Effect of Sugarcane Polyphenol Extract on α-Amylase Inhibition and Mechanism Exploration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. HPLC-MS/MS Profiling of the SP
2.3. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
2.4. CD Measurements
2.5. Fluorescence Quenching
2.6. Stability Analysis
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Molecular Dynamics
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Analysis of SP
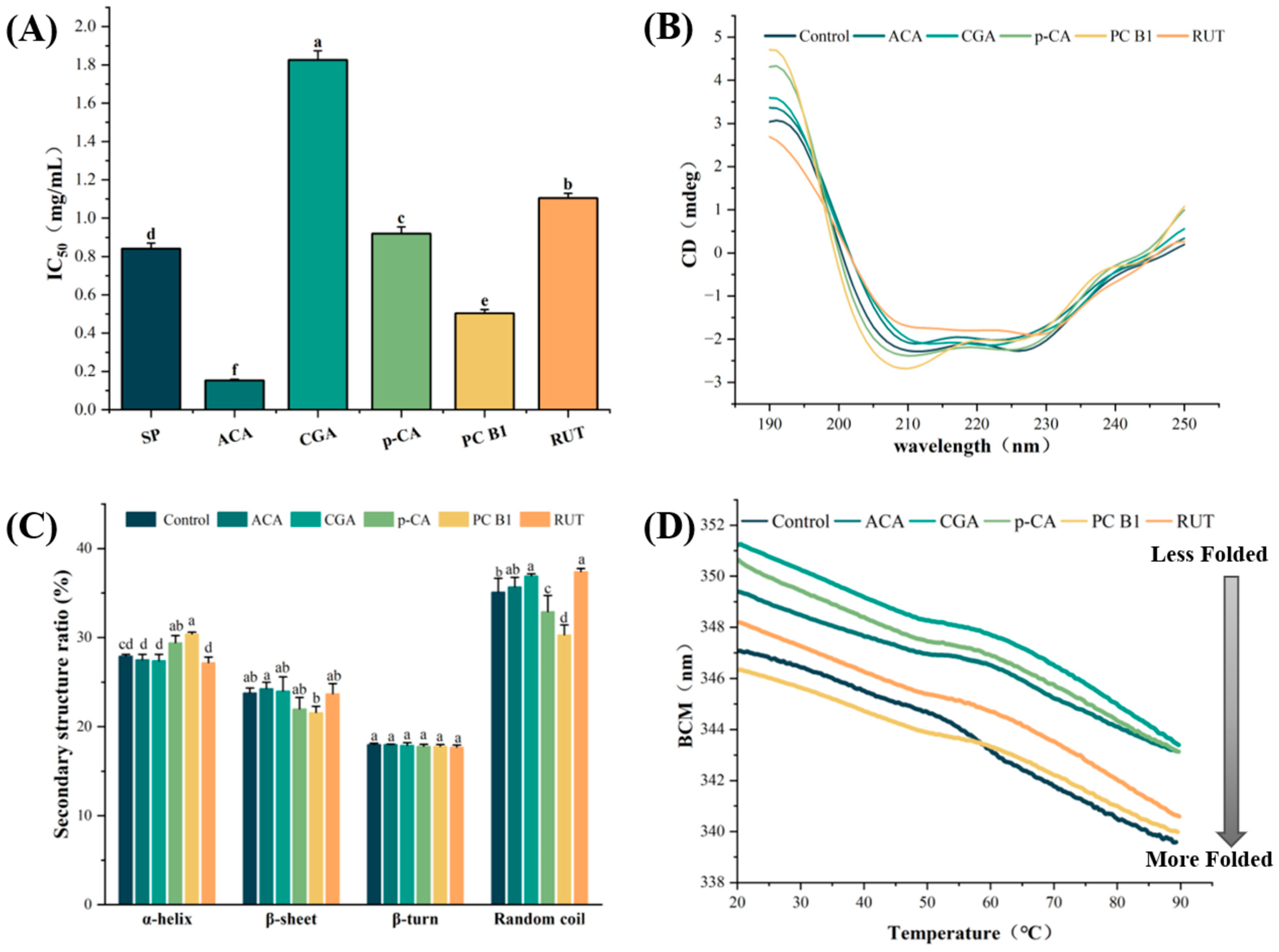
3.2. Inhibition Assays of the α-Amylase
3.3. CD Spectral Analysis
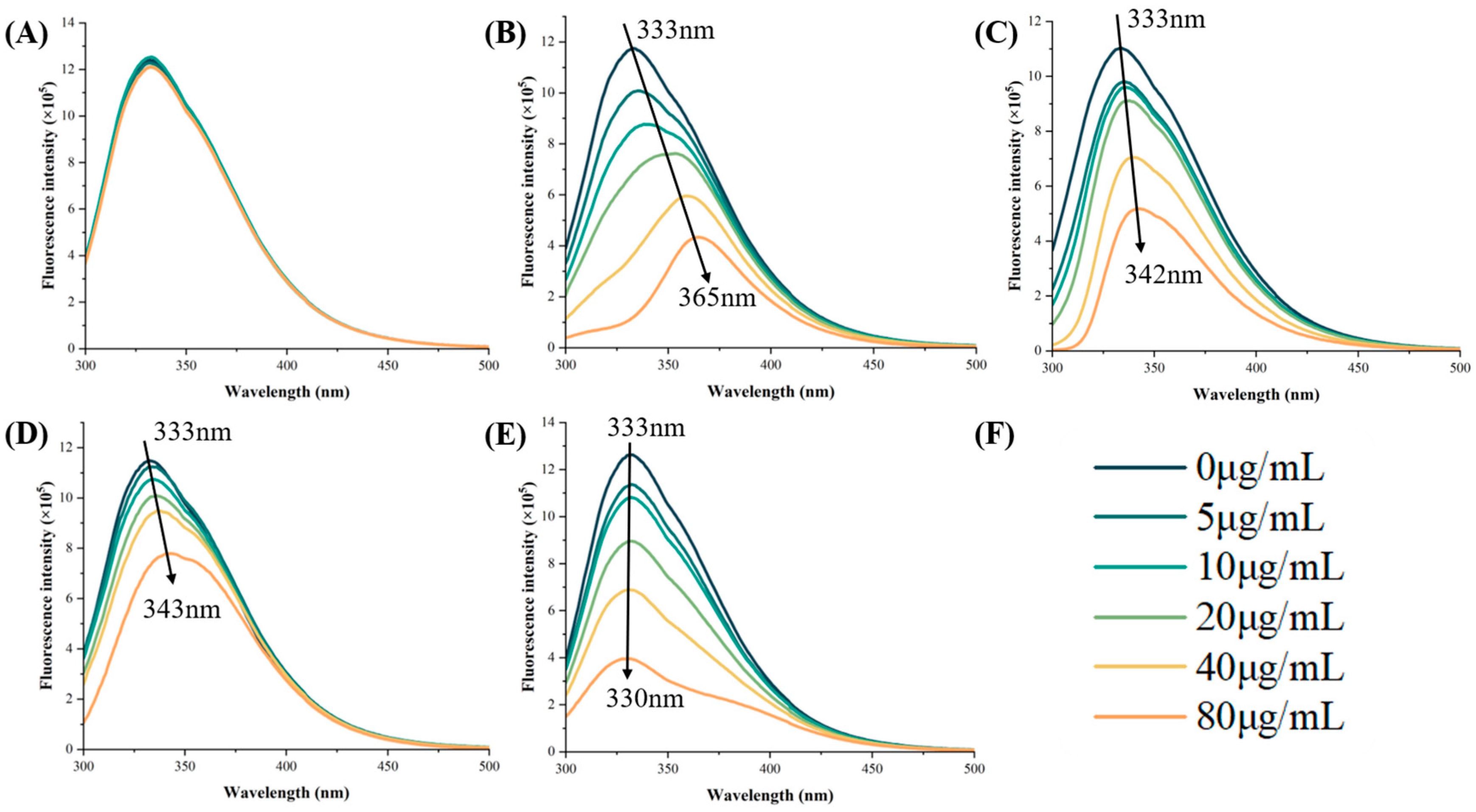
3.4. Fluorescence Quenching Analysis
3.5. Analysis of the α-Amylase Stability
3.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
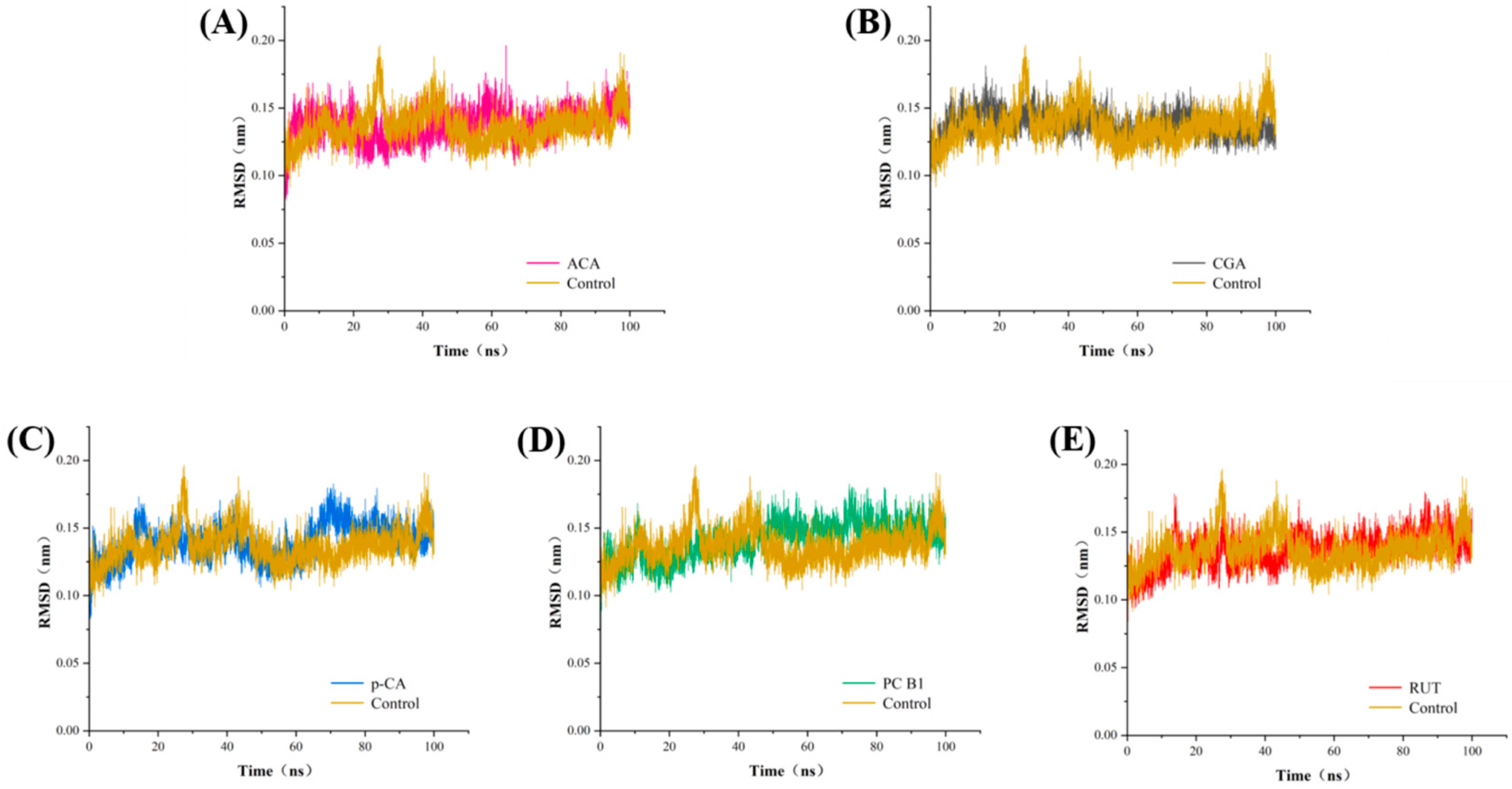
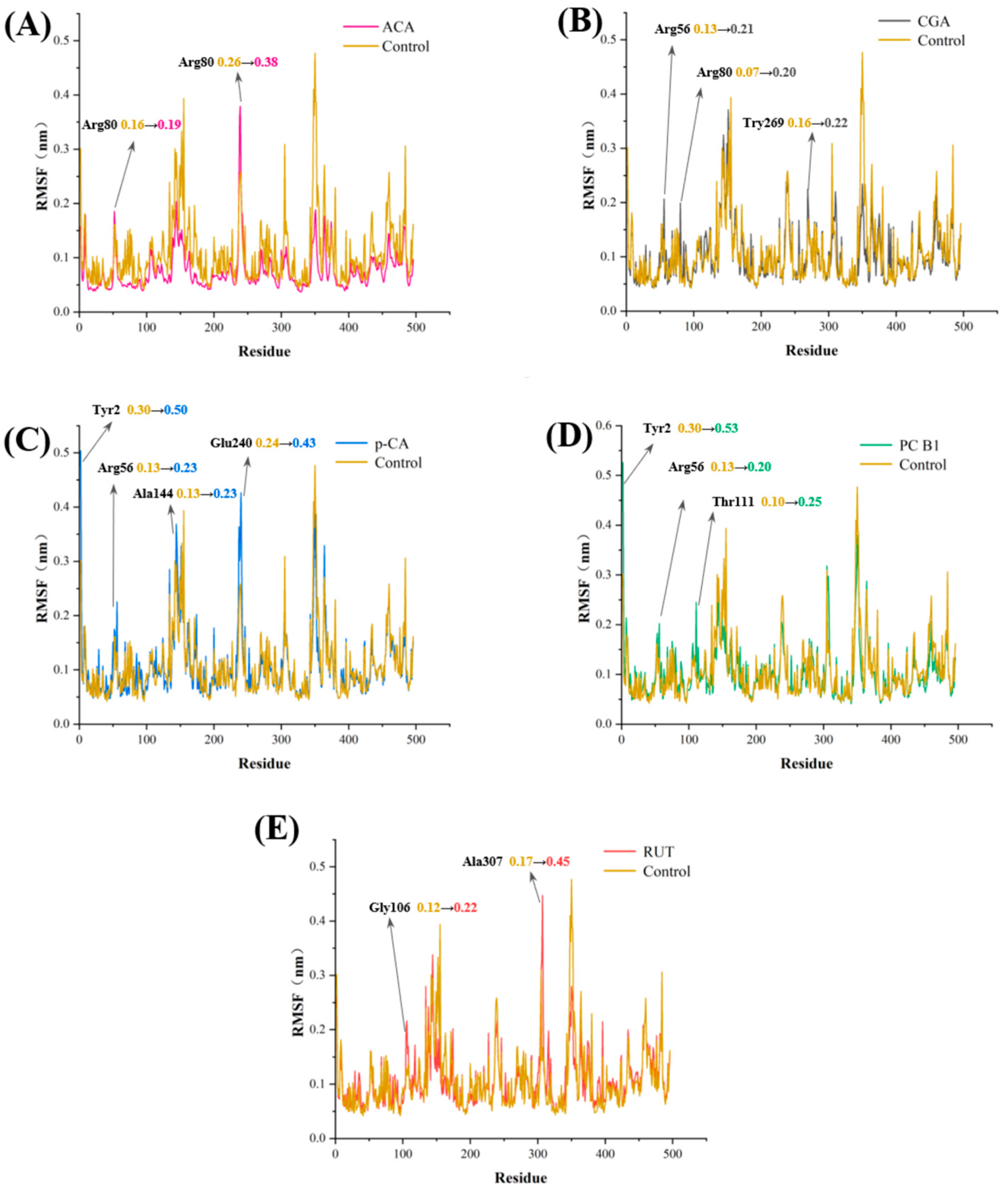
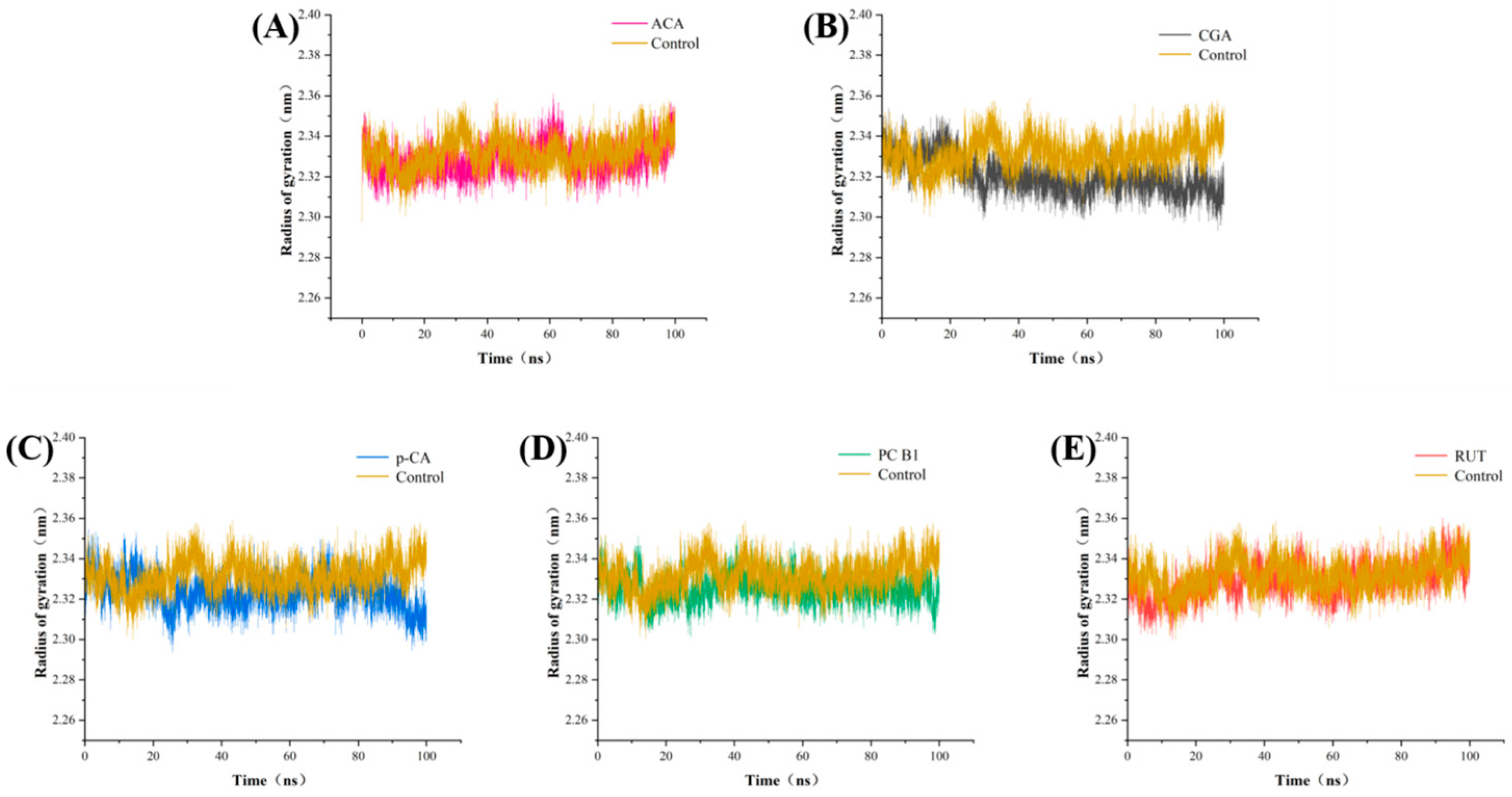
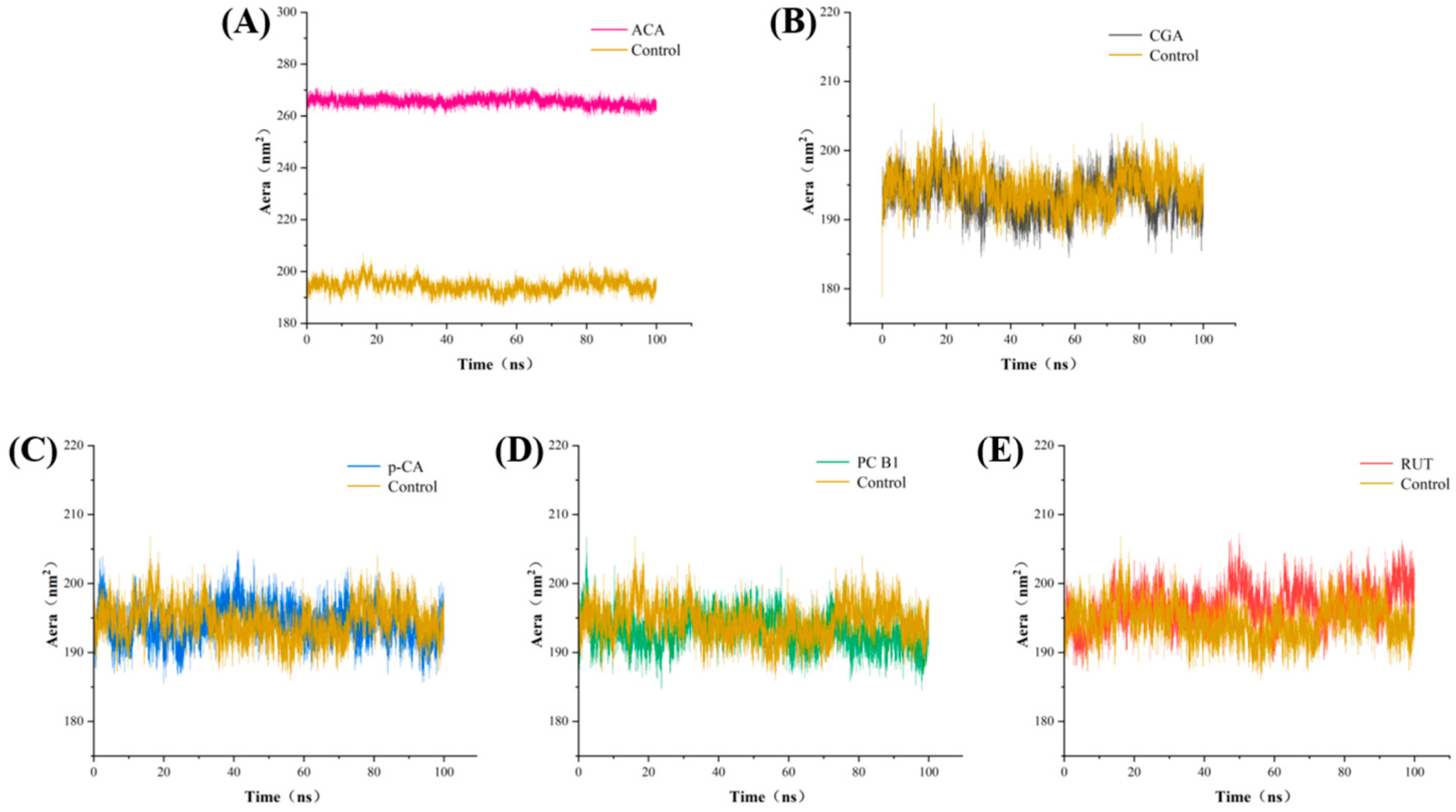
3.7. Molecular Dynamics Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SP | Sugarcane Polyohenol |
| ACA | Acarbose |
| CGA | Chlorogenic acid |
| p-CA | p-Coumaric acid |
| PC-B1 | Proanthocyanidin-B1 |
| RUT | Rutin |
| CD | Circular Dichroism |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| BCM | Barycentric mean |
| HPLC-MS/MS | High-performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
References
- Ungureanu, N.; Vladut, V.; Biris, S.-S. Sustainable Valorization of Waste and By-Products from Sugarcane Processing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Q.-U.-A.; Bashir, M.A.; Rehim, A.; Sial, M.U.; Ali Raza, H.M.; Atif, H.M.; Brito, A.F.; Geng, Y. Sugarcane Industrial Byproducts as Challenges to Environmental Safety and Their Remedies: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewawansa, U.H.A.J.; Houghton, M.J.; Barber, E.; Costa, R.J.S.; Kitchen, B.; Williamson, G. Flavonoids and phenolic acids from sugarcane: Distribution in the plant, changes during processing, and potential benefits to industry and health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yang, X.; Flavel, M.; Shields, Z.P.I.; Kitchen, B. Antioxidant and Anti-Diabetic Functions of a Polyphenol-Rich Sugarcane Extract. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.T.; Howell, K.; Suleria, H.; Zhang, P.; Gu, C.; Ng, K. Sugarcane polyphenol and fiber to affect production of short-chain fatty acids and microbiota composition using in vitro digestion and pig faecal fermentation model. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Flavel, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, O.C.Y.; Downey, L.; Stough, C.; Kitchen, B. A polyphenol rich sugarcane extract as a modulator for inflammation and neurological disorders. Pharmanutrition 2020, 12, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Flavel, M.; Xi, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Protective effects of sugarcane polyphenol against UV-B-induced photoaging in Balb/c mouse skin: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-glycosylation Effects. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3048–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Xie, J.; Zheng, B.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. The inhibition mechanism of bound polyphenols extracted from mung bean coat dietary fiber on porcine pancreatic α-amylase: Kinetic, spectroscopic, differential scanning calorimetric and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Chen, H.Z.; Jia, Y.; Peng, J.M.; Li, C.M. Inhibitory Effects against Alpha-Amylase of an Enriched Polyphenol Extract from Pericarp of Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana). Foods 2022, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.J.; Tang, M.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, X.X.; Wu, Y.W.; Ouyang, J. Endogenous bioactive compounds of naked oats (Avena nuda L.) inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kong, H.C.; Chitrakar, B.; Ban, X.F.; Gu, Z.B.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.F.; Li, C.M. The substitution sites of hydroxyl and galloyl groups determine the inhibitory activity of human pancreatic α-amylase in twelve tea polyphenol monomers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, J.; Ao, J.; Hou, Y.; Xi, M.; Cai, Y.; Li, M.; Luo, A. Structure-activity relationships and the underlying mechanism of a-amylase inhibition by hyperoside and quercetin: Multi-spectroscopy and molecular docking analyses. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 285, 121797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. In vitro inhibitory effects of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) leaves proanthocyanidins on pancreatic α-amylase and their interaction. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 101, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Safdar, B.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Ying, Z.; Liu, X. Identification of a novel α-amylase inhibitory activity peptide from quinoa protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.; Basilio, N.; Oliveira, J.; de Freitas, V.; Pina, F. A New Insight into the Degradation of Anthocyanins: Reversible versus the Irreversible Chemical Processes. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Shi, Y.; Duan, C.Q.; He, F. Reaction kinetics of the acetaldehyde-mediated condensation between (-)-epicatechin and anthocyanins and their effects on the color in model wine solutions. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, L.; Shao, J.J.; Jing, H.J.; Jiang, C.Y.; Wang, H.X.; Ma, C.Y. Three flavanols delay starch digestion by inhibiting α-amylase and binding with starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelli, V.; Harsha, P.S.C.S.; Ferranti, P.; Scarafoni, A.; Iametti, S. Grape skin phenolics as inhibitors of mammalian α-glucosidase and α-amylase—Effect of food matrix and processing on efficacy. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, H.; Peng, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, L. Caffeoyl substitution decreased the binding and inhibitory activity of quinic acid against α-amylase: The reason why chlorogenic acid is a relatively weak enzyme inhibitor. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, V.K.; Kayastha, A.M. Studies on α-amylase inhibition by acarbose and quercetin using fluorescence, circular dichroism, docking, and dynamics simulations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 314, 124160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Kumar, G.; Williamson, G.; Devkota, L.; Dhital, S. Molecular interactions between polyphenols and porcine α-amylase: An inhibition study on starch granules probed by kinetic, spectroscopic, calorimetric and in silico techniques. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, J.; Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ye, X. Inhibition mechanism of ferulic acid against α-amylase and α-glucosidasee. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, W.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Kong, X.; Tian, J.; Ye, X. Inhibition of porcine pancreatic α-amylase activity by chlorogenic acid. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, A.I.; Diaz-Sanchez, A.G.; de la Rosa, L.A.; Bustos-Jaimes, I.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E. Inhibition of α-amylase by flavonoids: Structure activity relationship (SAR). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 206, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Fu, X.; Ying, Z.; Liu, X. Proteinaceous α-amylase inhibitors: Purification, detection methods, types and mechanisms. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooran, N.; Kopra, K. Fluorescence-Based Protein Stability Monitoring-A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jia, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Tao, J.; Yue, H.; et al. Inhibitory activities and rules of plant gallotannins with different numbers of galloyl moieties on sucrase, maltase and α-amylase in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Elhenawy, A.A.; Rehman, M.U.; Alam, M.; Alam, A.; Rehman, N.U.; Ibrahim, M. Synthesis of novel 2-mercapto-1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives as potent urease inhibitors: In vitro and in silico investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1312, 138596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Warren, F.J.; Gidley, M.J. Natural products for glycaemic control: Polyphenols as inhibitors of alpha-amylase. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2019, 91, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar, M.A. Anti-Diabetic Potential of Phenolic Compounds: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, V.K.; Kayastha, A.M. Molecular modeling, docking and dynamics studies of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) α-amylase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 9297–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Qiao, L.; Hou, Y.; Ran, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Kuang, J.; Deng, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Antidiabetic and Antigout Properties of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Total Biflavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii Revealed by In Vitro and In Silico Studies. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, W.H.; Liu, W.L.; Zeng, X.Q.; Liu, G.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, H. Evaluating the capability of soybean peptides as calcium ion carriers: A study through sequence analysis and molecular dynamics simulations. Rsc Adv. 2024, 14, 15542–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, C.; Li, Z.; Xia, X.; Jiang, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Xiang, X. Inhibitory mechanism of phenolic compounds in rapeseed oil on α-amylase and α-glucosidase: Spectroscopy, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 289, 122251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, W.; Tang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Identification of the effective a-amylase inhibitors from Dalbergia odorifera: Virtual screening, spectroscopy, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 280, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Meng, F.; Guo, S.; Yuan, M.; Wang, H.; Chang, X. Inhibition of α-amylase digestion by a Lonicera caerulea berry polyphenol starch complex revealed via multi-spectroscopic and molecular dynamics analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, B.K.; Upadhyaya, S.R.; Bashyal, J.; Parajuli, N. In Silico and In Vitro Analyses to Repurpose Quercetin as a Human Pancreatic α-Amylase Inhibitor. Acs Omega 2023, 8, 43617–43631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liao, Y.; Hu, X.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. Inhibitory mechanism of α-glucosidase by liquiritigenin and its combined effect with acarbose: Multi-spectroscopic analyses and molecular docking simulation. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Joshi, T.; Joshi, T.; Chandra, S.; Tamta, S. Molecular dynamics simulation for screening phytochemicals as α-amylase inhibitors from medicinal plants. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 6524–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
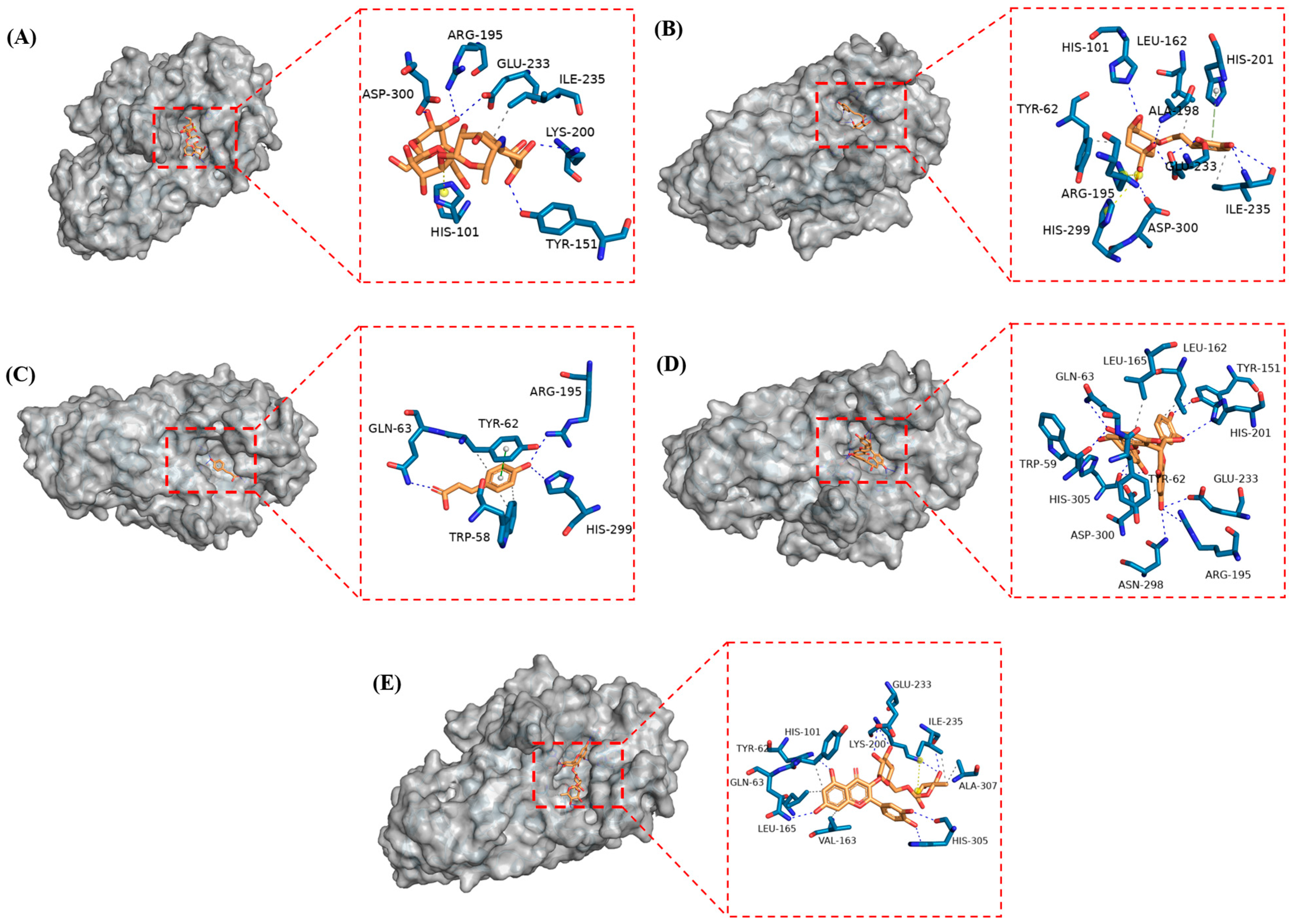
| Substance | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Hydrophobic Interaction | Hydrogen Bond | π-π Stacking | Salt Bridge | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACA | −6.9 | Ile235 | 1 | Tyr151, Arg195, Lys200, Glu233, Asp300 | 6 | ACA | −6.9 | Ile235 | 1 |
| CGA | −7.6 | Tyr62, Leu162, Ile235 | 3 | His101, Ala198, Glu233, Ile235, Asp300 | 7 | CGA | −7.6 | Tyr62, Leu162, Ile235 | 3 |
| p-CA | −6.2 | Trp58, Tyr62 | 3 | Gln63, Arg195, His299 | 3 | p-CA | −6.2 | Trp58, Tyr62 | 3 |
| PC-B1 | −7.8 | Tyr62, Leu162, Leu165, Asp300 | 4 | Trp59, Gln63, Tyr151, Arg195, His201, Glu233, Asn298, His305 | 9 | PC-B1 | −7.8 | Tyr62, Leu162, Leu165, Asp300 | 4 |
| RUT | −8.4 | Tyr62, Val163, Leu165, Ile235, Ala307 | 5 | Gln63, His101, Lys200, Glu233, Ile235, His305 | 8 | RUT | −8.4 | Tyr62, Val163, Leu165, Ile235, Ala307 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; An, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Li, H. Effect of Sugarcane Polyphenol Extract on α-Amylase Inhibition and Mechanism Exploration. Foods 2025, 14, 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132174
Wang Y, An J, Yao S, Zhang C, Zhou Y, Li L, Li H. Effect of Sugarcane Polyphenol Extract on α-Amylase Inhibition and Mechanism Exploration. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132174
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yumei, Jiulong An, Shenghong Yao, Chengfeng Zhang, Yanv Zhou, Lu Li, and He Li. 2025. "Effect of Sugarcane Polyphenol Extract on α-Amylase Inhibition and Mechanism Exploration" Foods 14, no. 13: 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132174
APA StyleWang, Y., An, J., Yao, S., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y., Li, L., & Li, H. (2025). Effect of Sugarcane Polyphenol Extract on α-Amylase Inhibition and Mechanism Exploration. Foods, 14(13), 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132174






