Activity Analysis and Inhibition Mechanism of Four Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared from Flammulina velutipes by Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
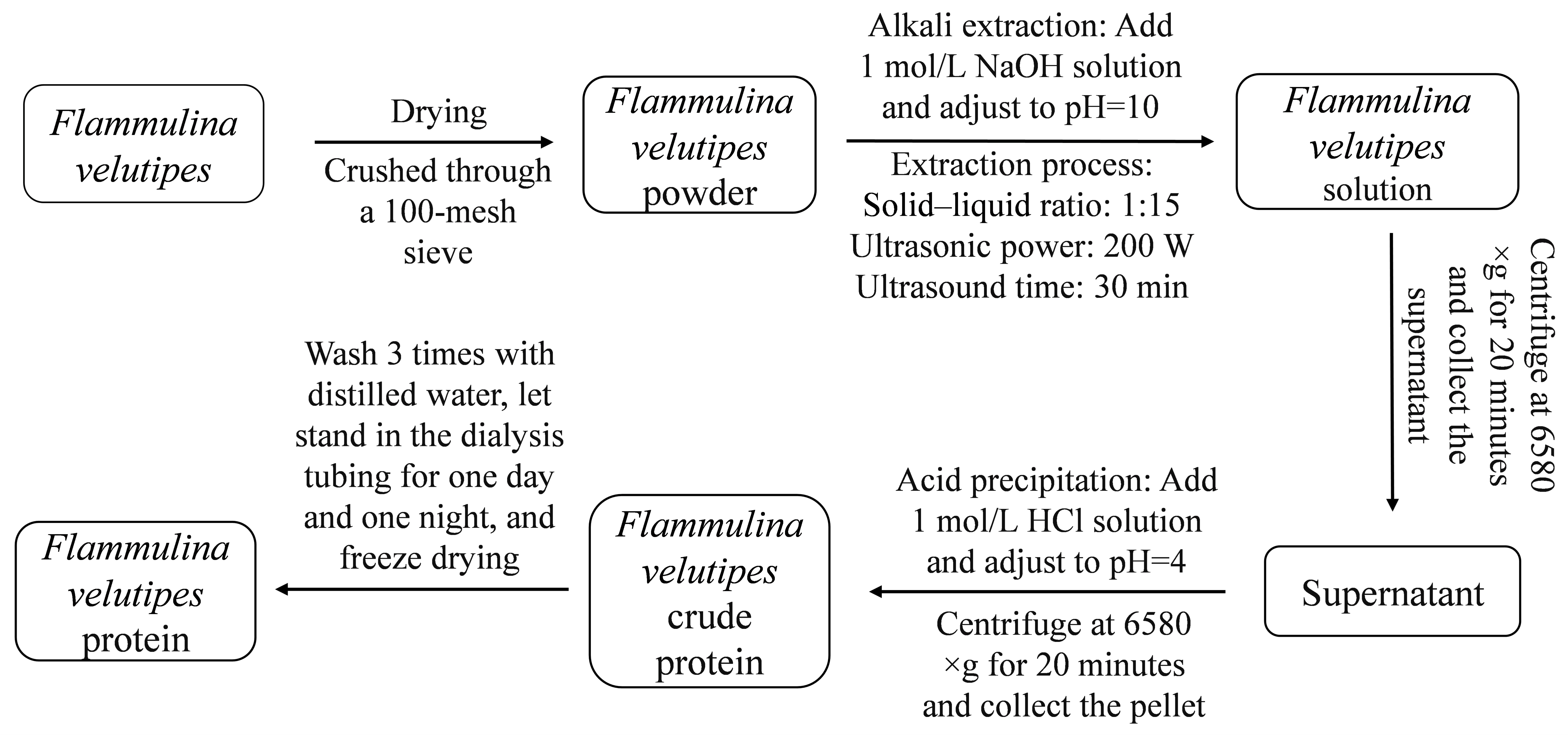
2.2. Extraction of F. velutipes Protein
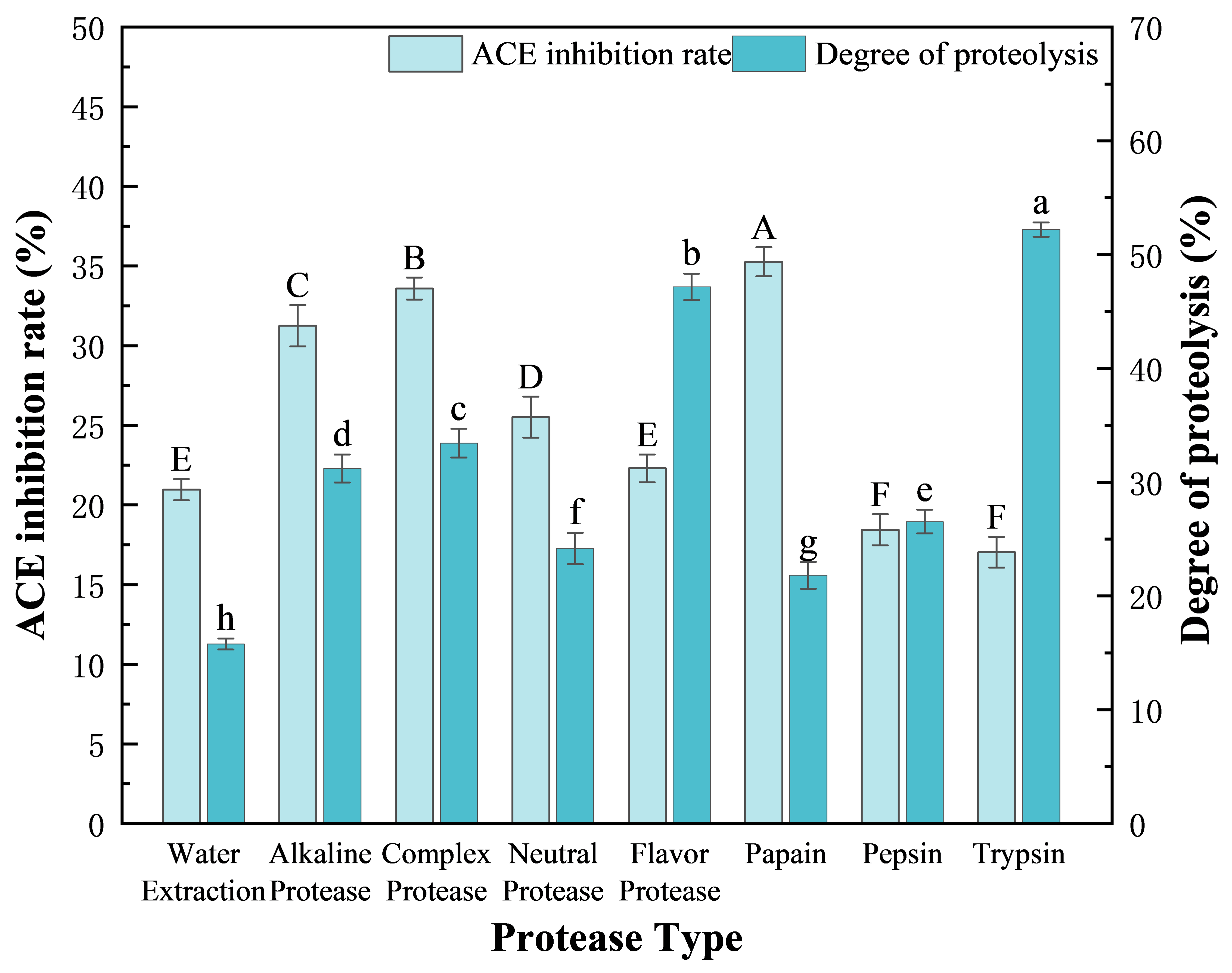
2.3. Screening of Proteases
2.4. Determination of Degree of Hydrolysis of Protein in F. velutipes
2.5. Determination of ACE Inhibitory Peptide Activity
| Reagent | A Sample (μL) | B Control (μL) |
|---|---|---|
| ACE (0.1 U/mL) | 10 | 10 |
| FAPGG (1 mmol/L) | 50 | 50 |
| ACEI | 40 | 0 |
| HEPES buffer (80 mmol/L) | 0 | 40 |
2.6. Response Surface Optimization
2.7. Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides Derived from F. velutipes
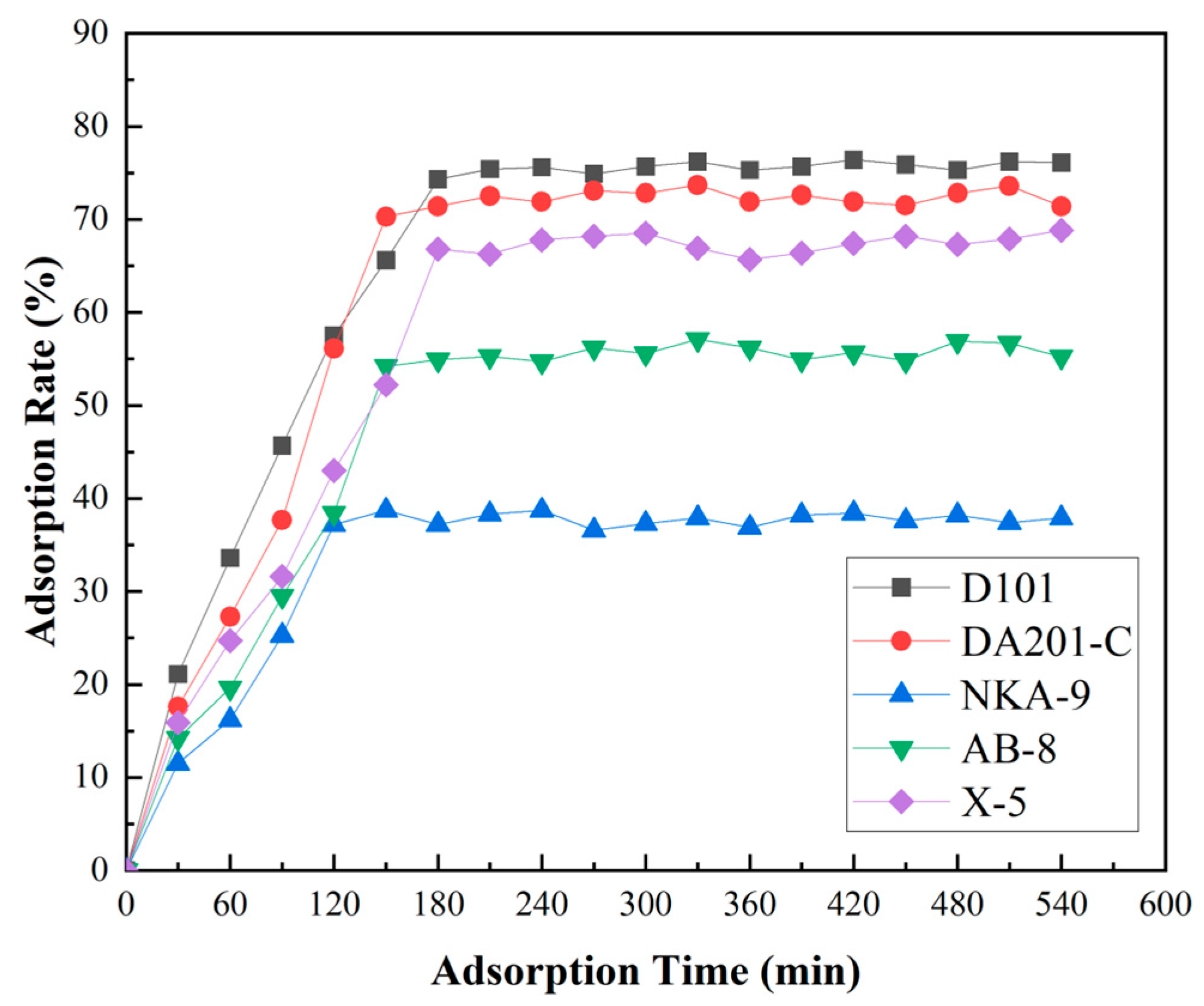
2.7.1. Macroporous Resin Separation
2.7.2. Gel Chromatography Purification and Classification
2.7.3. Purification by RP-HPLC
2.8. Determination of Molecular Weight of Polypeptide Before and After Purification
2.9. De Novo Peptide Sequencing
2.10. Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides with High Activity Using in Silico Analysis
2.11. Molecular Docking Technology for ACE Inhibitory Peptides from F. velutipes
2.12. Synthesis and Activity Verification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides Derived from F. velutipes
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Screening of Proteases
3.2. Optimization of Process Parameters for the Production of High-Activity ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Double-Enzymatic Hydrolysis Method
3.3. Separation and Purification
3.3.1. Screening of Macroporous Resin
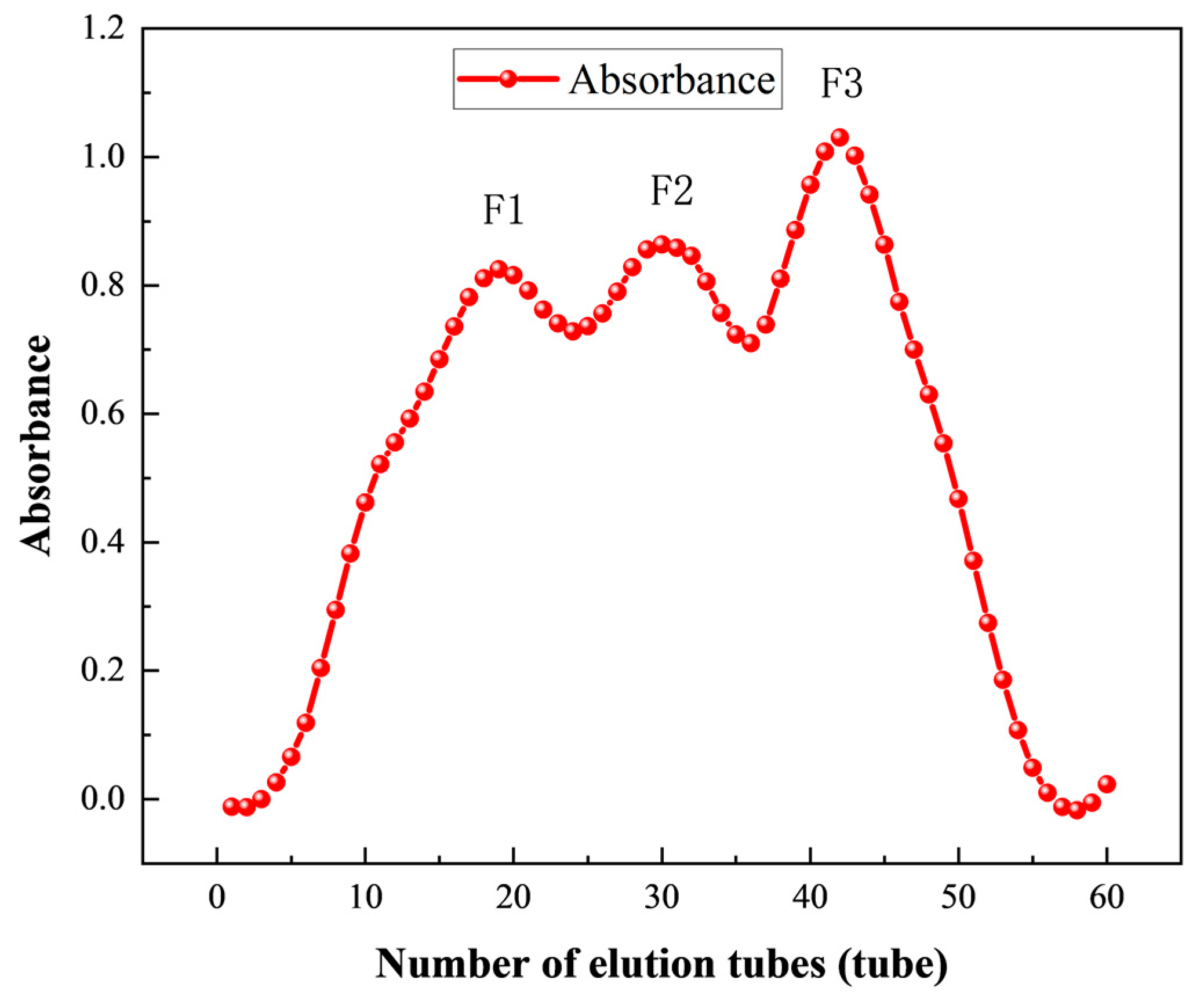
3.3.2. Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Gel Chromatography
3.3.3. Molecular Weight Distribution of the ACE Inhibitory Peptides Before and After Purification
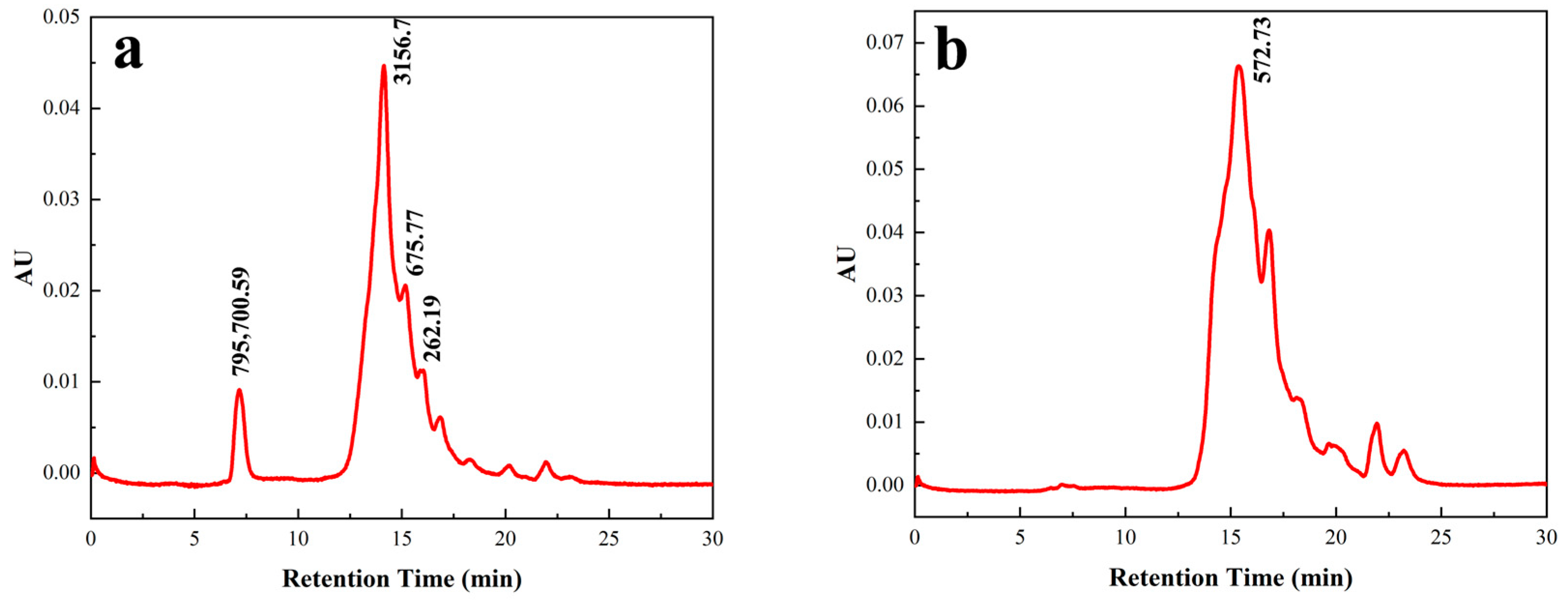
3.3.4. Purification by RP-HPLC
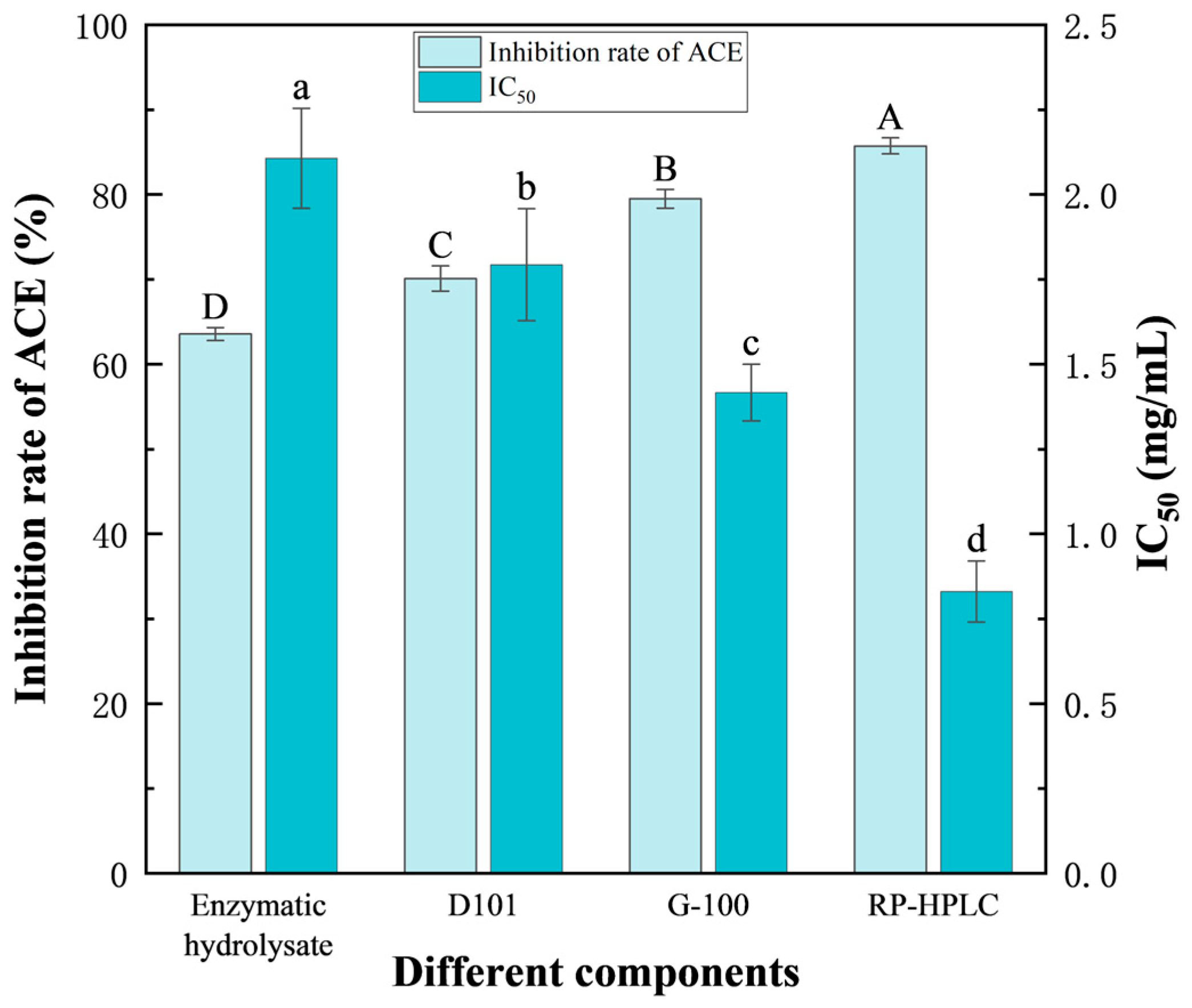
3.3.5. Comparison of ACE Inhibitory Activities of the Peptides Before and After Isolation and Purification
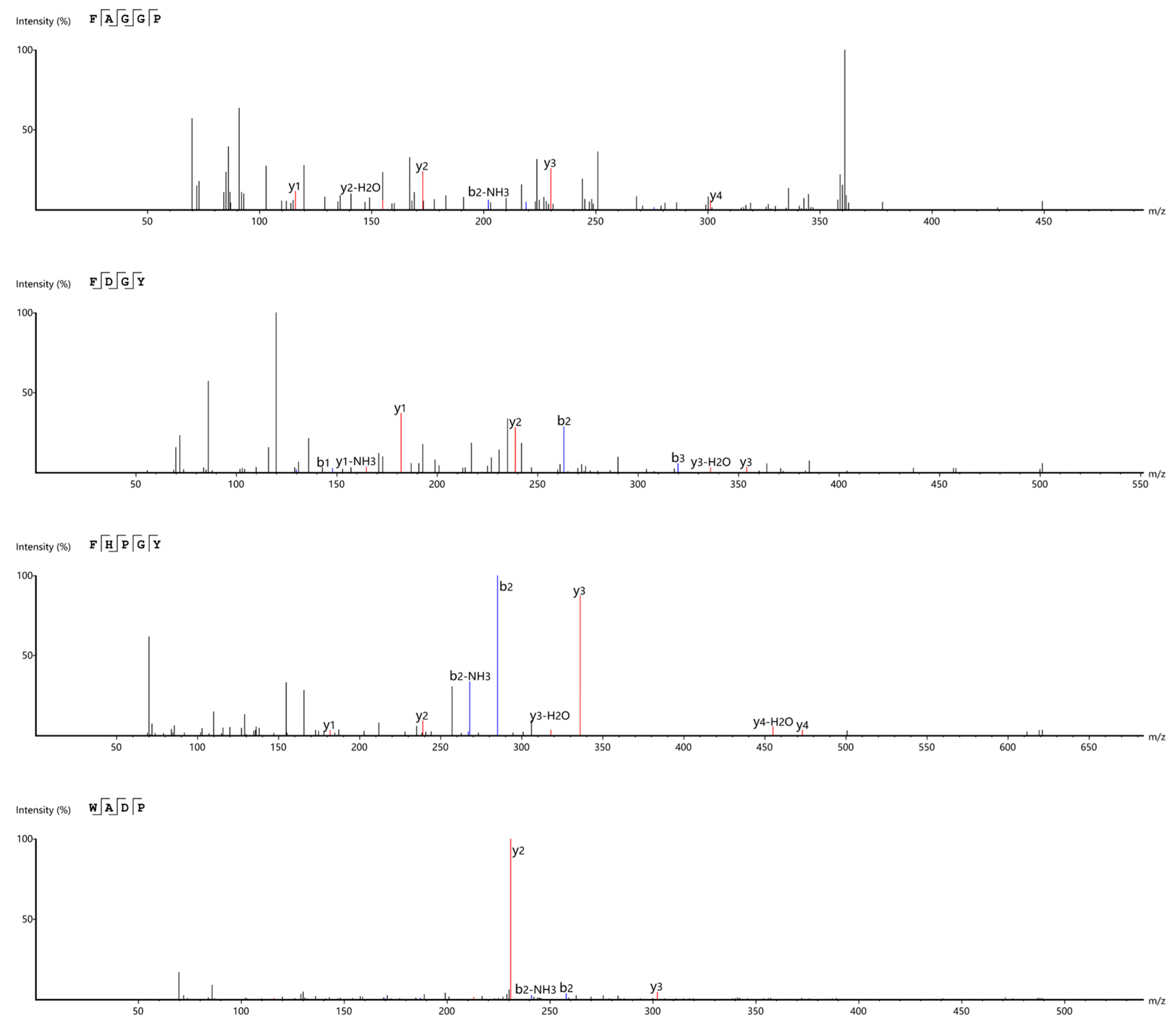
3.4. Screening and Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides Derived from F. velutipes
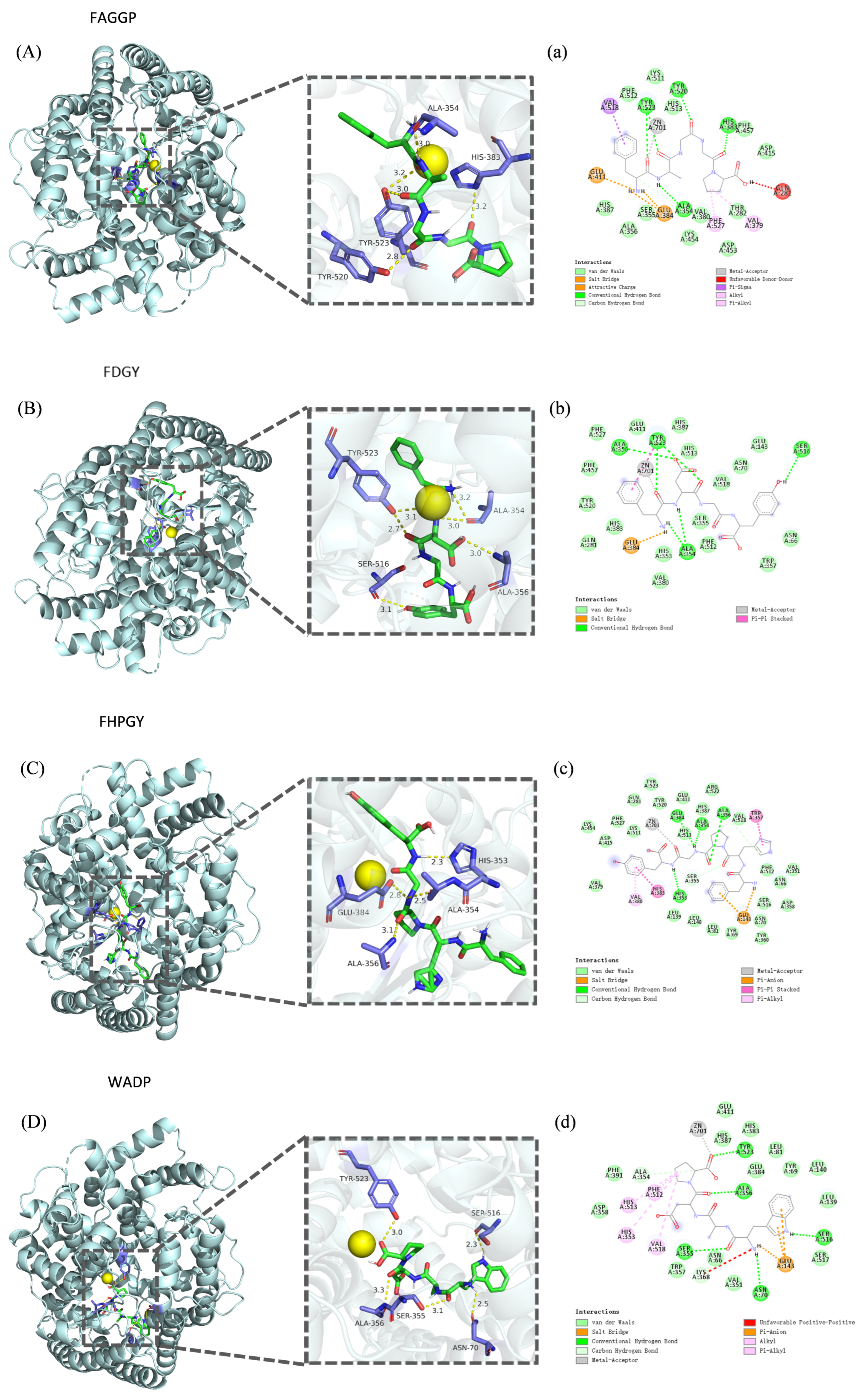
3.5. Molecular Docking Analysis
3.6. Validation of ACE Inhibitory Activity of the Selected Peptides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin I-converting enzyme |
| ACEI | Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| DH | The degree of hydrolysis |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| FAPGG | N-[3-(2-furylacryloyl)]-L-phenylalanyl-glycyl-glycine |
| IAM | Iodoacetamide |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| HEXXH | His-Glu-X-X-His |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| RP-HPLC | Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- Sun, X.; Acquah, C.; Aluko, R.; Udenigwe, C. Considering food matrix and gastrointestinal effects in enhancing bioactive peptide absorption and bio-availability. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandideh, F.; Liu, P.; Wu, J. Purification and identifi-cation of adipogenic-differentiating peptides from egg white hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisha, C.; Bhagwat, P.; Pillai, S. Emerging production techniques and potential health promoting properties of plant and animal protein-derived bioactive peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, L.N.; Guo, Y.; Katherine, D.; Christoph, M.; Liu, Y.; Mu, S. The link between immunity and hypertension in the kidney and heart. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1129384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Bu, G.; Chen, F. Identification and molecular interactions of novel ACE inhibitory peptides from rapeseed protein. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadimu, G.J.; Gan, C.Y.; Olalere, O.A.; Farahnaky, A.; Gill, H.; Truong, T. Novel antihypertensive peptides from lupin protein hydrolysate: An in-silico identification and molecular docking studies. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Ju, X.; He, R. Antihypertensive activity of the ACE–renin inhibitory peptide derived from Moringa oleifera protein. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8994–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Yang, Y.; Huo, X.; Long, P.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Multifunctional ACE-inhibitory peptides with antioxidant and ferrous-chelating capacities from ginkgo kernel glutelin-2 hydrolysates: Identification, virtual screening, inhibition mechanism, and gastrointestinal stability studies. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 217, 7117461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, L.; Dong, B.; Huang, J.; Huang, T.; Xiao, M.; Xiong, T.; et al. ACE inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of fermented black sesame seed: Random forest-based optimization, screening, and molecular docking analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 437, 137921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrell, S.; Alhomoud, I.S.; Mehta, A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Van Tassell, B.; Dixon, D.L. ACE-inhibitors in hypertension: A historical perspective and current insights. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memarpoor-Yazdi, M.; Asoodeh, A.; Chamani, J. Structure and ace-inhibitory activity of peptides derived from hen egg White Lysozyme. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Huang, T.; Xiao, M.; Xiong, T.; et al. Effects of fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NCU116 on the antihypertensive activity and protein structure of black sesame seed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Saha, A.; Dhar, P. Novel ACE inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of Channa punctata protein: In vitro and In silico assay of structure-activity relationship. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Qing, H.; Jing, K.; Yu, Q.; Chang, F.; Wang, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Yang, J.; Qin, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, H.; et al. Transport and action of sesame protein-derived ACE inhibitory peptides ITAPHW and IRPNGL. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Shi, P.; Li, G. Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an In Silico Approach: Characterization, In Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking. Molecules 2019, 24, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahingil, D.; Gokce, Y.; Celikbicak, O.; Hayaloglu, A.A. ACE-inhibitory activities of peptide fractions (<3 kDa) and identification of peptide sequence by MALDI-ToF-MS in model cheeses incorporating different Lactobacillus species. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Peptidomics-based study of antihypertensive activity: Discovery of novel ACE inhibiting peptides from peanut yogurt. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 6705–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Matanjun, P.; Budiman, C.; Shapawi, R.; Lee, J.S. Valorisation of Hybrid Grouper Bone Gelatine: Identification and In Silico Analysis of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides Obtained Via Ultrafiltration. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gu, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, W. Screening of Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides in Squid (Todarodes pacificus) Skin Hydrolysates: Preliminary Study of Its Mechanism of Inhibition. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhui, C.; Hwan, K.S.; Jin, H.K.; Taek, J.H.; Mooha, L.; Cheorun, J. Isolation and identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from thermolysin-injected beef M. longissimus. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Jia, Y.Q.; Liu, C.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhu, Z.Y. Structure identification and inhibitor y mechanism evaluation of three novel angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from small-aroma chicken. Process Biochem. 2023, 132, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yun, J.; Wang, S.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, F. Optimisation and Characterisation of Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared by Double Enzymatic Hydrolysis from Agaricus bisporus Scraps. Foods 2022, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paisansak, S.; Sangtanoo, P.; Srimongkol, P.; Saisavoey, T.; Reamtong, O.; Choowongkomon, K.; Karnchanatat, A. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from the shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhao, G.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Feng, J. Structure characterization and mechanism of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides modified by plastein reaction derived from tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus). Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 8, 1476134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimatu, M.B.; Zhao, L.; Biao, Y.; Ma, G.; Yang, W.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q. Antioxidant potential of edible mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) protein hydrolysates and their ultrafiltration fractions. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, I.R.; Delgado-Andrade, C. The beneficial role of edible mushrooms in human health. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hoo, P.C.X.; Tan, L.T.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Khan, T.M.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H.; Chan, K.G. Golden needle mushroom: A culinary medicine with evidenced-based biological activities and health promoting properties. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Advances in the extraction, purification, structural-property relationships and bioactive molecular mechanism of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran Dowom, S.; Rezaeian, S.; Pourianfar, H.R. [M41] Agronomic and environmental factors affecting cultivation of the winter mushroom or Enokitake: Achievements and prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Hu, Q.; Ren, J.; Zhao, H.; You, L.; Zhao, M. Effect of the structural features of hydrochloric acid-deamidated wheat gluten on its susceptibility to enzymatic hydrolysis. J Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5706–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, B. Investigation of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory tri-peptides: A combination of 3D-QSAR and molecular docking simulations. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35811–35819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Contreras, M.D.M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, A.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Montero, P. Identification of ace-inhibitory peptides from squid skin collagen after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Feng, Y.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tang, S.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Revealing the Sequence Characteristics and Molecular Mechanisms of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Comprehensive Characterization of 160,000 Tetrapeptides. Foods 2023, 12, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Q.; He, Q. Screening and mechanisms of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from rabbit meat proteins: A combined in silico and in vitro study. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.X.; Zhao, T.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhao, M.; Su, G. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128855–128899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Cheng, F.; Chen, H.; Shu, G. Preparation and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Moringa oleifera leaf. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 205, 116472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Lai, J.; He, P.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H. Screening, ACE-inhibitory mechanism and structure-activity relationship of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from Lepidium meyenii (Maca) protein hydrolysate. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanajon, P.; Hamzeh, A.; Tian, F.; Roytrakul, S.; Oluwagunwa, A.O.; Kadam, D.; Aluko, E.R.; Aueviriyavit, S.; Wongwanakul, R.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Hypotensive effect of potent angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from corn gluten meal hydrolysate: Gastrointestinal digestion and transepithelial transportation modifications. Food Chem. 2024, 462, 140953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, B. Studies on purification and the molecular mechanism of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, T.; Christensen, M.H. A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowacki, E.D.; Irimia-Vladu, M.; Bauer, S.; Sariciftci, N.S. Hydrogen-bonds in molecular solids from biological systems to organic electronics. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2013, 1, 3742–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Huang, H.; Shao, Y.; Hao, S.; Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from eel (Anguilla japonica) bone collagen: Preparation, identification, molecular docking, and protective function on HUVECs. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1462656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, C.; Xiao, G. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Two Peptides Derived from In Vitro Digestion Products of Pork Sausage with Partial Substitution of NaCl by KCl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10638–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, C.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, A. Two Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory and ACE2 Upregulating Peptides from the Hydrolysate of Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Seed Meal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10909–10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, D.; Rafiq, S.; Gat, Y.; Gat, Y.; Gat, P.; Waghmare, R.; Kuma, V. A Review on Bioactive Peptides: Physiological Functions, Bioavailability and Safety. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, D.; Shen, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L. Discovery of two novel ACE inhibitory peptides from soybeans: Stability, molecular interactions, and in vivo antihypertensive effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, S.; Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Henle, T. Identification and quantification of ACE-inhibiting peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of plant proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhong, H.; Cheng, J. Comprehensive Analysis of the Structure and Allergenicity Changes of Seafood Allergens Induced by Non-Thermal Processing: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Liao, W. Identification and characterization of gastrointestinal-resistant angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from egg white proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
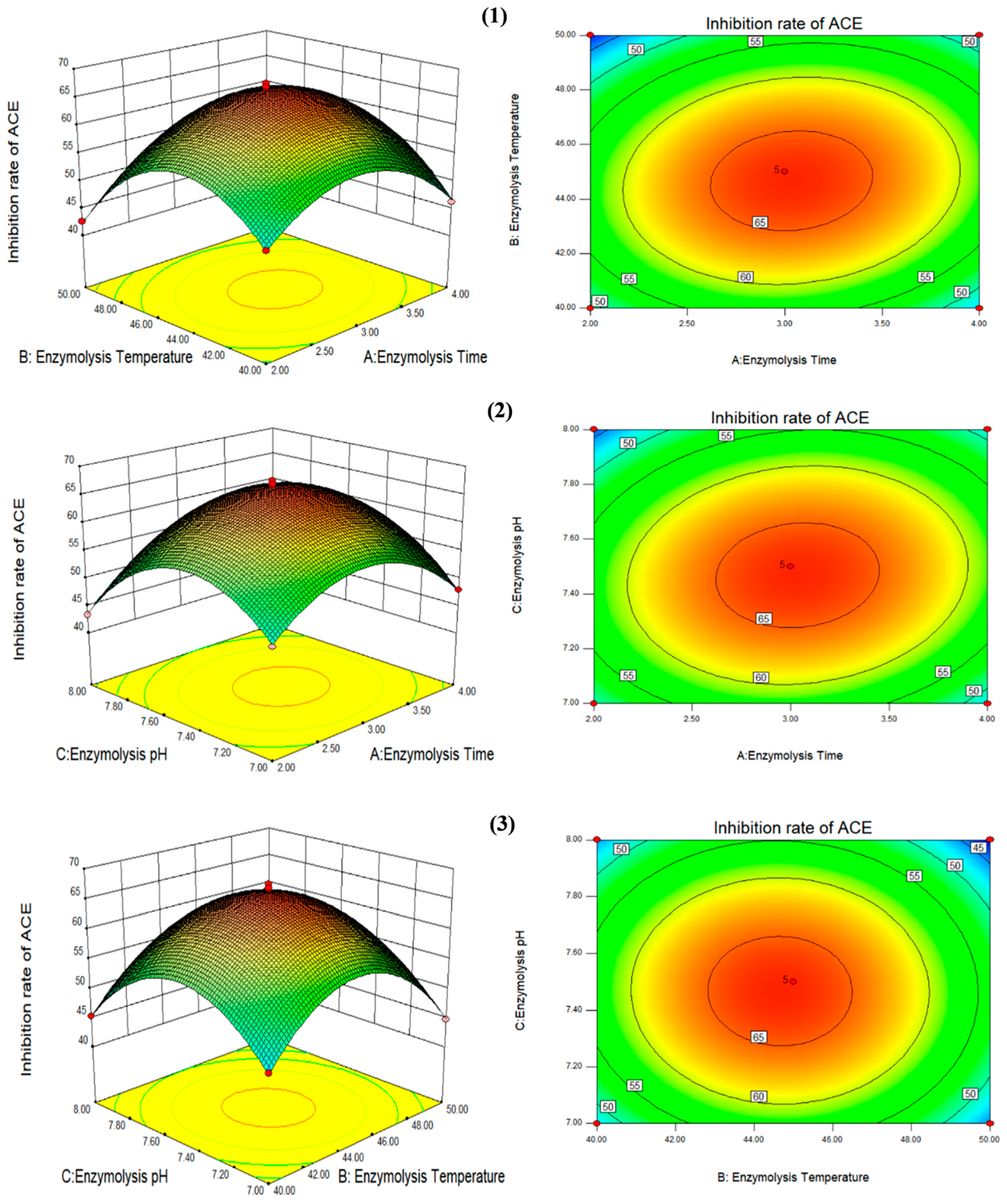

| Level | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A Enzymolysis Time /h | B Enzymolysis Temperature/°C | C Enzymolysis pH | |
| −1 | 2 | 40 | 7 |
| 0 | 3 | 45 | 7.5 |
| 1 | 4 | 50 | 8 |
| Serial Number | A Enzymolysis Time /h | B Enzymolysis Temperature /°C | C Enzymolysis pH | Inhibition Rate of ACE /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 49.38 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 42.61 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 44.78 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 66.61 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 41.26 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 65.39 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 48.87 |
| 8 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 47.63 |
| 9 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 43.36 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 65.73 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 66.92 |
| 12 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 48.02 |
| 13 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 49.22 |
| 14 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 45.39 |
| 15 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 46.25 |
| 16 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 47.19 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67.53 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1530.17 | 9 | 170.02 | 288.98 | <0.0001 | ** |
| A (enzymolysis time) | 4.15 | 1 | 4.15 | 7.05 | 0.0327 | * |
| B (enzymolysis temperature) | 20.00 | 1 | 20.00 | 34.00 | 0.0006 | ** |
| C (enzymolysis pH) | 14.93 | 1 | 14.93 | 25.38 | 0.0015 | * |
| AB | 14.25 | 1 | 14.25 | 24.22 | 0.0017 | * |
| AC | 11.80 | 1 | 11.80 | 20.06 | 0.0029 | * |
| BC | 0.41 | 1 | 0.41 | 0.70 | 0.4316 | |
| A2 | 321.48 | 1 | 321.48 | 546.42 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B2 | 545.33 | 1 | 545.33 | 926.89 | <0.0001 | ** |
| C2 | 445.87 | 1 | 445.87 | 757.84 | <0.0001 | ** |
| Residual error | 4.12 | 7 | 0.59 | |||
| Lack of fit | 1.06 | 3 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.7224 | |
| Pure error | 3.05 | 4 | 0.76 | |||
| Cor total | 1534.29 | 16 |
| Peptide Sequence | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | Van der Waals Interaction | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | Other Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAGGP | −9.5 | Tyr523, Tyr520, Ala354, His383 | His387, Ser355, Lys454, Thr282, Val380, Asp453, Phe512, His513, Lys511, Phe457, Asp415, Ala356 | Zn2+, Val518, Glu411, Glu384, Gln281, Phe527, Val379 | |
| FDGY | −9.4 | Ala354, Ser516, Ala356, Tyr523 | Val380, His353, His383, Gln281, Tyr520, Phe457, Phe527, Glu411, His387, Ser355, Phe512, His513, Trp357, Asn66, Val518, Glu143, Asn70 | Zn2+, Glu384 | |
| FHPGY | −10.3 | Glu384, Ala354, His353, Ala356 | Lys454, Asp415, Val379, Phe527, Lys511, Gln281, Tyr523, Tyr520, His513, Leu139, Glu411, Leu140, His387, Arg522, Leu81, Tyr69, Val518, Tyr360, Asn70, Phe512, Val351, Ser516, Asp358, Asn66 | Ser355 | Zn2+, His383, Glu143, Trp357, Val380 |
| WADP | −9.5 | Ser355, Ala356, Tyr523, Asn70, Ser516 | Glu411, His387, His383, Leu81, Tyr69, Leu140, Leu139, Ser517, Val351, Asn66, Phe391, Asp358, Glu384, Trp357 | Ala354, Lys368 | Zn2+, Glu143, Phe512, His513, His353, Val518 |
| Peptide Sequence | Mw (Da) | Inhibition Rate of ACE (%) | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAGGP | 433.46 | 85.92 ± 1.81 c | 29.17 ± 1.37 c |
| FDGY | 447.48 | 80.48 ± 0.84 e | 91.55 ± 1.09 a |
| FHPGY | 487.51 | 91.41 ± 1.01 b | 14.79 ± 0.34 d |
| WADP | 619.68 | 83.04 ± 0.68 d | 41.27 ± 0.70 b |
| Captopril | 98.64 ± 0.73 a | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Ye, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yun, J. Activity Analysis and Inhibition Mechanism of Four Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared from Flammulina velutipes by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Foods 2025, 14, 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152619
Zhang Y, Zhao X, Ma X, Li J, Ye X, Wang X, Zhang W, Yun J. Activity Analysis and Inhibition Mechanism of Four Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared from Flammulina velutipes by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152619
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yajie, Xueqi Zhao, Xia Ma, Jiaqi Li, Xiaoyu Ye, Xuerui Wang, Wenwei Zhang, and Jianmin Yun. 2025. "Activity Analysis and Inhibition Mechanism of Four Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared from Flammulina velutipes by Enzymatic Hydrolysis" Foods 14, no. 15: 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152619
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhao, X., Ma, X., Li, J., Ye, X., Wang, X., Zhang, W., & Yun, J. (2025). Activity Analysis and Inhibition Mechanism of Four Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared from Flammulina velutipes by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Foods, 14(15), 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152619





