Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community of Sichuan Industrial Paocai Fermented by Traditional Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Paocai Preparation and Sampling
2.2. Determination of Physiochemical Properties and Non-Volatile Compounds
2.3. Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds
2.4. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.5. DNA Library Construction and Sequencing
2.6. Amplicon Sequence Processing and Analysis
2.7. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
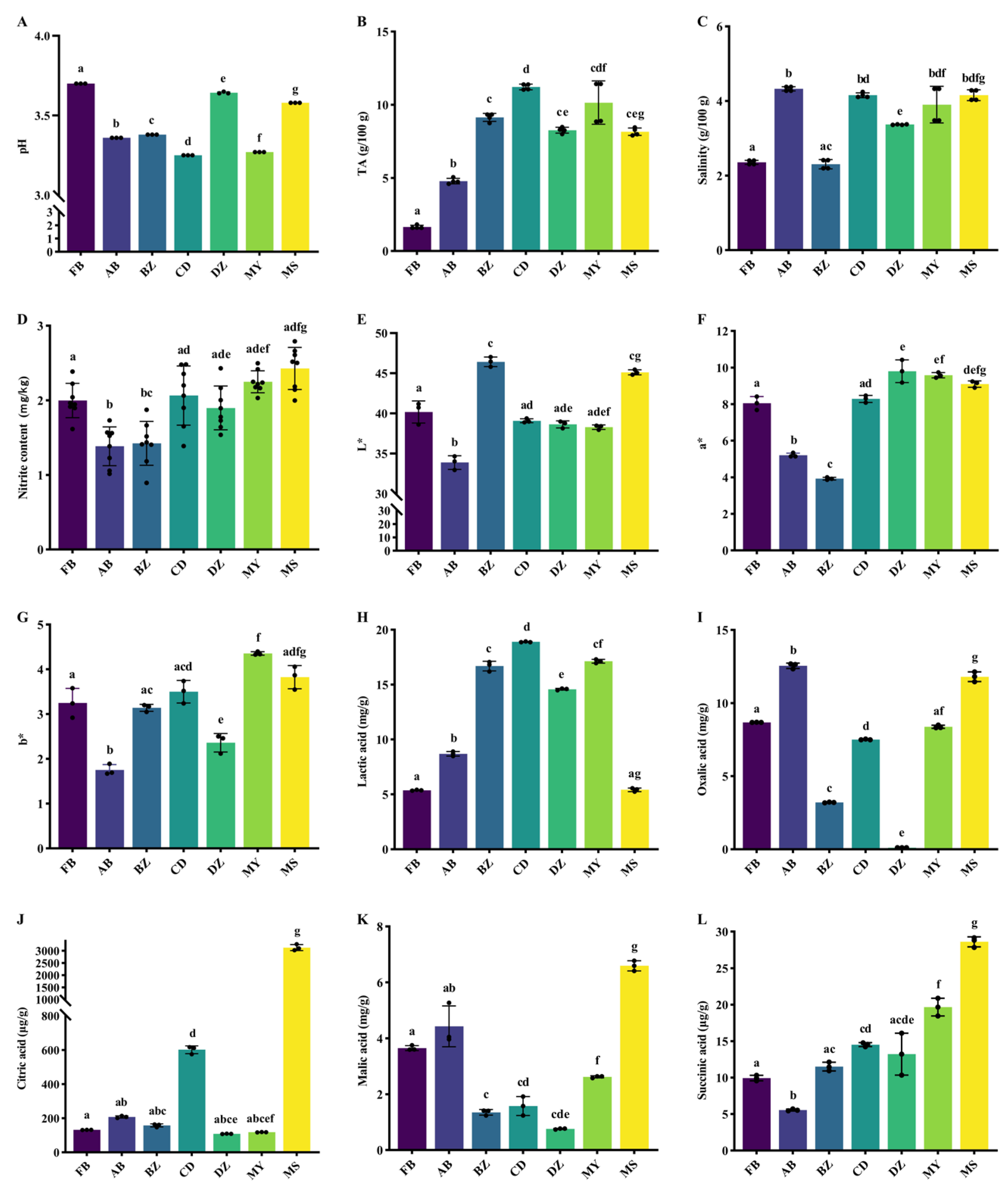
3.1. Physiochemical Characteristics Comparison of Spontaneously Fermented Industrial Sichuan Paocai from Different Producing Areas
3.2. Taste Comparison of Spontaneously Fermented Industrial Sichuan Paocai from Different Producing Areas
3.3. Flavors Comparison of Spontaneously Fermented Industrial Sichuan Paocai from Different Producing Areas
3.4. The Differences in Flavors of Spontaneously Fermented Industrial Sichuan Paocai from Different Producing Areas
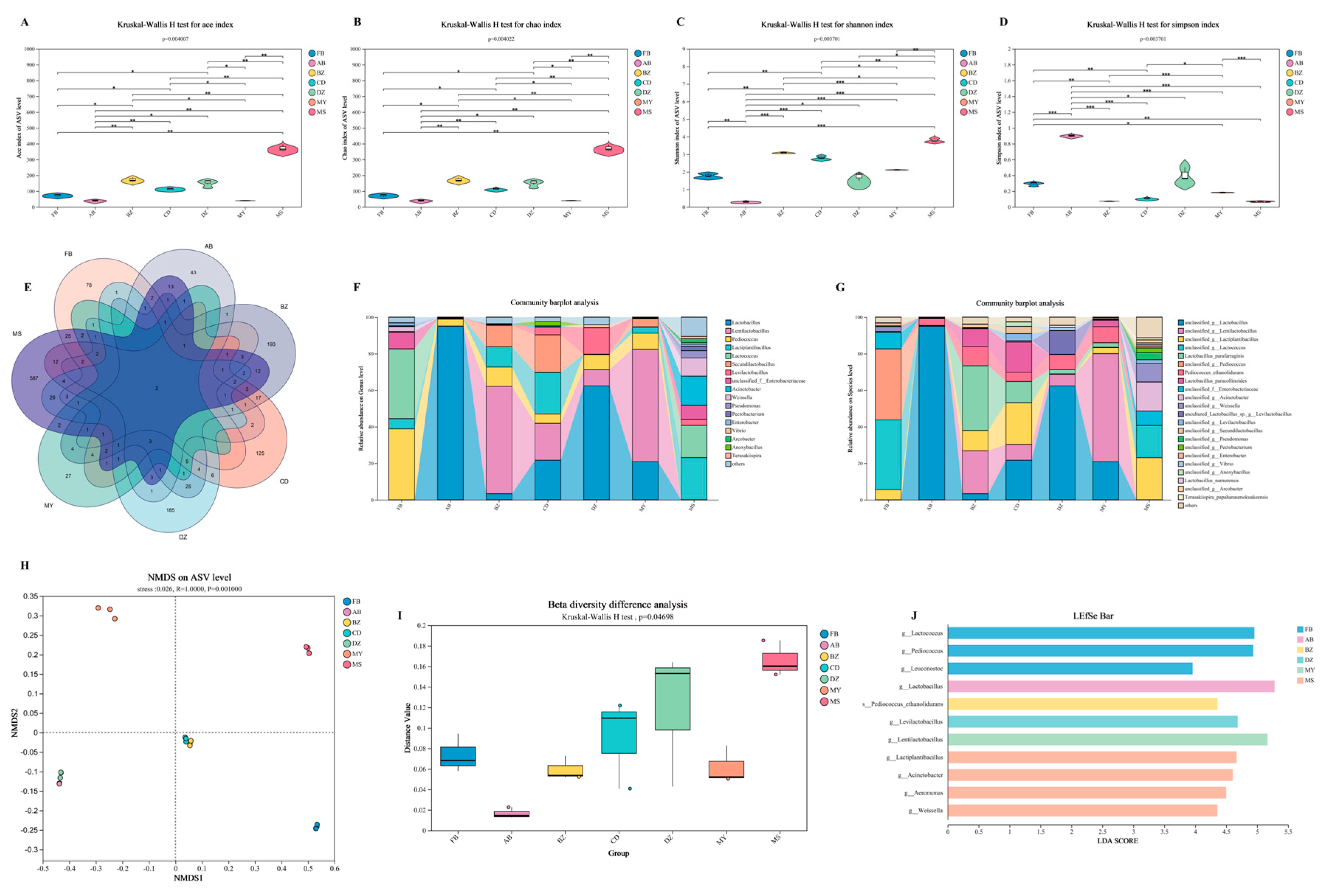
3.5. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure in Spontaneously Fermented Industrial Sichuan Paocai from Different Producing Areas
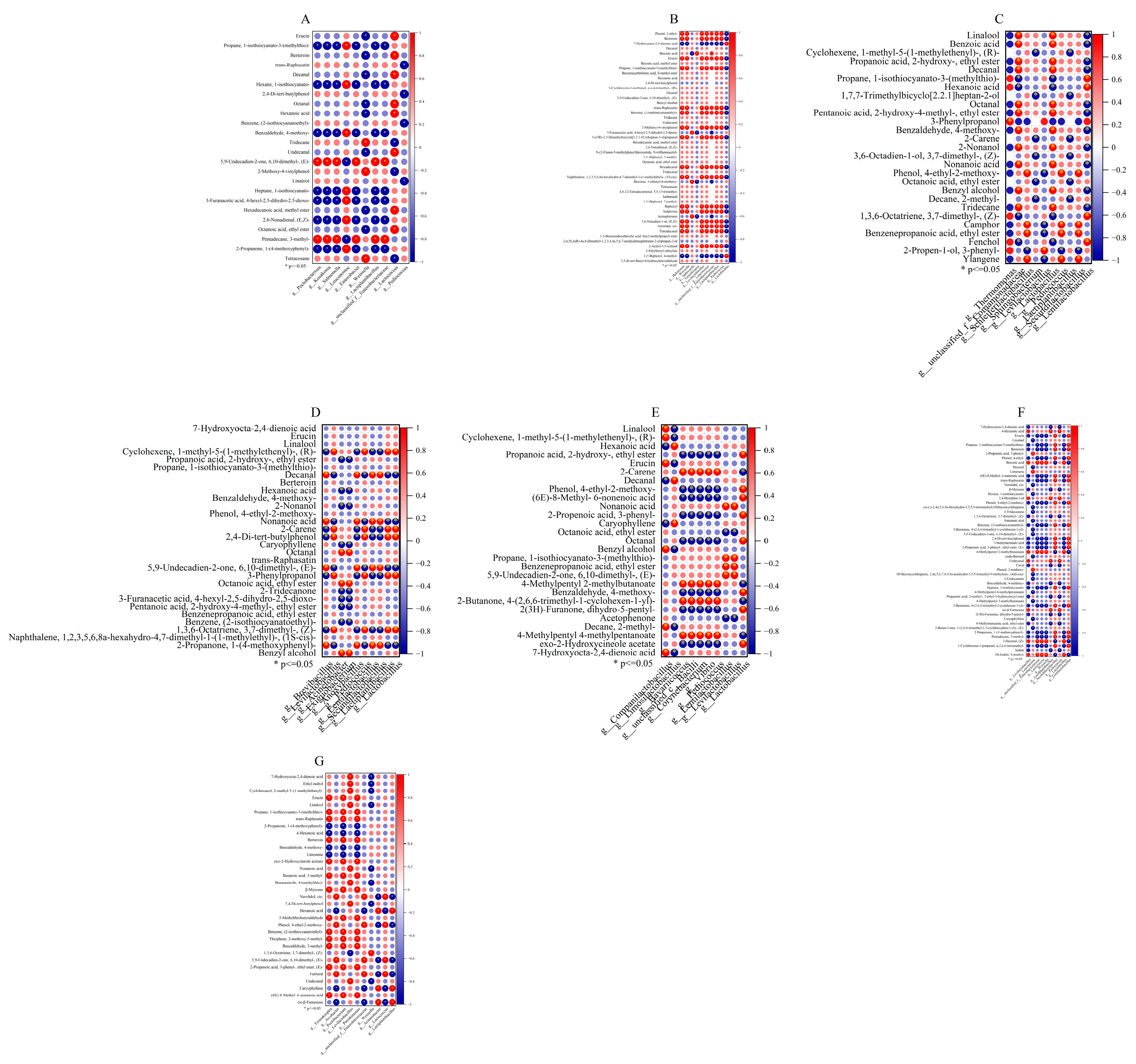
3.6. Multivariate Analysis of Microorganisms and Flavor Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, A.; Luo, W.; Peng, Y.; Niu, K.; Liu, X.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, H.; Luo, Q.; Li, S. Quality and microbial flora changes of radish paocai during multiple fermentation rounds. Food Control 2019, 106, 106733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, T.; Xu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Q.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Metatranscriptomics reveals the gene functions and metabolic properties of the major microbial community during Chinese Sichuan Paocai fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Integrating metabolomics and metatranscriptomics to explore the formation pathway of aroma-active volatile phenolics and metabolic profile during industrial radish paocai fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Miyao, S.; Zhang, W. Unraveling the flavor profile and microbial roles during industrial Sichuan radish paocai fermentation by molecular sensory science and metatranscriptomics. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Tang, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Characterization of aroma and bacteria profiles of Sichuan industrial paocai by HS-SPME-GC-O-MS and 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.J.; Xian, S.; Liu, X.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, X.; Chen, A. Metagenomic study on Chinese homemade paocai: The effects of raw materials and fermentation periods on the microbial ecology and volatile components. Foods 2022, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Huang, Y.L.; Lai, H.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Mei, Y.; Zeng, X.Q.; Yang, M.L.; Zhao, J.C.; Li, H.J.; Zhu, Y.Q.; et al. The role of abiotic and biotic factors of aged brine in directing microbial assembly and volatile profiles of Paocai during fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ge, L.; Lai, H.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zeng, X.; Su, Y.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, H.; Li, H.; et al. Seasonal alteration of environmental condition-driven shift in microbiota composition, physicochemical attributes and organic compound profiles in aged Paocai brine during intermittent back-slopping fermentation. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Gökırmaklı, Ç.; Greene, A.K. A comparison of milk kefir and water kefir: Physical, chemical, microbiological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, M.; Momoda, R.; Tanaka, M.; Zendo, T.; Nakayama, J. Dense tracking of the dynamics of the microbial community and chemicals constituents in spontaneous wheat sourdough during two months of backslopping. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Teng, M.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Jin, G.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Non-gene-editing microbiome engineering of spontaneous food fermentation microbiota—Limitation control, design control, and integration. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 22, 1902–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Dumba, T.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, C.; Cai, C.; Feng, F.; Zhao, M. Microbial diversity and chemical property analyses of sufu products with different producing regions and dressing flavors. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 144, 111245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Song, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, M.Y.; Chang, J.Y. Effect of seasonal production on bacterial communities in Korean industrial kimchi fermentation. Food Control 2018, 91, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uylaşer, V. Changes in phenolic compounds during ripening in Gemlik variety olive fruits obtained from different locations. CyTA–J. Food 2015, 13, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 12456-2021; Standard National Food Safety Standards Determination of Total Acids in Food. State Administration for Market Regulation; National Health Commission, PRC: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB5009.33-2016; Standard National Food Safety Standards Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate in Food. National Medical Products Administration; National Health Commission, PRC: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Xian, S.; Zhao, F.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Shen, G.; Li, M.; Chen, A. Effects of Pre-Dehydration Treatments on Physicochemical Properties, Non-Volatile Flavor Characteristics, and Microbial Communities during Paocai Fermentation. Foods 2024, 13, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Zhong, H.; Yi, B.; Liu, X.; Shen, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Q.; Li, S.; Zhou, M.; et al. Identification of pellicle formation related microorganisms in traditional Sichuan paocai through metagenomic sequence and the effects of Baijiu/Salt on pellicle and volatile components. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, G.; He, Z.; Zhao, M.; Cao, X.; Lin, X.; Ji, C.; Zhang, S.; Liang, H. Effects of salt concentration on the quality of paocai, a fermented vegetable product from China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6202–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Yang, B.; Lu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ge, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lai, H.; Paul Ross, R.; Chen, W.; et al. Divergent role of abiotic factors in shaping microbial community assembly of paocai brine during aging process. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2762-2022; Standard National Food Safety Standards Limits for Contaminants in Food. National Health Commission, PRC; State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Cai, M.; Peng, Z.; Xu, P.; Yu, M.; Diao, N.; Cao, Y.; Dong, S.; Fang, X. Comprehensive analysis of the flavor and color characteristics of light-fermented sour tea mediated by Aspergillus niger RAF106. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 143866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Du, T.; Liu, Q.; Huang, T.; Ren, H.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Organic acids drove the microbiota succession and consequently altered the flavor quality of Laotan Suancai across fermentation rounds: Insights from the microbiome and metabolome. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wen, R.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Role of lactic acid bacteria in flavor development in traditional Chinese fermented foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 62, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Yi, Y.; Qiao, M.; Fu, Y. Characterization of flavor and taste profile of different radish (Raphanus sativus L.) varieties by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC/IMS) and E-nose/tongue. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotzoll, N.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T. Quantitative Studies, Taste Reconstitution, and Omission Experiments on the Key Taste Compounds in Morel Mushrooms (Morchella deliciosa Fr.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, G.; Zhou, M.; Li, M.; Hou, X.; Li, S.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Impact of microorganisms on key processes of organic acid metabolism during the occurrence and disappearance of paocai pellicle. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 5047–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Ge, L.; Lai, H.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Su, Y.; Shi, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Unraveling the contribution of pre-salting duration to microbial succession and changes of volatile and non-volatile organic compounds in Suancai (a Chinese traditional fermented vegetable) during fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Cong, J.; Cheng, L.; Wan, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, J. Identification of key gene networks controlling monoterpene biosynthesis during grape ripening by integrating transcriptome and metabolite profiling. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Huang, H.Y.; Rudin, C.; Shaposhnik, Y. Understanding How Dimension Reduction Tools Work: An Empirical Approach to Deciphering t-SNE, UMAP, TriMap, and PaCMAP for Data Visualization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Sheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Shi, X. Effect of vacuum distillation, concentrated grape juice and oak barrel aging on the chemical, sensory and nutritional value of Marselan low-alcohol wine. Food Chem. 2025, 492, 145516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Qayyum, N.; Xu, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, Y.; Chu, L.; He, F.; Song, Y.; et al. Dynamic variations in the volatile aromatic compound profile of jujube pulp during fermentation by mixed microbial cultures. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andernach, L.; Schury, C.; Nickel, M.; Böttger, J.; Kaufmann, M.; Rohn, S.; Granvogl, M.; Hanschen, F.S. Non-enzymatic degradation of aliphatic Brassicaceae isothiocyanates during aqueous heat treatment. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 138939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandha, J.; Shumoy, H.; Devaere, J.; Schouteten, J.J.; Gellynck, X.; de Winne, A.; Matemu, A.O.; Raes, K. Effect of lactic acid fermentation of watermelon juice on its sensory acceptability and volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roswell, M.; Dushoff, J.; Winfree, R. A conceptual guide to measuring species diversity. Oikos 2021, 130, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Parente, E.; Ercolini, D. Metagenomics insights into food fermentations. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Jin, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C. Flavor compounds of traditional fermented bean condiments: Classes, synthesis, and factors involved in flavor formation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Wen, Y.; Kong, Q.; Xue, C. Systematic analysis of the fundamental quality parameters and identification of key flavor compounds in fermented shrimp sauce from China. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Yang, F.; Yan, L.; Wu, J.; Bi, S.; Liu, Y. Characterization of key aroma-active compounds in fresh and vacuum freeze-drying mulberry by molecular sensory science methods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-C.; Yeh, T.-H.; Jao, Y.-H.; Wang, T.-H.; Lo, H.-R. Efficacy of outer membrane permeabilization in promoting aromatic isothiocyanates-mediated eradication of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria and bacterial persisters. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
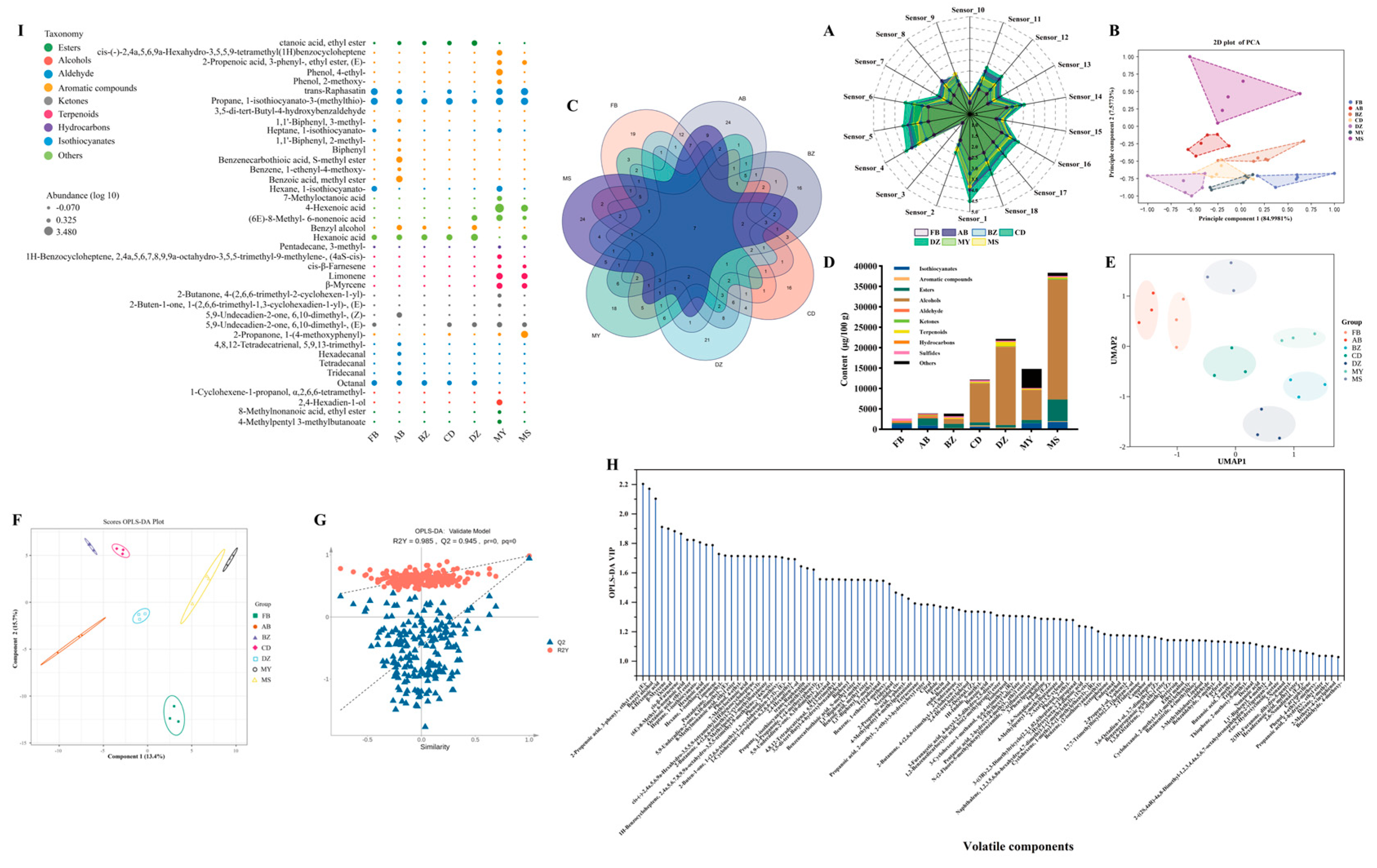
| Sensor Name | Performance Description | Sensor Name | Performance Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | propane and fumes | S10 | hydrogen |
| S2 | alcohol, fumes, isobutane, and formaldehyde | S11 | liquefied gas and alkanes |
| S3 | ozone | S12 | liquefied gas and methane |
| S4 | hydrogen sulfide | S13 | methane |
| S5 | ammonia | S14 | flammable gas and fumes |
| S6 | toluene, acetone, ethanol, and hydrogen | S15 | fumes and isobutane |
| S7 | methane, natural gas, and biogas | S16 | sulfides |
| S8 | liquefied gas | S17 | nitrides |
| S9 | toluene, formaldehyde, benzene, alcohol, and acetone | S18 | acetone and alcohol |
| Compounds | Taste Attributes | Threshold a (mg/g) | TAV b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB | AB | BZ | CD | DZ | MY | MS | |||
| Lactic acid | Sour | 1.261 | 4.262 ± 0.036 | 6.896 ± 0.162 | 13.238 ± 0.35 | 14.988 ± 0.034 | 11.565 ± 0.06 | 13.581 ± 0.133 | 4.296 ± 0.127 |
| Oxalic acid | Sour | 0.504 | 17.228 ± 0.017 | 24.894 ± 0.363 | 6.357 ± 0.056 | 14.888 ± 0.052 | 0.221 ± 0.001 | 16.628 ± 0.198 | 23.411 ± 0.658 |
| Citric acid | Sour | 0.499 | 0.066 ± 0 | 0.104 ± 0.003 | 0.079 ± 0.005 | 0.3 ± 0.011 | 0.054 ± 0.001 | 0.059 ± 0.001 | 1.561 ± 0.062 |
| Malic acid | Sour | 0.496 | 7.357 ± 0.176 | 8.927 ± 1.478 | 2.724 ± 0.2 | 3.177 ± 0.685 | 1.526 ± 0.044 | 5.286 ± 0.072 | 13.294 ± 0.372 |
| Succinic acid | Sour | 0.106 | 0.001 ± 0 | 0.001 ± 0 | 0.001 ± 0 | 0.002 ± 0 | 0.001 ± 0 | 0.002 ± 0 | 0.003 ± 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xian, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, G.; Chen, A. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community of Sichuan Industrial Paocai Fermented by Traditional Technology. Foods 2025, 14, 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183232
Xian S, Li H, Wang X, He X, Li Y, Liu X, Shen G, Chen A. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community of Sichuan Industrial Paocai Fermented by Traditional Technology. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183232
Chicago/Turabian StyleXian, Shuang, Hongchen Li, Xinyi Wang, Xiangchao He, Yanlan Li, Xinyan Liu, Guanghui Shen, and Anjun Chen. 2025. "Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community of Sichuan Industrial Paocai Fermented by Traditional Technology" Foods 14, no. 18: 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183232
APA StyleXian, S., Li, H., Wang, X., He, X., Li, Y., Liu, X., Shen, G., & Chen, A. (2025). Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor, and Microbial Community of Sichuan Industrial Paocai Fermented by Traditional Technology. Foods, 14(18), 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183232







