Critical Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Raw Milk Cheese in the Alpine Region of Austria, Italy, and Switzerland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
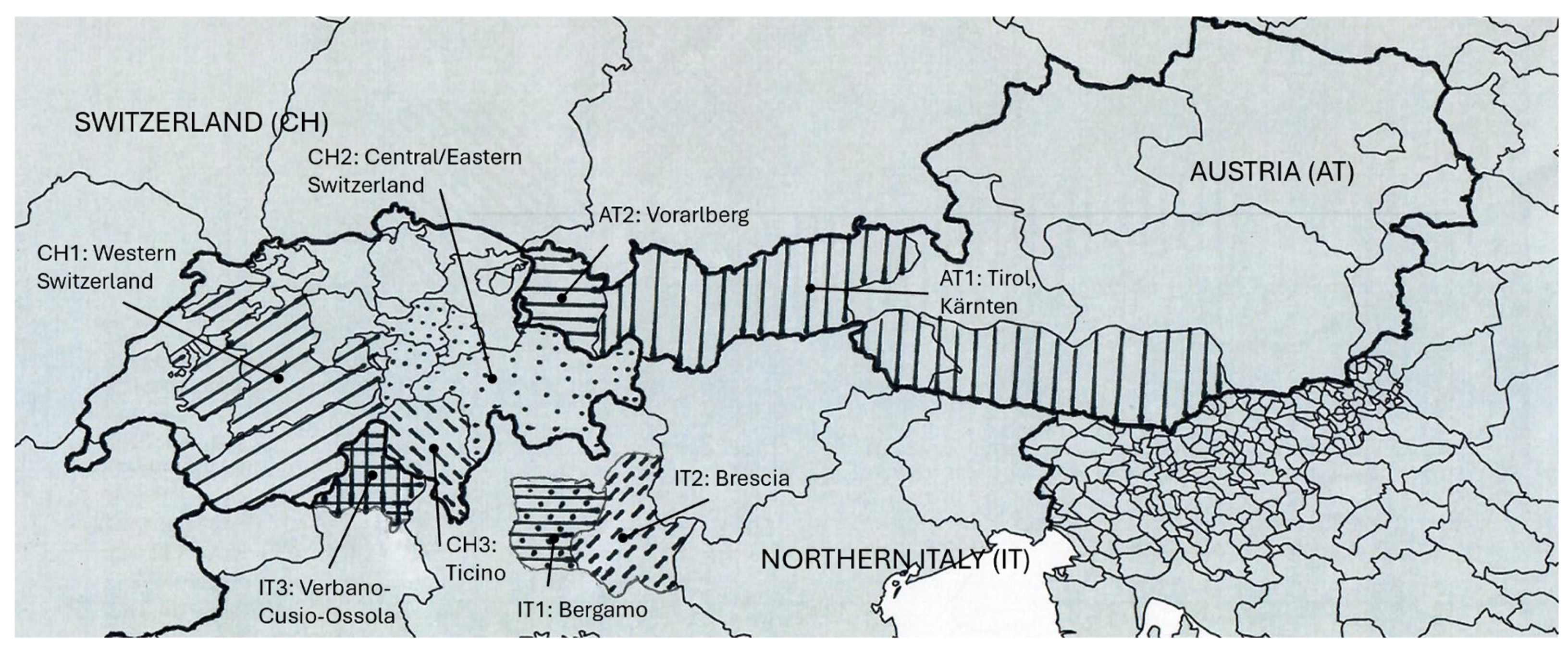
2.1. Sampling and Sample Collection
2.2. Collection of Data on Milk Processing and the Manufacturing Conditions for Cheese
2.3. Enumeration and Isolation of CPS
2.4. CPS Strains Identification
2.5. CPS Genotyping
2.6. SE Analysis in Cheese Samples
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Findings
3.2. Differences Between Countries and Regions
3.3. Differences Between Types of Raw and Thermized Milk and Cheese Varieties
3.4. Differences Between Types of Culture
3.5. Calculation of Risk Groups Based on a Selected Number of Hurdle Indices
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence of S. aureus and the Detection of SE in Cheese Samples
4.2. Factors Influencing the Growth of S. aureus and the Production of SEs
4.3. Hurdle Index as a Tool for Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seegers, H.; Fourichon, C.; Beaudeau, F. Production effects related to mastitis and mastitis economics in dairy cattle herds. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegg, P.L. A 100-Year Review: Mastitis detection, management, and prevention. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10381–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johler, S.; Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Acutis, P.L.; Gallina, S.; Decastelli, L. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated along the raw milk cheese production process in artisan dairies in Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuenberger, A.; Sartori, C.; Boss, R.; Resch, G.; Oechslin, F.; Steiner, A.; Moreillon, P.; Graber, H.U. Genotypes of Staphylococcus aureus: On-farm epidemiology and the consequences for prevention of intramammary infections. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3295–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, C.; Kuhnert, P.; Frey, J.; Miserez, R.; Kirchhofer, M.; Kaufmann, T.; Steiner, A.; Graber, H.U. Bovine Staphylococcus aureus: Association of virulence genes, genotypes and clinical outcome. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 85, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendimann, L.; Berger, T.; Graber, H.U.; Meier, S.; Hummerjohann, J.; Jakob, E. Effect of scalding temperature on growth of Staphylococcus aureus and formation of staphylococcal enterotoxin during the production of alpine cheese in a laboratory cheesemaking model. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosandey, A.; Boss, R.; Luini, M.; Artursson, K.; Bardiau, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Hehenberger, E.; Lam, T.; Mansfeld, M.; Michel, A.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus genotype B and other genotypes isolated from cow milk in European countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monistero, V.; Graber, H.U.; Pollera, C.; Cremonesi, P.; Castiglioni, B.; Bottini, E.; Ceballos-Marquez, A.; Lasso-Rojas, L.; Kroemker, V.; Wente, N.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Bovine Mastitis in Eight Countries: Genotypes, Detection of Genes Encoding Different Toxins and Other Virulence Genes. Toxins 2018, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, H.U.; Naskova, J.; Studer, E.; Kaufmann, T.; Kirchhofer, M.; Brechbuhl, M.; Schaeren, W.; Steiner, A.; Fournier, C. Mastitis-related subtypes of bovine Staphylococcus aureus are characterized by different clinical properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Borne, B.H.P.; Graber, H.U.; Voelk, V.; Sartori, C.; Steiner, A.; Haerdi-Landerer, M.C.; Bodmer, M. A longitudinal study on transmission of Staphylococcus aureus genotype B in Swiss communal dairy herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 136, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monistero, V.; Hossain, D.; Fusar Poli, S.; de Medeiros, E.S.; Cremonesi, P.; Castiglioni, B.; Biscarini, F.; Graber, H.U.; Mochettaz, G.; Ganio, S.; et al. Prevalence of Variant GTRI Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Dairy Cow Milk Samples in the Alpine Grazing System of the Aosta Valley and Its Association with AMR and Virulence Profiles. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, C.; Boss, R.; Bodmer, M.; Leuenberger, A.; Ivanovic, I.; Graber, H.U. Sanitation of Staphylococcus aureus genotype B-positive dairy herds: A field study. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6897–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesso, L.; Vanzetti, T.; Weber, J.; Romanò, A.; Bodmer, M.; Vaccani, M.; Riva Scettrini, P.; Sartori, C.; Bacciarini, L.N.; Struchen, R.; et al. District-wide herd sanitation and eradication of intramammary Staphylococcus aureus genotype B infection in dairy herds in Ticino, Switzerland. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 8299–8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC. Commission Regulation No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser, M.L.; Dufour, B.; Maire, M.; Lafarge, V. Implication of milk and milk products in food-borne diseases in France and in different industrialised countries. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergdoll, M.S. Staphylococcus aureus. In Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens; Doyle, M.P., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 463–524. [Google Scholar]
- Asao, T.; Kumeda, Y.; Kawai, T.; Shibata, T.; Oda, H.; Haruki, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Kozaki, S. An extensive outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning due to low-fat milk in Japan: Estimation of enterotoxin A in the incriminated milk and powdered skim milk. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 130, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, D.Y.; Steinberg, D.H.; Miller, R.D.; Kurantnick, M.J.; Murphy, T.F. Thermal inactivation of staphylococcal enterotoxin B and C. Appl. Microbiol. 1973, 26, 938–942. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/am.26.6.938-942.1973 (accessed on 20 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Hennekinne, J.A.; De Buyser, M.L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, G.; Bohach, G.A.; Nair, S.P.; Hiramatsu, K.; Jouvin-Marche, E.; Mariuzza, R. Standard nomenclature for the superantigens expressed by Staphylococcus. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 2334–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union One Health 2023 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Tamate, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Makino, S. Mass outbreak of food poisoning disease caused by small amounts of staphylococcal enterotoxins A and H. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2793–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkerroum, N. Staphylococcal enterotoxins and enterotoxin-like toxins with special reference to dairy products: An overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1943–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, A.; Tang, J.; Tang, C.; Chen, J. Comparative Effects of Food Preservatives on the Production of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin I from Staphylococcus aureus Isolate. J. Food Qual. 2017, 15, 9495314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, A.; Tang, J.; Tang, C.; Chen, J. Identification and measurement of staphylococcal enterotoxin M from Staphylococcus aureus isolate associated with staphylococcal food poisoning. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, H.U. Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus by Ribosomal Spacer PCR (RS-PCR). J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 117, 54623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummerjohann, J.; Naskova, J.; Baumgartner, A.; Graber, H.U. Enterotoxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus genotype B as a major contaminant in Swiss raw milk cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Weder, D.; Bridy, C.; Huguenin, M.C.; Robert, L.; Hummerjohann, J.; Stephan, R. Outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning among children and staff at a Swiss boarding school due to soft cheese made from raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2944–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmel, J.; Stessl, B.; Gonano, M.; Walcher, G.; Bereuter, O.; Fricker, M.; Grunert, T.; Wagner, M.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Staphylococcus aureus Entrance into the Dairy Chain: Tracking S. aureus from Dairy Cow to Cheese. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 13, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupescu, L.M.; Auvray, F.; Nicorescu, I.M.; Meheut, T.; Ciupescu, V.; Lardeux, A.L.; Tanasuica, R.; Hennekinne, J.A. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains and evidence for the involvement of non-classical enterotoxin genes in food poisoning outbreaks. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.J.; Mørk, T.; Høgåsen, H.R.; Rørvik, L.M. Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in bulk milk in Norway. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Giannini, P.; Jermini, M.; Hummerjohann, J.; Baumgartner, A.; Stephan, R. Further evidence for staphylococcal food poisoning outbreaks caused by egc-encoded enterotoxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, K.; Nakamura, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Nishina, N.; Yasufuku, K.; Hirai, Y.; Hirayama, T.; Goto, K.; Hase, A.; Ogasawara, J. Molecular and epidemiological characterization of staphylococcal foodborne outbreak of Staphylococcus aureus harboring seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, and selu genes without production of classical enterotoxins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 256, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duquenne, M.; Derzelle, S.; Fleurot, I.; Aigle, M.; Darrigo, C.; Hennekinne, J.A.; Mutel, I.; Bouix, M.; Deperrois-Lafarge, V.; Delacroix-Buchet, A. Milk maturation temperature and time are key technological parameters to limit staphylococcal enterotoxin production during uncooked semi-hard cheese manufacture. Food Control 2016, 59, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, R.A.; Heggebo, R.; Sunde, E.B.; Skjervheim, M. Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes in Norwegian raw milk cheese production. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, G.; Gonano, M.; Kümmel, J.; Barker, G.C.; Lebl, K.; Bereuter, O.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Wagner, M.; Stessl, B. Staphylococcus aureus reservoirs during traditional Austrian raw milk cheese production. J. Dairy Res. 2014, 81, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. Commission Regulation No 178/2002 laying down the general principles and requirements of food law, establishing the European Food Safety Authority and laying down procedures in matters of food safety. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, 31, 1–24. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2002/178/oj/eng (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Tiberti, R.; Rogora, M.; Tartari, G.; Callieri, C. Ecological impact of transhumance on the trophic state of alpine lakes in Gran Paradiso National Park. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2014, 415, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Transhumance—Sheep Drive in the Ötztal Alps. Knowledge Concerning Nature and the Universe in Tyrol, Inscribed. 2011. Available online: https://www.unesco.at/en/culture/intangible-cultural-heritage/national-inventory/news-1/article/transhumance-migratory-herding-of-sheep-in-the-oetztal-alps (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Primas, M. Bronzezeit Zwischen Elbe und Po. Strukturwandel in Zentraleuropa 2200-800 V. Chr. Universitätsforschungen zur Prähistorischen Archäologie; Habelt: Bonn, Germany, 2008; 267 p, Available online: https://www.antikmakler.de/bv8241 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Glick, F.; Poschlod, P. The origin of alpine farming: A review of archaeological, linguistical and archaeobotanical studies in the Alps. Holocene 2019, 29, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, L.; Dimanche, M.; Lasseur, J. Permanence and changes in pastoral farming in the Southern Alps. J. Alp. Res. Rev. Géogr. Alp. 2014, 102–2, 13pp. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurt, C.; Häberli, I.; Rossier, R. Transhumance farming in Swiss mountains: Adaptation to a changing environment. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, F. Mountain Anthroscapes, the Case of the Italian Alps. In Sustainable Land Management; Kapur, S., Eswaran, H., Blum, W.E.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 143–161. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Amalfitano, N.; Sturaro, E.; Schiavon, S.; Tagliapietra, F.; Bittante, G.; Carafa, I.; Franciosi, E.; Gallo, L. Effects of Summer Transhumance of Dairy Cows to Alpine Pastures on Body Condition, Milk Yield and Composition, and Cheese Making Efficiency. Animals 2019, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulet-Cabero, A.-I.; Torres-Gonzalez, M.; Geurts, J.; Rosales, A.; Farhang, B.; Marmonier, C.; Ulleberg, E.K.; Hocking, E.; Neiderer, I.; Gandolfi, I.; et al. The Dairy Matrix: Its Importance, Definition, and Current Application in the Context of Nutrition and Health. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, E.; Menéndez Gonzàlez, S. Leitlinie für die Gute Verfahrenspraxis bei der Milchgewinnung Und-Verarbeitung in Sömmerungsbetrieben; Schweizerischer Alpwirtschaftlicher Verband SAV: Berne, Switzerland, 2015; 127p, Available online: https://www.alpwirtschaft.ch/sav-branchenleitlinie// (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- BMG. Leitlinie für eine Gute Hygienepraxis und die Anwendung der Grundsätze des HACCP bei der Milchverarbeitung auf Almen; BMG-75220/0054-IV/B/10/2005; BMG: Vienna, Austria, 2005; Available online: https://www.verbrauchergesundheit.gv.at/Lebensmittel/buch/hygieneleitlinien/LL_Milchverarbeitung_auf_Almen.pdf?a2d5pz (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Leistner, L. Basic aspects of food preservation by hurdle technology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 55, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, F.; Seidl, I. Swiss alpine summer farming: Current status and future development under climate change. Rangel. J. 2018, 40, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Respinis, S.; Caminada, A.; Pianta, E.; Buetti-Dinh, A.; Riva Scettrini, P.; Petrini, L.; Tonolla, M.; Petrini, O. Fungal communities on alpine cheese rinds in Southern Switzerland. Bot. Stud. 2023, 64, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. Commission Regulation No 853/2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2004, 39, 55–205. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2004/853/oj/eng (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- ISO 6888-2, 1999; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus Aureus and Other Species). Part 2: Technique Using Rabbit Plasma Fibrinogen Agar Medium. International Standard Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 1–7.
- ISO 19020, 2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Immunoenzymatic Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Foodstuffs. International Standard Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–22.
- Taitini, S.R. Influence of Food Environments on Growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Production of Various Enterotoxins. J. Milk Food Technol. 1973, 36, 559–563. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0362028X23065407 (accessed on 20 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, R. Estimation of Staphylococcus aureus Growth Parameters from Turbidity Data: Characterization of Strain Variation and Comparison of Methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4862–4870. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aem.00251-06 (accessed on 20 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Zhao, C. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, and enterotoxin genes of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162 Pt A, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.; Schelin, J.; Rådström, P.; Butler, F.; Jordan, K. Classical enterotoxins of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk and products for raw milk cheese production in Ireland. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2012, 92, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.G.; Withers, S.E. Microbiological characterisation of artisanal farmhouse cheeses manufactured in Scotland. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.J.; Mørk, T.; Rørvik, L.M. The Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on a Farm with Small-Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3810–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rola, J.G.; Czubkowska, A.; Korpysa-Dzirba, W.; Osek, J. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on Farms with Small Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheeses in Poland. Toxins 2016, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borelli, B.M.; Ferreira, E.G.; Lacerda, I.C.A.; Santos, D.A.; Carmo, L.S.; Dias, R.S.; Silva, M.C.C.; Rosa, C.A. Enteroxigenic Staphylococcus spp. and other microbial contaminants during production of Canastra cheese, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.A.C.; Ferreira, F.A.; Rubio Cieza, M.Y.; Silva, N.C.C.; Miotto, M.; Carvalho, M.M.; Bazzo, B.R.; Botelho, L.A.B.; Dias, R.S.; De Dea Lindner, J. Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Traditional Artisanal Raw Milk Cheese from Southern Brazil: Diversity, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vasallo, A.; Ribot-Enríquez, A.; Riverón-Alemán, Y.; Remón-Díaz, D.; Martínez-García, Y.A.; Jacsens, L.; Uyttendaele, M. Staphylococcus aureus in the production chain of artisan fresh cheese. Rev. Salud Anim. 2019, 41, 1–9. Available online: https://censa.edicionescervantes.com/index.php/RSA/article/view/1002 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Canadien Food Inspection Agency. Bacterial Pathogens in Raw Milk Cheese—30 November 2014 to 31 March 2018. Food Microbiology—Targeted Surveys—Final Report. Available online: https://inspection.canada.ca/sites/default/files/legacy/DAM/DAM-food-aliments/STAGING/text-texte/bacterial_pathogens_raw_milk_cheese_nov_2014_mar_2018_full_pdf_1582740211933_eng.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Zeinhom, M.M.A.; Abed, A.H. Prevalence, Characterization, and Control of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Raw Milk and Egyptian Soft Cheese. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2021, 27, 152–160. Available online: https://jvmr.journals.ekb.eg/article_146885.html (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Kaan Tekinşen, K.; Özdemir, Z. Prevalence of foodborne pathogens in Turkish Van otlu (Herb) cheese. Food Control 2006, 17, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, H.-P.; Spahr, U. The fate of potentially pathogenic bacteria in Swiss hard and semihard cheeses made from raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 476–483. Available online: https://www.journalofdairyscience.org/article/S0022-0302(95)76657-7/pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Schuler-Schmid, U.; Schmidt-Lorenz, W. Temperature limits of growth, TNase and enterotoxin production of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from foods. International J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troller, J.A.; Stinson, J.V. Influence of water activity on growth and enterotoxin formation by Staphylococcus aureus in foods. J. Food Sci. 1975, 40, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekinne, J.-A. Chapter 7—Staphylococcus aureus as a Leading Cause of Foodborne Outbreaks Worldwide. In Staphylococcus aureus; Fetsch, A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 129–146. ISBN 9780128096710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Marc, Y.; Valík, L.; Medveďová, A. Modelling the effect of the starter culture on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, J.E. A discussion of the dynamics of salmonella enrichment. J. Hyg. 1962, 60, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.L.; Buchanan, R.L.; Palumbo, S.A. Effect of Food Environment on Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Synthesis: A Review. J. Food Prot. 1983, 46, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genigeorgis, C.A. Present state of knowledge on staphylococcal intoxication. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1989, 9, 327–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, W.M.A. Use of Starter Concentrates in Fermented Dairy Product Manufacture. 2006. Available online: https://www.dairyscience.info/index.php/cheese-starters/108-starter-concentrates.html (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Pretto, A.N.; Reck, C.; Menin, A.; Sant’Anna, V. Kinetic modeling of inactivation of foodborne bacterial pathogens in serrano artisanal cheese during ripening. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2021, 24, e2019322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanò, A.; Gazzola, A.; Bianchini, V.; Cortimiglia, C.; Maisano, A.M.; Cremonesi, P.; Graber, H.U.; Vezzoli, F.; Luini, M. Staphylococcus aureus From Goats Are Genetically Heterogeneous and Distinct to Bovine Ones. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 628. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/veterinary-science/articles/10.3389/fvets.2020.00628 (accessed on 20 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- FACE. European Guide for Good Hygiene Practices in the Production of Artisanal Cheese and Dairy Products Target: Farmhouse and Artisan Producers. FACE Network. 2016. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2017-12/biosafety_fh_guidance_artisanal-cheese-and-dairy-products_en.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Matlschweiger, C. Hygiene in der Milchverarbeitung auf der Alm; Ländliches Fortbildungs Institut LFI: Vienna, Austria, 2022; 31p, Available online: https://www.almwirtschaft.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Hygiene-in-der-Milchverarbeitung-auf-der-Alm.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Berger, T.; Jakob, E.; Haldemann, J. Milchprodukte von der Alp—Schmackhaft und sicher! Empfehlung für Alp-Berater. ALP Forum 2012, 92, 1–12. Available online: https://www.agroscope.admin.ch/agroscope/de/home/publikationen/suchen/reihen-bis-2013/alp-forum.html (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Cattaneo, S.; Masotti, F.; Silvetti, T.; Susca, A.; Tringali, S.; Tamburini, A.; Brasca, M. La stagionatura in miniera quale strategia di tipizzazione del formaggio. Il Latte 2023, 98, 54–61. Available online: https://iris.cnr.it/handle/20.500.14243/461482 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Zeppa, G.; Alessandria, V.; Scursatone, B.; Rantsiou, K.; Cocolin, L.S. Approccio multidisciplinare per la selezione di ceppi autoctoni per la produzione di Toma piemontese artigianale. Sci. Tec. Latt.-Cas. 2011, 62, 353–359. Available online: https://iris.unito.it/handle/2318/120663 (accessed on 20 June 2025).






| HI | log(CPS) [-] | FV [-] | Max. Temp. [°C] | Ripening [w] | pH [-] | Sample no. | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.06 | 4.972 | 1 | 28.00 | 1 | 4.62 | 79 | (a) |
| 6.56 | 2.206 | 1 | 28.00 | 1 | 4.27 | 78 | (a) |
| 9.59 | 5.223 | 0.1 | 37.00 | 14 | 5.40 | 4 | (b) |
| 9.77 | 5.170 | 0.1 | 37.00 | 14 | 5.30 | 1 | (b) |
| 15.76 | 5.724 | 0.5 | 39.00 | 4 | 4.95 | 15 | (b) |
| 22.70 | 5.431 | 1 | 37.00 | 4 | 6.52 | 135 | (c) |
| 29.52 | 0 | 1 | 62.00 | 2 | 4.20 | 84 | (d) |
| 29.86 | >5.477 | 1 | 43.60 | 4 | 5.84 | 13 | (c) |
| 30.71 | >5.477 | 1 | 41.00 | 4 | 5.34 | 11 | (e) |
| 34.44 | 0 | 1 | 62.00 | 3 | 5.40 | 83 | (d) |
| 34.72 | 0 | 1 | 38.00 | 5.5 | 6.02 | 129 | (f) |
| 35 | 0 | 1 | 49 | 4 | 5.6 | ||
| 57.27 | 0 | 1 | 45.10 | 8 | 6.3 | 43 | (g) |
| 79.00 | 5.516 | 1 | 39.50 | 12 | 6 | 103 | (h) |
| 83.02 | 5.079 | 1 | 55.00 | 8 | 5.30 | 80 | (i) |
| 114.17 | 0 | 1 | 42.00 | 14 | 5.15 | 34 | (j) |
| 207.69 | 2.493 | 1 | 45.00 | 24 | 5.20 | 86 | (k) |
| 207.69 | 5.415 | 1 | 45.00 | 24 | 5.20 | 87 | (k) |
| Parameter/Guideline | [48] | [82] | [47] | [81] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| milk quality of individual dairy animal (either CMT or SCC) | CMT | - | inconspicuous | inconspicuous | inconspicuous |
| SCC | - | <150,000/mL | <150,000/mL | <200,000/mL | |
| frequency | - | regular testing, e.g., every month | regular testing, e.g., 1–2x/month | regular testing, e.g., every 14 days | |
| Scalding temperature [°C] | HC | ≥48 | ≥52 | 50–57 | 50-53 |
| SHC | - | typically <46, eventually thermization | 40–48 | - | |
| FC | - | only with thermized milk | only with pasteurized milk | - | |
| Acidification rate pH [-] | HC | <6.2 (after 2 h) | - | <6.2 (after 2 h) | <6.2 (after 2 h) |
| SHC | <6.0 (after 2 h) | - | ≤5.4 (before salting) | <6.0 (after 2 h) | |
| FC | <5.0 | <4.5 (after 2 h) | <5.0 (after cutting) | - | |
| Ripening time [d] | HC | - | 120 | >120 | - |
| SHC | >60 d | >60 d | - | - | |
| FC | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berger, T.F.H.; Brasca, M.; Buchner, M.; Bütikofer, U.; Castiglioni, B.; Cremonesi, P.; Eliskases-Lechner, F.; Fritsch, L.; Morandi, S.; Schwendimann, L. Critical Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Raw Milk Cheese in the Alpine Region of Austria, Italy, and Switzerland. Foods 2025, 14, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132176
Berger TFH, Brasca M, Buchner M, Bütikofer U, Castiglioni B, Cremonesi P, Eliskases-Lechner F, Fritsch L, Morandi S, Schwendimann L. Critical Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Raw Milk Cheese in the Alpine Region of Austria, Italy, and Switzerland. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132176
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerger, Thomas F. H., Milena Brasca, Margaretha Buchner, Ueli Bütikofer, Bianca Castiglioni, Paola Cremonesi, Frieda Eliskases-Lechner, Lena Fritsch, Stefano Morandi, and Livia Schwendimann. 2025. "Critical Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Raw Milk Cheese in the Alpine Region of Austria, Italy, and Switzerland" Foods 14, no. 13: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132176
APA StyleBerger, T. F. H., Brasca, M., Buchner, M., Bütikofer, U., Castiglioni, B., Cremonesi, P., Eliskases-Lechner, F., Fritsch, L., Morandi, S., & Schwendimann, L. (2025). Critical Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Raw Milk Cheese in the Alpine Region of Austria, Italy, and Switzerland. Foods, 14(13), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132176









