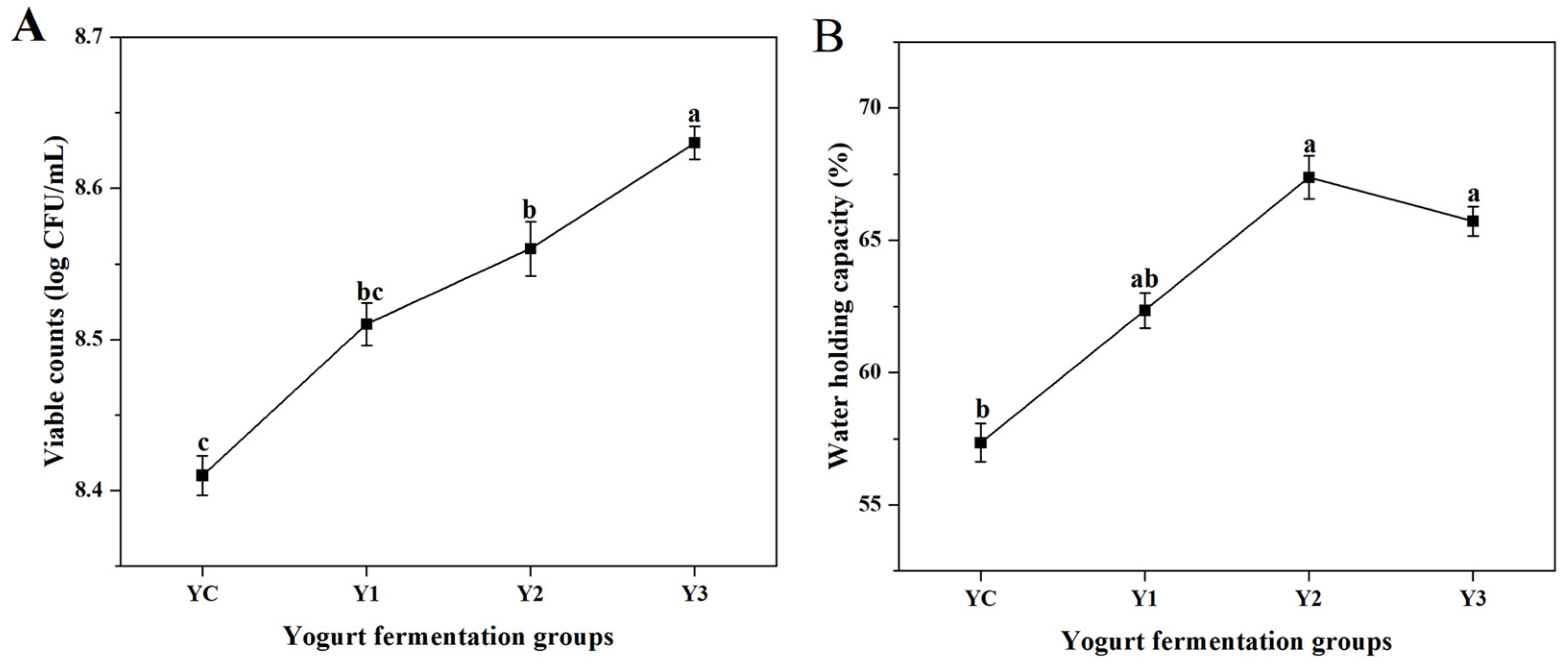
3.2. Changes in Viable Counts and WHC of Yogurt During Fermentation
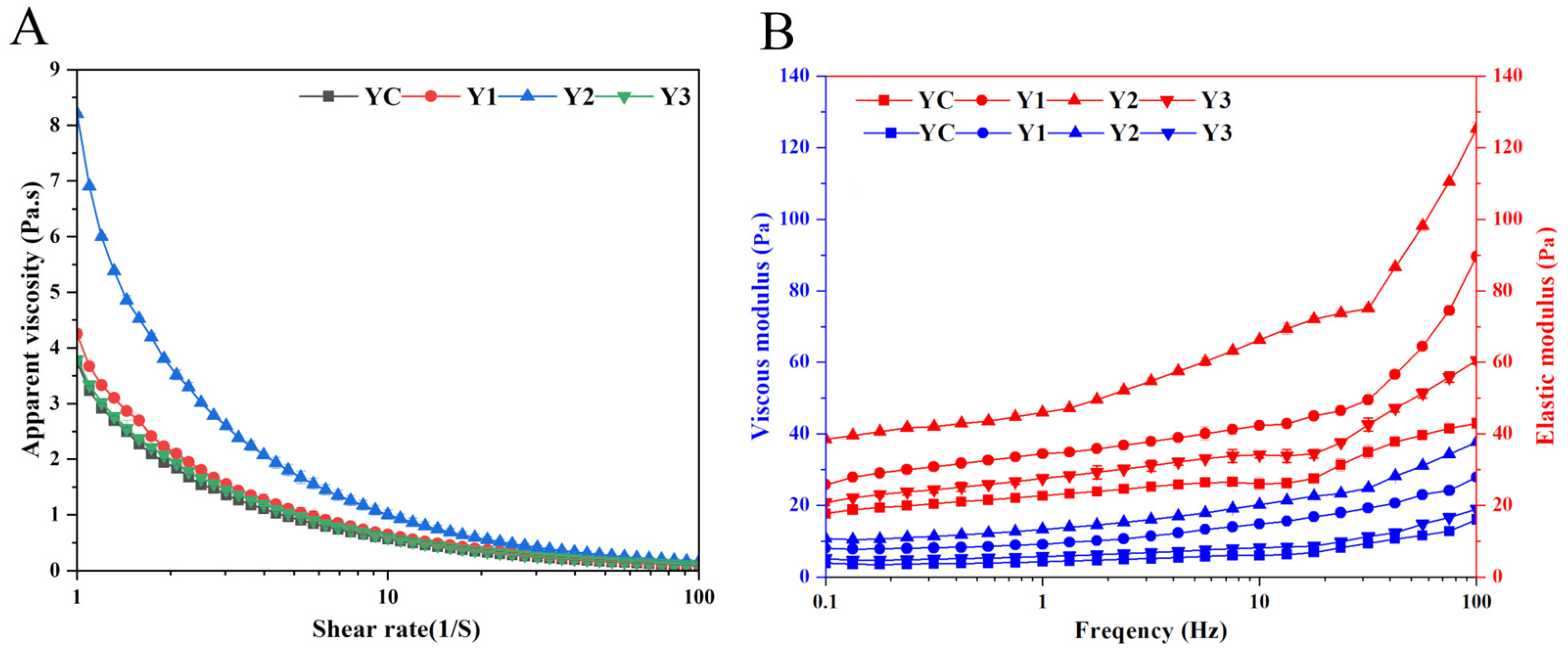
3.3. Rheological Properties of Yogurt
3.4. Texture Change in Yogurt
3.5. Antioxidant Activity Change in Yogurt
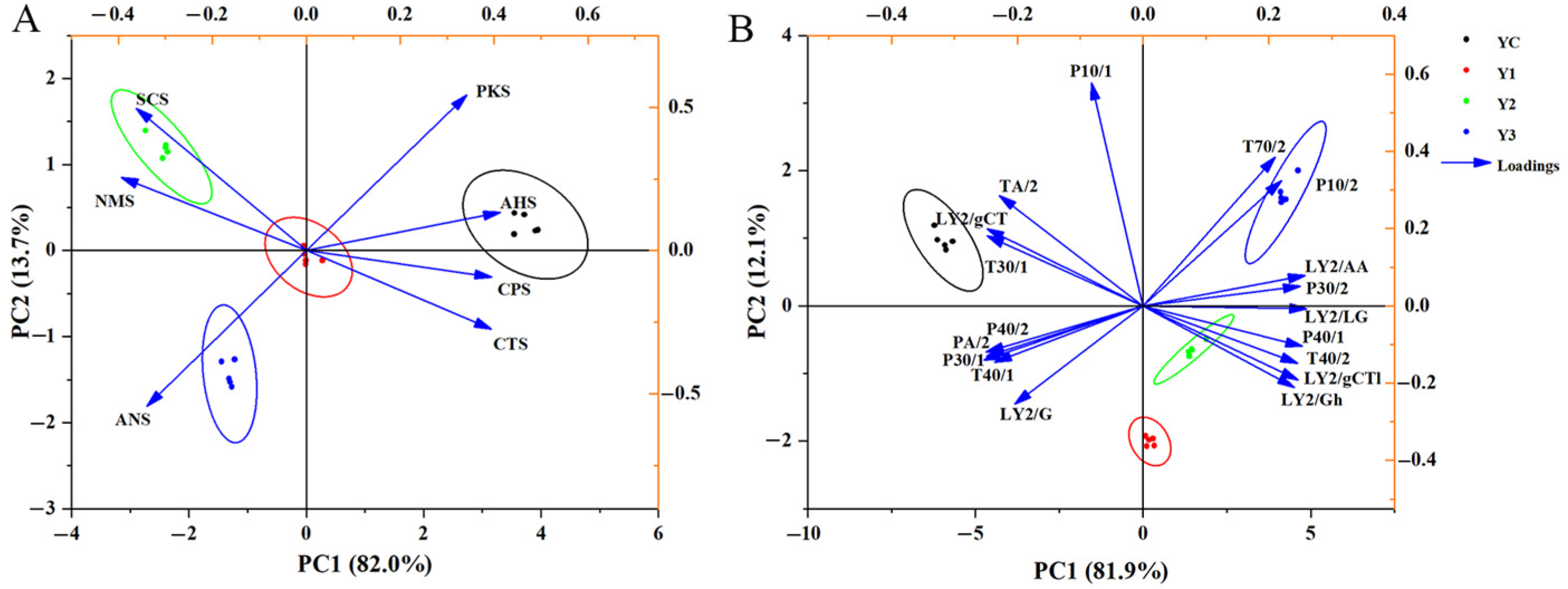
3.6. E-Tongue and E-Nose Analysis of Yogurt
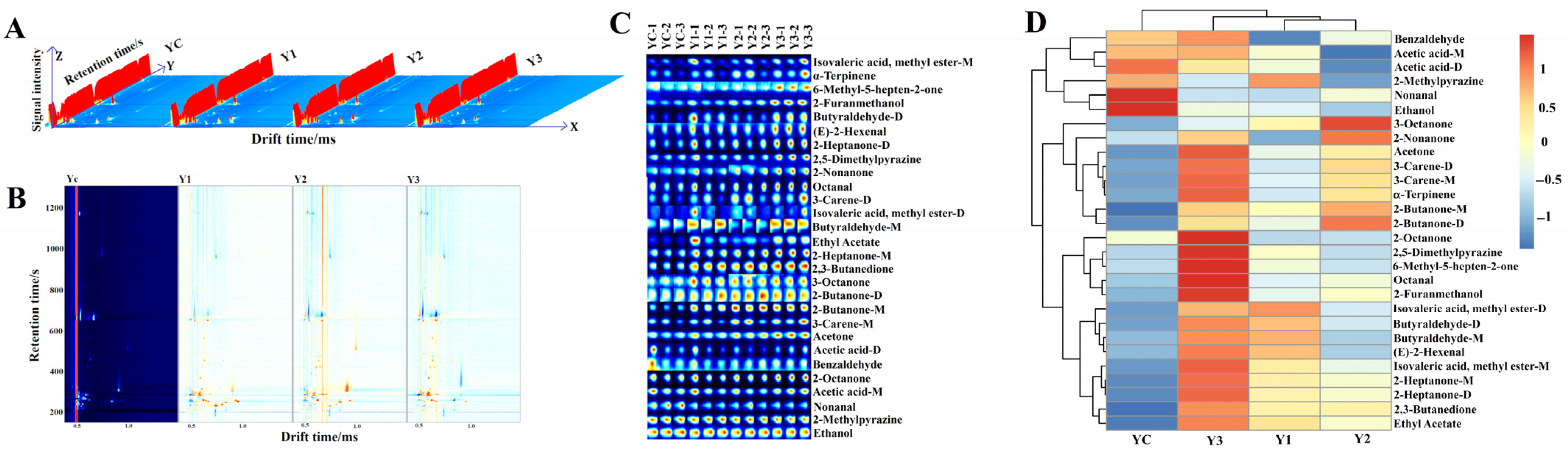
3.7. Volatile Aroma Compound Analysis of Yogurt (GC-IMS)
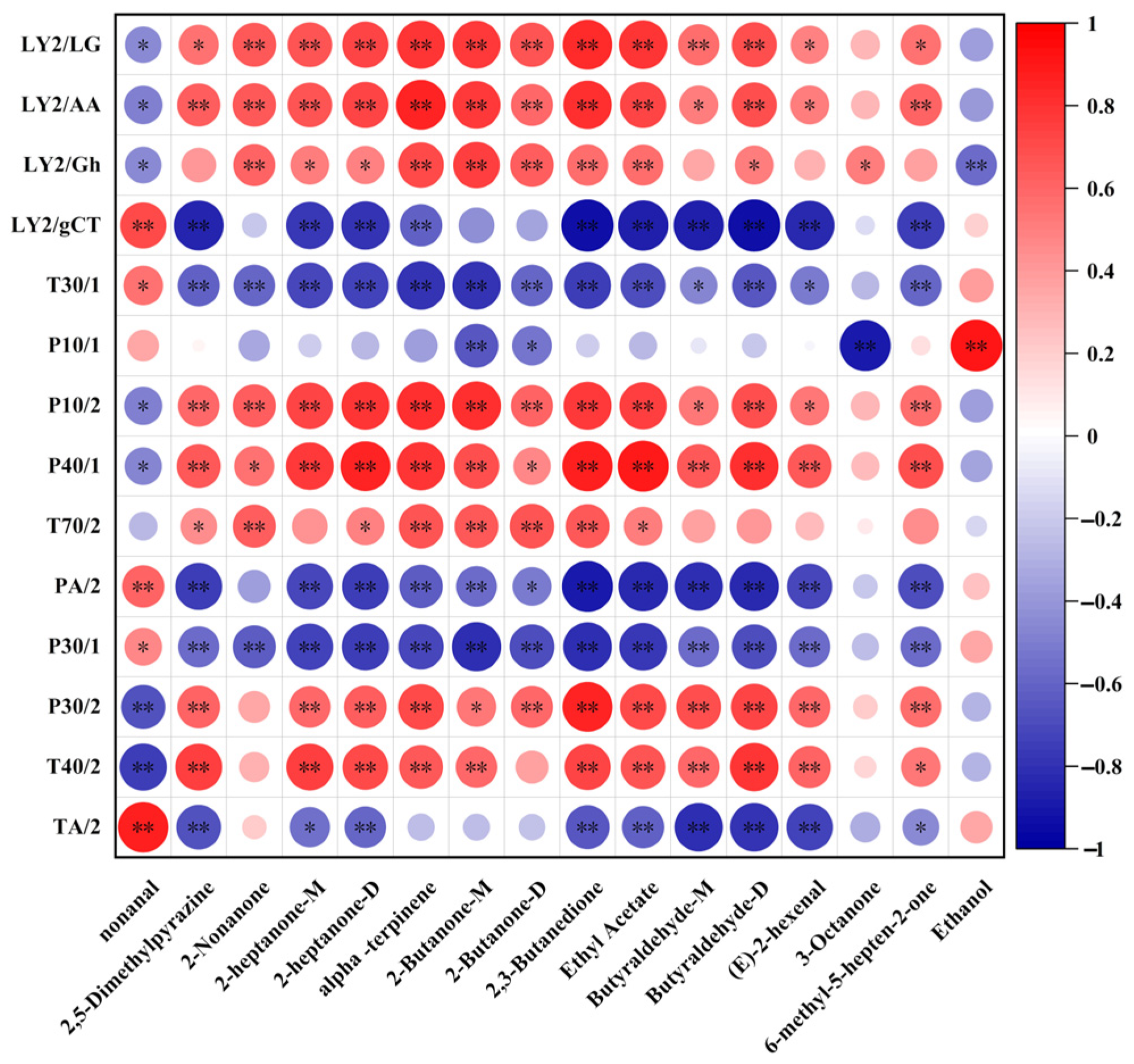
3.8. Correlation Between E-Nose and GC-IMS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, T.; Tu, M.; Du, Q.; Ling, N.; Wu, J.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Effects of Semen Ziziphi Spinosae Extract and Binary Probiotics Co-Fermentation on the Quality of Yogurt and Their Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Food Chem.-X 2024, 21, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoli, R.; Biver, E. Role of Fermented Dairy Products in the Health Benefits of a Mediterranean Diet. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, Y.; Kwon, K.H.; Jung, Y.J. Probiotic Functions in Fermented Foods: Anti-Viral, Immunomodulatory, and Anti-Cancer Benefits. Foods 2024, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.; Drunkler, D.A.; Colla, E. Probiotic Functional Yogurt: Challenges and Opportunities. Fermentation 2024, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J. Macrophage Polarization Induced by Probiotic Bacteria: A Concise Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Amrutha, R.; Ahire, J.J.; Taneja, N.K. Techno-Functional Assessment of Riboflavin-Enriched Yogurt-Based Fermented Milk Prepared by Supplementing Riboflavin-Producing Probiotic Strains of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Tuo, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Gu, Q.; et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZFM55 Improves Texture and Flavor of Yogurt, Increases Beneficial Metabolites, and the Co-Fermented Yogurt Promotes Human Gut Microbiota Health. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 198, 115929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chi, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Liu, L.; Li, A. Effects of Lactobacillus fermentum HY01 on the Quality Characteristics and Storage Stability of Yak Yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, V.; Chieffi, D.; Fanelli, F.; Montemurro, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Franz, C.M.A.P. The Weissella and Periweissella Genera: Up-to-Date Taxonomy, Ecology, Safety, Biotechnological, and Probiotic Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1289937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.K.; Devi, P.B.; Reddy, G.B.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Kavitake, D.; Shetty, P.H. Biosynthesis, Classification, Properties, and Applications of Weissella Bacteriocins. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1406904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Qin, S.; Shen, Y. Probiotic Potential of Weissella Strains Isolated from Horse Feces. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Dong, B.; Zhao, G. Effects of New Fermentation Strains: Weissella confusa GTA22 and Weissella koreensis QAY6 on the Quality of Dough and Steamed Bread. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammouri, A.; Ziadi, M.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Fguiri, I.; Sbissi, I.; Hammadi, M.; Khorchani, T. Characterization of Novel Exopolysaccharides from Weissella cibaria and Lactococcus lactis Strains and Their Potential Application as Bio-Hydrocolloid Agents in Emulsion Stability. Fermentation 2024, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Lei, D.; Xiong, J.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yao, J. Exploring the Mechanism of Weissella cibaria Cooperating with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum to Improve Volatile Flavor of Sichuan Pickle Using Dialysis Membranes. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Shi, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Du, L.; Tu, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; et al. Characterization of the Effects of Binary Probiotics and Wolfberry Dietary Fiber on the Quality of Yogurt. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Helmy, W.A.; Ibrahim, O.A. Evaluation of Lupine Seeds (Lupinus albus L.) Neutral Extract as a Texture Improver in Low-Fat Yogurt Production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Dai, M.; Zhang, S. Biofunctional Attributes and Storage Study of Milk Fermented by Enterococcus italicus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 423, 110844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shori, A.B. Proteolytic Activity, Antioxidant, and α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity of Yogurt Enriched with Coriander and Cumin Seeds. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 109912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Kong, B.; Yin, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q. Characterisation of Flavour Profile of Beef Jerky Inoculated with Different Autochthonous Lactic Acid Bacteria Using Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Meat Sci. 2022, 183, 108658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ben, A.; Qi, J. A Novel Strategy for Discriminating Different Cultivation and Screening Odor and Taste Flavor Compounds in Xinhui Tangerine Peel Using E-Nose, E-Tongue, and Chemometrics. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Guo, S.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Comparison of Volatile Metabolic Profiles in Fermented Milk of Streptococcus thermophilus during the Postripening Period at Different Incubation Temperatures. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Yang, S.-M.; Kim, H.-Y. Weissella and the Two Janus Faces of the Genus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Mi, T.; Ma, S.; Yi, X.; Huang, P.; Huang, P.; Wu, C. Insight into the Autochthonous Lactic Acid Bacteria as Starter Culture for Improving the Quality of Sichuan Radish Paocai: Changes in Microbial Diversity and Metabolic Profiles. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 425, 110877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, F.; Huo, Y.; Gao, W.; Dai, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, S. Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Characterization of Yogurt Fermented by Weissella confusa SW1 and Traditional Starters. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 201, 116229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Whon, T.W.; Roh, S.W.; Jeon, C.O. Unraveling Microbial Fermentation Features in Kimchi: From Classical to Meta-Omics Approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7731–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.H.; Liu, F.; Luo, S.Z.; Luo, J. Pomegranate Juice Powder as Sugar Replacer Enhanced Quality and Function of Set Yogurts: Structure, Rheological Property, Antioxidant Activity and in Vitro Bioaccessibility. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 115, 108479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Overview of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Weissella Genus—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, L.E.E.; Chaurin, V.; Auty, M.A.E.; Fenelon, M.A.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Use of Lactobacillus mucosae DPC 6426, an Exopolysaccharide-Producing Strain, Positively Influences the Techno-Functional Properties of Yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 40, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lai, T.; Yao, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z. Interaction of the Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 with Casein and Bioactivities of the Polymer Complex. Foods 2021, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payens, T.A.J. Association of Caseins and Their Possible Relation to Structure of the Casein Micelle1. J. Dairy Sci. 1966, 49, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cheng, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, J.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Guan, J. Chinese Traditional Pear Paste: Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities and Quality Evaluation. Foods 2023, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Exopolysaccharides of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Structure, Bioactivity and Associations: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simionescu, N.; Petrovici, A.-R. Enhancing the Antioxidant Potential of Weissella confusa PP29 Probiotic Media through Incorporation of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Anthocyanin Extract. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Heng, X.; Chu, W. Weissella confusa CGMCC 19,308 Strain Protects Against Oxidative Stress, Increases Lifespan, and Bacterial Disease Resistance in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, M.; Ji, X.; Chang, J.; Deng, Z.; Meng, G. Recognition Algorithms in E-Nose: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 20460–20472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; Bin, X.; Song, G.; Du, R. Structural Characterization and Biological Properties Analysis of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Weisella cibaria HDL-4. Polymers 2024, 16, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bai, M.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, Z. The Intricate Symbiotic Relationship between Lactic Acid Bacterial Starters in the Milk Fermentation Ecosystem. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 728–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H. Volatile Flavor Compounds in Yogurt: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, W.; Cai, H.; Guo, S.; Sun, Z. Effect of Different Isolation Sources of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis on Volatile Metabolites in Fermented Milk. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Barrientos, L.M.; Garcia, H.S.; Reyes-Díaz, R.; Estrada-Montoya, M.C.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B. Cooperation between Lactococcus lactis NRRL B-50571 and NRRL B-50572 for Aroma Formation in Fermented Milk. Foods 2019, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.; Kosma, I.; Badeka, A.V.; Kontominas, M.G. Profile of Volatile Compounds in Dessert Yogurts Prepared from Cow and Goat Milk, Using Different Starter Cultures and Probiotics. Foods 2021, 10, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, A.; Germond, J.E.; Baumgartner, M.; Chaintreau, A. Aroma Comparisons of Traditional and Mild Yogurts: Headspace Gas Chromatography Quantification of Volatiles and Origin of Alpha-Diketones. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Huang, N.; Yao, W.; Yu, H.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, C. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of the Flavor Production Mechanism in Yogurt by Traditional Starter Strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Landaverde, P.A.; Velazquez, G.; Torres, J.A.; Qian, M.C. Quantitative Determination of Thermally Derived Off-Flavor Compounds in Milk Using Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3764–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Different Proportional Combinations |
|---|---|
| YC | L. bulgaricus G119: S. thermophilus Q019 is 1:1 |
| Y1 | YC + W. cibaria G232 (3%) |
| Y2 | YC + W. cibaria G232 (5%) |
| Y3 | YC + W. cibaria G232 (7%) |
| Sensors | Performance Description |
|---|---|
| LY2/LG | Sensitive to oxidizing gas |
| LY2/G | Sensitive to ammonia, carbon monoxide |
| LY2/AA | Sensitive to ethanol |
| LY2/Gh | Sensitive to ammonia/organic amines |
| LY2/gCT1 | Sensitive to hydrogen sulfide |
| LY2/gCT | Sensitive to propane/butane |
| T30/1 | Sensitive to organic solvents |
| P10/1 | Sensitive to hydrocarbons |
| P10/2 | Sensitive to methane |
| P40/1 | Sensitive to fluorine |
| T70/2 | Sensitive to aromatic compounds |
| PA/2 | Sensitive to ethanol, ammonia/organic amines |
| P30/1 | Sensitive to polar compounds (ethanol) |
| P40/2 | Sensitive to heteroatom/chloride/aldehydes |
| P30/2 | Sensitive to alcohol |
| T40/2 | Sensitive to aldehydes |
| T40/1 | Sensitive to chlorinated compounds |
| TA/2 | Sensitive to air quality |
| Parameters | YC | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmness (g) | 212.85 ± 4.87 c | 236.16 ± 7.31 b | 259.12 ± 4.44 a | 245.91 ± 3.82 b |
| Consistency (g·s) | 936.02 ± 15.26 d | 1778.28 ± 13.84 b | 1986.75 ± 18.13 a | 1324.94 ± 8.16 c |
| Cohesiveness (g) | −56.06 ± 3.94 b | −46.95 ± 4.73 ab | −40.41 ± 4.82 a | −50.18 ± 7.22 ab |
| Volatile Flavor Compounds | CAS Registry Number | Molecule Formula | YC | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid-M | C64197 | C2H4O2 | 4.25 × 103 ± 4.79 × 102 a | 3.96 × 103 ± 6.94 × 102 a | 3.50 × 103 ± 4.40 × 102 a | 4.27 × 103 ± 2.43 × 102 a |
| Acetic acid-D | C64197 | C2H4O2 | 3.85 × 102 ± 1.04 × 102 a | 3.12 × 102 ± 1.06 × 102 a | 2.50 × 102 ± 43.02 a | 3.44 × 102 ± 40.66 a |
| Nonanal | C124196 | C9H18O | 3.81 × 103 ± 2.34 × 102 a | 2.54 × 103 ± 1.81 × 102 b | 2.84 × 103 ± 3.20 × 102 b | 2.58 × 103 ± 49.62 b |
| 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine | C123320 | C6H8N2 | 9.17 × 102 ± 51.61 b | 1.03 × 103 ± 1.32 × 102 b | 9.24 × 102 ± 66.22 b | 1.29 × 103 ± 58.32 a |
| 2-Octanone | C111137 | C8H16O | 9.25 × 103 ± 9.17 × 102 a | 8.89 × 103 ± 1.56 × 102 a | 8.92 × 103 ± 7.39 × 102 a | 1.04 × 104 ± 3.02 × 102 a |
| 2-Methylpyrazine | C109080 | C5H6N2 | 8.74 × 103 ± 3.31 × 102 a | 8.78 × 103 ± 3.46 × 102 a | 8.12 × 103 ± 2.91 × 102 a | 8.31 × 103 ± 47.33 a |
| Octanal | C124130 | C8H16O | 8.51 × 102 ± 1.33 × 102 a | 8.29 × 102 ± 1.37 × 102 a | 8.04 × 102 ± 95.03 a | 8.63 × 102 ± 27.26 a |
| 2-Nonanone | C821556 | C9H18O | 1.11 × 103 ± 36.43 ab | 1.05 × 103 ± 98.29 b | 1.33 × 103 ± 1.26 × 102 a | 1.27 × 103 ± 20.43 ab |
| Acetone | C67641 | C3H6O | 4.01 × 102 ± 20.15 c | 4.54 × 102 ± 37.53 bc | 4.90 × 102 ± 22.22 b | 5.48 × 102 ± 15.08 a |
| 2-Heptanone-M | C110430 | C7H14O | 1.16 × 103 ± 98.33 b | 1.38 × 103 ± × 1.41 × 102 ab | 1.33 × 103 ± 1.22 × 102 ab | 1.51 × 103 ± 20.52 a |
| 2-Heptanone-D | C110430 | C7H14O | 2.75 × 102 ± 34.11 b | 3.63 × 102 ± 59.44 ab | 3.34 × 102 ± 38.18 ab | 4.21 × 102 ± 9.48 a |
| 3-Carene-M | C13466789 | C10H16 | 5.09 × 102 ± 1.06 × 102 a | 5.94 × 102 ± 1.74 × 102 a | 7.13 × 102 ± 1.64 × 102 a | 8.08 × 102 ± 1.44 × 102 a |
| 3-Carene-D | C13466789 | C10H16 | 1.81 × 102 ± 43.73 a | 2.18 × 102 ± 68.89 a | 2.88 × 102 ± 90.04 a | 3.24 × 102 ± 82.34 a |
| α-Terpinene | C99865 | C10H16 | 1.40 × 102 ± 19.07 b | 1.67 × 102 ± 46.86 ab | 2.16 × 103 ± 50.74 ab | 2.56 × 102 ± 53.92 a |
| 2-Butanone-M | C78933 | C4H8O | 9.56 × 102 ± 91.59 c | 1.79 × 103 ± 1.76 × 102 b | 2.21 × 103 ± 1.45 × 102 a | 2.09 × 103 ± 24.04 a |
| 2-Butanone-D | C78933 | C4H8O | 5.21 × 102 ± 21.61 c | 5.52 × 102 ± 51.26 b | 5.97 × 102 ± 26.89 a | 5.78 × 102 ± 11.93 a |
| Ethanol | C64175 | C2H6O | 2.79 × 103 ± 13.18 a | 2.47 × 103 ± 7.23 b | 2.41 × 103 ± 28.16 c | 2.51 × 103 ± 14.21 b |
| 2,3-Butanedione | C431038 | C4H6O2 | 1.98 × 103 ± 80.30 c | 3.50 × 103 ± 1.18 × 102 b | 3.50 × 103 ± 3.04 × 102 b | 4.20 × 103 ± 98.20 a |
| Ethyl Acetate | C141786 | C4H8O2 | 1.00 × 102 ± 6.51 b | 2.50 × 102 ± 85.55 a | 2.10 × 102 ± 36.09 a | 3.02 × 102 ± 7.57 a |
| Butyraldehyde-M | C123728 | C4H8O | 2.10 × 102 ± 11.29 b | 3.60 × 102 ± 39.97 a | 2.24 × 102 ± 16.91 b | 3.78 × 102 ± 7.81 a |
| Butyraldehyde-D | C123728 | C4H8O | 81.01 ± 7.85 b | 2.30 × 102 ± 47.81 a | 1.31 × 102 ± 5.61 b | 2.57 × 102 ± 5.51 a |
| 2-Furanmethanol | C98000 | C5H6O2 | 1.53 × 103 ± 1.09 × 102 c | 1.74 × 103 ± 2.23 × 102 bc | 1.86 × 103 ± 91.15 b | 2.38 × 103 ± 6.59 a |
| Benzaldehyde | C100527 | C7H6O | 2.21 × 102 ± 58.58 a | 1.94 × 102 ± 16.22 a | 2.09 × 102 ± 10.15 a | 2.26 × 102 ± 8.72 a |
| (E)-2-Hexenal | C6728263 | C6H10O | 2.04 × 102 ± 11.26 b | 2.38 × 102 ± 17.68 a | 2.08 × 103 ± 10.04 b | 2.45 × 102 ± 5.51 a |
| Isovaleric acid, methyl ester-M | C556241 | C6H12O2 | 1.80 × 102 ± 23.57 a | 2.68 × 102 ± 97.63 a | 2.31 × 102 ± 48.19 a | 3.21 × 102 ± 61.19 a |
| Isovaleric acid, methyl ester-D | C556241 | C6H12O2 | 70.98 ± 3.09 a | 90.02 ± 24.14 a | 76.94 × 103 ± 7.79 a | 89.10 ± 12.06 a |
| 3-Octanone | C106683 | C8H16O | 1.36 × 102 ± 11.26 ab | 1.51 × 102 ± 3.68 ab | 1.67 × 102 ± 17.14 a | 1.44 × 102 ± 0.66 ab |
| 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one | C110930 | C8H14O | 2.58 × 102 ± 12.64 b | 2.71 × 102 ± 20.57 b | 2.60 × 102 ± 4.46 b | 3.16 × 103 ± 18.04 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tang, J. Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities, and Aromatic Profile of Yogurt Co-Fermented by Weissella cibaria G232 with Traditional Starters. Foods 2025, 14, 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091607
Huang Q, Ye H, Yang Y, Zhu C, Tang J. Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities, and Aromatic Profile of Yogurt Co-Fermented by Weissella cibaria G232 with Traditional Starters. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091607
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qian, Haixiao Ye, Yangyang Yang, Chenglin Zhu, and Junni Tang. 2025. "Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities, and Aromatic Profile of Yogurt Co-Fermented by Weissella cibaria G232 with Traditional Starters" Foods 14, no. 9: 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091607
APA StyleHuang, Q., Ye, H., Yang, Y., Zhu, C., & Tang, J. (2025). Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities, and Aromatic Profile of Yogurt Co-Fermented by Weissella cibaria G232 with Traditional Starters. Foods, 14(9), 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091607





