The Effect of Furcellaran Addition and High-Pressure Homogenization Process on the Physicochemical, Rheological and Sensory Properties of Chocolate Milk Drinks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Manufacture of Chocolate Milk Drinks
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.3.1. pH and Dry Matter Content Determination of the Chocolate Milk Drinks
2.3.2. Total Soluble Solids
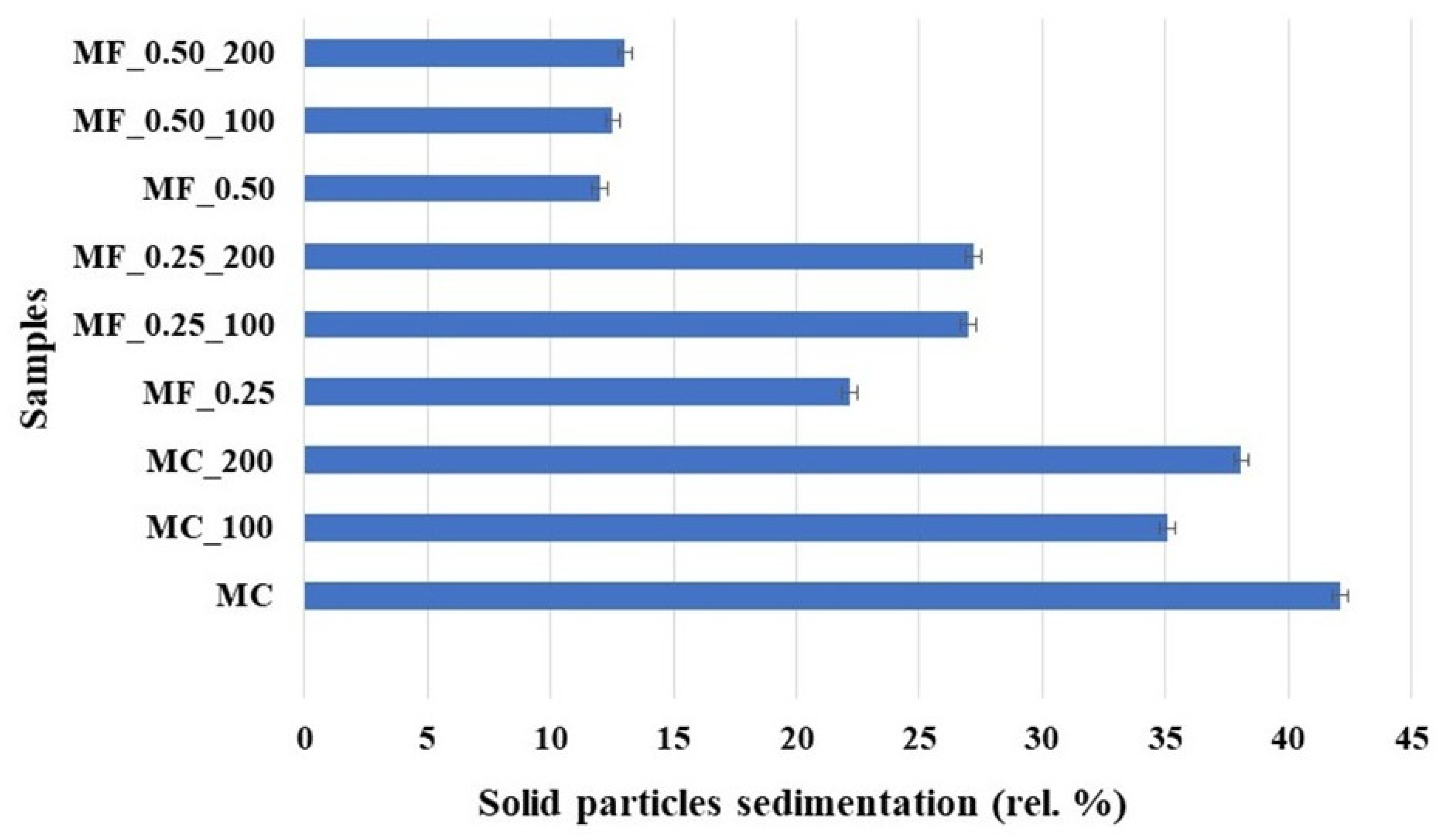
2.3.3. Solid Particle Sedimentation
2.4. Rheological Analysis
2.5. Sensory Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Psychicochemical Analysis
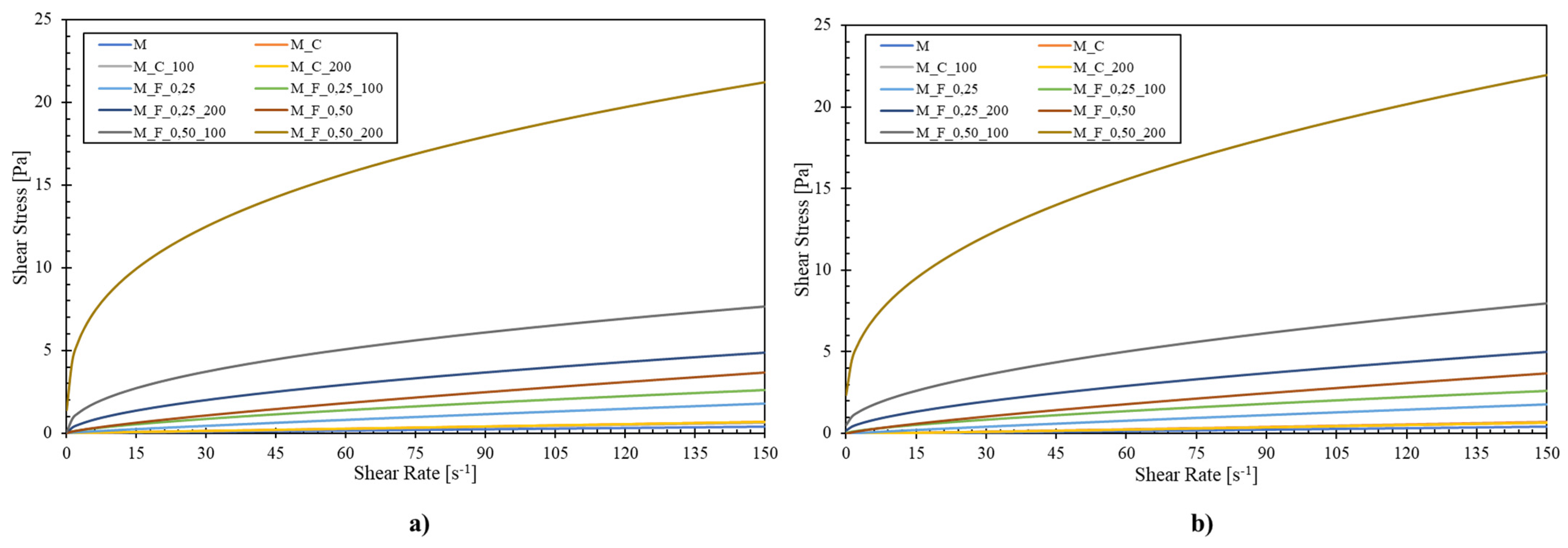
3.2. Rheological Analysis
3.3. Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özer, B.H.; Kirmaci, H.A. Functional milks and dairy beverages. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.M.; Douglass, J.S.; Johnson, R.K.; Spence, L.A. Drinking flavored or plain milk is positively associated with nutrient intake and is not associated with adverse effects on weight status in US children and adolescents. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, S.E.; Ness, A.R.; Northstone, K.; Emmett, P.; Newby, P.K. Associations between flavored milk consumption and changes in weight and body composition over time: Differences among normal and overweight children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, A.J.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Fermented beverages with health-promoting potential: Past and future perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneser, O.; Hosoglu, M.I.; Guneser, B.A.; Yuceer, Y.K. Engineering of milk-based beverages: Current status, developments, and consumer trends. In Milk-Based Beverages; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Pushpadass, H.A.; Emerald, F.M.E.; Balasubramanyam, B.V.; Patel, S.S. Rheological properties of milk-based beverages. In Milk-Based Beverages; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 373–396. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, S.A.; Icyer, N.C.; Karaca, A.C.; Bekiroglu, H.; Sagdic, O.; Toker, O.S. Determination of stabilizer concentration and process effect on the stability of milk-based cocoa beverage. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V. A critical review on the possible remediation of sediment in cocoa/coffee flavored milk. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M. Liquid milk products: Modified Milks. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Barišić, V.; Icyer, N.C.; Akyil, S.; Toker, O.S.; Flanjak, I.; Ačkar, Đ. Cocoa based beverages–Composition, nutritional value, processing, quality problems and new perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Voronin, G.L.; Roberts, R.F.; Coupland, J.N.; Ziegler, G.R.; Harte, F.M. The effect of high-pressure jet processing on cocoa stability in chocolate milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 11432–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hege, J.; Palberg, T.; Vilgis, T.A. Interactions of different hydrocolloids with milk proteins. J. Phys. Mater. 2020, 3, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S. Relating the tribo-rheological properties of chocolate flavoured milk to temporal aspects of texture. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 110, 104794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanes, M.; Durán, L.; Costell, E. Effect of hydrocolloid type and concentration on flow behaviour and sensory properties of milk beverages model systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Jafari, S.M. Recent advances in application of different hydrocolloids in dairy products to improve their techno-functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejdlová, A.; Vašina, M.; Lorencová, E.; Hružík, L.; Salek, R.N. Assessment of different levels of blackcurrant juice and furcellaran on the quality of fermented whey-based beverages using rheological and mechanical vibration damping techniques. Foods 2024, 13, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kůrová, V.; Salek, R.N.; Černíková, M.; Lorencová, E.; Zalešáková, L.; Buňka, F. Furcellaran as a substitute for emulsifying salts in processed cheese spread and the resultant storage changes. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2022, 75, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, L.M.; Vieira, R.P.; Jamróz, E.; Anjos, C.A.R. Furcellaran: An innovative biopolymer in the production of films and coatings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluri, M.; Kaljuvee, K.L.; Paalme, T.; Reile, I.; Tuvikene, R. Structural variability and rheological properties of furcellaran. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.C.; Ningtyas, D.W.; Geoffroy, Z.; Prakash, S. Protein-based hydrocolloids: Effect on the particle size distribution, tribo-rheological behaviour and mouthfeel characteristics of low-fat chocolate flavoured milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelany, M.A.; Rashwan, A.K.; Kabil, D.I.; Abdelshafy, A.M.; Osman, A.I.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Yemis, O. Effect of High-Pressure Homogenization Optimized by Response Surface Methodology on the Techno-Functional Properties of Protein Concentrate Isolated from Date Seed. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Monteagudo, S.I.; Yan, B.; Balasubramaniam, V.M. Engineering process characterization of high-pressure homogenization—From laboratory to industrial scale. Food Eng. Rev. 2017, 9, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, J.; Muhrer, G.; Mazzotti, M. High pressure homogenization of pharmaceutical solids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 66, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.S.; Kale, K. High pressure homogenizer in pharmaceuticals: Understanding its critical processing parameters and applications. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diels, A.M.; Michiels, C.W. High-pressure homogenization as a non-thermal technique for the inactivation of microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 32, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, F.; Lanciotti, R. Applications of high and ultra high pressure homogenization for food safety. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6731:2010; Milk, Cream and Evaporated Milk—Determination of Total Solids Content (Reference Method). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Coutinho, N.M.; Silveira, M.R.; Pimentel, T.C.; Freitas, M.Q.; Moraes, J.; Fernandes, L.M.; Cruz, A.G. Chocolate milk drink processed by cold plasma technology: Physical characteristics, thermal behavior and microstructure. LWT 2019, 102, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8589:2007; Sensory Analysis—General Guidance for the Design of Test Rooms. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Jenkins, T.C.; McGuire, M.A. Major advances in nutrition: Impact on milk composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, O.; Saricaoglu, F.T.; Mortas, M.; Atalar, I.; Yazici, F. Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on microstructure and rheological properties of hazelnut milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, N.; Chafer, M.; Rodriguez-Garcia, J.; Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C. Effect of high pressure homogenisation and heat treatment on physical properties and stability of almond and hazelnut milks. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.H.; Delshadian, Z.; Arefhosseini, S.R.; Alipour, B.; Jafarabadi, M.A. Effect of inulin and stevia on some physical properties of chocolate milk. Health Promot. Perspect. 2012, 2, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shchipunov, Y.A.; Chesnokov, A.V. Carrageenan gels in skim milk: Formation and rheological properties. Colloid J. 2003, 65, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Lucia, F.; Do Carmo, J.R.; Morais, C.S.N.; Nunes, C.A.; Pinheiro, A.C.M.; Ferreira, E.B.; Vilas Boas, E.V.D.B. Physicochemical and sensory quality of several commercial Brazilian chocolate milk beverages. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2016, 69, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, H.D.; Guo, Q. The role of hydrocolloids in the development of food structure. In Handbook of Food Structure Development; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Sala, G.; Scholten, E. Role of polysaccharide structure in the rheological, physical and sensory properties of low-fat ice cream. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushbu, S.; Sunil, C.K. Effect of particle size, concentration, temperature and pH on rheological properties of shallots flour. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codina-Torrella, I.; Guamis, B.; Ferragut, V.; Trujillo, A.J. Potential application of ultra-high-pressure homogenization in the physico-chemical stabilization of tiger nuts’ milk beverage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 40, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhäuser, J.; Hale, J.; Wefers, D.; Gaukel, V. Furcellaran: Impact of concentration, rheological properties, and structure on ice recrystallization inhibition activity. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 4535–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample * | HPH | Milk | Sugar | Cocoa Powder | Furcellaran |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | (% w/w) | (% w/w) | (% w/w) | (% w/w) | |
| MC | - | 88.5 | 10 | 1.5 | 0 |
| MC_100 | 10 | 88.5 | 10 | 1.5 | 0 |
| MC_200 | 20 | 88.5 | 10 | 1.5 | 0 |
| MF_0.25 | - | 88.25 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.25 |
| MF_0.25_100 | 10 | 88.25 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.25 |
| MF_0.25_200 | 20 | 88.25 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.25 |
| MF_0.50 | - | 88.0 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.50 |
| MF_0.50_100 | 10 | 88.0 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.50 |
| MF_0.50_200 | 20 | 88.0 | 10 | 1.5 | 0.50 |
| Sample * | Dry Matter Content (% w/w) | pH | TSS (°Bx) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | 12.96 ± 0.06 a | 6.76 ± 0.01 a | nd *** |
| M_C | 23.35 ± 0.01 b | 6.71 ± 0.01 a | 20.75 ± 0.02 a |
| MC_100 | 23.31 ± 0.03 b | 6.75 ± 0.02 a | 21.53 ± 0.03 b |
| MC_200 | 23.37 ± 0.01 b | 6.77 ± 0.01 a | 22.02 ± 0.01 c |
| MF_0.25 | 23.52 ± 0.03 c | 6.76 ± 0.01 a | 22.27 ± 0.02 c |
| MF_0.25_100 | 23.55 ± 0.04 c | 6.80 ± 0.01 a | 22.61 ± 0.01 c |
| MF_0.25_200 | 23.52 ± 0.02 c | 6.82 ± 0.01 a | 22.83 ± 0.02 c |
| MF_0.50 | 23.68 ± 0.08 c | 6.79 ± 0.02 a | 23.05 ± 0.03 d |
| MF_0.50_100 | 23.65 ± 0.01 c | 6.80 ± 0.01 a | 23.26 ± 0.01 d |
| MF_0.50_200 | 23.61 ± 0.01 c | 6.81 ± 0.01 a | 23.79 ± 0.02 d |
| Power-Law Model | Herschel–Bulkley Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample * | K [Pa·s] | n [-] | R2 [-] | τ0 | K [Pa·s] | n [-] | R2 [-] |
| M | 0.002 a | 1.05 a | 0.999 | 0.0008 a | 0.002 a | 1.07 a | 0.999 |
| M_C | 0.003 b | 1.06 a | 0.999 | 0.0009 b | 0.003 a | 1.07 a | 0.999 |
| M_C_100 | 0.003 b | 1.05 a | 0.999 | 0.0011 c | 0.003 a | 1.08 a | 0.999 |
| M_C_200 | 0.004 c | 1.03 a | 0.999 | 0.0021 d | 0.003 a | 1.07 a | 0.999 |
| M_F_0.25 | 0.022 d | 0.88 b | 0.999 | 0.0006 e | 0.021 b | 0.88 b | 0.999 |
| M_F_0.25_100 | 0.082 e | 0.69 c | 0.996 | 0.0171 f | 0.073 c | 0.71 c | 0.998 |
| M_F_0.25_200 | 0.031 f | 0.55 d | 0.995 | 0.1529 g | 0.222 d | 0.62 d | 0.999 |
| M_F_0.50 | 0.079 h | 0.77 e | 0.999 | 0.0044 h | 0.075 e | 0.78 c | 0.999 |
| M_F_0.50_100 | 0.814 i | 0.45 f | 0.988 | 0.5086 i | 0.482 f | 0.55 e | 0.999 |
| M_F_0.50_200 | 4.072 j | 0.33 g | 0.985 | 1.7271 j | 2.538 g | 0.41 f | 0.999 |
| Sample * | Appearance | Flavor | Thickness | Powderiness | Off-Flavor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | 2 a | 3 a | 2 a | 1 a | 5 a |
| MC_100 | 4 a | 4 b | 3 b | 3 b | 5 a |
| MC_200 | 3 b | 4 b | 3 b | 3 b | 5 a |
| MF_0.25 | 3 b | 3 a | 3 b | 3 b | 5 a |
| MF_0.25_100 | 4 c | 4 b | 4 c | 4 c | 5 a |
| MF_0.25_200 | 4 c | 4 b | 5 d | 4 c | 5 a |
| MF_0.50 | 4 c | 3 a | 4 c | 4 c | 5 a |
| MF_0.50_100 | 5 d | 5 c | 5 d | 5 d | 5 a |
| MF_0.50_200 | 5 d | 5 c | 5 d | 5 d | 5 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rejdlová, A.; Kůrová, V.; Lorencová, E.; Lazárková, Z.; Cmajdálková, L.; Zálešáková, L.; Nastaj, M.; Sołowiej, B.G.; Pětová, M.; Kašparovský, T.; et al. The Effect of Furcellaran Addition and High-Pressure Homogenization Process on the Physicochemical, Rheological and Sensory Properties of Chocolate Milk Drinks. Foods 2025, 14, 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223872
Rejdlová A, Kůrová V, Lorencová E, Lazárková Z, Cmajdálková L, Zálešáková L, Nastaj M, Sołowiej BG, Pětová M, Kašparovský T, et al. The Effect of Furcellaran Addition and High-Pressure Homogenization Process on the Physicochemical, Rheological and Sensory Properties of Chocolate Milk Drinks. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223872
Chicago/Turabian StyleRejdlová, Anita, Vendula Kůrová, Eva Lorencová, Zuzana Lazárková, Lucie Cmajdálková, Ludmila Zálešáková, Maciej Nastaj, Bartosz G. Sołowiej, Markéta Pětová, Tomáš Kašparovský, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of Furcellaran Addition and High-Pressure Homogenization Process on the Physicochemical, Rheological and Sensory Properties of Chocolate Milk Drinks" Foods 14, no. 22: 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223872
APA StyleRejdlová, A., Kůrová, V., Lorencová, E., Lazárková, Z., Cmajdálková, L., Zálešáková, L., Nastaj, M., Sołowiej, B. G., Pětová, M., Kašparovský, T., & Salek, R. N. (2025). The Effect of Furcellaran Addition and High-Pressure Homogenization Process on the Physicochemical, Rheological and Sensory Properties of Chocolate Milk Drinks. Foods, 14(22), 3872. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223872











