Sodium Alginate Modifications: A Critical Review of Current Strategies and Emerging Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Sodium Alginate
3. Physicochemical Properties of Sodium Alginate
3.1. Chemical Structure and Molecular Weight
3.2. Solubility
3.3. Gel Formation Ability
3.4. Biocompatibility
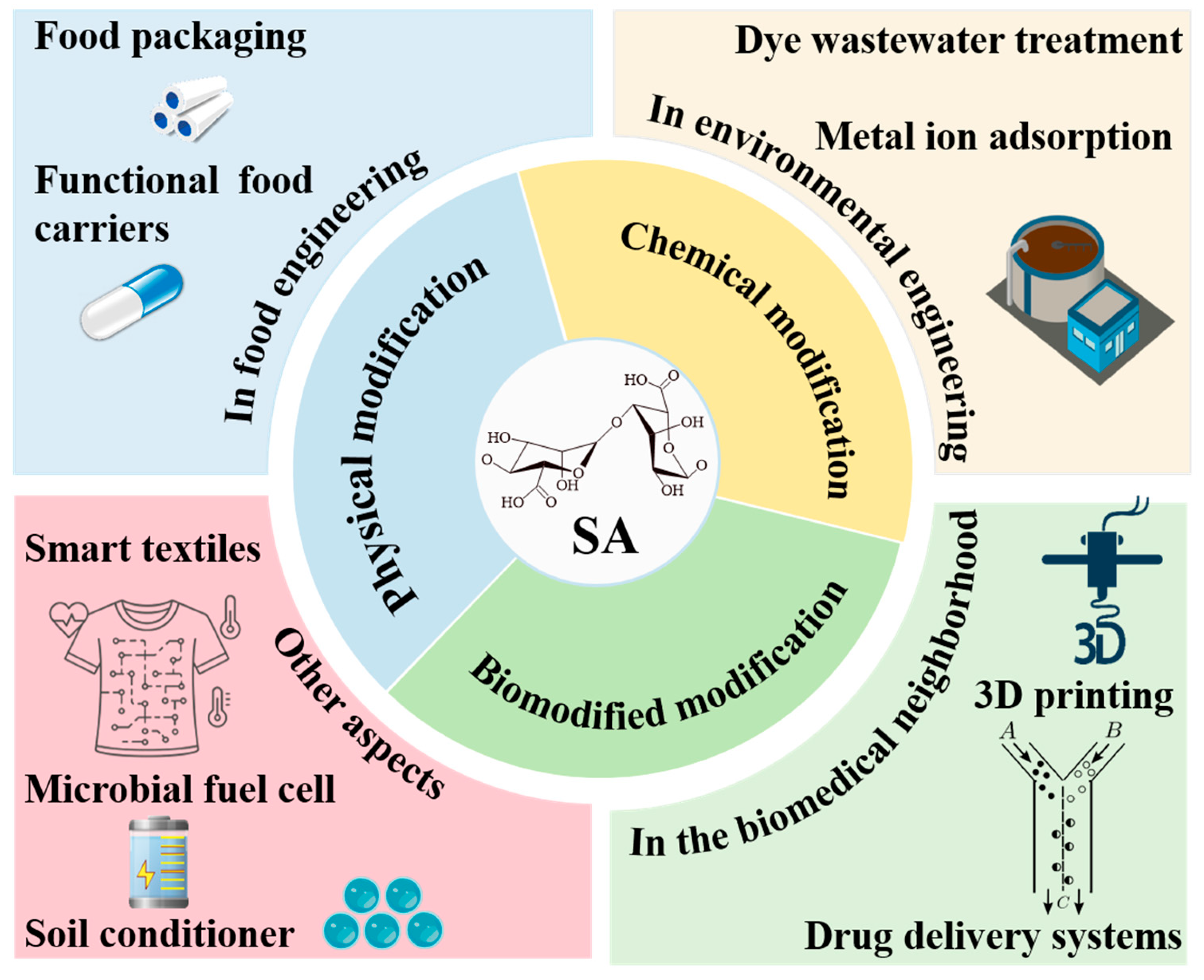
4. Modification Methods of Sodium Alginate
4.1. Chemical Modification
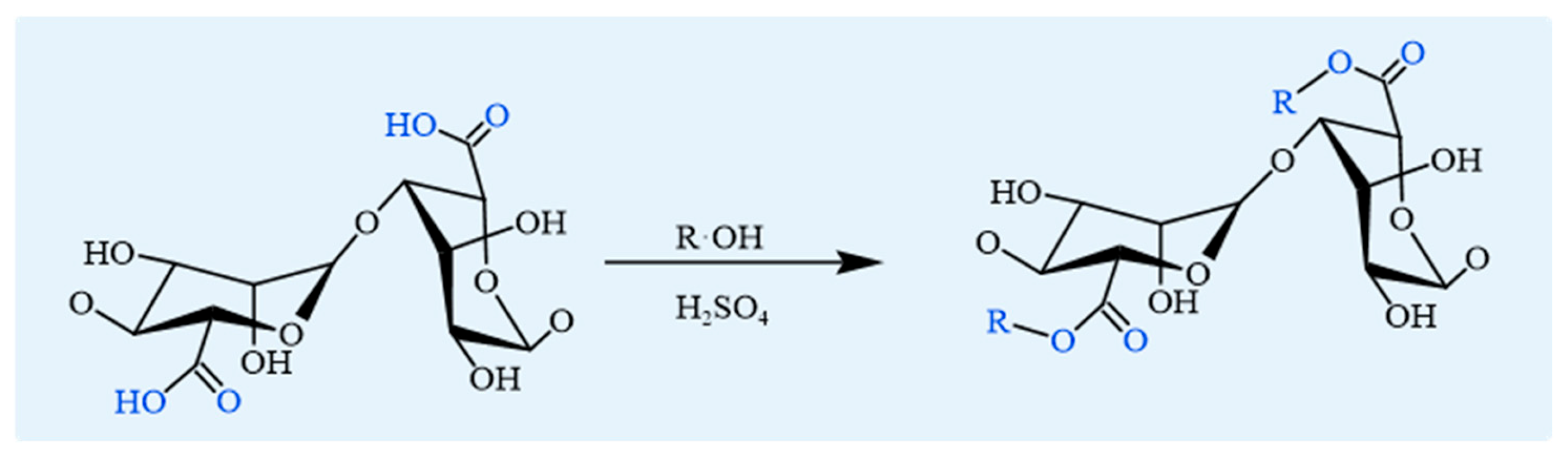
4.1.1. Esterification
4.1.2. Oxidization
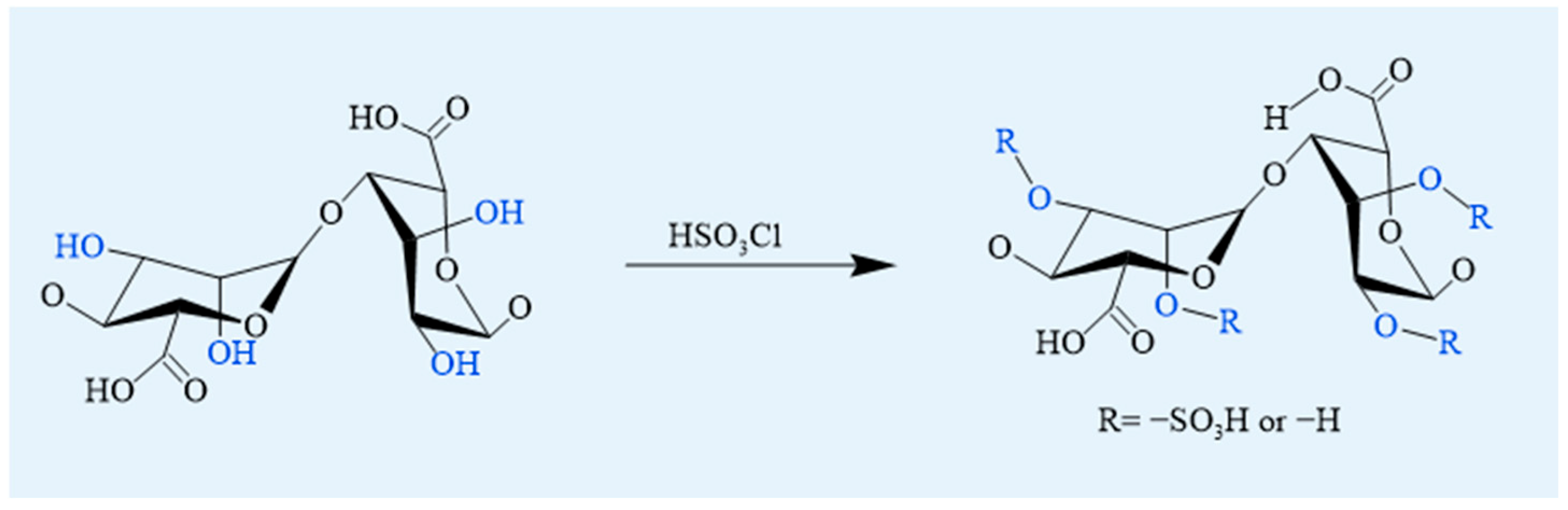
4.1.3. Sulfation
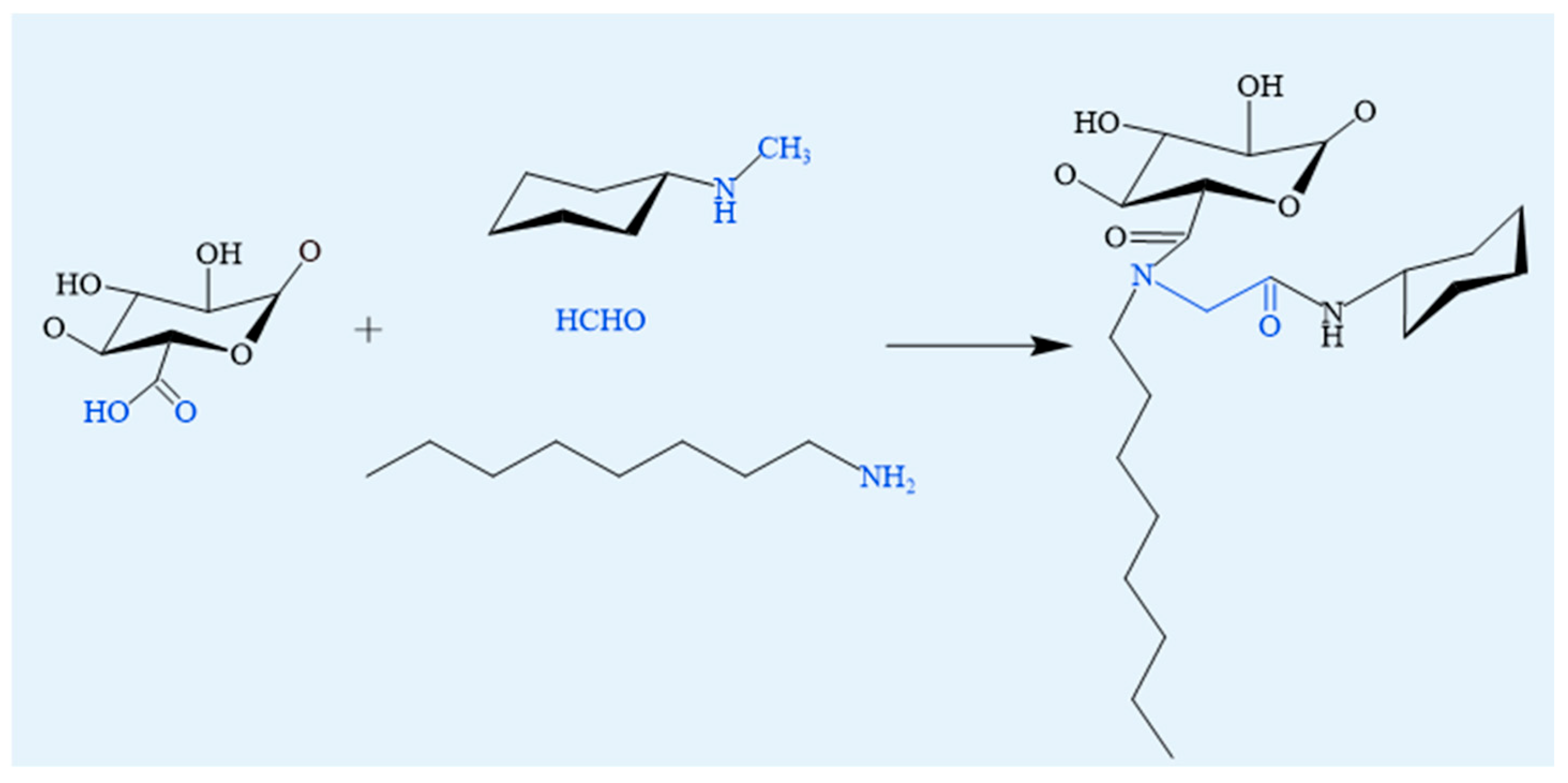
4.1.4. Ugi Reaction
4.1.5. Aldehyde Cross-Linking
4.1.6. Phosphorylation
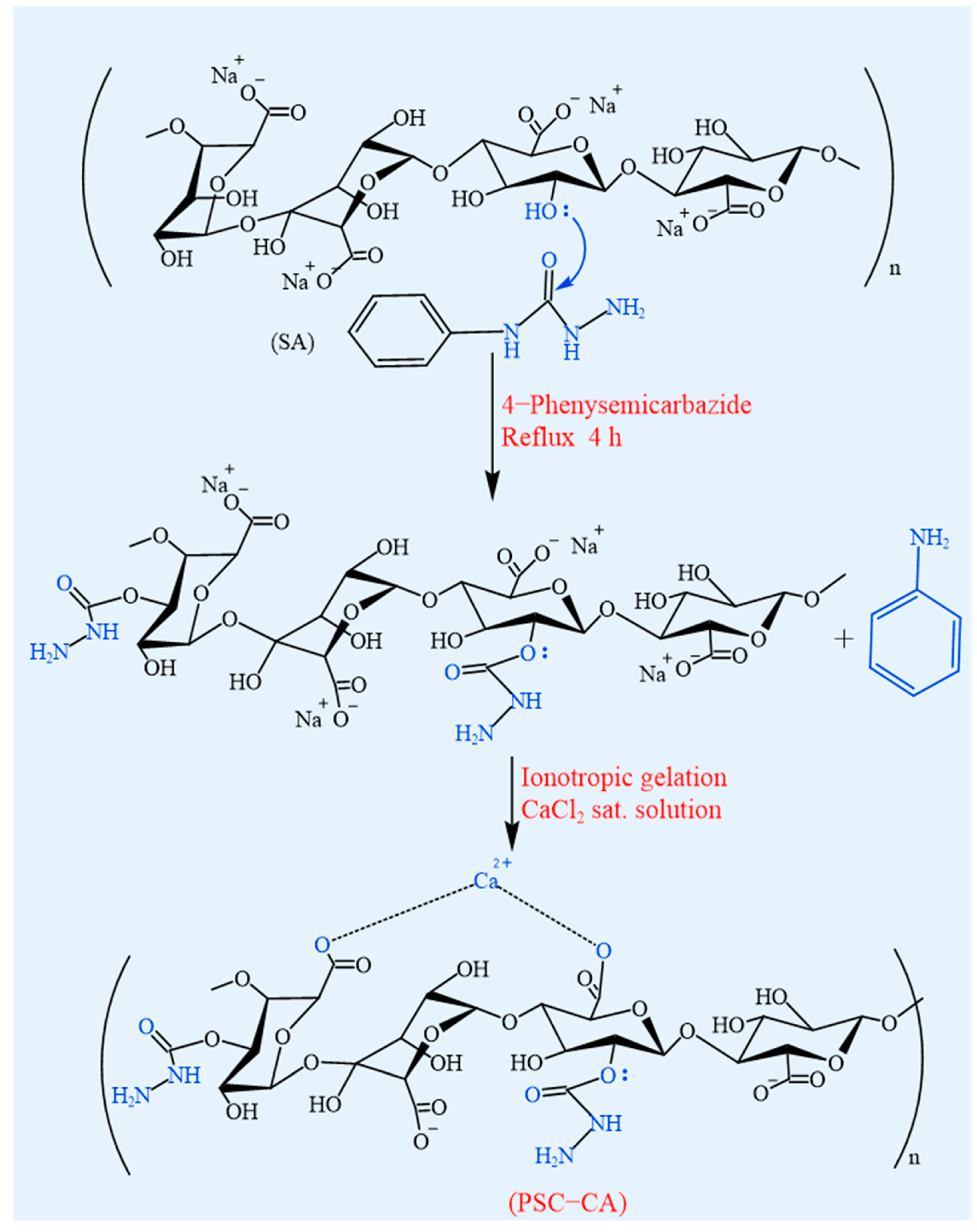
4.1.7. Amidation
4.1.8. Graft Modification
4.2. Physical Modification
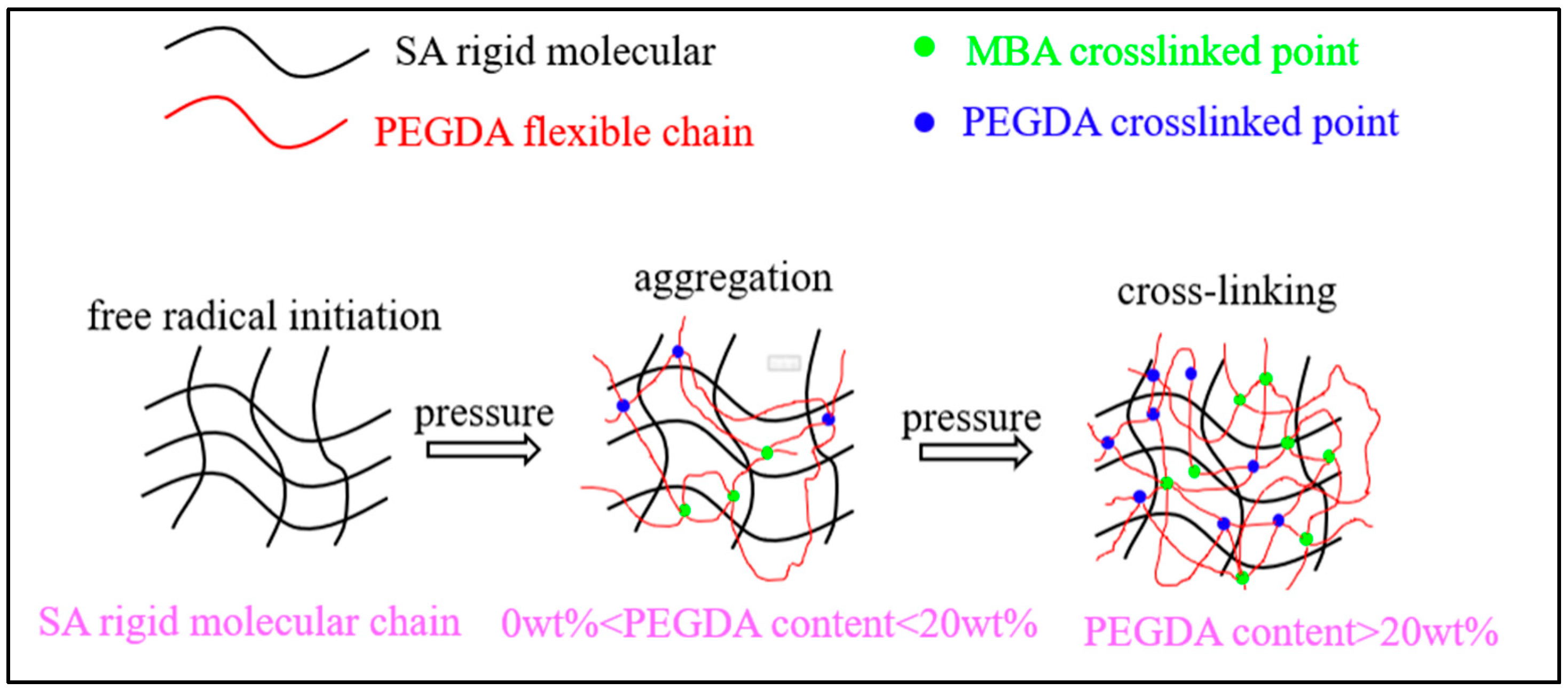
4.2.1. Composite Modification
Polymer Material Composite
Inorganic Material Composite
Nanomaterials
4.2.2. Physical Processing Technique
Ultrasonication
Irradiance
4.2.3. Physical Crosslinking
4.3. Biological Modification
4.4. Comparison of Modification Methods
5. Application of Modified SA
5.1. Food Industry
5.1.1. Food Packaging
| System | Modification | Food Matrix | Key KPl/Value | Condition/Note | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curdlan–SA active film | Polysaccharide blend | Volvariella volvacea (mushroom) | Shelf-life ↑; microbial load ↓; firmness retained | Cold storage | [163] |
| SA–Pectin + Cinnamic Acid | Phenolic ester (active, biodegradable) | General | ≈43.26% soil mass loss at 15 d; plastic-like mechanics | Soil burial vs. PE | [167] |
| SA + Tannic Acid (TA) edible film | Phenolic crosslinking | Produce/Meat (general) | WVP 1.24 × 10−6 → 0.54 × 10−6 g·m/(h·Pa); DPPH ≈ 89%; UV-block ~ 98%@280 nm | Lab films; edible/food-contact | [164] |
| PVA/SA/PVDF bilayer (alizarin sensor + antibacterial top) | Electrospun bilayer indicator | Pork | ΔE ≈ 48 (NH3); shelf-life +~24 h @25 °C | Pack test | [166] |
| PVA–SA + ZIF-8@alizarin (PA-SA-ZA) | MOF-stabilized dye sensor | Beef | ΔE < 5 under light aging; R2 ≈ 0.91 (TVB-N vs. color); contact angle ~ 52° | Pack test | [175] |
| PEO/SA nanofiber + phlorotannin | Electrospun antimicrobial | Chicken | Salmonella counts ↓; shelf-life ↑ | Cold storage | [180] |
| SA/Guar Gum + BOPE Pickering film | β-CD/persimmon pectin-stabilized oil emulsion | Mushrooms | Browning/shrinkage ↓; water/oxygen ingress ↓ | Postharvest | [184] |
| GG/AG/SA bilayer + TiO2 | Bilayer + Pickering + nanofillers | High-moisture produce | Barrier ↑; antifungal ↑ | Postharvest | [186] |

5.1.2. Functional Food Carrier
5.2. Biomedical Application
5.2.1. D Printing
5.2.2. Drug Delivery Systems
5.3. Environmental Engineering
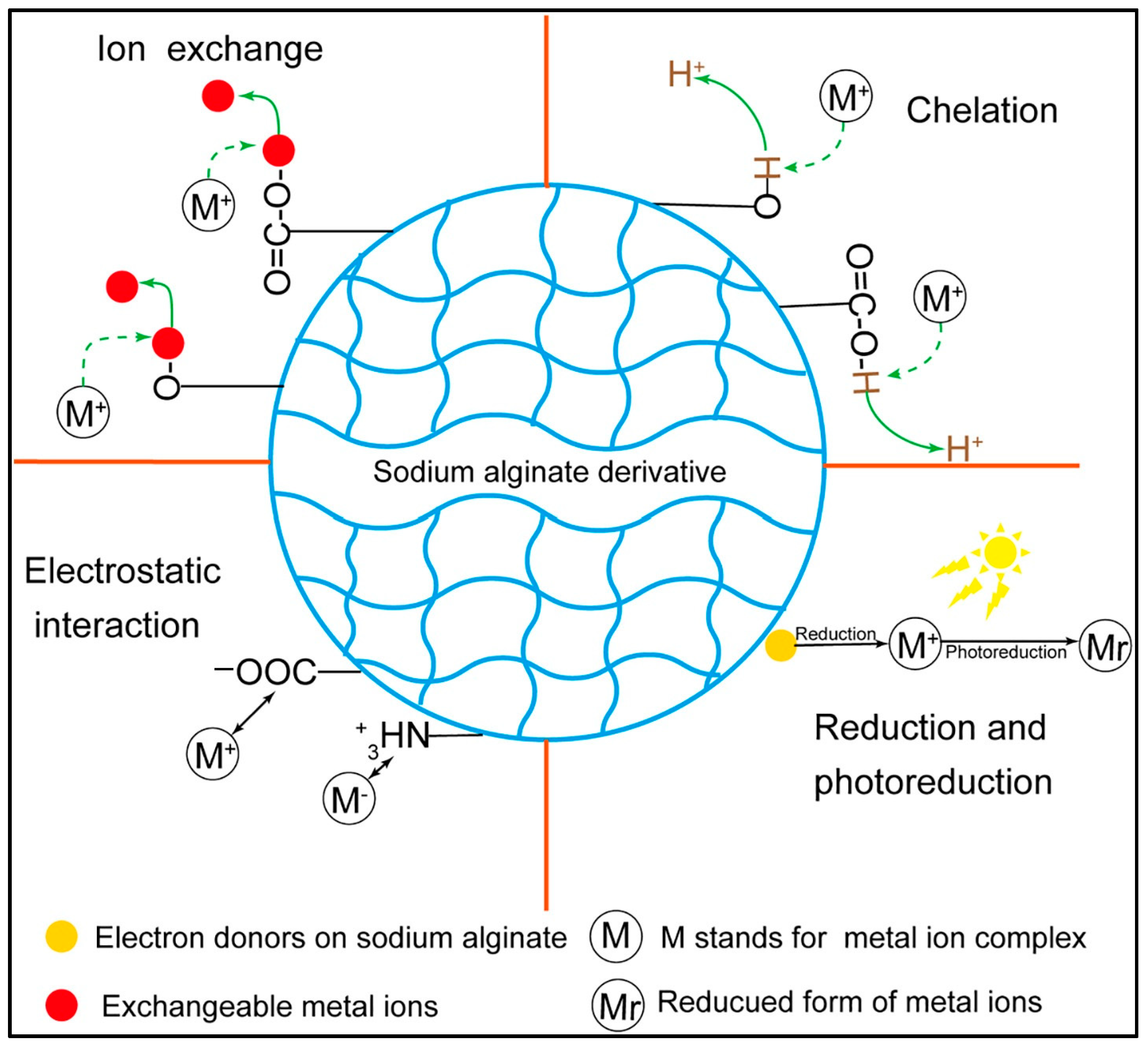
5.3.1. Metal Ion Adsorption
5.3.2. Dye Wastewater Treatment
5.4. Other Applications
5.4.1. Smart Textiles
5.4.2. Microbial Fuel Cell
5.4.3. Soil Conditioner
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbar, M.; Yaqoob, A.; Ahmad, A.; Luque, R. Chapter 1—Sodium Alginate: An Overview. In Sodium Alginate-Based Nanomaterials for Wastewater Treatment; Ahmad, A., Ahmad, I., Kamal, T., Asiri, A.M., Tabassum, S., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-0-12-823551-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K. Research Progress and Application of Sodium Alginate Grafted Copolymer Composites. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. IJRES 2024, 12, 238–257. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Food Additives. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L 354, 16–33. [Google Scholar]
- Commission of the European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 of 9 March 2012 Laying down Specifications for Food Additives Listed in Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, L 83, 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21, §184.1724—Sodium Alginate. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/part-184/section-184.1724 (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, M.; Hurren, C.; Wang, D. Photopolymerized Multifunctional Sodium Alginate-Based Hydrogel for Antibacterial and Coagulation Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Maity, M.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Chapter 7—Biocomposites of Alginates in Drug Delivery. In Alginates in Drug Delivery; Nayak, A.K., Hasnain, M.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 153–185. ISBN 978-0-12-817640-5. [Google Scholar]
- Łabowska, M.B.; Michalak, I.; Detyna, J. Methods of Extraction, Physicochemical Properties of Alginates and Their Applications in Biomedical Field—A Review. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 738–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-carmona, G.; McHugh, D.J.; Arvizu-Higuera, D.L.; Rodríguez-montesinos, Y.E. Pilot Plant Scale Extraction of Alginate from Macrocystis pyrifera. 1. Effect of Pre-Extraction Treatments on Yield and Quality of Alginate. J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauchel, P.; Arhaliass, A.; Legrand, J.; Kaas, R.; Baron, R. Decrease in dynamic viscosity and average molecular weight of alginate from Laminaria digitata during alkaline extraction. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Gomes, F.; Oliveira, F.; Morais, S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Microwave-Assisted Alginate Extraction from Portuguese Saccorhiza polyschides—Influence of Acid Pretreatment. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 9, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, X.; Cui, Y.; Xu, L.; Huo, S.; Ding, Z.; Hu, Q.; Xie, W.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, D. Efficient Extraction of Phycobiliproteins from Dry Biomass of Spirulina platensis Using Sodium Chloride as Extraction Enhancer. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssouf, L.; Lallemand, L.; Giraud, P.; Soulé, F.; Bhaw-Luximon, A.; Meilhac, O.; D’Hellencourt, C.L.; Jhurry, D.; Couprie, J. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Structural Characterization by NMR of Alginates and Carrageenans from Seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbour, M.; Hamoda, A.; Mintah, B.K.; Wahia, H.; Betchem, G.; Yolandani; Xu, H.; He, R.; Ma, H. Ultrasonic-Aided Extraction and Degossypolization of Cottonseed Meal Protein: Optimization and Characterization of Functional Traits and Molecular Structure. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 204, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Su, Y.; Sun, N.; Luo, L.; Ma, H.; He, R. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Dietary Fiber from Nannochloropsis Oceanica: A Comparison of Alkaline and Ultrasonic-Assisted Alkaline Extractions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 110080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayim, I.; Ma, H.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Ali, Z.; Zhou, C.; Donkor, P.O. Effect of Alkali Concentration on Functionality, Lysinoalanine Formation, and Structural Characteristics of Tea Residue Proteins. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummat, V.; Zhao, M.; Sivagnanam, S.P.; Karuppusamy, S.; Lyons, H.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Noore, S.; Rai, D.K.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; O’Donnell, C.; et al. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Alginate from Fucus Vesiculosus Seaweed By-Product Post-Fucoidan Extraction. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayim, I.; Ma, H.; Alenyorege, E.A. Optimizing and Predicting Degree of Hydrolysis of Ultrasound Assisted Sodium Hydroxide Extraction of Protein from Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Residue Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayim, I.; Ma, H.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Ali, Z.; Donkor, P.O. Influence of Ultrasound Pretreatment on Enzymolysis Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Sodium Hydroxide Extracted Proteins from Tea Residue. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.W.; Riaz, T.; Mahmood, S.; Bilal, M.; Manzoor, M.F.; Qamar, S.A.; Qi, X. Fucoidan-Based Nanomaterial and Its Multifunctional Role for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 354–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Rivers, A.; Stuckey, D.C.; Ward, K. Alginate Extraction from Sargassum Seaweed in the Caribbean Region: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.S.; Jameel, E.; Mohanta, B.; Dhara, A.K.; Alkahtani, S.; Nayak, A.K. Chapter 1—Alginates: Sources, Structure, and Properties. In Alginates in Drug Delivery; Nayak, A.K., Hasnain, M.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-0-12-817640-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Shi, C.; Zi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. A Review on the Chemical Modification of Alginates for Food Research: Chemical Nature, Modification Methods, Product Types, and Application. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; He, W. Research Progress on Chemical Modification of Alginate: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Egg-Box Model-Based Gelation of Alginate and Pectin: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Carmona, G.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Hernández-Garibay, E. 14—Conventional and Alternative Technologies for the Extraction of Algal Polysaccharides. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Domínguez, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 475–516. ISBN 978-0-85709-512-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.-Q.; Xu, D.; Dong, Q.-W.; Song, X.-J.; Chen, Y.-B.; Cui, Y.-L. Biomedical Potentials of Alginate via Physical, Chemical, and Biological Modifications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. Gelation Behavior and Mechanism of Alginate with Calcium: Dependence on Monovalent Counterions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.; Abraham, T.E. Polyionic Hydrocolloids for the Intestinal Delivery of Protein Drugs: Alginate and Chitosan—A Review. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abka-khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, S.; Hebden, A.; Goswami, P.; Du, C. A Brief Review on the Development of Alginate Extraction Process and Its Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck KGaA (Sigma-Aldrich). Sodium Alginate—Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material (PHR1471), CAS 9005-38-3. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/HK/en/product/sial/phr1471 (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Rostami, Z.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Rezaei, M. Relationship between Molecular Weights and Biological Properties of Alginates Extracted under Different Methods from Colpomenia Peregrina. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Tong, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, F. Rheological Properties of Pullulan-Sodium Alginate Based Solutions during Film Formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, P.; Latanska, I.; Paul, P.; Sujka, W.; Kolesinska, B. Modification of Alginates to Modulate Their Physic-Chemical Properties and Obtain Biomaterials with Different Functional Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate Derivatization: A Review of Chemistry, Properties and Applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Gao, R.; McClements, D.J. Development of Functional or Medical Foods for Oral Administration of Insulin for Diabetes Treatment: Gastroprotective Edible Microgels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4820–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Ions-Induced Gelation of Alginate: Mechanisms and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, W. Effects of the Structure and Gel Properties of Myofibrillar Protein on Chicken Breast Quality Treated with Ultrasound-Assisted Potassium Alginate. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikorski, P.; Mo, F.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Stokke, B. Evidence for Egg-Box-Compatible Interactions in Calcium−Alginate Gels from Fiber X-Ray Diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate Gel Particles-A Review of Production Techniques and Physical Properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; McClements, D.J.; Luo, S.; Ye, J.; Liu, C. Effect of Internal and External Gelation on the Physical Properties, Water Distribution, and Lycopene Encapsulation Properties of Alginate-Based Emulsion Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.P.; Neufeld, R.J.; Vilela, S.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F. Review and Current Status of Emulsion/Dispersion Technology Using an Internal Gelation Process for the Design of Alginate Particles. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, S.; Pitet, L.M. Ionic Crosslinking Strategies for Poly(Acrylamide)/Alginate Hybrid Hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2023, 191, 105676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Yuan, L.; Li, X.; Gao, R. Protein-Glutaminase-Mediated Functional Modification of Fish Myofibrillar Protein and Its Gelation Mechanism. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 223, 117782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.R.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wijaya, G.Y.A.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, L.; Jin, W.; Li, J.; Gao, R. Recent Developments in Maintaining Gel Properties of Surimi Products under Reduced Salt Conditions and Use of Additives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8518–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, X.; Shi, T.; Wijaya, G.Y.A.; Bai, F.; Wang, J.; Jin, W.; Yuan, L. Enhanced Physical Properties of Reduced-Salt Surimi Gels from Amur Sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) by l-Arginine and l-Histidine. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Guo, W.; He, S.; Liu, W. Alginate-Based Hydrogels Mediated Biomedical Applications: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Shahid, A.; Hossain, T.; Sheikh, S.; Rahman, S.; Uddin, N.; Rahim, A.; Khan, R.A.; Hossain, I. Sources, Extractions, and Applications of Alginate: A Review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Pan, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Zang, R. Structures, Properties, and Bioengineering Applications of Alginates and Hyaluronic Acid. Polymers 2023, 15, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Huang, Z.; Yin, L.; Gao, L.; et al. A Cell-Based Electrochemical Taste Sensor for Detection of Hydroxy-α-Sanshool. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, K.; Yuan, H. Preparation of Ag-Metal Organic Frameworks-Loaded Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for the Treatment of Periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Yan, D.; Xu, G.; Hong, H.; Gao, R. Effects of Chopping Temperature on the Gel Quality of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) Surimi: Insight from Gel-Based Proteomics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 8212–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Modification on Sodium Alginate for Food Preservation: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A.; Sadik, E.R.; Eldakiky, B.M.; Moustafa, H.; Fadl, E.; He, Z.; Elashtoukhy, E.Z.; Khalifa, R.E.; Zewail, T.M.M. Synthesis and Characterization of an Innovative Sodium Alginate/Polyvinyl Alcohol Bioartificial Hydrogel for Forward-Osmosis Desalination. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskhan, A.; Banat, F. Removal of Oil from Water by Calcium Alginate Hydrogel Modified with Maleic Anhydride. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2901–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrooznia, Z.; Kouhanestani, D.J.N. Preparation and Characterization of Thiolated Alginate Using Esterification Method for Biomedical Application. Conference Presentation, Iran, November 2023. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381861230 (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Gomez, C.G.; Rinaudo, M.; Villar, M.A. Oxidation of Sodium Alginate and Characterization of the Oxidized Derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, Z.; Ehsani, M.; Zandi, M.; Foudazi, R. Controlling Alginate Oxidation Conditions for Making Alginate-Gelatin Hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingerma, K.M.; Reile, I.; Tuvikene, R. Regioselective Sulfation of Alginate at 2-O-Position of Mannuronic Acid Unit with Py∙SO3 in DMSO. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 545, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare-Gachi, M.; Sadeghi, A.; Choshali, M.A.; Ghadimi, T.; Forghani, S.F.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Daemi, H. Degree of Sulfation of Freeze-Dried Calcium Alginate Sulfate Scaffolds Dramatically Influence Healing Rate of Full-Thickness Diabetic Wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Ye, T.; Li, Y.; Wu, H. Optimization of Preparation Conditions, Molecular Structure Analysis and Antitumor Activity of Sulfated Sodium Alginate Oligosaccharides. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 201, 112571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.-J. Biological Activities and Potential Industrial Applications of Fucose Rich Sulfated Polysaccharides and Fucoidans Isolated from Brown Seaweeds: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomohara, K.; Ohashi, N.; Uchida, T.; Nose, T. Synthesis of Natural Product Hybrids by the Ugi Reaction in Complex Media Containing Plant Extracts. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, A.; Kazmaier, U. A Half Century of the Ugi Reaction: Classic Variant. In Organic Reactions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–560. ISBN 978-0-471-26418-7. [Google Scholar]
- Putri, A.P.; Picchioni, F.; Harjanto, S.; Chalid, M. Alginate Modification and Lectin-Conjugation Approach to Synthesize the Mucoadhesive Matrix. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wen, Y.; Bao, C.; Liu, C.; Cao, S.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. Chemical Modification of Alginate with Tosylmethyl Isocyanide, Propionaldehyde and Octylamine via the Ugi Reaction for Hydrophobic Drug Delivery. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 7809–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Cao, S.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. Self-Assembled Oleylamine Grafted Alginate Aggregates for Hydrophobic Drugs Loading and Controlled Release. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2023, 72, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velema, W.A.; Lu, Z. Chemical RNA Cross-Linking: Mechanisms, Computational Analysis, and Biological Applications. JACS Au 2023, 3, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, D.R.; Weis, M.; Rai, J. Analyses of Lysine Aldehyde Cross-Linking in Collagen Reveal That the Mature Cross-Link Histidinohydroxylysinonorleucine Is an Artifact. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 6578–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.S.; Manning, J.M. Reaction of Glycolaldehyde with Proteins: Latent Crosslinking Potential of Alpha-Hydroxyaldehydes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3590–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumon, M.H.; Rahman, S.; Akib, A.A.; Sohag, S.; Rakib, R.A.; Khan, A.R.; Yesmin, F.; Shakil, M.S.; Rahman Khan, M.M. Progress in Hydrogel Toughening: Addressing Structural and Crosslinking Challenges for Biomedical Applications. Discov. Mater. 2025, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavarse, A.C.; Frachini, E.C.G.; da Silva, R.L.C.G.; Lima, V.H.; Shavandi, A.; Petri, D.F.S. Crosslinkers for Polysaccharides and Proteins: Synthesis Conditions, Mechanisms, and Crosslinking Efficiency, a Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 202, 558–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Tuszynska, M.; Kaźmierski, Ł.; Bartniak, M.; Bajek, A. Gelatin-Sodium Alginate Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Squaric Acid and Dialdehyde Starch as a Potential Bio-Ink. Polymers 2024, 16, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.J.; Lawrie, G.; Lambert, L.K.; Whittaker, M.; Jack, K.S.; Grøndahl, L. Phosphorylation of Alginate: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of in Vitro Mineralization Capacity. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Encapsulation of Caffeic Acid into Sodium Caseinate Using pH-Driven Method: Fabrication, Characterization, and Bioavailability. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Shi, Z.; Huang, F. Development of Alginate Macroporous Hydrogels Using Sacrificial CaCO3 Particles for Enhanced Hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.; Villiou, M.; Colombo, F.; La Cruz-García, A.D.; Tydecks, L.; Toelke, L.; Siemsen, K.; Selhuber-Unkel, C. Dynamic and Reversible Tuning of Hydrogel Viscoelasticity by Transient Polymer Interactions for Controlling Cell Adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2408616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.; Brault, L.; Gasparotto, E.; Vallée, R.; Morvan, P.-Y.; Ferrières, V.; Nugier-Chauvin, C. Formation of Amphiphilic Molecules from the Most Common Marine Polysaccharides, toward a Sustainable Alternative? Molecules 2021, 26, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, A.; Borazjani, N.; Kazemi-Aghdam, F.; Filo, J.; Lacík, I. DMTMM-Mediated Amidation of Sodium Alginate in Aqueous Solutions: pH-Dependent Efficiency of Conjugation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labre, F.; Mathieu, S.; Chaud, P.; Morvan, P.-Y.; Vallée, R.; Helbert, W.; Fort, S. DMTMM-Mediated Amidation of Alginate Oligosaccharides Aimed at Modulating Their Interaction with Proteins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, S.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. Chemical Modification of Alginate via the Oxidation-Reductive Amination Reaction for the Development of Alginate Derivative Electrospun Composite Nanofibers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 103113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenezi, H.; Gad, E.S.; Albassami, N.A.; Alatawi, I.S.; Alshareef, S.A.; Aljowni, M.A.; Jame, R.; Abdelaziz, M.A.; El-din, A.S.B.; Saleh, A.K. Development of Oxidized Sodium Alginate/Silica Hybrid as Efficient Adsorbent for Anionic and Cationic Dyes: Mechanism and Thermodynamic Studies. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2025, 15, 18247–18261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, Z.; He, R.; Ma, H. Structure and Functional Characteristics of Rapeseed Protein Isolate-Dextran Conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Singh, N.; Kumar, P. A Review on Sources, Modification Techniques, Properties and Potential Applications of Alginate-Based Modified Polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 213, 113078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, A.; Yadav, M.; Mishra, D.K.; Behari, K. Modification of Alginate by Grafting of N-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone and Studies of Physicochemical Properties in Terms of Swelling Capacity, Metal-Ion Uptake and Flocculation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Shehzad, H.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Sharif, A.; Ahmed, E.; Habiba, U.; Qaisar, F.; Fatima, N.-E.; Begum, R.; et al. Innovative Free Radical Induced Synthesis of WO3-Doped Diethyl Malonate Grafted Chitosan Encapsulated with Phosphorylated Alginate Matrix for UO22+ Adsorption: Parameters Optimisation through Response Surface Methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwesh, H.; Mohamed, R.R.; Soliman, S.M.A. Synthesis of Grafted Copolymer Alginate-g-Poly(1-Carboxylic 4-Acrylamidobenzenesulfonamide) and Its Application in Water Treatment. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 252, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, H.; Ahmed, E.; Sharif, A.; Din, M.I.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Nawaz, I.; Bano, R.; Iftikhar, M. Amino-Carbamate Moiety Grafted Calcium Alginate Hydrogel Beads for Effective Biosorption of Ag(I) from Aqueous Solution: Economically-Competitive Recovery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlı, O.; Olukman, M. Preparation of Ferric Ion Crosslinked Acrylamide Grafted Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Sodium Alginate Microspheres and Application in Controlled Release of Anticancer Drug 5-Fluorouracil. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, E.S.; Rojo, L.; Gentleman, E.; Sardinha, J.P.; Stevens, M.M. Strontium- and Zinc-Alginate Hydrogels for Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, E.; Şanlı, O. Novel Ionically Crosslinked Acrylamide-Grafted Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Sodium Alginate/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose pH-Sensitive Microspheres for Delivery of Alzheimer’s Drug Donepezil Hydrochloride: Preparation and Optimization of Release Conditions. Artif. Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Yu, Y.; Guo, J. Preparation of Calcium Alginate/Polyethylene Glycol Acrylate Double Network Fiber with Excellent Properties by Dynamic Molding Method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Yu, Y.; Guo, J. Sodium Alginate-Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate Based Double Network Fiber: Rheological Properties of Fiber Forming Solution with Semi-Interpenetrating Network Structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yu, K.-K.; Li, K.; Yu, X.-Q. A Biocompatible Polyethylene Glycol/Alginate Composite Hydrogel with Significant Reactive Oxygen Species Consumption for Promoting Wound Healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 6934–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Tu, Z.; Dai, W.; Xue, Y.; Tang, C.; Gao, W.; Mao, C.; Lei, B.; Lin, C. Bioactive Antibacterial Silica-Based Nanocomposites Hydrogel Scaffolds with High Angiogenesis for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing and Skin Repair. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4929–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberian, M.; Safari Roudsari, R.; Haghshenas, N.; Rousta, A.; Alizadeh, S. How the Combination of Alginate and Chitosan Can Fabricate a Hydrogel with Favorable Properties for Wound Healing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, S.; Xu, J.; He, J. Preparation and Properties of a Multi-Crosslinked Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel. Mater. Lett. 2024, 354, 135414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Ren, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y. Semi-Unzipping of Chitosan-Sodium Alginate Polyelectrolyte Gel for Efficient Capture of Metallic Mineral Ions from Tannery Effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, S.; Yu, K.; Wang, H.; Fu, J. Construction of Porous Structure-Based Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Sodium Alginate/Tea Polyphenols for Wound Dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Feng, Z.; Lyu, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Bai, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y. Electroactive Injectable Hydrogel Based on Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Carboxymethyl Chitosan for Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Han, X.; Duns, G.J.; Dessie, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Y.; Qin, Z.; Luo, X. Kaolin-Loaded Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Composite Sponges for Rapid Hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.A.; Mohd Saharuddin, S.N.D.; Muhamad, M.H. Unlocking the Potential of Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) as a Biocarrier for Enhanced Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 74, 107780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Yi, X.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; Ying, G.-G. Enhanced Biodegradation of Thiamethoxam with a Novel Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)/Sodium Alginate (SA)/Biochar Immobilized Chryseobacterium Sp H5. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y. Antibacterial Effect of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Biochar–Nano Silver/Sodium Alginate Gel Beads. Processes 2023, 11, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wu, P.; Zhuang, H.; Qin, Z.; Yu, P.; Fu, K.; Qiu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Nitric Oxide Releasing Polyvinyl Alcohol and Sodium Alginate Hydrogels as Antibacterial and Conductive Strain Sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, S.; Dacrory, S.; Hesemann, P.; Bettache, N.; Ali, L.M.A.; Postel, L.; Akl, E.M.; El-Sakhawy, M. Wound Dressings Based on Sodium Alginate-Polyvinyl Alcohol-Moringa Oleifera Extracts. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Shakoor, R.A.; Al-Qahtani, N.; Bhadra, J.; Al-Thani, N.J.; Kahraman, R. Polyolefin-Based Smart Self-Healing Composite Coatings Modified with Calcium Carbonate and Sodium Alginate. Polymers 2024, 16, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Fu, Y.; Huan, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Han, D. Thermal Responsive Sodium Alginate/Polyacrylamide/Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide) Ionic Hydrogel Composite via Seeding Calcium Carbonate Microparticles for the Engineering of Ultrasensitive Wearable Sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yap, J.X.; Leo, C.P.; Chang, C.K. Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Sodium Alginate Beads Incorporated with Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles and Bentonite for Phosphate Recovery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Quan, F.-Y.; Kong, Q.-S. Preparation and Characterization of Interpenetrating Networks of Sodium Alginate-Silicon Dioxide. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 25, 152–154. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288973139_Preparation_and_characterization_of_interpenetrating_networks_of_sodium_alginate-silicon_dioxide (accessed on 9 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Z.; Cui, L.; Li, C.; Ma, K.; Hu, X.; Feng, J. Entrapment of an ACE Inhibitory Peptide into Ferritin Nanoparticles Coated with Sodium Deoxycholate: Improved Chemical Stability and Intestinal Absorption. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, T.; Chen, L.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Chen, H.; Yu, X. Effect of Dialysate Type on Ultrasound-Assisted Self-Assembly Zein Nanocomplexes: Fabrication, Characterization, and Physicochemical Stability. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Bai, M.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. The Improvement of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate on the Electrospinning of Gelatin O/W Emulsions for Production of Core-Shell Nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Qiu, W.-Y.; Sun, L.; Ding, Z.-C.; Yan, J.-K. Preparation, Characterization, and Antioxidant Capacities of Selenium Nanoparticles Stabilized Using Polysaccharide–Protein Complexes from Corbicula Fluminea. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; He, W.-S.; Jia, C. A Novel Phytosterols Delivery System Based on Sodium Caseinate-Pectin Soluble Complexes: Improving Stability and Bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Hong, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, Y. Recent Trends and Applications of Cellulose Nanocrystals in Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.Z. Structurally Related Electromagnetic Properties of NixFeyO4 Nanomaterials Synthesized by Granulated Sodium Alginate. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Ge, S.; Li, H.; Su, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, W.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Synchronous Synthesis of Cu2O/Cu/rGO@carbon Nanomaterials Photocatalysts via the Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Template Method for Visible Light Photocatalytic Degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, A.; Said, N.M.; Islam, S.; Shah, Z.; Mahmuod, S.R.; Wakif, A. A Semi-Analytical Passive Strategy to Examine a Magnetized Heterogeneous Mixture Having Sodium Alginate Liquid with Alumina and Copper Nanomaterials near a Convectively Heated Surface of a Stretching Curved Geometry. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 139, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, F.; Cui, F.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Qian, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, J.; et al. Improved Postharvest Quality and Respiratory Activity of Straw Mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) with Ultrasound Treatment and Controlled Relative Humidity. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ding, X.; Dai, C.; Ma, H. Changes in the Structure and Dissociation of Soybean Protein Isolate Induced by Ultrasound-Assisted Acid Pretreatment. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Hong, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Ashokkumar, M.; Ma, H. Evaluation of Low-Temperature Ultrasonic Marination of Pork Meat at Various Frequencies on Physicochemical Properties, Myoglobin Levels, and Volatile Compounds. Meat Sci. 2024, 217, 109606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, H. Evaluation of Ultrasonic-Assisted Pickling with Different Frequencies on NaCl Transport, Impedance Properties, and Microstructure in Pork. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, B.; Zhou, C.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A.; Cai, Z.; Yu, X. Multi-Frequency Ultrasound-Assisted Dialysis Modulates the Self-Assembly of Alcohol-Free Zein-Sodium Caseinate to Encapsulate Curcumin and Fabricate Composite Nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenyorege, E.A.; Ma, H.; Ayim, I.; Aheto, J.H.; Hong, C.; Zhou, C. Reduction of Listeria Innocua in Fresh-Cut Chinese Cabbage by a Combined Washing Treatment of Sweeping Frequency Ultrasound and Sodium Hypochlorite. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, M.S.; Virk, M.A.; Liang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, M.; Tufail, T.; Rashid, A.; Qayum, A.; Rehman, A.; Ekumah, J.-N.; et al. Enhancing Storage and Gastroprotective Viability of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Encapsulated by Sodium Caseinate-Inulin-Soy Protein Isolates Composites Carried within Carboxymethyl Cellulose Hydrogel. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, A.; Ma, H.; Gasmalla, M.A.A.; Sarpong, F.; Awad, F.N.; Duan, Y. Effect of Multi-Frequency Counter-Current S Type Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Defatted Corn Germ Protein: Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Process Biochem. 2019, 87, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liang, Q.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Zhou, C.; Mahunu, G.K. Effects of Ultrasound and Ultrasound Assisted Alkaline Pretreatments on the Enzymolysis and Structural Characteristics of Rice Protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladejo, A.O.; Ma, H.; Qu, W.; Zhou, C.; Wu, B.; Yang, X.; Onwude, D.I. Effects of Ultrasound Pretreatments on the Kinetics of Moisture Loss and Oil Uptake during Deep Fat Frying of Sweet Potato (Ipomea batatas). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 43, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Rashid, A.; Qayum, A.; Tuly, J.A.; Ma, H.; Miao, S.; Ren, X. Sodium Caseinate/Pectin Complex-Stabilized Emulsion: Multi-Frequency Ultrasound Regulation, Characterization and Its Application in Quercetin Delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Otu, P.; Chen, L.; Niu, Y.; Yao, D.; Hua, C.; et al. Preparation of Umami Peptides from Chicken Breast by Ultrasound-Assisted Gradient Dilution Feeding Substrate and Study of Their Formation Mechanism. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, A.T.; Zhou, C.; Amanor-Atiemoh, R.; Ali, T.A.A.; Wahia, H.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y. Efficacy of Dual-Frequency Ultrasound and Sanitizers Washing Treatments on Quality Retention of Cherry Tomato. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, F.; Li, D.; Zhou, C.; Niu, L.; Xu, Y.; Feng, L.; Dai, Z.; He, W. Ultrasound Modification of Pectin and the Mechanism of Its Interaction with Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Rehman, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Miao, S.; Dabbour, M.; Ashraf, W.; Rasheed, H.A.; Assadpour, E.; Hussain, A.; Suleria, H.A.R.; et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Sonicated Peach Gum-Sodium Caseinate Nanocomplexes: Physicochemical, Spectroscopic, Morphological, and Correlation Analyses. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 2462–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, P.; Shu, Y.; Liang, P.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shan, X.; Wu, X. An Ultrasound-Triggered Injectable Sodium Alginate Scaffold Loaded with Electrospun Microspheres for on-Demand Drug Delivery to Accelerate Bone Defect Regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, D.; You, S.; Han, F. Influence of Sodium Alginate Pretreated by Ultrasound on Papain Properties: Activity, Structure, Conformation and Molecular Weight and Distribution. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaila, E.; Craciun, G.; Calina, I.C. Sodium Alginate-g-Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid Hydrogels Obtained by Electron Beam Irradiation for Soil Conditioning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Wang, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Swelling Behaviors of Sodium Alginate-g-Poly(Acrylic Acid)/Sodium Humate Superabsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou-kui, S. Effect of Sodium Alginate Coating and ~(60)Co-γ Irradiation Treatment on Fresh-Keeping of Golden Silk Jujube. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 33, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Cheng, H.; Tian, J.; Pan, H.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Chen, J. Photo-Crosslinking Modified Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for Targeting Delivery Potential by NO Response. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A. Synergistic Effect of Palygorskite Nanorods and Ion Crosslinking to Enhance Sodium Alginate-Based Hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, H.; Jia, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; et al. Percutaneous Electroosmosis of Berberine-Loaded Ca2+ Crosslinked Gelatin/Alginate Mixed Hydrogel. Polymers 2022, 14, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Li, D.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Green, Tough, and Heat-Resistant: A GDL-Induced Strategy for Starch-Alginate Hydrogels. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, D.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Ion-Assisted Fabrication of Neutral Protein Crosslinked Sodium Alginate Nanogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Liu, L.; Luo, L.; Ji, L. Preparation and Characterization of a Self-Crosslinking Sodium Alginate-Bioactive Glass Sponge. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2023, 111, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualrahman, M.A.Y.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Hu, J.; Yang, X. Thermal and Single Frequency Counter-current Ultrasound Pretreatments of Sodium Caseinate: Enzymolysis Kinetics and Thermodynamics, Amino Acids Composition, Molecular Weight Distribution and Antioxidant Peptides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4861–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualrahman, M.A.Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Ma, H.; Mao, L.; Wang, K. Effects of Ultrasound Pretreatment on Enzymolysis of Sodium Caseinate Protein: Kinetic Study, Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity, and the Structural Characteristics of the Hydrolysates. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noach, M.; Mampana, R.; Van Rensburg, E.; Goosen, N.; Pott, R. Chemical and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Alginate: A Review. Bot. Mar. 2024, 67, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Cha, Q.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Chen, X.-L. Degradation and Utilization of Alginate by Marine Pseudoalteromonas: A Review. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0036821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes Database (CAZy): An Expert Resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.T.; Ko, H.-J.; Kim, N.; Kim, D.; Lee, D.; Choi, I.-G.; Woo, H.C.; Kim, M.D.; Kim, K.H. Characterization of a Recombinant Endo-Type Alginate Lyase (Alg7D) from Saccharophagus Degradans. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yin, D.; Zhang, X.; Solairaj, D.; Xi, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Alginate Oligosaccharide-Driven Resistance in Debaryomyces Hansenii Y3: A Dual Omics Perspective. New Zealand J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2025, 53, 563–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, A.; Yamasaki, M.; Mikami, B.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Crystal Structure of Exotype Alginate Lyase Atu3025 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens*. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24519–24528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Chen, X.-L. Diversity of Three-Dimensional Structures and Catalytic Mechanisms of Alginate Lyases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02040-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Chen, L.; Dong, C.; Tang, M.; Wei, Y.; Lv, D.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z. Alginate Oligosaccharide and Gut Microbiota: Exploring the Key to Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Abraham, R.E.; Franco, C.M.M.; Puri, M. Production of Alginate Oligosaccharides (AOSs) Using Enhanced Physicochemical Properties of Immobilized Alginate Lyase for Industrial Application. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheto, J.H.; Huang, X.; Xiaoyu, T.; Bonah, E.; Ren, Y.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Chunxia, D. Investigation into Crystal Size Effect on Sodium Chloride Uptake and Water Activity of Pork Meat Using Hyperspectral Imaging. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Fu, L.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Povey, M.; Zou, X. Self-Healing Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel with Anthocyanin for Monitoring the Spoilage of Flesh Foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 165, 111270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Cheng, Q.; Li, C.; Khin, M.N.; Lin, L. Schiff Base Cross-Linked Dialdehyde β-Cyclodextrin/Gelatin-Carrageenan Active Packaging Film for the Application of Carvacrol on Ready-to-Eat Foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Ye, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, L. Enhancing Anti-E. Coli O157:H7 Activity of Composite Phage Nanofiber Film by D-Phenylalanine for Food Packaging. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 376, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Sobhy, R.; Khalifa, I.; Zou, X. Lemon-Derived Carbon Quantum Dots Incorporated Guar Gum/Sodium Alginate Films with Enhanced the Preservability for Blanched Asparagus Active Packaging. Food Res. Int. 2025, 202, 115736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Cui, F.-J.; Ullah, M.W.; Qayum, A.; Khalifa, I.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Ying, Z.-Z.; Khan, I.; Zeb, U.; Alarfaj, A.A.; et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Bioactive Curdlan and Sodium Alginate Films for Enhancing the Shelf Life of Volvariella volvacea. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Lv, S. Bioactive Edible Sodium Alginate Films Incorporated with Tannic Acid as Antimicrobial and Antioxidative Food Packaging. Foods 2022, 11, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Wu, R.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. Anthocyanin Loaded Composite Gelatin Films Crosslinked with Oxidized Alginate for Monitoring Spoilage of Flesh Foods. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 42, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Huang, X.; Arslan, M.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, Y.; Holmes, M.; Zou, X. High- Sensitivity Bilayer Nanofiber Film Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate/Polyvinylidene Fluoride for Pork Spoilage Visual Monitoring and Preservation. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.Y.; Ahmad Rafiee, A.R.; Leong, C.R.; Tan, W.-N.; Dailin, D.J.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Shelkh, M.; Nawaz, A.; Chuah, L.F. Development of Sodium Alginate-Pectin Biodegradable Active Food Packaging Film Containing Cinnamic Acid. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Gómez, P.L.; Al-Zamora, S.M.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Enhanced Composite Co-MOF-Derived Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Visual Films for Real-Time and in Situ Monitoring Fresh-Cut Apple Freshness. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Zhou, W. Sodium Alginate/Ager Colourimetric Film on Porous Substrate Layer: Potential in Intelligent Food Packaging. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, T. Preparation of a Dual-Functional Active Film Based on Bilayer Hydrogel and Red Cabbage Anthocyanin for Maintaining and Monitoring Pork Freshness. Foods 2023, 12, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. A Visual Bi-Layer Indicator Based on Roselle Anthocyanins with High Hydrophobic Property for Monitoring Griskin Freshness. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Qayum, A.; Shah Bacha, S.A.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kang, L.; Chi, Z.; Chi, R.; Han, X.; Ekumah, J.-N.; et al. Novel Pullulan-Sodium Alginate Film Incorporated with Anthocyanin-Loaded Casein-Carboxy Methyl Cellulose Nanocomplex for Real-Time Fish and Shrimp Freshness Monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Jayan, H.; Gao, M.; Hesham, R.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Novel pH-Sensitive Organic Ligand-Based Luminescent MOFs Modified CMC-Na/SA Films for Real-Time Monitoring of Fruit Freshness. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2025, 49, 101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Agyemang, K.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.-S.; Cui, H. Antibacterial Mechanism of Tetrapleura Tetraptera Extract against Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus and Its Application in Pork. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Sobhy, R.; Khalifa, I.; Zou, X. Ammonia-Responsive Colorimetric Film of Phytochemical Formulation (Alizarin) Grafted onto ZIF-8 Carrier with Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Sodium Alginate for Beef Freshness Monitoring. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 11706–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Balandrano, D.D.; Chai, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W. Gastrointestinal Fate of Blueberry Anthocyanins in Ferritin-Based Nanocarriers. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, P.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Polyphenolic Truxillic Acid Crosslinked Sodium Alginate Film with Notable Antimicrobial and Biodegradable Properties for Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, P.; Wang, K.; Yu, F.; Yi, L.; Sun, L.; Li, H. Gelatin/Sodium Alginate Multilayer Composite Film Crosslinked with Green Tea Extract for Active Food Packaging Application. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 662, 131013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Mei, C.; Shi, C.; Li, C.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Cui, H. Preparation and Characterization of Gelatin Active Packaging Film Loaded with Eugenol Nanoparticles and Its Application in Chicken Preservation. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendhiran, D.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Encapsulation of Phlorotannin in Alginate/PEO Blended Nanofibers to Preserve Chicken Meat from Salmonella Contaminations. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Qayum, A.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kang, L.; Chi, Z.; Chi, R.; Han, X.; Ekumah, J.-N.; et al. Preparation and Functional Characterization of Pullulan-Sodium Alginate Composite Film Enhanced with Ultrasound-Assisted Clove Essential Oil Nanoemulsions for Effective Preservation of Cherries and Mushrooms. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Hao, M.; Song, W.; Zou, X.; Huang, X. A Cell-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of Capsaicin. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 9341–9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Du, L.; Li, Z.; Xue, J.; Shi, J.; Tahir, H.E.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Sun, W.; et al. A Visual Bi-Layer Indicator Based on Mulberry Anthocyanins with High Stability for Monitoring Chinese Mitten Crab Freshness. Food Chem. 2023, 411, 135497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhai, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Sodium Alginate/Guar Gum Based Nanocomposite Film Incorporating β-Cyclodextrin/Persimmon Pectin-Stabilized Baobab Seed Oil Pickering Emulsion for Mushroom Preservation. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, Q. Caseinate Nanoparticles Co-Loaded with Quercetin and Avenanthramide 2c Using a Novel Two-Step pH-Driven Method: Formation, Characterization, and Bioavailability. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zou, X.; Xiao, J. Incorporation of Hawthorn Pectin/β-Cyclodextrin-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles for Improving the Physical, Biological, and Release Properties of Guar Gum/Agar/Sodium Alginate-Based Bilayer Films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 212, 118302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Pan, J.; Ma, C.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Huang, L.; Dai, C.; Ma, H.; He, R. Stereo-Hindrance Effect and Oxidation Cross-Linking Induced by Ultrasound-Assisted Sodium Alginate-Glycation Inhibit Lysinoalanine Formation in Silkworm Pupa Protein. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Rehman, A.; Khalifa, I.; Hussain, A.; Ashraf, W.; Miao, S.; Lianfu, Z. Encapsulation of Lutein Within Ultrasonicated Peach Gum-Sodium Caseinate Complex Nanoparticles Via Electrostatic Complexation: Physiochemical Properties, Structural Interaction Mechanisms, and In Vitro Release Analyses. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 4392–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, W.; Chai, Z.; Feng, J.; Teng, C.; Ma, K.; Hu, X.; Xu, L. Sodium Alginate Coated Ferritin as ACE Inhibitory Peptide Carrier: Prolonged Release Property and Enhanced Transepithelial Transport. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 34, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramathi, B.B.; Muniraj, B.A.; Kola, M.; Konidala, K.K.; Arthala, P.K.; Sharma, T.S.K. Alginate Biopolymeric Structures: Versatile Carriers for Bioactive Compounds in Functional Foods and Nutraceutical Formulations: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-H.; Song, Y.-B.; Chang, P.-S.; Lee, H.G. Microencapsulation of α-Tocopherol Using Sodium Alginate and Its Controlled Release Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 38, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, K.E.L.; Costa, A.M.M.; da Silva, J.P.L.; Alviano, D.S.; Bizzo, H.R.; Tonon, R.V. Microencapsulation of Marjoram Essential Oil as a Food Additive Using Sodium Alginate and Whey Protein Isolate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lv, H.; Wang, M.; Cho, C.-S.; Shin, J.; Cui, L.; Yan, C. Effect of Microencapsulation of Egg Yolk Immunoglobulin Y by Sodium Alginate/Chitosan/Sodium Alginate on the Growth Performance, Serum Parameters, and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 36, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matos, E.F.; Scopel, B.S.; Dettmer, A. Citronella Essential Oil Microencapsulation by Complex Coacervation with Leather Waste Gelatin and Sodium Alginate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Ren, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Yao, Y.; Chen, H. Fabrication of Fish Gelatin/Sodium Alginate Double Network Gels for Encapsulation of Probiotics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4398–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchepare, M.D.A.; Barin, J.S.; Cichoski, A.J.; Jacob-Lopes, E.; Wagner, R.; Fries, L.L.M.; Menezes, C.R.D. Microencapsulation of Probiotics Using Sodium Alginate. Ciênc. Rural 2015, 45, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Zhou, C.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, B. High Voltage Electrohydrodynamic Atomization of Bovine Lactoferrin and Its Encapsulation Behaviors in Sodium Alginate. J. Food Eng. 2022, 317, 110842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhou, J.; An, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. Modification, 3D Printing Process and Application of Sodium Alginate Based Hydrogels in Soft Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y. 3D Bioprinted Scaffolds for Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 925321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Du, X.; Zhu, M.; Tian, Z.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y. 3D Printing of Layered Mesoporous Bioactive Glass/Sodium Alginate-Sodium Alginate Scaffolds with Controllable Dual-Drug Release Behaviors. Biomed. Mater. Bristol Engl. 2019, 14, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hu, C.; Huang, X.; Qin, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Xie, F.; Fan, Z. 3D Printing Nacre Powder/Sodium Alginate Scaffold Loaded with PRF Promotes Bone Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 2418–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yao, G. Electrospinning/3D Printing Drug-Loaded Antibacterial Polycaprolactone Nanofiber/Sodium Alginate-Gelatin Hydrogel Bilayer Scaffold for Skin Wound Repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 129705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.; Ganguly, K.; More, U.A.; Reddy, K.R.; Dugge, T.; Naik, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Noolvi, M.N. Chapter 3—Sodium Alginate in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Areas. In Natural Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Hasnain, M.S., Nayak, A.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 59–100. ISBN 978-0-12-817055-7. [Google Scholar]
- Veronica, N.; Heng, P.W.S.; Liew, C.V. Alginate-Based Matrix Tablets for Drug Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubashynskaya, N.V.; Petrova, V.A.; Romanov, D.P.; Skorik, Y.A. pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery System Based on Chitin Nanowhiskers-Sodium Alginate Polyelectrolyte Complex. Molecules 2022, 15, 5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Deng, D.; Lv, J.; Zhang, W.; Tian, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Zhao, Y. A Novel Macroporous Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Sponge Dressing Capable of Rapid Hemostasis and Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth Reddy, O.; Subha, M.C.S.; Jithendra, T.; Madhavi, C.; Chowdoji Rao, K. Curcumin Encapsulated Dual Cross Linked Sodium Alginate/Montmorillonite Polymeric Composite Beads for Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Alginate Nanogel-Embedded Liposomal Drug Carriers Facilitate Drug Delivery Efficiency in Arthritis Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Liu, Z.; Shao, Y.; Su, J.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; et al. Nitric Oxide Enhances Rice Resistance to Rice Black-Streaked Dwarf Virus Infection. Rice 2020, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhou, Q.; Man, Z.; Guo, J.; Sun, W. Can Cadmium-Contaminated Rice Be Used to Produce Food Additive Sodium Erythorbate? Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Liang, H.; Chen, T.; Yang, W.; Ding, C. Influence of Long-Term Irrigation with Treated Papermaking Wastewater on Soil Ecosystem of a Full-Scale Managed Reed Wetland. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Hou, B.; Hao, C.; Li, X.; Wu, J. Construction of a Lignosulfonate–Lysine Hydrogel for the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yin, L.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Green Reduction of Silver Nanoparticles for Cadmium Detection in Food Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Coupled Multivariate Calibration. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Ni, X.; Xia, J.; Suo, H.; Yan, L.; Zou, B. Immobilized Lipase Based on SBA-15 Adsorption and Gel Embedding for Catalytic Synthesis of Isoamyl Acetate. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Guo, C.; Hao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Long, H.; Li, M. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions by Sodium Alginate Based Adsorbent-a Review and New Perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Jiang, G.; Xue, X.; Wu, D.; Sheng, T.; Sun, C.; Xu, X. Fe0-Fe3O4 Nanocomposites Embedded Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate Beads for Chromium (VI) Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Sun, F.; Han, Z.; Han, F.; He, J.; Ou, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, X. Graphene Oxide Encapsulated Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Microspheres for Cu (II) and U (VI) Removal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.C.; Dwivedi, A.D.; Le, T.T.; Seo, S.-H.; Kim, E.-J.; Chang, Y.-S. Magnetite Graphene Oxide Encapsulated in Alginate Beads for Enhanced Adsorption of Cr(VI) and As(V) from Aqueous Solutions: Role of Crosslinking Metal Cations in pH Control. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; Yao, J. In-Situ Gelation of Sodium Alginate Supported on Melamine Sponge for Efficient Removal of Copper Ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, C.Y.; Wirzal, M.D.H.; Bustam, M.A. A Review on Nanofibers Membrane with Amino-Based Ionic Liquid for Heavy Metal Removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatutlu, A.; Barhoum, A.; Sapelkin, A. Chapter 1—Liquid-Phase Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Materials. In Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architecture Nanostructures; Barhoum, A., Makhlouf, A.S.H., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–28. ISBN 978-0-323-51254-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Han, G.; Yang, S.; Su, S.; Sana, H.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J. Comprehensive Evaluation on a Prospective Precipitation-Flotation Process for Metal-Ions Removal from Wastewater Simulants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Alibakhshi, H.; Jashni, E.; Parvizian, F.; Shen, J.N.; Taheri, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Rafiei, N. A Novel Layer-by-Layer Heterogeneous Cation Exchange Membrane for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, S.K.; Katsaros, F.K.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Nolan, J.W.; Le Deit, H.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Heavy Metal Sorption by Calcium Alginate Beads from Laminaria Digitata. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Y. Novel Magnetic Beads Based on Sodium Alginate Gel Crosslinked by Zirconium(IV) and Their Effective Removal for Pb2+ in Aqueous Solutions by Using a Batch and Continuous Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, B.; Wan, Y. Entrapment of Ball-Milled Biochar in Ca-Alginate Beads for the Removal of Aqueous Cd(II). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Ruiz, D.; Bonfante, H.; De Ávila, G.; Herrera, A. Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherms and Desorption Studies of Mercury from Aqueous Solution at Different Temperatures on Magnetic Sodium Alginate-Thiourea Microbeads. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, X. Amine Functionalized Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Methyl Blue in Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Ning, S.; Wu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Fujita, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Yin, X.; et al. Novel Phosphate Functionalized Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for Efficient Adsorption and Separation of Nd and Dy from Co. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Song, G.; Lou, T. Microwave Assisted Copolymerization of Sodium Alginate and Dimethyl Diallyl Ammonium Chloride as Flocculant for Dye Removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Dong, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. An Ingenious Construction of Porous Sodium Alginate/TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Composite Aerogels for Efficient Adsorption of Crystal Violet Dyes in Wastewater. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 110, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shil, D.C.; Rahman, N.; Sultana, S.; Sardar, M.N.; Majumder, P.; Robel, F.N. Preparation & Characterization of Polyvinyl Alcohol-Sodium Alginate-Starch Based Hydrogel by Gamma Radiation and Its Application for the Treatment of Dye Containing Water. Adv. Environ. Eng. Res. 2023, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, M.; Ragab, A.H.; Gumaah, N.F.; Mubarak, M.F. Sodium Alginate-Encapsulated Nano-Iron Oxide Coupled with Copper-Based MOFs (Cu-BTC@Alg/Fe3O4): Versatile Composites for Eco-Friendly and Effective Elimination of Rhodamine B Dye in Wastewater Purification. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xiang, N.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Z.; Hou, L. Preparation and Characterization of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel with High Toughness and Electric Conductivity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, S.; Cheng, Y.; Shao, Z.; Xiang, H.; Chen, G.; Zhu, L.; Weng, W.; Bai, H.; et al. Smart Fibers for Energy Conversion and Storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7009–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Yu, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Xia, Y. Versatile Liquid Metal/Alginate Composite Fibers with Enhanced Flame Retardancy and Triboelectric Performance for Smart Wearable Textiles. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2023, 10, e2303406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.U.; Mushtaq, B.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, S.; Rasheed, A.; Nawab, Y. Development of Conductive Cotton Non-Woven Alginate Hydrogel Composite for Smart Textiles. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 3998–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S. Enhanced Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell with Polyaniline/Sodium Alginate/Carbon Brush Hydrogel Bioanode and Removal of COD. Energy 2020, 202, 117780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, I.A.; Supriyanto, A.; Pauzi, G.A. The Microbial Fuel Cell Characteristics of the PVA/Chitosan Membrane with Variations of Phosphate Acid and Sodium Alginate Derived from Vegetable Waste. J. Energy, Mater. Instrum. Technol. 2023, 4, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Gai, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, L. The Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell with Sodium Alginate and Super Activated Carbon Composite Gel Modified Anode. AMB Express 2024, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ai, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wei, X. Electricity Production Performance Enhancement of Microbial Fuel Cells with Double-Layer Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Bioanodes Driven by High-Salinity Waste Leachate. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, K.A.; Siyal, A.A.; Wu, Y.; Abbasi, B.; Solangi, F.; Lakhiar, I.A.; Zhou, G. An Assessment of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Soil Salinity in Combination with Field and Satellite Data: A Case Study in Sujawal District. Agronomy 2019, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xing, D.; Zhang, K.; Xie, J.; Yu, R.; Chen, T.; Duan, R. Effects of Foliage Spraying with Sodium Bisulfite on the Photosynthesis of Orychophragmus Violaceus. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fu, W.; Li, Y. Investigating the Resistance Levels and Mechanisms to Penoxsulam and Cyhalofop-Butyl in Barnyardgrass (Echinochloa Crus-Galli) from Ningxia Province, China. Weed Sci. 2021, 69, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, B.; Wan, Y.; Gao, B.; Rajput, V.D. Alginate-Based Composites as Novel Soil Conditioners for Sustainable Applications in Agriculture: A Critical Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yu, S.; Xue, N.; Li, T.; Sun, M. Persulfate Activation with Sodium Alginate/Sulfide Coated Iron Nanoparticles for Degradation of Tetrabromobisphenol a in Soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 114820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Chen, M.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, B. Calcium Alginate-Biochar Composite as a Novel Amendment for the Retention and Slow-Release of Nutrients in Karst Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Preparation and Application of a Natural Microspheric Soil Conditioner Based on Gelatin, Sodium Alginate, and Zeolite. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 5211–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, F.; Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, J. Enhancing Soil Aggregation and Acetamiprid Adsorption by Ecofriendly Polysaccharides Hydrogel Based on Ca2+-Amphiphilic Sodium Alginate. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 113, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Dimension | Chemical Modification | Physical Modification | Biological Modification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modification effect | Strong functionalization and high stability | Simple, fast, and environmentally friendly | High biocompatibility and strong specificity |
| Cost | High (reagents, purification) | Low (no need for complex equipment) | Extremely high (enzyme/genetic engineering) |
| Technological difficulty | Complex (requiring precise control of reaction conditions) | Simple (easy to industrialize) | Complex (requiring biotechnological conditions) |
| Toxic risk | Harmful substances may remain | None | None |
| Application | Industrial adsorbents and functional materials | Food packaging, sustained-release carriers | Biomedical, tissue engineering |
| Cargo/System | Matrix and Method | Key Readouts | Use-Case | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine lactoferrin (LFNP) | EHDA nanoparticles in NaAlg matrix | Size ~ 100–200 nm; |ζ| ~ 20 mV; stable dispersions | Iron-delivery/antioxidant | [197] |
| Marjoram essential oil (EO) | SA + WPI (ionic gel) | EE/size tuned by SA/WPI/Ca2+; stable aroma retention | Antimicrobial flavor delivery | [192] |
| α-Tocopherol | SA beads (ionic gel) | Release ~ 29% (SGF) vs. ~82% (SIF); T50% ~ 3.8 h; T70% ~ 12.3 h (SIF) | Gastric protection; intestinal delivery | [191] |
| Probiotics (Lactobacillus spp.) | Fish-gelatin/SA double-network (FG/SA-DN) | Encapsulation efficiency ~16%→~92% (FG ↑); GI/thermal survival ↑ | Fermented/baked foods | [195] |
| Technology | Key Advantages | Major Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane separation | Minimal chemical usage, compact system footprint, selective metal recovery | High membrane procurement cost, frequent fouling issues, restricted throughput capacity | [220] |
| Electrochemical recovery | High-purity metal recovery, ambient condition compatibility | Intensive energy demand, slow reaction kinetics, potential electrolyte contamination | [221] |
| Chemical precipitation | Simplified operational workflow, low infrastructure cost | Excessive sludge yield (high disposal burden), non-selective removal, risk of secondary contamination | [222] |
| Ion-exchange | Targeted metal binding capability, high regeneration efficiency | Elevated upfront investment, narrow pH operating range, recurrent maintenance expenses | [223] |
| SA (Ca2+-crosslinked) hydrogel beads | Abundant carboxylate groups for chelation; low cost; biocompatible; easy beadization; regenerable with mild eluents | Gel swelling/softening; dissolution at low pH or chelating eluents; limited selectivity; intraparticle diffusion limits | [224] |
| Magnetic SA/Fe3O4 beads | Rapid magnetic separation; easy recovery and reuse; good dispersion | Fe3O4 oxidation/leaching; capacity decay across cycles; acid instability; added material cost | [225] |
| SA–biochar/zeolite/clay hybrids | Low-cost supports; improved permeability and strength; resilience to turbidity | Batch-to-batch variability; competing ions; fines shedding | [226] |
| Thiol-functionalized SA (–SH, dithiocarbamate) | High selectivity for soft metal ions (e.g., Hg2+, Ag+, Pb2+, Cd2+) | Thiol oxidation; odor; multi-step synthesis; cost | [227] |
| Amine/EDA/PEI-functionalized SA | Strong complexation with Cu2+/Ni2+/Cr (VI); rapid kinetics | Amine protonation at low pH reduces capacity; polymer leaching; fouling | [228] |
| Phosphate/phosphonate-modified SA | High affinity for Pb2+, rare earths; improved selectivity in competing electrolytes | Synthesis complexity; potential ligand leaching; cost | [229] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Dabbour, M.; Dai, C.; Zhou, M.; He, R. Sodium Alginate Modifications: A Critical Review of Current Strategies and Emerging Applications. Foods 2025, 14, 3931. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223931
Wang W, Huang Y, Pan Y, Dabbour M, Dai C, Zhou M, He R. Sodium Alginate Modifications: A Critical Review of Current Strategies and Emerging Applications. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3931. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223931
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenning, Yuanyuan Huang, Yun Pan, Mokhtar Dabbour, Chunhua Dai, Man Zhou, and Ronghai He. 2025. "Sodium Alginate Modifications: A Critical Review of Current Strategies and Emerging Applications" Foods 14, no. 22: 3931. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223931
APA StyleWang, W., Huang, Y., Pan, Y., Dabbour, M., Dai, C., Zhou, M., & He, R. (2025). Sodium Alginate Modifications: A Critical Review of Current Strategies and Emerging Applications. Foods, 14(22), 3931. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223931






