Assessment of Phenotypic Characteristics, Polysaccharide Composition, and Hypoglycemic Potential in Different Commercial Grades of Lycium barbarum: A Comprehensive Study Using HPLC and NMR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Classification of L. barbarum Samples Based on Refined Commercial Grades
2.3. Measurement of Phenotypic Characteristics
2.4. Extraction and Quantification of Polysaccharides
2.5. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
2.6. 1H NMR Analysis
2.7. In Vitro Hypoglycemic Activity Assessment
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
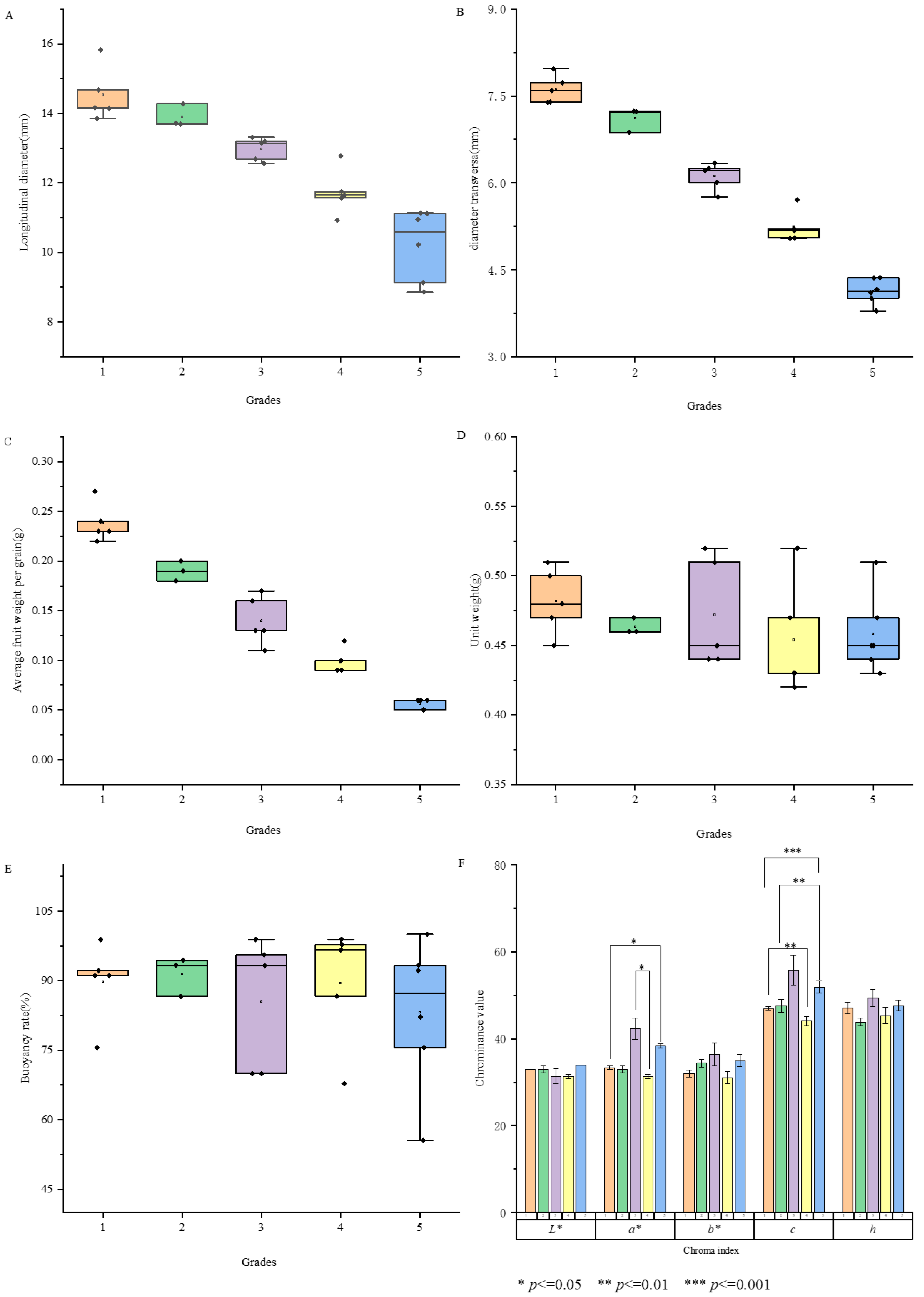
3.1. Phenotypic Analysis of Various L. barbarum Fruit Grades
3.2. LBPs Content Analysis
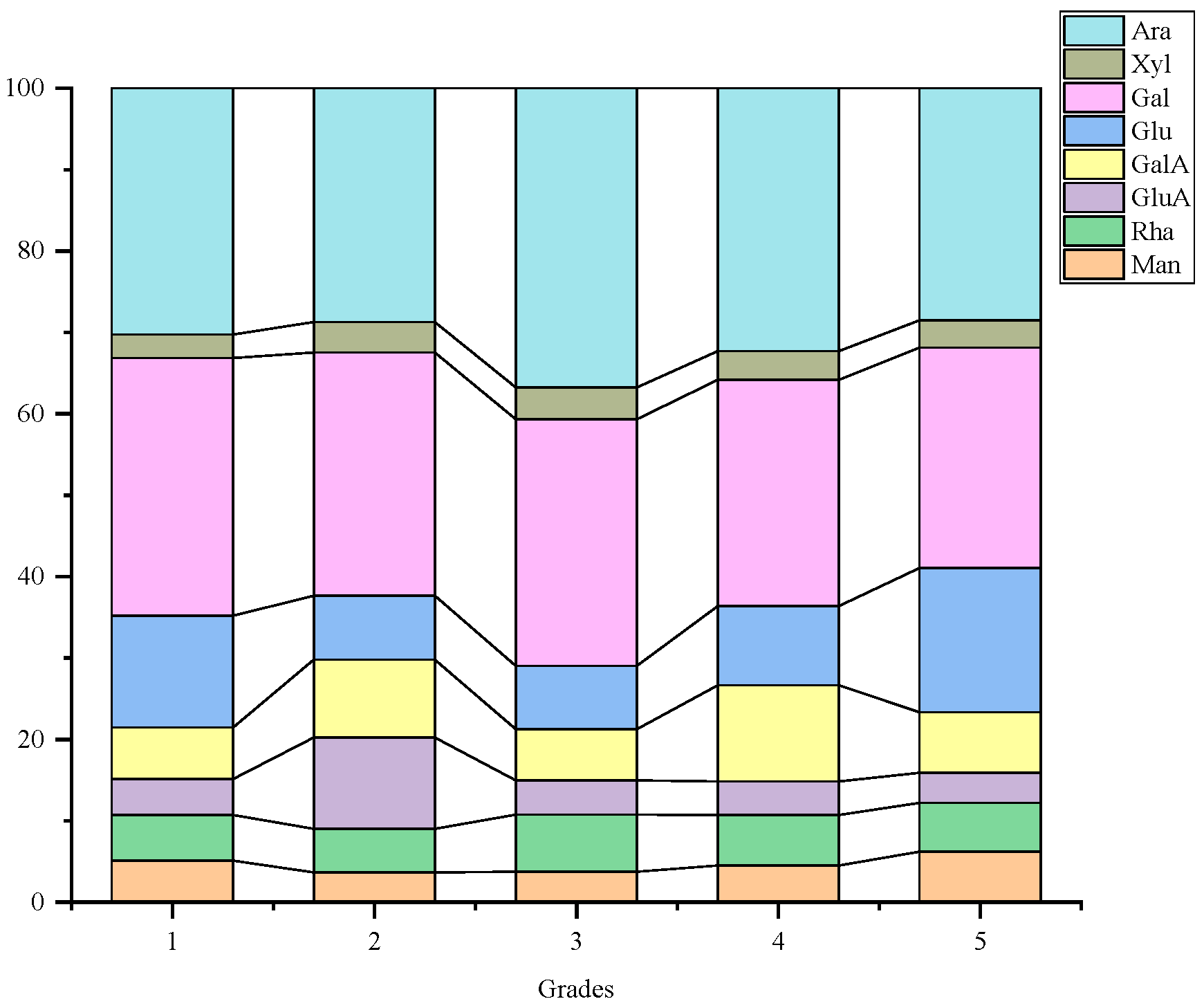
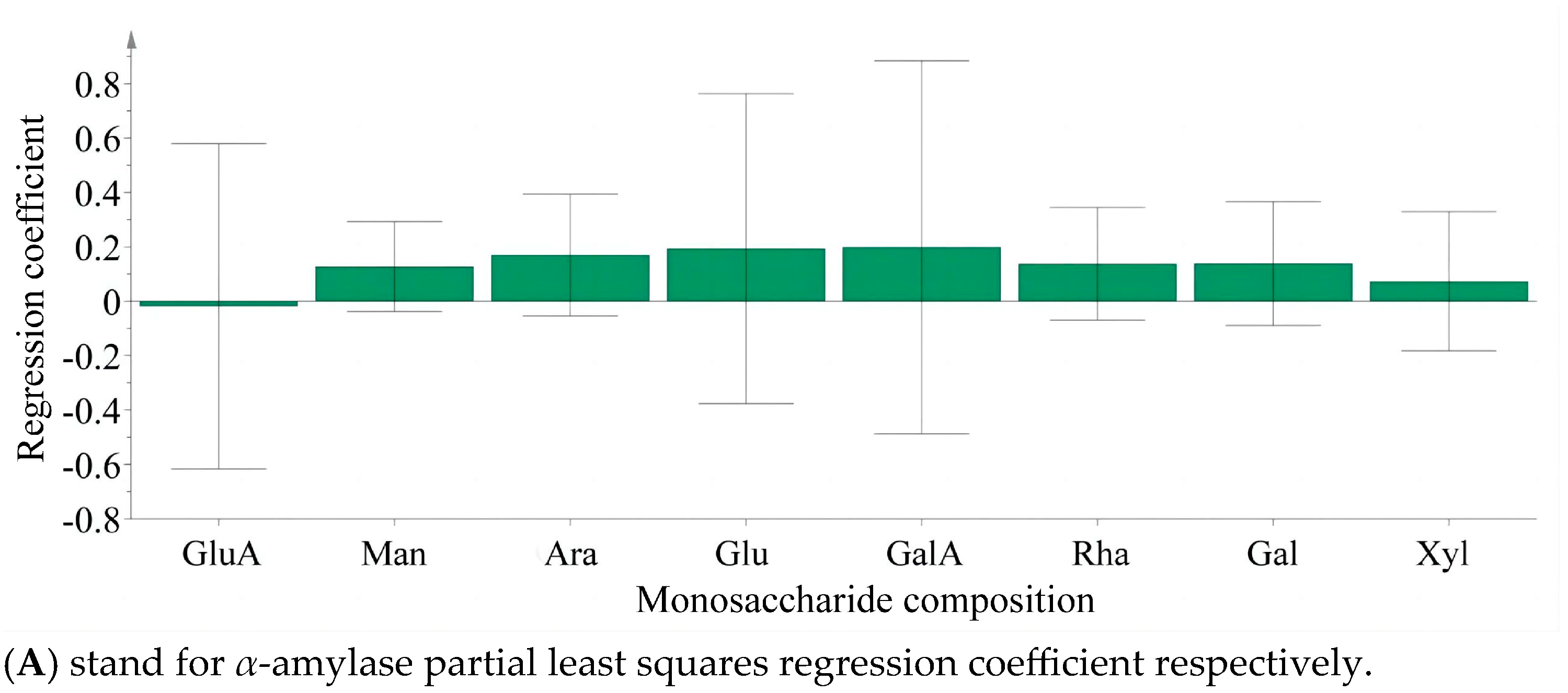
3.3. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of LBPs
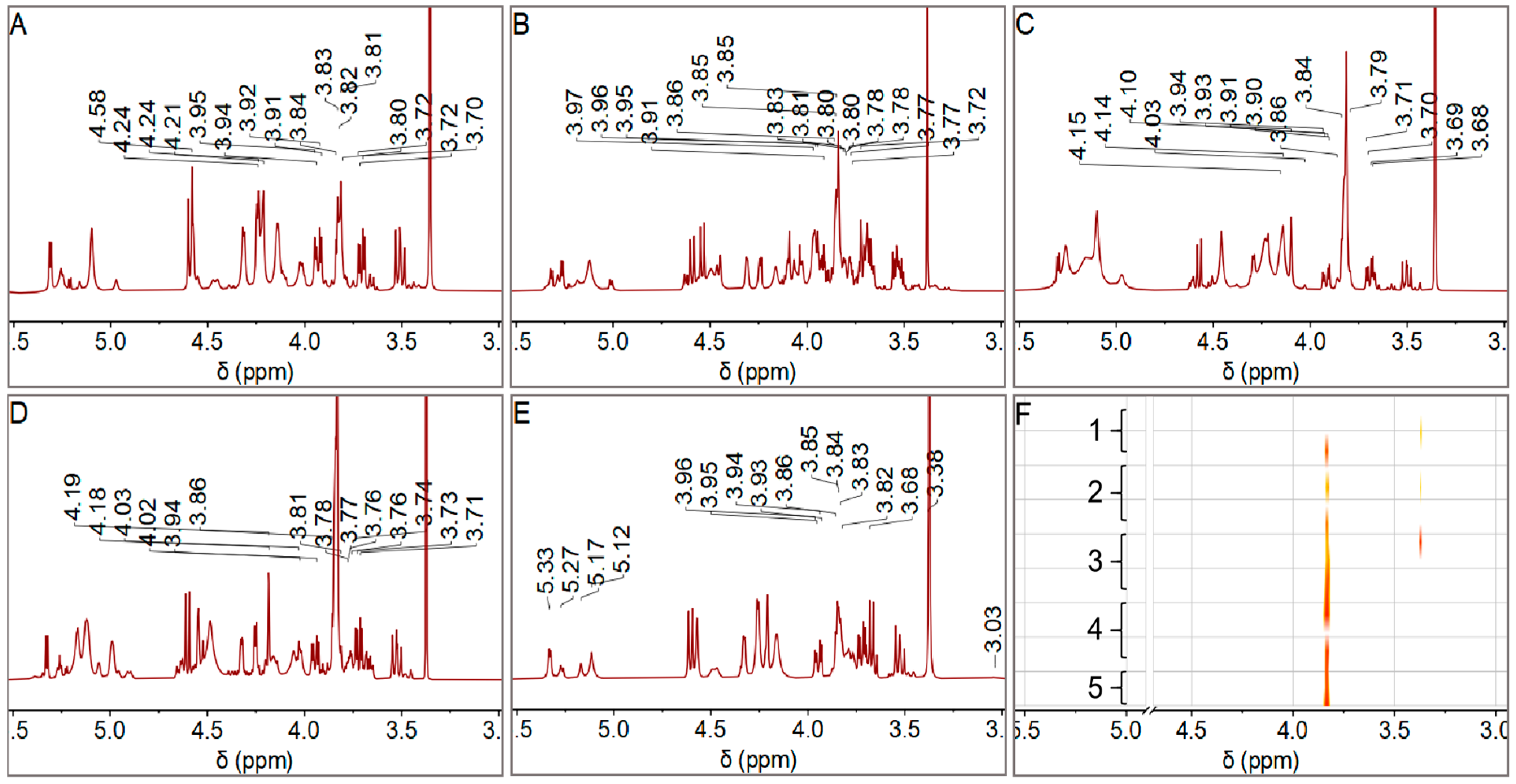
3.4. NMR Analysis
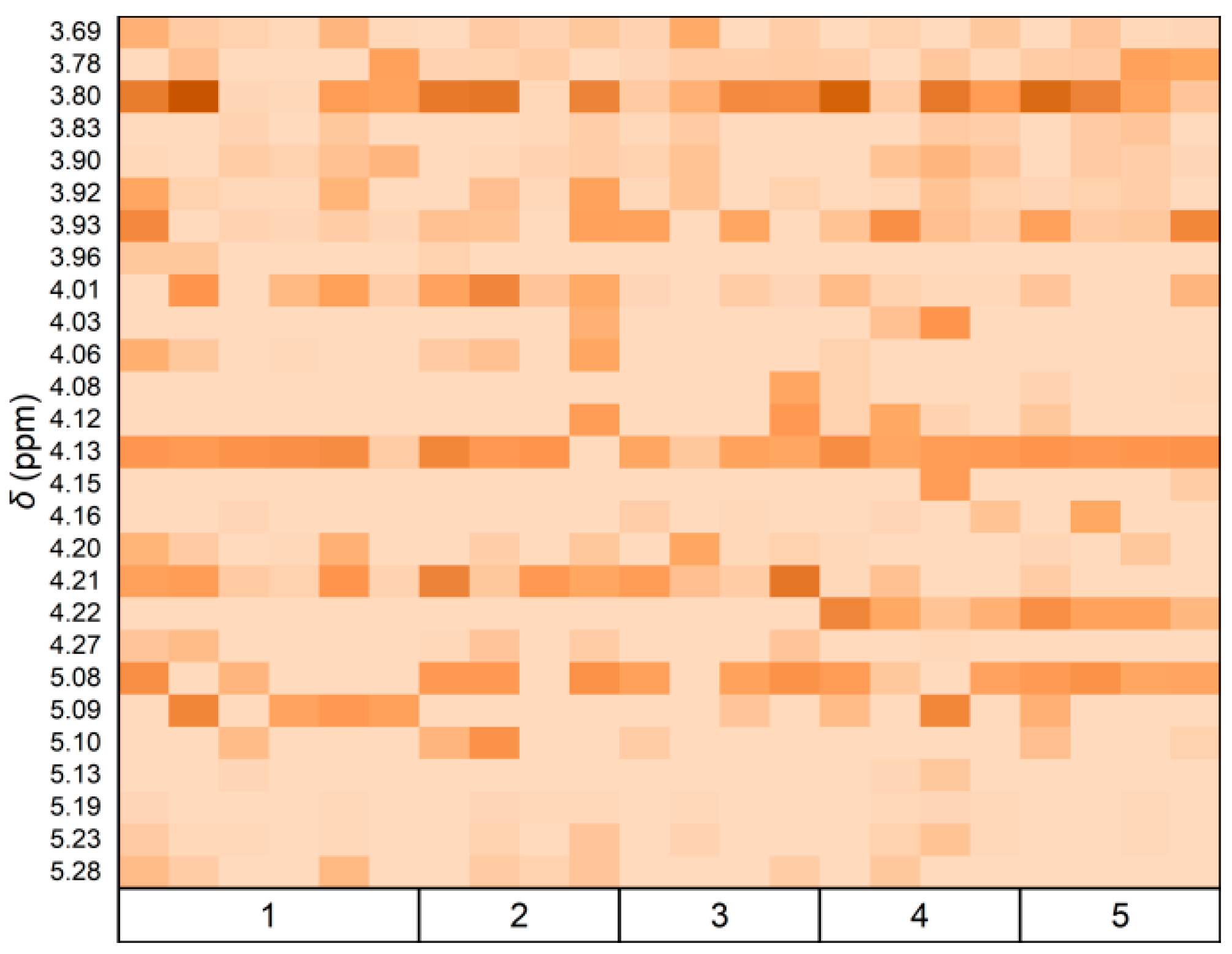
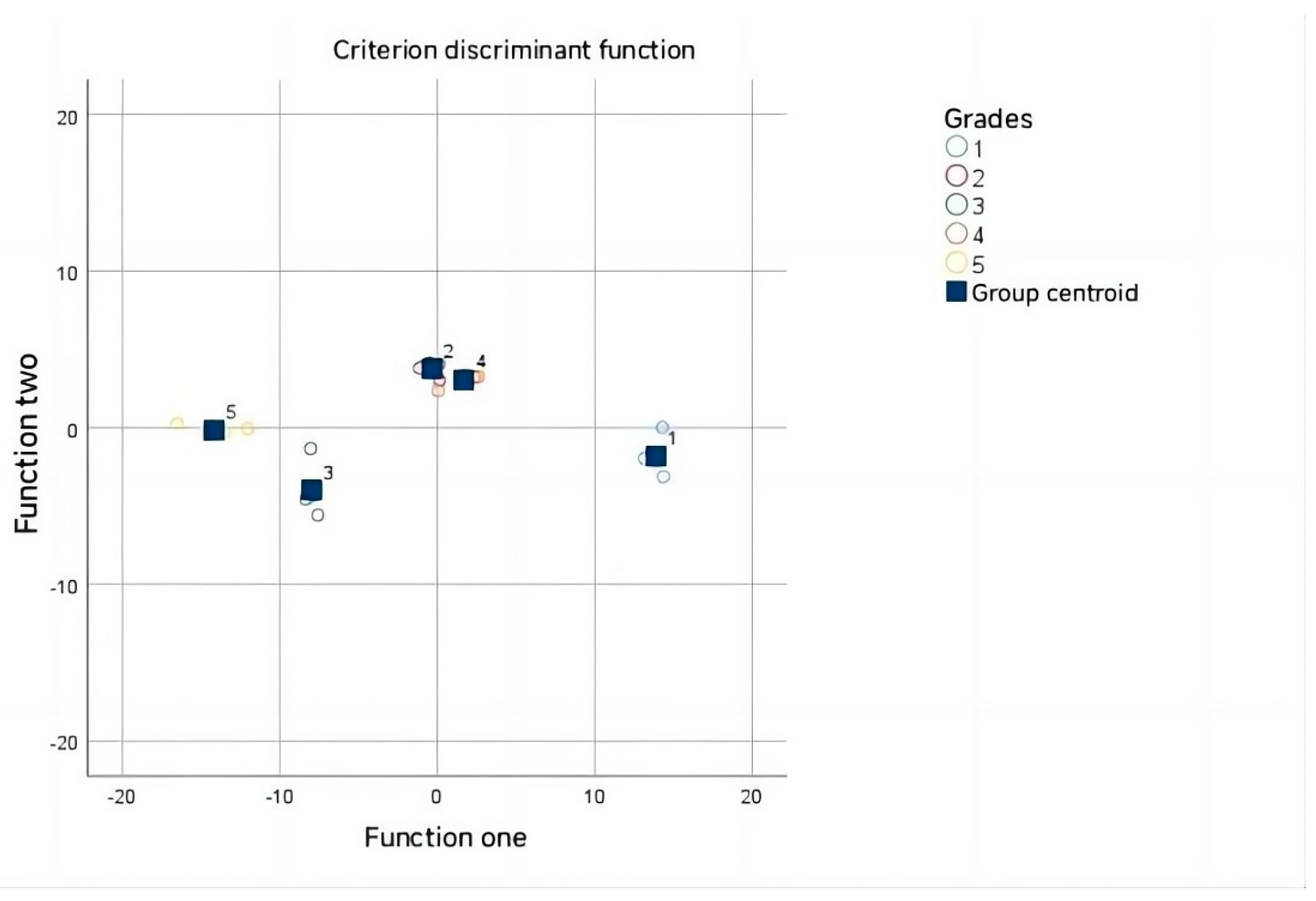
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Fruit Grades and 1H NMR Data
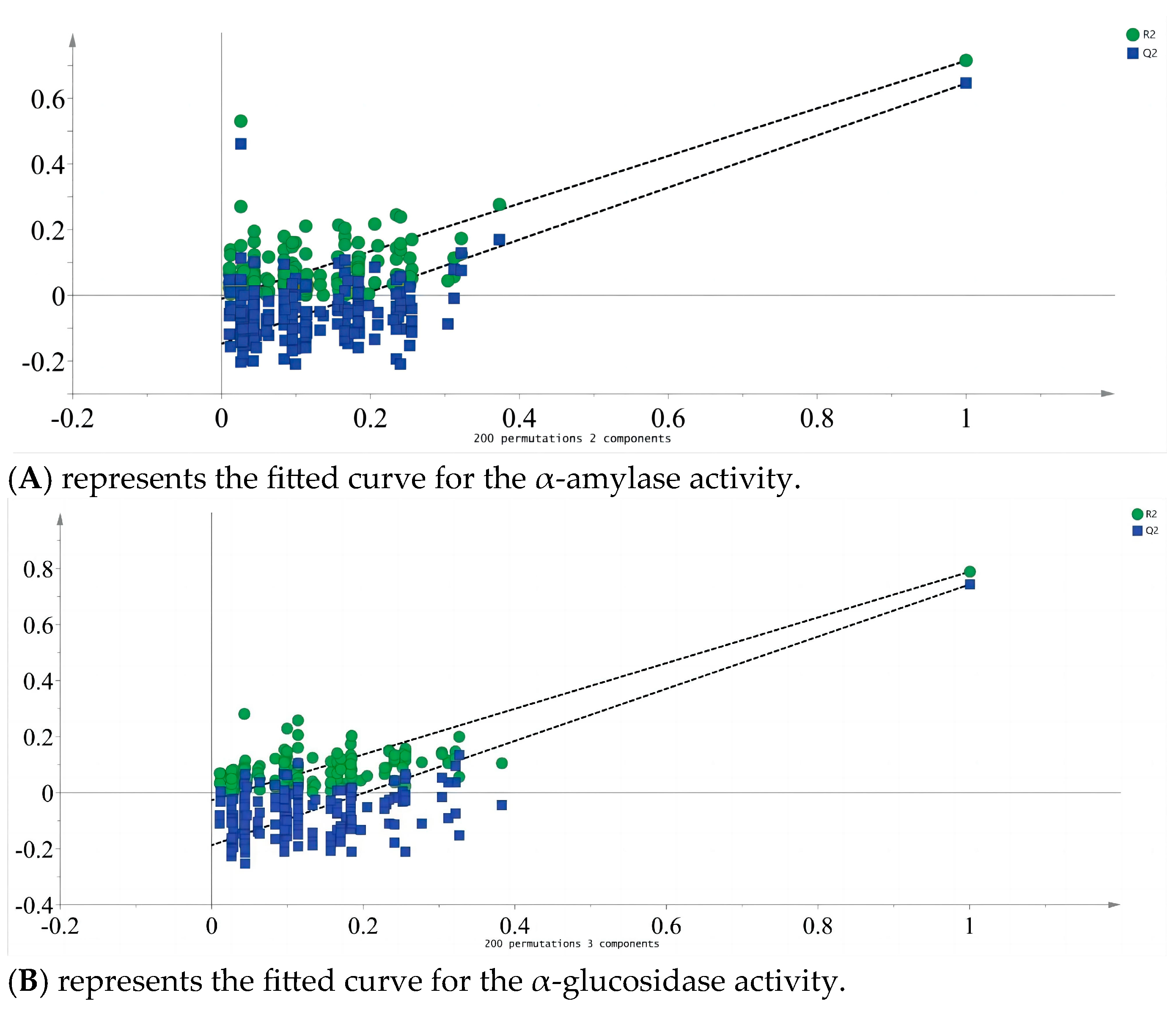
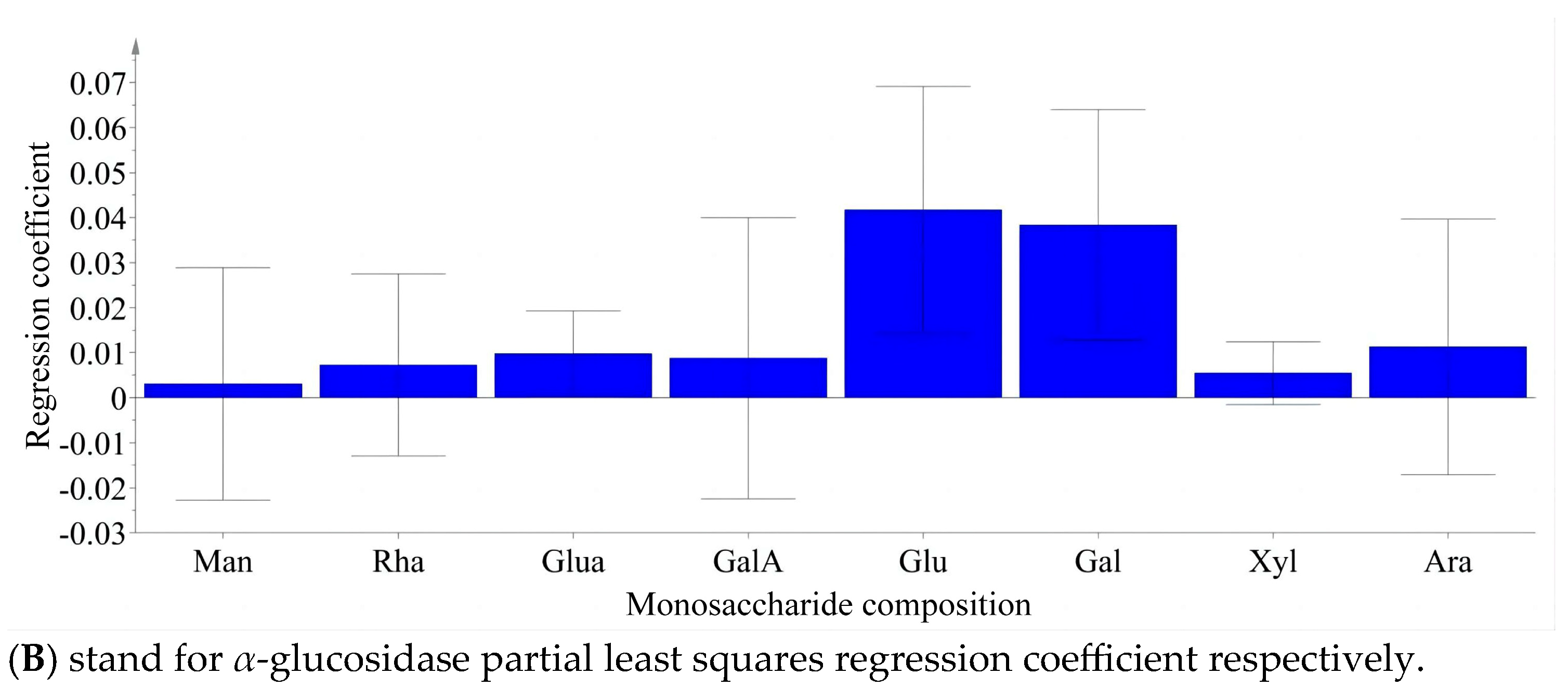
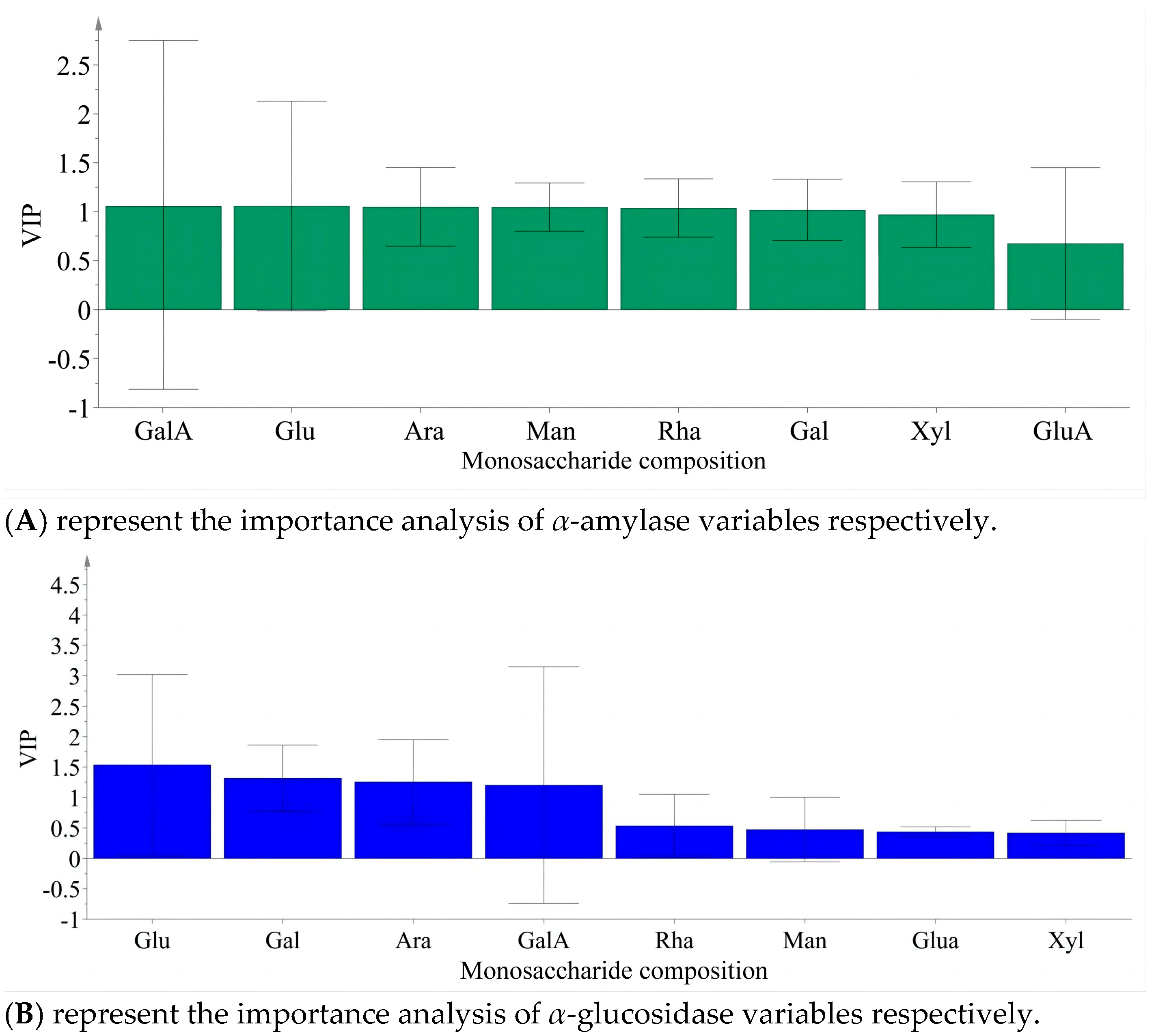
3.6. In Vitro Hypoglycemic Activity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magalhães, V.; Silva, A.R.; Silva, B.; Zhang, X.; Dias, A.C.P. Comparative studies on the anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant activities of black and red goji berries. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 92, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.; Silva, A.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Lycium barbarum Berries (Solanaceae) as Source of Bioactive Compounds for Healthy Purposes: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.F.; Zhang, H.; Teh, S.S.; Wang, C.W.; Zhang, Y.; Hayford, F.; Wang, L.; Ma, T.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Goji Berries as a Potential Natural Antioxidant Medicine: An Insight into Their Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2437397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, G.; Xin, N.; Liu, W.; Yao, H.; Hou, Y.; Qi, J. Inhibitory effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on cell apoptosis and senescence is potentially mediated by the p53 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. A review of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, structural-property relationships, and bioactive molecular mechanisms. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 544, 109230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 18672-2014; Standardization Administration of China: Wolfberry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Kafkas, N.E.; Oğuz, H.İ.; Oğuz, İ. Evaluation of fruit characteristics of various organically-grown goji berry (Lycium barbarum L., Lycium chinense Miller) species during ripening stages. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 101, 103846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, T.; Cao, Y.; An, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Qin, K.; Wang, X.; et al. Effect of potassium on the agronomic traits and fruit quality of Goji (Lycium barbarum L.). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Zhao, J. A novel quantitative evaluation strategy of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum L. fruits based on simultaneous quantification of total polysaccharides and polysaccharides with active structure characteristics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 229, 121023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, A.; Carradori, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Paolicelli, P.; Petralito, S.; Ragno, R.; Cesa, S. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, structural characterisation and evidence about hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic effects. A review. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.J.; Liu, F.L.; Zhang, Q.L.; He, J.J.; Li, F.Y.; Jin, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.H. Comparative analysis of the content of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide in Lycii Fructus from different places. W. China J. Pharm. 2020, 35, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Pei, D.; Liu, J.F.; Gong, Y.; Wang, M.H.; Di, D.L.; Guo, M. The study of HPLC fingerprint and chemical pattern recognition of Lycii fructus. Res. Dev. Nat. Prod. 2019, 31, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, M.; Tang, D.; Shi, Y. Composition of Carotenoids and Flavonoids in Narcissus Cultivars and their Relationship with Flower Color. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 142074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.G.; Wu, Z.G.; Yang, M.J.; Liu, J.; Li, H.R.; Hu, Z.Q.; Wang, Y. Feasibility Study on Identification of Producing Areas of Lycium barbarum with Moisture Absorption Rate and Floating Rate. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2020, 28, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J. Study on Main Economic Characters and Effective Components of Lycium barbarum L. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Luo, Y.; Sang, Y.; Kan, J. Isolation, purification, structural characterization, and hypoglycemic activity assessment of polysaccharides from Hovenia dulcis (Guai Zao). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redgwell, R.J.; Curti, D.; Wang, J.; Dobruchowska, J.M.; Gerwig, G.J.; Kamerling, J.P.; Bucheli, P.J.C.P. Cell wall polysaccharides of Chinese Wolfberry (Lycium barbarum): Part 2. Characterisation of arabinogalactan-proteins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: A Determination of Wolfberry Content; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 260–261.
- Yan, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Neutral monosaccharide composition analysis of plant-derived oligo- and polysaccharides by high performance liquid chromatography. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, C. Structural elucidation and anti-osteoporosis activities of polysaccharides obtained from Curculigo orchioides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 203, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, Z.; Men, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Activity Assay of Amylase and Xylanase Is Available for Quantitative Assessment of Strain Aging in Cultivated Culinary-Medicinal Morchella Mushrooms (Ascomycotina). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2023, 25, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, C.W.; Lee, J.I.; Vinh, L.B.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, I.S. An investigation of the inhibitory mechanism of α-glucosidase by chysalodin from Aloe vera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 35864-2018; State Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine State Standardization Administration Committee: Grain and Oil Inspection Bulk Weight Determination. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Yan, Y.M.; Mi, J.; Zhang, F.F.; Yu, J.; Ma, L.W.; Zhang, Z.L.; Dai, G.L.; Lu, L.; Cai, S.Q.; Qin, K. Study on the correlation between phenotype characters and main nutrient contents of dried fruits of Lycium barbarum L. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 1–16. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/10.1151.TS.20240918.1043.002 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Gao, X.X.; Wang, B.; Lin, Q.X.; Liang, W.L.; Kang, Z.Y.; Guo, C.D.; Wu, Z.B. Research on the Connotation of Different Commodity Grades and Specifications of Lycium barbarum Fruit in Xinjiang. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 162–166+192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Tian, L.; Liu, D. Exploring the mechanism of Lycium barbarum fruit cell wall polysaccharide remodeling reveals potential pectin accumulation contributors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 258, 128958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.A.; Liu, S.J.; Hou, S.Y.; Ge, Y.Y.; Xia, B.H.; Xie, M.X. Metabolomics distinguishes different grades of Scrophularia ningpoensis hemsl: Towards a biomarker discovery and quality evaluation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, Y.; Lou, W.; Wang, B.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Di, D. Mechanism regulating the inhibition of lung cancer A549 cell proliferation and structural analysis of the polysaccharide Lycium barbarum. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, T.; Wan, F.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Ma, L. Structural characterization of a polysaccharide from Lycium barbarum and its neuroprotective effect against β-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, N.; Ma, L.; Pei, D.; Di, D.; Liu, J. Polysaccharides from different cultivars of wolfberry: Physicochemical characteristics and protection against oxidative stress. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.Y.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Yin, J.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Xie, M.Y. A review of NMR analysis in polysaccharide structure and conformation: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Guo, Q. Fisher Discrimination Method and Its Application. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2008, 43, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, N. Information point: Wilks’ lambda. J. Clin. Nurs. 2000, 9, 381. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, H.; Kuma, C.; Iseri, T.; Matsumura, S.-I.; Kawase, A.; Matsuura, M.; Iwaki, M. Inhibitory Effect of Ocimum gratissimum Leaf Extract on Postprandial Increase of Blood Glucose. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, R.; Zuo, G.; Liu, J.; Di, D.; Guo, M. Structural properties and hypoglycaemic activity of polysaccharides extracted from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. using various extraction media. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Gong, G.; Huang, L. Revisiting the structure of arabinogalactan from Lycium barbarum and the impact of its side chain on anti-ageing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 286, 119282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Feng, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Qi, X.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M. Exploring the competitive inhibition of α-glucosidase by citrus pectin enzymatic hydrolysate and its mechanism: An integrated experimental and simulation approach. Food Chem. 2024, 464, 141819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-L.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.-K.; Sun, G.-J. Biochemical analysis and hypoglycemic activity of a polysaccharide isolated from the fruit of Lycium barbarum L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q. Differential regulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide components in cyclophosphamide-treated immunosuppressed mice: Reshaping of the gut microbiota. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2025, 11, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Wu, E.; Deng, X. Potential of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism disorders: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Zhang, W. Synthesis of New Coumarin Compounds and Its Hypoglycemic Activity and Structure-Activity Relationship. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 9835–9839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yan, Y.; Hou, C.; Shi, M.; Liu, Y. Structural characterization of a galacturonic acid-rich polysaccharide from Ziziphus Jujuba cv. Muzao. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 147, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grade | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit size (number of fruits per 50 g) | ≤180 | ≤220 | ≤280 | ≤370 | ≤580 |
| Grade | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Number | Quality Score % | Sample Number | Quality Score % | Sample Number | Quality Score % | Sample Number | Quality Score % | Sample Number | Quality Score % | |
| 1 | 3.20 ± 0.18 b | 3 | 3.55 ± 0.10 b | 6 | 3.41 ± 0.25 b | 7 | 4.55 ± 0.07 a | 9 | 3.41 ± 0.04 b | |
| 2 | 3.12 ± 0.14 b | 4 | 3.31 ± 0.27 b | 13 | 3.52 ± 0.02 b | 8 | 3.14 ± 0.25 cd | 33 | 3.61 ± 0.29 a | |
| 44 | 3.09 ± 0.15 b | 5 | 5.06 ± 0.04 a | 14 | 3.24 ± 0.10 c | 17 | 3.28 ± 0.19 c | 34 | 2.73 ± 0.14 d | |
| 10 | 2.37 ± 0.13 c | 11 | 2.93 ± 0.17 c | 15 | 5.69 ± 0.25 a | 19 | 4.51 ± 0.10 a | 40 | 2.54 ± 0.19 e | |
| 18 | 3.00 ± 0.34 b | 12 | 2.85 ± 0.10 c | 35 | 2.92 ± 0.31 c | 23 | 3.71 ± 0.22 b | 41 | 2.46 ± 0.16 f | |
| 21 | 3.62 ± 0.14 a | 16 | 3.35 ± 0.29 b | 36 | 2.65 ± 0.06 cd | 32 | 2.92 ± 0.55 d | 42 | 3.14 ± 0.07 c | |
| 29 | 2.85 ± 0.10 bc | 24 | 3.74 ± 0.20 b | 22 | 3.18 ± 0.08 c | 37 | 3.48 ± 0.38 bc | 43 | 2.57 ± 0.30 e | |
| 30 | 2.87 ± 0.18 bc | 25 | 2.21 ± 0.47 d | 27 | 1.94 ± 0.07 d | 38 | 2.65 ± 0.12 e | 48 | 3.11 ± 0.22 c | |
| 31 | 2.30 ± 0.12 c | 26 | 2.98 ± 0.73 c | 28 | 3.47 ± 0.14 b | 39 | 3.29 ± 0.02 c | - | - | |
| 20 | 3.04 ± 0.14 b | 45 | 3.46 ± 0.15 b | 46 | 3.64 ± 0.63 b | 47 | 3.34 ± 0.27 bc | - | - | |
| ± s | - | 2.95 ± 0.16 | - | 3.34 ± 0.25 | - | 3.37 ± 0.19 | - | 3.48 ± 0.21 | - | 2.94 ± 0.17 |
| Function | Characteristic Value | Variance% | Accumulate% | Canonical Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| one | 130.997 a | 86.8 | 86.8 | 0.996 |
| two | 10.361 a | 6.9 | 93.6 | 0.955 |
| three | 8.627 a | 5.7 | 99.4 | 0.947 |
| four | 0.967 a | 0.6 | 100.0 | 0.701 |
| Test of Function | Lambda for Wilks | Chi-Square | df | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| one to four | 0.000 | 102.541 | 68 | 0.004 |
| two to four | 0.005 | 53.714 | 48 | 0.265 |
| three to four | 0.053 | 29.412 | 30 | 0.496 |
| four | 0.508 | 6.766 | 14 | 0.943 |
| Categories | Prediction Group Members | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 | ||||
| Initial | Counting | 1.00 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 2.00 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | ||
| 3.00 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | ||
| 4.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | ||
| 5.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | ||
| % | 1.00 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | |
| 2.00 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 3.00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 4.00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 5.00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Grades | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | A | B | Number | A | B | Number | A | B | Number | A | B | Number | A | B | |
| 1 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 3 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 6 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 7 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 9 | 0.45 | 0.63 | |
| 2 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 4 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 13 | 0.71 | 0.97 | 8 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 33 | 0.48 | 0.82 | |
| 10 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 5 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 14 | 0.77 | 0.49 | 17 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 34 | 0.46 | 0.83 | |
| 18 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 11 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 15 | 0.72 | 0.59 | 19 | 0.42 | 0.81 | 40 | 0.49 | 0.69 | |
| 20 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 12 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 22 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 23 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 41 | 0.53 | 0.80 | |
| 21 | 0.90 | 0.71 | 16 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 27 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 32 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 42 | 0.52 | 0.69 | |
| 29 | 1.65 | 0.72 | 24 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 28 | 0.59 | 0.66 | 37 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 43 | 0.48 | 0.84 | |
| 30 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 25 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 35 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 38 | 0.57 | 0.89 | 48 | 0.49 | 0.66 | |
| 31 | 0.97 | 1.05 | 26 | 0.81 | 0.73 | 36 | 0.89 | 0.72 | 39 | 0.46 | 0.58 | - | - | - | |
| 44 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 45 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 46 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 47 | 0.43 | 0.61 | - | - | - | |
| ± s | - | 0.77 | 0.66 | - | 0.73 | 0.67 | - | 0.71 | 0.68 | - | 0.52 | 0.70 | - | 0.49 | 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Liu, F.; Ran, L.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, S.; Ge, X.; Jin, B.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Y. Assessment of Phenotypic Characteristics, Polysaccharide Composition, and Hypoglycemic Potential in Different Commercial Grades of Lycium barbarum: A Comprehensive Study Using HPLC and NMR. Foods 2025, 14, 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223862
Ma C, Liu F, Ran L, Mi J, Lu L, Wang S, Ge X, Jin B, Zhang L, Yan Y. Assessment of Phenotypic Characteristics, Polysaccharide Composition, and Hypoglycemic Potential in Different Commercial Grades of Lycium barbarum: A Comprehensive Study Using HPLC and NMR. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223862
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Caixia, Fei Liu, Linwu Ran, Jia Mi, Lu Lu, Siyu Wang, Xinyu Ge, Bo Jin, Lutao Zhang, and Yamei Yan. 2025. "Assessment of Phenotypic Characteristics, Polysaccharide Composition, and Hypoglycemic Potential in Different Commercial Grades of Lycium barbarum: A Comprehensive Study Using HPLC and NMR" Foods 14, no. 22: 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223862
APA StyleMa, C., Liu, F., Ran, L., Mi, J., Lu, L., Wang, S., Ge, X., Jin, B., Zhang, L., & Yan, Y. (2025). Assessment of Phenotypic Characteristics, Polysaccharide Composition, and Hypoglycemic Potential in Different Commercial Grades of Lycium barbarum: A Comprehensive Study Using HPLC and NMR. Foods, 14(22), 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223862







