Enhancement of Pea–Oat Composite Protein Gel Properties Through Ultrasound Treatment Affects Structural and Functional Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Oat Protein
2.3. Preparation of POPG by Ultrasonic Treatment
2.4. Gel Strength Analysis
2.5. Water Holding Capacity (WHC) Analysis
2.6. Rheological Analysis
2.6.1. Frequency Sweep Test
2.6.2. Strain Sweep Test
2.7. Thermal Stability Analysis
2.7.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.7.2. Thermogravimetric (TGA) Analysis
2.8. Free Sulfhydryl and Disulfide Bonds Analysis
2.9. Surface Hydrophobicity Analysis
2.10. Intermolecular Forces Analysis
2.11. Endogenous Fluorescence Spectrum Analysis
2.12. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer (FTIR) Analysis
2.13. Morphological Analysis
2.13.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.13.2. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Gel Strength and WHC of POPG
3.2. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Rheological Properties of POPG
3.3. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on Thermal Properties of POPG
3.4. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Free Sulfhydryl Groups and Disulfide Bonds of POPG
3.5. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Surface Hydrophobicity of POPG
3.6. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Intermolecular Forces of POPG
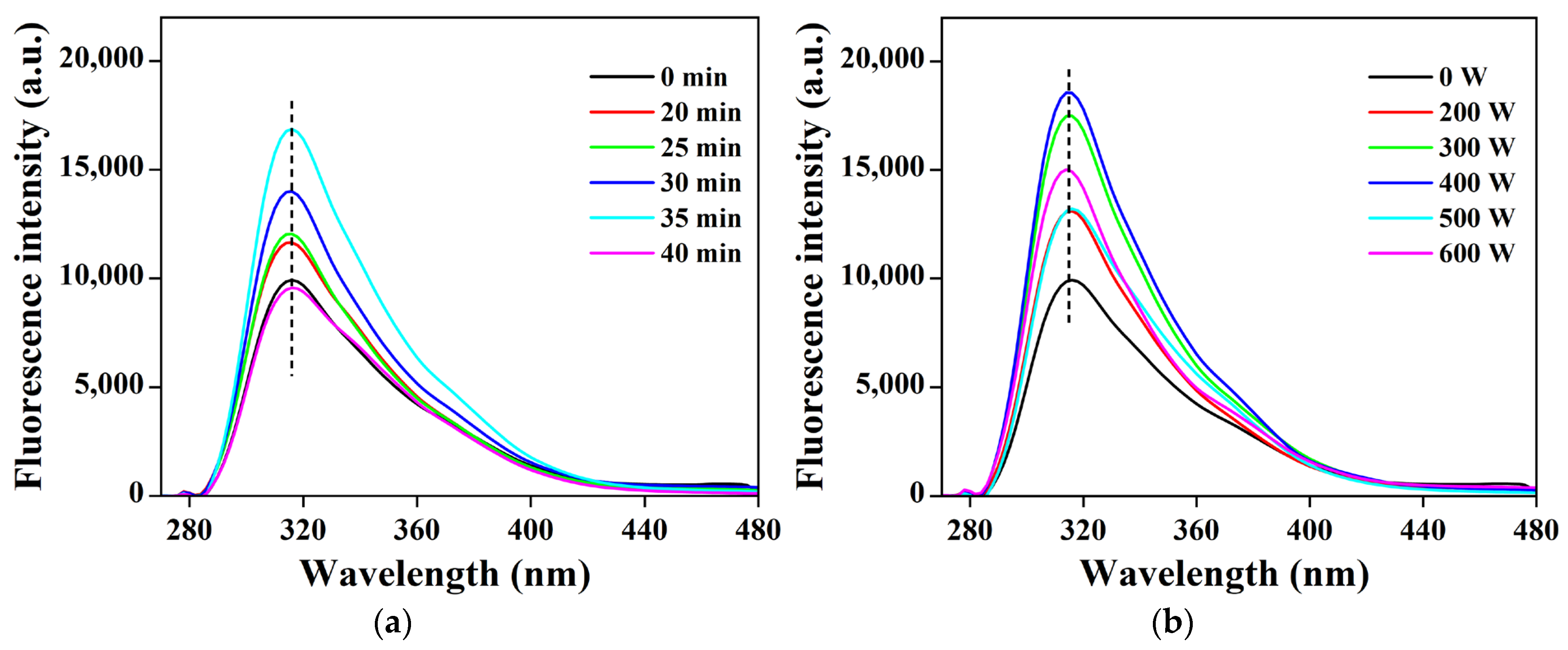
3.7. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Fluorescence Intensity of POPG
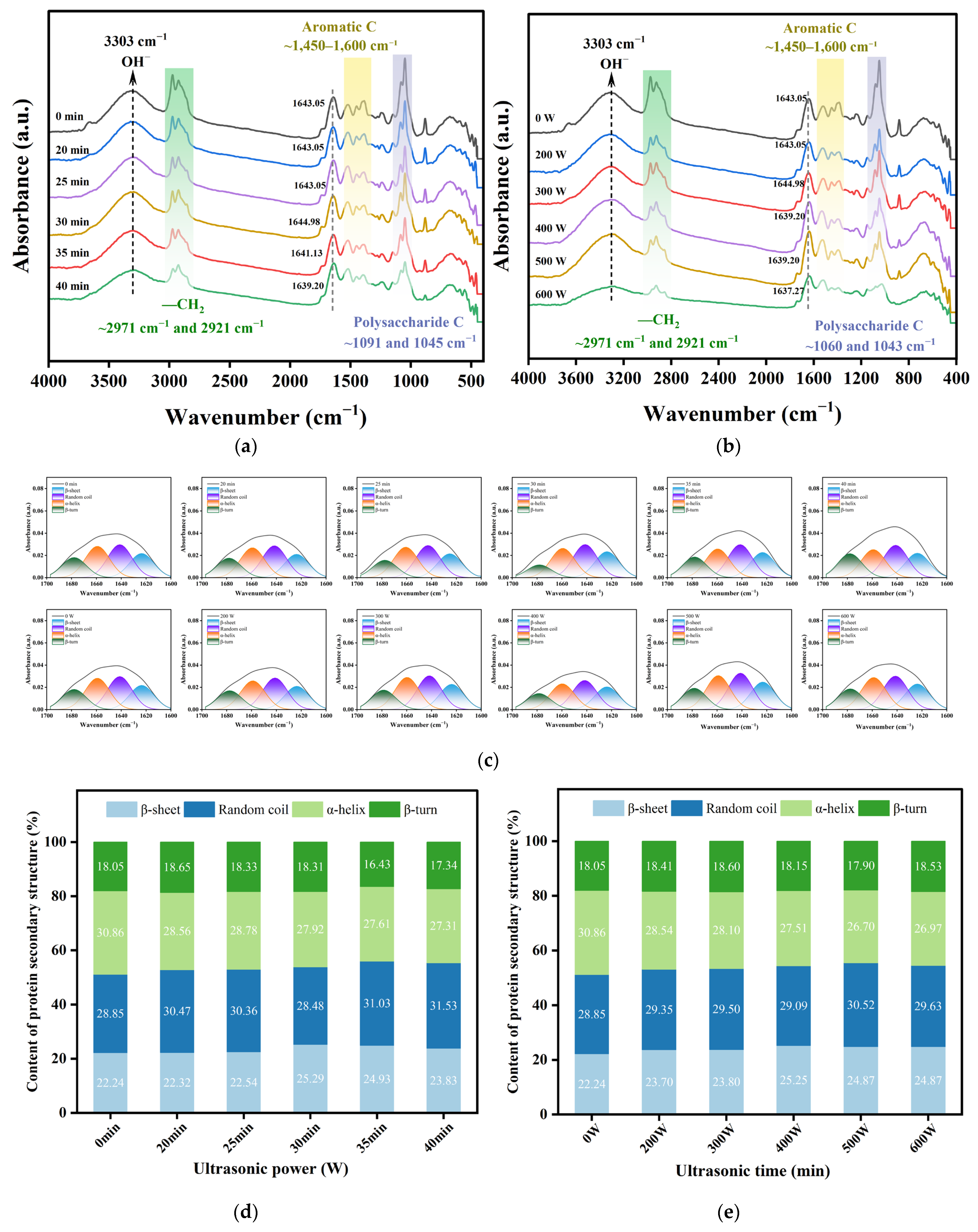
3.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectra (FTIR) Analysis of POPG
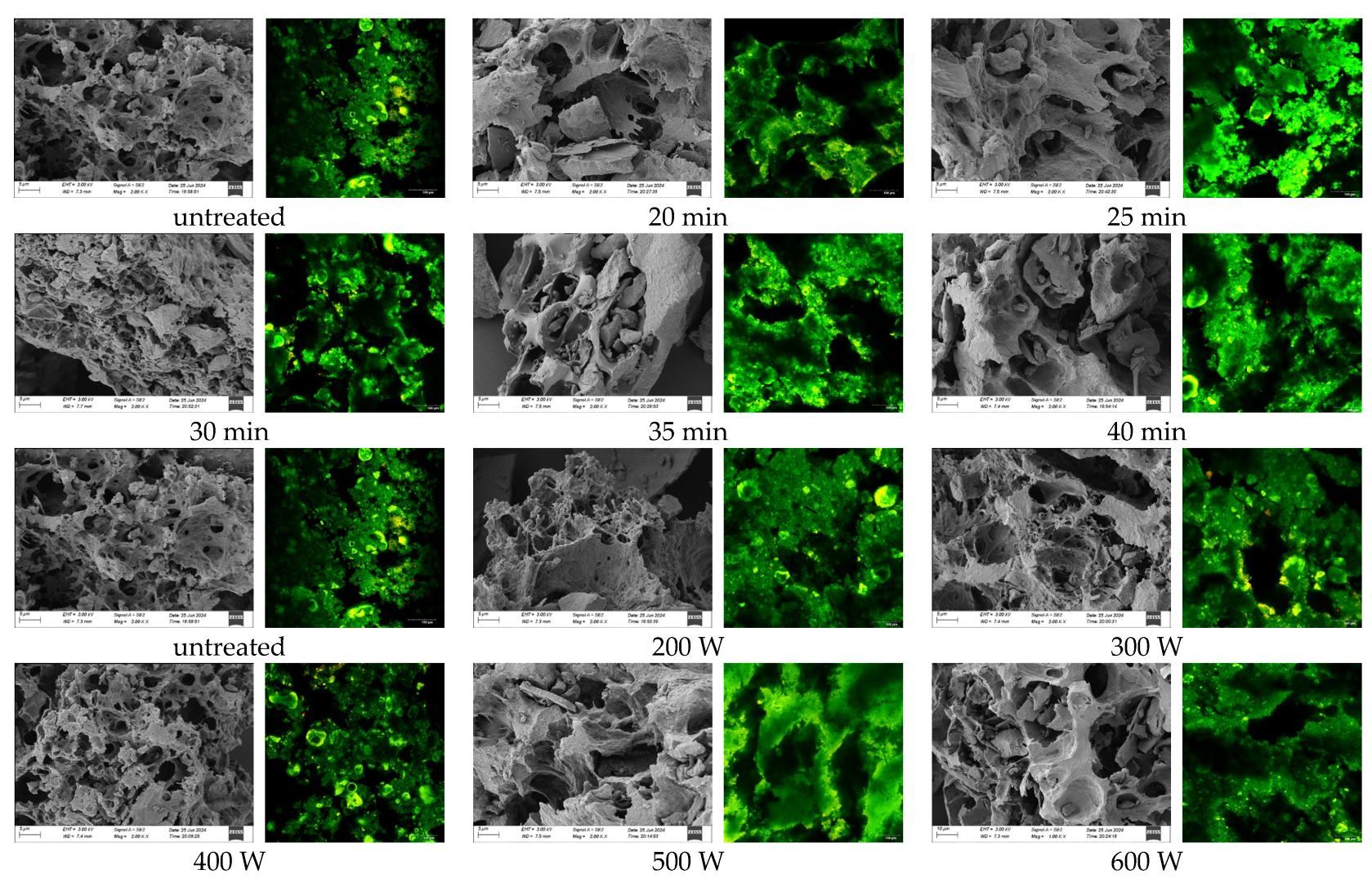
3.9. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Microstructure of POPG
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| POPG | Pea–oat Protein Gel |
| TG | Transglutaminase |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectra |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| CLSM | Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope |
References
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing Food’s Environmental Impacts through Producers and Consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Plant Proteins as High-Quality Nutritional Source for Human Diet. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J. Composition, Physicochemical Properties of Pea Protein and Its Application in Functional Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2593–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessio, G.; Flamminii, F.; Faieta, M.; Prete, R.; Di Michele, A.; Pittia, P.; Di Mattia, C.D. High Pressure Homogenization to Boost the Technological Functionality of Native Pea Proteins. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Kuang, J. Unraveling the Mechanisms of Pea Protein Isolate in Modulating Retrogradation Behavior of Pea Starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, O.; Sözer, N.; Ercili-Cura, D.; Poutanen, K. Protein from Oat: Structure, Processes, Functionality, and Nutrition. In Oats Nutrition and Technology; Wiley Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2016; pp. 255–288. [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen, M.; Kokkonen, T.; Huang, X.; Jouppila, K.; Maina, N.H.; Mäkelä-Salmi, N. Gelation Potential of Oat Protein Isolate: Influence of Extraction Method, Gelling Conditions, and Enzymatic Modification. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 143968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozmand, H.; Rousseau, D. Microstructure and Rheology Design in Protein–Protein–Polysaccharide Composites. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngarize, S.; Adams, A.; Howell, N.K. Studies on Egg Albumen and Whey Protein Interactions by FT-Raman Spectroscopy and Rheology. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, R.; Feng, X.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, B.; Ullah, N.; Chen, L. Effects of Low-Frequency and High-Intensity Ultrasonic Treatment Combined with Curdlan Gels on the Thermal Gelling Properties and Structural Properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.; Yu, B.; Yu, X.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; et al. Structural and Gelation Properties of Soy Protein Isolates–Sesbania Gum Gels: Effects of Ultrasonic Pretreatment and CaSO4 Concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 143215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, C.; Guo, M. Effects of High Intensity Ultrasound on Acid-Induced Gelation Properties of Whey Protein Gel. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 39, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xie, Y.; Yin, T.; Hu, Y.; You, J.; Xiong, S.; Liu, R. Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound on Gelation Properties of Silver Carp Surimi with Different Salt Contents. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 70, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Lv, D.; Du, F.; Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Li, T. Ultrasound Pretreatment Combined with Emulsion Coagulant: Synergistic Effects on Soybean Protein Gel Properties and Salt-Coagulated Tofu Quality. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2025, 120, 107437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zheng, H. Effects of High-Intensity Ultrasound on Physicochemical and Gel Properties of Myofibrillar Proteins from the Bay Scallop (Argopecten Irradians). Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 107, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Shen, R.; Li, Y. Investigation of the preparation and formula optimization of pea-oat complex protein gel. J. Light Ind. 2025, 40, 38–45, 55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Lei, H.; Li, L.-Q.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Yan, J.-K. Effects of Direct Addition of Curdlan on the Gelling Characteristics of Thermally Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Jiao, X.; Yan, B.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Fan, D. Effect of Fish Mince Size on Physicochemical and Gelling Properties of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys Molitrix) Surimi Gel. LWT 2021, 149, 111912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Du, M. Effect of Partial Replacement of Water-Soluble Cod Proteins by Soy Proteins on the Heat-Induced Aggregation and Gelation Properties of Mixed Protein Systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktak, W.; Nasri, R.; Hamdi, M.; Gomez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Karra-Chaâbouni, M. Physicochemical, Textural, Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Protein Isolate Gels Produced from European Eel (Anguilla Anguilla) by Heat-Induced Gelation Process. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraee, S.; Milani, J.M.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Physicochemical and Antifungal Properties of Bio-Nanocomposite Film Based on Gelatin-Chitin Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, X.; Rong, L.; Li, J.; Shen, M.; Xie, J. Effect of Gellan Gum on the Rheology, Gelling, and Structural Properties of Thermally Induced Pea Protein Isolate Gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effects of Combined Enzymatic and Ultrasonic Treatments on the Structure and Gel Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate. LWT 2022, 158, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Modulating the Structure of Lamb Myofibrillar Protein Gel Influenced by Psyllium Husk Powder at Different NaCl Concentrations: Effect of Intermolecular Interactions. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Song, H.; Sun, Z.; Guan, X. Exploring the Influence of Lysine Incorporation on the Physicochemical Properties of Quinoa Protein Gels Formed under Microwave versus Conventional Heating Conditions. Food Res. Int. 2025, 202, 115678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Sun, X.; Yang, S.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S. Ultrasound-Assisted Enhancement of Gel Properties in Hypomesus Olidus Surimi. Foods 2025, 14, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Liang, C.; Lin, T.; Zhong, R.; Cao, Y.; Lan, Y. Optimizing 3D Food Printing Inks: The Impact of Polysaccharides on Camellia Seed Protein Emulsion Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Freeze-Thaw Stability and Rheological Properties of Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Gels Induced by NaCl. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; McClements, D.J.; He, M.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Preparation of Okara Cellulose Hydrogels Using Ionic Liquids: Structure, Properties, and Performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, T.-X.; Li, X.-T.; Tang, C.-H. Novel Nanoparticles from Insoluble Soybean Polysaccharides of Okara as Unique Pickering Stabilizers for Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhu, L.; Delahaije, R.J.B.M.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Sagis, L.M.C. Acid-Induced Gels from Soy and Whey Protein Thermally-Induced Mixed Aggregates: Rheology and Microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Ren, X.; Shen, X.; Yang, X.; Li, L. Improvement of Physicochemical Properties and Quercetin Delivery Ability of Fermentation-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Gel Processed by Ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 107, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafarpour, R.; Koocheki, A. Effect of Ultrasonic Pretreatment on the Rheology and Structure of Grass Pea (Lathyrus Sativus L.) Protein Emulsion Gels Induced by Transglutaminase. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 92, 106278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; He, Z.; Chen, J. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Protein Extracts from Torreya Grandis Seeds. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Singh, S.; Ahmad, S.; Jan, S.; Gupta, A.; Jan, K.; Bashir, K. Ultrasonication Modifies the Structural, Thermal and Functional Properties of Pumpkin Seed Protein Isolate (PSPI). Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2025, 112, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, A.B.; Kaur, A.; Khatkar, S.K. Restructuring of Soy Protein Employing Ultrasound: Effect on Hydration, Gelation, Thermal, in-Vitro Protein Digestibility and Structural Attributes. LWT 2020, 132, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yu, D.; Pan, M. Emulsion Gels Stabilized by Soybean Protein Isolate and Pectin: Effects of High Intensity Ultrasound on the Gel Properties, Stability and β-Carotene Digestive Characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 79, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Pu, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q.; Mariga, A.M.; Zheng, H. Effect of Bound Water on the Quality of Dried Lentinus Edodes during Storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dnyaneshwar Patil, N.; Bains, A.; Kaur, S.; Yadav, R.; Ali, N.; Patil, S.; Goksen, G.; Chawla, P. Influence of Dual Succinylation and Ultrasonication Modification on the Amino Acid Content, Structural and Functional Properties of Chickpea (Cicer Arietinum L.) Protein Concentrate. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, X.-L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Qin, L.-K.; Jia, Y.-L. Preparation and Performance Characterization of Insoluble Dietary Fiber-Alginate-Pea Protein Ternary Composite Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 160, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Saini, C.S. Rheological and Structural Properties of Protein Isolates Extracted from Dephenolized Sunflower Meal: Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Structural and Functional Properties of Cactus (Opuntia Ficus-Indica) Seed Protein. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 97, 106465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H. Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound on the Structural, Rheological, Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Insoluble Potato Protein Isolates. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 85, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Qiu, W.; Xue, H.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Y. Improving the Gel Properties of Salted Egg White/Cooked Soybean Protein Isolate Composite Gels by Ultrasound Treatment: Study on the Gelling Properties and Structure. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 97, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of Plasma Chemistry on the Interfacial Performance of Protein and Polysaccharide in Emulsion. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xin, X.; Hu, H.; Qiu, W.; Ruan, D.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of Ultrasound and Tea Polyphenol Assisted Ultrasound Modification of Egg White Protein Gel. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 81, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Zisu, B.; Palmer, M.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Effects of Ultrasound on the Thermal and Structural Characteristics of Proteins in Reconstituted Whey Protein Concentrate. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2011, 18, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.-R.; Li-Sha, Y.-J.; Chen, H.-Q. Physicochemical, Structural and Gelation Properties of Arachin-Basil Seed Gum Composite Gels: Effects of Salt Types and Concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-X.; Li, Y.-Q.; Sun, G.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Hua, D.-L.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.-Z. The Improvement and Mechanism of Gelation Properties of Mung Bean Protein Treated by Ultrasound. LWT 2023, 182, 114811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, N.; Tong, L.; Fan, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, L. Comparison of Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Pea Protein and Mung Bean Protein-Based Yogurt. LWT 2021, 152, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tang, C.-H. Microfluidization as a Potential Technique to Modify Surface Properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Miao, Z.; Qi, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Mao, Y.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, J. Interactions of Soy Protein Isolate with Common and Waxy Corn Starches and Their Effects on Acid-Induced Cold Gelation Properties of Complexes. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Miao, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Chu, Z.; Yin, H.; Zheng, M.; Liu, J. Ultrasound-Induced Red Bean Protein–Lutein Interactions and Their Effects on Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Activities and Digestion Behaviors of Complexes. LWT 2022, 160, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q. Preservation of Chilled Beef Using Active Films Based on Bacterial Cellulose and Polyvinyl Alcohol with the Incorporation of Perilla Essential Oil Pickering Emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Tu, Z.; Sha, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, H. Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of Pectin–Fish Gelatin–Resveratrol Preservative Films. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 129832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülseren, İ.; Güzey, D.; Bruce, B.D.; Weiss, J. Structural and Functional Changes in Ultrasonicated Bovine Serum Albumin Solutions. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2007, 14, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dai, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hao, Y.; Wang, S.; Mao, X. Improved Gelling and Emulsifying Properties of Myofibrillar Protein from Frozen Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei) by High-Intensity Ultrasound. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, T.; Nie, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lin, L.; Lu, J. Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Composite Surimi Gels: The Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment and Olive Oil Concentration. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 88, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Kong, B.; Zheng, O.; Liu, S.; Dong, X. Effect of Protein Structure Changes during Different Power Ultrasound Thawing on Emulsification Properties of Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) Myofibrillar Protein. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 101, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Wan, L.; Tian, M.; Pan, S. The Effect of High Intensity Ultrasonic Pre-Treatment on the Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate Gel Induced by Calcium Sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shan, S.; Gao, X.; Shi, Y.; Lu, W. The Effect of Sweet Tea Polysaccharide on the Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Whey Protein Isolate Gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B.; Yan, J. Ultrasound Heat Treatment Effects on Structure and Acid-Induced Cold Set Gel Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

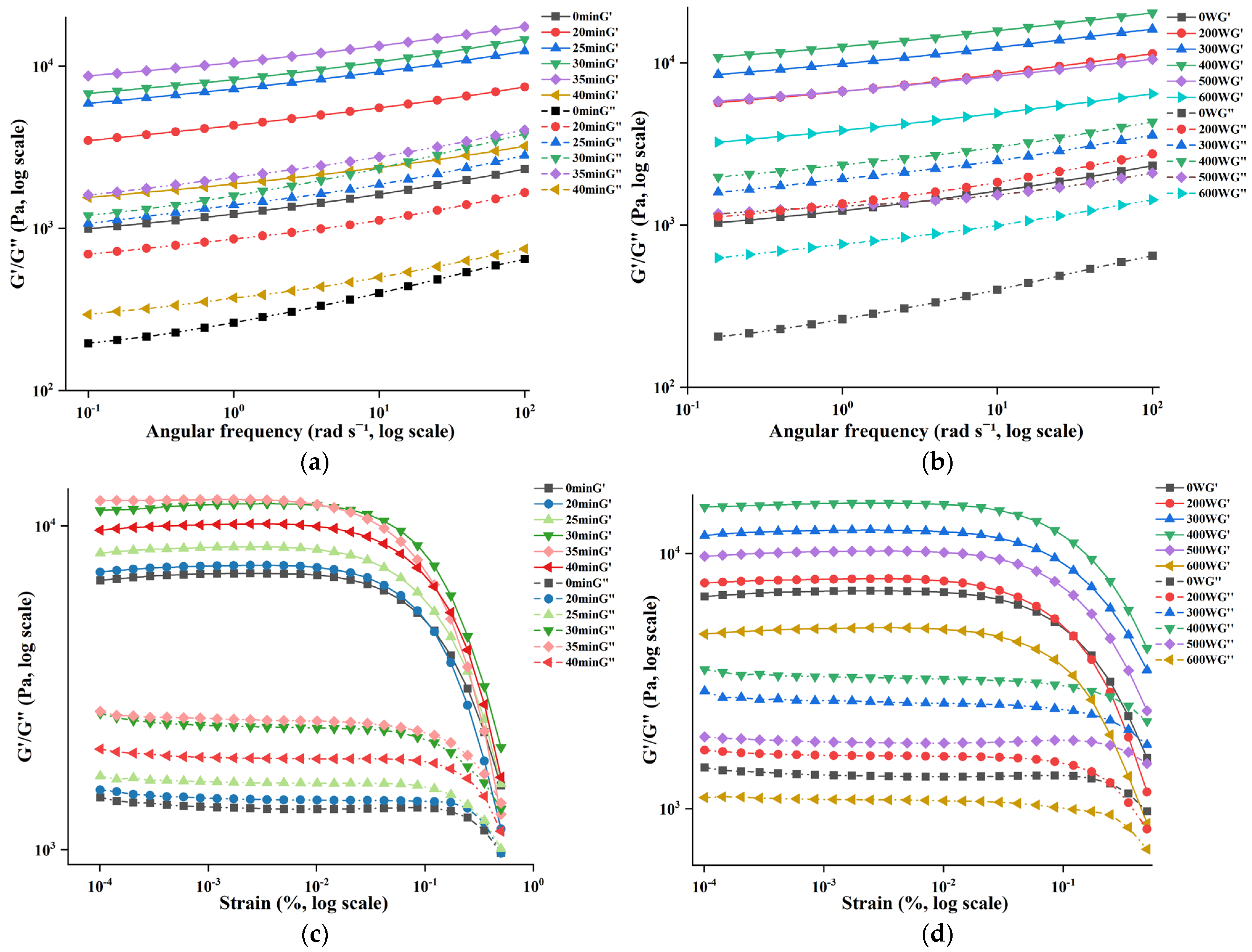
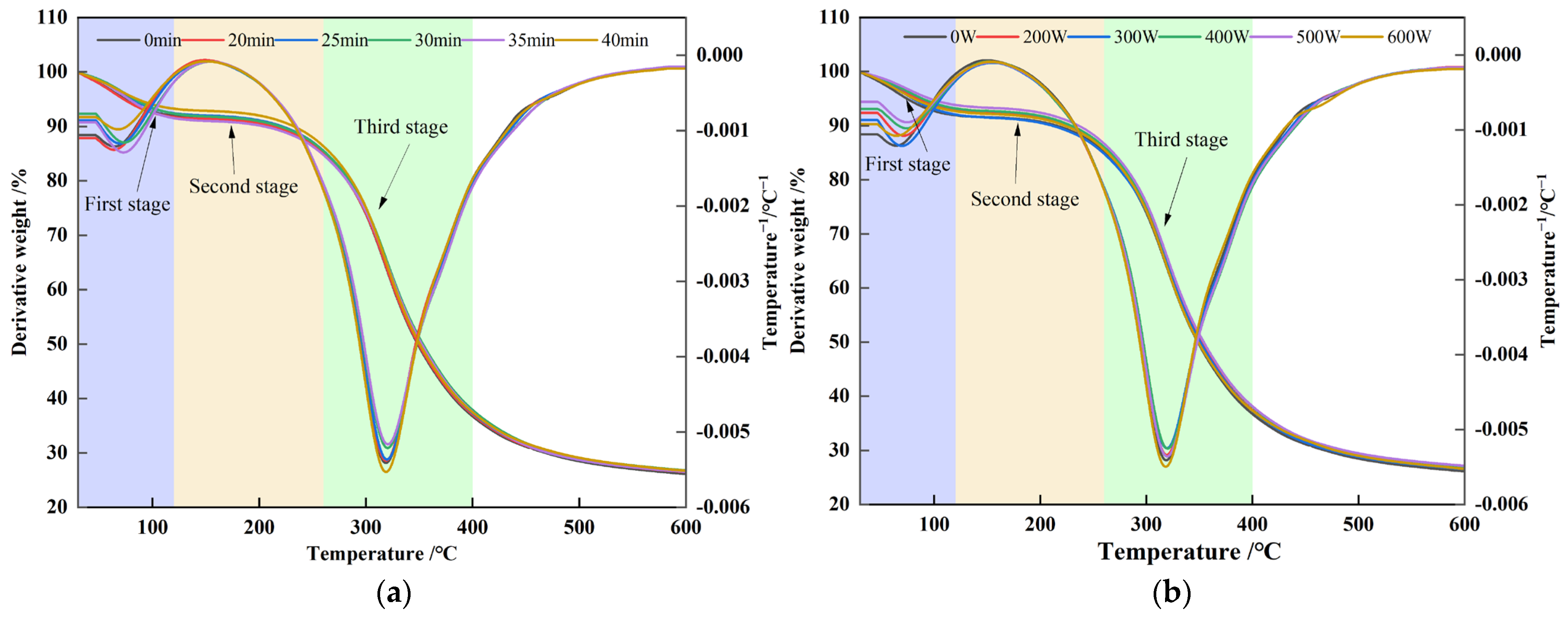
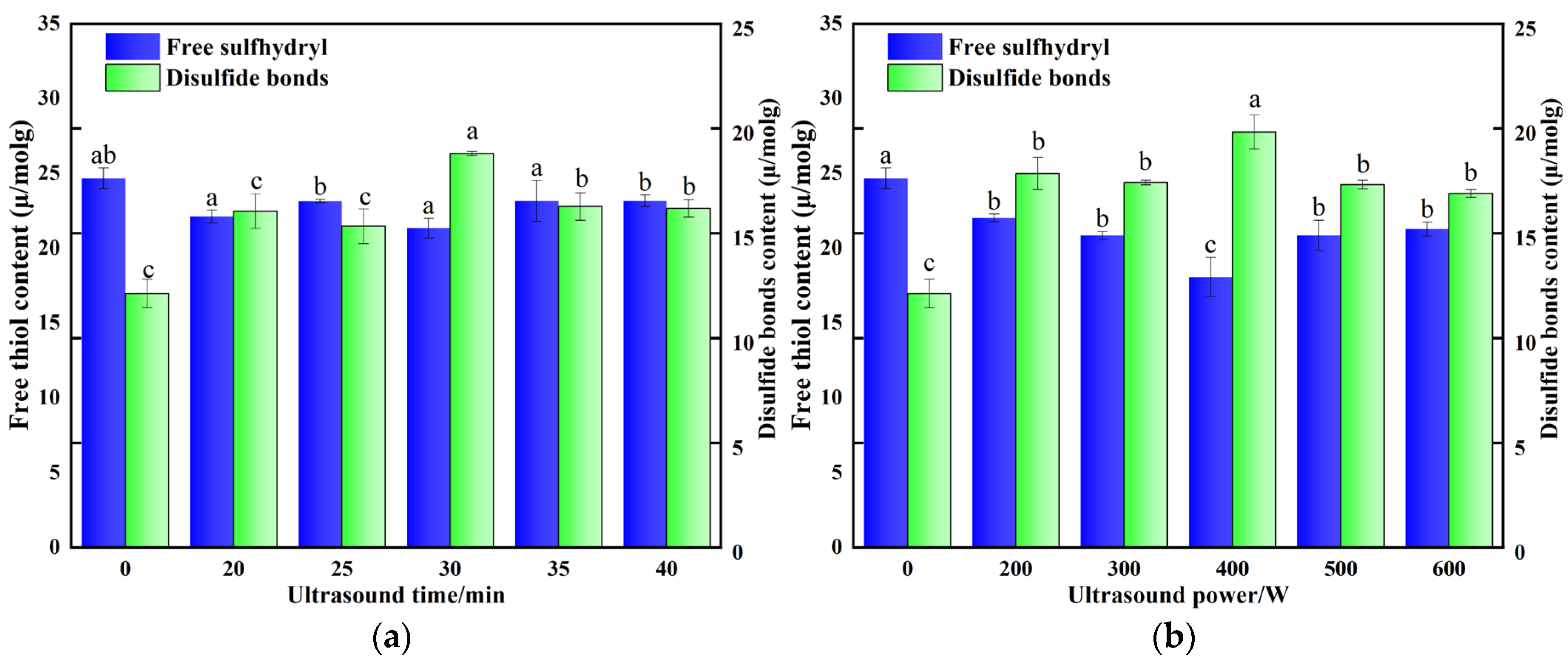
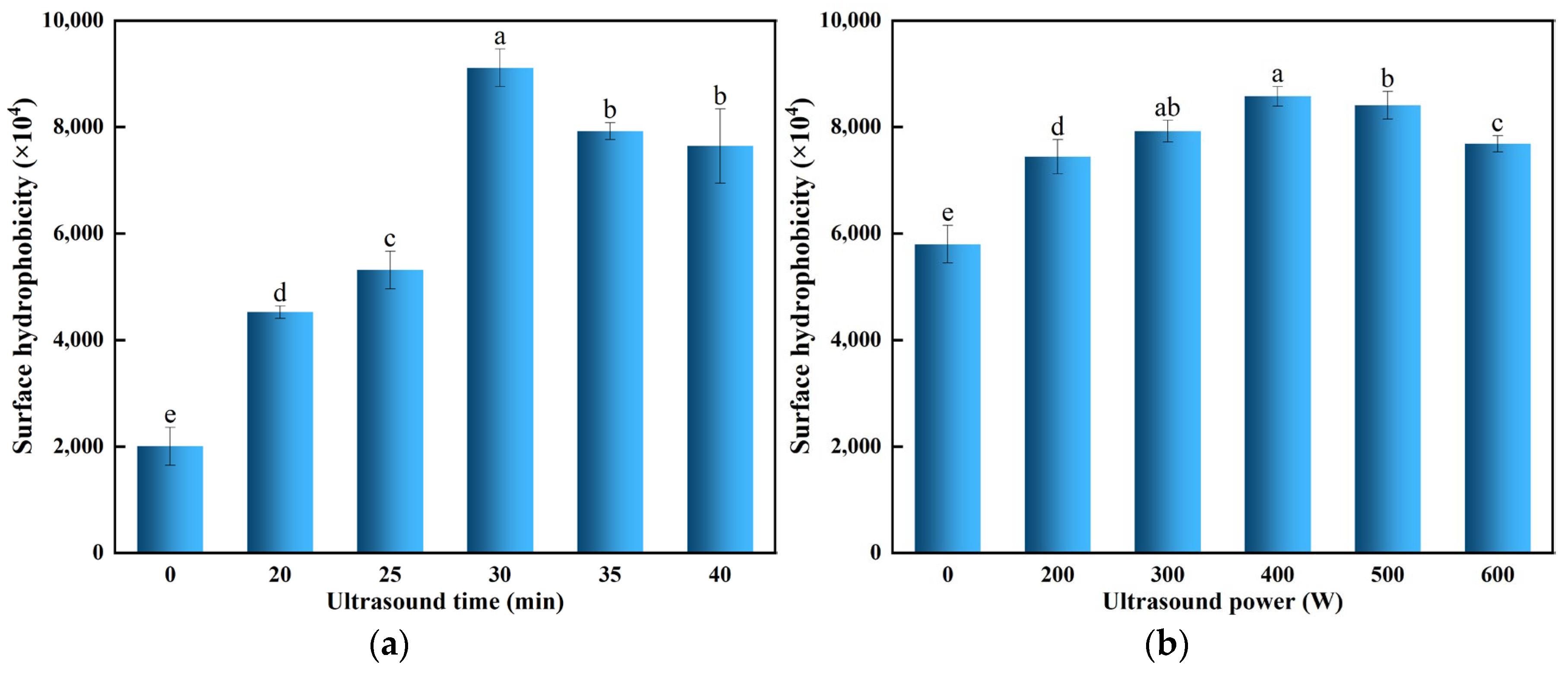
| Ultrasonic Conditions | To/°C | Tp/°C | Td/°C | ΔH/J·g−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Control | 62.37 ± 1.95 d | 89.76 ± 1.13 c | 101.88 ± 1.57 c | 1695.75 ± 7.55 c |
| 20 | 70.66 ± 1.79 c | 97.36 ± 1.11 b | 108.11 ± 1.24 bc | 1724.45 ± 18.85 bc | |
| 25 | 82.64 ± 2.22 b | 101.16 ± 1.42 ab | 108.82 ± 1.12 b | 1775.65 ± 19.75 ab | |
| 30 | 91.51 ± 0.97 a | 106.21 ± 2.03 a | 117.85 ± 4.14 a | 1822.35 ± 31.85 a | |
| 35 | 83.20 ± 1.77 b | 101.72 ± 1.18 ab | 110.44 ± 1.09 b | 1776.30 ± 8.90 ab | |
| 40 | 79.01 ± 1.56 b | 97.24 ± 1.91 b | 105.78 ± 1.14 bc | 1774.15 ± 28.45 ab | |
| Power (W) | Control | 62.38 ± 1.95 c | 89.77 ± 1.13 c | 101.89 ± 1.57 c | 1695.75 ± 7.55 b |
| 200 | 73.21 ± 2.89 b | 97.16 ± 1.74 b | 107.41 ± 1.98 bc | 1701.30 ± 19.90 b | |
| 300 | 77.30 ± 3.10 b | 98.84 ± 1.99 b | 108.56 ± 2.09 b | 1772.15 ± 18.25 ab | |
| 400 | 92.69 ± 2.63 a | 110.99 ± 2.33 a | 130.73 ± 2.04 a | 1842.35 ± 51.05 a | |
| 500 | 75.56 ± 3.89 b | 93.04 ± 2.72 bc | 105.75 ± 0.55 bc | 1835.15 ± 48.75 a | |
| 600 | 57.77 ± 2.55 c | 88.00 ± 1.68 c | 109.35 ± 2.03 b | 1726.65 ± 18.55 ab | |
| Ultrasonic Conditions | Ionic Bonds | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic Interactions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Control | 0.017 ± 0.010 ab | 0.131 ± 0.004 b | 0.765 ± 0.016 c |
| 20 | 0.024 ± 0.001 b | 0.105 ± 0.001 b | 0.739 ± 0.008 c | |
| 25 | 0.023 ± 0.001 ab | 0.149 ± 0.006 b | 0.791 ± 0.022 bc | |
| 30 | 0.020 ± 0.005 ab | 0.199 ± 0.010 a | 0.965 ± 0.020 a | |
| 35 | 0.024 ± 0.006 ab | 0.127 ± 0.001 b | 0.740 ± 0.036 c | |
| 40 | 0.048 ± 0.038 a | 0.219 ± 0.010 a | 0.848 ± 0.048 b | |
| Power (W) | Control | 0.017 ± 0.010 c | 0.131 ± 0.004 d | 0.765 ± 0.016 d |
| 200 | 0.016 ± 0.006 c | 0.282 ± 0.009 a | 1.026 ± 0.014 bc | |
| 300 | 0.068 ± 0.009 a | 0.206 ± 0.012 bc | 1.031 ± 0.029 bc | |
| 400 | 0.036 ± 0.004 b | 0.179 ± 0.011 cd | 1.240 ± 0.078 a | |
| 500 | 0.068 ± 0.133 a | 0.244 ± 0.008 ab | 0.995 ± 0.048 c | |
| 600 | 0.017 ± 0.010 c | 0.131 ± 0.004 d | 0.765 ± 0.016 d | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, M.; Dong, G.; Shen, R.; Dong, J.; Li, Y. Enhancement of Pea–Oat Composite Protein Gel Properties Through Ultrasound Treatment Affects Structural and Functional Characteristics. Foods 2025, 14, 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213751
Wang S, Li M, Dong G, Shen R, Dong J, Li Y. Enhancement of Pea–Oat Composite Protein Gel Properties Through Ultrasound Treatment Affects Structural and Functional Characteristics. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213751
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sai, Mengxiao Li, Guimei Dong, Ruiling Shen, Jilin Dong, and Yunlong Li. 2025. "Enhancement of Pea–Oat Composite Protein Gel Properties Through Ultrasound Treatment Affects Structural and Functional Characteristics" Foods 14, no. 21: 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213751
APA StyleWang, S., Li, M., Dong, G., Shen, R., Dong, J., & Li, Y. (2025). Enhancement of Pea–Oat Composite Protein Gel Properties Through Ultrasound Treatment Affects Structural and Functional Characteristics. Foods, 14(21), 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213751








