Type I Sourdough Preservation Strategies and the Contribution of Microbial Biological Resource Centers to Biodiversity Protection: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Economic Relevance of Sourdough-Derived Products and Innovation Need
3. Production, Maintenance, and Preservation of Traditional Sourdough (Type I)
4. Methods to Maintain and Preserve Type I Sourdough
4.1. Backslopping or Refreshment
4.2. Preservation of Sourdough Microbiomes at Low Temperatures
4.3. Freeze-Drying
4.4. Oven Drying
4.5. Spray-Drying
5. “De Novo” Design of Reconstructed Microbial Communities as a Sourdough Reproduction and Preservation Method
6. Microbial Culture Collections and Microbial Biological Resource Centers
7. Current and Future Challenges of MCCs and mBRCs
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| mBRC | Microbial biological resource center |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| USD | United States Dollar |
| CPC | Cooperative Patent Classification |
| MCC | Microbial culture collection |
| WDCM | World Data Centre for Microorganisms |
| ABS | Access and benefit-sharing |
| MIxS | Minimum Information about Any Sequence |
| GSC | Genomic Standards Consortium |
| FAIR | Findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable |
| JZ | Jiaozi starter |
| CPAs | Cryoprotectants |
References
- Arranz-Otaegui, L.; Gonzalez Carretero, M.N.; Ramsey, D.Q.; Fuller, D.Q.; Richter, T. Archaeobotanical evidence reveals the origins of bread 14,400 years ago in northeastern Jordan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7925–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diowksz, A.; Ambroziak, W. Sourdough. In Bakery Products: Science and Technology; Hui, Y.H., Corke, H., de Leyn, I., Nip, W.-K., Cross, N., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelle, S.; Guylaine, L.; Gänzle, M.; Gobbetti, M. History and social aspects of sourdough. In Handbook on Sourdough Biotechnology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Comasio, A.; Kerrebroeck, S.V. Sourdough production: Fermentation strategies, microbial ecology, and use of non-flour ingredients. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2447–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Di Cagno, R.; De Angelis, M. How the sourdough may affect the functional features of leavened baked goods. Food Microbiol. 2014, 37, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, M.D.; Madden, A.A.; Nichols, L.M.; Haddad, N.M.; Lahne, J.; Dunn, R.R.; McKenney, E.A. A review of sourdough starters: Ecology, practices, and sensory quality with applications for baking and recommendations for future research. PeerJ 2021, 9, 11389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. How to Prepare, Propagate, and Use Sourdough. In Basic Methods and Protocols on Sourdough. Methods and Protocols in Food Science; Gobbetti, M., Rizzello, C.G., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Ameur, H.; Polo, A.; Di Cagno, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. Thirty years of knowledge on sourdough fermentation: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Ecological parameters influencing microbial diversity and stability of traditional sourdough. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 171, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheirlinck, I.; Van der Meulen, R.; De Vuyst, L.; Vandamme, P.; Huys, G. Molecular source tracking of predominant lactic acid bacteria in traditional Belgian sourdoughs and their production environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourdough Market Trends. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/sourdough-market (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Albagli, G.; Finotelli, P.V.; Ferreira, T.F.; Amaral, P.F.F. Toward Sourdough Microbiome Data: A Review of Science and Patents. Foods 2023, 12, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espacenet-Patent Search. Available online: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/ (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Vogel, R.F.; Gaenzle, M.; Steudel, U. Conditioning Starter Cultures for Producing Fermented Cereal products, e.g. Sourdough, Comprises Subjecting the Culture to Sublethal Stress to Induce Tolerance to Stress during Processing and Storage. DE19938278A1, 15 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert Equipements. Fermenting Mixing Kneaders. US6508164B1, 21 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Institut Francais De Recherche Scientifique Pour Le Developpement En Cooperation ORSTOM. Nouvelles Souches De Bacteries Lactiques, Leur Procede De Culture Et Leurs Applications. FR2781811A1, 4 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst Boecker GmbH & CO KG. Process for Preparing a Sourdough with Homo- and Heterofermentative Lactobacillus. EP1110458A1, 27 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Payet, D. A Bread Containing Seaweed Extracts with Slimming Properties Used as an Aid to Slimming Prepared by a Sourdough Method Using a Leaven and a Poolish. FR2842994A1, 6 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bonjean, B.; Cappelle, S.; Dewilde, C.; Tossut Pierre, P.A. Liquid Leaven Composition. US2007243289A1, 18 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst Boecker GmbH & CO KG. Process for Preparing a Sourdough with Yeast and Homo- and Heterofermentative Lactobacilli. EP1258526A1, 20 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Skaanemejerier Ekonomisk Foerening. Sourdough Product. WO0010395A1, 2 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Siepmann, F.B.; Ripari, V.; Waszczynskyj, N.; Spier, M.R. Overview of Sourdough Technology: From Production to Marketing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 242–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Schrijvers, V.; Paramithiotis, S.; Hoste, B.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; Kalantzopoulos, G.; Tsakalidou, E.; Messens, W. The Biodiversity of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Greek Traditional Wheat Sourdoughs Is Reflected in Both Composition and Metabolite Formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 6059–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripari, V.; Gänzle, M.G.; Berardi, E. Evolution of Sourdough Microbiota in Spontaneous Sourdoughs Started with Different Plant Materials. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 232, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Reale, A. A Holistic Review on Euro-Asian Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Cereals and Vegetables. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Van Kerrebroeck, S.; Leroy, F. Microbial ecology and process technology of sourdough fermentation. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 100, 49–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; Pontonio, E.; Buchin, S.; De Angelis, M.; Lattanzi, A.; Valerio, F.; Gobbetti, M.; Calasso, M. Diversity of the lactic acid bacterium and yeast microbiota in the switch from firm-to liquid-sourdough fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3161–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, E.A.; Oliverio, A.M.; McKenney, E.A.; Nichols, L.M.; Kfoury, N.; Biango-Daniels, M.; Shell, L.K.; Madden, A.A.; Shapiro, L.; Sakunala, S.; et al. The diversity and function of sourdough starter microbiomes. eLife 2021, 10, e61644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collar, C. Review: Biochemical and technological assessment of the metabolism of pure and mixed cultures of yeast and lactic acid bacteria in breadmaking. Int. Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 2, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, R.; Nie, Y.; Yuan, W. Dynamics of microbial community and changes of metabolites during production of type Ι sourdough steamed bread made by retarded sponge-dough method. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, A.; Russo, N.; Solieri, L.; Sola, L.; Caggia, C.; Randazzo, C.L. Microbial consortia involved in traditional Sicilian sourdough: Characterization of lactic acid bacteria and yeast populations. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Ito, K.; Narushima, N.; Miyamoto, T. Identification of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts, and characterization of food components of sourdoughs used in Japanese bakeries. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhomme, E.; Urien, C.; Legrand, J.; Dousset, X.; Onno, B.; Sicard, D. Sourdough microbial community dynamics: An analysis during French organic bread-making processes. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaǧmur, G.; Tanguler, H.; Leventdurur, S.; Elmaci, S.B.; Turhan, E.Ü.; Francesca, N.; Settanni, L.; Moschetti, G.; Erten, H. Identification of predominant lactic acid bacteria and yeasts of Turkish sourdoughs and selection of starter cultures for liquid sourdough production using different flours and dough yields. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 66, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Sadiq, F.A.; Cai, Y.; Fan, D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Microbial diversity in traditional type I sourdough and jiaozi and its influence on volatiles in Chinese steamed bread. LWT 2019, 101, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, K.; Sagdic, O.; Durak, M.Z. Use of Phytase Active Yeasts and Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Sourdough in the Production of Whole Wheat Bread. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gastrow, L.; Amelot, R.; Segond, D.; Guézennec, S.; Valence, F.; Sicard, D. Microbial community dispersal in sourdough. bioRxiv 2021. bioRxiv:2021.10.18.464797. [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi, S.; Amaretti, A.; Rossi, M.; Fall, P.A.; Tabanelli, G.; Gardini, F.; Montanari, C. Evolution of microbial community and chemical properties of a sourdough during the production of Colomba, an Italian sweet leavened baked product. LWT 2017, 86, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, M.; Cristani, C.; Giovannetti, M.; Agnolucci, M. Identification and characterization of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts of PDO Tuscan bread sourdough by culture dependent and independent methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 250, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kerrebroeck, S.; Maes, D.; De Vuyst, L. Sourdoughs as a Function of Their Species Diversity and Process Conditions, a Meta-Analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, A.; Di Stasio, L.; Di Renzo, T.; De Caro, S.; Ferranti, P.; Picariello, G.; Addeo, F.; Mamone, G. Bacteria Do It Better! Proteomics Suggests the Molecular Basis for Improved Digestibility of Sourdough Products. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, M.; Momoda, R.; Tanaka, M.; Zendo, T.; Nakayama, J. Dense tracking of the dynamics of the microbial community and chemicals constituents in spontaneous wheat sourdough during two months of backslopping. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X. Contribution of spontaneously-fermented sourdoughs with pear and navel orange for the bread-making. LWT 2018, 89, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harth, H.; van Kerrebroeck, S.; de Vuyst, L. Community dynamics and metabolite target analysis of spontaneous, backslopped barley sourdough fermentations under laboratory and bakery conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 228, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Georgalaki, M.; Alexandraki, V.; Kazou, M.; Anastasiou, R.; Tsakalidou, E. Sourdough Bread. In Innovations in Traditional Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 127–158. ISBN 978-0-12-814887-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, C.; de Melo Nazareth, T.; Dopazo, V.; Meca, G.; Luz, C. Enhancing Bread Quality and Extending Shelf Life Using Dried Sourdough. LWT 2024, 2023, 116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Neysens, P. The sourdough microflora: Biodiversity and metabolic interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafti, A.G.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Hesari, J.; Bahrami, A.; Bonab, E.S. Physico-chemical and functional properties of spray-dried sourdough in breadmaking. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2013, 19, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertop, H.M.; Ilter, S.M.; Yilmaz, F.; Baltaci, C.; Gündogdu, A. Quality properties of wheat breads incorporated with dried sourdoughs produced with different fermentation and drying methods. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 24, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Vermeulen, N.; Vogel, R.F. Carbohydrate, peptide and lipid metabolism of lactic acid bacteria in sourdough. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Minervini, F.; Pontonio, E.; Di Cagno, R.; De Angelis, M. Drivers for the establishment and composition of the sourdough lactic acid bacteria biota. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 239, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; Dinardo, F.R.; Celano, G.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Lactic Acid bacterium population dynamics in artisan sourdoughs over one year of daily propagations is mainly driven by flour microbiota and nutrients. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Vrancken, G.; Ravyts, F.; Rimaux, T.; Weckx, S. Biodiversity, ecological determinants, and metabolic exploitation of sourdough microbiota. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; Lattanzi, A.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Influence of artisan bakery- or laboratory-propagated sourdoughs on the diversity of lactic acid bacterium and yeast microbiotas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5328–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermelho, A.B.; Moreira, J.V.; Junior, A.N.; da Silva, C.R.; Cardoso, V.D.S.; Akamine, I.T. Microbial Preservation and Contamination Control in the Baking Industry. Fermentation 2024, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccari, M.; Aquilanti, L.; Polverigiani, S.; Osimani, A.; Garofalo, C.; Milanović, V.; Clementi, F. Microbial diversity of type I sourdoughs prepared and back-slopped with wholemeal and refined soft (Triticum aestivum) wheat flours. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M1996–M2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, S.A.; Hertel, C. Impact of ecological factors on the stability of microbial associations in sourdough fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrancken, G.; Rimaux, T.; Weckx, S.; Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Influence of Temperature and Backslopping Time on the Microbiota of a Type I Propagated Laboratory Wheat Sourdough Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2716–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kerrebroeck, S.; Bastos, F.C.C.; Harth, H.; De Vuyst, L. A Low PH Does Not Determine the Community Dynamics of Spontaneously Developed Backslopped Liquid Wheat Sourdoughs but Does Influence Their Metabolite Kinetics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 239, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.T.M.; Hosken, B.D.O.; De Dea Lindner, J.; Menezes, L.A.A.; Pirozi, M.R.; Martin, J.G.P. How to Deliver Sourdough with Appropriate Characteristics for the Bakery Industry? The Answer May Be Provided by Microbiota. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, A.; Minervini, F.; Gobbetti, M. Assessment of Comparative Methods for Storing Type-I Wheat Sourdough. LWT 2014, 59, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Contribution of reutericyclin production to the stable persistence of Lactobacillus reuteri in an industrial sourdough fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 80, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Semumu, T.; Gamero, A. Non-Conventional Yeasts as Alternatives in Modern Baking for Improved Performance and Aroma Enhancement. Fermentation 2021, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siragusa, S.; Di Cagno, R.; Ercolini, D.; Minervini, F.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. Taxonomic structure and monitoring of the dominant population of lactic acid bacteria during wheat flour sourdough type I propagation using Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis starters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, A.; Di Renzo, T.; Preziuso, M.; Panfili, G.; Cipriano, L.; Messia, M.C. Stabilization of Sourdough Starter by Spray Drying Technique: New Breadmaking Perspective. LWT 2019, 99, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, S.; Shao, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. The state of water is associated with the viability and acidification capacity of Lactobacilli in frozen sourdough. Czech J. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Qu, J. Fermentation properties and functional stability of dough starter Jiaozi and Laomian after frozen storage. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1379484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; Di Cagno, R.; Lattanzi, A.; De Angelis, M.; Antonielli, L.; Cardinali, G.; Cappelle, S.; Gobbetti, M. Lactic acid bacterium and yeast microbiotas of 19 sourdoughs used for traditional/typical Italian breads: Interactions between ingredients and microbial species diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tan, W.; Cheng, H.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Chen, J. The protective effect of freezing temperatures on different lactic acid bacteria and its mechanism. LWT 2025, 215, 117226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.J.; Schloter, M.; Berg, G.; Kostic, T.; Kinkel, L.L.; Eversole, K.; Macklin, J.A.; Schelkle, B.; Kazou, M.; Sarand, I.; et al. Development of Microbiome Biobanks—Challenges and Opportunities. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhof, F.M.; Courtens, E.N.P.; Geirnaert, A.; Hoefman, S.; Ho, A.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Jauregui, R.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Van De Wiele, T.; et al. Optimized cryopreservation of mixed microbial communities for conserved functionality and diversity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, M.; Eck, A.; Koenen, M.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.M.; Budding, A.E.; Venema, K. Evaluation of an optimal preparation of human standardized fecal inocula for in vitro fermentation studies. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 117, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Reddy, A.; Simmons, C.; Simmons, B.; Singer, S.; VanderGheynst, J. Preservation of microbial communities enriched on lignocellulose under thermophilic and high-solid conditions. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teotônio, D.d.O.; Costa, B.A.F.d.; Gomes, P.T.G.; Santos, M.P.; Amaral, E.F.G.; Clerici, M.T.P.S.; Leoro, M.G.V.; Schmiele, M. Fructo-oligosaccharides, hydrolyzed soy protein and yeast (Saccharomyces sp.) extract as potential cryoprotectans in gluten-free frozen dough and bread quality. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e44510313556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Zhao, G. Ice inhibition for cryopreservation: Materials, strategies, and challenges. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pržić, D.S.; Ružić, N.L.J.; Petrović, S.D. Lyophilization: The process and industrial use. Chem. Ind. 2004, 58, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, S.; Stevanovic Janezic, T.; Ratti, C. Freeze-Drying of Plant-Based Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, D.; Da Silva, A.P.M.; Bisutti, I.L. Optimization of a freeze-drying process for the biocontrol agent Pseudomonas spp. and its influence on viability, storability and efficacy. Biol. Control 2016, 94, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto-Shinohara, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Sukenobe, J.; Murakami, Y.; Kawamura, S.; Komatsu, Y. Survival Rate of Microbes after Freeze-Drying and Long-Term Storage. Cryobiology 2000, 41, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, N.; Ermis, E.; Durak, M.Z. Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Sourdough Powders: Properties and Evaluation of Their Use in Breadmaking. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santivarangkna, C.; Kulozik, U.; Foerst, P. Alternative Drying Processes for the Industrial Preservation of Lactic Acid Starter Cultures. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, L.B.; Gul, O.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Dertli, E.; Con, A.H. Optimization of Cryoprotectant Formulation to Enhance the Viability of Lactobacillus brevis ED25: Determination of Storage Stability and Acidification Kinetics in Sourdough. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanello, R.F.; Nabeshima, E.H.; Iamanaka, B.T.; Ludwig, A.; Fries, L.L.M.; Bernardi, A.O.; Copetti, M.V. Survival and stability of Lactobacillus fermentum and Wickerhamomyces anomalus strains upon lyophilisation with different cryoprotectant agents. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valdez, G.F.; Diekmann, H. Freeze-drying conditions of starter cultures for sourdoughs. Cryobiology 1993, 30, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanello, R.F.; Machado, A.A.R.; Pasqualin Cavalheiro, C.; Bartholomei Santos, M.L.; Nabeshima, E.H.; Copetti, M.V.; Fries, L.L.M. Trehalose as a Cryoprotectant in Freeze-Dried Wheat Sourdough Production. LWT 2018, 89, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertop, M.H.; Coşkun, Y. Shelf-life, physicochemical, and nutritional properties of wheat bread with optimized amount of dried chickpea sourdough and yeast by response surface methodology. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.D.; Hashib, S.A.; Ibrahim, U.K.; Rahman, N.A. Development of carrier material for food applications in spray drying technology: An overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.T.C.; Martins, E.; Perrone, Í.T.; de Freitas, R.; Queiroz, L.S.; de Carvalho, A.F. Challenges associated with spray drying of lactic acid bacteria: Understanding cell viability loss. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3267–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, M.J. Industrial Production of Sourdoughs for the Baking Branch—An Overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 302, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.H.; Tafti, A.G.; Hesari, J. Application of spray drying for preservation of lactic acid starter cultures: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Roby, B.H.; Muhialdin, B.J.; Abadl, M.M.T.; Mat Nor, N.A.; Marzlan, A.A.; Lim, S.A.H.; Mustapha, N.A.; Meor Hussin, A.S. Physical properties, storage stability, and consumer acceptability for sourdough bread produced using encapsulated kombucha sourdough starter culture. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, F.M.; Ameur, H.; Nikoloudaki, O.; Celano, G.; Vacca, M.; JFLemos, W., Jr.; Manzari, C.; Vertè, F.; Di Cagno, R.; Pesole, G.; et al. Metabolic Framework of Spontaneous and Synthetic Sourdough Metacommunities to Reveal Microbial Players Responsible for Resilience and Performance. Microbiome 2022, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, H.B.; Senewiratne, N.P.; Lucas, S.K.; Wolfe, B.E.; Oliverio, A.M. Genomics and synthetic community experiments uncover the key metabolic roles of acetic acid bacteria in sourdough starter microbiomes. Msystems 2024, 9, e00537-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekle, M.; Houben, A.; Mitzscherling, M.; Becker, T. Effects of selected lactic acid bacteria on the characteristics of amaranth sourdough. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2326–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; McCluskey, K.; Stackebrandt, E. Investment into the future of microbial resources: Culture collection funding models and BRC business plans for biological resource centres. Springerplus 2014, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Data Centre for Microorganisms (WDCM-CCINFO). Available online: https://ccinfo.wdcm.org/ (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Biological Resource Centres: Underpinning the Future of Life Sciences and Biotechnology; OECD: Paris, France, 2001; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/sti/emerging-tech/38777417.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- ISO 9001:2015; Quality Management Systems—Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 20387:2018; Biotechnology—Biobanking—General Requirements for Biobanking. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Lima, N. Preserving and utilizing microbial diversity for innovation and sustainability. Microbiology 2025, 171, 001544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Martins da Silva, J.F.; Sampaio, P.; Lima, N. Quality and competence management in microbial biobanks. In Importance of Microbiology Teaching and Microbial Resource Management for Sustainable Futures; Kurtböke, İ., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from Their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity. 2010. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/abs/doc/protocol/nagoya-protocol-en.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). Available online: https://www.cbd.int/convention/text (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Beato, M.S.; Veneroso, V. The Nagoya Protocol on access and benefit sharing: The neglected issue of animal health. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1124120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ABS Clearing-House. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/abs/theabsch.shtml#:~:text=The%20Access%20and%20Benefit-sharing%20Clearing-House%20%28ABS%20Clearing-House%2C%20ABSCH%29,under%20Article%2018%2C%20paragraph%203%20of%20the%20Convention (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- EU Regulation 511/2014. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32014R0511 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wu, L.; Sun, Q.; Desmeth, P.; Sugawara, H.; Xu, Z.; Mccluskey, K.; Smith, D.; Alexander, V.; Lima, N.; Ohkuma, M. World data centre for microorganisms: An information infrastructure to explore and utilize preserved microbial strains worldwide. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Culture Collections’ Organisation (ECCO). Available online: https://www.eccosite.org/ (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Asian Consortium for the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Microbial Resource (ACM). Available online: https://www.acm-mrc.asia/ (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- United States Culture Collections Network (USCCN). Available online: https://usccn.org/ (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Latin American Federation for Culture Collections (AAM). Available online: https://www.aam.org.ar/ (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Arez, A.P.; Souto, A.; da Silva, M.; do Nascimento, C.R.S.; Couto, I.; Belo, S.; Lima, N. Biobanking for tropical health: Leveraging collaborative initiatives in the Lusophone world. Front Trop Dis 2024, 5, 1438842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccuti, M.; d’Acierno, A.; Donetti, S.; Contaldo, S.G.; Romano, P.; Varese, G.C. ICT Infrastructure Supporting the Italian Research Infrastructure on Microbial Resources MIRRI-IT. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Research Data Infrastructure, Karlsruhe, Germany, 12–14 September 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaregola, S.; Vasilenko, A.; Romano, P.; Robert, V.; Ozerskaya, S.; Kopf, A.; Glöckner, F.O.; Smith, D. An Information System for European culture collections: The way forward. Springerplus 2016, 5, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourdough Library (Puratos). Available online: https://sourdoughlibrary.puratos.com/en/ (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Smedt, K.D. The Sourdough Library. NC State University Libraries, Fermentology 2021. Available online: https://doi.org/10.52750/512507 (accessed on 13 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- De Vero, L.; Boniotti, M.B.; Budroni, M.; Buzzini, P.; Cassanelli, S.; Comunian, R.; Gullo, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Mannazzu, I.; Musumeci, R.; et al. Preservation, Characterization and Exploitation of Microbial Biodiversity: The Perspective of the Italian Network of Culture Collections. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Higgins, L.M.; Gore, J. Community Structure Follows Simple Assembly Rules in Microbial Microcosms. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MICRObiome Biobanking (RI) Enabler (Horizon Europe 2023–2027). Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101094353 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Implementation And Sustainability Of Microbial Resource Research Infrastructure For The 21st Century – IS_MIRRI21. Available online: https://ismirri21.mirri.org/about/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Smenderovac, E.; Emilson, C.; Rheault, K.; Brazeau, É.; Morency, M.J.; Gagné, P.; Venier, L.; Martineau, C. Drying as an effective method to store soil samples for DNA-based microbial community analyses: A comparative study. Sci Rep. 2024, 14, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smenderovac, E.; Hoage, J.; Porter, T.M.; Emilson, C.; Fleming, R.; Basiliko, N.; Hajibabei, M.; Morris, D.; Venier, L. Boreal Forest Soil Biotic Communities Are Affected by Harvesting, Site Preparation with No Additional Effects of Higher Biomass Removal 5 Years Post-Harvest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 528, 120636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Schüngel, M.; Martin, D.; Smith, D. The Microbial Resource Research Infrastructure MIRRI: Strength through Coordination. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance Document on the Scope of Application and Core Obligations of Regulation (EU) No 511/2014 of the Euro-pean Parliament and of the Council on the Compliance Measures for Users from the Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilisation in the Union (2021/C 13/01). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=oj:JOC_2021_013_R_0001#:~:text=This%20document%20is%20intend-ed%20to%20provide%20guidance%20on,%281%29%20%28%E2%80%98the%20EU%20ABS%20Regulation%E2%80%99%20or%20%E2%80%98the%20Regulation%E2%80%99%29 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Moretti, M.; Tartaglia, J.; Accotto, G.P.; Beato, M.S.; Bernini, V.; Bevivino, A.; Boniotti, M.B.; Budroni, M.; Buzzini, P.; Carrara, S.; et al. Treasures of Italian Microbial Culture Collections: An Overview of Preserved Biological Resources, Offered Services and Know-How, and Management. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Kottmann, R.; Field, D.; Knight, R.; Cole, J.R.; Amaral-Zettler, L.; Gilbert, J.A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Johnston, A.; Cochrane, G.; et al. Minimum information about a marker gene sequence (MIMARKS) and minimum information about any (x) sequence (MIxS) specifications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, E.; Ricciardi, A. A Comprehensive View of Food Microbiota: Introducing FoodMicrobionet v5. Foods 2024, 13, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

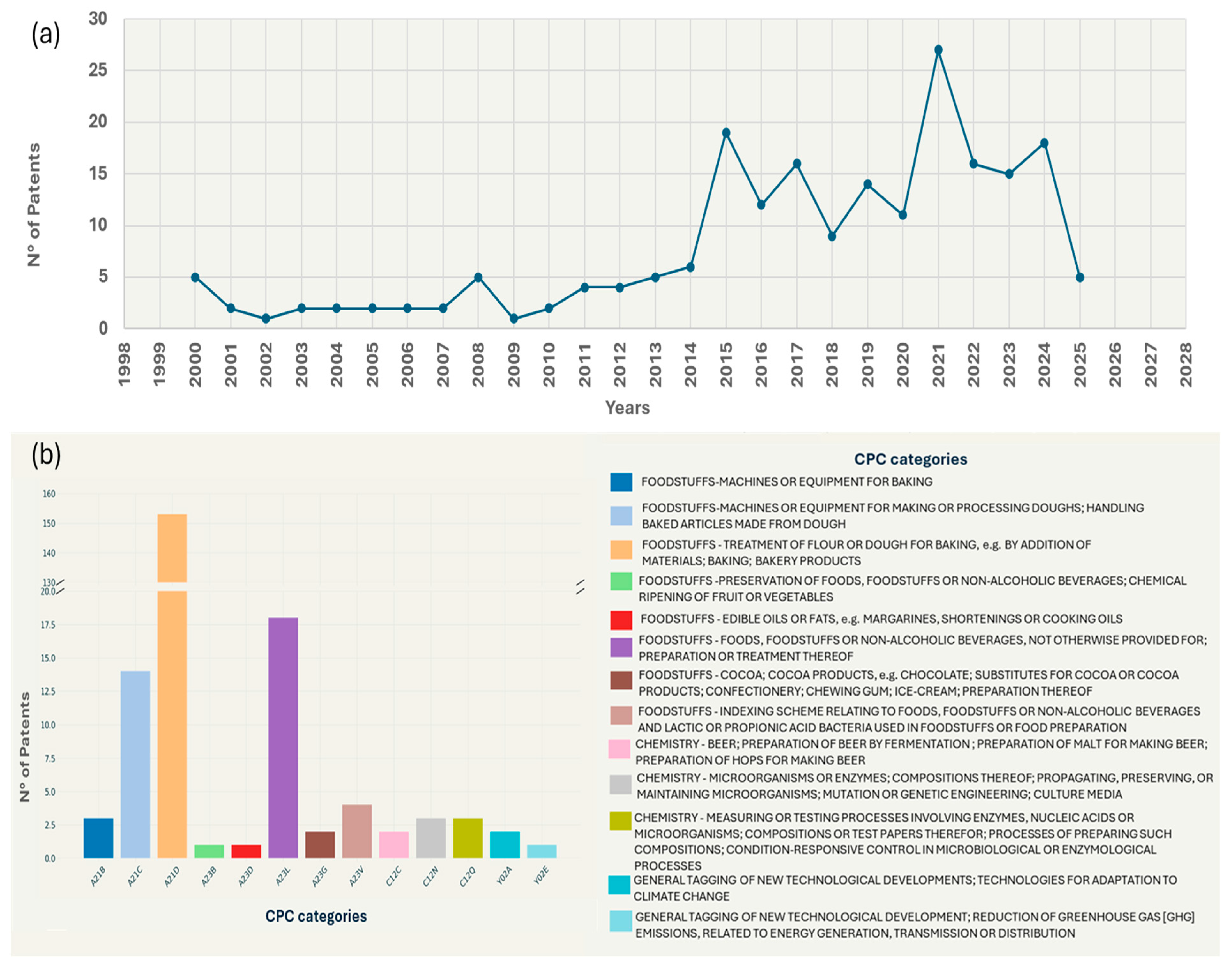
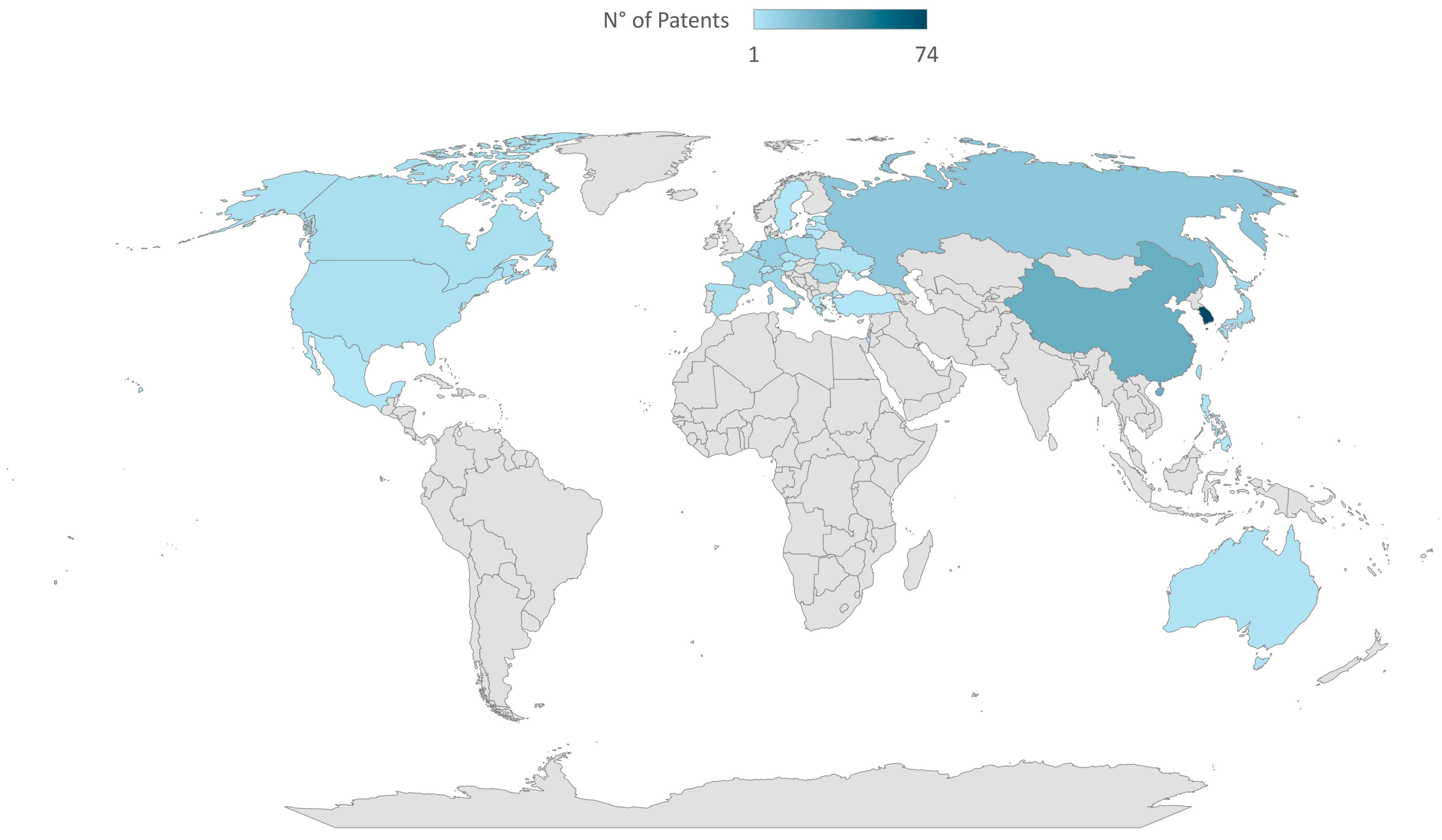
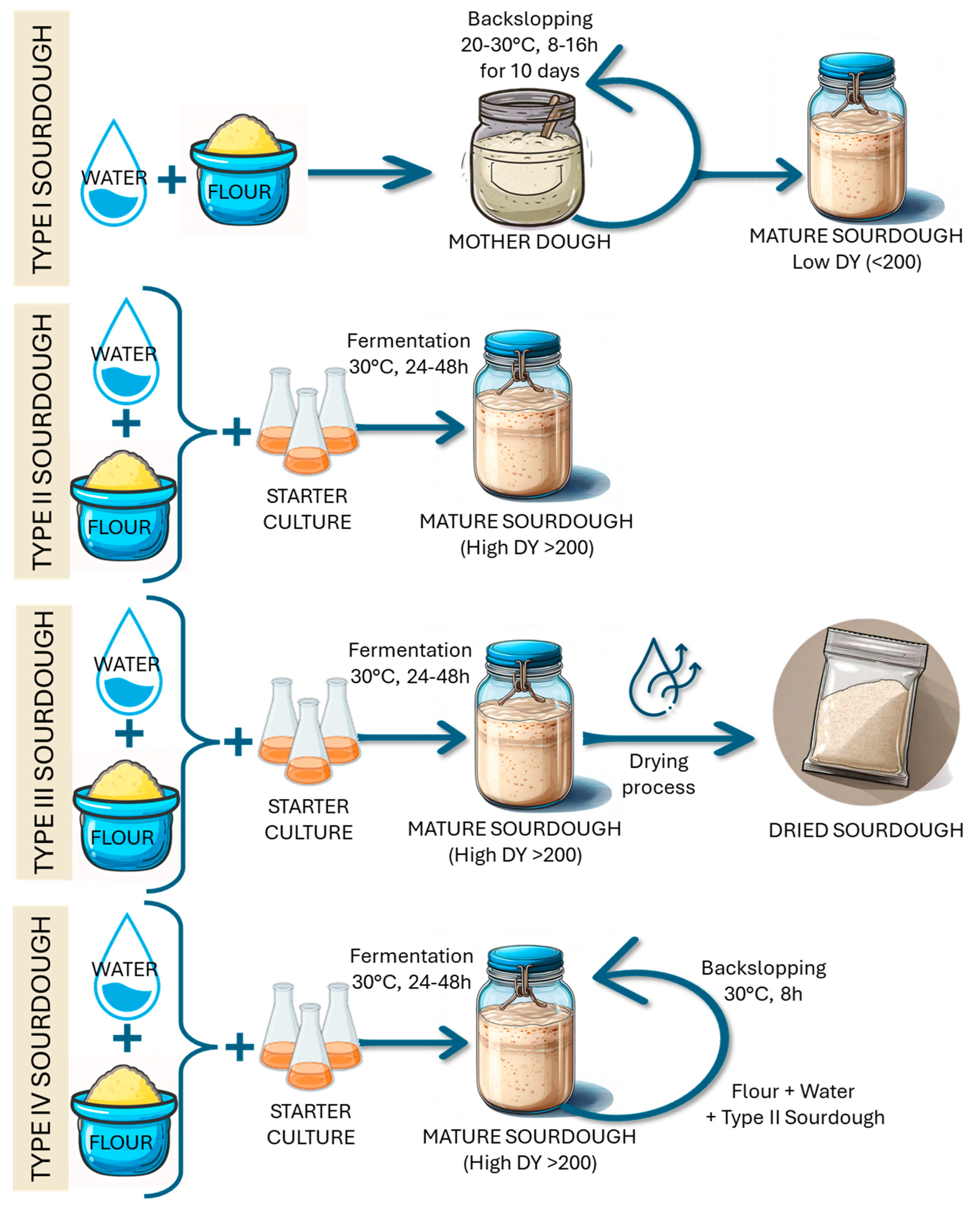
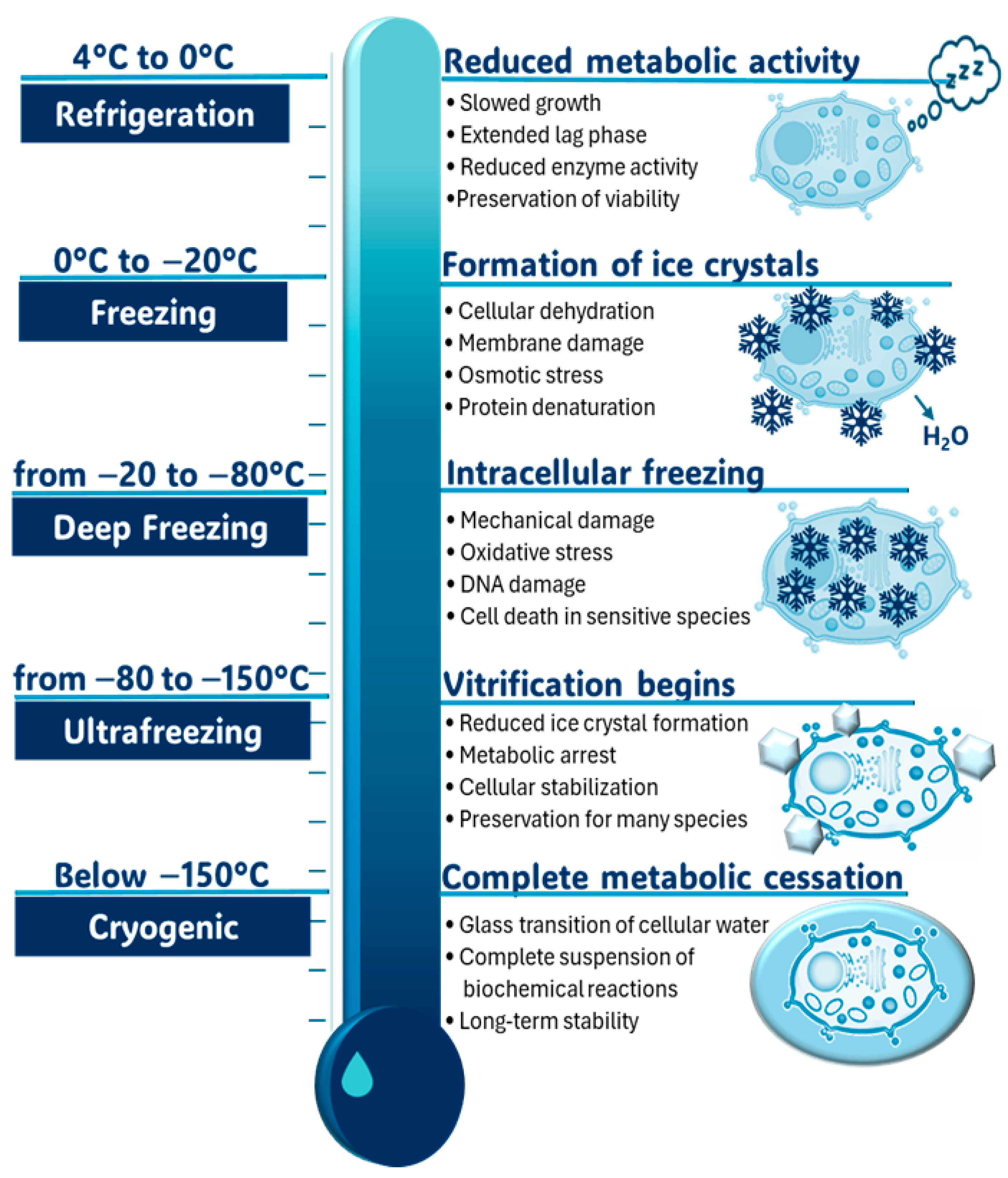
| Sourdough Type | Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) | Yeast | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis, Lactobacillus pontis. | S. cerevisiae, Kazachstania humilis. | [30] |
| Levilactobacillus brevis, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Lacticaseibavillus rhamnosus. | Wickerhamomyces anomalus, S. cerevisiae, Torulaspora delbruekii, Pichia kluyveri, Candida boidinii, Candida diddensiae. | [31] | |
| L. brevis, Lactobacillus alimentarius, Lactobacillus pentosus. | S. cerevisiae, K. humilis. | [32] | |
| Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis, L. plantarum, Lactobacillus kimchi, Lactobacillus sakei, Lactobacillus hamesii, L. pentosus. | Kazachstania bulderi, Candida humilis, Kazachstania unispora, T. delbruekii, Rhodotorula mucillaginosa, Candida carpophila, S. cerevisiae, Hyphopichia pseudoburtonii. | [33] | |
| L. plantarum, L. sanfranciscensis, Lactobacillus spicheri, Lactobacillus rossiae, Lactobacillus namurensis, Lactobacillus zymae, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus mindensis, Lactobacillus acetotolerans, Lactobacillus farciminis, Lactobacillus paralimentarius, Pediococcus pentosaceus, Enterococcus durans, Enterococcus faecium, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Weissella confuse. | S. cerevisiae, Pichia guiliermondii, T. delbrueckii, Candida parapsilosis, Candida pararugosa. | [34] | |
| L. sanfranciscensis, W. cibaria, Lactobacillus fermentum, L. plantarum, L. pontis, L. paralimentarius. | S. cerevisiae, C. humilis, W. anomalus. | [35] | |
| Weissella viridescens, P. pentosaceus, Pediococcus acidilactici, L. brevis, Lactobacillus parabuchneri. | S. cerevisiae, Pichia membranifaciens. | [36] | |
| F. sanfranciscensis, Companilactobacillus paralimentarius, L. brevis. | S. cerevisiae, K. humilis, K. bulderi. | [37] | |
| L. curvatus, F. sanfranciscensis, Leuconostoc citreum, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides, P. pentosaceus, Lactobacillus acidifarinae. | C. humilis, T. delbrueckii, S. cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces marxianus. | [38] | |
| F. sanfranciscensis. | Candida milleri, S. cerevisiae. | [39] | |
| Lactobacillus fructivorans, L. plantarum, Lactobacillus reuteri, Lactobacillus delbrueckii, Weisella spp. | C. humilis, S. cerevisiae, P. kudriavzevii. | [40] | |
| F. sanfranciscensis, W. cibaria, L. plantarum, L. reuteri, L. pontis. | S. cerevisiae, Kazachstania exigua. | [41] | |
| Type II | Leuconostoc citreum, Lactococcus lactis, W. confusa, W. cibaria, L. plantarum, Lactobacillus paraplantarum, L. brevis. | W. anomalus, Kazachstania unispora, S. cerevisiae. | [42] |
| L. curvatus, P. pentosaceus, L. brevis, L. plantarum, L. mesenteroides, L. rossiae. | S. cerevisiae. | [43] | |
| L. plantarum, L. reuteri, L. delbrueckii. | S. cerevisiae, W. anomalus, Saccharomyces bayanus, T. delbrueckii. | [40] | |
| L. fermentum, L. plantarum, L. brevis, W. confusa, P. pentosaceus. | S. cerevisiae. | [44] | |
| L. plantarum, L. fermentum, L. reuteri, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus johnsonii, Lactobacillus farciminis, L. delbrueckii, Lactobacillus amylovorus, L. fermentum, L. sanfranciscensis, L. brevis, L. pontis, Lactobacillus panis, Lactobacillus frumenti, Weissella spp. | S. cerevisiae (added). | [45] | |
| Type III | P. pentosacesus. | S. cerevisiae (added). | [46] |
| L.brevis, L. fermentum, L. frumenti, L. pontis, L. panis, L. reuteri, L. sanfranciscensis, W. confusa, L. acidophilus, L. delbrueckii, L. amylovorus(rye), L. farciminis, L. johnsonii. | S. cerevisiae (added). | [47] | |
| L. paralimentarius. | S. cerevisiae (added). | [48] | |
| L. delbrueckii, L. brevis, L. plantarum | [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coronas, R.; Bianco, A.; Sanna, A.M.L.; Zara, G.; Budroni, M. Type I Sourdough Preservation Strategies and the Contribution of Microbial Biological Resource Centers to Biodiversity Protection: A Narrative Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152624
Coronas R, Bianco A, Sanna AML, Zara G, Budroni M. Type I Sourdough Preservation Strategies and the Contribution of Microbial Biological Resource Centers to Biodiversity Protection: A Narrative Review. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoronas, Roberta, Angela Bianco, Anna Maria Laura Sanna, Giacomo Zara, and Marilena Budroni. 2025. "Type I Sourdough Preservation Strategies and the Contribution of Microbial Biological Resource Centers to Biodiversity Protection: A Narrative Review" Foods 14, no. 15: 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152624
APA StyleCoronas, R., Bianco, A., Sanna, A. M. L., Zara, G., & Budroni, M. (2025). Type I Sourdough Preservation Strategies and the Contribution of Microbial Biological Resource Centers to Biodiversity Protection: A Narrative Review. Foods, 14(15), 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152624








