Nutrient Availability and Pathogen Clearance Impact Microbiome Composition in a Gnotobiotic Kimchi Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Media Preparation, Strains Used, and Culture Conditions
2.2. Experimental Culture, CFU Quantification, and pH Measurement
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification, Library Preparation, Sequencing
2.4. Computational Analysis
3. Results
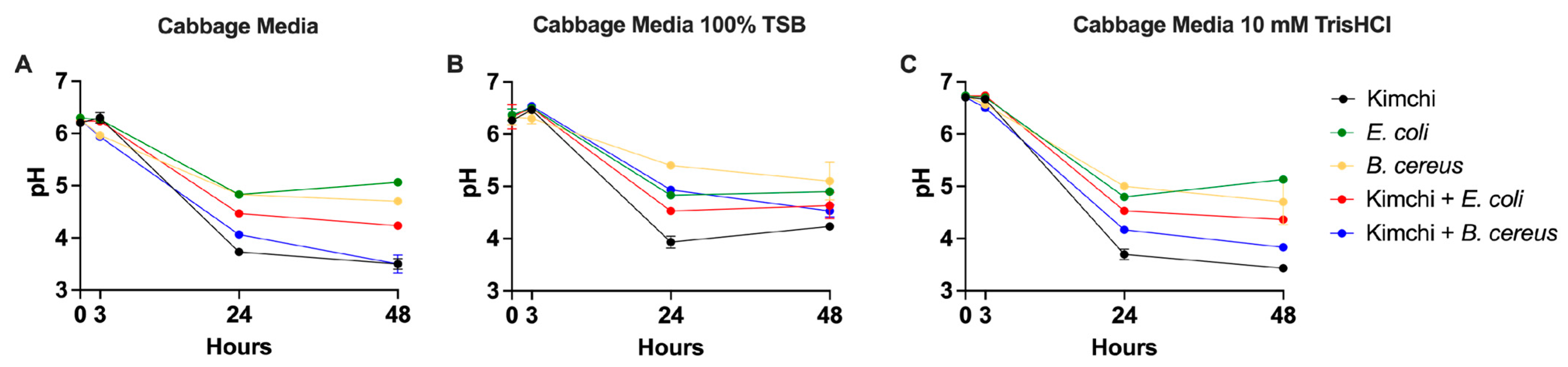
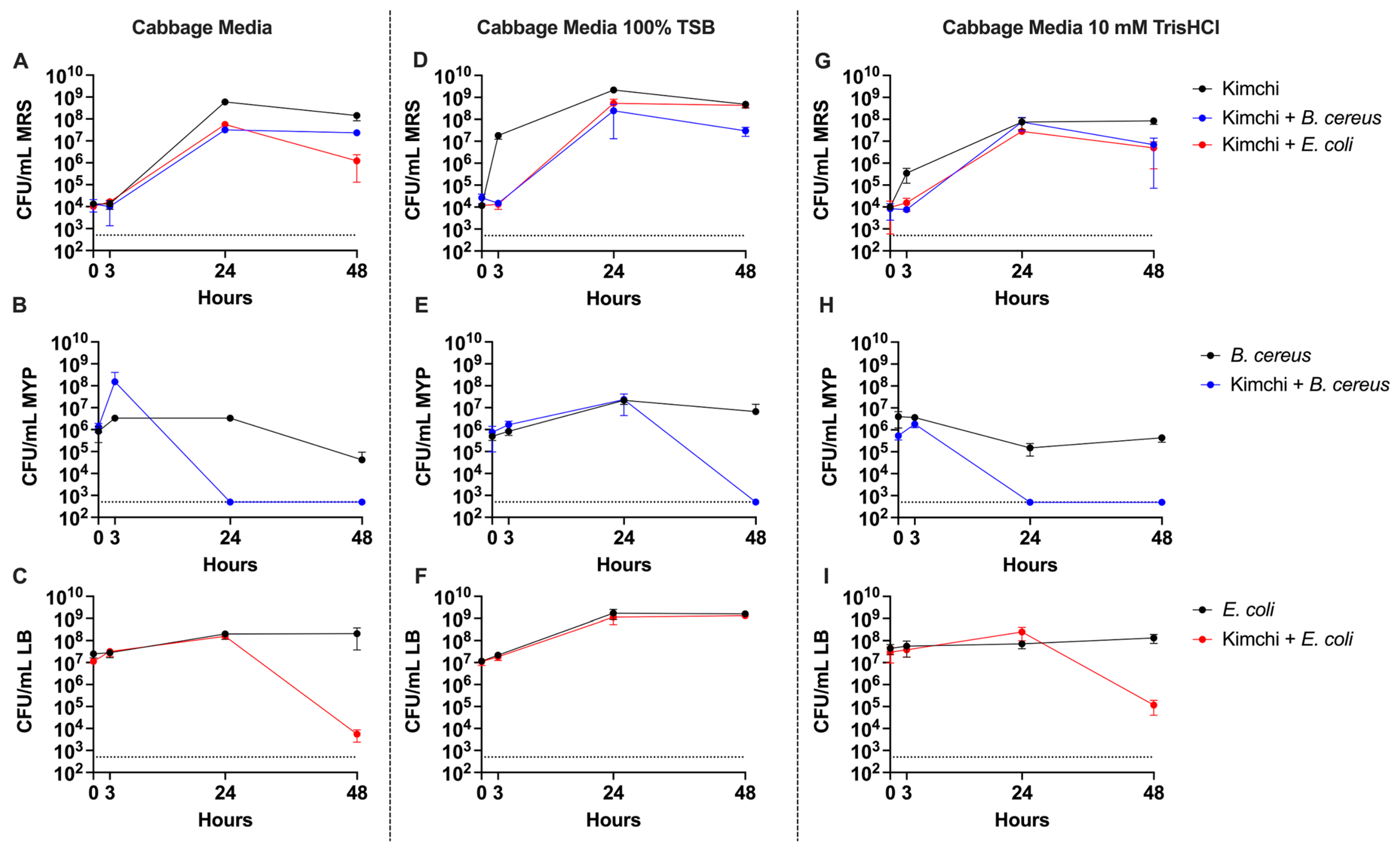
3.1. LAB-Mediated Inhibition of Pathogens Depends on pH and Nutrient Availability
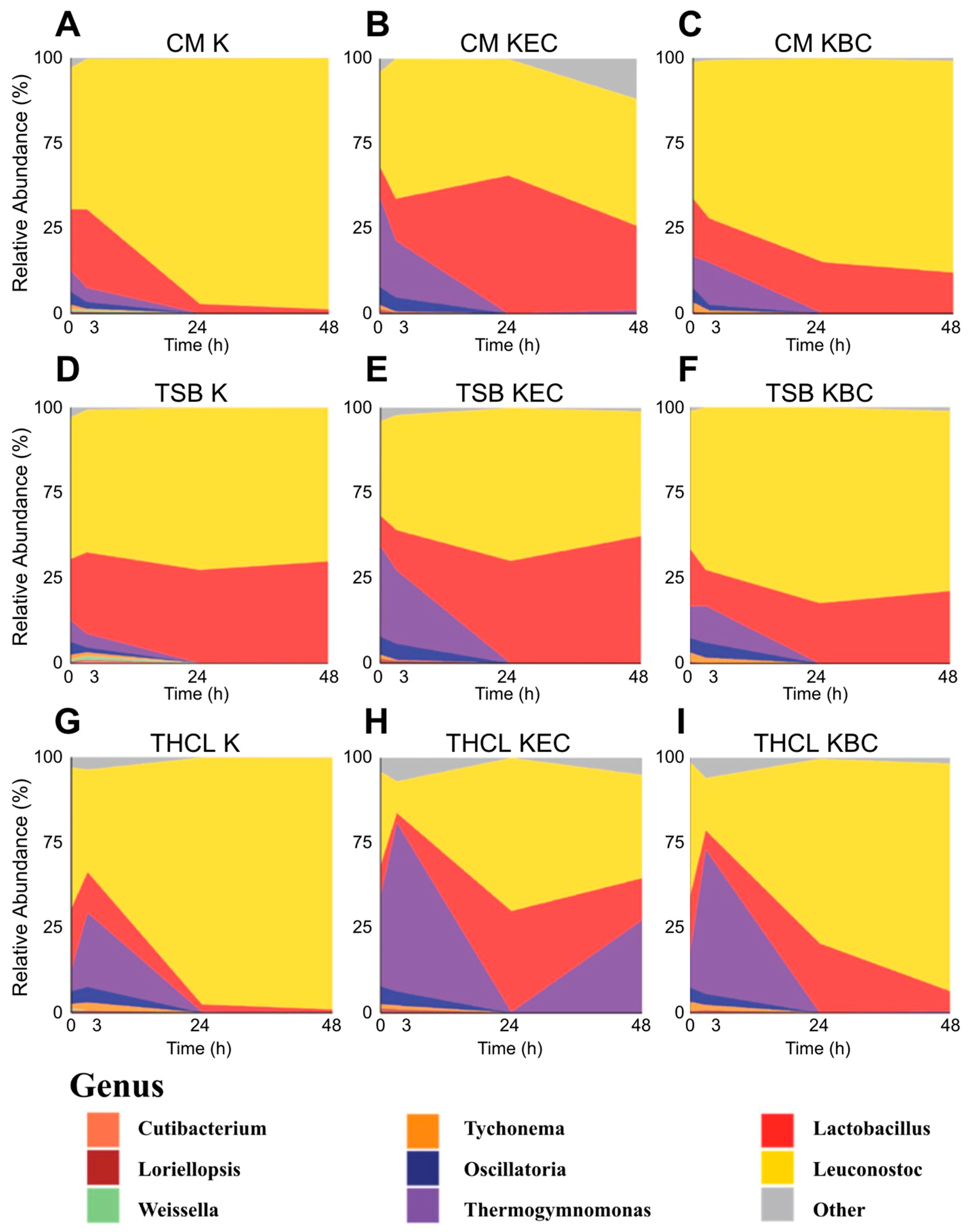
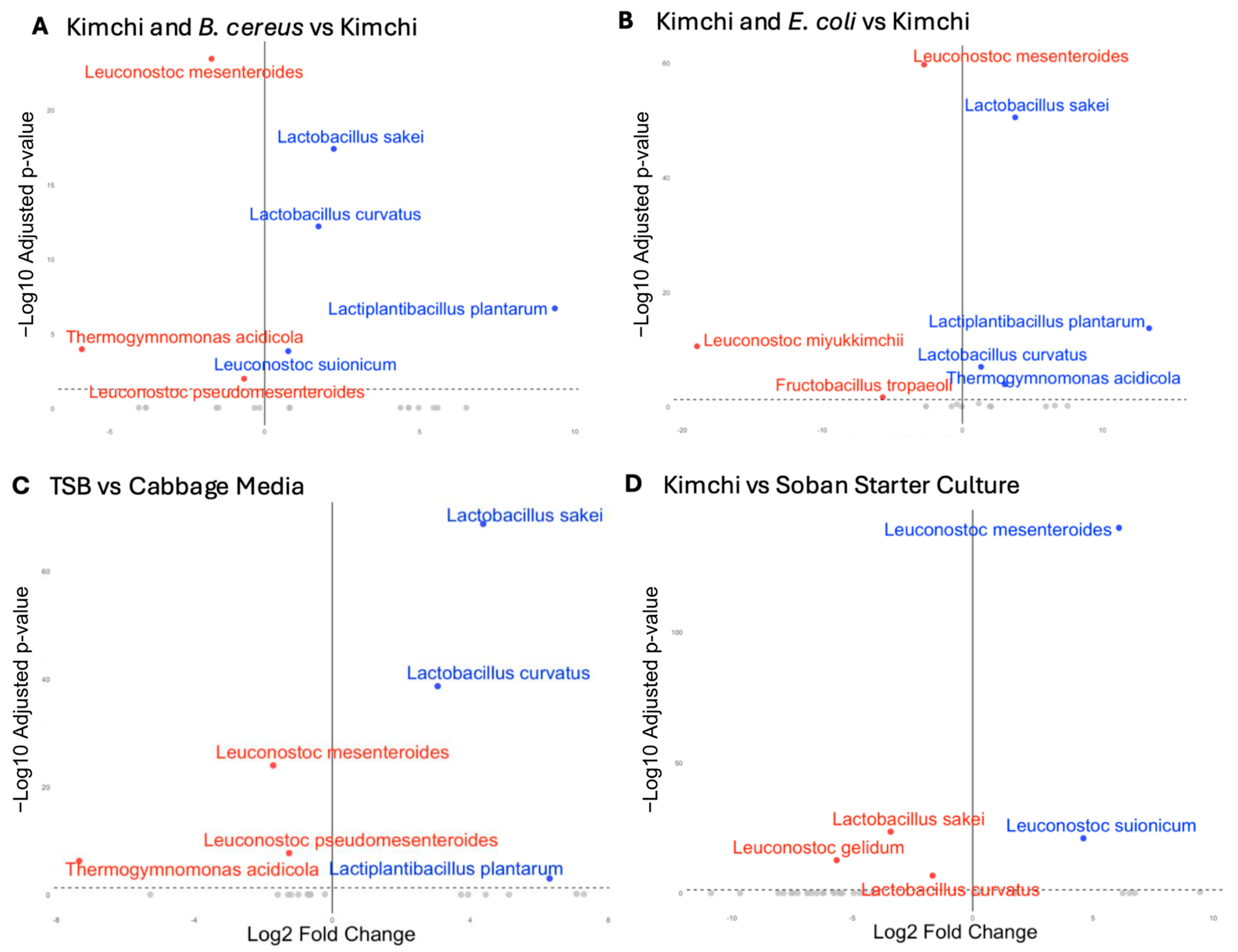
3.2. Distinct Fermentation Microbiomes Shaped by Media Composition and Pathogen Challenge
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diez-Ozaeta, I.; Astiazaran, O.J. Fermented foods: An update on evidence-based health benefits and future perspectives. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surya, R.; Nugroho, D. Kimchi throughout millennia: A narrative review on the early and modern history of kimchi. J. Ethn. Foods 2023, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabat, M.A.; Sano, W.H.; Cabral, D.J.; Wurster, J.I.; Belenky, P. The impact of vegan production on the kimchi microbiome. Food Microbiol. 2018, 74, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Chun, J. Bacterial community structure in kimchi, a Korean fermented vegetable food, as revealed by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 103, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-A.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Chon, S.-Y.; Chung, Y.B.; Park, S.-H.; Yun, Y.-R.; Min, S.G.; Yang, H.-C.; Seo, H.-Y. Effects of salt type on the metabolites and microbial community in kimchi fermentation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, S.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Rhee, J.-K.; Roh, S.W. Effects of the main ingredients of the fermented food, kimchi, on bacterial composition and metabolite profile. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-E.; Cho, K.-M.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, E.-J.; Seo, S.-H.; Jeong, D.; Chung, H.-J.; Son, H.-S. Effects of the addition of starches with different amylose contents on kimchi microbiota and metabolites. LWT 2023, 175, 114475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Han, D.M.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, C.O. Effects of glutinous rice paste and fish sauce on kimchi fermentation. LWT 2023, 173, 114253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, J. Effects of Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria on Reducing Biological Hazards in Kimchi. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.; McMahon, T.; Ferrato, C.; Chui, L. Survival of O157 and non-O157 shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Korean style kimchi. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Zheng, Z.B.; Shin, D.H. Growth inhibitory effects of kimchi (Korean traditional fermented vegetable product) against Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Chang, H.C. Growth inhibition of foodborne pathogens by kimchi prepared with bacteriocin-producing starter culture. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M72–M78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Choi, H.J.; Zin, H.; Kim, E.; Yang, S.-M.; Hwang, J.; Kwak, H.-S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.-Y. Effect of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli on Microbial Communities during Kimchi Fermentation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Oh, H.; Choi, K.-H.; Yoon, Y. Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella Can Survive in Kimchi during Fermentation. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, D.E.; Kotrola, J.S. Growth and survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 under acidic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q. Cereulide and Emetic Bacillus cereus: Characterizations, Impacts and Public Precautions. Foods 2023, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raddadi, N.; Cherif, A.; Mora, D.; Brusetti, L.; Borin, S.; Boudabous, A.; Daffonchio, D. The autolytic phenotype of the Bacillus cereus group. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.R.; O’Mara Schwartz, J.; Cox, G.; Wolfe, B.E. A Gnotobiotic System for Studying Microbiome Assembly in the Phyllosphere and in Vegetable Fermentation. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 160, e61149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, N.F.; Bragança, S.M.; Simões, L.C.; Cerqueira, L.; Almeida, C.; Keevil, C.W.; Vieira, M.J. Proposal for a method to estimate nutrient shock effects in bacteria. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jenkins, C.L.; Bean, H.D. Dependence of the Staphylococcal Volatilome Composition on Microbial Nutrition. Metabolites 2020, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, K.D.; Wang, Q.; Nute, M.G.; Tyshaieva, A.; Reeves, E.; Soriano, S.; Wu, Q.; Graeber, E.; Finzer, P.; Mendling, W.; et al. Emu: Species-level microbial community profiling of full-length 16S rRNA Oxford Nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Waste Not, Want Not: Why Rarefying Microbiome Data Is Inadmissible. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvage, T.; Cormier, A.; Delphine, P. A comparison of Oxford nanopore library strategies for bacterial genomics. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Yang, Z.; Aweya, J.J.; Jin, R.; Liang, D.; Weng, W.; Ren, Z.; Yang, S. Selection of antimicrobial peptides derived from Bacillus cereus: Investigation of their antimicrobial activity and mechanism of action against Staphylococcus aureus. LWT 2025, 216, 117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijsink Vincent, G.H.; Skeie, M.; Middelhoven, P.H.; Brurberg May, B.; Nes Ingolf, F. Comparative Studies of Class IIa Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeliere, F.; Sola, L.; Busi, E.; Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Raimondi, S. The Metabolism of Leuconostoc Genus Decoded by Comparative Genomics. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeon, C.O. Leuconostoc miyukkimchii sp. nov., isolated from brown algae (Undaria pinnatifida) kimchi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.; Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Franco, D. Chapter 3-Main Groups of Microorganisms of Relevance for Food Safety and Stability: General Aspects and Overall Description. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation; Barba, F.J., Sant’Ana, A.S., Orlien, V., Koubaa, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 53–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zabat, M.A.; Sano, W.H.; Wurster, J.I.; Cabral, D.J.; Belenky, P. Microbial Community Analysis of Sauerkraut Fermentation Reveals a Stable and Rapidly Established Community. Foods 2018, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Alegría, Á.; Bron Peter, A.; de Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; Lemos José, A.; Linares Daniel, M.; Ross, P.; Stanton, C.; et al. Stress Physiology of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 837–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Wang, B.H.; Xu, X.; der Meister, T., Jr.; Tabγač, H.T.; Hwang, F.F.; Liu, Z. Extrusion of Dissolved Oxygen by Exopolysaccharide From Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Its Implications in Relief of the Oxygen Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koponen, J.; Laakso, K.; Koskenniemi, K.; Kankainen, M.; Savijoki, K.; Nyman, T.A.; de Vos, W.M.; Tynkkynen, S.; Kalkkinen, N.; Varmanen, P. Effect of acid stress on protein expression and phosphorylation in Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1357–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.C.; Fleming, H.P.; Hassan, H.M. Acid Tolerance of Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgason, E.; Okstad, O.A.; Caugant, D.A.; Johansen, H.A.; Fouet, A.; Mock, M.; Hegna, I.; Kolstø, A.B. Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus thuringiensis—One species on the basis of genetic evidence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2627–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, M.; Kakinuma, K.; Kawaguchi, R. Phylogenetic analysis of Salmonella, Shigella, and Escherichia coli strains on the basis of the gyrB gene sequence. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bemis, D.H.; Camphausen, C.E.; Liu, E.; Dantus, J.J.; Navarro, J.A.; Dykstra, K.L.; Paltrowitz, L.A.; Dzhelmach, M.; Joerg, M.; Tamelessio, P.; et al. Nutrient Availability and Pathogen Clearance Impact Microbiome Composition in a Gnotobiotic Kimchi Model. Foods 2025, 14, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111948
Bemis DH, Camphausen CE, Liu E, Dantus JJ, Navarro JA, Dykstra KL, Paltrowitz LA, Dzhelmach M, Joerg M, Tamelessio P, et al. Nutrient Availability and Pathogen Clearance Impact Microbiome Composition in a Gnotobiotic Kimchi Model. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111948
Chicago/Turabian StyleBemis, Devin H., Carly E. Camphausen, Esther Liu, Joshua J. Dantus, Josue A. Navarro, Kieren Leif Dykstra, Leila A. Paltrowitz, Mariia Dzhelmach, Markus Joerg, Pamil Tamelessio, and et al. 2025. "Nutrient Availability and Pathogen Clearance Impact Microbiome Composition in a Gnotobiotic Kimchi Model" Foods 14, no. 11: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111948
APA StyleBemis, D. H., Camphausen, C. E., Liu, E., Dantus, J. J., Navarro, J. A., Dykstra, K. L., Paltrowitz, L. A., Dzhelmach, M., Joerg, M., Tamelessio, P., & Belenky, P. (2025). Nutrient Availability and Pathogen Clearance Impact Microbiome Composition in a Gnotobiotic Kimchi Model. Foods, 14(11), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111948





