The Silent Revolution of Brewer’s Spent Grain: Meat/Food Innovations Through Circularity, Resource Recovery, and Nutritional Synergy—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Origin and Generation of Brewer’s Spent Grain
2.1. Brewing Process, Yield, and Production
2.2. Chemical Composition
2.3. Thermal Processing and Drying
2.4. Technologies for the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds
2.4.1. Phenolic Compounds
2.4.2. Bioactive Proteins and Peptides
2.4.3. Polysaccharides and Dietary Fiber
β-Glucans
Arabinoxylans
2.4.4. Lipids
2.4.5. Vitamins and Minerals
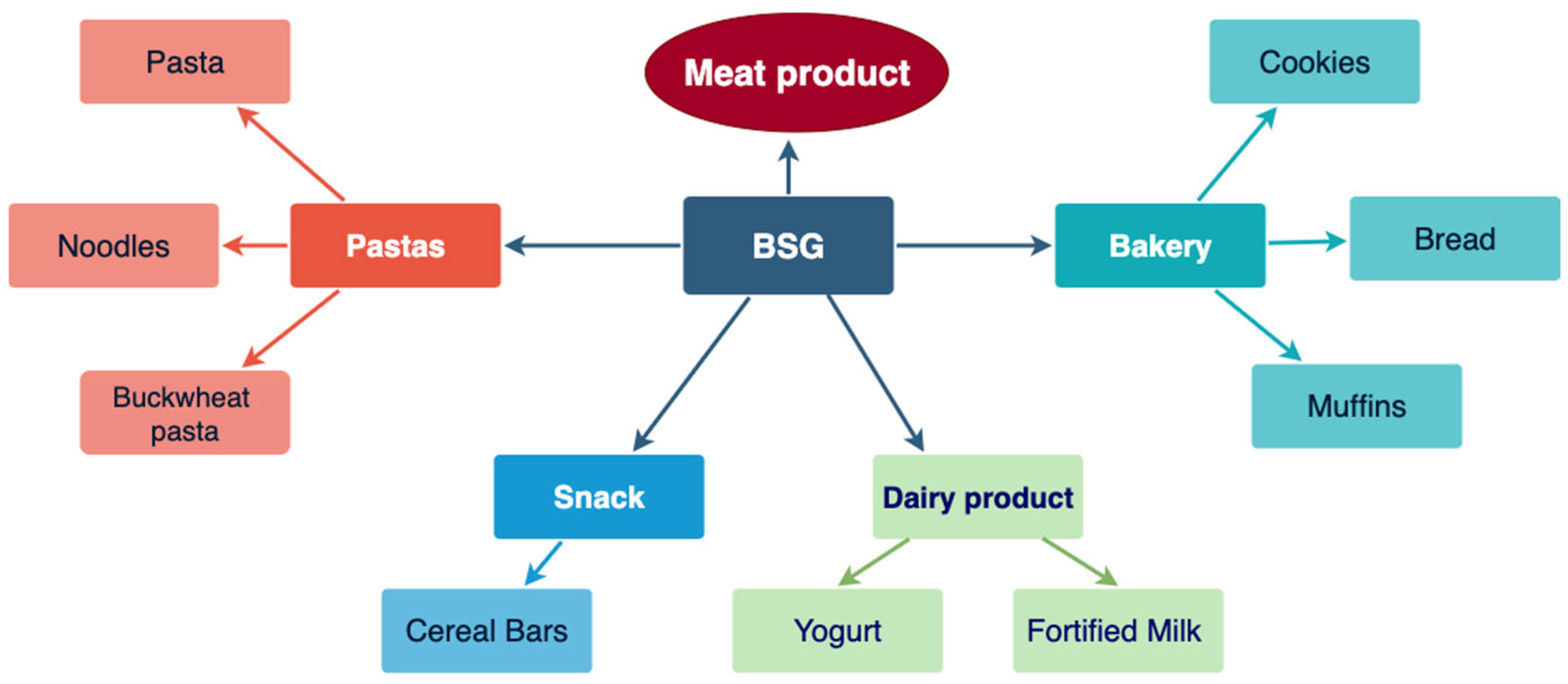
3. Use of BSG in Food Production
4. Development of Meat Products Incorporating BSG
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ Spent Grain: Generation, Characteristics and Potential Applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, G.D.; Garzón, A.G.; Cian, R.E.; Drago, S.R. Gastrointestinal and Colonic Bioaccessibility of Calcium and Ferulic Acid from Microcapsules Made with Brewer Spent Grain Arabinoxylans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, N.G.; Martins, S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Influence of Extraction Solvents on the Recovery of Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds from Brewer’s Spent Grains. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.A.; I’Anson, K.J.A.; Treimo, J.; Faulds, C.B.; Brocklehurst, T.F.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Waldron, K.W. Profiling Brewers’ Spent Grain for Composition and Microbial Ecology at the Site of Production. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisha, A.; Kaushik, D.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, A.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Proestos, C.; Khan, M.R.; Elobeid, T.; Kaur, J.; Oz, F. Volarisation of Brewer’s Spent Grain for Noodles Preparation and Its Potential Assessment against Obesity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 3154–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A.; Fiore, A.; Rutigliano, M.; Gatta, B.L. Application of a Multivariate Approach to the Study of Chemometric and Sensory Profiles of Cookies Fortified with Brewers’ Spent Grain. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 62, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, C.F.; Almeida, T.S.F.D.; Arelhano, G.E.; Alvarado, A.V.R.; Menezes, M.B.D.; Argandoña, E.J.S.; Gomes, I.L.D.A.; Moya, A.M.T.M.; Filho, P.S.L.; Santos, E.F.D. Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain as a Nutritional Ingredient in Bakery Products. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2024, 80, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-T.; Wang, W.; Hasenbeck, A.; Stone, D.; Zhao, Y. Investigation of Physicochemical, Nutritional, and Sensory Qualities of Muffins Incorporated with Dried Brewer’s Spent Grain Flours as a Source of Dietary Fiber and Protein. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3943–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; İbanoğlu, S. The Recycling of Brewer’s Processing By-Product into Ready-to-Eat Snacks Using Extrusion Technology. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2025–2034; OECD Publishing: Paris, France; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sanwal, N.; Bareen, M.A.; Barua, S.; Sharma, N.; Joshua Olatunji, O.; Prakash Nirmal, N.; Sahu, J.K. Trends in Functional Beverages: Functional Ingredients, Processing Technologies, Stability, Health Benefits, and Consumer Perspective. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 113046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Schilstra, L.; Fischer, A.R. Paradoxical Consumers in Four European Countries: Meat-Eating Justification and Willingness to Pay for Meat from Animals Treated by Alternatives to Surgical Castration. Meat Sci. 2022, 188, 108777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, P.; FitzSimmons, M.; Goodman, M.; Warner, K. Shifting Plates in the Agrifood Landscape: The Tectonics of Alternative Agrifood Initiatives in California. J. Rural Stud. 2003, 19, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D. Further Processing of Poultry. In Poultry Meat Processing and Quality; Mead, G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 108–134. ISBN 978-1-85573-727-3. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, S.; Pandey, P.; Mishra, H.N. Novel Approaches for Co-Encapsulation of Probiotic Bacteria with Bioactive Compounds, Their Health Benefits and Functional Food Product Development: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, P.D.; Araújo, W.M.C.; Patarata, L.; Fraqueza, M.J. Understanding the Main Factors That Influence Consumer Quality Perception and Attitude towards Meat and Processed Meat Products. Meat Sci. 2022, 193, 108952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Delgado-Pando, G. Fibre-enriched meat products. In En Fibre-Rich and Wholegrain Foods: Improving Quality; Delcour, J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 329–330. ISBN 978-0-85709-578-7. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Conway, J. Annual Consumption of Beer Worldwide in 2022, by Country (in 1,000 Kiloliters). Statista. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/271358/annual-consumption-of-beer-in-selected-countries/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).[Green Version]
- Conway, J. Worldwide Beer Production 2021. Statista. 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/270275/worldwide-beer-production/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).[Green Version]
- Palmer, J.J. How to Brew: Everything You Need to Know to Brew Great Beer Every Time; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017; ISBN 1-938469-36-4. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Roberto, I.C. Acid Hydrolysis and Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain to Produce Xylitol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Mathias, T.R.; Alexandre, V.M.F.; Cammarota, M.C.; de Mello, P.P.M.; Sérvulo, E.F.C. Characterization and Determination of Brewer’s Solid Wastes Composition. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.R.A.C.; Baêta, B.E.L.; Damgaard, A. Life-Cycle Assessment as a Prospection Stage for the Biochemical Methane Potential of Pretreated Lignocellulosic Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 386, 129584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.M. The Physiology of Malting—A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 1967, 73, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Lan, Y.; Ohm, J.-B.; Gillespie, J.; Schwarz, P.; Chen, B. Physicochemical Composition, Fermentable Sugars, Free Amino Acids, Phenolics, and Minerals in Brewers’ Spent Grains Obtained from Craft Brewing Operations. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 104, 103413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, Y.; Jabasingh, S.A. Lactic acid production from brewer’s spent grain by Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 8014. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2020, 79, 610–613. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361114927_Lactic_acid_production_from_Brewer’s_Spent_Grain_by_Lactobacillus_plantarum_ATCC_8014 (accessed on 25 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Gbenebor, O.P.; Olanrewaju, O.A.; Usman, M.A.; Adeosun, S.O. Lignin from Brewers’ Spent Grain: Structural and Thermal Evaluations. Polymers 2023, 15, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Fernandes, M.; Roberto, I.C. Lignin Recovery from Brewer’s Spent Grain Black Liquor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchami, M.; Agnihotri, S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Aqueous Ethanol Organosolv Process for the Valorization of Brewer’s Spent Grain (BSG). Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.; Piggott, C.O.; FitzGerald, R.J. Characterisation of Protein-Rich Isolates and Antioxidative Phenolic Extracts from Pale and Black Brewers’ Spent Grain. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Cermeno, M.; Crowley, D.; O’Callaghan, Y.; O’Brien, N.; FitzGerald, R. Characterisation of the in Vitro Bio-active Properties of Alkaline and Enzyme Extracted Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein Hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, T.; Slizyte, R.; Jensen, I.-J.; Falch, E. Effect of Moderate Heating during Alkaline Extraction on Composition and Functional Properties of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein Concentrates. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Díaz, R.L.; Saldarriaga-Hernandez, S.; Ramírez-Aguirre, M.D.; Guerrero-Higareda, S.; García-Cayuela, T.; García-Amezquita, L.E.; Carrillo-Nieves, D. Valorization of Brewer’s Spent Grains through Ganoderma lucidum Cultivation: Functional Food Ingredients and Bread Prototypes. LWT 2024, 214, 117131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río, J.C.; Prinsen, P.; Gutiérrez, A. Chemical Composition of Lipids in Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Promising Source of Valuable Phytochemicals. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaş, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Dulf, F.V.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Diaconeasa, Z. Volatile Profile, Fatty Acids Composition and Total Phenolics Content of Brewers’ Spent Grain By-Product with Potential Use in the Development of New Functional Foods. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, M. Composition and Nutrient Value Proposition of Brewers Spent Grain. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2232–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, D.; O’Callaghan, Y.; McCarthy, A.L.; Connolly, A.; Fitzgerald, R.J.; O’Brien, N.M. Aqueous and Enzyme-Extracted Phenolic Compounds from Brewers’ Spent Grain (BSG): Assessment of Their Antioxidant Potential. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.J.; Malunga, L.N.; Eskin, M.; Eck, P.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Thiyam-Hollander, U. Valorization of Heat-Treated Brewers’ Spent Grain Through the Identification of Bioactive Phenolics by UPLC-PDA and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Activities. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanho, M.N.; de Souza do Prado, K.; de Paiva, J.M.F. Developing Thermoplastic Corn Starch Composites Filled with Brewer’s Spent Grain for Applications in Biodegradable Films. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludka, F.R.; Klosowski, A.B.; Camargo, G.A.; Justo, A.S.; Andrade, E.A.; Beltrame, F.L.; Olivato, J.B. Brewers’ Spent Grain Extract as Antioxidants in Starch-Based Active Biopolymers. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchami, M.; Ferreira, J.A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Starch and Protein Recovery from Brewer’s Spent Grain Using Hydrothermal Pretreatment and Their Conversion to Edible Filamentous Fungi—A Brewery Biorefinery Concept. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantason, N.; Suphantharika, M.; Wipatanawin, A.; Chansong, S.; Payongsri, P. Valorization of Spent Grains from Beer Production through β-Glucan Extraction. Foods 2024, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.; Kupetz, M.; Becker, T. Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment of Brewer’s Spent Grain on the Concentration and Molecular Weight Distribution of 1,3-1,4-β-D-Glucan and Arabinoxylan. Foods 2023, 12, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielke, C.; Teixeira, C.; Ding, H.; Cui, S.; Nyman, M.; Nilsson, L. Analysis of β-Glucan Molar Mass from Barley Malt and Brewer’s Spent Grain with Asymmetric Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (AF4) and Their Association to Proteins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.E.N.; Colpini, L.M.S. All-around Characterization of Brewers’ Spent Grain. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, M.; Simsek, S. Arabinoxylans and Human Health. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, S.; Bala, M. Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Review of Its Potentials and Applications. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomé, B.; Santos, M.; Jiménez, J.; Del Nozal, M.; Gómez-Cordovés, C. Pentoses and Hydroxycinnamic Acids in Brewer’s Spent Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ Spent Grain: A Review with an Emphasis on Food and Health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Jiménez, J.J.; Bartolomé, B.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; del Nozal, M.J. Variability of Brewer’s Spent Grain within a Brewery. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Barrios, S.; Budelli, E.; Pérez, N.; Lema, P.; Heinzen, H. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds in Fresh and Freeze-Dried Vitis Vinifera Cv Tannat Grape Pomace. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 124, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazsefidpar, N.; Ghandehari Yazdi, A.P.; Karimi, A.; Yahyavi, M.; Amini, M.; Ahmadi Gavlighi, H.; Simal-Gandara, J. Brewers Spent Grain Protein Hydrolysate as a Functional Ingredient for Muffins: Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Sensory Evaluation. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, S.; Kumbhar, P.; Patil, O.; Landage, K.; Kabade, R.; Manjappa, A.; Disouza, J. Lyophilization: Principle, Methods, and Applications. Drug Pharm. Sci. Arch. 2021, 1, 10–14. Available online: https://dap.sciencearchives.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Drug-and-Pharmaceutical-Science-Archives-2021-Vol.-1-1-10-14.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- ElNaker, N.A.; Daou, M.; Ochsenkühn, M.A.; Amin, S.A.; Yousef, A.F.; Yousef, L.F. A Metabolomics Approach to Evaluate the Effect of Lyophilization versus Oven Drying on the Chemical Composition of Plant Extracts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, T.H.; Bustillos, R.D.A.; Olson, D.A.; Pan, Z.; Kurzrock, D.J.; Schwartz, J.L. Intermittent Infrared Drying for Brewery-Spent Grain. Unpublished/Tech Report. 2020. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/f9/e3/bd/52c1685aca895b/US20190301797A1.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Thai, S.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Alves, P.; Pan, J.; Osorio-Ruiz, A.; Miller, J.; Tam, C.; Rolston, M.R.; Teran-Cabanillas, E.; Yokoyama, W.H.; et al. Influence of Drying Methods on Health Indicators of Brewers Spent Grain for Potential Upcycling into Food Products. Anim. Feed Res. 2022, 2, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Anisha, A.; Kaushik, D.; Kaur, J.; Shubham, S.; Rusu, A.V.; Rocha, J.M.; Trif, M. Combinations of Spent Grains as Sources of Valuable Compounds with Highly Valuable Functional and Microbial Properties. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Walsh, D.; Griffin, T.P.; Islam, N.; Lyng, J.G.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K. Impact of Pulsed Electric Field Pre-Treatment on Nutritional and Polyphenolic Contents and Bioactivities of Light and Dark Brewer’s Spent Grains. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, E.E.; Görgüç, A.; Gençdağ, E.; Yılmaz, F.M. Physicochemical, Functional and Emulsifying Properties of Plant Protein Powder from Industrial Sesame Processing Waste as Affected by Spray and Freeze Drying. LWT 2022, 154, 112646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiros, C.; Christakopoulos, P. Biotechnological Potential of Brewers Spent Grain and Its Recent Applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2012, 3, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.; Jukic, M.; Lukinac, J.; Yilmaz, B.; Özogul, F.; Rocha, J. Valorization and Functionalization of Cereal-Based Industry By-Products for Nutraceuticals. In Nutraceutics from Agri-Food By-Products; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 173–222. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, D.M.; Jacob, F.; Titze, J.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Fibre, Protein and Mineral Fortification of Wheat Bread through Milled and Fermented Brewer’s Spent Grain Enrichment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaș, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Chiș, M.S.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P.; Becze, A.; Török, A.I.; Cadar, O.; Coldea, T.E.; Igual, M. In Vitro Digestibility of Minerals and B Group Vitamins from Different Brewers’ Spent Grains. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merten, D.; Erman, L.; Marabelli, G.; Leners, B.; Ney, Y.; Nasim, M.; Jacob, C.; Tchoumtchoua, J.; Cajot, S.; Bohn, T. Potential Health Effects of Brewers’ Spent Grain as a Functional Food Ingredient Assessed by Markers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Following Gastro-Intestinal Digestion and in a Cell Model of the Small Intestine. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5327–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Ortiz, A.; Hernández-Rodríguez, L.; Sandoval-Castilla, O.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Cuevas-Bernardino, J.C. Impact of Spontaneous Fermentation and Heat Treatment on the Physicochemical, Functional and Antioxidant Properties of BSG. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2025, 19, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Pandey, S.; Bhushan, K. Recent Developments in Extraction, Molecular Characterization, Bioactivity, and Application of Brewers Spent Grain Arabinoxylans. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnani, B.; Moran, G.C.; Grossmann, L. Extraction, Composition, Functionality, and Utilization of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein in Food Formulations. Foods 2023, 12, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.; Fernández-Delgado, M.; López-Linares, J.C.; García-Cubero, M.T.; Coca, M.; Lucas, S. A Techno-Economic Perspective on a Microwave Extraction Process for Efficient Protein Recovery from Agri-Food Wastes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Barrutia, M.B.; Cozzano, S.; Arcia, P.; del Castillo, M.D. An Insight into the Use of Extruded Brewers’ Spent Grain as a Healthy Human Snack Ingredient. Effects on Food Structure, Sensory Quality, Satiety and Gastrointestinal Tolerance. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Garbett, R.; Serna-Hernández, S.O.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Phenolic Compounds from Brewer’s Spent Grains: Toward Green Recovery Methods and Applications in the Cosmetic Industry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 681684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quideau, S.; Deffieux, D.; Douat-Casassus, C.; Pouységu, L. Plant Polyphenols: Chemical Properties, Biological Activities, and Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Phenolics and Polyphenolics in Foods, Beverages and Spices: Antioxidant Activity and Health Effects—A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 820–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, H.; Passarelli, S.; Szeto, J.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The Role of Polyphenols in Human Health and Food Systems: A Mini-Review. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant Polyphenols as Dietary Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio-Lopes, T.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M. Toxicity and Antihypertensive Activity of Brewer’s Spent Grain Extracts. In Proceedings of the Conference: Food Chemistry, Sevilla, España, 17–19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jesus, M.S.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Pereira, R.N.; Genisheva, Z.; Carvalho, A.C.; Pereira-Wilson, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Domingues, L. Ohmic Heating Polyphenolic Extracts from Vine Pruning Residue with Enhanced Biological Activity. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Functionality of Food Components and Emerging Technologies. Foods 2021, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, D.B.; Barba, F.J.; Granato, D.; Galanakis, C.M.; Herceg, Z.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Putnik, P. Pressurized Hot Water Extraction (PHWE) for the Green Recovery of Bioactive Compounds and Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni Leaves. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfarazi, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Rajabzadeh, G.; Galanakis, C.M. Evaluation of Microwave-Assisted Extraction Technology for Separation of Bioactive Components of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio-Lopes, T.; Vilas-Boas, A.; Machado, M.; Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Pereira, R.N.; Campos, D.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M. Exploring the Bioactive Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain Ohmic Extracts. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 76, 102943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.L.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; Piggott, C.O.; FitzGerald, R.J.; O’Brien, N.M. Brewers’ Spent Grain: Bioactivity of Phenolic Component, Its Role in Animal Nutrition and Potential for Incorporation in Functional Foods—A Review. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.M.; Morais, S.; Carvalho, D.O.; Barros, A.A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Guido, L.F. Brewer’s Spent Grain from Different Types of Malt: Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity and Identification of the Major Phenolic Compounds. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Riaño, P.; Sanz, M.; Benito-Román, O.; Beltrán, S.; Trigueros, E. Subcritical Water as Hydrolytic Medium to Recover and Fractionate the Protein Fraction and Phenolic Compounds from Craft Brewer’s Spent Grain. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.; Cermeño, M.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E.; FitzGerald, R.J. Generation of Phenolic-Rich Extracts from Brewers’ Spent Grain and Characterisation of Their in Vitro and in Vivo Activities. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Linares, J.C.; Campillo, V.; Coca, M.; Lucas, S.; García-Cubero, M.T. Microwave-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Brewer’s Spent Grain. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, K.A.; MacCallum, J.L. The Protein-Folding Problem, 50 Years On. Science 2012, 338, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehninger, A.L.; Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 4th ed.; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-7167-4339-6. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.; Johansen, A.Z.; Mussatto, S.I. Evaluation of Different Pretreatment Strategies for Protein Extraction from Brewer’s Spent Grains. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. The Effects of Malting and Mashing on Barley Protein Extractability. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.; Sahin, A.W.; Nyhan, L.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Functional Properties of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein Isolate: The Missing Piece in the Plant Protein Portfolio. Foods 2023, 12, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L.; Temelli, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Functionality of Barley Proteins Extracted and Fractionated by Alkaline and Alcohol Methods. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederix, S.; Greden, K. Protein Powder. U.S. Patent US20220295824A1, 22 September 2022. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20220295824A1/en?assignee=evergrain&oq=evergrain (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Vieira, M.C.; Brandelli, A.; Thys, R.C.S. Evaluation of the Technological Functional Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Protein Hydrolysate Obtained from Brewers’ Spent Grain. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Oliveira, R.; Martins, Z.; Faria, M.; Sousa, J.; Ferreira, I.; Diniz, C. Protein Hydrolysates from Brewing By-Products as Natural Alternatives to ACE-Inhibitory Drugs for Hypertension Management. Life 2022, 12, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izydorczyk, M.S.; Dexter, J.E. Barley β-Glucans and Arabinoxylans: Molecular Structure, Physicochemical Properties, and Uses in Food Products—A Review. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 850–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupetz, M.; Procopio, S.; Sacher, B.; Becker, T. Critical Review of the Methods of β-Glucan Analysis and Its Significance in the Beer Filtration Process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission. The State of Food and Agriculture 1992. In Codex Alimentarius; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1992; ISBN 92-5-103629-2. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/5a2f148a-9c72-4e31-9d80-161b70a1dc63/content (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Cummings, J.; Stephen, A. Carbohydrate Terminology and Classification. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, S5–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Understanding the Codex Alimentarius; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 92-5-109236-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, R.; Jaiswal, A.K. Exploitation of Food Industry Waste for High-Value Products. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procentese, A.; Raganati, F.; Olivieri, G.; Russo, M.E.; De La Feld, M.; Marzocchella, A. Agro Food Wastes and Innovative Pretreatments to Meet Biofuel Demand in Europe. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.-L.; Ko, K.-C.; Li, X.; Ke, X.; Cheng, W.-Y.; Chen, T.; You, L.; Kwan, H.-S.; Cheung, P.C.-K. In Vitro Infant Faecal Fermentation of Low Viscosity Barley β-Glucan and Its Acid Hydrolyzed Derivatives: Evaluation of Their Potential as Novel Prebiotics. Molecules 2019, 24, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobelev, K.V.; Gribkova, I.N.; Kharlamova, L.N.; Danilyan, A.V.; Zakharov, M.A.; Lazareva, I.V.; Kozlov, V.I.; Borisenko, O.A. Study of Brewer’s Spent Grain Environmentally Friendly Processing Ways. Molecules 2023, 28, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, H.; Coldea, T.E.; Zhao, H. Improving the Emulsifying Capacity of Brewers’ Spent Grain Arabinoxylan by Carboxymethylation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Strain, C.R.; Johnson, C.; Patangia, D.; Stanton, C.; Koc, F.; Gil-Martinez, J.; O’Riordan, P.; Sahin, A.W.; Ross, R.P. Extraction and Characterisation of Arabinoxylan from Brewers Spent Grain and Investigation of Microbiome Modulation Potential. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4393–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete-Torre, I.; Sabater, C.; Montilla, A.; Moreno, F.; Riestra, S.; Margolles, A.; Ruiz, L. Physicochemical Characterization and Microbiota Modulatory Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain and Arabinoxylan-Derived Fractions: A Valorization Study. LWT 2023, 185, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.-Y.I.; Miri, T.; Onyeaka, H. Valorization of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Brewer’s Spent Grain (BSG) for Sustainable Food Waste Recycling. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, L.F.; Moreira, M.M. Techniques for Extraction of Brewer’s Spent Grain Polyphenols: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, C.; Azzollini, D.; Jouppila, K.; Laaksonen, J.; Derossi, A.; De Pilli, T. Effect of Enzymatic and Technological Treatments on Solubilisation of Arabinoxylans from Brewer’s Spent Grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M. Novel Route to Stabilization of Bioactive Antioxidants by Encapsulation in Electrospun Fibers of Zein Prolamine. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Encinas, E.G.; Carvajal-Millán, E.; Calderón de la Barca, A.M.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Márquez-Escalante, J.A.; Islas-Rubio, A.R. Extraction and Characterization of Arabinoxylans Obtained from Nixtamalized Brewers’ Spent Grains. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2023, 29, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.F.; Coelho, E.; Coimbra, M.A.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Improved Efficiency of Brewer’s Spent Grain Arabinoxylans by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 24, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetrariu, A.; Dabija, A. Spent Grain from Malt Whisky: Assessment of the Phenolic Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, G.F., Jr.; McClung, J.P. The Vitamins: Fundamental Aspects in Nutrition and Health, 5th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-0-12-802965-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, A.; Procopio, S.; Becker, T. Influence of Malting and Lactic Acid Fermentation on Functional Bioactive Components in Cereal-Based Raw Materials: A Review Paper. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucker, B.; Wakeling, L.; Vriesekoop, F. Vitamins in Brewing: Presence and Influence of Thiamine and Riboflavin on Wort Fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, V.; Diósi, G. Using Brewer’s Spent Grain as a Byproduct of the Brewing Industry in the Bakery Industry. Élelmiszervizsgálati Közlemények 2021, 67, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bokhorst-van de Veen, H.; Berendsen, L.; Helmond, M.; Nierop Groot, M. In Situ Fortification of Protein-Enriched Brewer’s Spent Grain with Vitamin B12 by Fermentation with Priestia megaterium and Propionibacterium freudenreichii. LWT 2024, 205, 116520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, A.I.; Petron, M.J.; Lopez, A.M.; Timon, M.L. Optimization of Extraction Conditions to Improve Phenolic Content and In Vitro Antioxidant Activity in Craft Brewers’ Spent Grain Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Foods 2020, 9, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afify, A.E.-M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; El-Salam, S.M.A.; Omran, A.A. Biochemical Changes in Phenols, Flavonoids, Tannins, Vitamin E, β–Carotene and Antioxidant Activity during Soaking of Three White Sorghum Varieties. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Bao, J.; Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Guo, M. Applicability of Wheat Brewer’s Spent Grain in Steamed Bread-Making Based on Physicochemical and Visual Profiles Assessment of Doughs and Breads. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2024, 10820132241260453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 123 Tu, C.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Li, N.; Zhao, R.; Jiao, L.; Ran, J.; Huang, J. Effect of Dried Distillers Grains on Quality of Dough and Bread. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 124, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Ropciuc, S.; Dabija, A.; Saitan, O.; Boestean, O.; Paiu, S.; Rumeus, I.; Leatamborg, S.; Lupascu, G.; Codină, G.G. Effect of Brewers’ Spent Grain Addition to a Fermented Form on Dough Rheological Properties from Different Triticale Flour Cultivars. Foods 2024, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira de Freitas, F.P.; da Silva Lannes, S.C. Composition and Sensory Properties of Breads Supplemented with Brewers’ Spent Grain from Three Different Craft Beer Styles. Cereal Chem. 2024, 101, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păcală, M.-L.; Sîrbu, A.; Șipoș, A. Non-Conventional Brewers’ Spent Grains, an Alternative Raw Material in Bread-Making. Foods 2024, 13, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira de Freitas, F.P.; Steel, C.J.; da Silva Lannes, S.C. Brewers’ Spent Grain from Three Styles of Craft Beer: Characterization and Their Rheological Effects on Wheat Flour Dough. Cereal Chem. 2023, 100, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileoni, V.; Alfeo, V.; Bravi, E.; Belardi, I.; Marconi, O. Upcycling of a By-Product of the Brewing Production Chain as an Ingredient in the Formulation of Functional Shortbreads. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 98, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neylon, E.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E.; Sahin, A.W. Fermentation as a Tool to Revitalise Brewers’ Spent Grain and Elevate Techno-Functional Properties and Nutritional Value in High Fibre Bread. Foods 2021, 10, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocente, F.; Natale, C.; Galassi, E.; Taddei, F.; Gazza, L. Using Einkorn and Tritordeum Brewers’ Spent Grain to Increase the Nutritional Potential of Durum Wheat Pasta. Foods 2021, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettino, R.; Verni, M.; Acin-Albiac, M.; Vincentini, O.; Krona, A.; Knaapila, A.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Coda, R. Bioprocessed Brewers’ Spent Grain Improves Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of Pasta. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.; Hardiman, K.; Atzler, J.; Vogelsang-O’Dwyer, M.; Valdeperez, D.; Münch, S.; Cattaneo, G.; O’Riordan, P.; Arendt, E. Rejuvenated Brewer’s Spent Grain: The Impact of Two BSG-Derived Ingredients on Techno-Functional and Nutritional Characteristics of Fibre-Enriched Pasta. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.C.; Castura, J.C.; Nguyen, D.D.L.; Varela, P. Identifying Temporal Sensory Drivers of Liking of Biscuit Supplemented with Brewer’s Spent Grain for Young Consumers. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 113049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.; Palma, M.L.; Reis, R.; Amaro, R.; Fernandes, J.; Gonçalves, E.M.; Silva, M.; Lageiro, M.; Charmier, A.; Maurício, E.; et al. Assessing the Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain to Enhance Cookie Physicochemical and Nutritional Profiles. Foods 2025, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Leong, Z.N.; Zhang, W.; Jin, X.; Kong, J.W.; Chan, G.C.; Kim, J.E. Impact of Brewers’ Spent Grain-Containing Biscuit on Postprandial Glycaemic Response in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome: A Crossover Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cong, L.; Mirosa, M.; Hou, Y.; Bremer, P. Food Technology Neophobia Scales in Cross-National Context: Consumers’ Acceptance of Food Technologies between Chinese and New Zealand. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 3551–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermeño, M.; Dermiki, M.; Kleekayai, T.; Cope, L.; McManus, R.; Ryan, C.; Felix, M.; Flynn, C.; FitzGerald, R.J. Effect of Enzymatically Hydrolysed Brewers’ Spent Grain Supplementation on the Rheological, Textural and Sensory Properties of Muffins. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciulli, M.; Sogari, G.; Rodolfi, M.; Parenti, O.; Andreani, G.; Chiavaro, E. Fostering Circular Economy: Brewing By-Products as Innovative Ingredients for Cereal Bar Formulation. Foods 2024, 13, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombini, C.; Dacoreggio, M.V.; Kempka, A.P.; Feltes, M.M.C.; De Mello, J.M.M.; Dalcanton, F. High-Dietary Fibers Cereal Bars Containing Malt Bagasse by-Product from the Brewing Industry. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 61, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubaszek, A.; Wojciechowicz-Budzisz, A.; Spychaj, R.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Effect of Added Brewer’s Spent Grain on the Baking Value of Flour and the Quality of Wheat Bread. Molecules 2022, 27, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoriello, T.; Mellara, F.; Galli, V.; Amoriello, M.; Ciccoritti, R. Technological Properties and Consumer Acceptability of Bakery Products Enriched with Brewers’ Spent Grains. Foods 2020, 9, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocente, F.; Taddei, F.; Galassi, E.; Gazza, L. Upcycling of Brewers’ Spent Grain by Production of Dry Pasta with Higher Nutritional Potential. LWT 2019, 114, 108421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Sandoval, N.G.; Granados-Nevárez, M.d.C.; Calderón de la Barca, A.M.; Vásquez-Lara, F.; Malunga, L.N.; Apea-Bah, F.B.; Beta, T.; Islas-Rubio, A.R. Phenolic Acids, Antioxidant Capacity, and Estimated Glycemic Index of Cookies Added with Brewer’s Spent Grain. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Sagdic, O.; Tornuk, F.; Yetim, H. Effect of Wheat Sprout Powder Incorporation on Lipid Oxidation and Physicochemical Properties of Beef Patties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Ton, N.; Le, N.; Le, V. Addition of Brewing Spent Grains from Malt and Rice Adjunct to the Formulation of High Fiber Biscuit: Effects of Particle Size of Brewing Spent Grains on the Product Quality. Food Res 2020, 4, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubaszek, A.; Wojciechowicz-Budzisz, A.; Spychaj, R.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Baking Properties of Flour and Nutritional Value of Rye Bread with Brewer’s Spent Grain. LWT 2021, 150, 111955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, F.; Trivisonno, M.C.; Iacovino, S.; Messia, M.C.; Marconi, E. Sustainable Re-Use of Brewer’s Spent Grain for the Production of High Protein and Fibre Pasta. Foods 2022, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, J.; Fernández-Fernández, A.M.; Briozzo, F.; Díaz, S.; Dorgans, A.; Tajam, V.; Medrano, A. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis of brewer’s spent grain on bioactivity, techno-functional properties, and nutritional value when added to a bread formulation. Foods 2021, 6, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Pinto, F.J.; Miranda-Medina, J.D.; Natera-Maldonado, A.; Vara-Aldama, Ó.; Ortueta-Cabranes, M.P.; del Mercado-Pardiño, J.A.V.; El-Aidie, S.A.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Castro-Munoz, R. Arabinoxylans: A Review on Protocols for Their Recovery, Functionalities and Roles in Food Formulations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannini, E.; Bravo Núñez, Á.; Sahin, A.W.; Arendt, E.K. Arabinoxylans as Functional Food Ingredients: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fărcas, A.; Socaci, S.; Chis, M.; Pop, O.; Fogarasi, M.; Paucean, A.; Igual, M.; Michiu, D. Reintegration of Brewers Spent Grains in the Food Chain: Nutritional, Functional and Sensorial Aspects. Plants 2021, 10, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktenioudaki, A.; Chaurin, V.; Reis, S.F.; Gallagher, E. Brewer’s Spent Grain as a Functional Ingredient for Breadsticks. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Costa, R.; de Almeida, S.S.; Cavalcanti, E.; d’Avila, C.; Freire, D.M.G.; Moura-Nunes, N.; Monteiro, M.; Perrone, D. Enzymes Produced by Solid State Fermentation of Agro-Industrial by-Products Release Ferulic Acid in Bioprocessed Whole-Wheat Breads. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, S.; Özboy, Ö.; Cavidoğlu, İ.; Köksel, H. Effects of Brewer’s Spent Grain on the Quality and Dietary Fibre Content of Cookies. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delić, J.; Peulić, T.; Radmilo Čolović, P.I.; Peulić, T.; Jokanović, M.; Slađana Rakita, V.B. Mechanically Deboned Poultry Meat and Brewer’s Processing by-Product as Promising Ingredients for Nutritionally Valuable Extruded Snacks. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 32, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastanjević, K.; Perković, I.; Škrivanko, M.; Kovačević, D.; Biondić, H.; Habschied, K. Effect of the Addition of Brewers’ Spent Grain (BSG) on the Physicochemical and Consumer Liking Attributes of Croatian Indigenous Cooked Sausage “Bijela Krvavica”. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Silva, G.; Vásquez-Lara, F.; Heredia-Sandoval, N.G.; Islas-Rubio, A.R. Effect of High-Protein and High-Fiber Breaders on Oil Absorption and Quality Attributes in Chicken Nuggets. Foods 2023, 12, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Esposito, C.; Piccinocchi, R.; De Lellis, L.F.; Santarcangelo, C.; Minno, A.D.; Baldi, A.; Buccato, D.G.; Khan, A.; Piccinocchi, G.; et al. Postprandial Glycemic and Insulinemic Response by a Brewer’s Spent Grain Extract-Based Food Supplement in Subjects with Slightly Impaired Glucose Tolerance: A Monocentric, Randomized, Cross-Over, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hwang, K.; Song, D.; Lee, S.; Choi, M.; Lim, Y.; Choi, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, C. Effects of Dietary Fiber Extracts from Brewer’s Spent Grain on Quality Characteristics of Chicken Patties Cooked in Convective Oven. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2013, 33, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Socaci, S.A.; Pop, C.R.; Rotar, A.M.; Sălăgean, C.D.; Tofană, M. Utilization of Brewer’s Spent Grain and Mushrooms in Fortification of Smoked Sausages. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fogarasi, M.; Socaci, S.A.; Tofană, M.; Semeniuc, C.; Sălăgean, D.; Țibulcă, D.; Muresan, C. Evaluation of Sensory and Physical-Chemical Properties of Smoked Sausage Based On Food Waste Sources. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol 2018, 24, 219–223. Available online: https://journal-of-agroalimentary.ro/admin/articole/17045XL32_Melinda_Fogarasi_2018_24(3)_219-222.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).[Green Version]
- Saraiva, B.; Agustinho, B.; Vital, A.; Staub, L.; Pintro, P. Effect of Brewing Waste (Malt Bagasse) Addition on the Physicochemical Properties of Hamburgers. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, 14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, K.C.G.; de Farias, A.K.N.; Becker, G.; de Britto, G.C.S.; Soares, W.P.; Nascimento, E.; Scabora, M.H.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Picanço, N.F.M.; de Faria, R.A.P.G. Quality Measurements of Cuiabana-Type Pork Sausages Added with Brewing by-Product Flours. Meat Sci. 2021, 179, 108441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talens, C.; Llorente, R.; Simo-Boyle, L.; Odriozola-Serrano, I.; Tueros, I.; Ibarguen, M. Hybrid Sausages: Modelling the Effect of Partial Meat Replacement with Broccoli, Upcycled Brewer’s Spent Grain and Insect Flours. Foods 2022, 11, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özvural, E.B.; Vural, H.; Gökbulut, İ.; Özboy-Özbaş, Ö. Utilization of Brewer’s Spent Grain in the Production of Frankfurters. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, S.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Microencapsulation of Extracted Bioactive Compounds from Brewer’s Spent Grain to Enrich Fish-Burgers. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-S.; Hwang, K.-E.; Song, D.-H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, C.-J. Effects of brewer’s spent grain dietary fiber on quality characteristics of low-fat chicken sausages. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour. 2014, 34, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.M.M.; Lima, M.A.; Koksel, F.; Sato, A.C.K. Incorporation of Brewer’s Spent Grain into Plant-Based Meat Analogues: Benefits to Physical and Nutritional Quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 3870–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Annamalai, P.K.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S. Characteristics of Faba Bean Protein-Based High-Moisture Meat Analogues Incorporating Brewers’ Spent Grain through Extrusion. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 100, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curutchet, A.; Arcia, P.; Prisco, F.; Tarrega, A. Brewer’s Spent Grain Used in Fiber-Enriched Burgers—Influence of Sustainability Information on Consumer Responses. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, K.; Tabib, M.; Salameh, S.J.; Koubaa, M.; Ziegler-Devin, I.; Brosse, N.; Khelfa, A. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Lignin from Brewer’s Spent Grains. Polymers 2024, 16, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinoto, K.; Ling, J.K.-U.; Park, J.-W.; Tran, T.-T.; Pu, S. Extraction of Brewer’s Spent Grain Protein Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Compared to Alkaline Extraction: Evaluating Their Yields, Physicochemical Characteristics, and Functionalities. Food Bioprod. Process. 2025, 150, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airouyuwa, J.O.; Mostafa, H.; Riaz, A.; Stathopoulos, C.; Maqsood, S. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Microwave-Assisted Green Extraction for Efficient Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from by-Products of Date Fruit (Phoenix Dactylifera L.) Processing: Modeling, Optimization, and Phenolic Characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 824–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardi, I.; Marrocchi, A.; Alfeo, V.; Sileoni, V.; De Francesco, G.; Paolantoni, M.; Marconi, O. Sequential Extraction and Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in the Biorefining of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Molecules 2023, 28, 4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiro, F.; Esteves, M.P.; Parajó, J.C.; Pereira, H.; Gírio, F.M. Production of Oligosaccharides by Autohydrolysis of Brewery’s Spent Grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.D.; Jisaka, J.S.; Pereira, A.C.; Steel, C.J. Thermoplastic Extrusion Technology as a Tool for Adding Value to Brewer’s by-Products. LWT 2023, 189, 115487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, T.A.; Calado, V.; Carvalho, C.W. Effect of Brewer’s Spent Grain and Temperature on Physical Properties of Expanded Extrudates from Rice. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thokachichu, S. Optimization of Brewers Spent Grain Fortification to Develop Value-Added Breakfast Cereal Using a Single Screw Extrusion Process Based on Physicochemical, Nutritional, and Sensory Properties. 2023. Available online: http://digital.library.wisc.edu/1793/84862 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Qazanfarzadeh, Z.; Masek, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Kumaravel, V. Development of Brewer’s Spent Grain-Derived Bio Nanocomposites through a Multiproduct Biorefinery Approach for Food Packaging. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez, S.A.; Fermentation Using A. Evaluation of in Vitro Bioactive Properties of Protein Hydrolysates of Brewers’ Spent Grain (BSG) Obtained through Solid-State Fermentation Using A. oryzae and Functional Characteriation of BSG. 2022. Available online: https://repositorioslatinoamericanos.uchile.cl/handle/2250/7716528 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Verni, M.; Pontonio, E.; Krona, A.; Jacob, S.; Pinto, D.; Rinaldi, F.; Verardo, V.; Díaz-de-Cerio, E.; Coda, R.; Rizzello, C.G. Bioprocessing of Brewers’ Spent Grain Enhances Its Antioxidant Activity: Characterization of Phenolic Compounds and Bioactive Peptides. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalić, A.; Jagelavičiūtė, J.; Rezić, T.; Trivunović, Z.; Žadeikė, D.; Bašinskienė, L. From Bakery Leftovers to Brewing Sustainability: Fermentation of Spent Grain with Yarrowia lipolytica and Lactobacillus acidophilus. Sustainability 2025, 17, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Barrutia, M.; Cozzano, S.; Arcia, P.; del Castillo, M. In Vitro Digestibility and Bioaccessibility of Nutrients and Non-Nutrients Composing Extruded Brewers’ Spent Grain. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Technology | Target Compounds | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Solid–Liquid Extraction | Phenolic compounds, lipids | Simple, well-established, relatively low cost; suitable for various solvents (e.g., ethanol, methanol). | Low selectivity; long extraction times; possible degradation of heat-sensitive compounds; high solvent use and disposal concerns. |
| Microwave-Assisted Extraction | Phenolics, proteins, polysaccharides | High extraction efficiency in a short time; reduced solvent use; effective cell wall disruption. | Non-uniform heating can reduce reproducibility; high equipment cost; limited scalability. |
| Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction | Phenolics, polysaccharides, proteins | Enhance mass transfer; low temperature process preserves bioactivity; relatively low cost. | Possible degradation of sensitive compounds due to cavitation; scalability challenges for uniform energy distribution. |
| Enzymatic Hydrolysis | Proteins (bioactive peptides), polysaccharides (β-glucans, arabinoxylans) | Highly selective; mild processing preserves functional properties; generates high-purity extracts. | High cost of enzymes; requires precise control of pH and temperature; potential long processing times. |
| Alkaline Hydrolysis | Bound phenolics, proteins | Efficient for breaking ester bonds and releasing bound phenolics; relatively inexpensive. | May degrade sensitive bioactives; environmental concerns from alkaline waste; reduced suitability for food applications without purification. |
| Supercritical Fluid Extraction | Lipids, non-polar compounds | Solvent-free extracts; preserves thermo-labile compounds; environmentally friendly; tunable selectivity via pressure/temperature. | High capital and operating costs; not ideal for highly polar compounds without co-solvents. |
| Pressurized Hot Water Extraction (PHWE/Subcritical Water Extraction) | Phenolics, polysaccharides | High efficiency; avoids organic solvents; eco-friendly; effective release from lignocellulosic matrix. | Requires high-pressure, high-temperature equipment; risk of thermal degradation of heat-sensitive compounds. |
| Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction | Phenolics, polysaccharides | Green, biodegradable solvents; high solubility for phenolics; potential to replace hazardous solvents. | Limited industrial validation: viscosity of solvents may hinder large-scale processing. |
| Infrared Drying + Milling Pre-treatment | General compounds (preparation step) | Reduces drying time and energy; preserves aroma and color; improves downstream extraction efficiency. | Requires investment in specialized equipment; it may not be suitable for all bioactives. |
| Type of Product Analyzed | BSG Onboarding | Functionality Technology | Main Finding | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sausage Hybrids | Partial meat substitution (35%) with BSG, broccoli and insects | Modeling with simplex design and optimization by desirability function | Protein enhancement, traditional sausage-like texture, sensory acceptance | [164] |
| Cuiabana sausage | Partial replacement of meat with BSG meal (up to 6%) | Physical–chemical and microbiological analysis | Increased fiber and protein, no lipid oxidation | [163] |
| Burgers | Fat replacement with malt bagasse (up to 3%) | Antioxidant evaluation and texture | Higher fiber, lower calories, improved cooking parameters | [162] |
| Frankfurters | BSG Fat replacement | Textural and compositional analysis | Improved texture and fat reduction without affecting quality | [165] |
| Fish burgers | Microencapsulation of BSG bioactive compounds | Bioactive enrichment | Increase in bioactive compounds without altering sensory properties | [166] |
| Low-fat chicken sausages | Replacing Fat with BSG Dietary Fiber | Textural and nutritional profile analysis | Better nutritional quality and texture in reduced-fat products | [167] |
| Chicken burgers | Addition of BSG Dietary Fiber | Convective oven cooking | Better moisture retention and firm texture | [159] |
| Vegetable meat analogues | Incorporation of BSG as an ingredient (up to 20%) | Extrusion in vegetable mixtures | Improved fibrous texture and nutritional profile (protein and fiber) | [168] |
| Extruded snacks | Mixing BSG with poultry meal | High temperature extrusion | Snacks rich in fiber and protein, acceptable for consumption | [155] |
| Bean meat analogues | Addition of enzymatically treated BSG | Texture improvement using enzymes | More meat-like structure, better cohesion and bite | [169] |
| Enriched burgers | BSG as a source of fiber (3.6%) | Sustainability Perception Survey | Increased acceptance when communicating environmental benefits | [170] |
| Traditional cooked sausage | Addition of BSG (2–4%) | Stability analysis during storage | Maintenance of physicochemical quality and shelf life of 21 days | [156] |
| Chicken Nuggets | Using BSG as a High-Fiber Breader | Oil Absorption Evaluation | Reduction in absorbed oil, higher nutritional quality | [157] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tapia, D.; Quiñones, J.; Martinez, A.; Millahual, E.; Campagnol, P.C.B.; Sepúlveda, N.; Diaz, R. The Silent Revolution of Brewer’s Spent Grain: Meat/Food Innovations Through Circularity, Resource Recovery, and Nutritional Synergy—A Review. Foods 2025, 14, 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193389
Tapia D, Quiñones J, Martinez A, Millahual E, Campagnol PCB, Sepúlveda N, Diaz R. The Silent Revolution of Brewer’s Spent Grain: Meat/Food Innovations Through Circularity, Resource Recovery, and Nutritional Synergy—A Review. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193389
Chicago/Turabian StyleTapia, Daniela, John Quiñones, Ailin Martinez, Erika Millahual, Paulo Cezar Bastianello Campagnol, Néstor Sepúlveda, and Rommy Diaz. 2025. "The Silent Revolution of Brewer’s Spent Grain: Meat/Food Innovations Through Circularity, Resource Recovery, and Nutritional Synergy—A Review" Foods 14, no. 19: 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193389
APA StyleTapia, D., Quiñones, J., Martinez, A., Millahual, E., Campagnol, P. C. B., Sepúlveda, N., & Diaz, R. (2025). The Silent Revolution of Brewer’s Spent Grain: Meat/Food Innovations Through Circularity, Resource Recovery, and Nutritional Synergy—A Review. Foods, 14(19), 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193389








