Transglutaminase-Cross-Linked Tofu Suppressed Soybean-Induced Allergic Reactions by Enhancing Intestinal Mucosa Immune Tolerance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Mice
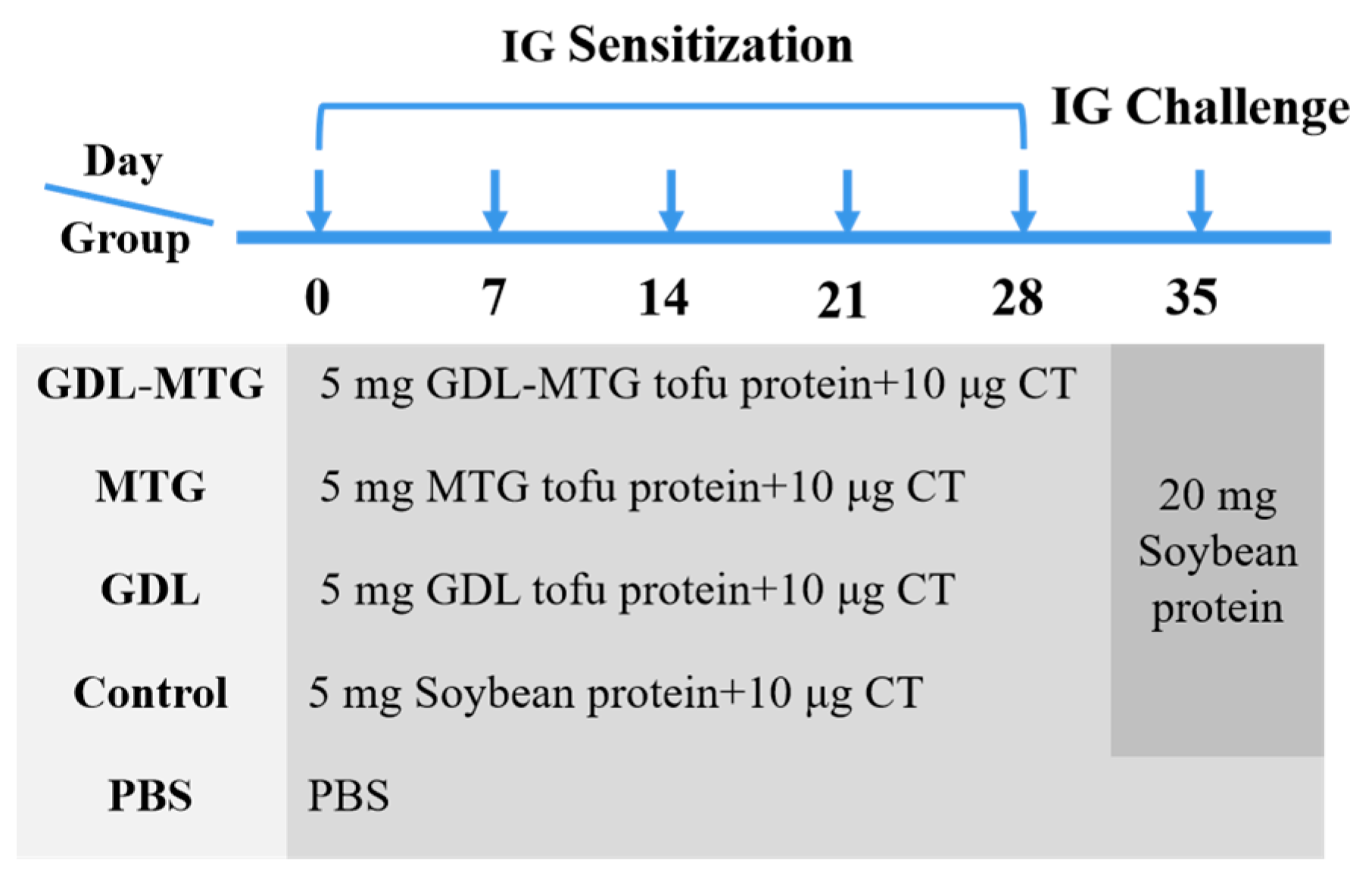
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Analysis of Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
2.6. Preparation of PP and MLN Cell Suspension
2.7. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Immune Cells
2.7.1. Detection of DCs
2.7.2. Detection of T Lymphocyte Subsets
2.8. HE
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Allergic Mouse Model
3.2. Role of DC Presentation
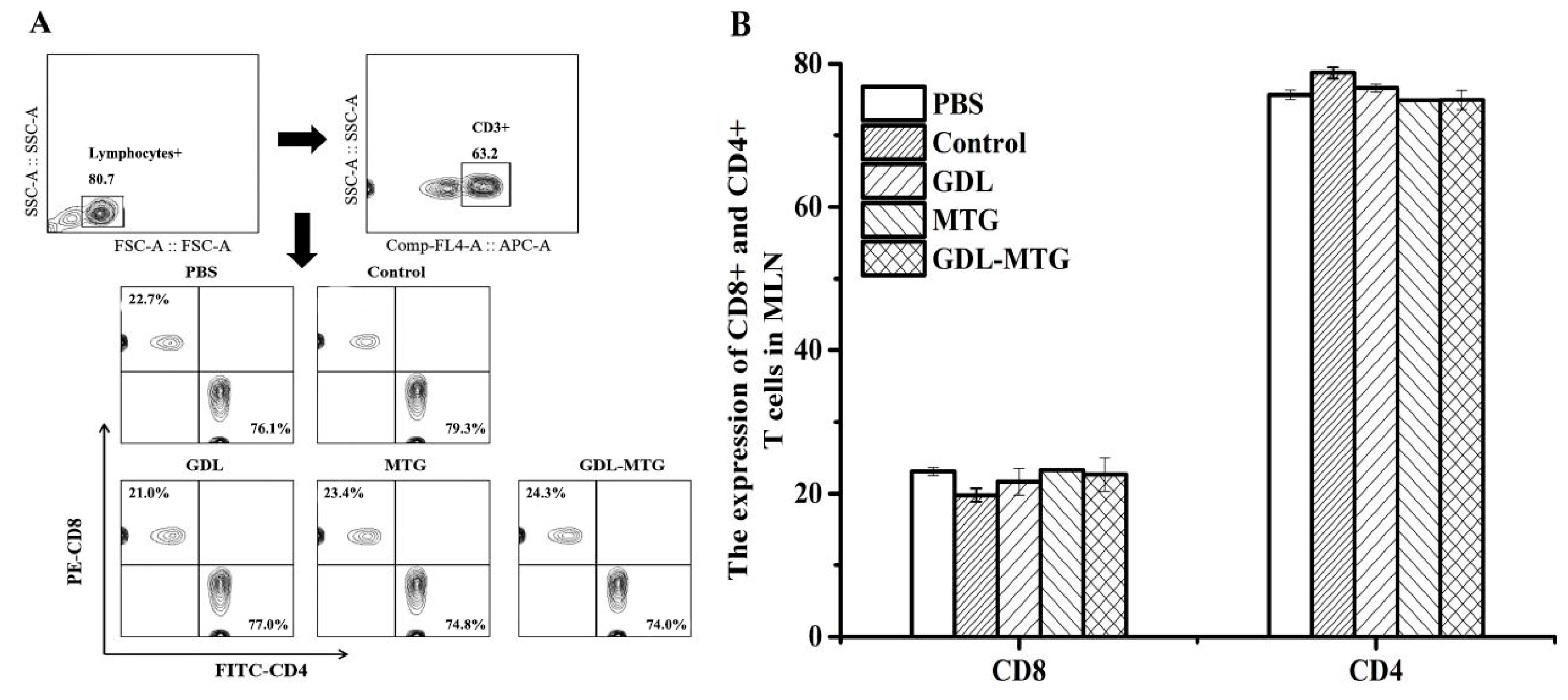
3.3. Detection of CD4/CD8 Cells
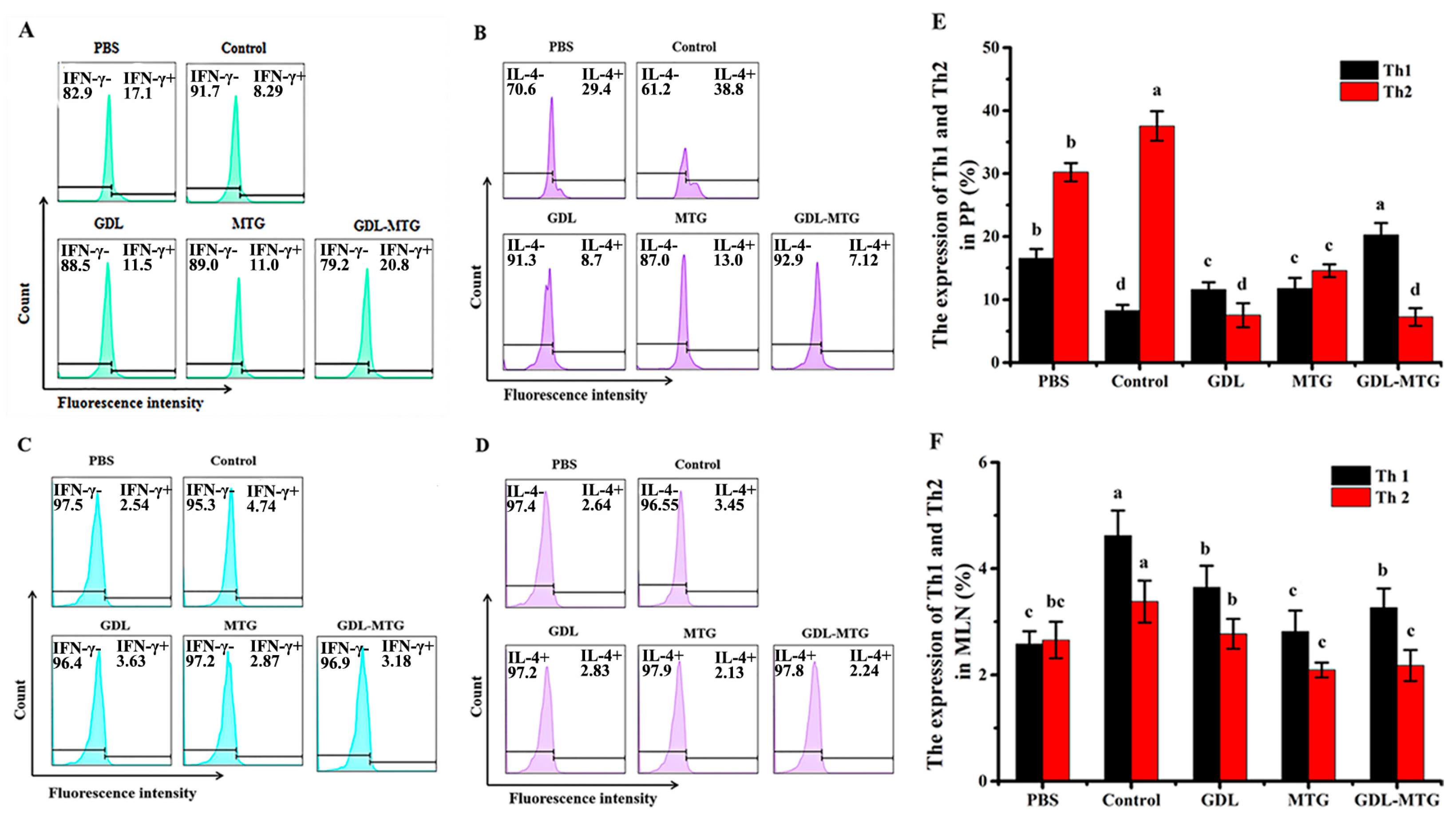
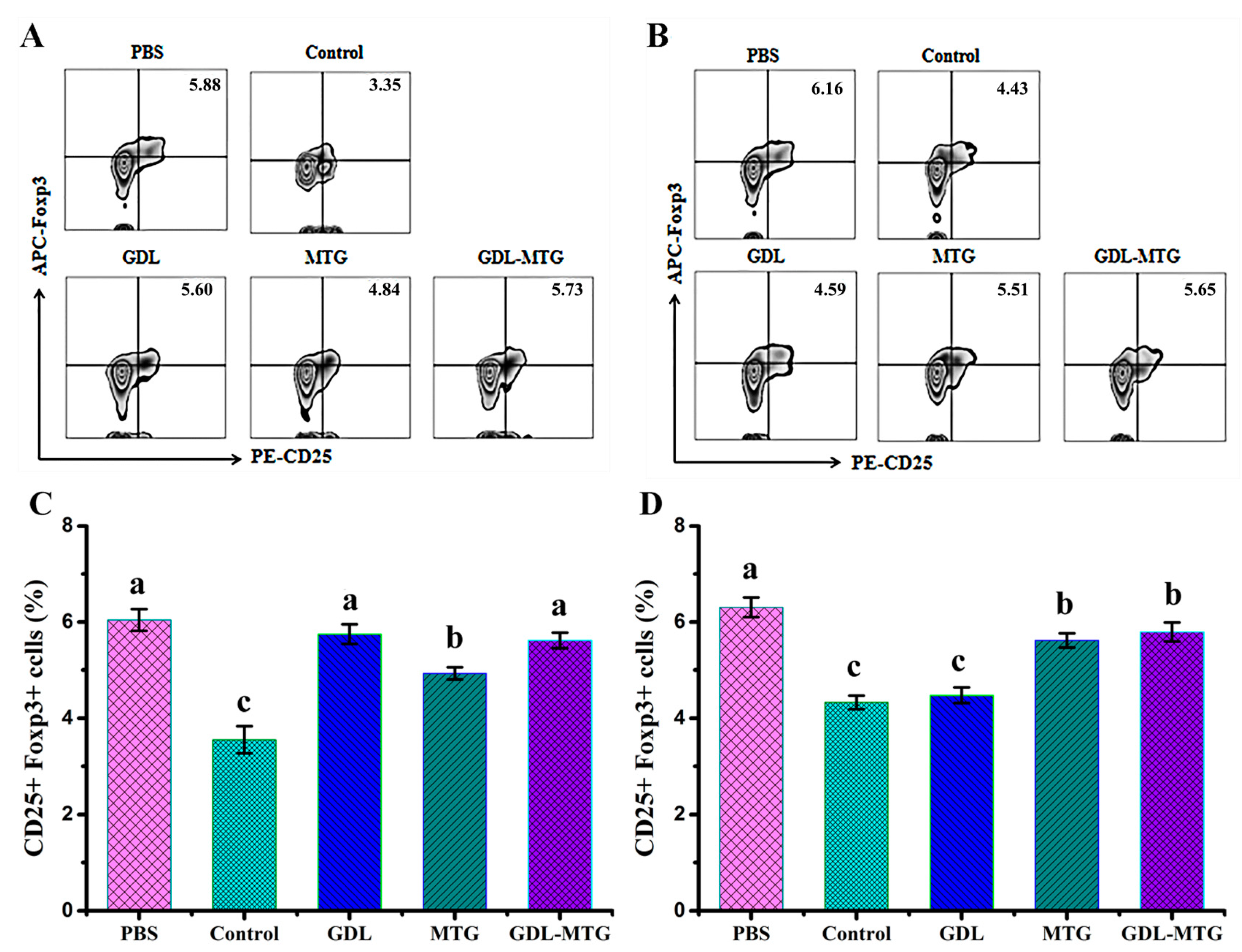
3.4. Identification of T Lymphocyte Subsets
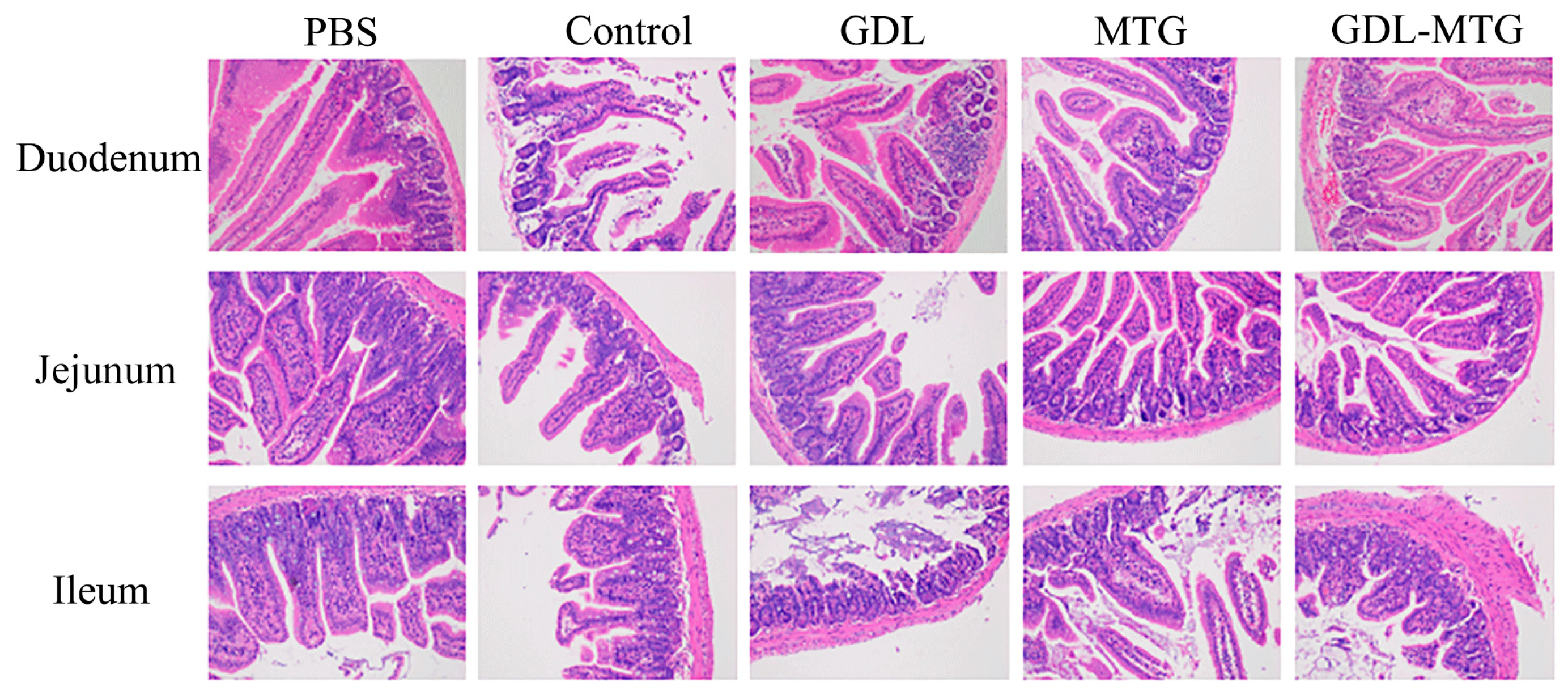
3.5. Histopathological Section of the Intestine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossi, F.; Felis, G.E.; Martinelli, A.; Calcavecchia, B.; Torriani, S. Microbiological characteristics of fresh tofu produced in small industrial scale and identification of specific spoiling microorganisms (SSO). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 70, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Bowei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG alleviates β-conglycinin-induced allergy by regulating the T cell receptor signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10554–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchi, A.; Burks, W.; Bahna, S.L.; Bielory, L.; Boyle, R.J.; Cocco, R.; Dreborg, S.; Goodman, R.; Kuitunen, M.; Haahtela, T.; et al. Clinical Use of Probiotics in Pediatric Allergy (CUPPA): A World Allergy Organization Position Paper. World Allergy Organ J. 2012, 5, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, Y.; Ono, T.; Nakasato, K.; Toda, K. Homogeneity and microstructure of tofu depends on 11S/7S globulin ratio in soymilk and coagulant concentration. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2009, 15, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.T.; Yang, A. Interactions of protein content and globulin subunit composition of soybean proteins in relation to tofu gel properties. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Luo, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z. Transglutaminase-set soy globulin-stabilized emulsion gels: Influence of soy β-conglycinin/glycinin ratio on properties, microstructure and gelling mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Shiau, S.; Chen, F.; Lin, F. Effect of microbial transglutaminase on the rheological and textural characteristics of black soybean packed tofu coagulating with Agar. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, S.; Sutton, K.; Newberry, M.; Andrews, N.; Gerrard, J. The impact of transglutaminase on soy proteins and tofu texture. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Rui, X.; Dong, M.; Mariniello, L. Microbial transglutaminase-mediated polymerization in the presence of lactic acid bacteria affects antigenicity of soy protein component present in bio-tofu. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 53, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, A.; Horikawa, T.; Shimizu, H.; Sarayama, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Sjolander, S.; Tanaka, A.; Moriyama, T. Soybean β-conglycinin as the main allergen in a patient with food dependent exerciseinduced anaphylaxis bytofu: Food processing alters pepsin resistance. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Xia, X.; Yang, A.; Chen, H. Gut microbiota: A target for prebiotics and probiotics in the intervention and therapy of food allergy. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 64, 3623–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, A.; Chen, K.; Chorny, A.A. Immunoglobulin responses at the mucosal interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caubet, J.; Szajewska, H.; Shamir, R.; Nowak-Węgrzyn, A. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergies in children. Pediat. Allerg. Imm. 2017, 28, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Arakawa, H.; Ishii, N.; Ubukata, C.; Michimori, M.; Noda, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kaminogawa, S.; Hosono, A. Dietary Fructo-Oligosaccharides Attenuate Early Activation of CD4+ T Cells Which Produce both Th1 and Th2 Cytokines in the Intestinal Lymphoid Tissues of a Murine Food Allergy Model. Int. Arch. Allergy Imm. 2017, 174, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tordesillas, L.; Mondoulet, L.; Blazquez, A.B.; Benhamou, P.H.; Sampson, H.A.; Berin, C. Epicutaneous immunotherapy induces gastrointestinal LAP+ Tregs and prevents food-induced anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin Immun. 2017, 139, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wu, Y.; Wen, X.; Gao, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Dietary Linolenic Acid Increases Sensitizing and Eliciting Capacities of Cow’s Milk Whey Proteins in BALB/c Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villas-Boas, M.B.; Vieira, K.P.; Trevizan, G.; de Lima Zollner, R.; Netto, F.M. The effect of transglutaminase-induced polymerization in the presence of cysteine on β-lactoglobulin antigenicity. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; di Pierro, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Mariniello, L. Transglutaminase-mediated modification of ovomucoid: Effects on its trypsin inhibitory activity and antigenic properties. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, F.; Tang, C. Properties and microstructure of transglutaminase-set soy protein-stabilized emulsion gels. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Tan, Y.; Chang, S.; Li, J.; Maleki, S.; Puppala, N. Peanut allergen reduction and functional property improvement by means of enzymatic hydrolysis and transglutaminase crosslinking. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, S.; Martínez-Blanco, M.; López-Fandiño, R.; Molina, E. IgE-Binding and Immunostimulating Properties of Enzymatic Crosslinked Milk Proteins as Influenced by Food Matrix and Digestibility. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Qazi, I.M.; Luo, C.; Gao, X.; Khan, M.U.; Iqbal, A.; Guo, Y.; et al. Tyrosinase/caffeic acid cross-linking alleviated shrimp (Metapenaeus ensis) tropomyosin-induced allergic responses by modulating the Th1/Th2 immunobalance. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Hu, M.; Sun, L.; Han, X.; Liu, Q.; Alcocer, M.; Fei, D.; Cao, M.; Liu, G. Allergenicity and Oral Tolerance of Enzymatic Cross-Linked Tropomyosin Evaluated Using Cell and Mouse Models. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Hui, J.; Lu, Q.; Yang, A.; Yuan, J.; Gao, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Effect of transglutaminase cross-linking on the allergenicity of tofu based on a BALB/c mouse model. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Deng, H.; Yang, A.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Effect of microbial transglutaminase cross-linking on the quality characteristics and potential allergenicity of tofu. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5485–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Screening of anti-allergy Lactobacillus and its effect on allergic reactions in BALB/c mice sensitized by soybean protein. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Mazliah, D.; Langhorne, J. CD4 T-Cell Subsets in Malaria: TH1/TH2 Revisited. Front. Immunol. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaat, R.M.; Mohamed, S.F.; Bassyouni, I.H.; Raouf, A.A. Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Cytokine 2015, 72, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.T.; Nadeau, K.C. Lessons learned from mice and man: Mimicking human allergy through mouse models. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 155, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaratham, C.; Sallis, B.F.; Fiebiger, E. Experimental Models for Studying Food Allergy. Cell. Mol. Gastroenter. 2018, 6, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schülke, S.; Albrecht, M. Mouse Models for Food Allergies: Where Do We Stand? Cells 2019, 8, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castan, L.; Bøgh, K.L.; Maryniak, N.Z.; Epstein, M.M.; Kazemi, S.; O’Mahony, L.; Bodinier, M.; Smit, J.J.; Bilsen, J.H.M.; Blanchard, C.; et al. Overview of in vivo and ex vivo endpoints in murine food allergy models: Suitable for evaluation of the sensitizing capacity of novel proteins? Allergy 2020, 75, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gramberg, J.L.; de Veer, M.J.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Meeusen, E.N.T.; Bischof, R.J. Use of Animal Models to Investigate Major Allergens Associated with Food Allergy. J. Allergy 2013, 2013, 635695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Li, T.; Liang, D.; Gong, H.; Zhao, L.; Mao, X. Maternal obesity exacerbates the responsiveness of offspring BALB/c mice to cow’s milk protein-induced food allergy. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2023, 12, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krempski, J.W.; Lama, J.K.; Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Matsunaga, M.; Kita, H. A mouse model of the LEAP study reveals a role for CTLA-4 in preventing peanut allergy induced by environmental peanut exposure. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2022, 150, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Shi, Q.; Tong, P.; Gao, J. Aflatoxin B1 can aggravate BALB/c mice allergy to ovalbumin through changing their Th2 cells immune responses. Toxicon 2023, 228, 107121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Yan, X.; Gu, S.; Jia, X.; Fu, W.; Meng, X.; Xue, W. Assessment of immune responses and intestinal flora in BALB/c mice model of wheat food allergy via different sensitization methods. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2023, 12, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, H.; Dang, X.; Jing, Y.; Meng, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Insight analysis of the cross-sensitization of multiple fish parvalbuminsvia the Th1/Th2 immunological balance and cytokine release from the perspective of safe consumption of fish. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, 690–699. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, J.J.; Bol-Schoenmakers, M.; Hassing, I.; Fiechter, D.; Boon, L.; Bleumink, R.; Pieters, R.H.H. The role of intestinal dendritic cells subsets in the establishment of food allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, A.B.; Berin, M.C. Gastrointestinal Dendritic Cells Promote Th2 Skewing via OX40L. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4441–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, N.; Klems, M.; Heiden, D.; Bauer, R.; Kitzmüller, C.; Weidmann, E.; Ret, D.; Ondracek, A.S.; Duschl, A.; Horejs Hoeck, J.; et al. Nitrated food proteins induce a regulatory immune response associated with allergy prevention after oral exposure in a Balb/c mouse food allergy model. Allergy 2020, 75, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kivit, S.; Kostadinova, A.I.; Kerperien, J.; Morgan, M.E.; Muruzabal, V.A.; Hofman, G.A.; Knippels, L.M.J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Garssen, J.; Willemsen, L.E.M. Dietary, nondigestible oligosaccharides and Bifidobacterium breve M-16V suppress allergic inflammation in intestine via targeting dendritic cell maturation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchielli, M.L.; Walker, W.A. The role of gut-associated lymphoid tissues and mucosal defence. Brit. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Arsenescu, R.I.; Arsenescu, V. Targeting Immunomodulatory Agents to the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 237–261. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Kang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, T.; Zeng, X.; Qiu, S. The role of dendritic cells in allergic diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 113, 109449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Saini, S.; Khan, S.; Lele, S.S.; Prabhakar, B.S. Restoring Self-tolerance in Autoimmune Diseases by Enhancing Regulatory Tcell. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 339, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Park, M.; Ji, K.; Lee, H.; Jang, J.; Yoon, I.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.; Jeong, Y.; Yun, C.; et al. Bacterial β-(1,3)-glucan prevents DSS-induced IBD by restoring the reduced population of regulatory T cells. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, M.N.; Chatila, T.A. Regulatory T cells in allergic diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 138, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiem, M.; Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk, U. Intestinal Barrier Permeability in Allergic Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Zuo, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Degradation of major allergens and allergenicity reduction of soybean meal through solid-state fermentation with microorganisms. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Yang, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, H. Allergenicity characteristics of germinated soybean proteins in a BALB/c mouse model. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2015, 72, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, N.; Klems, M.; Untersmayr, E. The role of gastrointestinal permeability in food allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Score | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptoms |
| 1 | Scratching nose and mouth |
| 2 | Swelling around the eyes and mouth; pillar erection; reduced activity; higher breathing rate |
| 3 | Shortness of breath; blue rash around the mouth and tail; higher breathing rate |
| 4 | No activity after stimulation; shivering and muscle contractions |
| 5 | Death by shock |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Yang, A.; Chen, H. Transglutaminase-Cross-Linked Tofu Suppressed Soybean-Induced Allergic Reactions by Enhancing Intestinal Mucosa Immune Tolerance. Foods 2024, 13, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081206
Bai J, Zhou Y, Xia X, Wu Z, Li X, Tong P, Yang A, Chen H. Transglutaminase-Cross-Linked Tofu Suppressed Soybean-Induced Allergic Reactions by Enhancing Intestinal Mucosa Immune Tolerance. Foods. 2024; 13(8):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081206
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Jing, Yiling Zhou, Xinlei Xia, Zhihua Wu, Xin Li, Ping Tong, Anshu Yang, and Hongbing Chen. 2024. "Transglutaminase-Cross-Linked Tofu Suppressed Soybean-Induced Allergic Reactions by Enhancing Intestinal Mucosa Immune Tolerance" Foods 13, no. 8: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081206
APA StyleBai, J., Zhou, Y., Xia, X., Wu, Z., Li, X., Tong, P., Yang, A., & Chen, H. (2024). Transglutaminase-Cross-Linked Tofu Suppressed Soybean-Induced Allergic Reactions by Enhancing Intestinal Mucosa Immune Tolerance. Foods, 13(8), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081206






