Characterization of the Quality and Flavor in Chinese Sausage: Comparison Between Cantonese, Five-Spice, and Mala Sausages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Treatment
2.2. Sensory Evaluation
2.3. Electronic Nose (E-Nose) Analysis
2.4. Electronic Tongue (E-Tongue) Analysis
2.5. Free Amino Acid (FAA) Analysis
2.6. HS-GC-IMS Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
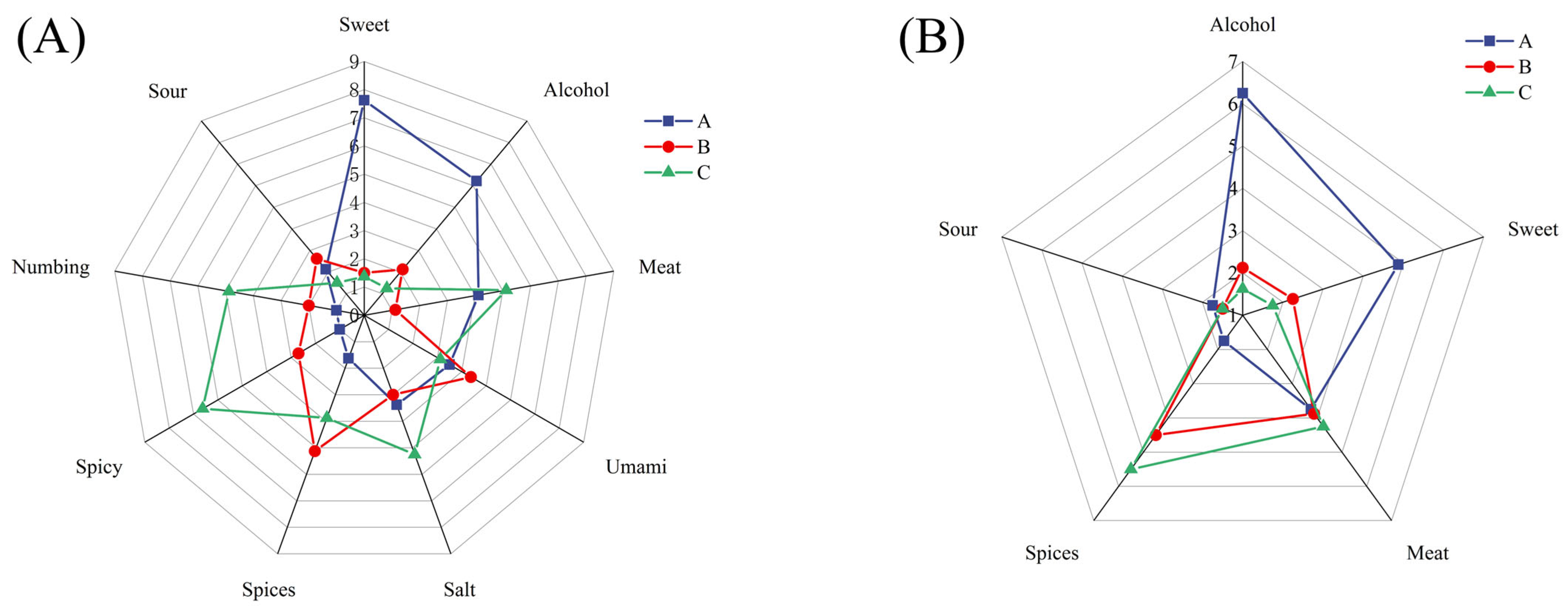
3.1. Sensory Analysis
3.2. E-Nose Analysis
3.3. E-Tongue Analysis
3.4. FAAs
3.5. Volatile Compounds in Sausages
3.5.1. GC-IMS Analysis of Volatile Compounds
3.5.2. Identification and Comparison of Flavor Compounds
3.5.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Sausages
3.5.4. Screening and Analysis of Volatile Characteristic Markers of Various Sausage Types
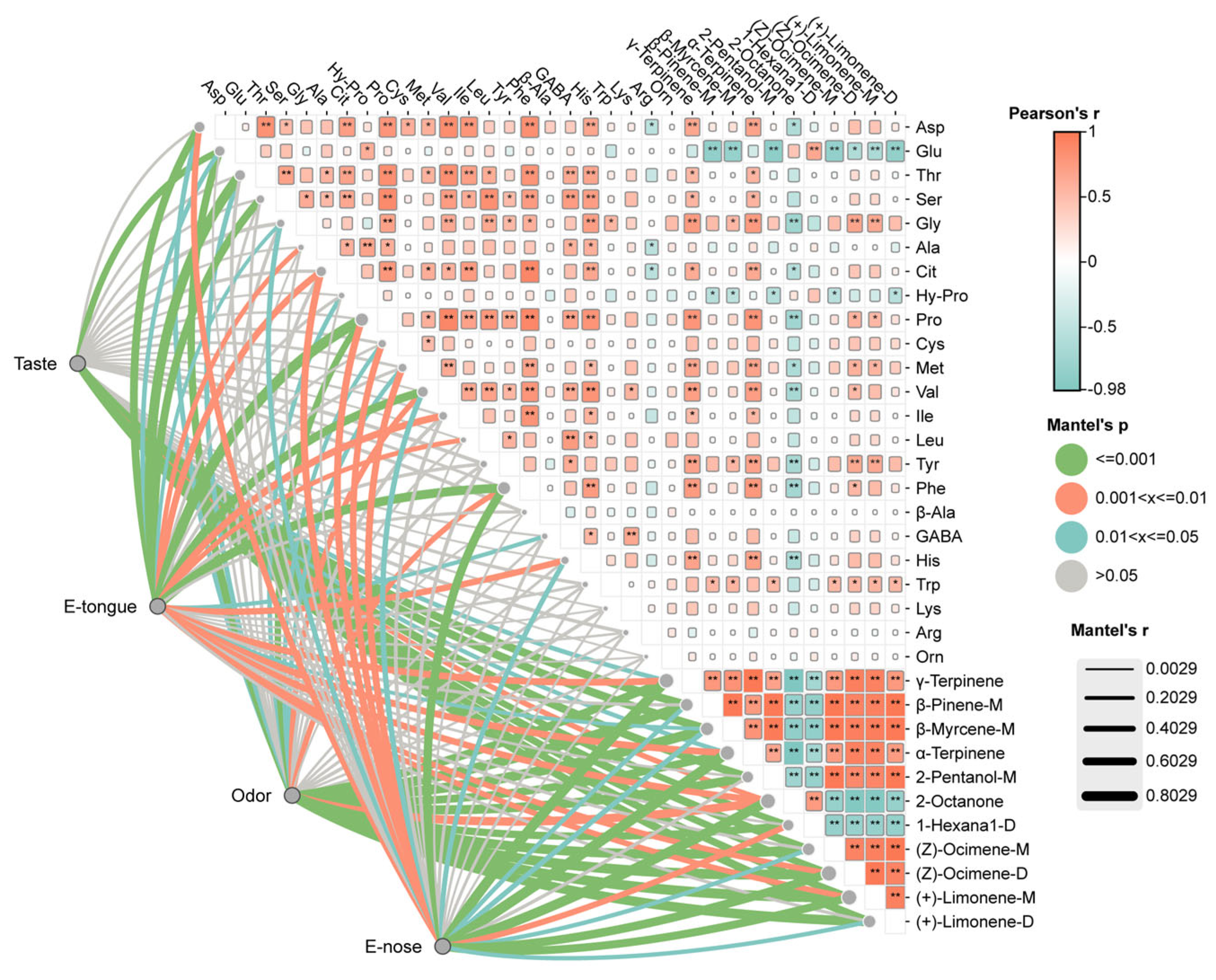
4. Relationship Between Sensory Evaluation, E-Nose, E-Tongue, FAAs, and VOAs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Bedia, M.; Bañón, S. Relationship between Flavour Deterioration and the Volatile Compound Profile of Semi-Ripened Sausage. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sui, Y.; Liu, J.; Kong, B.; Li, H.; Qin, L.; Chen, Q. Analysis and Comparison of the Quality and Flavour of Traditional and Conventional Dry Sausages Collected from Northeast China. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, S.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y. Interrelationship between Myoglobin Oxidation and Lipid Oxidation during the Processing of Cantonese Sausage with D-sodium Erythorbate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Niu, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.; Yang, M.; Zhou, K.; Chen, S.; He, L.; et al. Effect of Oxidized Lipids Stored under Different Temperatures on Muscle Protein Oxidation in Sichuan-Style Sausages during Ripening. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wen, R.; Wang, Y.; Qin, L.; Kong, B. Characterisation of the Flavour Profile of Dry Fermented Sausages with Different NaCl Substitutes Using HS-SPME-GC-MS Combined with Electronic Nose and Electronic Tongue. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Xu, N.; Sun, J.; Xu, X. Effects of Different Mixed Starter Cultures on Microbial Communities, Taste and Aroma Compounds of Traditional Chinese Fermented Sausages. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Huang, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, X. Evolution of Free Amino Acids, Biogenic Amines and Volatile Compounds in Fermented Sausages Inoculated with Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum and Staphylococcus Simulans. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 3642–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; An, Y.; Dong, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Yan, J.; Fang, B.; Ren, F.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Commercially Available Flavor Oil Sausages and Smoked Sausages. Molecules 2024, 29, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lv, Y.; Wen, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Characterization of Selected Harbin Red Sausages on the Basis of Their Flavour Profiles Using HS-SPME-GC/MS Combined with Electronic Nose and Electronic Tongue. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, E.-S.; Kim, B.-M.; Oh, M.-H. Potential Correlation between Microbial Diversity and Volatile Flavor Compounds in Different Types of Korean Dry-Fermented Sausages. Foods 2022, 11, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Characterization of Key Volatile Flavor Compounds in Dried Sausages by HS-SPME and SAFE, Which Combined with GC-MS, GC-O and OAV. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cacho, M.P.R.; Galán-Soldevilla, H.; León Crespo, F.; Molina Recio, G. Determination of the Sensory Attributes of a Spanish Dry-Cured Sausage. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Yue, J. Impact of Cinnamaldehyde on the Formation of Biogenic Amines, Microbiological, Physicochemical, and Sensory Quality of Smoked Horsemeat Sausage. LWT 2024, 195, 115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, M.T.; Nys, A.; Kvarberg, R.; Hersleth, M. Effects of NaCl Substitution on the Sensory Properties of Sausages: Temporal Aspects. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serikkyzy, M.; Baybolova, L.; Kulazhanov, T.; Balev, D.; Vlahova-Vangelova, D. Enhancing the Quality and Shelf Life of Semi-smoked Sausages with Sesame Seed Additions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 2727–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Xiong, H.; Cai, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Miao, B. Evaluation of Loquat Jam Quality at Different Cooking Times Based on Physicochemical Parameters, GC-IMS and Intelligent Senses. Foods 2024, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Yi, Y.; Qiao, M.; Fu, Y. Characterization of Flavor and Taste Profile of Different Radish (Raphanus Sativus L.) Varieties by Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry (GC/IMS) and E-Nose/Tongue. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, C.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Cai, X.; Li, X.; Qiao, M. Identification of Characteristic Flavor Quality of Ceramic-Pot Sealed Meat after Reheating Based on HS-GC-IMS, Bionic Sensory Combined Chemometrics. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisnerospineda, O.; Torrestapia, L.; Gutierrezpacheco, L.; Contrerasmartin, F.; Gonzalezestrada, T.; Perazasanchez, S. Capsaicinoids Quantification in Chili Peppers Cultivated in the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, S.; Ho, C.-T. Chemical Composition, Sensory Properties and Application of Sichuan Pepper (Zanthoxylum Genus). Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.Y.; Jang, Y.; Cho, H.; Lee, C.; Jang, K.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Shin, J.; Oh, U. Hydroxy-α-sanshool Activates TRPV1 and TRPA1 in Sensory Neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smutzer, G.; Devassy, R.K. Integrating TRPV1 Receptor Function with Capsaicin Psychophysics. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 2016, 1512457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvis, I.C.J.; Luning, P.A.; Klose, N.; Jansen, M.; Van Ruth, S.M. Similarities and Differences of the Volatile Profiles of Six Spices Explored by Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Qiao, L.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Huang, D.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, D. Explorative Study on Volatile Organic Compounds of Cinnamon Based on GC-IMS. Metabolites 2024, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kong, B.; Han, Q.; Xia, X.; Xu, L. The Role of Bacterial Fermentation in Lipolysis and Lipid Oxidation in Harbin Dry Sausages and Its Flavour Development. LWT 2017, 77, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhu, C.; Deng, J.; Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, H. Effect of Sichuan Pepper (Zanthoxylum Genus) Addition on Flavor Profile in Fermented Ciba Chili (Capsicum Genus) Using GC-IMS Combined with E-Nose and E-Tongue. Molecules 2023, 28, 5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, K.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, H.; Xiong, S.; An, Y.; Hu, Y. Insights into the Potential Mechanism of Liquid Nitrogen Spray Freezing’s Influence on Volatile Compounds in Surimi Gels with Different Cross-Linking Degrees: Focus on Oxidation, Protein Structure, Intermolecular Force and Free Amino Acid Alterations. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Guan, S.; Liu, C.; Yu, C.; Yao, Z.; Wan, H.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y. Detection and Analysis of VOCs in Chili Pepper Based on HS-SPME-GC × GC-TOFMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS Techniques. Veg. Res. 2024, 4, e021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivane, N.M.A.; Haruna, S.A.; Zekrumah, M.; Roméo Elysé, F.K.; Hassan, M.O.; Hashim, S.B.H.; Tahir, H.E.; Zhang, D. Composition, Mechanisms of Tingling Paresthesia, and Health Benefits of Sichuan Pepper: A Review of Recent Progress. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Finardi, S.; De Souza, C.K.; Meinert, C.; Pateiro, M.; Hoffmann, T.G.; Domínguez, R.; Bertoli, S.L.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Applications of Electronic Nose, Electronic Eye and Electronic Tongue in Quality, Safety and Shelf Life of Meat and Meat Products: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, W.; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, A.; Kumakura, K.; Matsuoka, H. Metabolism of Glutamic Acid to Alanine, Proline, and Γ-aminobutyric Acid during Takuan-zuke Processing of Radish Root. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, T.; Li, P. Effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum and Staphylococcus Xylosus on Flavour Development and Bacterial Communities in Chinese Dry Fermented Sausages. Food Res. Int. 2020, 135, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthan, R.; Subhash, K.; Longvah, T. Capsaicinoids, Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Profiles in Different Fruit Components of the World Hottest Naga King Chilli (Capsicum Chinense Jacq). Food Chem. 2018, 238, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinther Schmidt, C.; Olsen, K.; Mouritsen, O.G. Umami Potential of Fermented Beverages: Sake, Wine, Champagne, and Beer. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 128971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, A.; Chen, W.; Hu, L.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Characterisation of Key Volatile Compounds in Fermented Sour Meat after Fungi Growth Inhibition. LWT 2022, 165, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Gómez, B.; Salahange, L.; Tapia, J.A.; Martín, M.T.; Ares, A.M.; Bernal, J. Fast Chromatographic Determination of Free Amino Acids in Bee Pollen. Foods 2022, 11, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljanec, I.; Marušić Radovčić, N.; Petričević, S.; Karolyi, D.; Listeš, E.; Medić, H. Proteolysis and Protein Oxidation throughout the Smoked Dry-Cured Ham Process. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.D.S.; Figueiredo, H.M.D.; Stamford, T.L.M.; Silva, L.H.M.D. Inhibition of Listeria Monocytogenes by Melaleuca Alternifolia (Tea Tree) Essential Oil in Ground Beef. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 293, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, K.; Guo, H.; Geng, Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Qin, P.; Ren, G. Characterization of Volatile Compounds in Differently Coloured Chenopodium Quinoa Seeds before and after Cooking by Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Liao, G.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G. Identification of Characteristic Flavor Compounds and Small Molecule Metabolites during the Ripening Process of Nuodeng Ham by GC-IMS, GC–MS Combined with Metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, P.; Song, J.; Lin, S. The Characteristic Terpenes in Sea Cucumber Soaked in Star Anise Solution Were Characterized by HS-SPME-GC–MS and PCA Analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkara, K.T.; Amanpour, A.; Guclu, G.; Kelebek, H.; Selli, S. GC-MS-Olfactometric Differentiation of Aroma-Active Compounds in Turkish Heat-Treated Sausages by Application of Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.N.; Ray, C.A. Control of Maillard Reactions in Foods: Strategies and Chemical Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4537–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | Ingredients |
|---|---|
| Mala sausage | chili powder, Sichuan pepper powder, salt, sugar, soy sauce, cooking wine, ginger, five-spice powder |
| Five-Spice sausage | salt, sugar, soy sauce, cooking wine, ginger, five-spice powder |
| Cantonese sausage | salt, sugar, soy sauce, cooking wine, ginger, white pepper powder |
| No. | Compounds | CAS | Formula | MW | RI | Rt [sec] | Dt [a.u.] | Peak Intensity Value/mv | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||||||||
| a1 | (+)-Limonene-D | C138863 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1210.8 | 744.349 | 1.29503 | 1381.73 ± 101.36 c | 6054.77 ± 144.94 b | 6821.58 ± 156.63 a |
| a2 | (+)-Limonene-M | C138863 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1210.8 | 744.349 | 1.2165 | 835.75 ± 27.48 c | 2602.98 ± 73.14 b | 4107.22 ± 51.94 a |
| a3 | (Z)-Ocimene-D | C470826 | C10H18O | 154.3 | 1212.3 | 749.263 | 1.72854 | 302.26 ± 25.22 c | 1444.51 ± 71.30 b | 2587.69 ± 115.52 a |
| a4 | (Z)-Ocimene-M | C470826 | C10H18O | 154.3 | 1211.5 | 746.632 | 1.2874 | 1165.85 ± 96.94 c | 5728.16 ± 143.35 b | 6508.91 ± 162.47 a |
| a5 | α-Terpinene | C99865 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1185 | 667.244 | 1.21285 | 131.57 ± 14.59 c | 662.74 ± 22.79 b | 2836.15 ± 140.22 a |
| a6 | β-Myrcene-D | C123353 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1168.8 | 630.266 | 1.28241 | 464.38 ± 16.44 c | 872.67 ± 5.69 b | 1696.69 ± 22.66 a |
| a7 | β-Myrcene-M | C123353 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1169.1 | 630.862 | 1.21729 | 547.26 ± 44.83 c | 2342.59 ± 63.78 b | 2856.67 ± 41.45 a |
| a8 | β-Pinene-D | C127913 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1122.8 | 525.358 | 1.64156 | 52.33 ± 3.49 c | 419.40 ± 17.42 b | 1347.47 ± 48.22 a |
| a9 | β-Pinene-M | C127913 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1125.9 | 532.452 | 1.22173 | 941.54 ± 99.78 c | 6463.46 ± 122.14 b | 7441.16 ± 157.46 a |
| a10 | γ-Terpinene | C99854 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1253.6 | 883.746 | 1.20841 | 197.11 ± 9.43 c | 1112.88 ± 16.59 b | 4289.87 ± 187.44 a |
| a11 | Butylbenzene | C104518 | C10H14 | 134.2 | 1301.1 | 1036.685 | 1.55305 | 413.79 ± 16.28 b | 1042.79 ± 47.63 a | 194.57 ± 7.08 c |
| a12 | 1-Butano1-D | C71363 | C4H10O | 74.1 | 1152.1 | 592.094 | 1.38008 | 351.63 ± 16.77 b | 907.42 ± 41.08 a | 234.38 ± 18.40 c |
| a13 | 1-Butano1-M | C71363 | C4H10O | 74.1 | 1151.6 | 591.003 | 1.18211 | 845.36 ± 43.08 b | 1437.00 ± 27.07 a | 449.59 ± 26.02 c |
| a14 | 1-Pentanol-D | C71410 | C5H12O | 88.1 | 1270.1 | 937.241 | 1.50791 | 602.58 ± 25.21 a | 461.03 ± 57.09 b | 163.60 ± 9.41 c |
| a15 | 1-Pentanol-M | C71410 | C5H12O | 88.1 | 1269.8 | 936.371 | 1.24896 | 2560.00 ± 68.33 b | 2433.33 ± 90.68 c | 3078.24 ± 93.57 a |
| a16 | 2-Methyl-1-propanol | C78831 | C4H10O | 74.1 | 1103.3 | 480.693 | 1.17181 | 1055.47 ± 32.06 c | 2060.64 ± 91.48 a | 1758.26 ± 88.98 b |
| a17 | 1-Propanol-D | C71238 | C3H8O | 60.1 | 1048.1 | 406.778 | 1.25236 | 2631.11 ± 116.51 a | 2345.42 ± 43.46 b | 1058.19 ± 44.46 c |
| a18 | 1-Propanol-M | C71238 | C3H8O | 60.1 | 1049.1 | 407.995 | 1.11553 | 2337.42 ± 92.51 a | 2281.30 ± 101.36 a | 1458.09 ± 19.21 b |
| a19 | 2-Butanol | C586629 | C10H16 | 136.2 | 1292.2 | 1009.333 | 1.21881 | 209.95 ± 20.42 c | 625.60 ± 8.25 b | 1609.68 ± 118.15 a |
| a20 | 2-Methy1-1-butanol-D | C137326 | C5H12O | 88.1 | 1219 | 771.205 | 1.47937 | 1604.34 ± 81.59 c | 3155.10 ± 77.85 a | 1789.69 ± 43.06 b |
| a21 | 2-Methy1-1-butanol-M | C137326 | C5H12O | 88.1 | 1218.4 | 769.028 | 1.23527 | 3379.02 ± 92.35 b | 3695.32 ± 73.21 a | 3132.56 ± 88.50 c |
| a22 | 2-Pentanol-D | C6032297 | C5H12O | 88.1 | 1128.3 | 537.853 | 1.44523 | 226.92 ± 29.53 c | 2432.11 ± 134.72 a | 415.10 ± 19.74 b |
| a23 | 2-Pentanol-M | C6032297 | C5H12O | 88.1 | 1127.8 | 536.743 | 1.2028 | 286.17 ± 28.75 b | 2791.81 ± 42.58 a | 2879.83 ± 48.30 a |
| a24 | 3-Heptanol | C589822 | C7H16O | 116.2 | 1270.4 | 938.417 | 1.32364 | 853.40 ± 27.72 a | 671.10 ± 41.74 b | 426.99 ± 40.25 c |
| a25 | 1-Penten-3-one | C1629589 | C5H8O | 84.1 | 1022 | 374.919 | 1.0843 | 861.75 ± 22.21 a | 658.41 ± 7.14 b | 666.85 ± 13.69 b |
| a26 | 2-Butanone | C78933 | C4H8O | 72.1 | 919.8 | 299.424 | 1.24261 | 5066.95 ± 80.04 a | 5394.54 ± 104.05 a | 3974.76 ± 164.59 b |
| a27 | 2-Heptanone-D | C110430 | C7H14O | 114.2 | 1193.2 | 687.111 | 1.63358 | 1325.02 ± 113.11 b | 3516.69 ± 105.37 a | 405.89 ± 51.08 c |
| a28 | 2-Heptanone-M | C110430 | C7H14O | 114.2 | 1193.4 | 687.778 | 1.2581 | 1611.74 ± 120.39 b | 2353.83 ± 19.21 a | 798.64 ± 42.34 c |
| a29 | 2-Octanone | C111137 | C8H16O | 128.2 | 1301.6 | 1038.18 | 1.33107 | 11,548.01 ± 683.56 a | 8926.33 ± 173.69 b | 2943.59 ± 326.65 c |
| a30 | 2-Pentanone | C107879 | C5H10O | 86.1 | 998.5 | 346.255 | 1.37465 | 6582.67 ± 125.44 b | 17,218.75 ± 106.71 a | 4952.58 ± 206.68 c |
| a31 | 4-Methyl-2-pentanone | C108101 | C6H12O | 100.2 | 1023.4 | 376.556 | 1.17907 | 1179.89 ± 76.30 c | 1368.02 ± 54.63 b | 1560.64 ± 37.58 a |
| a32 | Ethyl 2-methy lpropionate | C97621 | C6H12O2 | 116.2 | 982.3 | 335.319 | 1.56858 | 457.42 ± 20.30 b | 410.31 ± 16.78 c | 1202.13 ± 87.16 a |
| a33 | Ethyl caproate-D | C123660 | C8H16O2 | 144.2 | 1246 | 858.818 | 1.79845 | 2840.88 ± 155.85 a | 1635.47 ± 67.24 c | 2205.41 ± 113.37 b |
| a34 | Ethyl caproate-M | C123660 | C8H16O2 | 144.2 | 1246 | 858.818 | 1.33659 | 5389.05 ± 207.21 a | 3737.74 ± 81.61 b | 3624.88 ± 50.89 b |
| a35 | Ethyl-pentanoate-D | C539822 | C7H14O2 | 130.2 | 1140.2 | 564.987 | 1.67641 | 319.18 ± 18.13 a | 170.08 ± 8.96 b | 299.52 ± 21.97 a |
| a36 | Ethyl pentanoate-M | C539822 | C7H14O2 | 130.2 | 1141.9 | 568.842 | 1.26702 | 1089.80 ± 48.93 a | 946.63 ± 38.65 b | 1004.78 ± 34.03 a |
| a37 | Ethyl propanoate | C105373 | C5H10O2 | 102.1 | 969.9 | 328.166 | 1.44773 | 2058.83 ± 77.05 b | 1942.57 ± 61.99 b | 2646.72 ± 144.53 a |
| a38 | Hexyl formate | C629334 | C7H14O2 | 130.2 | 1371.3 | 1247.021 | 1.32883 | 2503.58 ± 125.40 a | 1843.61 ± 61.36 b | 561.38 ± 29.67 c |
| a39 | Isoamyl formate-D | C110452 | C6H12O2 | 116.2 | 1076.2 | 441.009 | 1.65656 | 417.59 ± 16.06 b | 259.12 ± 20.96 c | 886.02 ± 42.70 a |
| a40 | Isoamyl formate-M | C110452 | C6H12O2 | 116.2 | 1079.3 | 444.825 | 1.26587 | 1755.11 ± 35.54 b | 1313.40 ± 43.31 c | 2448.57 ± 37.91 a |
| a41 | Ethyl butyrate | C105544 | C6H12O2 | 116.2 | 1045.1 | 403.106 | 1.56142 | 2151.89 ± 65.15 b | 1578.53 ± 64.89 c | 4186.98 ± 180.72 a |
| a42 | Hexyl butyrate | C2639636 | C10H20O2 | 172.3 | 1408.5 | 1358.583 | 1.47487 | 1395.45 ± 44.60 a | 1165.37 ± 358.99 a | 1451.94 ± 255.91 a |
| a43 | Ethyl 3-Aminobutyrate-D | C108645 | C7H14O2 | 130.2 | 1059.1 | 420.171 | 1.65735 | 315.60 ± 13.29 b | 303.94 ± 22.09 b | 758.60 ± 42.16 a |
| a44 | Ethyl 3-Aminobutyrate-M | C108645 | C7H14O2 | 130.2 | 1057.8 | 418.611 | 1.24472 | 1528.04 ± 22.94 c | 1724.34 ± 49.32 b | 2482.35 ± 47.11 a |
| a45 | 1-Hexana1-D | C66251 | C6H12O | 100.2 | 1098.9 | 470.772 | 1.56793 | 7863.17 ± 193.38 a | 5146.35 ± 1059.19 ab | 4176.00 ± 1573.27 b |
| a46 | 1-Hexana1-M | C66251 | C6H12O | 100.2 | 1099.9 | 473.061 | 1.26225 | 2972.14 ± 66.10 a | 2268.20 ± 51.31 b | 2427.26 ± 226.44 b |
| a47 | 2-Methyl propanal | C78842 | C4H8O | 72.1 | 822.2 | 243.266 | 1.09122 | 1575.01 ± 64.09 b | 1211.87 ± 32.74 c | 2767.80 ± 107.16 a |
| a48 | Butanal | C123728 | C4H8O | 72.1 | 861.8 | 266.053 | 1.1196 | 15,649.29 ± 108.50 a | 14,586.89 ± 135.27 b | 13,708.93 ± 87.22 c |
| a49 | Propanal | C123386 | C3H6O | 58.1 | 767.7 | 211.985 | 1.04748 | 1967.36 ± 70.15 a | 1695.08 ± 34.16 b | 2012.86 ± 81.27 a |
| a50 | Benzaldehyde | C100527 | C7H6O | 106.1 | 1520.8 | 1695.416 | 1.14217 | 13,676.70 ± 366.67 a | 8215.54 ± 1233.37 b | 14,210.80 ± 1007.29 a |
| a51 | Heptaldehyde | C111717 | C7H14O | 114.2 | 1197.3 | 700.409 | 1.32526 | 1989.19 ± 29.67 a | 1510.19 ± 58.38 b | 1226.10 ± 66.75 c |
| a52 | 2,6-Dimethyl pyrazine | C108509 | C6H8N2 | 108.1 | 1360.8 | 1215.695 | 1.14064 | 1375.41 ± 109.97 b | 554.80 ± 42.02 c | 2367.37 ± 142.44 a |
| a53 | 2-Pentyl furan | C3777693 | C9H14O | 138.2 | 1241.6 | 844.547 | 1.25208 | 2222.82 ± 106.41 a | 1455.03 ± 62.57 b | 2244.39 ± 41.95 a |
| a54 | Triethylamine | C121448 | C6H15N | 101.2 | 772.3 | 214.611 | 1.09247 | 979.49 ± 36.46 a | 689.55 ± 28.97 c | 804.28 ± 45.08 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, K.; Peng, Y.; Xv, P.; Dong, P.; Qiao, M.; Fan, W. Characterization of the Quality and Flavor in Chinese Sausage: Comparison Between Cantonese, Five-Spice, and Mala Sausages. Foods 2025, 14, 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111982
Cai X, Zeng Y, Zhu K, Peng Y, Xv P, Dong P, Qiao M, Fan W. Characterization of the Quality and Flavor in Chinese Sausage: Comparison Between Cantonese, Five-Spice, and Mala Sausages. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111982
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xuemei, Yi Zeng, Kaixian Zhu, Yiqin Peng, Pei Xv, Ping Dong, Mingfeng Qiao, and Wenjiao Fan. 2025. "Characterization of the Quality and Flavor in Chinese Sausage: Comparison Between Cantonese, Five-Spice, and Mala Sausages" Foods 14, no. 11: 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111982
APA StyleCai, X., Zeng, Y., Zhu, K., Peng, Y., Xv, P., Dong, P., Qiao, M., & Fan, W. (2025). Characterization of the Quality and Flavor in Chinese Sausage: Comparison Between Cantonese, Five-Spice, and Mala Sausages. Foods, 14(11), 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111982








