Monitoring the Spoilage of Fresh Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) During Storage at 4 °C by Mid-Infrared and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Coupled with Chemometric Tools
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Fish Sample Preparation
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.4. Sensory Analysis
2.5. Measurement of Physicochemical Properties
2.6. Colour Measurements
2.7. Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
2.8. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
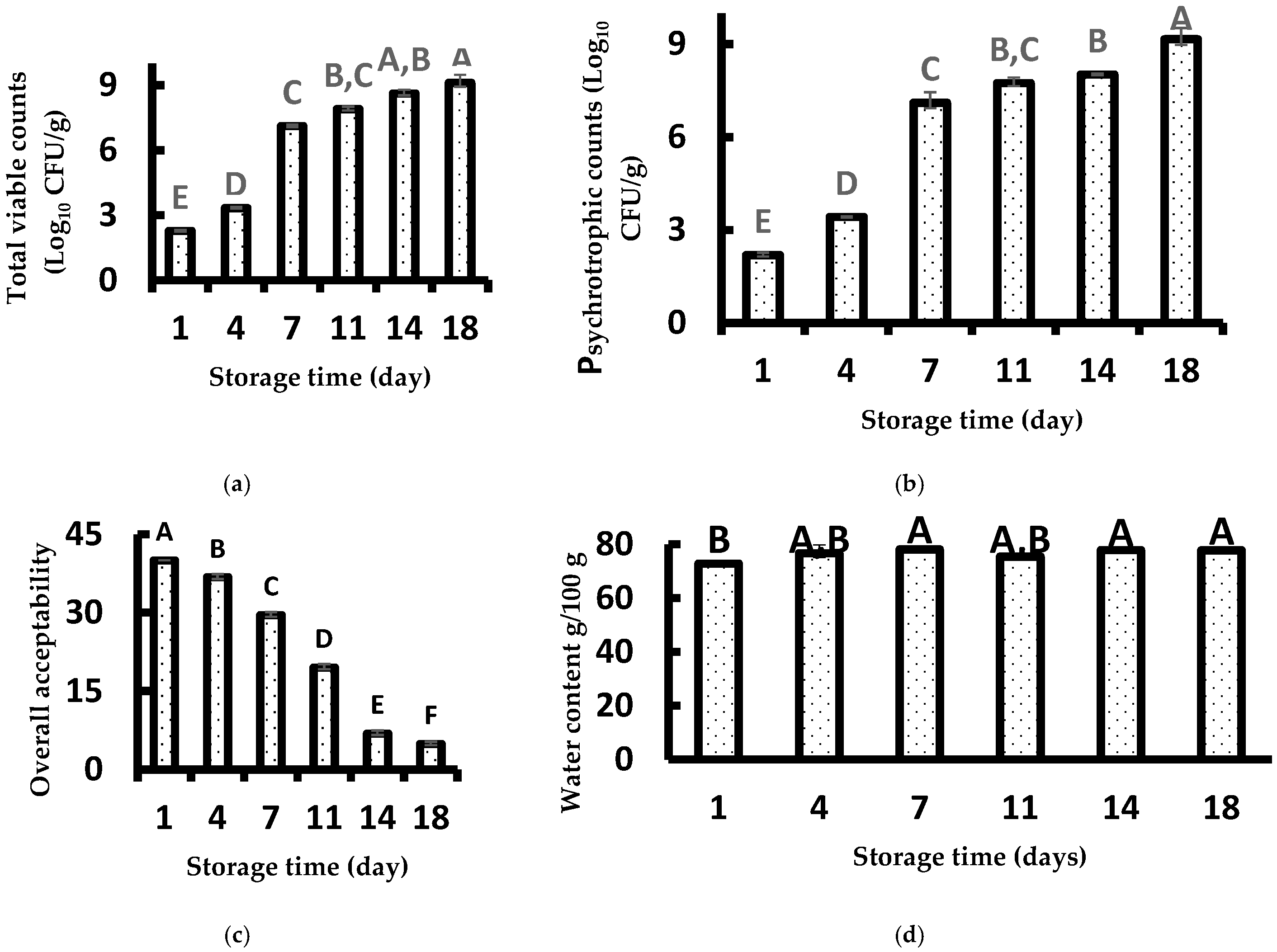
3.1. Microbiological Analysis
3.2. Sensory Analysis
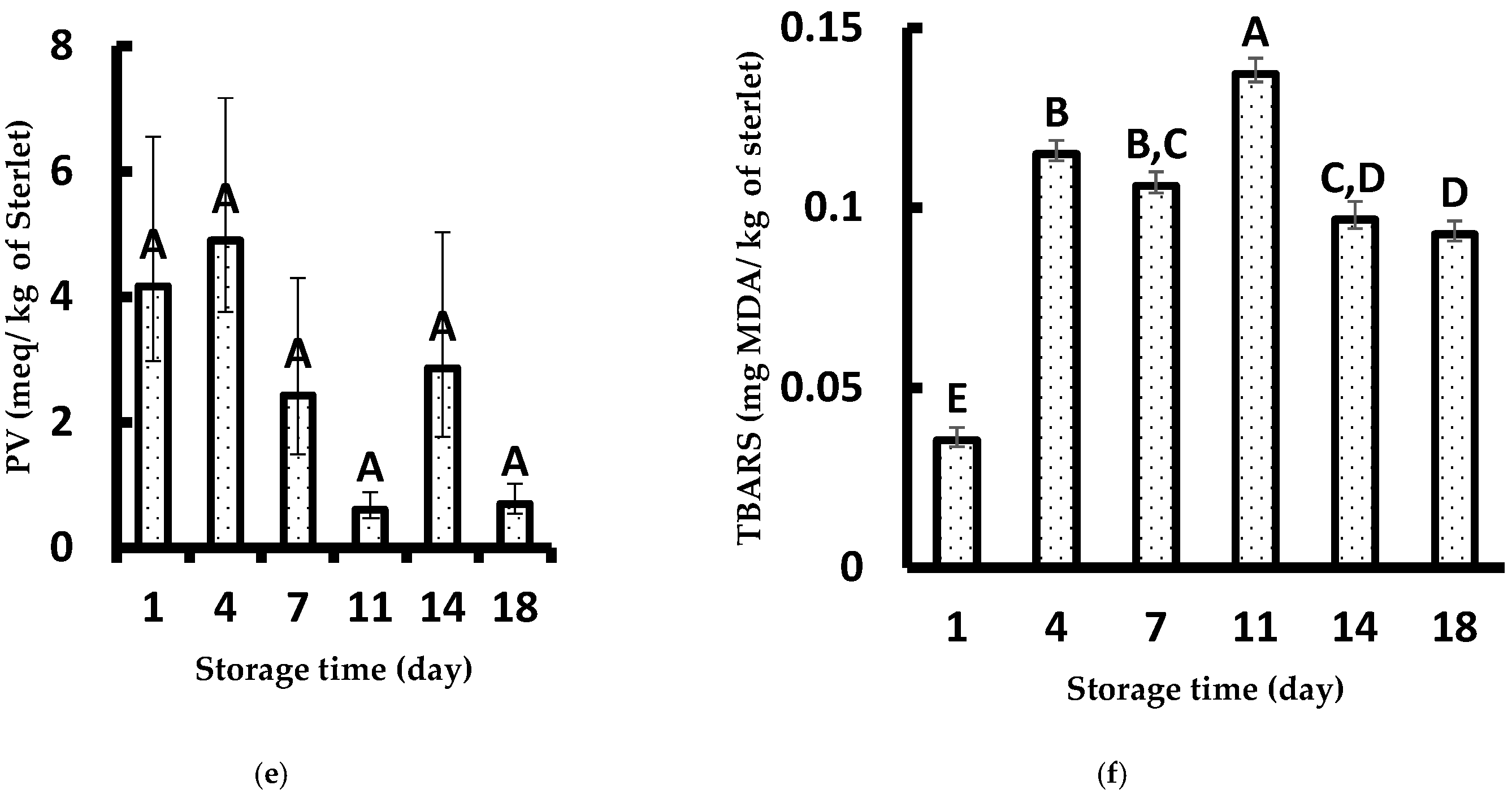
3.3. Physicochemical Measurements
3.4. Colour Measurements
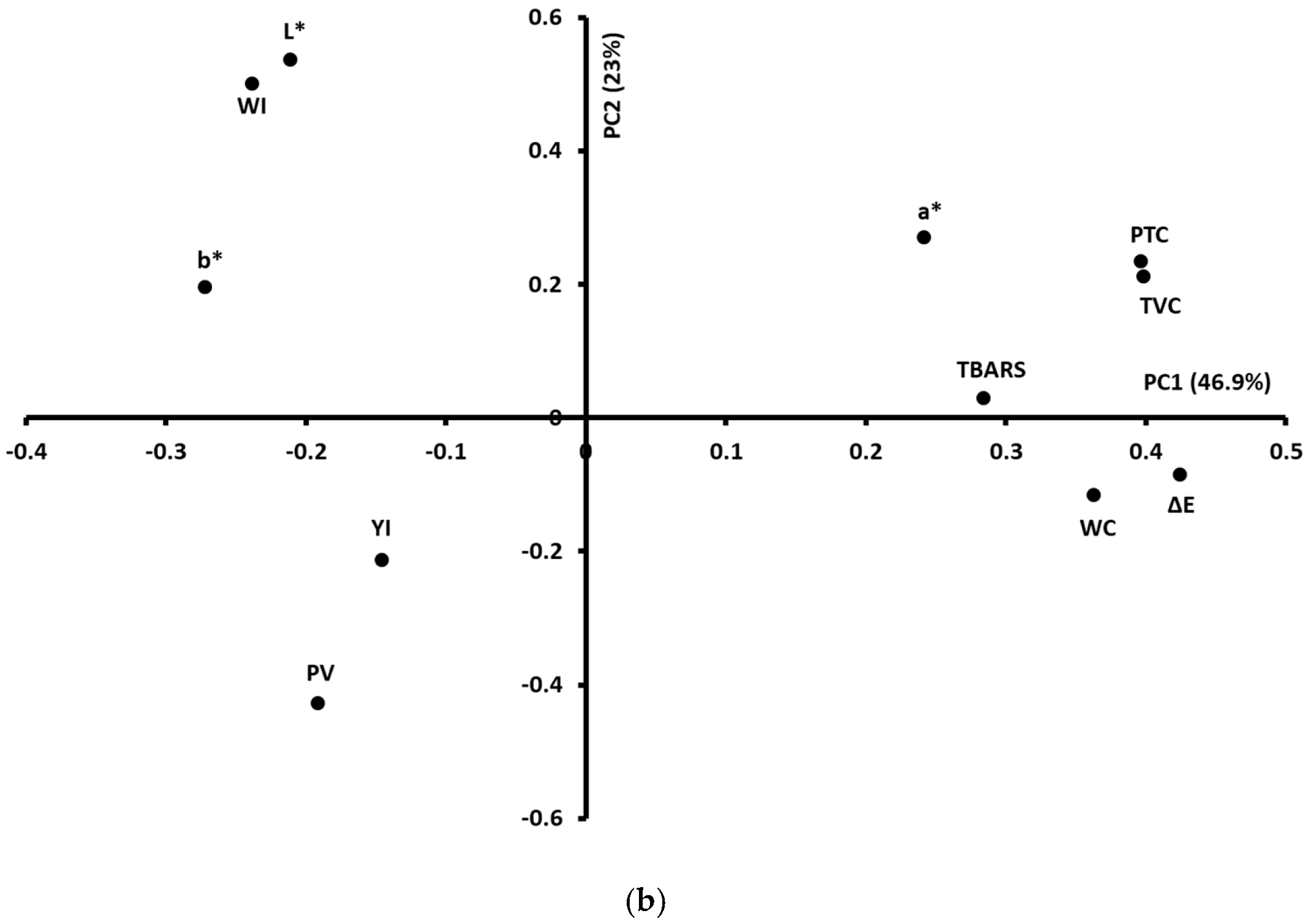
3.5. Global Analyses of the Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Colour Measurements
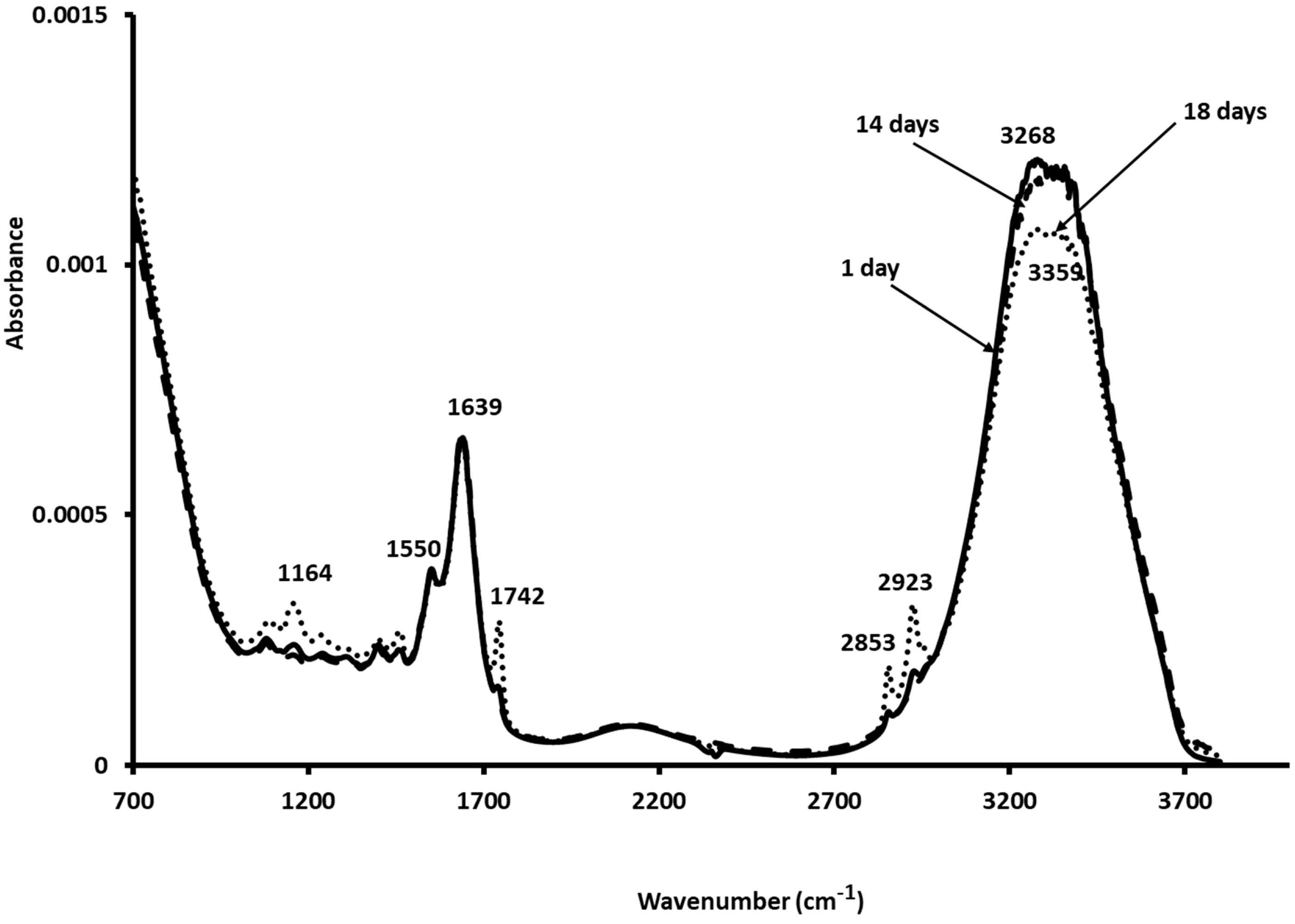
3.6. Mid-Infrared Measurements
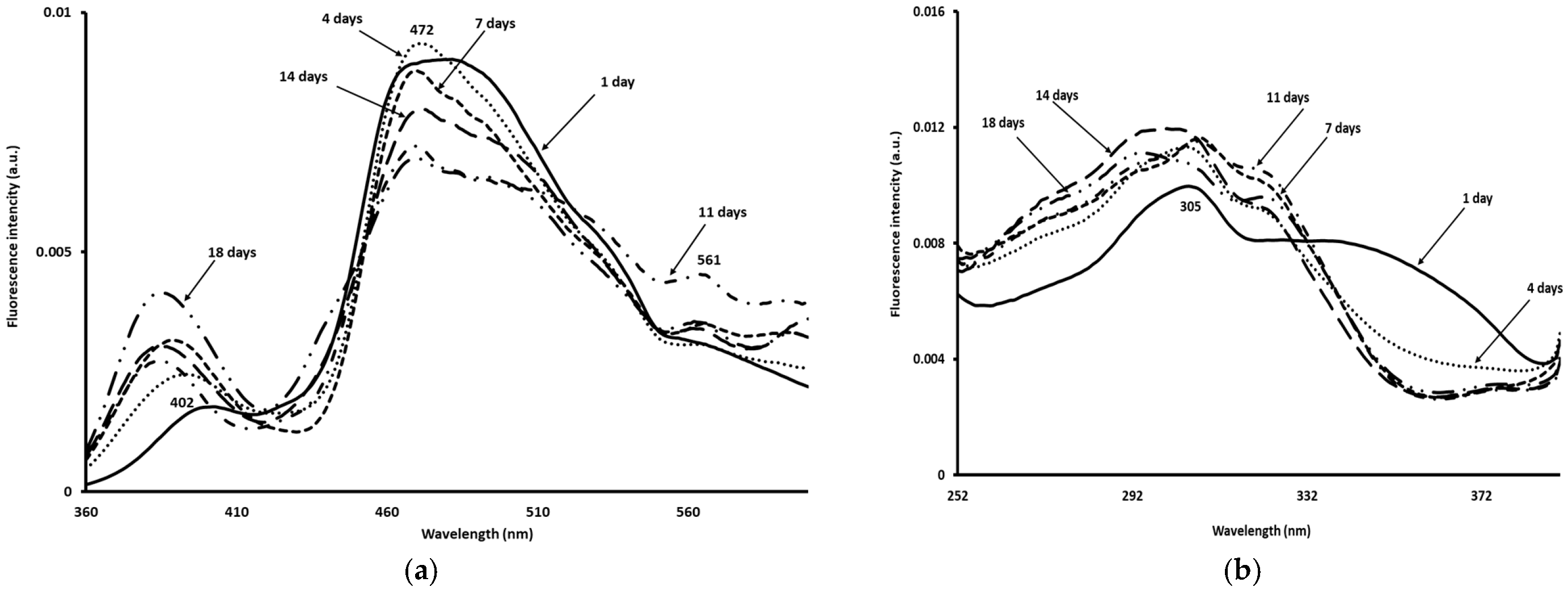
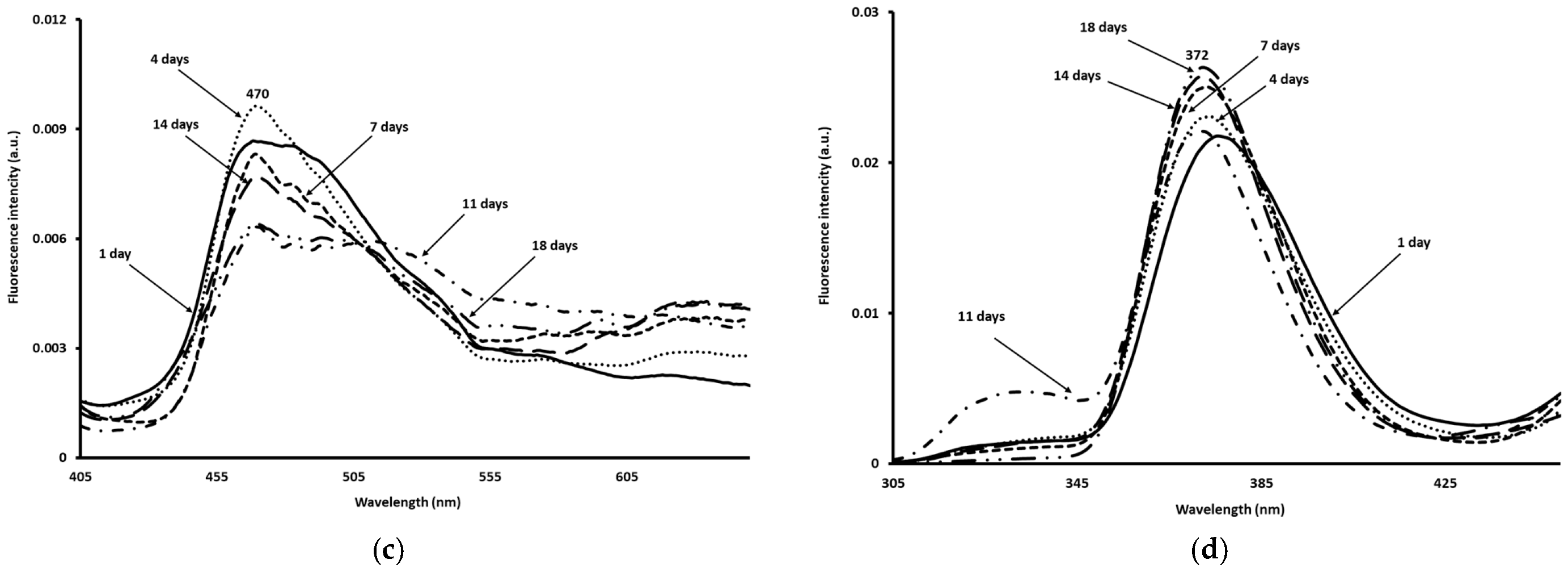
3.7. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Measurements
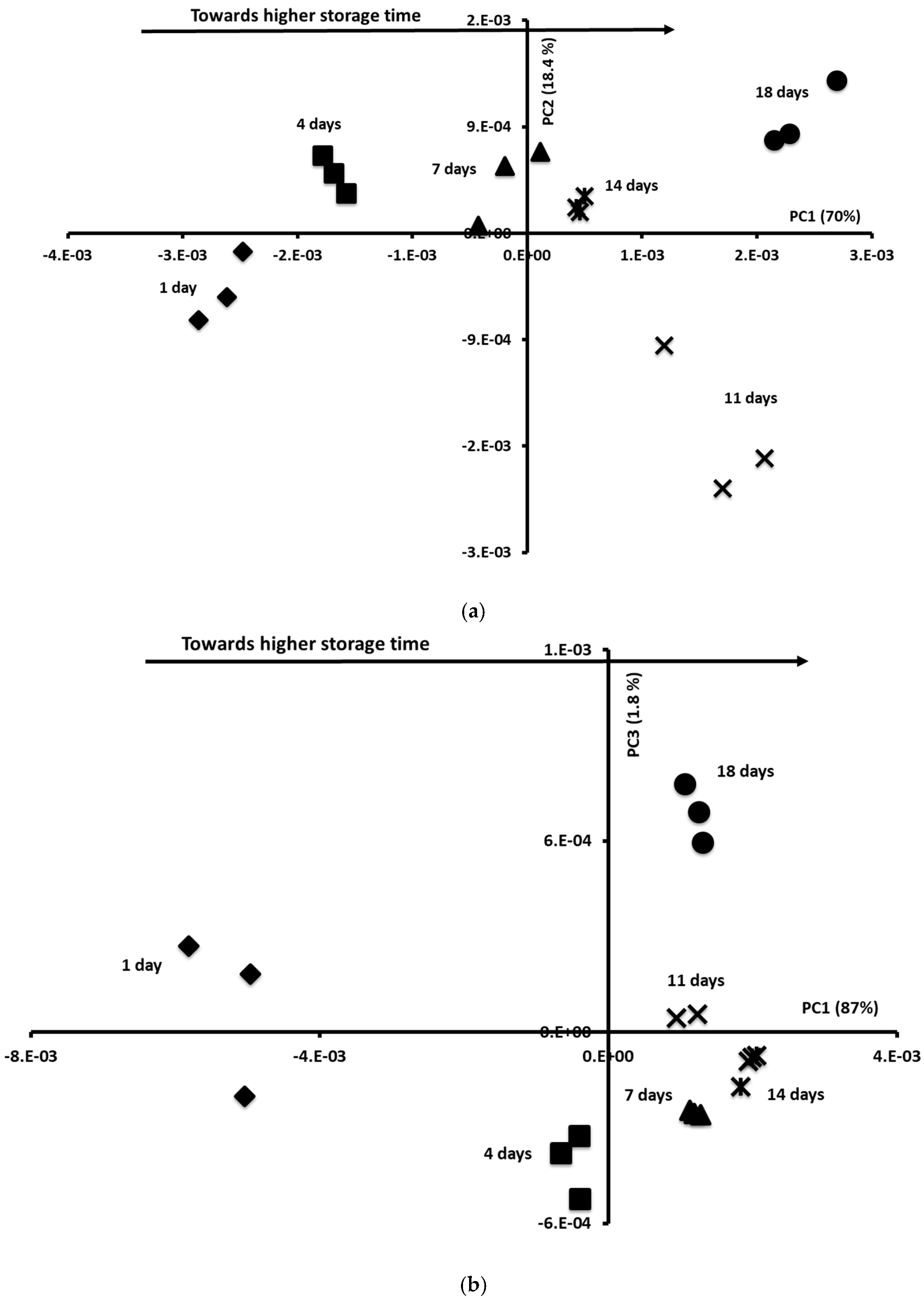
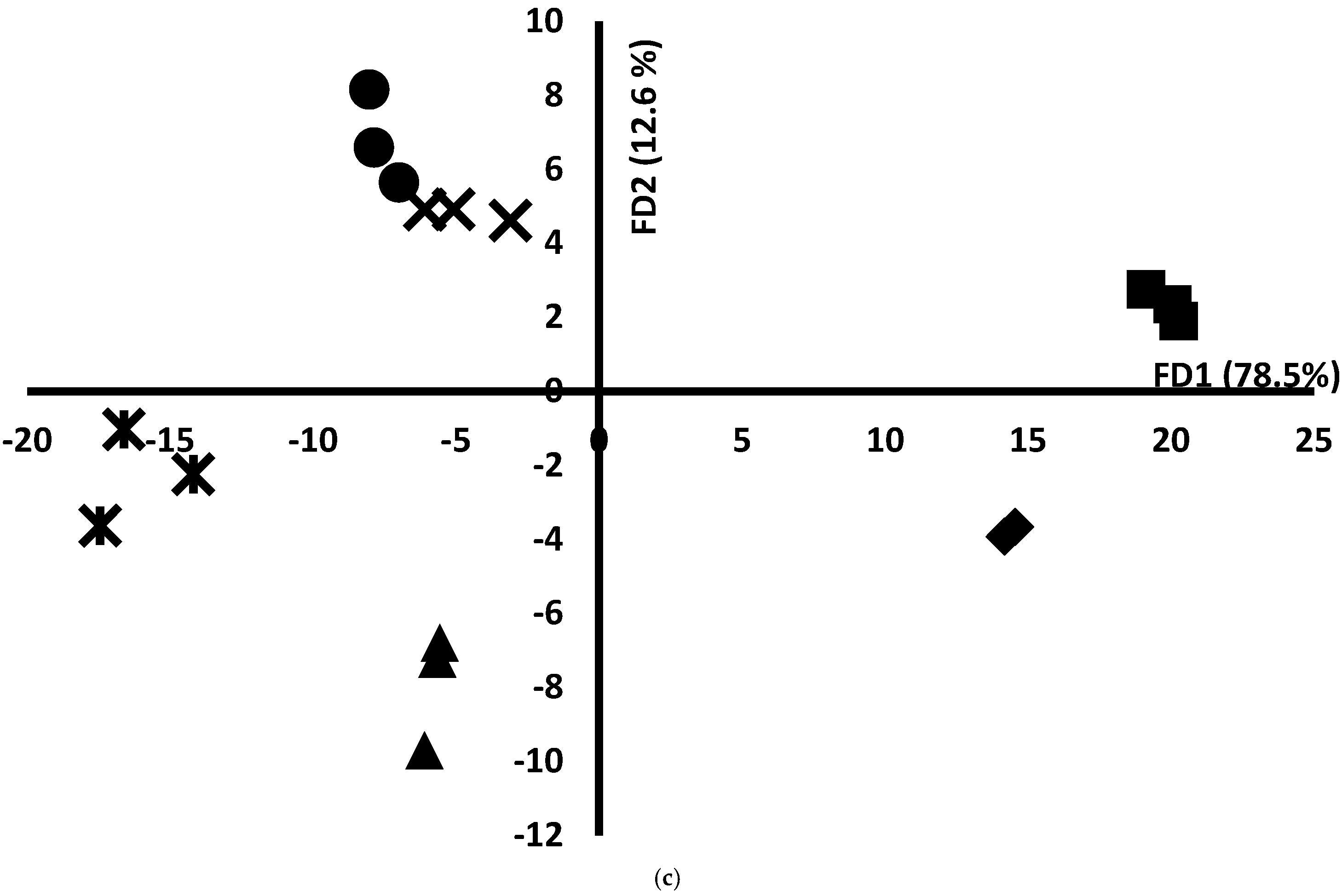
3.8. Storage Oversight Using Mid-Infrared and Fluorescence Data by Applying Chemometric Tools: PCA and FDA
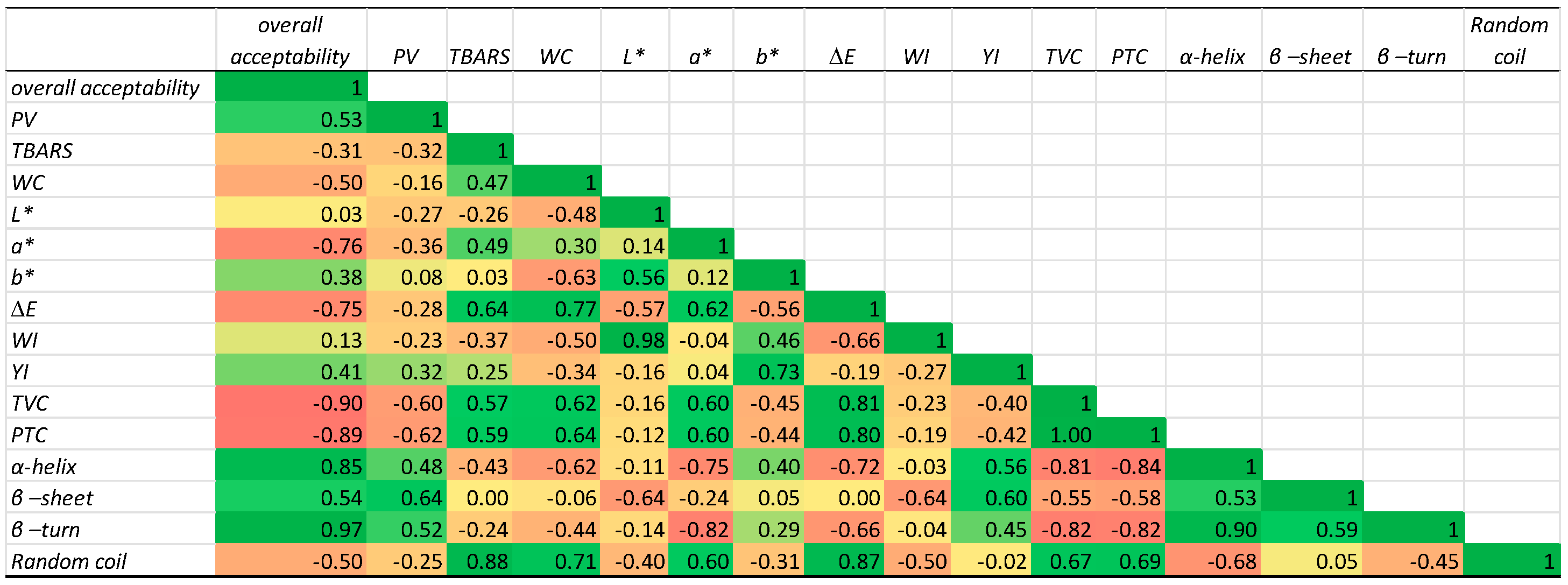
3.9. Correlation Between Structure and Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties of PPI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement:
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Litvak, M. The sturgeons (Family: Acipenseridae). Finfish Aquac. Diversif. 2010, 17, 178–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Stöck, M.; Kneitz, S.; Klopp, C.; Woltering, J.M.; Adolfi, M.C.; Feron, R.; Prokopov, D.; Makunin, A.; Kichigin, I.; et al. The sterlet sturgeon genome sequence and the mechanisms of segmental rediploidization. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Xin, M.; Gela, D.; Rodina, M.; Tučková, V.; Kašpar, V.; Siddique, M.A.M.; Shelton, W.L.; Linhart, O. Optimization of sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) egg incubation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 215, 106334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronzi, P.; Chebanov, M.; Michaels, J.T.; Wei, Q.; Rosenthal, H.; Gessner, J. Sturgeon meat and caviar production: Global update 2017. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 35, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, M.R.; Nikoo, M.; Pourshamsian, K. Omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acid ratio in cultured Beluga sturgeon. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 21, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschelli, L.; Berardinelli, A.; Dabbou, S.; Ragni, L.; Tartagni, M. Sensing technology for fish freshness and safety: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodanazary, A. Freshness assessment of shrimp Metapenaeus affinis by quality index method and estimation of its shelf life. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.; Barat, J.M.; Garcia-Breijo, E.; Ibañez, J.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Soto, J.; Llobet, E.; Brezmes, J.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Toldrá, F. Fish freshness analysis using metallic potentiometric electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 131, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjyo, Y.; Yao, T. Rapid measurement of fish freshness indices by an amperometric flow-injection system with a 16-way switching valve and immobilized enzyme reactors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 470, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Barbri, N.; Llobet, E.; El Bari, N.; Correig, X.; Bouchikhi, B. Application of a portable electronic nose system to assess the freshness of Moroccan sardines. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.; Unal Sengor, G.F.; Yilmaz, M.T. Nanoencapsulation of liquid smoke/thymol combination in chitosan nanofibers to delay microbiological spoilage of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2018, 229, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Ruzeiqi, M.H.; Al-Sabahi, J.N.; Sureshchandran, S. Effects of brine concentration on lipid oxidation and fatty acids profile of hot smoked tuna (Thunnus albacares) stored at refrigerated temperature. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; You, J.; Xiong, S. Evaluation of freshness in freshwater fish based on near infrared reflectance spectroscopy and chemometrics. LWT 2019, 106, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-W.; Hsiao, T.-C.; Chu, S.-C.; Hu, H.-H.; Chen, J.-C. Fibreoptic fluorescence spectroscopy for monitoring fish freshness. Opt. Biopsy X 2012, 8220, 82200H. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Dai, Q.; Sun, D.W.; Zeng, X.-A.; Liu, D.; Pu, H.-B. Applications of non-destructive spectroscopic techniques for fish quality and safety evaluation and inspection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughattas, F.; Vilkova, D.; Kondratenko, E.; Karoui, R. Targeted and untargeted techniques coupled with chemometric tools for the evaluation of sturgeon (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii) freshness during storage at 4 °C. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Front-face fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with chemometric tools for monitoring fish freshness stored under different refrigerated conditions. Food Control 2015, 54, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Hassoun, A. Efficiency of rosemary and basil essential oils on the shelf-life extension of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets stored at 2 °C. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Hassoun, A.; Ethuin, P. Front face fluorescence spectroscopy enables rapid differentiation of fresh and frozen-thawed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2017, 202, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojagh, S.M.; Rezaei, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Effect of chitosan coatings enriched with cinnamon oil on the quality of refrigerated rainbow trout. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Kong, C.; Luo, Y. Effect of cinnamon essential oil on bacterial diversity and shelf-life in vacuum-packaged common carp (Cyprinus carpio) during refrigerated storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, 18th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 20877–22417. [Google Scholar]
- Eymard, S. Mise en Evidence et Suivi de L’oxydation des Lipides au Cours de la Conservation et de la Transformation du Chinchard (Trachurus trachurus): Choix des Procédés; Universite De Nantes: Nantes, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Karoui, R.; Kemps, B.; Bamelis, F.; De Ketelaere, B.; Merten, K.; Schoonheydt, R.; Decuypere, E.; De Baerdemaeker, J. Development of a rapid method based on front-face fluorescence spectroscopy for the monitoring of egg freshness: 2—Evolution of egg yolk. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 223, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Mazerolles, G.; Bosset, J.O.; Debaerdemaeker, J.; Dufour, E. Utilisation of mid-infrared spectroscopy for determination of the geographic origin of Gruyère PDO and L’Etivaz PDO Swiss cheeses. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, S.; Rezaie, M.; Soltani, M.; Kamali, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Ahmadabad, M.K.; Nemati, M. Effect of whey Protein Concentrate Coating Cinamon Oil on Quality and Shelf Life of Refrigerated Beluga Sturegeon (Huso huso). J. Food Qual. 2016, 39, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Mohammadnabi, S. Effect of novel bioactive edible coatings based on jujube gum and nettle oil-loaded nanoemulsions on the shelf-life of Beluga sturgeon fillets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuás-Rey, M.; García-Soto, B.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Fuertes-Gamundi, J.R.; Aubourg, S.P. Effect of a two-step natural organic acid treatment on microbial activity and lipid damage during blue whiting (Micromesistius poutassou) chilling. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Monitoring changes in whiting (Merlangius merlangus) fillets stored under modified atmosphere packaging by front face fluorescence spectroscopy and instrumental techniques. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira De Abreu, D.A.; Paseiro Losada, P.; Maroto, J.; Cruz, J.M. Natural antioxidant active packaging film and its effect on lipid damage in frozen blue shark (Prionace glauca). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2011, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Leaw, T.; Benjakul, S.; Gokoglu, N.; Nalinanon, S. Changes in lipids and fishy odour development in skin from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) stored in ice. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, S.; Benjakul, S. Synergistic effect of tannic acid and modified atmospheric packaging on the prevention of lipid oxidation and quality losses of refrigerated striped catfish slices. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.D.; López, M.B.; Álvarez, A.; Ferrandini, E.; García, B.G.; Garrido, M.D. Sensory, physical, chemical and microbiological changes in aquacultured meagre (Argyrosomus regius) fillets during ice storage. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tironi, V.; LeBail, A.; De Lamballerie, M. Effects of pressure-shift freezing and pressure-assisted thawing on sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) quality. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piranavatharsan, U.; Jinadasa, B.K.K.K.; Jayasinghe, C.V.L. Validation of Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) Method for Measuring Secondary Lipid Oxidation Products in Fresh Indian Mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta). Food Hum. 2023, 1, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergiadis, A.; Mubiru, E.; Van Langenhove, H.; De Meulenaer, B. Malondialdehyde measurement in oxidized foods: Evaluation of the spectrophotometric thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) test in various foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, C.M.B.; Brandelli, A.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.d.C. Structural features of myofibrillar fish protein interacting with phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Li, H. Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on protein and lipid oxidation in rabbit meat. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3004–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Vidal, A.; Pantoja-De La Rosa, J.; Cuadros-Rodríguez, L.; Ayora-Cañada, M.J. Authentication of canned fish packing oils by means of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airado-Rodríguez, D.; Skaret, J.; Wold, J.P. Assessment of the quality attributes of cod caviar paste by means of front-face fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5276–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (a) | ||||||||
| Parameters | Storage Time (day) | |||||||
| 1 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 18 | |||
| L* | 54.85 ± 0.10 B | 52.62 ± 0.51 C | 51.78 ± 0.12 D | 54.42 ± 0.07 B | 50.68 ± 0.04 E | 55.55 ± 0.16 A | ||
| a* | 7.15 ± 0.15 D | 9.54 ± 0.09 C | 6.91 ± 0.10 D | 10.16 ± 0.06 B | 10.20 ± 0.07 B | 10.73 ± 0.12 A | ||
| b* | 14.80 ± 0.03 A,B | 14.58 ± 0.03 B | 13.39 ± 0.37 D | 15.22 ± 0.05 A | 13.64 ± 0.05 C,D | 13.93 ± 0.04 C | ||
| ΔE | 0.00 ± 0.00 D | 3.20 ± 0.19 C | 3.40 ± 0.19 C | 3.08 ± 0.13 C | 5.30 ± 0.12 A | 3.81 ± 0.08 B | ||
| WI | 51.94 ± 0.13 A | 49.53 ± 0.46 C | 49.47 ± 0.04 C | 50.87 ± 0.04 B | 47.81 ± 0.06 D | 52.17 ± 0.19 A | ||
| YI | 38.56 ± 0.15 B | 39.58 ± 0.32 A,B | 36.94 ± 0.93 C | 39.96 ± 0.7 A | 38.45 ± 0.17 B | 35.83 ± 0.21 C | ||
| (b) | ||||||||
| Secondary Structure | Storage Time (day) | |||||||
| 1 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 18 | |||
| α-helix (%) | 11.83 ± 0.46 A | 11.5 ± 0.10 A,B | 11.5 ± 0.10 A,B | 11.46 ± 0.05 A,B | 11.36 ± 0.05 A,B | 11.00 ± 0.00 B | ||
| β-sheet (%) | 33.76 ± 0.63 A | 34.33 ± 0.45 A | 33.66 ± 0.68 A | 33.46 ± 0.23 A | 33.96 ± 0.28 A | 33.08 ± 0.40 A | ||
| β-turn (%) | 47.06 ± 1.96 A | 46.96 ± 1.51 A | 46.93 ± 0.68 A | 46.60 ± 0.95 A | 46.33 ± 0.63 A | 46.06 ± 1.10 A | ||
| Random coil (%) | 7.36 ± 1.67 A | 8.63 ± 0.61 A | 7.96 ± 0.90 A | 8.13 ± 0.37 A | 8.20 ± 0.43 A | 8.10 ± 0.60 A | ||
| (c) | ||||||||
| Predicted/Observed | Storage Time (day) | |||||||
| 1 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 18 | % of Correct Classification | ||
| Mid-infrared spectra | ||||||||
| 1 day | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 4 days | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 7 days | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 11 days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 14 days | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 66.67% | |
| 18 days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100.00% | |
| Total | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 94.44% | |
| NADH fluorescence emission spectra | ||||||||
| 1 day | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 4 days | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 7 days | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 11 days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 66.67% | |
| 14 days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 100.00% | |
| 18 days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 100.00% | |
| Total | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 94.44% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilkova, D.; Sangaré, M.; Snoussi, A.; Karoui, R. Monitoring the Spoilage of Fresh Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) During Storage at 4 °C by Mid-Infrared and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Coupled with Chemometric Tools. Foods 2025, 14, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122051
Vilkova D, Sangaré M, Snoussi A, Karoui R. Monitoring the Spoilage of Fresh Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) During Storage at 4 °C by Mid-Infrared and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Coupled with Chemometric Tools. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122051
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilkova, Daria, Moriken Sangaré, Ahmed Snoussi, and Romdhane Karoui. 2025. "Monitoring the Spoilage of Fresh Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) During Storage at 4 °C by Mid-Infrared and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Coupled with Chemometric Tools" Foods 14, no. 12: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122051
APA StyleVilkova, D., Sangaré, M., Snoussi, A., & Karoui, R. (2025). Monitoring the Spoilage of Fresh Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) During Storage at 4 °C by Mid-Infrared and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Coupled with Chemometric Tools. Foods, 14(12), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122051





