Machine Learning-Enabled Rapid Assessment of Plant-Based Protein Digestibility Through Physicochemical Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Protein Isolates
2.2.2. Measurement of Protein Content
2.2.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurement
2.2.4. Solubility
2.2.5. Identification of Intermolecular Interactions
2.2.6. Secondary Structure Analysis
2.2.7. In Vitro Digestion with INFOGEST 2.0
2.3. Machine Learning
2.3.1. Data Preprocessing
2.3.2. Data Augmentation
2.3.3. FNN Model Construction and Training
2.3.4. FNN Model Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties of Different Types of Plant-Based Proteins
3.1.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
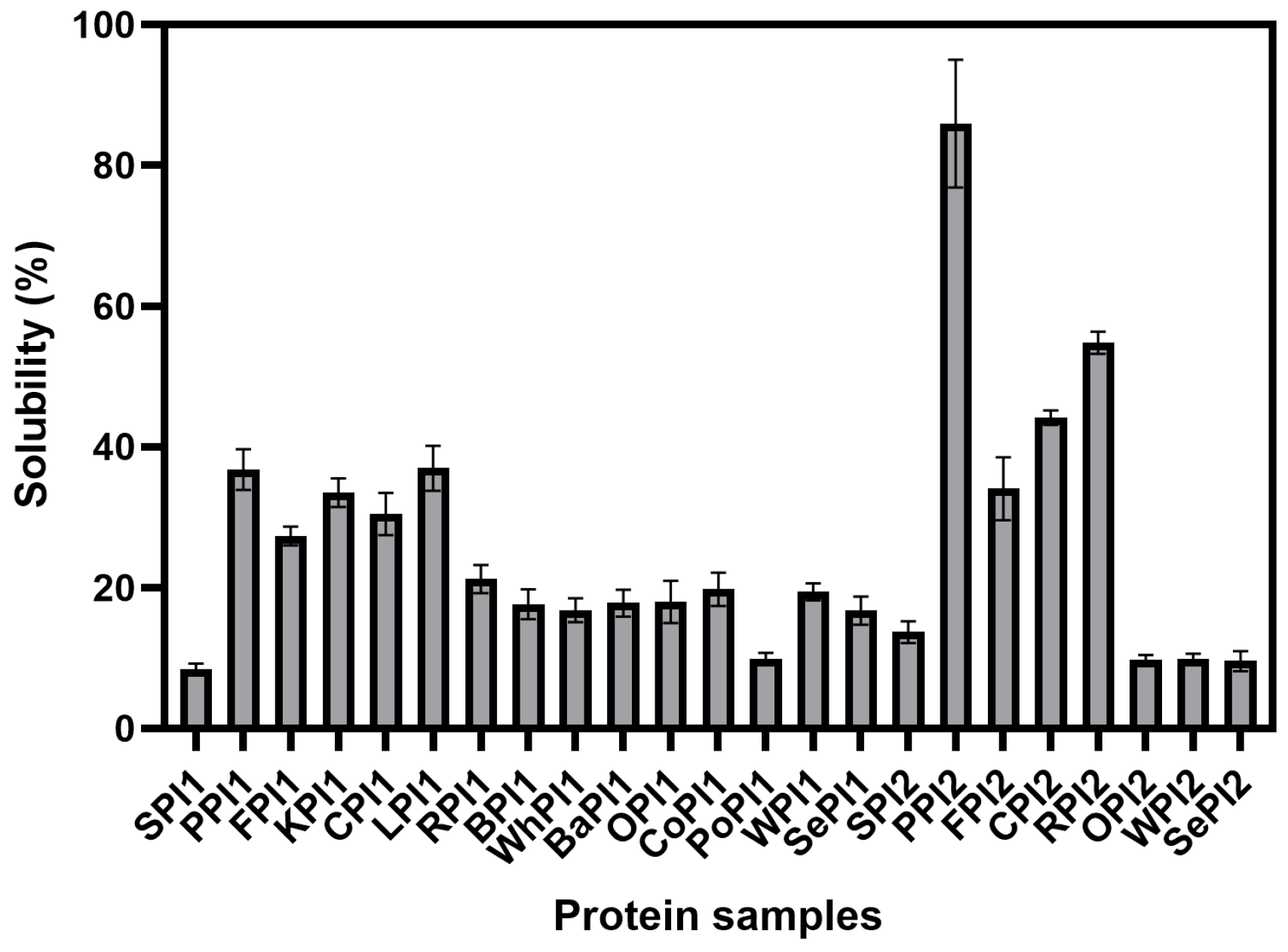
3.1.2. Solubility
3.1.3. Intermolecular Forces
3.1.4. Secondary Structure
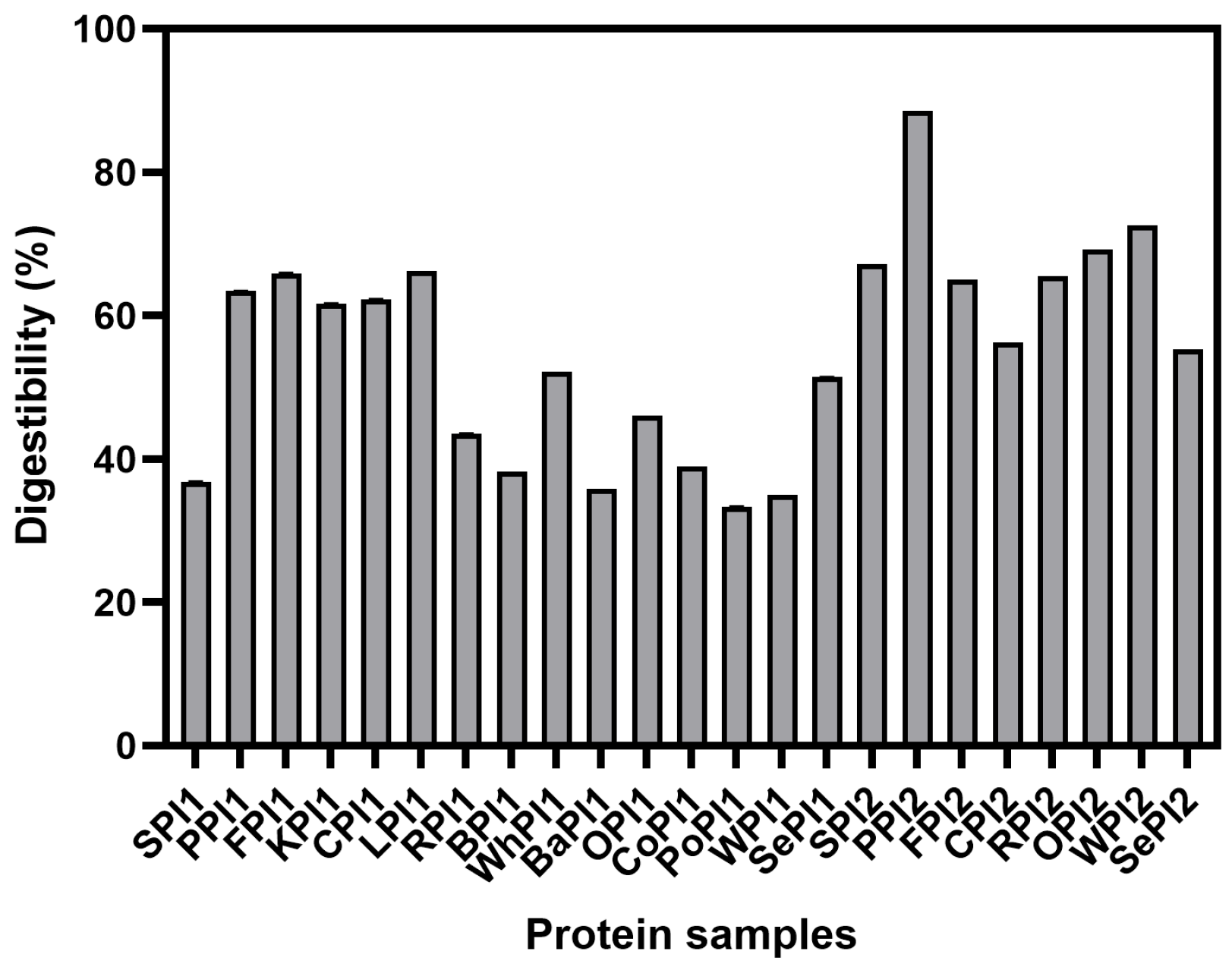
3.2. Analysis of In Vitro Digestibility of Different Types of Plant-Based Proteins
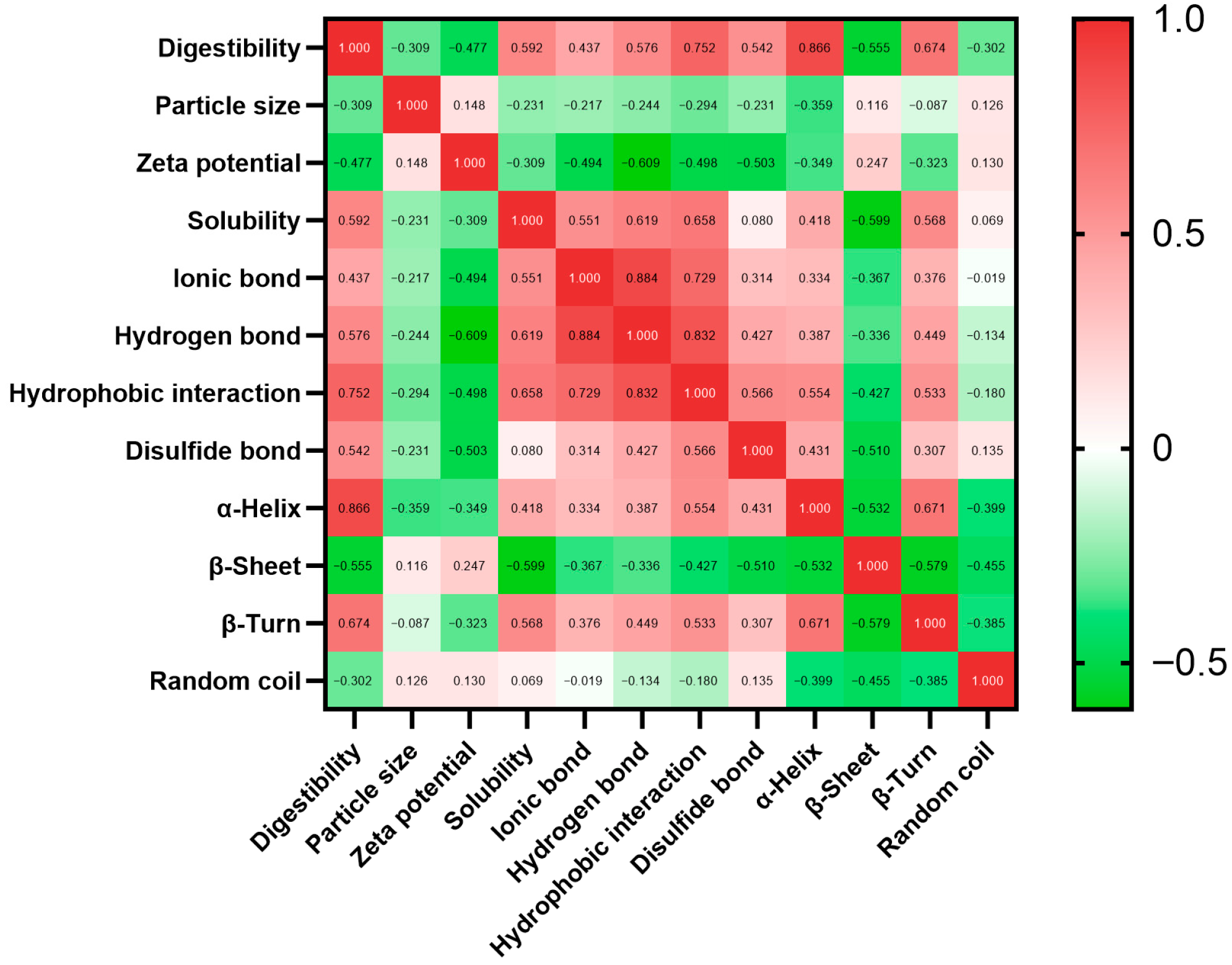
3.3. Linear Regression Analysis of the Physicochemical Profile and Digestibility
3.4. Construction of the Protein Digestibility Prediction Model
3.4.1. Data Augmentation
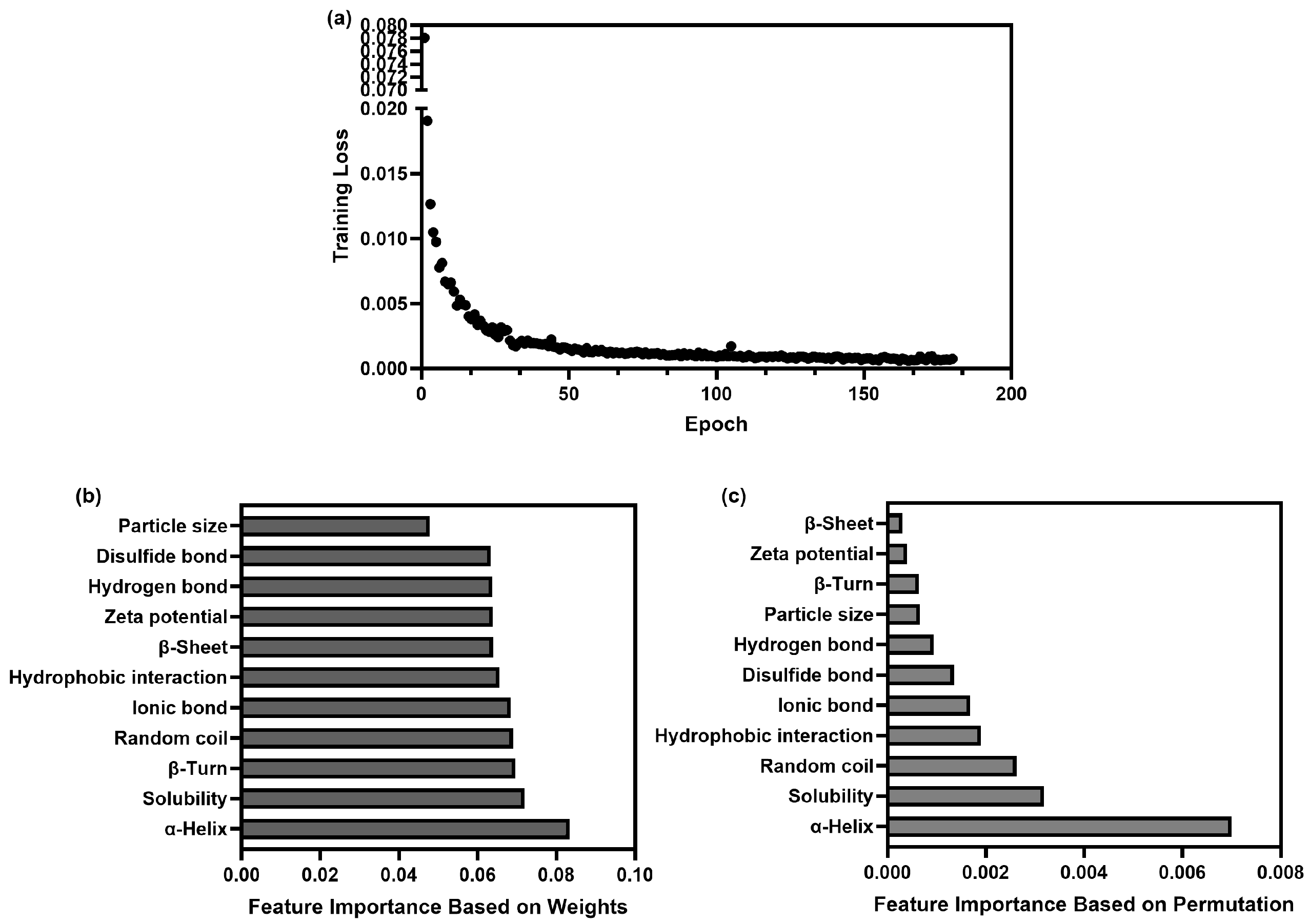
3.4.2. Training and Validation of the Prediction Model
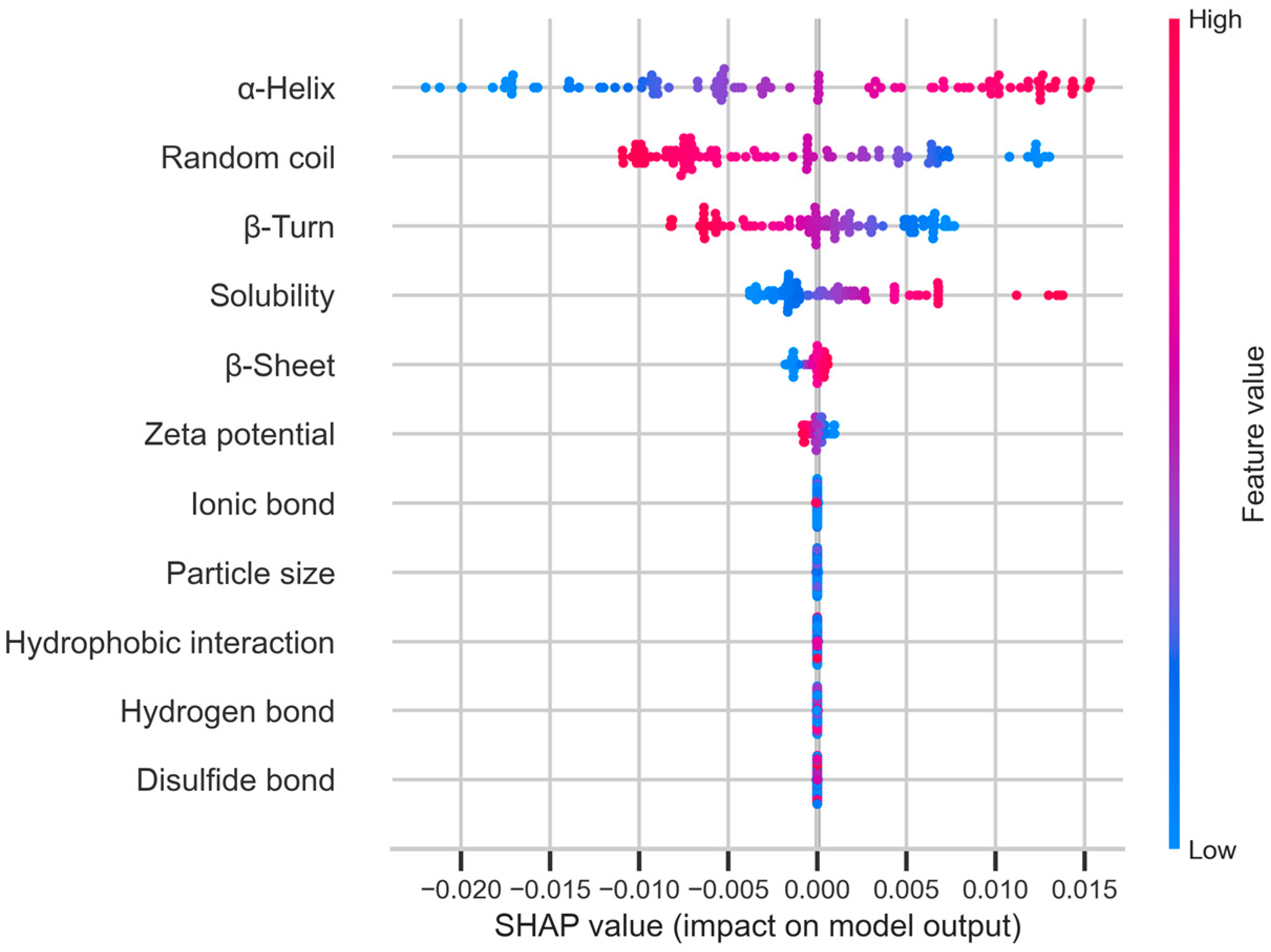
3.4.3. Screening of Potential Characteristics for Predicting Digestibility
3.4.4. The Application of the Simplified FNN Model with Three Inputs to Estimate Protein Digestibility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Punia, S.; Dhakane-Lad, J.; Dhumal, S.; Changan, S.; Senapathy, M.; Berwal, M.K.; Sampathrajan, V.; Sayed, A.A.S.; et al. Plant-based proteins and their multifaceted industrial applications. LWT 2022, 154, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Dun, B.; Wei, Z.; Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Ren, G.; Yao, Y. Peptides Released from Extruded Adzuki Bean Protein through Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion Exhibit Anti-inflammatory Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7028–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grácio, M.; Oliveira, S.; Lima, A.; Boavida Ferreira, R. RuBisCO as a protein source for potential food applications: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 135993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, S.; Burd, N.A.; van Loon, L.J.C. The Skeletal Muscle Anabolic Response to Plant- versus Animal-Based Protein Consumption1. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlieu, C.; Ménard, O.; Bouzerzour, K.; Mandalari, G.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A.R.; Dupont, D. Specificity of infant digestive conditions: Some clues for developing relevant in vitro models. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1427–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaei, F.; McClements, D.J.; Hadidi, M. Ultrasound processing for enhanced digestibility of plant proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos-Vazquez, A.; Mojica, L.; Sánchez-Velázquez, O.A.; Castillo-Herrera, G.; Urías-Silvas, J.E.; Doyen, A.; Moreno-Vilet, L. Techno-functional properties and structural characteristics of cricket protein concentrates affected by pre-treatments and ultrafiltration/diafiltration processes. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, N.E.; El Tinay, A.H. Effect of fermentation on sorghum protein fractions and in vitro protein digestibility. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2001, 56, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Guo, S.; Lv, Y. Effects of heat treatment on protein molecular structure and in vitro digestion in whole soybeans with different moisture content. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.T.; Liu, K.; Ning, M.; Jatoi, M.A.; Muzaffar, N.; Usman, H. A gastronomic exploration of protein digestibility, antioxidant activity, and bioavailability of selenium-enriched germinated brown rice under various cooking methods. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borugadda, P.; Kalluri, H.K. A Comprehensive Analysis of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Computer Vision in Food Science. J. Future Foods 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Guo, C.; Lu, W.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, C. Rapid quantification of royal jelly quality by mid-infrared spectroscopy coupled with backpropagation neural network. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Li, A.; Yu, N.; Li, Y.; Bahadur, R.; Wang, Q.; Ahuja, J.K. Application of machine learning for estimating label nutrients using USDA Global Branded Food Products Database, (BFPD). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 100, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, N.; Dagar, P.; Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, S.; Singh, B.K.; Bhardwaj, R.; Chand Rana, J.; Riar, A. Comparative analysis of modified partial least squares regression and hybrid deep learning models for predicting protein content in Perilla (Perilla frutescens L.) seed meal using NIR spectroscopy. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zou, Z. Machine learning modeling and prediction of peanut protein content based on spectral images and stoichiometry. LWT 2022, 169, 114015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S. Alkaline-heat induced the conformationally flexible regions of soy protein and their effect on subunit aggregation. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50095-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Protein in Food. Ministry of Health: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Nie, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, D.; Cao, X.; Fan, H. Effects of thermal treatment and Glucono-δ-lactone on the quality of alkaline dough and steamed buns. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, J. Cysteine-induced disulfide cleavage enhances the solubility of alkali-treated pea protein and its elasticity contribution in low-salt hybrid meat gels. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Modulating the structure of lamb myofibrillar protein gel influenced by psyllium husk powder at different NaCl concentrations: Effect of intermolecular interactions. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanger, C.; Andlinger, D.J.; Brümmer-Rolf, A.; Engel, J.; Kulozik, U. Quantification of protein-protein interactions in highly denatured whey and potato protein gels. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, C.; Wang, L. Effects of ultrasound-assisted alkaline isoelectric precipitation on the structure and functionality of Auricularia delicata protein. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2025, 106, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.; Mao, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Ran, M.; Hao, L. Evaluation of the nutritional quality of yeast protein in comparison to animal and plant proteins using growing rats and INFOGEST model. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, D.; Mandalari, G.; Molle, D.; Jardin, J.; Léonil, J.; Faulks, R.M.; Wickham, M.S.; Mills, E.N.; Mackie, A.R. Comparative resistance of food proteins to adult and infant in vitro digestion models. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Xia, S.; Song, J.; Hou, Y.; Hao, T.; Shen, S.; Li, K.; Xue, C.; Jiang, X. Yeast protein as a novel protein source: Processing, functional properties, and potential applications in foods. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2024, 93, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, M.-m. Functional, conformational and topographical changes of succinic acid deamidated wheat gluten upon freeze- and spray-drying: A comparative study. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliete, B.; Yassine, S.A.; Cases, E.; Saurel, R. Drying method determines the structure and the solubility of microfluidized pea globulin aggregates. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Food proteins: A review on their emulsifying properties using a structure–function approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, D.R.; Nickerson, M.T. Effect of pH on the formation of electrostatic complexes within admixtures of partially purified pea proteins (legumin and vicilin) and gum Arabic polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z. Pea protein/carboxymethyl cellulose complexes prepared using a pH cycle strategy as stabilizers of high internal phase emulsions for 3D printing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 131967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Espinoza, M.A.; Ayed, C.; Foster, T.; Camacho, M.D.M.; Martínez-Navarrete, N. The Impact of Freeze-Drying Conditions on the Physico-Chemical Properties and Bioactive Compounds of a Freeze-Dried Orange Puree. Foods 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.; Ahern, N.; Sahin, A.W.; Nyhan, L.; Mes, J.J.; van der Aa, C.; Vrasidas, I.; Arendt, E.K. Dynamic in-vitro system indicates good digestibility characteristics for novel upcycled plant protein; correlation to techno-functional properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2024, 92, 103571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mao, X.; Diao, X.; Yang, K.; Shan, K.; Li, C. Effects of sodium tripolyphosphate on the quality and digestion properties of PSE pork. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Yu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Qian, J.-Y. Insights into transglutaminase on structural and rheological properties of gels from adzuki bean protein pretreated by electric fields. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 161, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benrezkallah, D. Molecular dynamics simulations at high temperatures of the Aeropyrum pernix L7Ae thermostable protein: Insight into the unfolding pathway. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2024, 127, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Du, M.; Wu, C. Reducing disulfide bonds as a robust strategy to facilitate the self-assembly of cod protein fabricating potential active ingredients-nanocarrier. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 222, 113080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.K.; Mangaraj, S. Processing Influences on Composition and Quality Attributes of Soymilk and its Powder. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, A. Data Storage and Representation. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Ranganathan, S., Gribskov, M., Nakai, K., Schönbach, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Moderately mechanically activated starch in improving protein digestibility: Application in noodles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 139856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Mena, N.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Pérez-Won, M.; Herrera-Lavados, C.; Moreno-Osorio, L. Influence of starch-protein interactions on the digestibility and chemical properties of a 3D-printed food matrix based on salmon by-product proteins. Food Res. Int. 2024, 179, 114035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatko, M.; Konefał, R.; Njoku, S.; Zwoliński, K.; Andruniów, T.; Szweda, R. Solvent effect on secondary structures of discrete, isotactic, oligourethane motif–towards engineering protein-like features in abiotic polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 239, 114262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, A.; Afseth, N.K.; Böcker, U.; Knutsen, S.H.; Kirkhus, B.; Mæhre, H.K.; Ballance, S.; Wubshet, S.G. Improved estimation of in vitro protein digestibility of different foods using size exclusion chromatography. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Valle, D.E.; López-Silva, M.; Santos-Martínez, G.; Hernández-Pérez, V.; Figueroa-González, J.J. Chemical, structural characterization and in vitro protein digestibility of cicada (Cicadidae) flour. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, R.; Frosi, I.; Papetti, A. Chapter 1–Food protein digestion by in vitro static approaches. In Protein Digestion-Derived Peptides; Martínez-Villaluenga, C., Hernández-Ledesma, B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.A.; Hussain, T.; Ullah, A.; Ullah, W.; Del Ser, J.; Muhammad, K.; Sajjad, M.; Baik, S.W. Modelling Electricity Consumption During the COVID19 Pandemic: Datasets, Models, Results and a Research Agenda. Energy Build. 2023, 294, 113204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Yi, S.; Zhu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Prediction of the freshness of horse mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) using E-nose, E-tongue, and colorimeter based on biochemical indexes analyzed during frozen storage of whole fish. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, D.; Gong, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, F.; Zhou, G.; Deng, Y. Generative adversarial network integrated with metabolomics identifies potential biomarkers related to quality changes of atemoya (Annona cherimola × Annona squamosa) stored at 10 and 25 °C. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Qiao, C.; Jing, K.; Zhu, X.; Ren, K. Biomarkers identification for Schizophrenia via VAE and GSDAE-based data augmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbashi, S.; Maselesele, T.L.; Njobeh, P.B.; Molelekoa, T.B.J.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Makhuvele, R.; Adebo, O.A. Application of a generative adversarial network for multi-featured fermentation data synthesis and artificial neural network (ANN) modeling of bitter gourd–grape beverage production. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; You, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Q.; Dong, H.; Qian, M.; Xiao, S.; Yu, L.; Hu, X. Back propagation artificial neural network (BP-ANN) for prediction of the quality of gamma-irradiated smoked bacon. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Lei, H.; Ullah, I.; El-Meligy, M.; El Hindi, K.; Javed, M.F.; Ahmad, F. Predictive modeling for durability characteristics of blended cement concrete utilizing machine learning algorithms. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, M.; Ghoneim, A.S.; Abdelhamid, L.; Atia, A. Fusing CNNs and attention-mechanisms to improve real-time indoor Human Activity Recognition for classifying home-based physical rehabilitation exercises. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 184, 109399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Song, A.; Li, M.; Yao, X.; Cai, Y.; Dong, L.; Kang, D.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of the freshness (TVB-N) of pork patty during storage based on PLS-DA, SVM and BP-ANN models. Food Control 2025, 171, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.Z.I.; Leung, A.A.; Walker, R.L.; Sikdar, K.C.; O’Beirne, M.; Quan, H.; Turin, T.C. A comparison of machine learning algorithms and traditional regression-based statistical modeling for predicting hypertension incidence in a Canadian population. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Lan, T.; Goh, Y.M.; Safiena, S.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lytle, B.; He, Y. An interpretable clustering approach to safety climate analysis: Examining driver group distinctions. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2024, 196, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrosan, M.; Madi Almajwal, A.; Al-Qaisi, A.; Gammoh, S.; Alu’datt, M.H.; Al Qudsi, F.R.; Tan, T.-C.; Razzak Mahmood, A.A.; Bani-Melhem, K. Trehalose-conjugated lentil-casein protein complexes prepared by structural interaction: Effects on water solubility and protein digestibility. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrosan, M.; Almajwal, A.M.; Al-Qaisi, A.; Gammoh, S.; Alu’datt, M.H.; Al Qudsi, F.R.; Tan, T.-C.; Razzak Mahmood, A.A.; Maghaydah, S.; Al-Massad, M. Evaluation of digestibility, solubility, and surface properties of trehalose-conjugated quinoa proteins prepared via pH shifting technique. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, K.R.; Buvaneswaran, M.; Bhavana, M.R.; Sinija, V.R.; Rawson, A.; Hema, V. Effects of ultrasound and high-pressure assisted extraction of pearl millet protein isolate: Functional, digestibility, and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Kranthi Vanga, S.; Raghavan, V. Influence of high-intensity ultrasound on the IgE binding capacity of Act d 2 allergen, secondary structure, and In-vitro digestibility of kiwifruit proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Shuang, Q.; Bao, X. High-pressure processing-assisted limited enzymatic hydrolysis improves the luminosity, functional properties, and digestibility of sunflower meal protein. LWT 2025, 227, 117989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| VAE | latent_dim | 10 |
| encoder_layers | 3 | |
| decoder_layers | 3 | |
| learning_rate | 0.001 | |
| loss_function | MSELoss | |
| GAN | latent_dim | 10 |
| learning_rate | 0.001 | |
| loss_function | MSELoss | |
| Mixup | alpha | 0.3 |
| num_samples | 450 | |
| KNN | k | 20 |
| num_samples | 2 | |
| distance_metric | c | |
| alpha_range | (0.1, 0.9) |
| Hyperparameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Data processing | test_size | 80% train, 20% test |
| batch_size | 16 | |
| scaler | StandardScaler | |
| FNN architecture | input_dim | 11 |
| fc1 | Linear (input_dim→128) | |
| fc2 | Linear (128→64) | |
| fc3 | Linear (64→32) | |
| fc4 | Linear (32→1) | |
| activation | ReLU | |
| dropout | p = 0.3 (applied after fc1 and fc2) | |
| Training parameters | num_epochs | 300 |
| learning_rate | 0.0005 | |
| optimizer | Adam | |
| loss_function | MSELoss | |
| early_stopping_patience | 15 | |
| Feature importance | weight_importance | Mean absolute value of fc1.weight |
| permutation_importance | Difference in the MSE after permuting each feature |
| Plant Sources | Solubility | α-Helix Content | Random Coil Content | Digestibility | Prediction Results | Percentage Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lentil protein | 92.7 | 10.44 | 17.43 | 84.9 | 93.5 | 10.13 |
| Quinoa protein | 82.94 | 19.99 | 16.91 | 81.07 | 83.58 | 3.1 |
| 87 | 17.49 | 18.24 | 84.06 | 82.39 | 1.99 | |
| 88.53 | 16.74 | 18.44 | 85.15 | 92.07 | 8.13 | |
| Pearl millet protein | 60 | 30.19 | 25.79 | 71.73 | 65.92 | 8.1 |
| 62.35 | 21.48 | 32.8 | 75.89 | 69.16 | 8.87 | |
| Kiwifruit protein | 16.51 | 15 | 33 | 35 | 35.28 | 0.8 |
| 14.54 | 10 | 32 | 44 | 43.56 | 1 | |
| Sunflower meal protein | 64.48 | 15.54 | 17.69 | 93.67 | 83.97 | 10.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Zhang, R.; Yin, H.; Zhong, Y.; Fang, Y.; Sun, C.; Deng, Y. Machine Learning-Enabled Rapid Assessment of Plant-Based Protein Digestibility Through Physicochemical Profiles. Foods 2025, 14, 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223874
Liu M, Zhang R, Yin H, Zhong Y, Fang Y, Sun C, Deng Y. Machine Learning-Enabled Rapid Assessment of Plant-Based Protein Digestibility Through Physicochemical Profiles. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223874
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Meichen, Ruoyan Zhang, Hao Yin, Yu Zhong, Yapeng Fang, Cuixia Sun, and Yun Deng. 2025. "Machine Learning-Enabled Rapid Assessment of Plant-Based Protein Digestibility Through Physicochemical Profiles" Foods 14, no. 22: 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223874
APA StyleLiu, M., Zhang, R., Yin, H., Zhong, Y., Fang, Y., Sun, C., & Deng, Y. (2025). Machine Learning-Enabled Rapid Assessment of Plant-Based Protein Digestibility Through Physicochemical Profiles. Foods, 14(22), 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223874






