Research Progress on the Nutritional Components, Bioactivity, Health Effects, and Food Applications of Passion Fruit Peel (PFP)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nutrients
2.1. Carbohydrates and Dietary Fiber
2.2. Vitamins
2.3. Minerals, Lipids, and Proteins
| Nutrient | Origin | Content | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate | YPFP | 85.78 ± 0.00 g/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 80.71 ± 0.00 g/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 76 g/kg | [25] | |
| PPFP | 78.267 ± 0.517% | [29] | |
| DF | YPFP | 45.18 ± 0.83 g/100 g | [13] |
| YPFP | 61.16 ± 1.02 g/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 61.68 ± 1.31 g/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 577 g/kg | [25] | |
| PPFP | 62.459 ± 2.857% | [29] | |
| YPFP | 69.69 ± 0.88 g/100 g | [31] | |
| VA | YPFP | 22.71 ± 0.98 μg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 59.69 ± 2.55 μg/100 g | [27] | |
| VC | PPFP | 4.58 g/kg | [25] |
| P | YPFP | 140 ± 1.30 mg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 70,00 ± 1.12 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| PFP | 240 ± 1.71 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| S | YPFP | 7000 ± 0.40 mg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 160 ± 1.35 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| Na | YPFP | 2.20 ± 0.02 mg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 7.30 ± 0.12 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 54.107 mg/kg | [29] | |
| Mg | YPFP | 120 ± 0.90 mg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 130 ± 0.97 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 1.60 g/kg | [25] | |
| PPFP | 836.964 mg/kg | [29] | |
| K | YPFP | 2600 ± 15.7 mg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 2800 ± 16.3 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 31,065.357 mg/kg | [29] | |
| Ca | YPFP | 250 ± 1.98 mg/100 g | [27] |
| PPFP | 310 ± 1.69 mg/100 g | [27] | |
| PPFP | 2833.036 mg/kg | [29] | |
| YPFP | 0.226 g/100 g | [31] | |
| Zn | PPFP | 6.071 mg/kg | [30] |
| Lipid | YPFP | 4.20 ± 0.02 g/100 g | [13] |
| PFP | 3.47 ± 0.3 g/100 g | [29] | |
| PPFP | 6 g/kg | [25] | |
| PFP | 8410 mg/100 g | [29] | |
| Protein | YPFP | 3.14 ± 0.31 g/100 g | [13] |
| YPFP | 3.40 ± 0.06 g/100 g | [23] | |
| PPFP | 6.47 ± 0.04 g/100 g | [27] | |
| PFP | 8.41 ± 0.1 g/100 g | [29] | |
| PPFP | 34 g/kg | [25] | |
| PPFP | 7.571 ± 0.232% | [29] |
3. Phytochemical Composition
3.1. Polysaccharides
3.2. Total Phenolics (TPC) and Total Flavonoid (TFC) Compounds
3.3. Natural Pigments
| Bioactive Ingredients | Origin | Extraction | Content | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pectin | YPFP | Acid extraction | 37.67 ± 0.97 g/100 g | [28] |
| PPFP | Acid extraction | 32.85 ± 1.20 g/100 g | [28] | |
| PPFP | Ultrasound-assisted conventional extraction | 12.67% | [28] | |
| PFP | High-pressure heating and conventional heating | 14.34% | [49] | |
| PFP | Enzymatic extraction | 26 g/100 g | [50] | |
| PFP | Subcritical water and pressurized natural deep eutectic solvents | 15.70% | [51] | |
| PFP | Magnetic induction electric field treatment to assist three-phase distribution | 6.58% | [52] | |
| TPC | PPFP | Organic solvent extraction | 24 ± 1 mg GAE/g | [26] |
| PFP | Ultrasound-assisted pressurized liquid extraction | 2.07 ±0.05 mg GAE/g | [53] | |
| Gallic acid | PPFP | L-Proline: Citric Acid (Pro-CA) Extract | 8.22 ± 0.15 μg/g | [42] |
| Epicatechin | PPFP | L-Proline: Citric Acid (Pro-CA) Extract | 2.74 ± 0.08 μg/g | [42] |
| Quercetin | YPFP | Acid extraction | 760.21 ± 32.07 mg/100 g | [28] |
| PPFP | L-Proline: Citric Acid (Pro-CA) Extract | 1.57 ±0.14 μg/g | [42] | |
| Rutin | PPFP | L-Proline: Citric Acid (Pro-CA) Extract | 6.66 ± 0.73 μg/g | [42] |
| Carotenoid | PFP | Ultrasound-assisted extraction of vegetable oils | 1176.195 μg/100 g | [54] |
| YPFP | Organic solvent extraction | 918.41 ± 36.81 μg/100 g | [28] | |
| PPFP | Organic solvent extraction | 1244 ± 52.5 μg/100 g | [28] | |
| Anthocyanin | PPFP | Acid extraction | 103,686.48 ± 542.11 μg/100 g | [28] |
| PPFP | Microwave-assisted extraction | 0.156 ± 0.0024 mg C3G/g | [29] | |
| PPFP | Solvent extraction | 577.59 mg C3G 100/g | [55] | |
| Cellulose nanocrystals | PFP | Acid extraction | 58.1 ± 1.7% | [56] |
4. Biological Effects
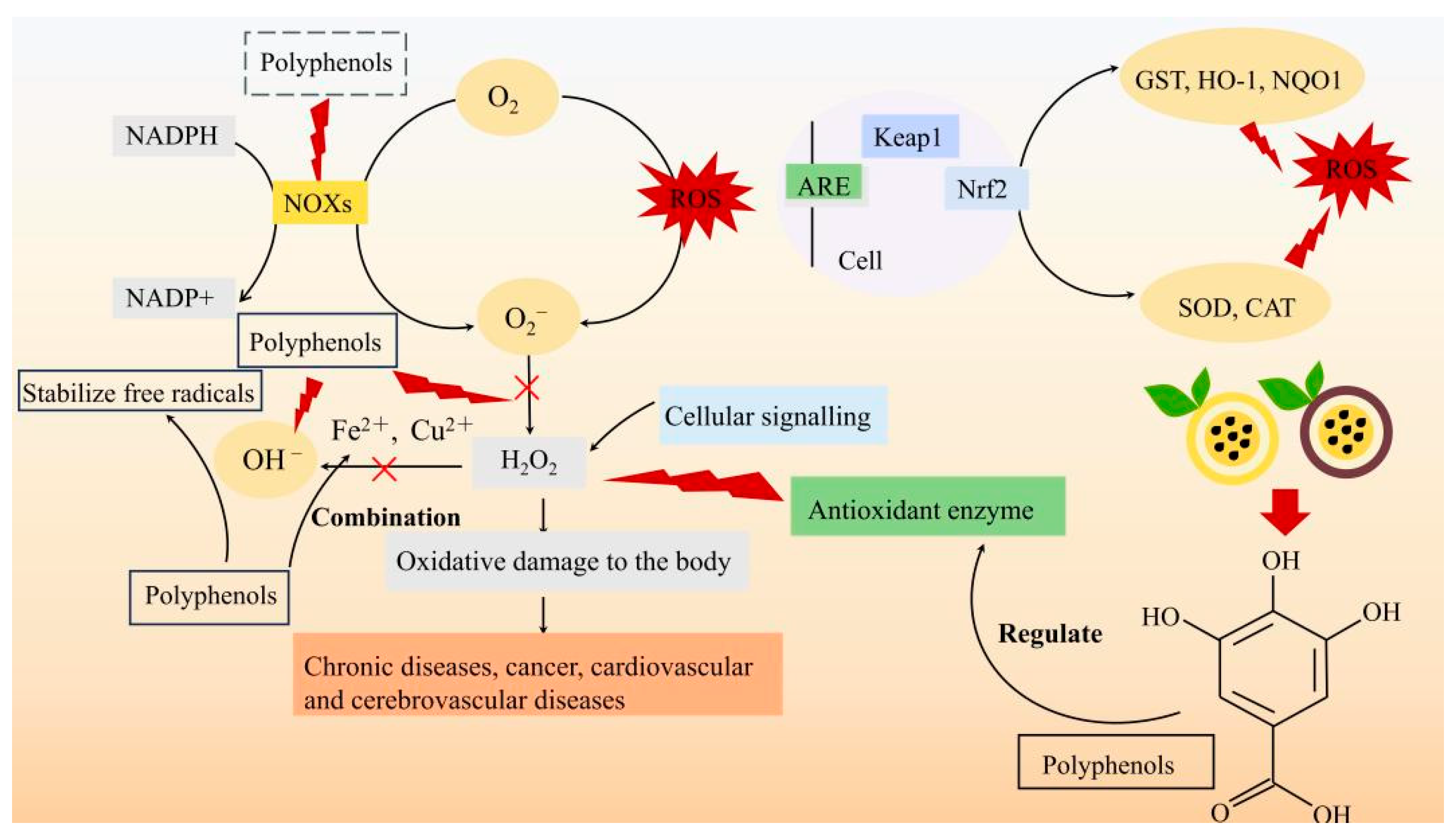
4.1. Antioxidant
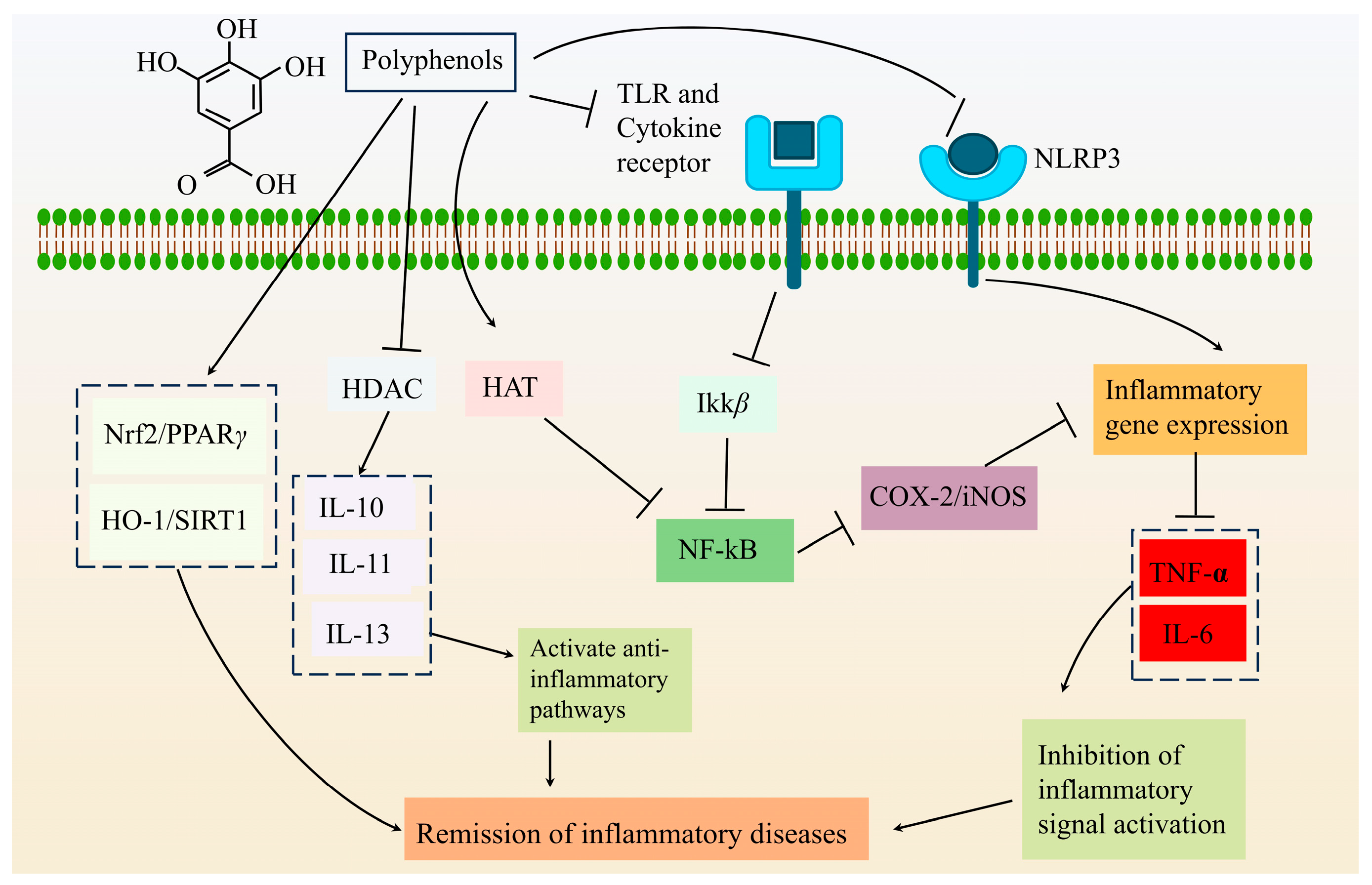
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory
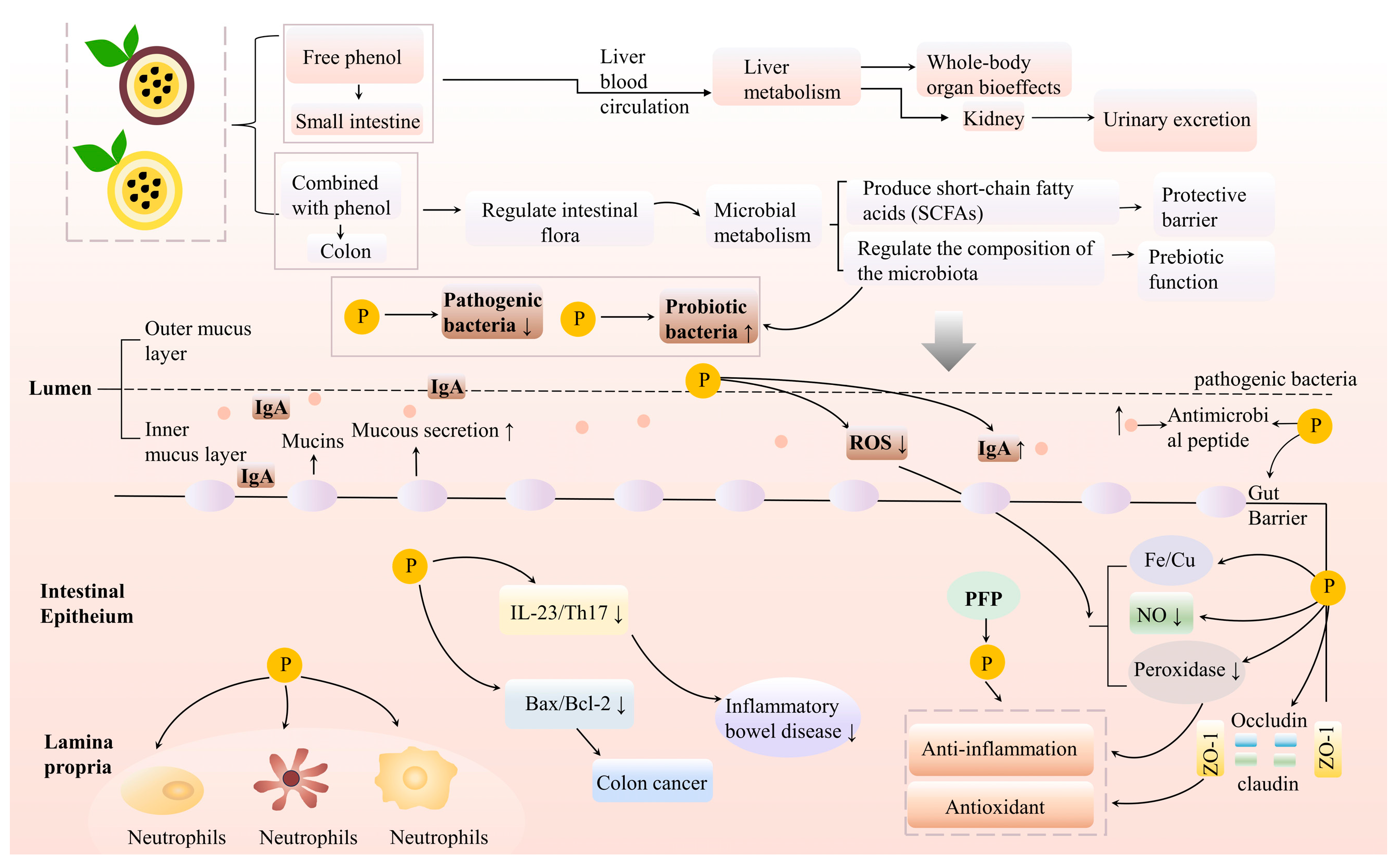
4.3. Improvement of Intestinal Health
4.4. Additional Biological Effects
| Physiological Function | Research Material | Research Type | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant | PFP | In vitro study | Eliminate ROS, such as DPPH, ABTS, and superoxide anion radicals | [44] |
| PFSP60, UPFSP60 | In vitro study | Enhance the ability to scavenge free radicals | [36] | |
| PFP | Animal experiment | Up-regulate the expression of antioxidant genes | [60] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | PFPF | Animal experiment | Inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhance the intestinal barrier, and increase short-chain fatty acids | [61] |
| PFSP60, UPFSP60 | In vitro study | Down-regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory factors | [36] | |
| PFP | In vitro study | It has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities | [43] | |
| Improve intestinal health | YPFP | In vitro digestion simulation | Promote beneficial bacteria (Prevosiella, Megalococcus) and inhibit harmful bacteria (Escherichia, Shigella) | [14] |
| YPFP | Animal experiment | Improve intestinal morphology and microbiota, and enhance immunity | [62] | |
| PFPF | Animal experiment | Increase the diversity of cecal microorganisms and enhance antioxidant and anti-inflammatory metabolic properties | [64] | |
| PFP | Animal experiment | Relieve intestinal mucositis caused by 5-FU, reduce oxidative stress and inflammation | [66] | |
| PFP | Animal experiment | Improve constipation, protect colon structure, and reduce inflammatory infiltration | [69] | |
| Lower blood sugar | PFP | In vitro study | Inhibit α-amylase, α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase | [43] |
| PFP | Animal experiment | Improve blood sugar control and protect heart and kidney functions | [73] | |
| PFP | Animal experiment | Lower blood sugar and circulating lipids | [74] | |
| Anti-fatigue | PPFP | Animal experiment | Reduce lactic acid and urea nitrogen, increase liver glycogen, and improve oxidative stress and inflammation | [75] |
| Liver protection and kidney protection | PPFP | Animal experiment | It is superior to other colors of PFP and is related to the content of polyphenols and flavonoids | [76] |
| Other functions | PFP | A variety of studies | Anti-aging, improve memory, antibacterial and so on | [77,78,79] |
5. Bioavailability/Bioaccessibility
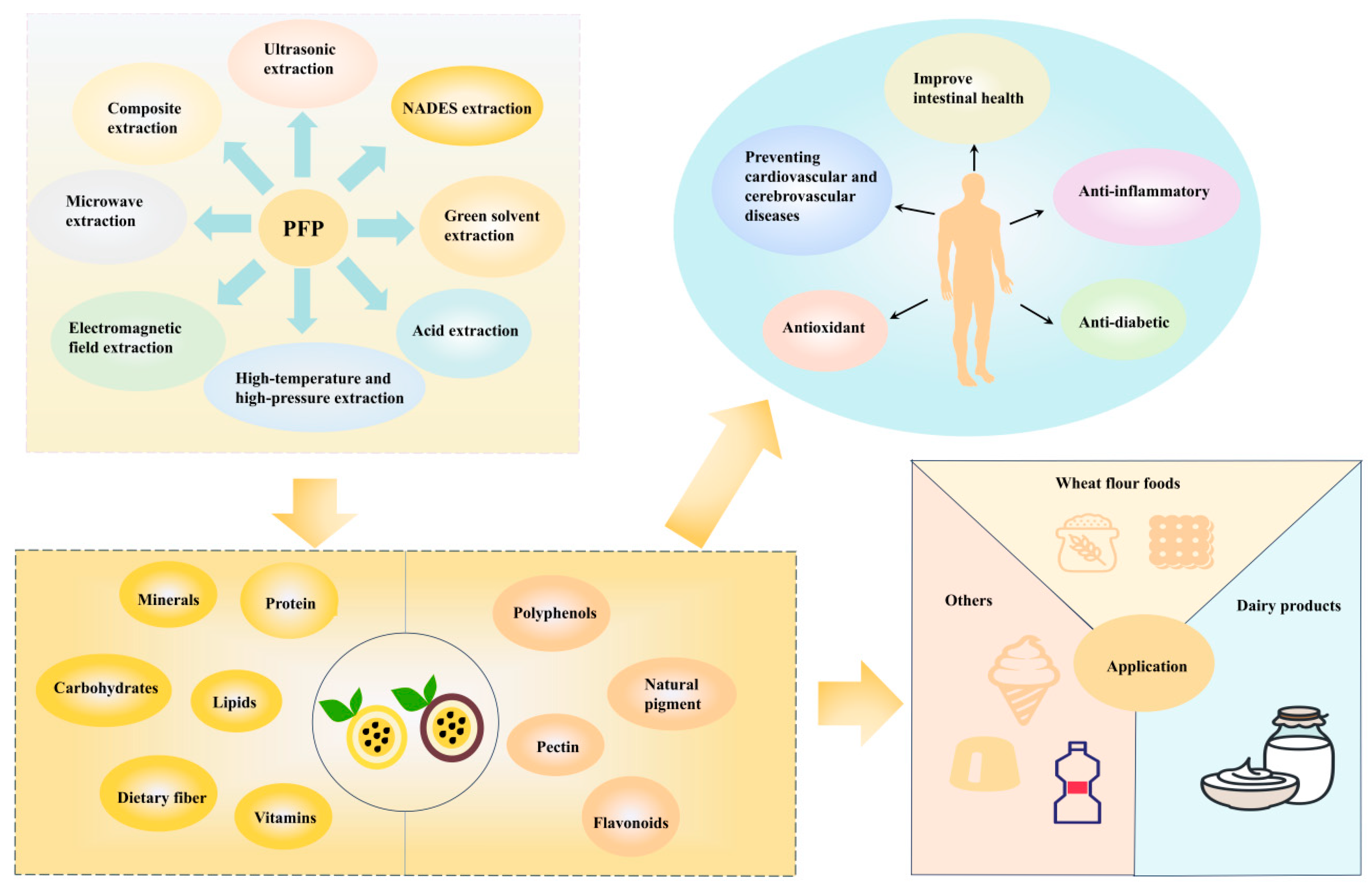
6. The Application in the Food Industry
6.1. Wheat Flour Foods
6.2. Dairy Products
6.3. Other Products
6.4. Food Packaging
6.5. Application of High-Value-Added Products
| Foods | Addition Amount | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | 100% | DPPH↑, TPC↑, color↓ | [86] |
| Biscuits | 8.5–17% | protein↑, ash content↑, DF↑, sensory quality↑ | [87] |
| 30% | DF↑, microbial content↓ | [88] | |
| 0–9% | DPPH↑, TPC↑, DF↑, color↓ | [89] | |
| 10–30% | vitamins↑, minerals↑, DF↑ | [90] | |
| Wrap | 1–3 mL | Antioxidant content↑, antibacterial properties↑ | [91] |
| Noodles | 0–9% | DPPH↑, TPC↑, DF↑ | [11] |
| Yogurt | 0–2.5% | TPC↑, TFC↑, flavonoid glycoside↑, flavor↑ | [92] |
| 0.025%, 0.05% | lactic acid bacteria↑, WHC↑, texture↑, apparent viscosity↑, dynamic viscoelasticity↑, flavor↑ | [14] | |
| 0–0.4% | stability↑, lipid↓ | [35] | |
| Jelly | 1, 3, 5% | Escherichia coli↓, yeast↓, mold↓ | [96] |
| Ice cream | 0.4, 0.8% | TPC↑, Antioxidant capacity↑, Probiotic survival rate↑ | [97] |
| Beverage | 0.025% | anthocyanin↑ | [29] |
| 73.2 g | DF↑, Antioxidant capacity↑ | [103] |
7. Challenges and Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| PFP | Passion fruit peel |
| DF | Dietary Fiber |
| PPFP | Purple Passion Fruit Peel |
| VA | Vitamin A |
| YPFP | Yellow Passion Fruit Peel |
| VC | Vitamin C |
| P | Phosphorus |
| S | Sulfur |
| Na | Sodium |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| K | Potassium |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Ca | Calcium |
| HMP | High-Methoxy Pectin |
| LMP | Low-Methoxy Pectin |
| HG | High Galacturonic Acid Polysaccharides |
| RGI | Rhamnogalacturonic Acid Polysaccharide I |
| RGII | Rhamnogalacturonic Acid Polysaccharide II |
| XG | Xylogalacturonic Acid Polysaccharides |
| TPC | Total Phenolics |
| TFC | Total Flavonoid |
| NADES | Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents |
| UAE | Ultrasound-assisted Extraction |
| TTC | Total Terpenoids |
| UA | Ursolic Acid |
| dw | Dry Weight |
| GAE | Gallic Acid Equivalent |
| C3G | Cyanidin-3-Glucoside |
| EFP | Enzymatically PFP |
| OEA | Anti-Inflammatory-Related Metabolites |
| SDF | Soluble Dietary Fiber |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid |
| CP | Citrus Pectin |
| SIC | Synbiotic Ice Cream |
References
- Cubillo, Q.M.; Díaz, V.S.; Quirós, O.J.; Valverde, A.V.; León, S.R. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Potential of Passiflora edulis (Passion fruit) at Three Ripening Stages for Waste Valorization. Molecules 2025, 30, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.N.; Dong, S.S.; Zhang, S.C.; Wei, X.Q.; Xie, Q.J.; Ding, Q.S.; Xia, R.; Zhang, X.T. Chromosome-level reference genome assembly provides insights into aroma biosynthesis in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D.; Vidal, R.F.; Brym, M.; Stafne, E.T.; Resende, M.F.R.; Viana, A.P.; Chambers, A.H. Genotyping-by-sequencing of passion fruit (Passiflora spp.) generates genomic resources for breeding and systematics. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2022, 69, 2769–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, Z.C.; dos Anjos Cruz, J.M.; Corrêa, R.F.; Sanches, E.A.; Campelo, P.H.; de Araújo Bezerra, J. Passion fruit (Passiflora spp.) pulp: A review on bioactive properties, health benefits and technological potential. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.M.A.; Geraldi, M.V.; Junior, M.R.M.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Rocha, S.M. Purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. edulis): A comprehensive review on the nutritional value, phytochemical profile and associated health effects. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, S.Y.; Hou, G.G.; Zhao, F.L.; Meng, Q.G.; Tan, S.P. Phytochemistry, nutritional composition, health benefits and future prospects of Passiflora: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.; Nagar, J.C.; Mukim, M. Pharmacological and medicinal importance of Passiflora edulis: A review. Int. J. Res. Rev. 2022, 9, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyya, G.; Belay, A.; Tadesse, E. Passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) by-products as a source of bioactive compounds for non-communicable disease prevention: Extraction methods and mechanisms of action: A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1340511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Isabella, D.A.E.; Dragan, M.; Karla, B.T.; de Oliveira, L.D.L.; Maria, C.A. Brazilian passion fruit as a new healthy food: From its composition to health properties and mechanisms of action. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10498–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguengo, L.M.; do Nascimento, R.D.P.; de Faria Machado, A.P.; Junior, M.R.M. Signaling pathways and the potential anticarcinogenic effect of native Brazilian fruits on breast cancer. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.D.; Pan, X.L.; Chen, Z.L.; Liu, Q.P.; Du, W.; Cao, X.H.; Wang, L. Evaluation of passion fruit mesocarp flour on the paste, dough, and quality characteristics of dried noodles. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3247–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Shuai, L.; Luo, D.; Ba, L. The inhibitory mechanism of eugenol on Lasiodiplodia theobromae and its induced disease resistance of passion fruit. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martinez, L.X.; Villegas-Ochoa, M.A.; Dominguez-Avila, J.A.; Yahia, E.M.; Gonzalez, G.A. Techno-Functional and bioactive properties and chemical composition of guava, mamey sapote, and passion fruit peels. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2023, 73, 173–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Wu, L.B.; Liu, X.Z.; Zhao, L.C.; Li, L.Q.; Jin, M.Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Li, L.; et al. In vitro simulated digestion and fermentation characteristics of pectic polysaccharides from fresh passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa L.) peel. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, M.A.; Mondal, S.; Khan, M.F.; Mamia, M.M.; Shohan, M.A.R.; Miah, M.P.; Khan, T.; Kabir, M.H.; Rahman, M.N.; Akther, F. Comparative analyses of proximate composition, bioactive compound and antioxidant activity in different parts of green and ripe passion fruit. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 15, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, W.; Shinohara, T.; Samaniego, I.; Sanada, A.; Terada, N.; Ron, L.; Suárez-Tapia, A.; Koshio, K. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of Passiflora spp. germplasm grown in Ecuador. Plants 2022, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Lu, X. Apple pomace as a potential valuable resource for full-components utilization: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Nickhil, C.; Deka, S.C. Comprehensive review on the nutritional and therapeutic value of banana by-products and their applications in food and non-food sectors. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczkowska, E.; Serek, P. Health-Promoting properties and the use of fruit pomace in the food industry—A review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The burden of carbohydrates in health and disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlnerhanssen, B.K.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Beglinger, C.; Islam, M.S. Metabolic effects of the natural sweeteners xylitol and erythritol: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante-Neta, A.A.; de Carvalho, Á.A.O.; D’Almeida, A.P.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; de Albuquerque, T.L. Xylitol production from passion fruit peel hydrolysate: Optimization of hydrolysis and fermentation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 414, 131628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, M.L.L.; Viana, E.B.M.; da Silva, L.E.; Zanuto, M.E.; de Souza, C.C.E. Coprodutos agroindustriais de maracujá do mato (Passiflora cincinnata Mast): Qualidade nutricional e funcional. Res. Soc. Dev. 2023, 12, e1281242788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspari, M. The seventh macronutrient: How sodium shortfall ramifies through populations, food webs and ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Kang, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. Physiological functions of the by-products of passion fruit: Processing, characteristics and their applications in food product development. Foods 2025, 14, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.M.A.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Rocha, S.M. From physicochemical characteristics variability to purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. edulis) powders nutritional value: On the path of zero-waste. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, T. Vitamins and Human Health: Editorial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, L.C.R.; Facco, E.M.P.; Salvador, M.; Flôres, S.H.; de Oliveira, R.A. Antioxidant potential and physicochemical characterization of yellow, purple and orange passion fruit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2679–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra-Castillo, O.; Hernández-Carrión, M.; Sánchez-Camargo, A.D.P. Revalorization of purple passion fruit peel: Compositional analysis, anthocyanin microwave-assisted extraction, and beverage application. Future Foods. 2025, 11, 100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.D.P.; Tarley, C.R.T. Bioaccessibility estimation of metallic macro and micronutrients Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu and Mn in flours of oat and passion fruit peel. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibele, F.D.O.; Giordani, D.; Lutckemier, R.; Gurak, P.D.; Cladera-Olivera, F.; Marczak, L.D.F. Extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel assisted by ultrasound. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.M.P.; Coimbra, J.S.R.; Souza, V.G.L.; Sousa, R.C.S. Structure and applications of pectin in food, biomedical, and pharmaceutical industry: A review. Coatings 2021, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.M.P.; Sousa, R.C.S.; Dias, M.M.S.; Coimbra, J.S.R. Extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.E.; Amaro, R.C.; Bustamante, C.C.C.; Guerra, M.H.A.; Soares, L.C.; Froes, R.E.S. Extraction of pectin from agroindustrial residue with an ecofriendly solvent: Use of FTIR and chemometrics to differentiate pectins according to degree of methyl esterification. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Ai, B.L.; Zheng, L.L.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xiao, D.; Sheng, Z.W.; Yang, J.S.; Wang, S.W. Passion fruit peel-derived low-methoxyl pectin: De-esterification methods and application as a fat substitute in set yogurt. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 347, 122664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; He, Z.G.; Li, X.Y.; Shen, W.D.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, D.; Sun, H.; Xu, X.L.; Li, C.L.; Zha, X.Q. Chemical structure, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of two novel pectin polysaccharides from purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulia Sims) peel. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1264, 133309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, G.H.; dos Santos, E.C.; da Silva, G.B.; da Silva, M.G.L.; da Silva, J.M.; Rocha, G.J.D.M.; Pita, W.D.B.; Ribeiro, E. Full utilization of the yellow passion fruit peel: Chemical characterization and valorization to reduce biomass waste. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.L.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, L.L.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xiao, D.; Wang, S.W.; Ai, B.L.; Sheng, Z.W. Extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel: Composition, structural characterization and emulsion stability. Foods 2022, 11, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.C.; Wu, L.B.; Li, L.Q.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, L.; Yan, J.K. Physicochemical, structural, and rheological characteristics of pectic polysaccharides from fresh passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa L.) peel. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.P.; Phan, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.P.; Nguyen, V.K.; Dang, T.C.T.; Nguyen, L.G.K.; Chung, T.Q.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Chau, P.T.T.; Thinh, L.D.A.; et al. Green extraction of phenolics and terpenoids from passion fruit peels using natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Food Process. Eng. 2024, 47, e14503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.P.; Nguyen, N.T.U.; Le, V.H.; Phan, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.Y.; Nguyen, D.Q. Optimizing ultrasonic-assisted and microwave-assisted extraction processes to recover phenolics and flavonoids from passion fruit peels. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 37226–37239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.X.; Dai, J.C.; Yuan, S.Y.; Cheng, X.Q.; Pan, Y.G.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.M. Eco-friendly simultaneous extraction of pectins and phenolics from passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) peel: Process optimization, physicochemical properties, and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 243, 125229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniawska, M.; Wojdyło, A. Polyphenol profiling by LC QTOF/ESI-MS and biological activity of purple passion fruit epicarp extract. Molecules 2023, 28, 6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.A.R.D.; Machado, G.G.L.; Rodrigues, L.J.; Barros, H.E.A.D.; Natarelli, C.V.L.; Boas, E.V.D.B.V. Phenolic compounds profile and antioxidant activity of purple passion fruit’s pulp, peel and seed at different maturation stages. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Rodriguez, G.; Garcia, M.C.; Plaza, M.; Marina, M.L. Revalorization of Passiflora species peels as a sustainable source of antioxidant phenolic compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Hernandez, J.C.; Taborda-Ocampo, G.; Valdez, J.C.; Bolling, B.W.; González-Correa, C.H. Polyphenol extracts from three Colombian passifloras (Passion fruits) prevent inflammation-induced barrier dysfunction of Caco-2 cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghada, B.; Pereira, E.; Pinela, J.; Prieto, M.A.; Pereira, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Stojković, D.; Sokóvić, M.; Zaghdoudi, K.; Barros, L.; et al. Recovery of anthocyanins from passion fruit epicarp for food colorants: Extraction process optimization and evaluation of bioactive properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasoe, H.; Wakamatsu, M.; Hamada, S.; Arata, Y.; Nagayoshi, K.; Uchida, R.; Yamashita, R.; Kishita, T.; Yamanouchi, H.; Minami, Y.; et al. Analysis of natural colourant extracted from the pericarp of passion fruit. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 136, 110412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.F.D.; Gurak, P.D.; Cladera-Olivera, F.; Marczak, L.D.F.; Karwe, M. Combined effect of high-pressure and conventional heating on pectin extraction from passion fruit peel. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 9, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco-Correa, J.; Zapata, A.D.Z. Enzymatic extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa) at laboratory and bench scale. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 80, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.T.V.; Méndez-Albiana, P.; Mendiola, J.A.; Villamiel, M.; Cifuentes, A.; Martínez, J.; Ibáñez, E. An eco-friendly extraction method to obtain pectin from passion fruit rinds (Passiflora edulis sp.) using subcritical water and pressurized natural deep eutectic solvents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 326, 121578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Y.; Yan, J.K.; Jin, M.Y.; Li, L.Q.; Yu, Y.H.; Xu, L. Preparation, physicochemical and functional characterization of pectic polysaccharides from fresh passion fruit peel by magnetic-induced electric field-assisted three-phase partitioning. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.T.V.; Barrales, F.M.; Pereira, E.; Viganó, J.; Iglesias, A.H.; Reyes, F.G.R.; Martínez, J. Phenolic compounds from passion fruit rinds using ultrasound-assisted pressurized liquid extraction and nanofiltration. J. Food Eng. 2022, 325, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, H.; Mahanta, C.L. Green ultrasound and microwave extraction of carotenoids from passion fruit peel using vegetable oils as a solvent: Optimization, comparison, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Ramirez, J.; Meneses-Marente, N.; Díaz, M.P.T. Optimizing the extraction of anthocyanins from purple passion fruit peel using response surface methodology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, C.J.; Saputra, S.N.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Putro, J.N.; Lin, C.X.; Kurniawan, A.; Ju, Y.H.; Ismadji, S. Cellulose nanocrystals from passion fruit peels waste as antibiotic drug carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Modulation of reactive oxygen species in health and disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, K.; Malik, A.; Almalki, W.H.; Sahebkar, A.; Kesharwani, P. Reactive oxygen species and its manipulation strategies in cancer treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 32, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahani, M.Y.; Bano, U.; Shahani, S.B.; Shaikh, P.; Memon, S.G.; Memon, S. Possible prevention of reactive oxygen species induced human trabecular meshwork cell damage by resveratrol and ascorbic acid. Prof. Med. J. 2019, 26, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outama, P.; Linh, N.V.; Xuan, C.L.; Wannaviji, S.; Tongsiri, S.; Chitmanat, C.; Montha, N.; Doan, H.V. Passionfruit (Passiflora edulis) peel powder stimulates the immune and antioxidant defense system in nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, cultivated in a biofloc system. Fishes 2022, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte-Herrera, B.H.; Domínguez-Avila, J.A.; Wall-Medrano, A.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Preciado-Saldaña, A.M.; Salazar-López, N.J.; López-Martínez, L.X.; Yahia, E.M.; Robles-Sánchez, R.M.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Lesser-consumed tropical fruits and their by-products: Phytochemical content and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, A.R.; Linh, N.V.; Srinual, O.; Fontana, C.M.; Tayyamath, K.; Wannavijit, S.; Ninyamasiri, P.; Uttarotai, T.; Tapingka, W.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; et al. Effects of passion fruit peel (Passiflora edulis) pectin and red yeast (Sporodiobolus pararoseus) cells on growth, immunity, intestinal morphology, gene expression, and gut microbiota in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 73194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Charoensiddhi, S.; Xue, X.F.; Sun, B.Q.; Liu, Y.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Wang, K. A review on the gastrointestinal protective effects of tropical fruit polyphenols. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 7130–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Huang, L.L.; Luo, H.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, X.Y.; Chen, G.; Gui, J.; Liu, Z.L.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.Z. Passion fruit peel and its zymolyte enhance gut function in Sanhuang broilers by improving antioxidation and short-chain fatty acids and decreasing inflammatory cytokines. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimisa, R.; Prasongsuk, S.; Bankeeree, W.; Pongcharoen, P.; Arboleya, S.; Nogacka, A.M.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Hwanhlem, N.; Gueimonde, M. In vitro assessment of the impact of passion fruit peel—extracted pectin added with probiotic strains on the human intestinal microbiota and metabolic activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 213, 117082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.S.D.; Abboud, K.Y.; Schiebel, C.S.; de Oliveira, N.M.T.; Bueno, L.R.; Braga, L.L.V.D.M.; Silveira, B.C.D.; dos Santos, I.W.F.; Gomes, E.D.S.; Gois, M.B.; et al. Polysaccharides from Passion Fruit Peels: From an Agroindustrial By-Product to a Viable Option for 5-FU-Induced Intestinal Damage. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, B.C.D.; Platner, F.D.S.; Rosa, L.B.D.; Silva, M.L.C.; Silva, K.S.D.; Oliveira, N.M.T.D.; Moffa, E.B.; Silva, K.F.; Lima-Neto, L.G.; Maria-Ferreira, D.; et al. Oral treatment with the pectin fibre obtained from yellow passion fruit peels worsens sepsis outcome in mice by affecting the intestinal barrier. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, L.R.; Soley, B.D.S.; Abboud, K.Y.; França, I.W.; Silva, K.S.D.; Oliveira, N.M.T.D.; Barros, J.S.; Gois, M.B.; Cordeiro, L.M.C.; Maria-Ferreira, D. Protective effect of dietary polysaccharides from yellow passion fruit peel on DSS-induced colitis in mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6298662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.T.; Li, X.H.; Wei, X.S.; Duan, X.Q.; Wang, Y.H. Passion fruit peel fermentation extract and its active component kaempferol alleviate constipation and hemorrhoids in mice by downregulating ESR1 and PI3K/Akt pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 115, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, J.; Jose, S. Antidiabetic and antioxidant profile of three varieties of passion fruit. FoodSci Indian. J. Res. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Cooper, G.J.S. Mechanisms underlying the antidiabetic activities of polyphenolic compounds: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 798329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuolo, M.M.; Lima, G.C.; Batista, N.G.; Carazin, C.B.B.; Cintra, D.E.; Prado, M.A.; Júnior, M.R.M. Passion fruit peel intake decreases inflammatory response and reverts lipid peroxidation and adiposity in diet-induced obese rats. Nutr. Res. 2020, 76, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, B.; Galdino, O.A.; Gomes, I.D.S.; Alves, J.S.F.; Marques, J.I.; de Souza, K.S.C.; da Silva, R.M.; Abreu, B.J.; Lopes, N.P.; Zucolotto, S.M.; et al. Bioactive extracts from the industrial byproduct of passion fruit promote better glycemic control in an adjuvant treatment with insulin and prevent kidney and heart damage in rats with type 1 Diabetes mellitus. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 124, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthar, R.D.O.; Maciel, A.P.O.A.; Ferreira, C.C.D. Benefícios da farinha do maracujá amarelo (Passiflora edulis F. Flavicarpa Deg.) no tratamento do Diabetes mellitus tipo 2: Uma revisão narrativa. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e1091018404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Du, J.; Du, L.D.; Luo, Q.S.; Xiong, J.H. Anti-fatigue activity of purified anthocyanins prepared from purple passion fruit (P. edulis Sim) epicarp in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerdy, N.; Ritarwan, K. Hepatoprotective activity and nephroprotective activity of peel extract from three varieties of the passion fruit (Passiflora sp.) in the albino rat. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 3176–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazliniwaty, N.; Harun, F.R.; Putra, E.D.L.; Nerdy, N. Antiaging activity of gel preparation containing three varieties of passion fruit peel ethanolic extract. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 3462–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sie, Y.Y.; Chen, L.C.; Li, C.W.; Wang, C.C.; Li, C.J.; Liu, D.Z.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, L.G.; Hou, W.C. Extracts and scirpusin B from recycled seeds and rinds of passion fruits (Passiflora edulis var. Tainung No. 1) exhibit improved functions in scopolamine-induced impaired-memory ICR mice. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwana, H.; Otibi, F.A.; Al-malki, N. Chemical composition, FTIR studies and antibacterial activity of Passiflora edulis f. edulis (Fruit). J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 13, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Tran, N.T.K.; Le, T.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Nguyen, L.T.M.; Tran, T.V. Passion fruit peel pectin/chitosan based antibacterial films incorporated with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles for wound healing application. Alexandria Eng. J. 2023, 69, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry Bioavailability and Bioequivalence, Studies Submitted in NDAs or INDs- General Considerations. 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/88254/download (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Nikou, T.; Sakavitsi, M.E.; Kalampokis, E.; Halabalaki, M. Metabolism and bioavailability of olive bioactive constituents based on in vitro, in vivo and human studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.Q.; Teng, J.W.; Wei, B.Y.; Huang, L.; Xia, N. Phenolic compounds, bioactivity, and bioaccessibility of ethanol extracts from passion fruit peel based on simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.N.; Huynh, A.T.; Barcenas, M.; Le, T.M.; Vu, H.T.K.; Vu, N.T. Biochemical conversion of passion fruit waste into highly bioaccessible, stable, and selectively functional products. Waste Biomass Valor. 2025, 16, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.B.D.; Jonathan, M.; Saad, S.M.I.; Schols, H.A.; Venema, K. Characterization and in vitro digestibility of by-products from Brazilian food industry: Cassava bagasse, orange bagasse and passion fruit peel. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2018, 16, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.C.C.; Correia, V.T.D.V.; Silva, V.D.M.; Pereira, D.T.V.; Augusti, R.; Melo, J.O.F.; Pires, C.V.; de Paula, A.C.C.F.F.; Fante, C.A. Development and characterization of yellow passion fruit peel flour (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa). Metabolites 2023, 13, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, R.F.; Lima, V.D.C.; Bungart, G.A.M.; Correia, L.D.B.; Tobal, T.M. Flour of winged-stem passion fruit peel: Nutritional composition, incorporation in cookies, and sensory acceptability. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2022, 65, e2200776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Wu, J.J.; Luo, Z.H.; Chen, Y.; Mo, Z.M.; Luo, R.H.; Bai, C.J.; Du, W.; Wang, L. Cookies fortified with purple passion fruit epicarp flour: Impact on physical properties, nutrition, in vitro starch digestibility, and antioxidant activity. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.V.; Milani, M.S.; Ries, E.F. Production optimization of passion fruit peel flour and its incorporation into dietary food. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2020, 26, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, N.C.; de Medeiros, H.I.R.; Pereira, I.C.; de Oliveira, R.E.D.S.; de Medeiros, I.L.; Junior, F.C.D.M. Elaboração de biscoito com a farinha da casca do maracujá (Passiflora edulis). Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e9734333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, H.; Harahap, H.; Iriany; Yustira, A.; Julianti, E.; Jaafar, M. Innovative edible food wraps from tilapia fish bone gelatin and passion fruit peel extract. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Yang, T.X.; Chen, J.L.; Yang, C.Z.; Niu, J.Q.; Duan, X.; Ren, G.Y.; Li, L.L. The impact of passion fruit peel powder on the physicochemical, sensory properties, and antioxidant activity of goat milk yoghurt. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 4567–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Wu, L.B.; Li, L.Q.; Jin, M.Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Yu, X.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Li, L.; Yan, J.K. Effect of pectic polysaccharides from fresh passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa L.) peel on physicochemical, texture and sensory properties of low-fat yoghurt. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.G.; Resende, E.D.D. Potential of the passion fruit mesocarp flour as a source of pectin and its application as thickener and gelling agent. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 5678–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.C.E.S.D.; Araujo, J.M.E.S.D.; Rezende, A.J.D.; Claro, P.S.; Araújo, R.L.D.O. Elaboração de geleia de goji berry, produzida de maneira artesanal, com adição de pectina da casca do maracujá. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e963454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, I.P.C.; Morais, S.K.O.; Coutinho, E.B.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Gouveia, D.S.; Vieira, P.P.F.; Mota, M.M.D.A.; Martins, J.J.A. Avaliação da estabilidade de geleia de maracujá adicionada da farinha da casca do maracujá e inulina por meio de indicadores físicos, físico-químicos e microbiológicos. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e11111133902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimisa, R.; Bankeeree, W.; Maneerat, S.; Pongcharoen, P.; Prasongsuk, S.; Hwanhlem, N. Extraction and characterization of pectin from passion fruit peel, and its application in synbiotic ice cream: A study from Phetchabun, Thailand. Fut. Foods 2024, 10, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhoz, D.R.; Moreira, F.K.V.; Bresolin, J.D.; Bernardo, M.P.; de Sousa, C.P.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Sustainable production and in vitro biodegradability of edible films from yellow passion fruit coproducts via continuous casting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15563–15575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Le, T.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Nguyen, L.T.M.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Tran, T.V. Characterizations and antibacterial activities of passion fruit peel pectin/chitosan composite films incorporated Piper betle L. leaf extract for preservation of purple eggplants. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, J.B.; Singh, K.; Sinuraya, J.S.; Supeno, M.; Sembiring, H.; Tarigan, K.; Rambe, S.M.; Karo-karo, J.A.; Sitepu, E.K. Waste passion fruit peel as a heterogeneous catalyst for room-temperature biodiesel production. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7885–7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, S.D.S.; Nobre, F.X.; Lobo, W.V.; Duvoisin, S.; Souza, C.A.S.D.; Herminio, V.L.D.Q.; Pereira, I.H.; Silva, E.P.; Iglauer, S.; Freitas, F.A.D. Eco-friendly biodiesel production using passion fruit peels and cupuaçu seeds: Catalyst development and process optimization. Biofuels, Bioprod. Bioref. 2024, 18, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.V.; Santos, L.A.; Valença, R.B.; Porto, T.S.; Sobrinho, M.A.D.M.; Gomes, G.J.C.; Jucá, J.F.T.; Santos, A.F.M.S. Cellulase production to obtain biogas from passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) peel waste hydrolysate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur-Ancona, D.; Pérez-Navarrete, C.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Sosa-Crespo, I.; Sandoval-Peraza, V. Functional, bioactive, and sensory properties of nutraceutical beverages enriched with passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) peel fiber. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 7, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ba, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Cao, S.; Luo, D. Research Progress on the Nutritional Components, Bioactivity, Health Effects, and Food Applications of Passion Fruit Peel (PFP). Foods 2025, 14, 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193397
Ba L, Luo C, Li X, Cao S, Luo D. Research Progress on the Nutritional Components, Bioactivity, Health Effects, and Food Applications of Passion Fruit Peel (PFP). Foods. 2025; 14(19):3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193397
Chicago/Turabian StyleBa, Liangjie, Chenglin Luo, Xue Li, Sen Cao, and Donglan Luo. 2025. "Research Progress on the Nutritional Components, Bioactivity, Health Effects, and Food Applications of Passion Fruit Peel (PFP)" Foods 14, no. 19: 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193397
APA StyleBa, L., Luo, C., Li, X., Cao, S., & Luo, D. (2025). Research Progress on the Nutritional Components, Bioactivity, Health Effects, and Food Applications of Passion Fruit Peel (PFP). Foods, 14(19), 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193397






