Exploring the Potential of an Industry-Scale Microfluidizer for Modifying Rice Starch: Multi-Layer Structures and Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. ISM Treatment of Rice Starch
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Granule Size Distributions
2.5. Determination of Damaged Starch Content
2.6. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.9. Rapid Visco Analyzer (RVA) Analysis
2.10. Rheological Properties Analysis
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology
3.2. Granule Size Distributions
3.3. Damaged Starch
3.4. Long-Range Crystalline Structure
3.5. Short-Range Ordered Structure
3.6. Thermal Properties
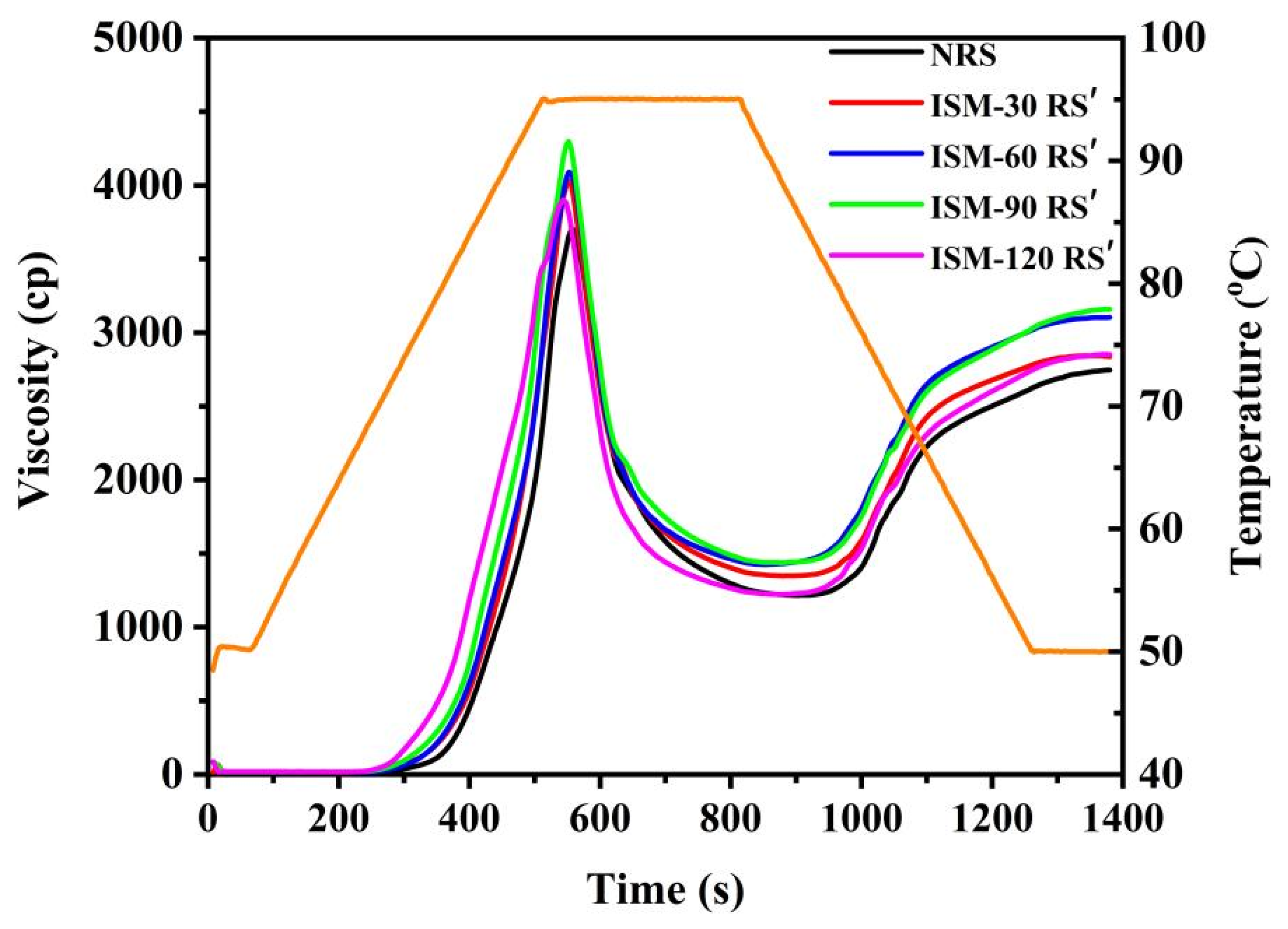
3.7. Pasting Properties
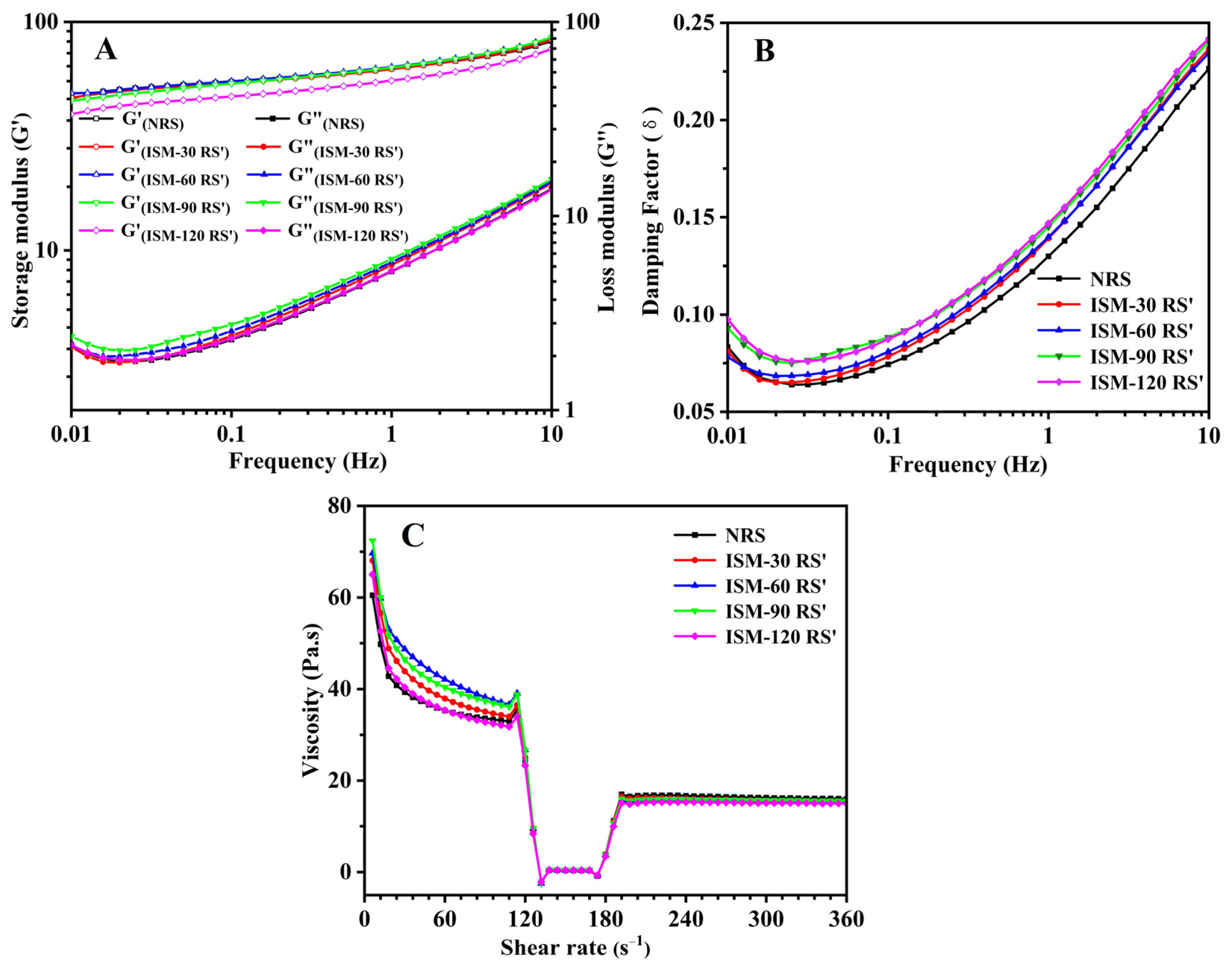
3.8. Rheological Properties
3.8.1. Dynamic Viscoelastic Rheological Properties
3.8.2. In-Shear Structural Recovery Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Qin, L.; Chen, T.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ji, X.; Xie, J. Modification of starch by polysaccharides in pasting, rheology, texture and in vitro digestion: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermansson, A.M.; Svegmark, K. Developments in the understanding of starch functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, H.; Nowacka, M.L.G.; Colussi, R.; Frasson, S.F.; Demirkesen, I.; Mert, B.; Singha, P.; Singh, S.K.; Falsafi, S.R. Impact of emerging non-thermal processing treatments on major food macromolecules: Starch, protein, and lipid. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, H.; Yildirim-Yalcin, M.; Demirkesen, I.; Toker, O.S.; Colussi, R.; do Nascimento, L.A.; Sahin, S.; Falsafi, S.R. Improving physicochemical and nutritional attributes of rice starch through green modification techniques. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jia, M.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, S.; Lin, P.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the physicochemical properties of buckwheat starch: Based on the ultrasonic power and moisture content. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2025, 116, 107333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Sun, Z.; Ge, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, W. Modification of multi-scale structure, physicochemical properties, and digestibility of rice starch via microwave and cold plasma treatments. LWT. 2022, 153, 112483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Luo, S.J.; Chen, M.S.; Xia, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.M. Effect of industry-scale microfluidization on structural and physicochemical properties of potato starch. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 60, 102278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Chen, M.S.; Deng, L.Z.; Liang, Y.-Z.Z.; Liu, Y.K.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.M. Whole soybean milk produced by a novel industry-scale micofluidizer system without soaking and filtering. J. Food Eng. 2021, 291, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Xu, K.; Ai, F.; Dai, T.; Chen, J. CFD simulation and structure optimization of the industry-scale microfluidization interactive chamber. Food Mach. 2024, 40, 73–81+89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.T.; Deng, L.Z.; Dai, T.T.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.M. Microfluidization: A promising food processing technology and its challenges in industrial application. Food Control. 2022, 137, 108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Dai, T.; Liang, R.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. A new partially-gelatinized granular starch prepared by industry-scale microfluidization treatment of pea starch. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 86, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, K.O.; Christopher, A.S. Physical, functional, pasting and thermal properties of flours and starches of six Nigerian rice cultivars. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yu, D. Properties of OSA-modified starch and emulsion prepared with different materials: Glutinous rice starch, japonica rice starch, and indica rice starch. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y. Optimizing processing sequences in combined techniques for rice starch modification: A mini review of current understanding. J. Cereal Sci. 2025, 123, 104179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, B.; Tan, C.P.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q. Effects of limited moisture content and storing temperature on retrogradation of rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chi, C. Impact of long-term storage on multi-scale structures and physicochemical properties of starch isolated from rice grains. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Du, J.; Feng, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, G.; Fu, N.; Yang, T. Physical modification of cassava starch by alternating magnetic field treatment: Effects on fine structure, retrogradation and in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmeda, R.; Noorlaila, A.; Norziah, M.H. Relationships of damaged starch granules and particle size distribution with pasting and thermal profiles of milled MR263 rice flour. Food Chem. 2016, 191, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasumarthi, P.; Malleshi, N.; Manickavasagan, A. Effect of different milling methods on isolation of pinto bean starch, and the characteristics of the isolated starches. Food Chem. 2025, 466, 142216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, X.; Han, S.; Fu, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Guo, P. Effects of dual modification by cold plasma and heat-moisture treatment on the structure and in vitro digestibility of waxy maize starch. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 102, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zheng, F.; Yu, J.; Lv, P.; Ban, H.; Liu, H.; Cai, D.; Xiu, L.; Liu, J. Effects of static magnetic field treatment on the digestive, structural and physicochemical characteristics of germinated corn starch. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.; Thomas, L.; Arfat, Y.A.; Joseph, A. Rheological, structural and functional properties of high-pressure treated quinoa starch in dispersions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Wang, S. Structural and functional properties of starches from Chinese chestnuts. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. AACC International Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Chen, T. Effects of creeping fig seed polysaccharide on pasting, rheological, textural properties and in vitro digestibility of potato starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Wang, R.S.; Liang, R.H.; Chen, J.; He, X.H.; Chen, R.Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.M. Dynamic high-pressure microfluidization assisting octenyl succinic anhydride modification of rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Cao, Z.; Shi, C.; Cheng, F. Influence of environmental temperature during grain filling period on granule size distribution of rice starch and its relation to gelatinization properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Q.; Zhu, F.; Song, H.; Wang, C.; Guan, X. Effect of vacuum combined ultrasound treatment on the fine structure and physiochemical properties of rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, X. A review of milling damaged starch: Generation, measurement, functionality and its effect on starch-based food systems. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F. Properties of damaged starch granules: Composition and swelling properties of maize, rice, pea and potato starch fractions in water at various temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, Q.; Li, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, A.; Liu, J. The effect of heat moisture treatment times on physicochemical and digestibility properties of adzuki bean, pea, and white kidney bean flours and starches. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chen, X.D.; Mao, Z.H. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on the structure and thermal properties of maize starch. J. Food Eng. 2008, 87, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Li, R.; Liang, W.; Lin, Q.; Niu, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, W. Effect of microwave treatment on the structural and physicochemical properties of amylose partially removed sorghum starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 300, 140285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Guo, B.; Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Chen, J.; Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Modification of potato starch by using superheated steam. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, I.; Zhuo, G.-Y.; Chakraborty, I.; Melanthota, S.K.; Mal, S.S.; Sarmah, B.; Baruah, V.J.; Mahato, K.K.; Mazumder, N. Investigation of structural and physico-chemical properties of rice starch with varied amylose content: A combined microscopy, spectroscopy, and thermal study. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Xu, X. Microstructure, gelatinization and pasting properties of rice starch under acid and heat treatments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M. Effects of konjac glucomannan on pasting and rheological properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 89, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, H.-W.; Park, J.-D.; Choi, H.-D.; Hong, J.S. Impact of annealing and incorporation of vegetable oils on physicochemical and rheological properties of wheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Jane, J.-l. Gelatinization and rheological properties of starch. Starch-Starke 2015, 67, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, C.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yu, D. Effect of microwave plasma power on the properties of pea starch: Granule morphology, gelatinization behavior, and gel properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 102, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, B. The effects of ultra-high pressure on the structural, rheological and retrogradation properties of lotus seed starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
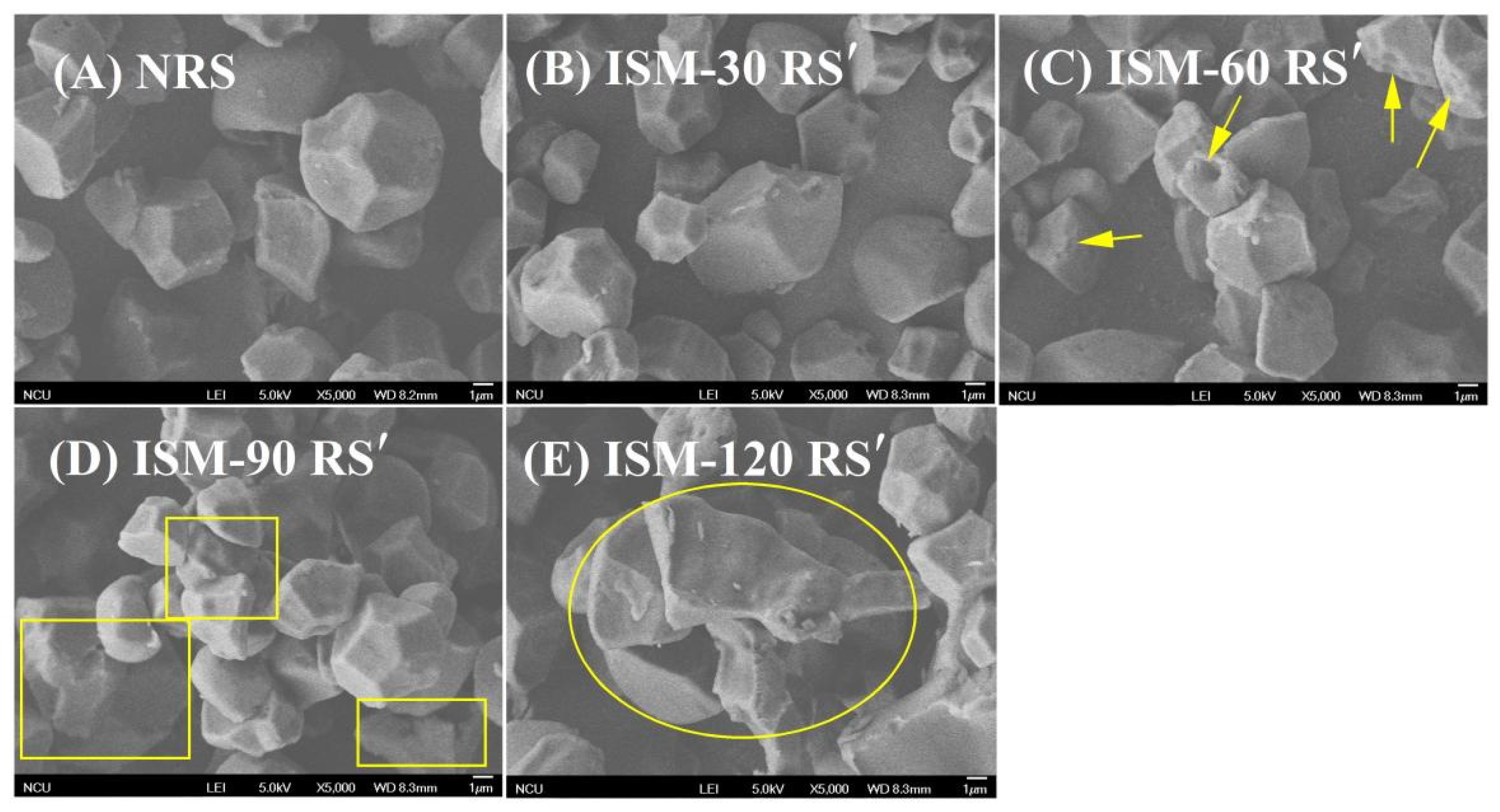
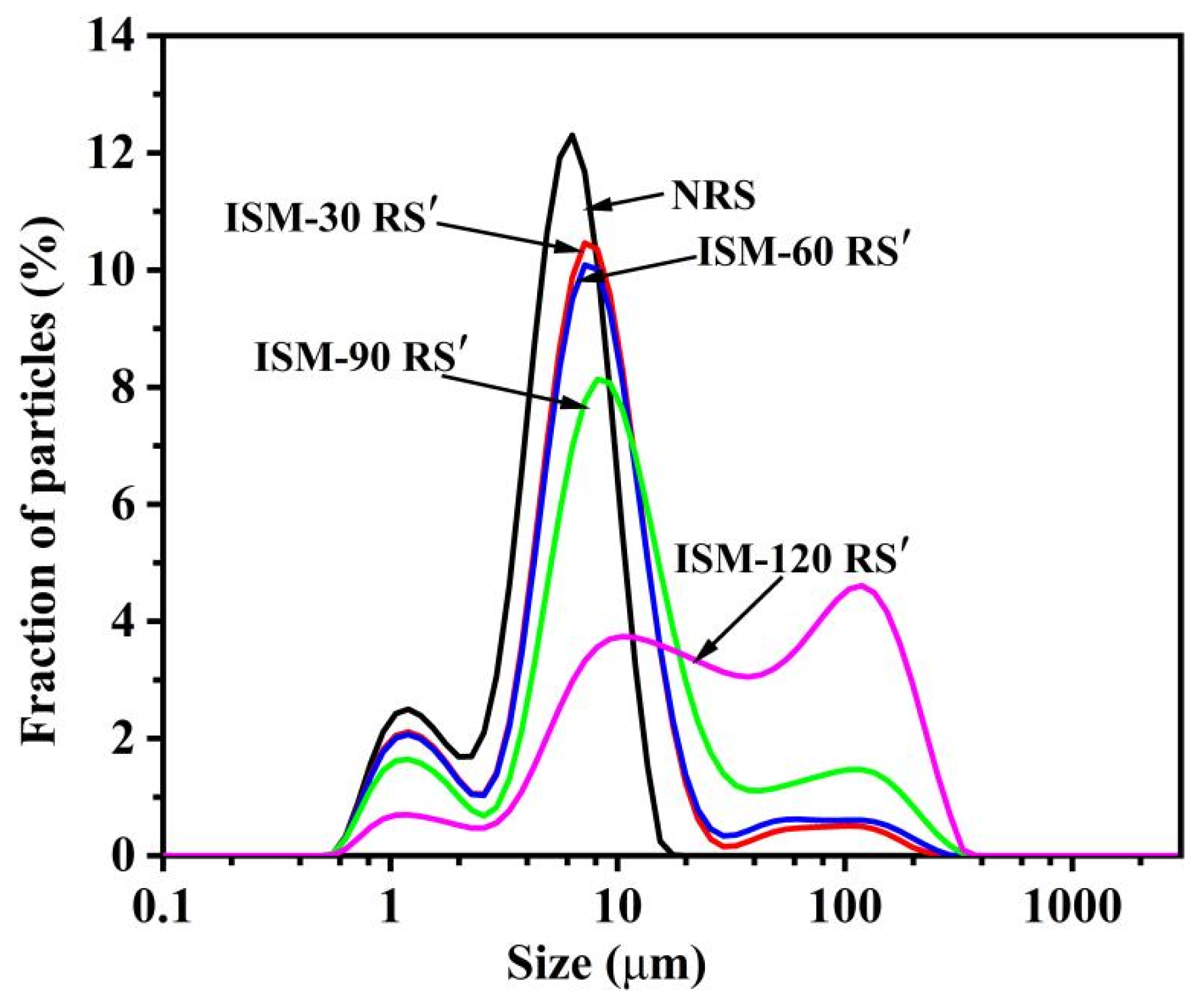
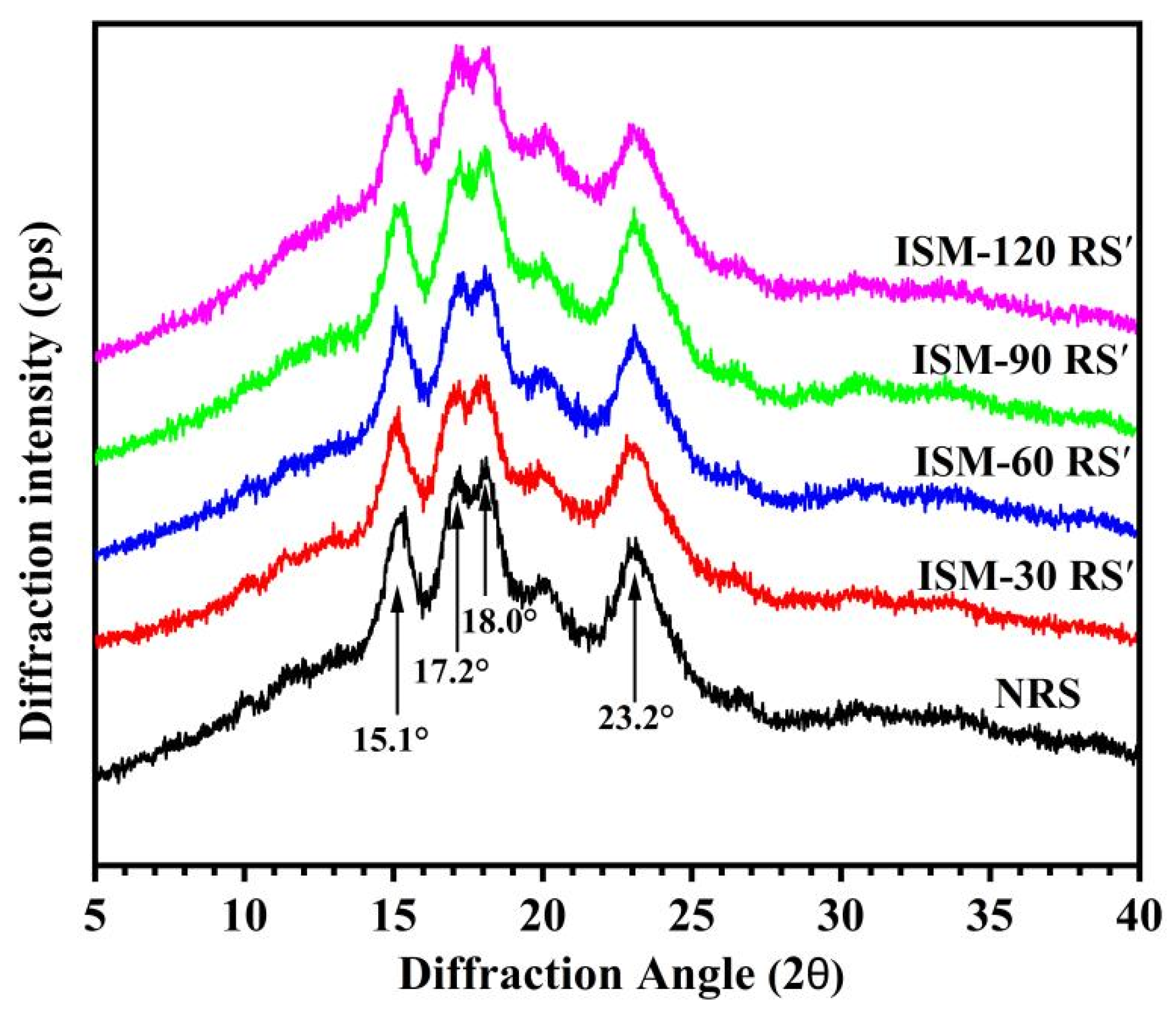
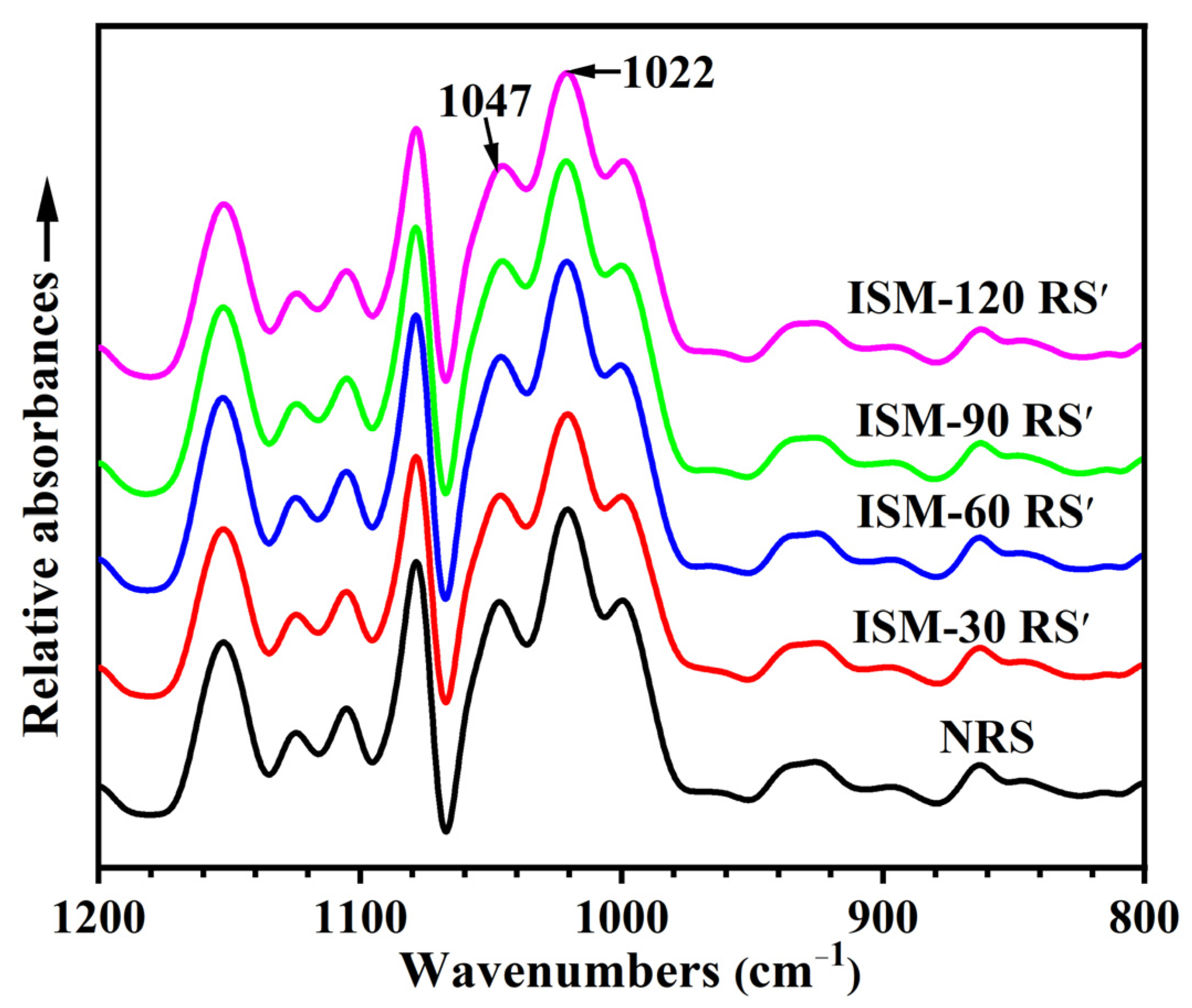
| Samples | D[4,3] | Damaged Starch Content (%) | Relative Crystallinity (%) | 1047 cm−1/1022 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRS | 5.9 ± 0.3 d | 4.25 ± 0.07 d | 29.01 ± 0.18 a | 0.88 ± 0.01 a |
| ISM-30 RS′ | 11.8 ± 0.2 cd | 4.52 ± 0.05 cd | 28.33 ± 0.18 a | 0.85 ± 0.03 b |
| ISM-60 RS′ | 13.7 ± 0.5 c | 4.82 ± 0.08 c | 27.78 ± 0.11 a | 0.85 ± 0.02 b |
| ISM-90 RS′ | 25.0 ± 0.6 b | 5.68 ± 0.06 b | 26.46 ± 0.45 b | 0.76 ± 0.02 c |
| ISM-120 RS′ | 59.9 ± 3.1 a | 17.99 ± 0.40 a | 20.74 ± 0.47 c | 0.73 ± 0.01 d |
| Samples | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (mJ/mg) | DG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRS | 61.67 ± 0.07 b | 66.40 ± 0.27 a | 73.28 ± 0.07 a | 6.61 ± 0.04 a | 0 |
| ISM-30 RS′ | 60.07 ± 0.15 c | 63.74 ± 0.14 b | 71.60 ± 0.11 a | 6.40 ± 0.19 ab | 3.10 ± 2.88 c |
| ISM-60 RS′ | 59.91 ± 0.08 c | 63.84 ± 0.00 b | 70.64 ± 0.30 a | 6.22 ± 0.13 bc | 5.90 ± 1.92 bc |
| ISM-90 RS′ | 60.06 ± 0.43 c | 64.13 ± 0.85 b | 70.69 ± 2.40 a | 5.90 ± 0.23 c | 10.74 ± 3.42 b |
| ISM-120 RS′ | 63.21 ± 0.01 a | 66.96 ± 0.02 a | 72.34 ± 0.16 a | 4.53 ± 0.06 d | 31.39 ± 0.96 a |
| Samples | PV (cp) | TV (cp) | BD (cp) | FV (cp) | SB (cp) | In-Shear Structural Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRS | 3740.7 ± 35.7 d | 1231.0 ± 13.5 d | 2509.7 ± 22.4 d | 2756.7 ± 36.2 c | 1525.7 ± 38.7 c | 42.9 ± 1.1 a |
| ISM-30 RS′ | 4072.7 ± 40.5 b | 1361.3 ± 12.7 c | 2711.3 ± 32.0 b | 2890.3 ± 45.8 b | 1519.0 ± 26.6 c | 41.0 ± 2.8 a |
| ISM-60 RS′ | 4053.0 ± 46.7 b | 1411.7 ± 23.1 b | 2641.3 ± 24.7 c | 3083.7 ± 45.1 a | 1672.0 ± 22.1 ab | 38.5 ± 5.4 a |
| ISM-90 RS′ | 4317.7 ± 37.6 a | 1445.7 ± 16.9 a | 2872.0 ± 20.8 a | 3136.3 ± 19.6 a | 1690.7 ± 31.0 a | 38.1 ± 2.6 a |
| ISM-120 RS′ | 3914.0 ± 15.6 c | 1222.0 ± 0.0 d | 2692.0 ± 15.6 b | 2848.5 ± 3.5 b | 1626.5 ± 3.5 b | 40.7 ± 1.3 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Exploring the Potential of an Industry-Scale Microfluidizer for Modifying Rice Starch: Multi-Layer Structures and Physicochemical Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122067
He X, Yang Z, Wang X, Xu Z, Cheng Y, Liu W, Liu C, Chen J. Exploring the Potential of an Industry-Scale Microfluidizer for Modifying Rice Starch: Multi-Layer Structures and Physicochemical Properties. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122067
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaohong, Zhimeng Yang, Xufeng Wang, Zhou Xu, Yunhui Cheng, Wei Liu, Chengmei Liu, and Jun Chen. 2025. "Exploring the Potential of an Industry-Scale Microfluidizer for Modifying Rice Starch: Multi-Layer Structures and Physicochemical Properties" Foods 14, no. 12: 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122067
APA StyleHe, X., Yang, Z., Wang, X., Xu, Z., Cheng, Y., Liu, W., Liu, C., & Chen, J. (2025). Exploring the Potential of an Industry-Scale Microfluidizer for Modifying Rice Starch: Multi-Layer Structures and Physicochemical Properties. Foods, 14(12), 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122067






