Insights into the Stability and Lipid Oxidation of Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions: Roles of the Concentration of the Emulsifier, Aqueous Phase, and NaCl
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of W/O Emulsions
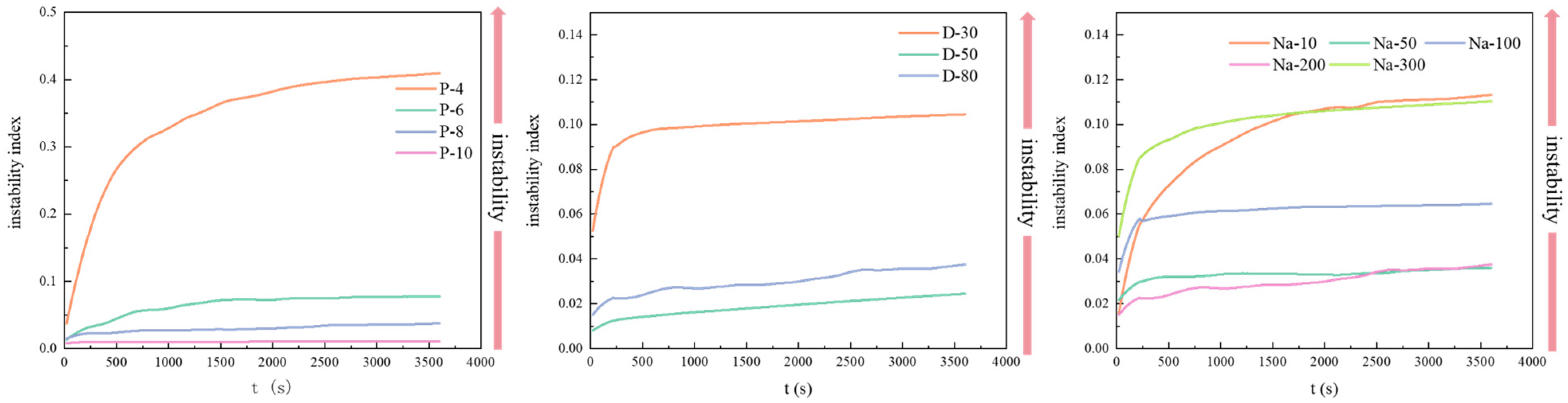
2.3. Physical Stability and Physical Instability Index (PII)
2.4. Measurement of Lipid Oxidation Parameters
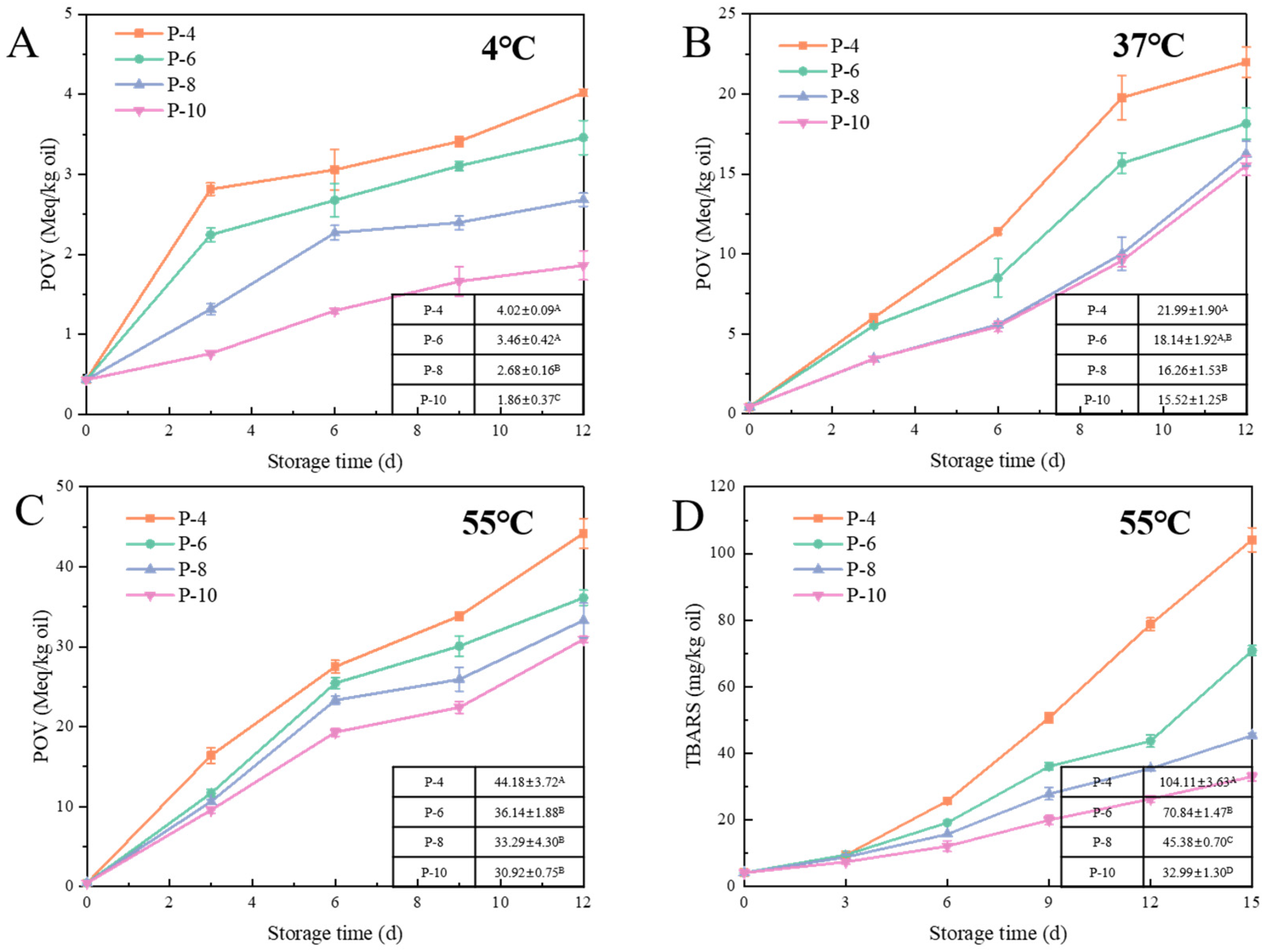
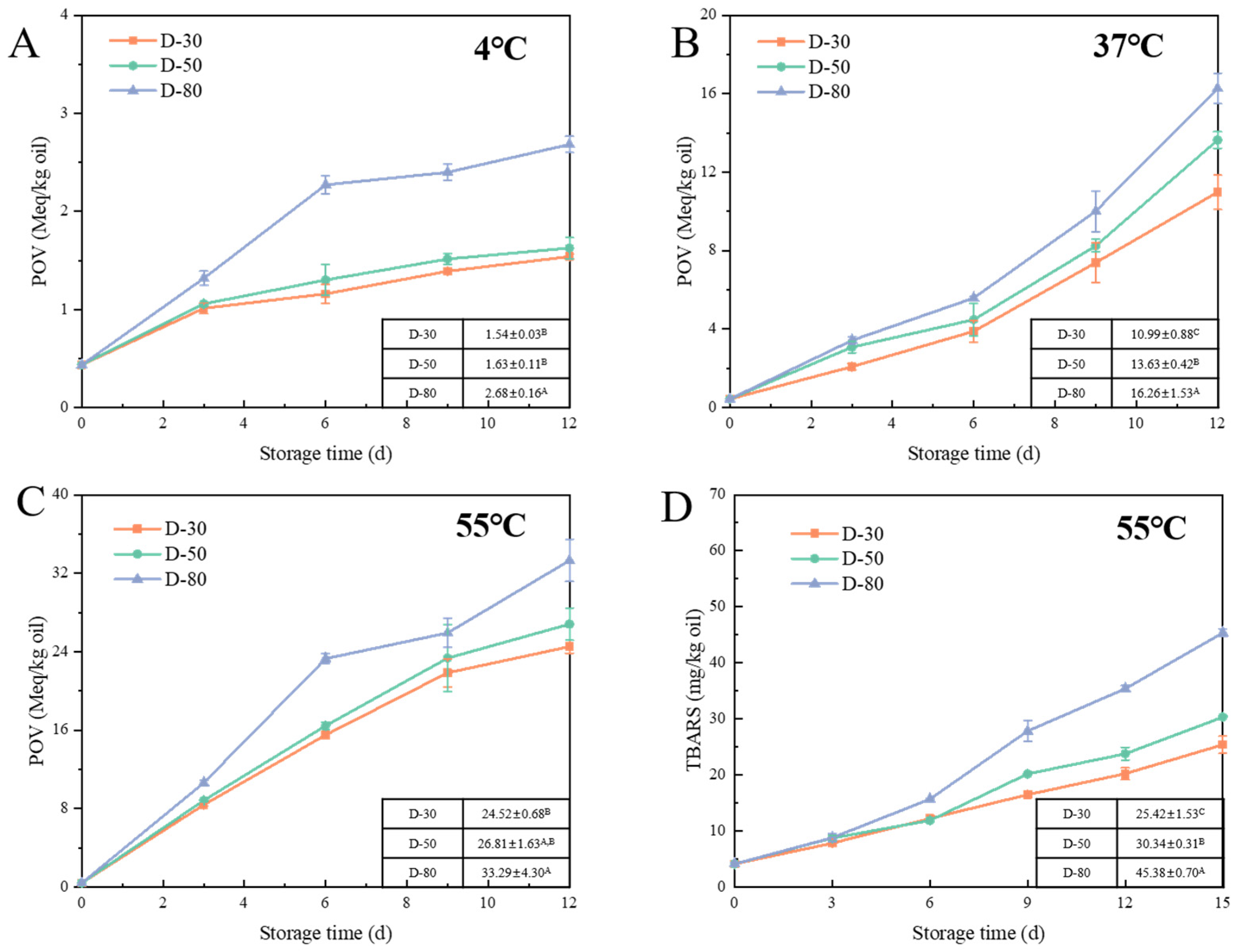
2.4.1. Peroxide Value (POV)
2.4.2. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactants (TBARS)
2.5. Oxidation Kinetic Model
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Stability and Storage Stability of W/O HIPEs
3.2. Lipid Oxidation
3.2.1. Effect of Exogenous Factors on Lipid Oxidation of W/O Emulsions
3.2.2. Effect of Emulsifier on Lipid Oxidation of W/O HIPEs
3.2.3. Effect of Aqueous Phase Content on Lipid Oxidation of W/O HIPEs
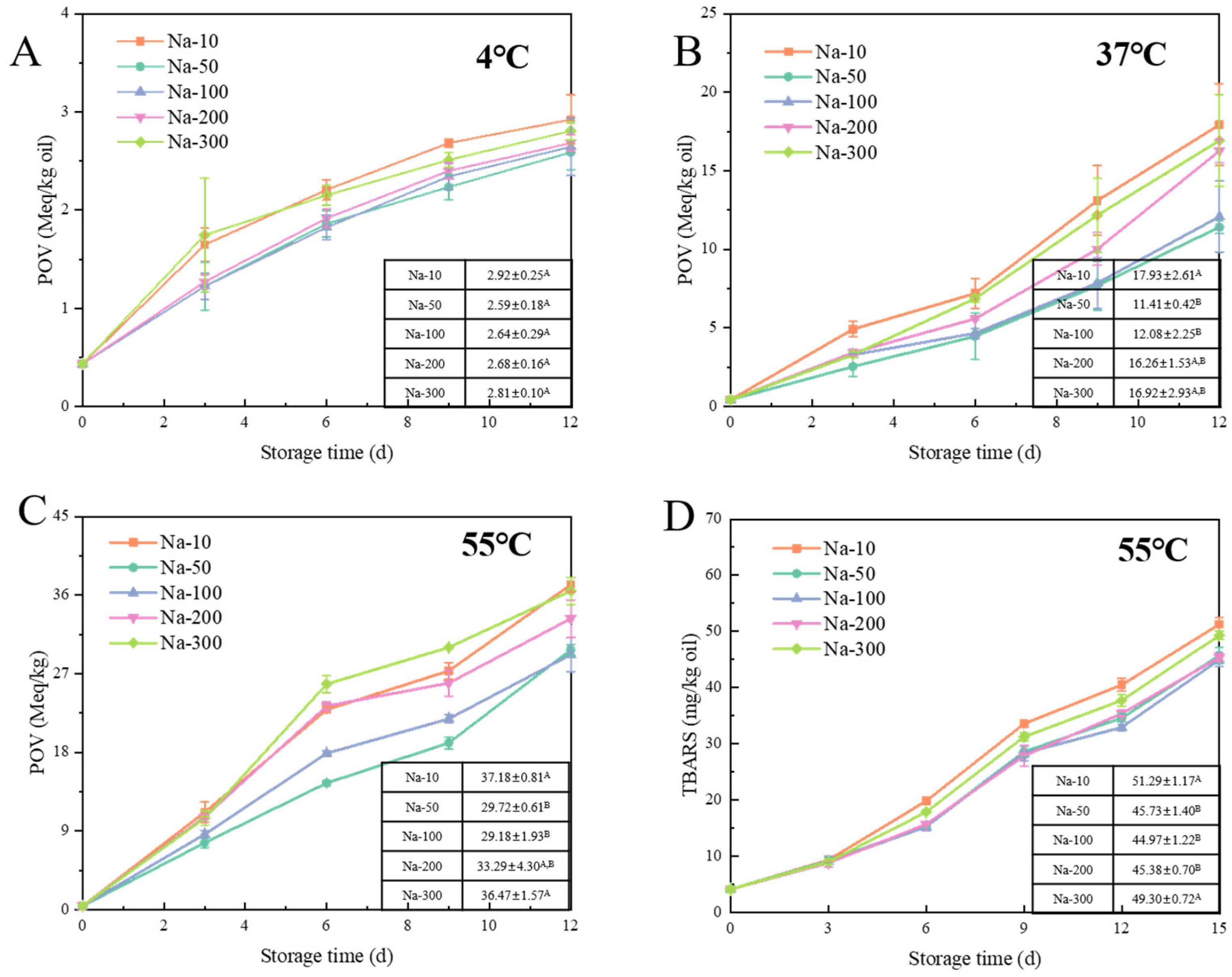
3.2.4. Effect of NaCl on Lipid Oxidation of W/O HIPEs
3.3. Oxidation Kinetic Model of W/O Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hennebelle, M.; Villeneuve, P.; Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; van Duynhoven, J.; Meynier, A.; Yesiltas, B.; Jacobsen, C.; Berton-Carabin, C. Lipid oxidation in emulsions: New insights from the past two decades. Prog. Lipid Res. 2024, 94, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, N.; Ghavami, M.; Rashidi, L.; Gharachorloo, M.; Nateghi, L. Effects of adding green tea extract on the oxidative stability and shelf life of sunflower oil during storage. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Ropers, M.-H.; Genot, C. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 945–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions: Impact of molecular environment on chemical reactions in heterogeneous food systems. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.F.; Pignitter, M. Mechanisms of lipid oxidation in water-in-oil emulsions and oxidomics-guided discovery of targeted protective approaches. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 2678–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, S.; Fan, L.; Li, J. All-natural gel-in-gel water-in-oil high internal phase emulsions featuring biphasic network stabilization and application of 3D printing. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 678, 132529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, J.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Lim, W.S. Polyglycerol polyricinoleate stabilised water-in-oil emulsion: Structural characteristics and functional performance. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoia, L.; Wagner, J.; Marquez, A. Margarine-Like Emulsions Prepared with Coconut and Palm Oils: Analysis of Microstructure and Freeze–Thaw Stability by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Li, B.; Wan, L.T.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Fabrication and characterization of fat crystal-stabilized W/O high internal phase Pickering emulsions (HIPPEs) as a low-fat alternative margarine. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 115798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Tan, C.; Ravanfar, R.; Abbaspourrad, A. Ultrastable Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions Featuring Interfacial and Biphasic Network Stabilization. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26433–26441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Mao, L.; Yuan, F. Roles of NaCl in Enhancing the Stability of Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, O.M.; Manan, S.; Shahzad, A.; Ul-Islam, M.; Ullah, M.W.; Yang, G. Biobased materials for active food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.R.; Williams, P.A.; Sharif, M.K.; Abbas, S.; Majeed, H.; Masamba, K.G.; Safdar, W.; Zhong, F. Current progress in the utilization of native and modified legume proteins as emulsifiers and encapsulants—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.Q.; Shen, P.Y.; Gao, Z.L.; Yi, J.H.; Chen, B.C. New Insights into the Impact of Sodium Chloride on the Lipid Oxidation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4321–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguerre, M.; Bayrasy, C.; Panya, A.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J.; Lecomte, J.; Decker, E.A.; Villeneuve, P. What Makes Good Antioxidants in Lipid-Based Systems? The Next Theories Beyond the Polar Paradox. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Li, J. High internal phase emulsion gels stabilized by phosphorylated perilla protein isolate for protecting hydrophobic nutrients: Adjusting emulsion performance by incorporating chitosan-protocatechuic acid conjugate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzun-Cojocaru, T.; Cayot, P.; Loupiac, C.; Cases, E. Effect of iron chelates on oil-water interface, stabilized by milk proteins: The role of phosphate groups and pH. Prediction of iron transfer from aqueous phase toward fat globule surface by changes of interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Ning, J.Q.; Zhu, Z.B.; Cui, L.Q.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Impact of interfacial composition on co-oxidation of lipids and proteins in oil-in-water emulsions: Competitive displacement of casein by surfactants. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn-Barnes, H.T.; Akoh, C.C. Copper-catalyzed oxidation of a structured lipid-based emulsion containing α-tocopherol and citric acid: Influence of pH and NaCl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6851–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.Y.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Evidence of iron association with emulsion droplets and its impact on lipid oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 5072–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, H.X.; McClements, D.J.; Zeng, H.Y.; Ma, L.; Zou, L.Q.; Miao, J.Y.; Wu, X.L.; Tan, J.N.; Liang, R.H.; et al. Impact of polysaccharide mixtures on the formation, stability and EGCG loading of water-in-oil high internal phase emulsions. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.N.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, J.J.; Gao, Y.X.; Mao, L.K. Enhanced freeze-thawing stability of water-in-oil Pickering emulsions stabilized by ethylcellulose nanoparticles and oleogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 312, 120814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Gao, Y.X.; Mao, L.K. Surfactant addition to modify the structures of ethylcellulose oleogels for higher solubility and stability of curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raviadaran, R.; Ng, M.H.; Manickam, S.; Chandran, D. Ultrasound-assisted water-in-palm oil nano-emulsion: Influence of polyglycerol polyricinoleate and NaCl on its stability. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 52, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.C.; Damitz, R.; Chauhan, A. Relating emulsion stability to interfacial properties for pharmaceutical emulsions stabilized by Pluronic F68 surfactant. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cui, J.; Ma, L.; Fan, G.; Deng, J. Study on stability and characterization of high internal phase water-in-oil compound collector emulsion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 703, 135315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, M.Y.; Yurtov, E.V. Effect of ionic strength of dispersed phase on Ostwald ripening in water-in-oil emulsions. Colloid. J. 2003, 65, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, D. Investigation into the Physicochemical Stability and Rheological Properties of β-Carotene Emulsion Stabilized by Soybean Soluble Polysaccharides and Chitosan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8604–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoosh, R. Critical kinetic parameters and rate constants representing lipid peroxidation as affected by temperature. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Estrada, P.; School, E.; van der Goot, A.J.; Berton-Carabin, C.C. Double emulsions for iron encapsulation: Is a high concentration of lipophilic emulsifier ideal for physical and chemical stability? J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4540–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Zhu, Z.B.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Influence of Aqueous Phase Emulsifiers on Lipid Oxidation in Water-in-Walnut Oil Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuchi, C.D.; Hernandez, P.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Ability of lipid hydroperoxides to partition into surfactant micelles and alter lipid oxidation rates in emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5445–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysan, U.; Yildirim, A.; Takma, D.K.; Koç, M. Physical and chemical stability of sweet walnut oil emulsion: Influence of homogenization conditions and stabilizer ratio. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S. Effects of protein concentration and oil-phase volume fraction on the stability and rheology of menhaden oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein isolate with xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, M.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I.T. The effect of interfacial microstructure on the lipid oxidation stability of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Effects of interface generation, droplet size and antioxidant partitioning on the oxidation rate and oxidative stability of water–in–oil emulsions: A comparison of coarse emulsions and nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiokias, S.N.; Dimakou, C.P.; Tsaprouni, I.V.; Oreopoulou, V. Effect of compositional factors against the thermal oxidative deterioration of novel food emulsions. Food Biophys. 2006, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampi, A.M.; Yang, Z.; Mustonen, O.; Piironen, V. Potential of faba bean lipase and lipoxygenase to promote formation of volatile lipid oxidation products in food models. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.Q.; Cho, H.T.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y. Effects of salts on oxidative stability of lipids in Tween-20 stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruehwirth, S.; Egger, S.; Kurzbach, D.; Windisch, J.; Jirsa, F.; Flecker, T.; Ressler, M.; Reiner, A.T.; Firat, N.; Pignitter, M. Ingredient-Dependent Extent of Lipid Oxidation in Margarine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, G.; Guo, Q.; Xiao, S.; Peng, Y.; Song, L.; Qiao, M.; et al. Preparation of flaxseed oil nanoemulsion and its effect on oxidation stability of flaxseed oil and prediction of shelf life. Lwt 2025, 217, 117404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, S.; Lucci, P.; Milani, A.; Rovellini, P.; Lagazio, C.; Conte, L.; Nicoli, M.C. Application of accelerated shelf-life test (ASLT) procedure for the estimation of the shelf-life of extra virgin olive oils: A validation study. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Sonnemberg, M.N.; Souza, E.F.; Ventura, M.; Simionatto, E.; Fiorucci, A.R. Investigation of curcumin antioxidant efficiency on oxidation stability of biodiesel from soybean oil and beef tallow, contaminated with metals: Kinetic and storage studies. Fuel 2024, 368, 131520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Hennebelle, M.; van Duynhoven, J.P.M.; Dubbelboer, A.; Boerkamp, V.J.P.; Wierenga, P.A. Mechanistic kinetic modelling of lipid oxidation in vegetable oils to estimate shelf-life. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Progress in the application of lecithins in water-in-oil emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancebo-Campos, V.; Salvador, M.D.; Fregapane, G. Modelling Virgin Olive Oil Potential Shelf-Life from Antioxidants and Lipid Oxidation Progress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
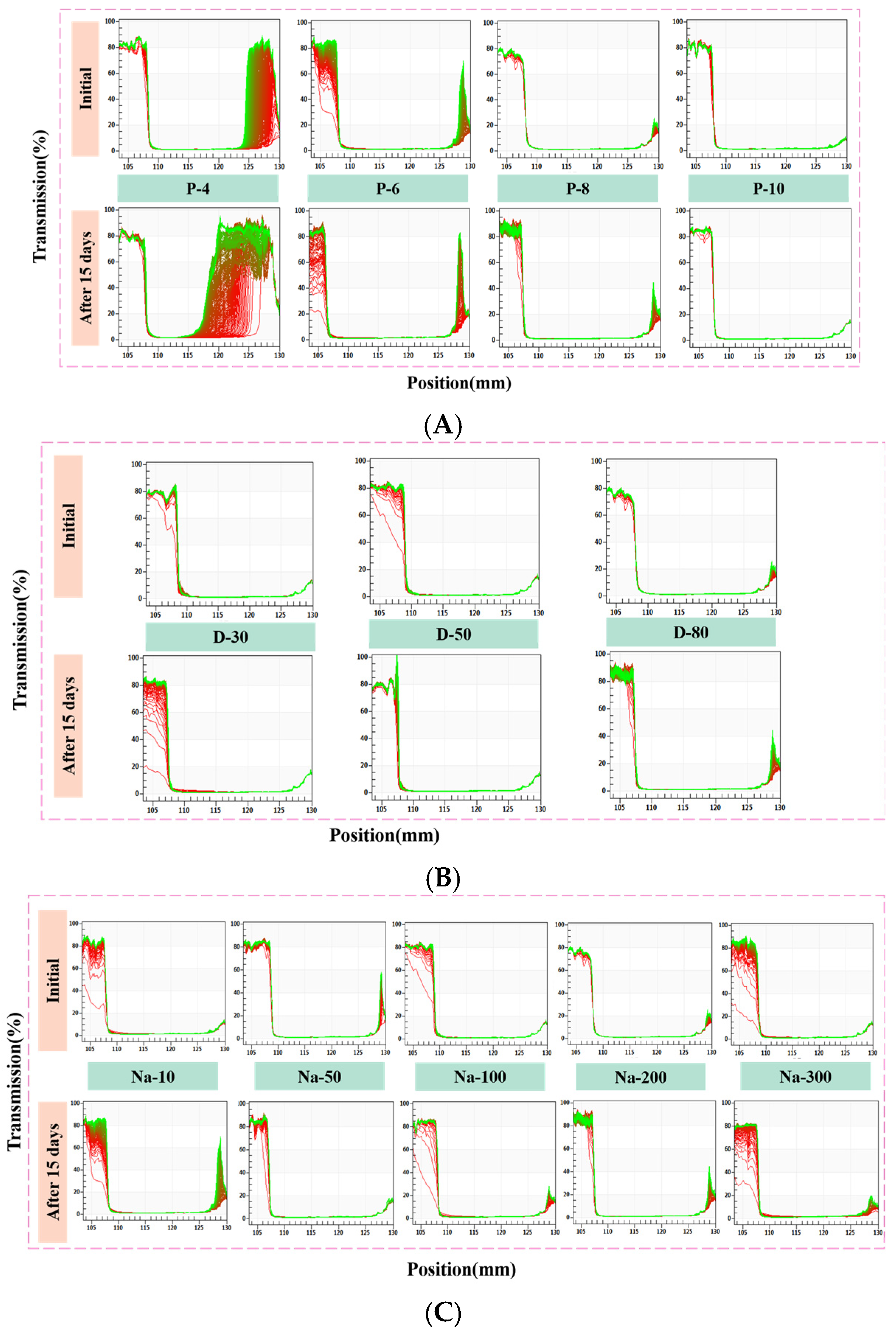
| Sample | PGPR Concentration (wt%) | Aqueous Phase Volume Fraction (v/v) | NaCl Concentration (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-4 | 4 | 80% | 200 |
| P-6 | 6 | ||
| P-8 | 8 | ||
| P-10 | 10 | ||
| D-30 | 8 | 30% | 200 |
| D-50 | 50% | ||
| D-80 | 80% | ||
| Na-10 | 8 | 80% | 10 |
| Na-50 | 50 | ||
| Na-100 | 100 | ||
| Na-200 | 200 | ||
| Na-300 | 300 |
| Sample | 4 °C | 37 °C | 55 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-4 | y = 0.2589x + 1.1937 (R2 = 0.74) | y = 1.8962x + 0.5439 (R2 = 0.97) | y = 3.4974x + 3.3416 (R2 = 0.97) |
| P-6 | y = 0.2303x + 1.0020 (R2 = 0.81) | y = 1.5192x + 0.5383 (R2 = 0.97) | y = 2.9935x + 2.7933 (R2 = 0.95) |
| P-8 | y = 0.1859x + 0.7051 (R2 = 0.87) | y = 1.2748x−0.5049 (R2 = 0.94) | y = 2.7001x + 2.5147 (R2 = 0.94) |
| P-10 | y = 0.1252x + 0.4521 (R2 = 0.97) | y = 1.2102x−0.3769 (R2 = 0.95) | y = 2.4603x + 1.7693 (R2 = 0.97) |
| Sample | 4 °C | 37 °C | 55 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| D-30 | y = 0.0863x + 0.5895 (R2 = 0.89) | y = 0.8799x − 0.3260 (R2 = 0.96) | y = 2.0542x + 1.8182 (R2 = 0.97) |
| D-50 | y = 0.0947x + 0.6184 (R2 = 0.87) | y = 1.0520x − 0.3385 (R2 = 0.93) | y = 2.2422x + 1.7255 (R2 = 0.97) |
| D-80 | y = 0.1859x + 0.7051 (R2 = 0.87) | y = 1.2748x − 0.5049 (R2 = 0.94) | y = 2.7001x + 2.5147 (R2 = 0.94) |
| Sample | 4 °C | 37 °C | 55 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na-10 | y = 0.2003x + 0.7764 (R2 = 0.89) | y = 1.4393x + 0.0797 (R2 = 0.98) | y = 2.9886x + 1.8645 (R2 = 0.98) |
| Na-50 | y = 0.1773x + 0.6046 (R2 = 0.96) | y = 0.9034x − 0.1134 (R2 = 0.97) | y = 2.3337x + 0.2789 (R2 = 0.98) |
| Na-100 | y = 0.1846x + 0.5856 (R2 = 0.97) | y = 0.9292x + 0.0897 (R2 = 0.96) | y = 2.3567x + 0.0897 (R2 = 0.98) |
| Na-200 | y = 0.1859x + 0.7051 (R2 = 0.87) | y = 1.2748x − 0.5049 (R2 = 0.94) | y = 2.7001x + 2.5147 (R2 = 0.94) |
| Na-300 | y = 0.1837x + 1.1456 (R2 = 0.85) | y = 1.3952x − 0.4352 (R2 = 0.98) | y = 3.0530x + 2.3207 (R2 = 0.94) |
| Sample | ln(k) = −Ea/RT + ln(A) | R2 | Ea (KJ/mol) | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-4 | y = −4730.15402x + 15.75783 | 0.98 | 39.33 | 7.02 × 106 |
| P-6 | y = −4628.61652x + 15.25867 | 0.99 | 38.48 | 4.23 × 106 |
| P-8 | y = −4810.96413x + 15.69495 | 0.99 | 40.00 | 6.58 × 106 |
| P-10 | y = −5407.27597x + 17.47865 | 0.98 | 44.96 | 3.93 × 107 |
| D-30 | y = −5716.4043x + 18.20629 | 0.99 | 47.55 | 8.89 × 107 |
| D-50 | y = −5744.46278x + 18.41839 | 0.98 | 47.77 | 1.01 × 108 |
| D-80 | y = −4810.96413x + 15.69495 | 0.99 | 40.00 | 6.58 × 106 |
| Na-10 | y = −4870.84828x + 15.99132 | 0.99 | 40.49 | 8.80 × 106 |
| Na-50 | y = −4538.96615x + 14.61999 | 0.99 | 37.75 | 2.23 × 106 |
| Na-100 | y = −4488.16459x + 14.47879 | 0.99 | 37.31 | 1.95 × 106 |
| Na-200 | y = −4810.96413x + 15.69495 | 0.99 | 40.00 | 6.58 × 106 |
| Na-300 | y = −5055.40355x + 16.56701 | 0.99 | 42.03 | 1.56 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Shang, J.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F.; Mao, L. Insights into the Stability and Lipid Oxidation of Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions: Roles of the Concentration of the Emulsifier, Aqueous Phase, and NaCl. Foods 2025, 14, 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091606
Wei J, Shang J, Gao Y, Yuan F, Mao L. Insights into the Stability and Lipid Oxidation of Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions: Roles of the Concentration of the Emulsifier, Aqueous Phase, and NaCl. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091606
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jiao, Jingwen Shang, Yanxiang Gao, Fang Yuan, and Like Mao. 2025. "Insights into the Stability and Lipid Oxidation of Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions: Roles of the Concentration of the Emulsifier, Aqueous Phase, and NaCl" Foods 14, no. 9: 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091606
APA StyleWei, J., Shang, J., Gao, Y., Yuan, F., & Mao, L. (2025). Insights into the Stability and Lipid Oxidation of Water-in-Oil High Internal Phase Emulsions: Roles of the Concentration of the Emulsifier, Aqueous Phase, and NaCl. Foods, 14(9), 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091606







