Research Progress on Flavor Differences and the Formation Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar
2.1. Sorghum Vinegar
2.2. Rice Vinegar
2.3. Wheat Vinegar
2.4. Buckwheat Vinegar
2.5. Oat Vinegar
2.6. Barley Vinegar
2.7. Other Cereal Vinegar
3. Differences in Key Flavor Compounds of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar
3.1. Differences in Organic Acid Composition in Cereal Vinegar
3.2. Differences in Amino Acid Composition in Cereal Vinegar
3.3. Differences in Volatile Flavor Compounds in Cereal Vinegar
4. Key Factors Affecting the Flavor of Cereal Vinegar
4.1. Differences in Fermentation Materials of Different Cereal Vinegars
4.2. Differences in the Fermentation Process of Different Cereal Vinegars
4.3. Differences in Fermentation Environments of Different Cereal Vinegars
4.4. Differences in the Starter of Different Cereal Vinegars
5. Mechanism of Flavor Compounds Formation
5.1. Dominant Microorganisms in the Fermentation Process
5.2. Sources of Key Flavor Compounds in Cereal Vinegar
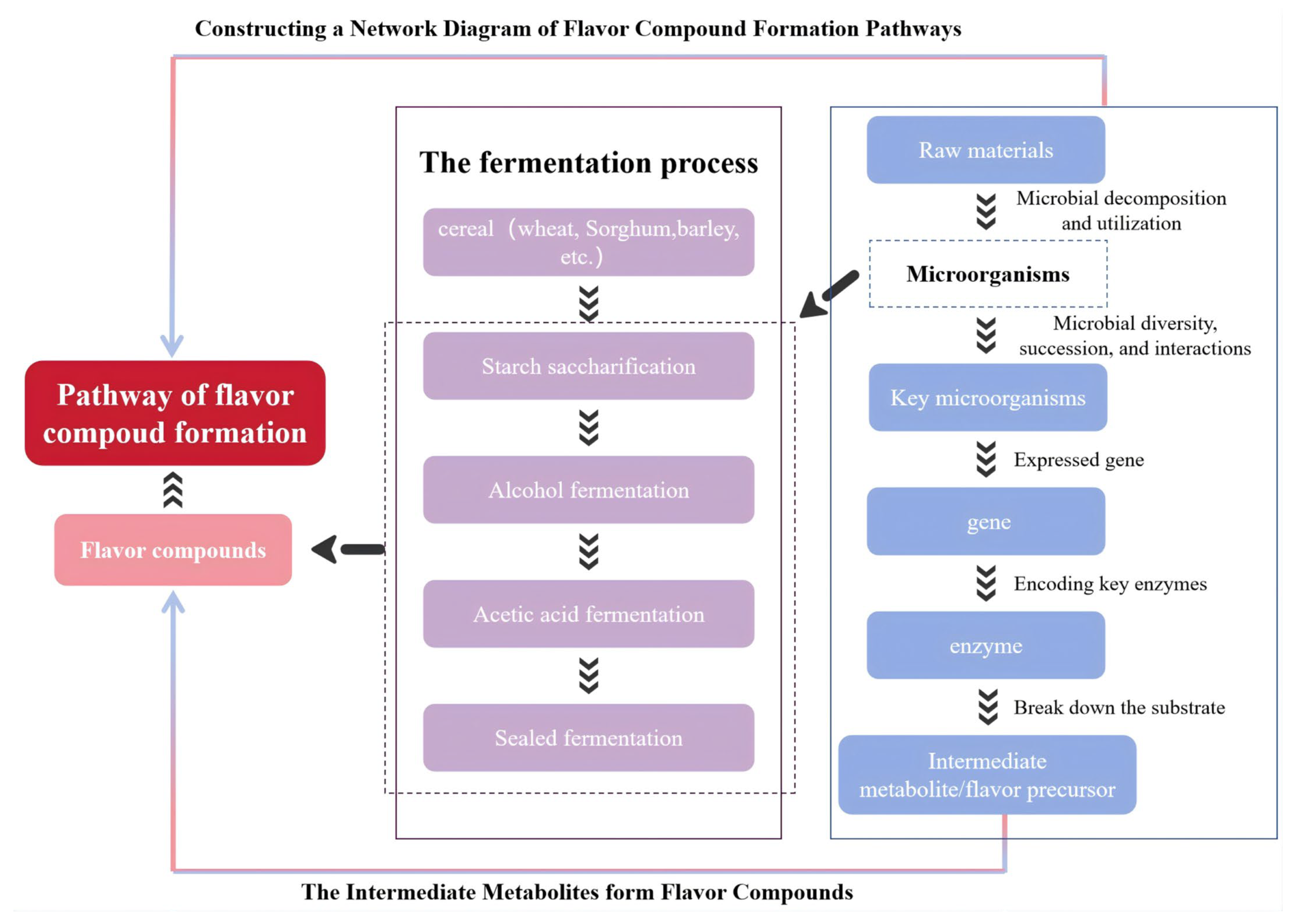
5.3. Formation Pathways of Key Flavor Compounds of Cereal Vinegar
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Z.M.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Mao, J.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Microbial Ecology of Cereal Vinegar Fermentation: Insights for Driving the Ecosystem Function. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, E.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Ma, H.; Ho, C.T.; Liao, L. Accelerating Aroma Formation of Raw Soy Sauce Using Low Intensity Sonication. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wu, R.A.; Yin, L.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, H.; Luo, L.; Ma, H.; Dai, C. Antioxidation and Memory Protection Effects of Solid-State-Fermented Rapeseed Meal Peptides on D-Galactose-Induced Memory Impairment in Aging-Mice. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, J.A.; Ma, H. Bioconversion of Food Industrial Waste Okara by Microbial Fermentation: Scope of Omics Study and Possibility. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Huang, R.; Xie, J.; Shen, M. Characterization and Identification of Different Chinese Fermented Vinegars Based on Their Volatile Components. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Wang, Z.; Amir, R.M.; Younas, S.; Wali, A.; Adowa, N.; Ayim, I. Potential Uses of Vinegar as a Medicine and Related in Vivo Mechanisms. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2016, 86, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; El-Shabasy, R.M.; Tahir, H.E.; Abo-Atya, D.M.; Saeed, A.; Abolibda, T.Z.; Guo, Z.; Zou, X.; Zhang, D.; Du, M.; et al. Vinegar—A Beneficial Food Additive: Production, Safety, Possibilities, and Applications from Ancient to Modern Times. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 10262–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Yan, Y.; Lang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Unraveling the Metabolic Network of Organic Acids in Solid-State Fermentation of Chinese Cereal Vinegar. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4375–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Fu, S.; Xu, N.; Li, P.; Song, J.; Wang, C. Characteristics and Dis-crimination of the Commercial Chinese Four Famous Vinegars Based on Flavor Compositions. Foods 2023, 12, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, R.; Zhao, G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X. Research Advances in Technologies and Mechanisms to Regulate Vinegar Flavor. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Lu, Z.M.; Peng, M.Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Chai, L.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Shi, J.S.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.H. Combined Effects of Fermentation Starters and Environmental Factors on the Microbial Community Assembly and Flavor Formation of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, F.; Huang, X.; Aheto, J.H.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y. Fast Monitoring the Dynamic Change of Total Acids during Apple Vinegar Fermentation Process Using a Colorimetric IDA Sensor Array. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Z.; Ma, H.; Ayim, I.; Wali, A. Efficacy of New Beverage Made of Dates Vinegar and Garlic Juice in Improving Serum Lipid Profile Parameters and Inflammatory Biomarkers of Mildly Hyperlipidemic Adults: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Ma, H.; Rashid, M.T.; Wali, A.; Younas, S. Preliminary Study to Evaluate the Phytochemicals and Physiochemical Properties in Red and Black Date’s Vinegar. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liang, K.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J.; Qiu, J. The Complexity of Chinese Cereal Vinegar Flavor: A Compositional and Sensory Perspective. Foods 2024, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhang, B.; Duan, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M. Nutrients and Bioactive Components from Vinegar: A Fermented and Functional Food. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; Ma, H. Preliminary Study on Ultrasonic Ageing Zhenjiang Vinegar Mechanism Based on Maillard Simulation System. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 1087863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Zhang, F.F.; Chen, F.S. Biodiversity of Yeasts, Lactic Acid Bacteria and Acetic Acid Bacteria in the Fermentation of “Shanxi Aged Vinegar”, a Traditional Chinese Vinegar. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, K.; Li, J.; Duran-Guerrero, E.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, A. Microbial Characterization of Sichuan Baoning Vinegar: Lactic Acid Bacteria, Acetic Acid Bacteria and Yeasts. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jo, Y.; Chung, N.h.; Gu, S.-I.; Jung, Y.; Kwon, J.-H. Physicochemical Qualities and Flavor Patterns of Traditional Chinese Vinegars Manufactured by Different Fermentation Methods and Aging Periods. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 22, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Awika, J.M. Effect of Sorghum Bran Addition on Antioxidant Activities, Sensory Properties, and in Vitro Starch Digestibility of Chinese Southern-Style Steamed Bread. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 9652–9659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cai, M.; Chen, G. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds from Red Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Bran and Their Biological Activities and Polyphenolic Compositions. Ind. Crop Prod. 2018, 112, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Meng, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, R.; Bo, T.; Zhang, J.; Fan, S.; Yang, Y. Extraction of Phenolic Acids and Tetramethylpyrazine in Shanxi Aged Vinegar Base on Vortex-Assisted Liquid-Liquid Microextraction-Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent: COSMO-RS Calculations and ANN-GA Optimization. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Jianlong, X. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zuo, M.; Liu, S. Integrated Analysis of Metabolome and Volatile Profiles of Germinated Brown Rice from the Japonica and Indica Subspecies. Foods 2021, 10, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Su, J.; Yang, N.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z.; Cui, B.; Wu, F. Changes in the Nutritional Value, Flavor, and Antioxidant Activity of Brown Glutinous Rice during Fermentation. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Pan, T.; Li, G. Evaluation of the Physicochemical Content and Solid-State Fermentation Stage of Zhen-jiang Aromatic Vinegar Using near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, 16, 20200127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Huang, W.H.; Li, S.T.; Yuan, J.J.; Chen, H.B.; Ma, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.F. Dynamic Changes of Bacterial and Fungal Diversities in Yongchun Aged Vinegar during Production and Storage. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Fang, L.; He, C.; Aweya, J.J.; Li, Q. Multidimensional Flavor Analysis of Yongchun Aged Vinegar: Impact of Aging on Quality and Flavor Profile. Food Chem. X 2025, 27, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.X.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Optimisation of Lactic Acid Fermentation for Improved Vinegar Flavour during Rosy Vinegar Brewing. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Hey, S.J. The Contribution of Wheat to Human Diet and Health. Food Energy Secur. 2015, 4, 178–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Chen, S.; Ao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zou, L.; Chen, R. Multiple Rounds of Aspergillus niger Biofortification Confer Relatively Stable Quality with Minor Changes of Microbial Community during Industrial-Scale Baoning Vinegar Production. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Peng, Y.; Ao, X.; Pan, W.; Chen, S.; He, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, F.; Du, D.; Liu, S. Effects of Aspergillus Niger Biofortification on the Microbial Community and Quality of Baoning Vinegar. LWT 2020, 131, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzah, C.S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Boateng, N.A.S.; Ma, H. Ultrasound-Induced Lipid Peroxidation: Effects on Phenol Content and Extraction Kinetics and Antioxidant Activity of Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) Water Extract. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, Q.; Xia, Q.; Zha, B.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Shi, Y.-C. Intact Endosperm Cells in Buckwheat Flour Limit Starch Gelatinization and Digestibility in Vitro. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wu, D.; Ren, G.; Hu, Y.; Peng, L.; Zhao, J.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Carpena, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Cao, H. Bioactive Compounds, Health Benefits, and Industrial Applications of Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, W.; Huanlu, S.; Changzhong, R.; Zaigui, L. Key Aroma Compounds in Shanxi Aged Tartary Buckwheat Vinegar and Changes during Its Thermal Processing. Flavour Fragr. J. 2012, 27, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, C.; Bao, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Oat: Current State and Challenges in Plant-Based Food Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Obadi, M.; Shi, J.; Xu, B.; Shi, Y.-C. Rheological and Thermal Properties of Oat Flours and Starch Affected by Oat Lipids. Cereal Sci. 2021, 102, 103337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Obadi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xu, B. Effect of Steaming and Defatting Treatments of Oats on the Processing and Eating Quality of Noodles with a High Oat Flour Content. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, H.-N.; Ma, A.M.; Zhou, J.Z.; Xia, X.D. Synergetic Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Rhizopus oryzae on Physicochemical, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of Whole-Grain Oats (Avena sativa L.) during Solid-State Fermentation. LWT 2022, 154, 112687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ren, C.; Fan, J.; Li, Z. Antioxidant Activities of Aged Oat Vinegar in Vitro and in Mouse Serum and Liver. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yang, M.; Dong, J.; Shen, R. Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidant Capacities and Phenolic Compounds of Oat and Buckwheat Vinegars During Production Processes. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Ansi, W.; Mushtaq, B.S.; Mahdi, A.A.; Al-Maqtari, Q.A.; AL-Adeeb, A.; Ahmed, A.; Fan, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Jinxin, L. Molecular Structure, Morphological, and Physicochemical Properties of Highlands Barley Starch as Affected by Natural Fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Ansi, W.; Mahdi, A.A.; Al-Maqtari, Q.A.; Sajid, B.M.; Al-Adeeb, A.; Ahmed, A.; Fan, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Jinxin, L.; et al. Characterization of Molecular, Physicochemical, and Morphological Properties of Starch Isolated from Germinated Highland Barley. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Lang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, F. Highland Barley Replaces Sorghum as Raw Material to Make Shanxi Aged Vinegar. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, H.; Bai, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Q. Health-Promoting Properties of Barley: A Review of Nutrient and Nutraceutical Composition, Functionality, Bioprocessing, and Health Benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Xiao, J.; Abdallah, H.M. Nutritional Value of Barley Cereal and Better Opportunities for Its Processing as a Value-Added Food: A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Tan, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, X. Fermented Barley β-Glucan Regulates Fat Deposition in Caenorhabditis Elegans. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, C.; Bai, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, X.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, X. Fermented Barley Extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum Dy-1 Decreased Fat Accumulation of Caenorhabditis Elegans in a Daf-2-Dependent Mechanism. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Pan, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Cui, H. Lactobacillus plantarum Dy-1 Fermented Barley Extraction Activates White Adipocyte Browning in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Xu, T.; Bai, J.; Xia, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum Fermented Barley on Plasma Glycolipids and Insulin Sensitivity in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Bai, J.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Sun, X.J.; Dong, Y. Supplementation of Fermented Barley Extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum Dy-1 Inhibits Obesity via a UCP1-Dependent Mechanism. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, X.H. Fermented Barley Extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum Dy-1 Rich in Vanillic Acid Modulate Glucose Consumption in Human HepG2 Cells. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Shi, L.; Xu, T.; Wu, F. The Anti-Obesity Effect of Fermented Barley Extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum Dy-1 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.W.; Oh, H.H.; Moon, K.E.; Oh, B.M.; Jeong, D.Y.; Song, G.S. Lactic Acid Bacteria-Malted Vinegar: Fermentation Characteristics and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Effect. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedghi, M.; Akbari Moghaddam Kakhki, R. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Barley Malt Extract and Malt Vinegar on Growth Performance, Jejunal Morphology and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. J. 2018, 6, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu-jun, C.; Jun-mei, Z.; Yue, S.H.I.; Le, L.I.; Jia-yi, L.I.; Cui-lian, W.; Jie, Z.; Hui-ya, X.; Meng-yue, W.U. Optimization of Vacuum Freeze Drying Technology of Miscellaneous Grains Vinegar Powder by Response Surface Methodology. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2018, 39, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Chen, G.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H.; Huang, D. Dynamic Changes and Correlation of Organic Acids, Physicochemical Properties, and Microbial Communities during Fermentation of Sichuan Bran Vinegar. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liao, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Gui, Y. Analyzing Fungal Community Succession and Its Correlation to Flavor Compounds in the Cupei Fermentation Process of Sichuan Shai Vinegar. Food Microbiol. 2025, 128, 104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Dang, B.; Yang, X.; Nie, M.; Chen, Z.; Lin, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.T. Deeply Analyzing Dynamic Fermentation of Highland Barley Vinegar: Main Physicochemical Factors, Key Flavors, and Dominate Microorganisms. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, J. Characterization of Organic Acids and Phenolic Compounds of Cereal Vinegars and Fruit Vinegars in China. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, K.J.; Elly, O.; Jin, K.Y.; Kyoung-Sook, C.; Oran, K. Oxidation of Fatty Acid May Be Enhanced by a Combination of Pomegranate Fruit Phytochemicals and Acetic Acid in HepG2 Cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2013, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.O.; de Moraes, W.M.A.M.; da Silva, G.A.R.; Prestes, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J. Vinegar (Acetic Acid) Intake on Glucose Metabolism: A Narrative Review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Ma, Q.Y.; Zhang, F.; Tang, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.F. Changes in Bioactive and Volatile Aroma Compounds in Vinegar Fermented in a Rotary Drum Bioreactor. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Maturation of Zhenjiang Vinegar. Ultrason. Sonochem 2017, 39, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Kuang, G.; Li, J.; Hadiatullah, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Pan, Z.H.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Aldehydes and Hydroxy Acids as the Main Contribution to the Traditional Chinese Rose Vinegar by Flavor and Taste Analyses. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, M.; Shafiei, R.; Zarmehrkhorshid, R.; Hamouda, A.; Alaoui, M.I.; Thonart, P. Simultaneous Production of Acetic and Gluconic Acids by a Thermotolerant Acetobacter Strain during Acetous Fermentation in a Bioreactor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Kang, J.; Guo, Y.; Meng, L.; Li, Z.; Qin, X. Bacterial Interactions Mediated by Acetic Acid and Their Impact on Flavor Profile during Acetic Acid Fermentation Stage of Shanxi Aged Vinegar. Food Biosci. 2025, 64, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Pan, W.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, K.; Hu, X.; Han, G.; et al. Seasonal Dynamics of Microbiota and Physicochemical Indices in the Industrial-Scale Fermentation of Sichuan Baoning Vinegar. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mazza, G.; Zhang, X. Metagenomic Analysis Revealing the Metabolic Role of Microbial Communities in the Free Amino Acid Biosynthesis of Monascus Rice Vinegar during Fermentation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Fu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Luo, R.; Li, L. Investigating the Mechanism of the Flavor Formation in Sichuan Sun Vinegar Based on Flavor-Orientation and Metagenomics. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, S.; Jian, D.; Cui, P.; Zhong, F.; Mao, J. Investigation of the 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural and Furfural Content of Chinese Traditional Fermented Vinegars from Different Regions and Its Correlation with the Saccharide and Amino Acid Content. LWT 2020, 124, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.H.; Liu, C.W.; Yang, D.J.; Wu, Y.H.S.; Chen, Y.C. Amino Acid, Mineral, and Polyphenolic Profiles of Black Vinegar, and Its Lipid Lowering and Antioxidant Effects in Vivo. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamato, K.; Minami, K.; Hirayama, S.; Hoshino, Y.; Hoshino, M.; Kida, T.; Sasaki, M.; Matsumori, Y. Recovery and Liquefaction of Nitrogen-Containing Component and Minerals from Food Processing Wastes of Vinegar Using Subcritical Water. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Aheto, J.H.; Chang, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Coupling Electronic Nose with GC–MS Improves Flavor Recognition and Grade Differentiation of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Koysomboon, C.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F. Vinegar Volatile Organic Compounds: Analytical Methods, Constituents, and Formation Processes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 907883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-H.; Zhu, J.; Wu, B.; Huang, D.-P.; Sun, J.; Dai, C.-X. Classification of Chinese Vinegar Varieties Using Electronic Nose and Fuzzy Foley–Sammon Transformation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y. Aroma Patterns of Beijing Rice Vinegar and Their Potential Biomarker for Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegars. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo-Bastante, C.; Durán-Guerrero, E.; García-Barroso, C.; Castro-Mejías, R. Comparative Study of Sub-merged and Surface Culture Acetification Process for Orange Vinegar. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P.; Bekatorou, A.; Dimitrellou, D.; Plioni, I.; Giannopoulou, K. Health Promoting Properties of Cereal Vinegars. Foods 2021, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, P.; Feng, F.; Luo, L.X. Microbial Diversity and Their Roles in the Vinegar Fermentation Process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4997–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Xie, J.; Hou, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.-G. Aroma Constituents in Shanxi Aged Vinegar before and after Aging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7597–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.L.; Tong, S.G.; Yang, Z.Y.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Lv, X.C.; Weng, Q.; Yu, K.; Liu, G.R.; Luo, X.Q.; Wei, T. The Dynamics of Microbial Community and Flavor Metabolites during the Acetic Acid Fermentation of Hongqu Aromatic Vinegar. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayek, N.M.; Xiao, J.; Farag, M.A. A Multifunctional Study of Naturally Occurring Pyrazines in Biological Systems; Formation Mechanisms, Metabolism, Food Applications and Functional Properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5322–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Zhong, F.; Mao, J. Dynamic Changes in Physico-Chemical Attributes and Volatile Compounds during Fermentation of Zhenjiang Vinegars Made with Glutinous and Non-Glutinous Japonica Rice. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, F.; Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chang, X. Investigating Flavor Sensory Properties of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar and Factors Impacting Perception Using Quantitative Descriptive Analysis and Temporal Dominance of Sensations. J. Sens. Stud. 2023, 38, e12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, W.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Huang, X. Identification of Characteristic Volatiles of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar Using HS-SPME-GC/MS Coupled with Multivariate Analysis. Flavour Fragr. J. 2024, 39, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jian, D.; Gong, M.; Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, F.; Mao, J. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in Aged Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar by Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry-Mass Spectrometry, Quantitative Measurements, Aroma Recombination and Omission Experiments. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Duan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, B.; Zhang, B.; Xu, B.; de la Cruz, C.B.V.; El-Seedi, H.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Polyphenol-Rich Extract of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar Ameliorates High Glucose-Induced Insulin Resistance by Regulating JNK-IRS-1 and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N. Comparative Analysis of Flavour Profile and Aroma Components of Shanxi Aged Vinegar From China. Flavour Fragr. J. 2025, 40, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, K.; Román-Camacho, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Song, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Identification of Aroma Active Compounds in Shanxi Aged Vinegar and Tracing the Source in the Entire Pro-duction Process. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudici, P.; Corradini, G.; Bonciani, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, F.; Lemmetti, F. The Flavor and Taste of Cereal Chinese Vinegars. Acetic Acid Bact. 2017, 6, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalali, S.; Zheng, F.; Sun, B.; Chen, F. Characterization and Comparison of Aroma Profiles and Aro-ma-Active Compounds between Traditional and Modern Sichuan Vinegars by Molecular Sensory Science. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5154–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, N.; Hu, K.; Liu, S.; Blaiotta, G.; Zhou, J. Uncovering the Microbial Community Dynamics and Metabolic Pathways of Primary Organic Acids in Sichuan Baoning Vinegar through Metagenomics. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y. Characterization of the Volatile Flavor Pro-files of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar Combining a Novel Nanocomposite Colorimetric Sensor Array with HS-SPME-GC/MS. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.Y.; Chai, L.J.; Zhong, X.Z.; Jiang, Y.J. Deciphering the Succession Patterns of Bacterial Community and Their Correlations with Environmental Factors and Flavor Compounds during the Fermentation of Zhejiang Rosy Vinegar. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 341, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, X.; Yao, Y.; Qu, A.; Ding, K.; Zhao, G.; Liu, S.Q. Insights into the Microbiota and Driving Forces to Control the Quality of Vinegar. LWT 2022, 157, 113085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Xia, M.; Wang, M. Unraveling the Correlation between Microbiota Succession and Metabolite Changes in Traditional Shanxi Aged Vinegar. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, N.; Li, Q.; Zhao, K.; Tu, M.; Li, J.; Hu, K.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, A. Metagenomics and Meta-genome-Assembled Genomes: Analysis of Cupei from Sichuan Baoning Vinegar, One of the Four Traditional Renowned Vinegars in China. Foods 2025, 14, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, R.; Li, L. Role of Bacterial Community Succession in Flavor Formation during Sichuan Sun Vinegar Grain (Cupei) Fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2023, 135, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, T.; Xiong, F.; Cui, P.; Gao, G.; Ye, X.; Zhai, X.; Lu, Z.; Zou, X. Dynamics in Microbial Communities and Flavor Characteristics before and after the End-Point of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar Fermentation Revealed by Macro-Transcriptomics and Metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.Y.; Mu, X.J.; Huang, B.W.; Wu, G.Z.; Jiang, Y.J. Fungal Biodiversity and Interaction Complexity Were the Important Drivers of Multifunctionality for Flavor Production in a Spontaneously Fermented Vinegar. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 83, 103259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, T.; Saeed, F.; Tufail, T.; Bader Ul Ain, H.; Hussain, M.; Noreen, S.; Shah, M.A. Exploring the Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Cereal Bran Cell Wall-Enriched Diets. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-Y.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Huang, T.; Deng, Y.-J.; Chai, L.-J.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Distinct Co-Occurrence Patterns and Driving Forces of Abundant and Rare Bacterial Communities in the Multispecies Sol-id-State Fermentation Process of Cereal Vinegar. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanuf. 2022, 2, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Fan, S.; Zhu, L.; Song, C.; Xiao, X. Recent Developments in Fermented Cereals on Nutritional Constituents and Potential Health Benefits. Foods 2022, 11, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y. Subcritical Water Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds from Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Bran and Their Biological Activities. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadi, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Highland Barley: Chemical Composition, Bioactive Compounds, Health Effects, and Applications. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruirong, P.; Hassane Hamadou, A.; Xu, B. Germination in Improving the Nutrition, Health Benefits and Processing of Highland Barley. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jia, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Xu, B. Study of Shanxi Aged Vinegar by Non-Targeted Metabolomics Techniques and Antioxidant Activity Characteristics. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Lu, Z.M.; Yu, Y.J.; Li, G.Q.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Batch-to-Batch Uniformity of Bacterial Community Succession and Flavor Formation in the Fermentation of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Food Microbiol. 2015, 50, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zou, X.; Shen, T.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Holmes, M.; Li, G. Determination of Total Acid Content and Moisture Content during Solid-State Fermentation Processes Using Hyperspectral Imaging. J. Food Eng. 2016, 174, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J. Dynamic Changes of Quality and Flavor Characterization of Zhejiang Rosy Vinegar during Fermentation and Aging Based on Untargeted Metabolomics. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklós, V.; Dan, B.I.; Uwe, H. Temperature Fluctuations in a Changing Climate: An Ensemble-Based Experimental Approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xia, T.; Du, P.; Duan, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Characteristic of Traditional and Industrial Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegars during the Aging Process. Molecules 2018, 23, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K. Seasonal Environmental Factors Drive Microbial Community Succession and Flavor Quality during Acetic Acid Fermentation of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1442604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, Z.; Mao, J.; Shi, J.; Battino, M.; Routledge, M.N.; Gong, Y.; Zou, X. Spatial-Temporal Distribution of Deoxynivalenol, Aflatoxin B1, and Zearalenone in the Solid-State Fermentation Basin of Traditional Vinegar and Their Potential Correlation with Microorganisms. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Song, J.; Fan, B.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Mou, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Elucidation and Regulation of Polyphenols in the Smoking Process of Shanxi Aged Vinegar. Foods 2021, 10, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perestrelo, R.; Silva, C.L.; Silva, P.; Câmara, J.S. Impact of Storage Time and Temperature on Volatomic Signature of Tinta negra Wines by LLME/GC-ITMS. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Liang, K.; Lang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Impact of Spatial Heterogeneity on Fermentation Characteristics of Cereal Vinegar: A Comparison of Manual and Mechanical Methods. LWT 2025, 217, 117415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, N. Unraveling the Microbial Community and Succession during the Maturation of Chinese Cereal Vinegar Daqu and Their Relationships with Flavor Formation. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Deng, K.; Zhang, Y. Isolation and Screening of High-Quality Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeast Strains in Kefir Grains and Preparation of Kefir Compound Fermentation Starter. J. Food Process Preserv. 2022, 46, e17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Lu, Z.M.; Peng, M.Y.; Chai, L.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Shi, J.S.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.H. Constructing a Defined Starter for Multispecies Vinegar Fermentation via Evaluation of the Vitality and Dominance of Functional Microbes in an Autochthonous Starter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e02175-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Lang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Sequential Bioaugmentation of the Dominant Microorganisms to Improve the Fermentation and Flavor of Cereal Vinegar. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 101952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D. Engineering Corynebacterium crenatum for Enhancing Succinic Acid Production. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, N.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Wen, X.P.; Cao, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, R. Synthesis of an Autochthonous Microbial Community by Analyzing the Core Microorganisms Responsible for the Critical Flavor of Bran Vinegar. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maske, B.L.; de Mello, A.F.M.; Vale, A.d.S.; Martin, J.G.P.; Soares, D.L.d.O.; Lindner, J.D.D.; Soccol, C.R.; Pereira, G.V.d.M. Exploring Diversity and Functional Traits of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Traditional Vinegar Fermentation: A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 412, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, W.; Dai, C.; Sun, L.; Tang, Y.; He, R.; Ma, H. Sterilization of Bacillus tequilensis Isolated from Aerogenic Vinegar by Intense Pulsed Light. LWT 2020, 118, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Li, W.; Rao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Guo, W.; Lü, X.; Sun, J.; Ai, L.; Ni, L. Microbiomics and Metabolomics Insights into the Microbial Regulation on the Formation of Flavor Components in the Traditional Fermentation Process of Chinese Hongqu Aged Vinegar. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, P. Exploring the Ecological Interactions of Bacillus and Their Contribution to Characteristic Aroma Components in Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.-J.; Qiu, T.; Lu, Z.-M.; Deng, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Modulating Microbiota Metabolism via Bioaugmentation with Lactobacillus casei and Acetobacter pasteurianus to Enhance Acetoin Accumulation during Cereal Vinegar Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C. Evaluating the Feasibility of Fermentation Starter Inoculated with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for Improving Acetoin and Tetramethylpyrazine in Baoning Bran Vinegar. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 255, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Li, W.; Xu, Q.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, H.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z. Exploring the Correlation of Metabolites Changes and Microbial Succession in Solid-State Fermentation of Sichuan Sun-Dried Vinegar. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Li-Li, Z.; Ying, S.; Yu-Yu, Z.; Bao-Guo, S.; Hai-Tao, C. Determination of the Free Amino Acid, Organic Acid, and Nucleotide in Commercial Vinegars. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Giudici, P.; Chen, F. Vinegar Functions on Health: Constituents, Sources, and Formation Mechanisms. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-H.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yu, Y.-J.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Metagenomics Reveals Flavour Metabolic Network of Cereal Vinegar Microbiota. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, G.; Kan, Q.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q.; Lan, Y. Applications of Multi-Omics Techniques to Unravel the Fermentation Process and the Flavor Formation Mechanism in Fermented Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 8367–8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hou, Z.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Dai, T.; Wang, X.; Zeng, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, S. Genomic and Metabolic Features of an Unexpectedly Predominant, Thermophilic, Assistant Starter Microorganism, Thermus thermophilus, in Chinese Inner Mongolian Cheese. Foods 2021, 10, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Leng, W.; Xue, J.; Yuan, L.; Liu, H.; Gao, R. A Multi-Omics-Based Investigation into the Flavor Formation Mechanisms during the Fermentation of Traditional Chinese Shrimp Paste. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, L. Correlation between Dominant Bacterial Community and Non-Volatile Organic Compounds during the Fermentation of Shrimp Sauces. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.-T.; Guo, R.-R.; Ye, Q.; Zhao, H.-L.; Huang, X.-H. The Regulation of Key Flavor of Traditional Fermented Food by Microbial Metabolism: A Review. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Liang, K.; Cao, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Abiotic Factors Modulating Metabolic Pathways of Lactic Acid in Solid-State Fermentation of Cereal Vinegar. LWT 2024, 214, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, B.; Liang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Tu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Identification of Phenols and Their Formation Network during the Brewing Process of Shanxi Aged Vinegar. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Simon, C.; Mumm, R.; Hall, R.D. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Volatiles as a New Tool for Understanding Aroma and Flavour Chemistry in Processed Food Products. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

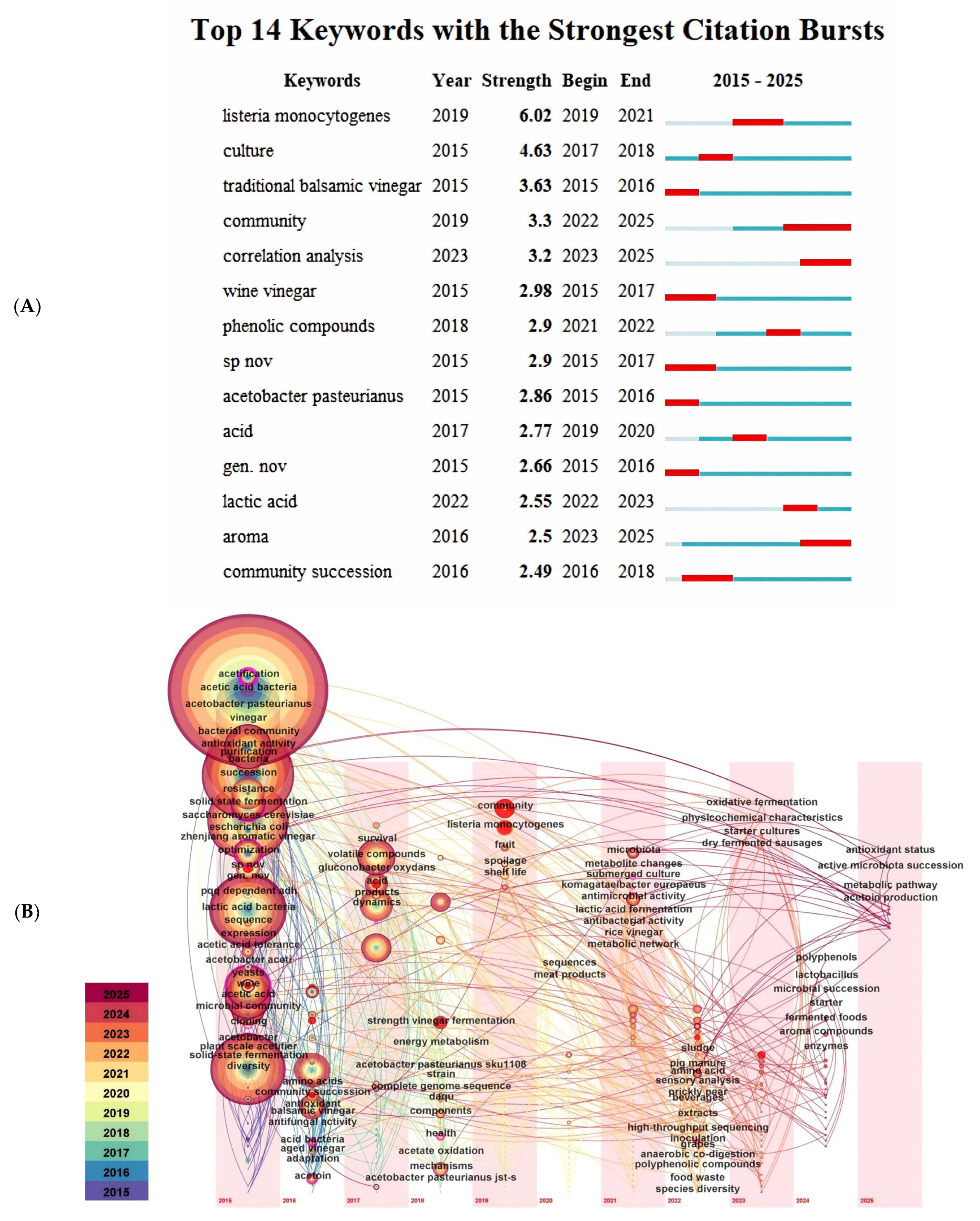
| Varieties | Key Flavor Compounds | Aroma | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shanxi Aged Vinegar (SAV) | acetic acid, furfuryl alcohol, 2,3-dimethylpyrazine, lactic acid, phenol, propyl acetate, ethyl propionate, and 2(5H)-furanone | Acidity, alcohol, orange peel, and yeast aromas | [91,92,93] |
| Sichuan Baoning Vinegar (SBV) | Lactic acid, 2-hydroxy-3-butanone acetate, butyrolactone, furan-2-aminoformaldehyde, acetic acid and 3-oxobutane-2-yl acetate | Fruity, sweet, baking, spicy, and woody | [94,95] |
| Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar (ZAV) | Acetic acid, furfural, aldehyde ketone, ethyl acetate, 3-methylbutyric acid, tetramethylpyrazine, isobutyric acid, ethyl phenylacetate, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, 2, 3-butanedione, 2-acetofurfural, tetramethylpyrazine, phenyl ethyl ester, and phenylethanol | Caramel and buttery fruity, smoky, bran, and almond flavors | [89,96] |
| Yongchun Aged Vinegar (YCAV) | Isobutyl acetate, 2-acetoxy-3-butanone, and heptanoic acid, whereas octanoic acid, 2-dodecanol, butyric acid, styrene, ethyl caproate, and 1-nonanol | Aromas of fruit, ester, jackfruit, apple, banana, and keto | [29,84] |
| Zhejiang Rosy Vinegar (ZRV) | Acetic acid, lactic acid, ethyl acetate, and acetoin | Fruit, cream, butter, and caramel | [97] |
| Varieties | Raw Materials | Fermentation Process | Key Microorganisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanxi Aged Vinegar (SAV) | Sorghum, bran | Solid state fermentation (Use daqu instead of grain; Special fumigation technique; sun-drying and winter ice scoting) | Acetobacter (50.9%), Lactobacillus (47.9%), Saccharomyces | [99] |
| Sichuan Baoning Vinegar (SBV) | Bran, wheat, glutinous rice | Solid state fermentation (Fermentation in the same pool) | Acetilactobacillus, Lactobacillus, Limosilactobacillus, Acetobacter, Weizmannia, and Lactiplantibacillus | [19,100,101] |
| Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar (ZAV) | Rice, rice husk, bran | Solid state fermentation (solid-state layered fermentation) | Bacteria: Lactobacillus, Acetobacter Fungi: Moulds and yeasts | [11,102] |
| Yongchun Aged Vinegar (YCAV) | Glutinous rice and sesame seeds | Liquid fermentation (Liquid deep fermentation) | Bacillus, Rhodococcus, Saccharomycelales and Pichia membranifaciens | [28,84] |
| Zhejiang Rosy Vinegar (ZRV) | Indica rice | Liquid fermentation (Three-sided fermentation) | Acetobacter, Lactobacillus | [97,103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Bian, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Fan, S.; Xiao, X. Research Progress on Flavor Differences and the Formation Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar. Foods 2025, 14, 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132263
Zhang J, Bian X, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Bai J, Fan S, Xiao X. Research Progress on Flavor Differences and the Formation Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132263
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiayan, Xuefen Bian, Yansheng Zhao, Ying Zhu, Juan Bai, Songtao Fan, and Xiang Xiao. 2025. "Research Progress on Flavor Differences and the Formation Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar" Foods 14, no. 13: 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132263
APA StyleZhang, J., Bian, X., Zhao, Y., Zhu, Y., Bai, J., Fan, S., & Xiao, X. (2025). Research Progress on Flavor Differences and the Formation Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Cereal Vinegar. Foods, 14(13), 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132263









