Enhancing Oxidative Stability and Nutritional Quality of Flaxseed Oil Using Apricot, Sesame, and Black Cumin Oil Blends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cold Pressing
2.2. Oil Blending
2.3. Determination of the Fatty Acid Composition
2.4. Determination of Tocopherol Composition
2.5. Oxidative Stability—The OXITEST Method
2.6. Thrombogenicity and Atherogenicity Index
2.7. Measurement of the Antioxidant Capacity
2.8. Total Phenolic Compounds
2.9. Principal Phenolic Compound Measurement
2.10. Statistical Analysis and Description of the Results
2.11. Use and Potential Use of AI
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fatty Acid Composition and Nutritive Indices
3.2. Tocopherol Content
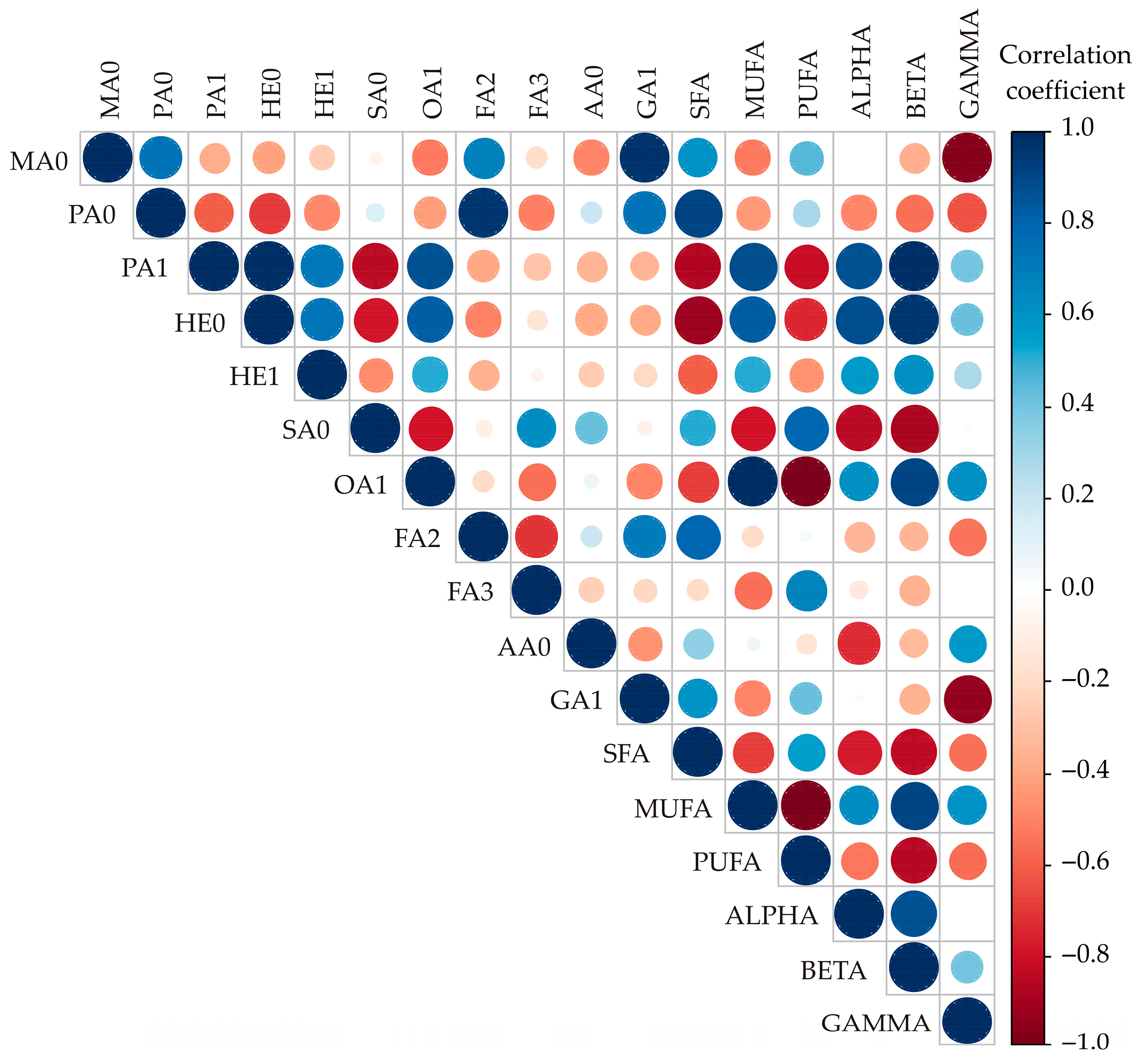
3.3. Correlation Analysis
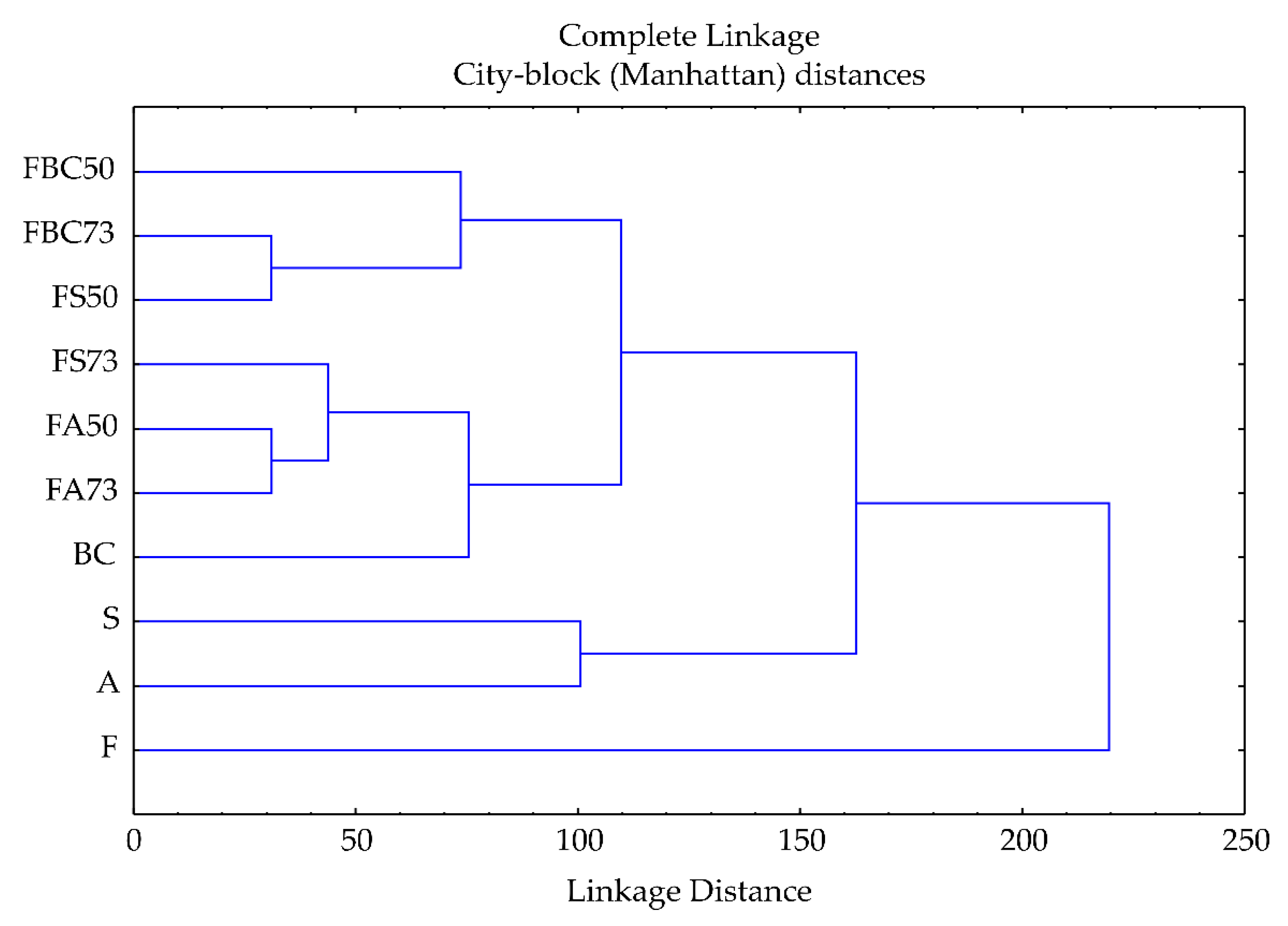
3.4. Cluster Analysis
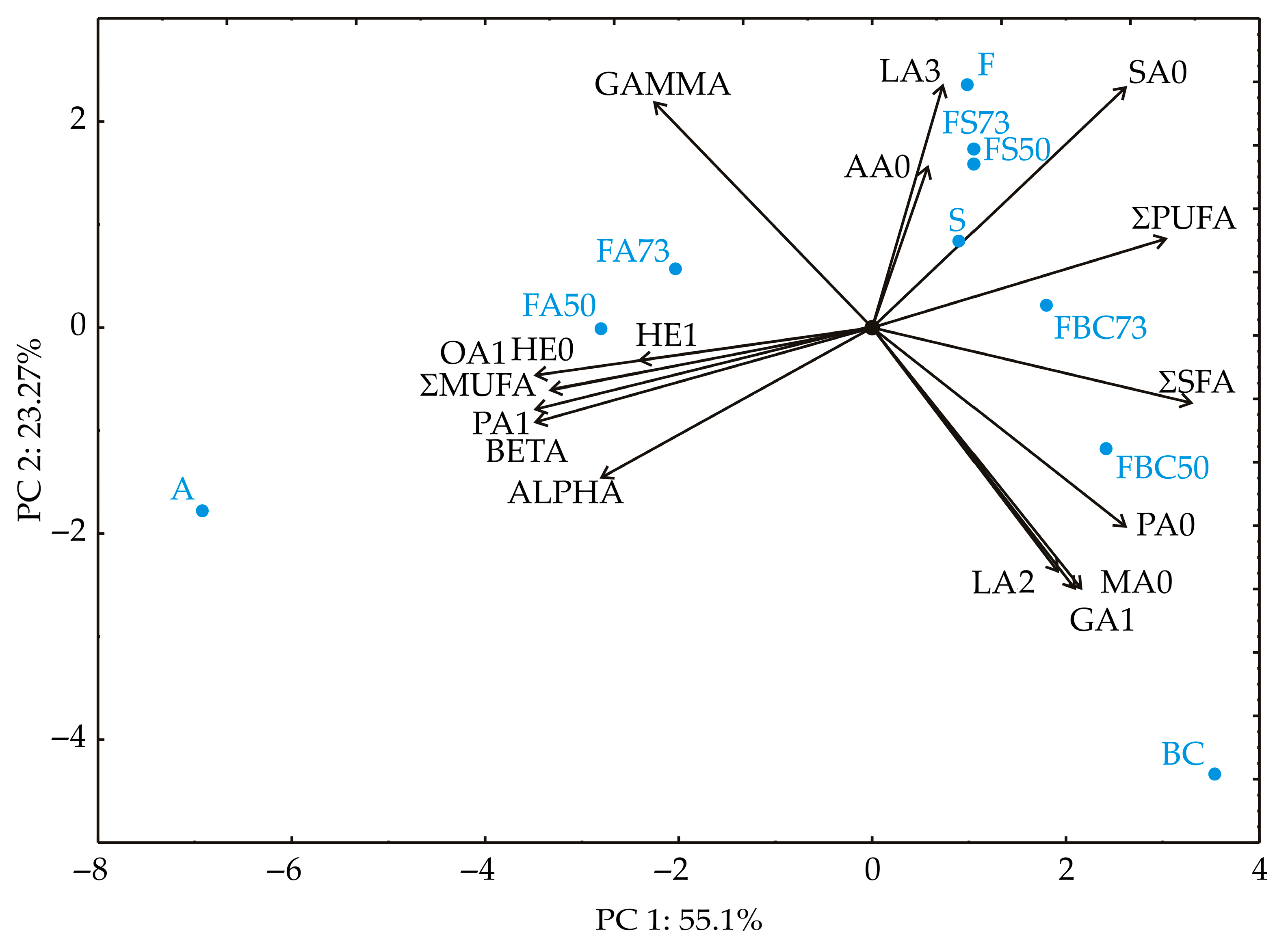
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
3.6. Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity
3.7. Principal Phenolic Compounds
3.8. Oxidative Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALPHA | α tocopherol |
| BC | Black cumin oil |
| BETA | β tocopherol |
| F | Flaxseed oil |
| FA50 | Flaxseed–apricot kernel oil blend 50% |
| FA73 | 70% flaxseed, 30% apricot kernel oil blend |
| FBC50 | Flaxseed–black cumin oil blend 50% |
| FBC73 | 70% flaxseed, 30% black cumin oil blend |
| FS50 | Flaxseed–sesame oil blend 50% |
| FS73 | 70% flaxseed, 30% sesame oil blend |
| GA1 | Gondoic acid |
| GAMA | γ tocopherol |
| HE0 | Heptadecanoic acid |
| HE1 | Heptadecenoic acid |
| HPLC | High-pressure liquid chromatography |
| IP | Induction period |
| LA2 | Linoleic acid and isomers |
| LA3 | Linolenic acid |
| MA0 | Myristic acid |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated fatty acids |
| OA1 | Oleic acid |
| PA0 | Palmitic acid |
| PA1 | Palmitoleic acid |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| S | Sesame oil |
| SA0 | Stearic acid |
| SFA | Saturated fatty acids |
| TI | Thrombogenicity index |
References
- Valgimigli, L. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant protection. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guéraud, F.; Atalay, M.; Bresgen, N.; Cipak, A.; Eckl, P.M.; Huc, L.; Jouanin, I.; Siems, W.; Uchida, K. Chemistry and biochemistry of lipid peroxidation products. Free Radical Res. 2010, 44, 1098–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykter, M.; Kymalainen, H.-R. Quality characteristics of edible linseed oil. Agric. Food Sci. 2006, 15, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teneva, O.; Zlatanov, M.; Antova, G.; Angelova-Romova, M.; Marcheva, M. Lipid composition of flax seed oil. Mod. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 2, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, V.; Gruia, A.; Raba, D.-N.; Dumbrava, D.; Moldovan, C.; Bordean, D.; Mateescu, C. Fatty acids composition and oil characteristics of linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) from Romania. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2012, 18, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Teneva, O.; Zlatanov, M. Stabilization of flaxseed oil with different antioxidants. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Young Scientists, Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 13–15 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- El-Beltagi, H.; Salama, Z.; El-Hariri, D. Evaluation of fatty acids profile and the content of some secondary metabolites in seeds of different flax cultivars (Linum usitatissimum L.). Gen. Appl. Plant Physiol. 2007, 33, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kostik, V.; Memeti, S.; Bauer, B. Fatty acid composition of edible oils and fats. Hygenic Eng. Design. 2013, 4, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Teneva, O.; Zlatanov, M.; Antova, G.; Marcheva, M. The changes of phospholipid and fatty acid composition during development of flax seeds. J. Food Packag. Sci. Tech. Technol. 2013, 1, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gandova, V.; Teneva, O.; Petkova, Z.; Iliev, I.; Stoyanova, A. Lipid composition and physicochemical parameters of flaxseed oil (Linum usitatissimum L.) from Bulgaria. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacchia, R.; Preti, R.; Vinci, G. Chemical Composition and Health Benefits of Flaxseed. Austin J. Nutri. Food Sci. 2014, 2, id1045. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, P.; Du, M.; Teng, Y.; Banwell, M.G.; Nie, H.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Wang, Y. Structural modifications of a flaxseed lignan in pursuit of higher liposolubility: Evaluation of the antioxidant and permeability properties of the resulting derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 14152–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, A.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Effects of a flaxseed-derived lignan supplement in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized, Double-Blind, Cross-Over trial. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, A.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Ye, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Qi, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effects of a flaxseed-derived lignan supplement on C-reactive protein, IL-6 and retinol-binding protein 4 in type 2 diabetic patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 101, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Tang, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, L.; Liu, L.; Deng, Q.; Yao, P. Flaxseed lignans alleviate high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice: Potential involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K. Hypocholesterolemic and antiatherosclerotic effect of flax lignan complex isolated from flaxseed. Atherosclerosis 2005, 179, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Madhagy, S.; Ashmawy, N.S.; Mamdouh, A.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Farag, M.A. A comprehensive review of the health benefits of flaxseed oil in relation to its chemical composition and comparison with other omega-3-rich oils. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, S.; Mahmoodi, M.S.; Komaki, A.; Sadeghian, R. The comparison of omega-3 and flaxseed oil on serum lipids and lipoproteins in hyperlipidemic male rats. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Khan, A.S.; Shoker, M. Flaxseed and its components in treatment of hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Angiol. 2020, 29, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.; Leach, C.; Ah-Sing, E.E.; Hussain, N.; Miller, G.J.; Millward, D.J.; Griffin, B.A. Influence of α-linolenic acid and fish-oil on markers of cardiovascular risk in subjects with an atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype. Atherosclerosis 2005, 181, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Sawane, K.; Ookoshi, K.; Kawashima, R. Supplementation with flaxseed oil rich in alpha-linolenic acid improves verbal fluency in healthy older adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajczak, N.; Tańska, M. Effect of initial quality and bioactive compounds content in cold-pressed flaxseed oils on oxidative stability and oxidation products formation during one-month storage with light exposure. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2022, 26, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilsu, A.F. A Review: Use of plants for antioxidant purposes in fish oil microencapsulation. Aquat. Food Stud. 2023, 3, AFS210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Shan, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, X. Stabilizing flaxseed oil with individual antioxidants and their mixtures. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadyro, O.I.; Sosnovskaya, A.A.; Edimecheva, I.P. Flaxseed oil stabilization using natural and synthetic antioxidants. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1700079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanić, R.; Lužaić, T.; Pezo, L.; Radić, B.; Kravić, S. Omega 3 Blends of Sunflower and Flaxseed Oil—Modeling Chemical Quality and Sensory Acceptability. Foods 2024, 13, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryjecka, M.; Kiełtyka-Dadasiewicz, A.; Michalak, M.; Rachoń, L.; Głowacka, A. Chemical Composition and antioxidant properties of oils from the seeds of five apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) cultivars. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmaz, G.; Karabulut, İ.; Topçu, A.; Asiltürk, M.; Kutlu, T. Roasting-Related changes in oxidative stability and antioxidant capacity of apricot kernel oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 87, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, S.H.M.; Emadi, B.; Sanaeimoghadam, A.; Aghkhani, M.H. Effect of moisture content and temperature on thermal behaviour of sesame seed. AUDJG–Food Technol. 2014, 38, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, P.S.; Candido, C.J.; Jaques, J.A.; Nunes, Â.A.; Caires, A.R.; Michels, F.S.; Almeida, J.A.; Filiú, W.F.; Hiane, P.A.; Nascimento, V.A.; et al. Oxidative Stability of sesame and flaxseed oils and their effects on morphometric and biochemical parameters in an animal model. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3359–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharby, S.; Harhar, H.; Guillaume, D.; Roudani, A.; Boulbaroud, S.; Ibrahimi, M.; Ahmad, M.; Sultana, S.; Hadda, T.B.; Chafchaouni-Moussaoui, I.; et al. Chemical investigation of Nigella sativa L. seed oil produced in Morocco. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2013, 14, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albakry, Z.; Karrar, E.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Oz, E.; Proestos, C.; El Sheikha, A.F.; Oz, F.; Wu, G.; Wang, X. Nutritional Composition and Volatile Compounds of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seed, Fatty Acid Composition and Tocopherols, Polyphenols, and Antioxidant Activity of Its Essential Oil. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Uddin, M.J.; Dash, R.; Sikder, M.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Timalsina, B.; Munni, Y.A.; Sarker, P.P.; et al. Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.; Idrus, R.H.; Mokhtar, M.H. Effects of Nigella sativa on type-2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.; Turan, S.; Kiralan, M.; Ramadan, M.F. Antioxidant Properties of thymol, carvacrol, and thymoquinone and its efficiencies on the stabilization of refined and stripped corn oils. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 15, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabrenović, B.B.; Dimić, E.B.; Novaković, M.M.; Tešević, V.V.; Basić, Z.N. The most important bioactive components of cold pressed oil from different pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) seeds. LWT 2013, 55, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Grover, K.; Kaur, G. Development of rice bran oil blends for quality improvement. Food Chem. 2014, 173, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 12966-2; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Gas Chromatography of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters—Part 2: Preparation of Methyl Esters of Fatty Acids. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 12966-4; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Gas Chromatography of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters—Part 4: Determination by Capillary Gas Chromatography. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Gimeno, E.; Castellote, A.I.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; De La Torre, M.C.; López-Sabater, M.C. Rapid determination of vitamin E in vegetable oils by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 881, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnala, R.S.; Dunford, N.T.; Dashiell, K.E. Tocopherol, phytosterol and phospholipid compositions of new high oleic peanut cultivars. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.K.; Khoo, M.Z.; Ng, S.Y.; Thoo, Y.Y.; Wan Aida, W.M.; Ho, C.W. Effect of ethanol concentration, extraction time and extraction temperature on the recovery of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Orthosiphon stamineus extracts. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Kua, S.F.; Adan, D.; Teh, H.F.; Lim, C.M.; Ong, A.; Ismail, S.; Lee, H.H. Preservation of phytonutrients, antioxidants, and minor lipids in palm oil through mild thermal processing. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radočaj, O.; Vujasinović, V.; Dimić, E.; Basić, Z. Blackberry (Rubus fruticosus L.) and raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) seed oils extracted from dried press pomace after longterm frozen storage of berries can be used as functional food ingredients. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyan, Z.; Bedgood, D.R.; Bishop, A.G.; Prenzler, P.D.; Robards, K. Endogenous biophenol, fatty acid and volatile profiles of selected oils. Food Chem. 2006, 100, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasioula-Margari, M.; Tsabolatidou, E. Extraction, separation, and identification of phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil by HPLC-DAD and HPLC-MS. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizzi, L.; Chatzitzika, C.; Gatt, R.; Valdramidis, V. HPLC analysis of phenolic compounds and flavonoids with overlapping Peaks. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 58, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasote, D.M.; Badhe, Y.S.; Hegde, M.V. Effect of mechanical press oil extraction processing on quality of linseed oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 42, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Elimam, D.M.; Afifi, S.M. Outgoing and potential trends of the omega-3 rich linseed oil quality characteristics and rancidity management: A comprehensive review for maximizing its food and nutraceutical applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrygiannis, I.; Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Bozinou, E.; Mantzourani, C.; Chatzilazarou, A.; Makris, D.P.; Lalas, S.I. Exploring the chemical composition and antioxidant properties of apricot kernel oil. Separations 2023, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symoniuk, E.; Ratusz, K.; Ostrowska-Ligęza, E.; Krygier, K. Impact of selected chemical characteristics of cold-pressed oils on their oxidative stability determined using the rancimat and pressure differential scanning calorimetry method. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 11, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.F.; Wahdan, K.M.M. Blending of corn oil with black cumin (Nigella sativa) and coriander (Coriandrum sativum) seed oils: Impact on functionality, stability and radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2011, 132, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupkin, M.; Zambelli, A. Detrimental impact of trans fats on human health: Stearic acid-rich fats as possible substitutes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkhoud, H.; M’Rabet, Y.; Ali, M.G.; Mezni, M.; Hosni, K. Essential oils as flavoring and preservative agents: Impact on volatile profile, sensory attributes, and the oxidative stability of flavored extra virgin olive oil. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličkovska, S.K.; Moţ, A.C.; Mitrev, S.; Gulaboski, R.; Brühl, L.; Mirhosseini, H.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R.; Matthäus, B. Bioactive compounds and “in vitro” antioxidant activity of some traditional and non-traditional cold-pressed edible oils from Macedonia. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, J.; Kruk, J. RP-LC for determination of plastochromanol, tocotrienols and tocopherols in plant oils. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, I.A.; Billedo, G.; El-Doush, I.I. Levels of selenium, dl-α-tocopherol, dl-γ-tocopherol, all-trans-retinol, thymoquinone and thymol in different brands of Nigella sativa seeds. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, P.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Lundgren, L.N.; Åman, P. HPLC Method for analysis of secoisolariciresinol diglucoside in flaxseeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5216–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.A.; El-Ahmady, S.H. Prediction of thymoquinone content in black seed oil using multivariate analysis: An efficient model for its quality assessment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 124, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, N.T. Oxidative stability of sunflower seed oil. In Sunflower: Chemistry, Production, Processing, and Utilization; Martínez-Force, E., Dunford, N.T., Salas, J.J., Eds.; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2015; pp. 465–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, A.E. The chemical composition and the content of volatile oil: Potential factors that can contribute to the oxidative stability of Nigella sativa L. crude oil. J. Diet. Suppl. 2011, 8, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, A.S.; Moshtaghi, H.; Kiani, H.; Ardakani, S.A.Y.; Marvast, G.H.P. Antioxidant efficacy of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) cake extract on stability of refined sesame oil during storage time. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluata, S. Effect of extraction method on biochemical properties and oxidative stability of apricot seed oil. In Proceedings of the Akademik Gıda Conference, Malatya, Turkey, 10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Chen, W.; Huyan, Z.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Yu, X. Impact of linolenic acid on oxidative stability of rapeseed oils. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3184–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K. Synergistic Effect of Sesame Lignans and Tocopherols. In Food and Free Radicals; Hiramatsu, M., Yoshikawa, T., Inoue, M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component (%) | F | A | S | BC | FA73 | FA50 | FS73 | FS50 | FBC73 | FBC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA0 | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 f | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 bc | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 bc | 0.08 ± 0.00 d | 0.12 ± 0.01 e |
| PA0 | 5.82 ± 0.05 b | 5.21 ± 0.06 a | 10.06 ± 0.08 f | 13.11 ± 0.05 g | 5.35 ± 0.06 a | 5.43 ± 0.09 a | 6.88 ± 0.06 c | 7.82 ± 0.08 d | 7.90 ± 0.11 d | 9.27 ± 0.11 e |
| PA1 | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.93 ± 0.02 d | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.49 ± 0.02 b | 0.53 ± 0.01 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| HE0 | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a |
| HE1 | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| SA0 | 4.43 ± 0.03 h | 0.54 ± 0.01 a | 3.83 ± 0.06 f | 2.48 ± 0.02 c | 3.21 ± 0.04 d | 2.28 ± 0.04 b | 4.29 ± 0.04 gh | 4.16 ± 0.04 g | 3.87 ± 0.04 f | 3.44 ± 0.05 e |
| OA1 | 22.91 ± 0.11 a | 69.45 ± 0.18 i | 42.21 ± 0.20 g | 24.93 ± 0.11 c | 36.20 ± 0.11 f | 45.96 ± 0.17 h | 28.42 ± 0.10 d | 32.14 ± 0.12 e | 23.16 ± 0.08 a | 23.76 ± 0.08 b |
| LA2 | 14.33 ± 0.08 a | 23.57 ± 0.09 e | 43.37 ± 0.07 i | 58.80 ± 0.07 j | 17.02 ± 0.11 b | 18.74 ± 0.08 c | 22.80 ± 0.09 d | 28.53 ± 0.11 g | 27.02 ± 0.08 f | 35.72 ± 0.08 h |
| LA3 | 52.27 ± 0.17 f | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 37.34 ± 0.10 de | 26.80 ± 0.13 b | 37.30 ± 0.17 d | 27.05 ± 0.04 bc | 37.75 ± 0.15 e | 27.46 ± 0.11 c |
| AA0 | 0.09 ± 0.00 b | 0.07 ± 0.00 ab | 0.28 ± 0.01 e | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.08 ± 0.00 ab | 0.07 ± 0.00 ab | 0.15 ± 0.01 c | 0.18 ± 0.01 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 ab | 0.06 ± 0.00 a |
| GA1 | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.20 ± 0.01 g | 0.09 ± 0.00 d | 0.08 ± 0.00 c | 0.08 ± 0.00 c | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.11 ± 0.00 e | 0.13 ± 0.00 f |
| ΣSFA | 10.42 ± 0.02 d | 5.93 ± 0.07 a | 14.20 ± 0.13 h | 15.86 ± 0.06 i | 8.75 ± 0.01 c | 7.88 ± 0.13 b | 11.39 ± 0.02 e | 12.21 ± 0.05 f | 11.96 ± 0.15 f | 12.91 ± 0.06 g |
| ΣMUFA | 22.97 ± 0.11 a | 70.46 ± 0.16 i | 42.27 ± 0.20 g | 25.13 ± 0.12 c | 36.81 ± 0.13 f | 46.57 ± 0.18 h | 28.50 ± 0.10 d | 32.20 ± 0.12 e | 23.27 ± 0.08 a | 23.89 ± 0.08 b |
| ΣPUFA | 66.60 ± 0.08 j | 23.60 ± 0.09 a | 43.52 ± 0.06 b | 59.00 ± 0.06 f | 54.36 ± 0.21 d | 45.54 ± 0.05 c | 60.10 ± 0.08 g | 55.58 ± 0.07 e | 64.76 ± 0.07 i | 63.18 ± 0.03 h |
| AI | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.005 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| TI | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.005 | 0.07 ± 0.004 | 0.08 ± 0.003 | 0.10 ± 0.008 | 0.08 ± 0.007 | 0.11 ± 0.009 |
| ALPHA (mg/100 g) | 0.96 ± 0.04 d | 2.38 ± 0.06 g | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 1.09 ± 0.04 d | 1.43 ± 0.03 e | 1.70 ± 0.04 f | 0.67 ± 0.03 c | 0.51 ± 0.02 b | 1.03 ± 0.06 d | 1.04 ± 0.05 d |
| BETA (mg/100 g) | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 3.08 ± 0.06 d | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.91 ± 0.04 b | 1.53 ± 0.02 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| GAMMA (mg/100 g) | 30.85 ± 0.13 d | 37.36 ± 0.11 g | 38.98 ± 0.18 h | 11.27 ± 0.11 a | 31.35 ± 0.09 d | 32.42 ± 0.17 e | 33.06 ± 0.11 e | 34.16 ± 0.13 f | 22.18 ± 0.40 c | 15.79 ± 0.19 b |
| IP (h) | 7.15 | 55.17 | 33.47 | 30.49 | 9.23 | 11.42 | 8.31 | 10.53 | 8.56 | 10.35 |
| Oil/Blend | Phenolics mg GAE/g Oil | Antioxidant Capacity μmol TE/g Oil |
|---|---|---|
| F | 1.0 | 25 ± 1.4 |
| A | 0.8 | 20 ± 1.0 |
| S | 1.2 | 30 ± 1.6 |
| BC | 2.5 | 75 ± 3.5 |
| FA73 | 0.9 | 24.7 ± 1.2 |
| FA50 | 0.9 | 24.5 ± 1.3 |
| FS73 | 1.1 | 28.3 ± 1.4 |
| FS50 | 1.1 | 30.5 ± 1.5 |
| FBC73 | 1.4 | 44.5 ± 2.2 |
| FBC50 | 1.8 | 57.5 ± 2.4 |
| Oil | Principal Phenolics | Amount mg/g Oil |
|---|---|---|
| F | Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside | 0.29 |
| A | Hydroxycinnamic acids | 0.20 |
| Flavonoids | 0.17 | |
| S | Sesamin | 4.10 |
| Sesamolin | 0.85 | |
| BC | Thymoquinone | 2.10 |
| Carvacrol | 0.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhović, D.; Cvijanović, G.; Bajagić, M.; Pezo, L.; Pejić, L.; Rabrenović, B. Enhancing Oxidative Stability and Nutritional Quality of Flaxseed Oil Using Apricot, Sesame, and Black Cumin Oil Blends. Foods 2025, 14, 2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14112000
Muhović D, Cvijanović G, Bajagić M, Pezo L, Pejić L, Rabrenović B. Enhancing Oxidative Stability and Nutritional Quality of Flaxseed Oil Using Apricot, Sesame, and Black Cumin Oil Blends. Foods. 2025; 14(11):2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14112000
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhović, Dino, Gorica Cvijanović, Marija Bajagić, Lato Pezo, Lazar Pejić, and Biljana Rabrenović. 2025. "Enhancing Oxidative Stability and Nutritional Quality of Flaxseed Oil Using Apricot, Sesame, and Black Cumin Oil Blends" Foods 14, no. 11: 2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14112000
APA StyleMuhović, D., Cvijanović, G., Bajagić, M., Pezo, L., Pejić, L., & Rabrenović, B. (2025). Enhancing Oxidative Stability and Nutritional Quality of Flaxseed Oil Using Apricot, Sesame, and Black Cumin Oil Blends. Foods, 14(11), 2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14112000






