Quality Enhancement and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles via Adding Different Improvers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Noodle Preparation
2.3. Color Measurement
2.4. Microstructure Determination
2.5. Determination of Cooking Properties
2.6. Mechanical Analysis
2.7. Thermal Properties
2.8. In Vitro Digestive Properties
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
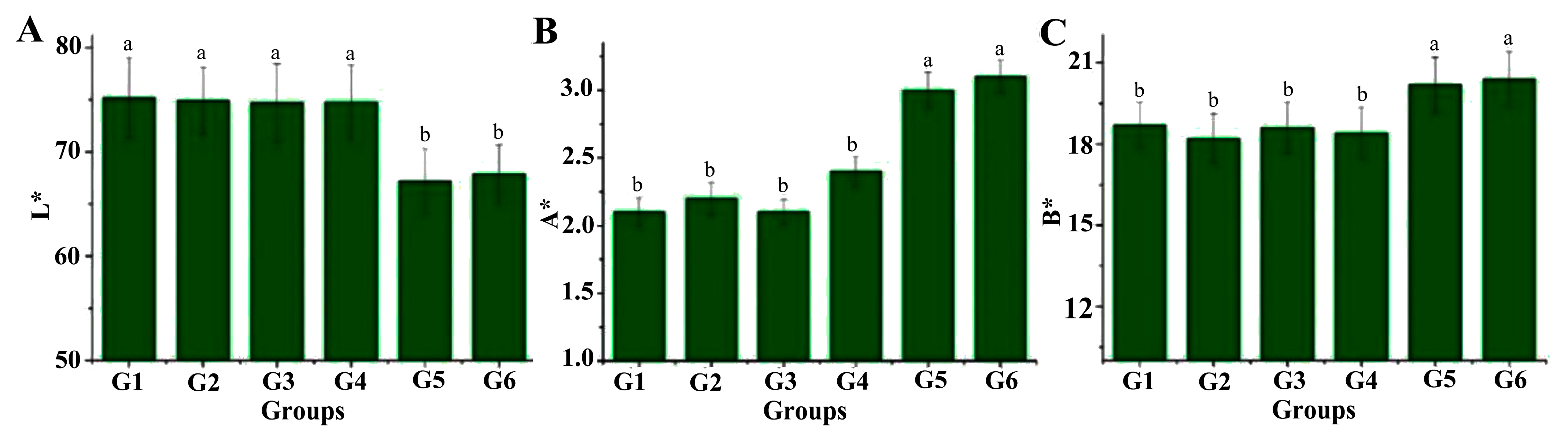
3.1. Effect on Noodle Color
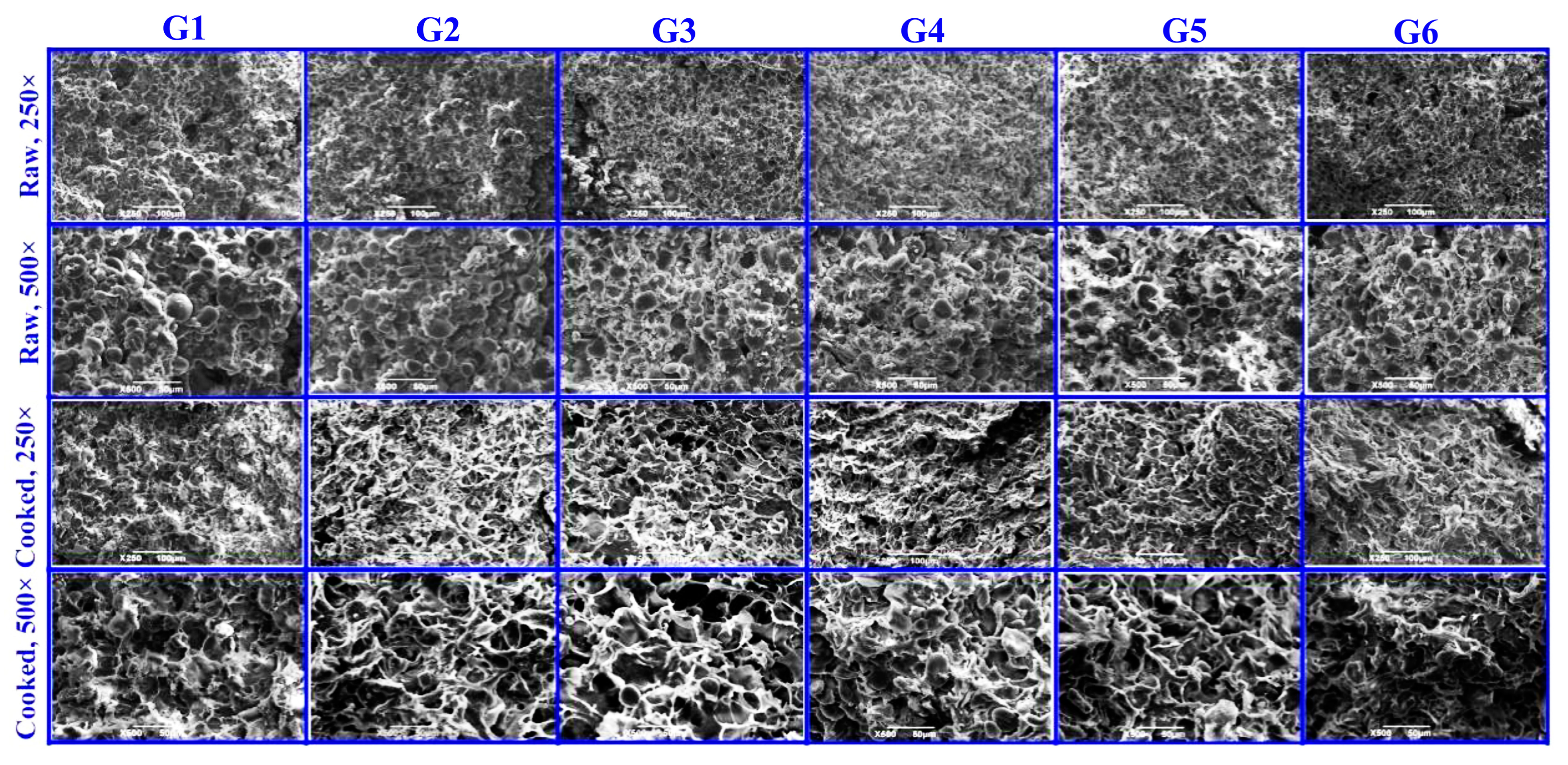
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
3.3. Cooking Properties
3.4. Mechanical Properties
3.5. Thermal Analysis
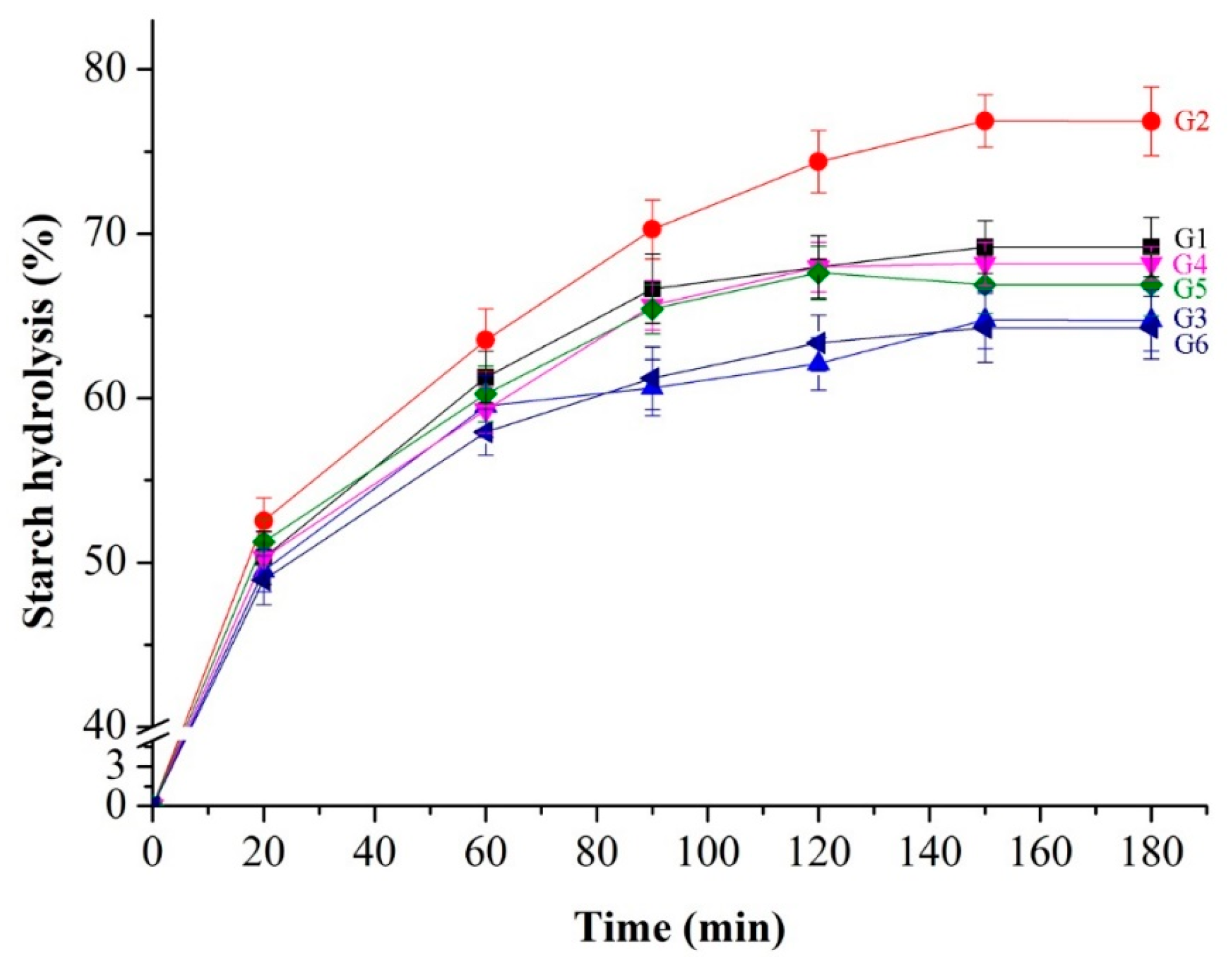
3.6. In Vitro Starch Digestibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dini, C.; Quiroga, A.V.; Viña, S.Z.; García, M.A. Extraction and characterization of proteins from Pachyrhizus ahipa roots: An unexploited protein-rich crop. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2021, 76, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Pan, J.; Xu, X.; Nie, S.; Lu, L.; Jing, Y.; Yang, F.; Ji, G.; Xu, H. Chinese yam polysaccharide enhances anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in colorectal cancer through alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 143323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, M.; Titikshya, S.; Aradwad, P.; Kumar, V.; Naik, S.N. Study of the drying behaviour and color kinetics of convective drying of yam (Dioscorea hispida) slices. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.-N.; Liao, A.-M.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Huang, J.-H.; Wei, Z.-J. Microstructural, textural, sensory properties and quality of Wheat–Yam composite flour noodles. Foods 2019, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Wang, X.-W.; Zhang, J.-W.; Peng, X.; Tanokura, M.; Xue, Y.-L. Recovery of Yam soluble protein from Yam starch processing wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, P.; Gao, Y.; Chen, P.; Lv, C.; Zhao, G. Recent advances in the study of wheat protein and other food components affecting the gluten network and the properties of noodles. Foods 2022, 11, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xie, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B. Soybean protein isolate treated with transglutaminase (TGase) enhances the heat tolerance of selected lactic acid bacteria strains to spray drying. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, N.J.D.; Rocha, E.B.M.; Gusma, T.A.S.; Nascimento, A.; Lisboa, H.M.; de Gusma, R.P. Optimizing gluten-free pasta quality: The impacts of transglutaminase concentration and kneading time on cooking properties, nutritional value, and rheological characteristics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 189, 115485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, W.; Kim, Y.; Liu, R.; Tilley, M. Effects of transglutaminase on the rheological and noodle-making characteristics of oat dough containing vital wheat gluten or egg albumin. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantumur, M.-A.; Hussain, M.; Li, J.; Hui, M.; Bai, X.; Sukhbaatar, N.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Modification of fermented whey protein concentrates: Impact of sequential ultrasound and TGase cross-linking. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolan, F.; Urbano, K.; Netto, F.M.; Steel, C.J. Chemical and structural characteristics of proteins of non-vital and vital wheat glutens. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-Y.; Mu, T.-H.; Zhang, M.; Ma, M.-M. Effects of different polysaccharides and proteins on dough rheological properties, texture, structure and in vitro starch digestibility of wet sweet potato vermicelli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Guo, P.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Xia, N.; Xiao, B. Tuning egg yolk granules/sodium alginate emulsion gel structure to enhance β-carotene stability and in vitro digestion property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-H.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wang, D.-D.; Chen, H.-H. Effects of sodium alginate and locust bean gum on dough rheology and microstructures, and bread quality. Cereal Chem. 2022, 99, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Nishijima, N.; Oda, Y.; Handa, A.; Majumder, K.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y. Utilization of egg white solids to improve the texture and cooking quality of cooked and frozen pasta. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Ni, Z.J.; Thakur, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.G.; Shang, Y.F.; Wei, Z.J. Effect of grape seed power on the structural and physicochemical properties of wheat gluten in noodle preparation system. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangpring, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Ratanasumawong, S. The effect of sodium chloride on microstructure, water migration, and texture of rice noodle. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Guo, S.; Zhang, S. Effects of flour free lipids on textural and cooking qualities of Chinese noodles. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Shen, C.; Li, Y.; Xiong, S.; Li, F. The Quality characteristics comparison of stone-milled dried whole wheat noodles, dried wheat noodles, and commercially dried whole wheat noodles. Foods 2023, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xu, M.; Zou, Y.; Yang, B. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Donner, E.; Yada, R.Y.; Liu, Q. Physicochemical properties and in vitro starch digestibility of potato starch/protein blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatcher, D.W.; Symons, S.J.; Manivannan, U. Developments in the use of image analysis for the assessment of oriental noodle appearance and colour. J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.-Y.; Alkarkhi, A.F.M.; Easa, A.M. Effect of cross-linking agents on physicochemical, textural properties and microstructure of canned soy protein isolate-yellow alkaline noodles prepared by retort processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2014, 38, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Hou, G.G.; Kindelspire, J.; Krishnan, P.; Zhao, S. Microstructural, textural, and sensory properties of whole-wheat noodle modified by enzymes and emulsifiers. Food Chem. 2017, 223, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Tian, L.; Xiong, D.; Jia, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Duan, X. Effects of egg white on physicochemical and functional characteristics of steamed cold noodles (a wheat starch gel food). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 169, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.; Xu, X. Effect of sodium alginate on the quality of highland barley fortified wheat noodles. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 140, 110719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.-J.; Wang, B.-J.; Weng, Y.-M. Preparation of white salted noodles using rice flour as the principal ingredient and the effects of transglutaminase on noodle qualities. Food Biosci. 2020, 33, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redd, A.J.; Pike, O.A.; Ahlborn, G.J. Effects of microbial transglutaminase on gluten-free sourdough bread structure and loaf characteristics. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 115, 103833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lu, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.; Chakravarty, B.; Jin, L.; Cao, X. Nutrient and specification enhancement of fortified Asian noodles by chickpea flour substitution and transglutaminase treatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.-Y.; Cheng, L.-H.; Azahari, B.; Easa, A.M. In-vitro digestibility and amino acid composition of soy protein isolate cross-linked with microbial transglutaminase followed by heating with ribose. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.L.; Bae, I.Y.; Lee, H.G. In vitro starch digestibility of noodles with various cereal flours and hydrocolloids. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups | YP (g) | WF (g) | VWG (g) | TGase (g) | EWP (g) | SA (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 30 | 70 | / | / | / | / |
| G2 | 30 | 70 | 10 | / | / | / |
| G3 | 30 | 70 | / | 3 | / | / |
| G4 | 30 | 70 | 10 | 3 | / | / |
| G5 | 30 | 70 | / | / | 10 | 3 |
| G6 | 30 | 70 | / | 3 | 10 | 3 |
| Groups | Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness (g) | Springiness (g) | Cohesiveness (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 11,199 ± 32.6 a | 1276.69 ± 8.5 ab | 0.388 ± 0.041 a | 0.39 ± 0.029 a |
| G2 | 12,141.9 ± 27.8 b | 1358.57 ± 30.2 b | 0.250 ± 0.036 b | 0.386 ± 0.061 a |
| G3 | 11,801.2 ± 20.9 ab | 1105.38 ± 3.5 c | 0.339 ± 0.034 a | 0.338 ± 0.052 b |
| G4 | 13,696.9 ± 39.1 c | 1550.88 ± 14.3 d | 0.391 ± 0.019 a | 0.390 ± 0.051 a |
| G5 | 10,122.4 ± 36.1 d | 1140.76 ± 28.9 ca | 0.251 ± 0.046 b | 0.321 ± 0.029 c |
| G6 | 8993.6 ± 20.7 e | 1237.27 ± 8.2 a | 0.417 ± 0.038 c | 0.332 ± 0.039 b |
| Groups | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tc − To (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 61.88 ± 0.18 b | 101.36 ± 0.48 b | 157.34 ± 0.68 b | 95.46 ± 0.34 c | 132.9 ± 0.64 d |
| G2 | 69.60 ± 0.34 a | 116.69 ± 0.57 a | 164.06 ± 0.57 a | 94.46 ± 0.61 c | 137.4 ± 0.62 d |
| G3 | 58.88 ± 0.51 bc | 98.25 ± 0.61 b | 148.36 ± 0.87 c | 89.48 ± 0.27 d | 153.3 ± 0.78 c |
| G4 | 59.32 ± 0.24 b | 103.49 ± 0.38 b | 162.87 ± 0.64 a | 103.55 ± 0.36 b | 157.6 ± 0.53 bc |
| G5 | 54.96 ± 0.39 c | 92.72 ± 0.41 c | 160.57 ± 0.78 ab | 105.61 ± 0.51 b | 162.6 ± 0.58 b |
| G6 | 51.23 ± 0.42 d | 91.60 ± 0.63 c | 164.83 ± 0.61 a | 113.6 ± 0.42 a | 179.0 ± 0.42 a |
| Groups | RDS | SDS | RS |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 55.21 ± 0.42 b | 24.32 ± 0.32 bc | 20.47 ± 0.15 b |
| G2 | 57.70 ± 0.36 a | 26.02 ± 0.27 b | 16.28 ± 0.27 c |
| G3 | 54.36 ± 0.34 b | 17.28 ± 0.21 d | 28.35 ± 0.29 a |
| G4 | 52.13 ± 0.24 bc | 23.42 ± 0.19 c | 21.28 ± 0.27 b |
| G5 | 47.28 ± 0.49 c | 31.49 ± 0.37 a | 21.23 ± 0.37 b |
| G6 | 45.73 ± 0.51 c | 33.81 ± 0.34 a | 20.46 ± 0.43 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Sun, K.-N.; Peng, Q.-J.; Ma, R.-H.; Ni, Z.-J.; Thakur, K.; Wei, Z.-J. Quality Enhancement and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles via Adding Different Improvers. Foods 2025, 14, 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101654
Hu S, Sun K-N, Peng Q-J, Ma R-H, Ni Z-J, Thakur K, Wei Z-J. Quality Enhancement and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles via Adding Different Improvers. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101654
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shuo, Kai-Nong Sun, Qiu-Jia Peng, Run-Hui Ma, Zhi-Jing Ni, Kiran Thakur, and Zhao-Jun Wei. 2025. "Quality Enhancement and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles via Adding Different Improvers" Foods 14, no. 10: 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101654
APA StyleHu, S., Sun, K.-N., Peng, Q.-J., Ma, R.-H., Ni, Z.-J., Thakur, K., & Wei, Z.-J. (2025). Quality Enhancement and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles via Adding Different Improvers. Foods, 14(10), 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101654






