Physicochemical, Structural Structural and Functional Properties of Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Proso Millet Protein
2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.4. Protein Solubility
2.5. Surface Hydrophobicity (S0)
2.6. Emulsifying Properties
2.7. Water Absorption Capacity (WAC) and Oil Absorption Capacity (OAC)
2.8. Intrinsic Fluorescence
2.9. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.10. Thermodynamic Properties
2.11. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Spectrum Analysis
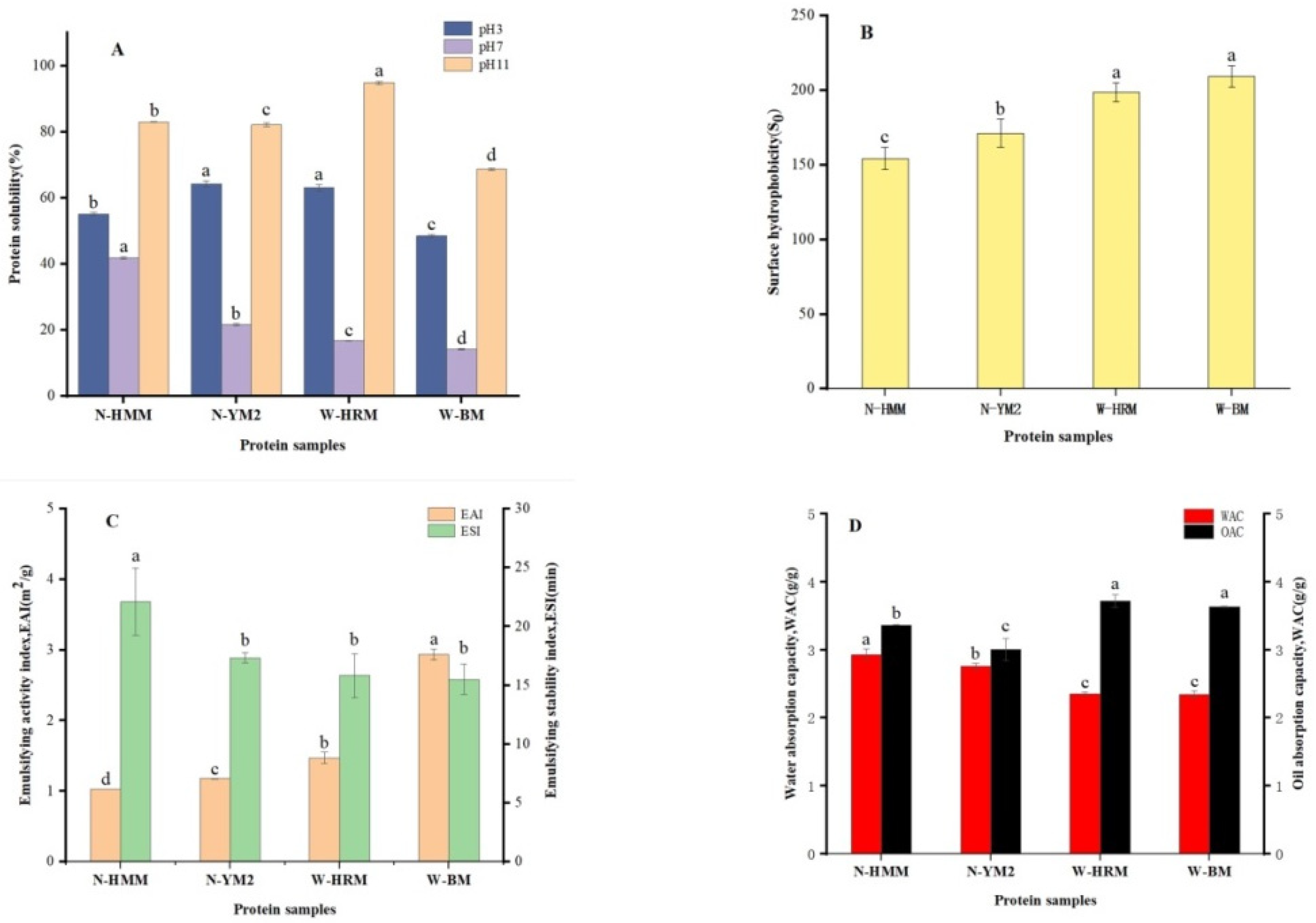
3.2. Protein Solubility
3.3. Surface Hydrophobicity (S0)
3.4. Emulsifying Properties
3.5. WAC and OAC
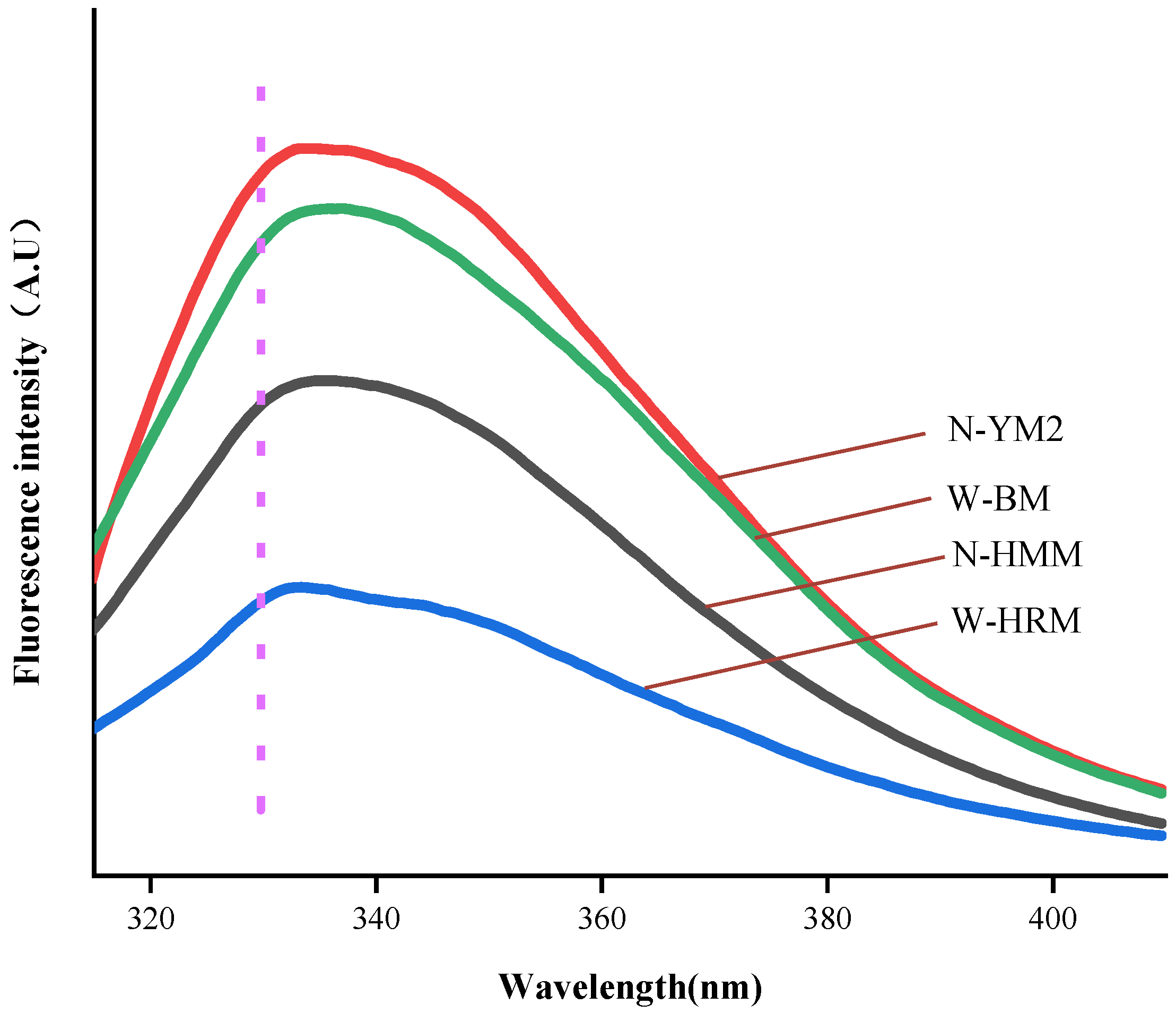
3.6. Intrinsic Fluorescence
3.7. XRD
3.8. Thermal Properties
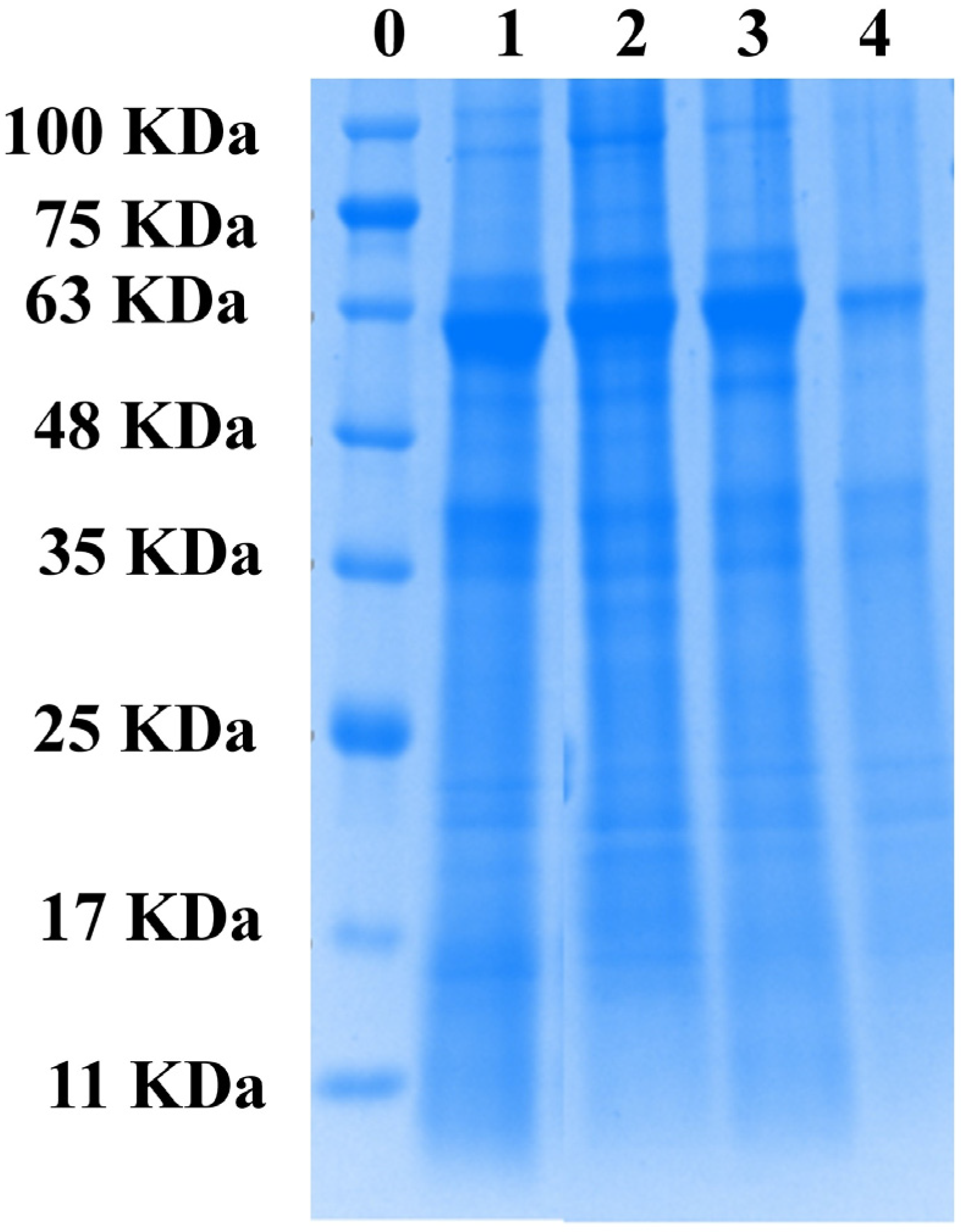
3.9. Electrophoresis Pattern (SDS-PAGE)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Bilali, H.; Callenius, C.; Strassner, C.; Probst, L. Food and nutrition security and sustainability transitions in food systems. Food Energy Secur. 2019, 8, e00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Sarkar, K.; Baral, R.; Laskar, S. Some chemical investigations of Amoora rohituka seed proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, H.; Shi, S.; Hu, J.; Peng, H.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, W. Physicochemical and functional properties of the protein isolate and major fractions prepared from Akebia trifoliata var. australis seed. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Peschel, A.O. Consumer perception of plant-based proteins: The value of source transparency for alternative protein ingredients. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henchion, M.; Hayes, M.; Mullen, A.M.; Fenelon, M.; Tiwari, B. Future Protein Supply and Demand: Strategies and Factors Influencing a Sustainable Equilibrium. Foods 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Setia, R.; Dai, Z.; Nickerson, M.T.; Sopiwnyk, E.; Malcolmson, L.; Ai, Y. Impacts of short-term germination on the chemical compositions, technological characteristics and nutritional quality of yellow pea and faba bean flours. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinova, J.; Moudry, J. Content and Quality of Protein in Proso Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) Varieties. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2006, 61, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.S.M.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Shen, Q. Millet Grains: Nutritional Quality, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annor, G.A.; Tyl, C.; Marcone, M.; Ragaee, S.; Marti, A. Why do millets have slower starch and protein digestibility than other cereals? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D.N.; Galante, M.; Robson, M.; Boeris, V.; Spelzini, D. Amaranth, quinoa and chia protein isolates: Physicochemical and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarpa-Parra, M.; Wong, L.; Wismer, W.; Temelli, F.; Han, J.; Huang, W.; Eckhart, E.; Tian, Z.; Shi, K.; Sun, T.; et al. Quality characteristics of angel food cake and muffin using lentil protein as egg/milk replacer. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.K.; Zhu, K.; Issoufou, A.; Fatmata, T.; Zhou, H. Functionality, in Vitro Digestibility and Physicochemical Properties of Two Varieties of Defatted Foxtail Millet Protein Concentrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5224–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindran, G. Seed protein of millets: Amino acid composition, proteinase inhibitors and in-vitro protein digestibility. Food Chem. 1992, 44, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, N.I.; Makarenko, N.I.; Orlova, S. Effect of Cooking on Protein Digestibility of Millets and Their Amino Acid Composition. Nahrung 1974, 18, 517–522. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4437607 (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Gong, X.; Feng, B. Physicochemical Properties of Starches in Proso (Non-Waxy and Waxy) and Foxtail Millets (Non-Waxy and Waxy). Molecules 2019, 24, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, F.; Ji, X.; Feng, B.; Liang, J.; Yu, X.; Du, S.-K. Structure, physicochemical, functional and in vitro digestibility properties of non-waxy and waxy proso millet starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 224, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akharume, F.; Santra, D.; Adedeji, A. Physicochemical and functional properties of proso millet storage protein fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-L.; Huang, G.-Q.; Wang, H.-O.; Xiao, J.-X. Effect of high coacervation temperature on the physicochemical properties of resultant microcapsules through induction of Maillard reaction between soybean protein isolate and chitosan. J. Food Eng. 2018, 234, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-Q.; Luo, S.-Z.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, S.-T.; Zheng, Z. Changes in chemical interactions and protein conformation during heat-induced wheat gluten gel formation. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Fu, S.; Wu, C.; Qi, B.; Teng, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. The investigation of protein flexibility of various soybean cultivars in relation to physicochemical and conformational properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Rana, J.C.; Kaur, A. Relationship between physicochemical and functional properties of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) protein isolates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, D.; Wan, C.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Gao, X.; Feng, B. Improving the Functionality of Proso Millet Protein and Its Potential as a Functional Food Ingredient by Applying Nitrogen Fertiliser. Foods 2021, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xiong, H.; Selomulya, C.; Chen, X.D.; Huang, S.; Ruan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, W. Effects of Spray Drying and Freeze Drying on the Properties of Protein Isolate from Rice Dreg Protein. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Chen, Y.; Kaur, A.; Yu, L. Pulse proteins: Secondary structure, functionality and applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zamani, S.; Liang, L.; Chen, L. Extraction methods significantly impact pea protein composition, structure and gelling properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, N.A.; Riar, C.S.; Singh, S. Effect of pH and holding time on the characteristics of protein isolates from Chenopodium seeds and study of their amino acid profile and scoring. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokni Ghribi, A.; Maklouf Gafsi, I.; Sila, A.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Bougatef, A.; Besbes, S. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on conformational and functional properties of chickpea protein isolate. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Kadivar, M.; Shahedi, M. Effects of succinylation and deamidation on functional properties of oat protein isolate. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Withana-Gamage, T.S.; Wanasundara, J.P.D.; Pietrasik, Z.; Shand, P.J. Physicochemical, thermal and functional characterisation of protein isolates from Kabuli and Desi chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A comparative study with soy (Glycine max) and pea (Pisum sativum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liang, Q.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Zhou, C.; Mahunu, G.K. Effects of ultrasound and ultrasound assisted alkaline pretreatments on the enzymolysis and structural characteristics of rice protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Lv, R.; Balaso Watharkar, R.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Effect of pH-shifting treatment on structural and functional properties of whey protein isolate and its interaction with (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.A.; Sharma, H.K.; Saini, C.S. Effect of gamma irradiation on structural, molecular, thermal and rheological properties of sunflower protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundi, S.; Aluko, R.E. Effects of NaCl and pH on the structural conformations of kidney bean vicilin. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhan, F.; Gani, A.; Noor, N.; Shah, A. Nanoreduction of Millet Proteins: Effect on Structural and Functional Properties. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihi, M.-L.; Mession, J.-l.; Sok, N.; Saurel, R. Heat-Induced Soluble Protein Aggregates from Mixed Pea Globulins and β-Lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | β-Sheet (%) | Random Coils (%) | ɑ-Helix (%) | β-Turn (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-HMM | 55.63 ± 0.22 a | 9.91 ± 2.62 b | 14.75 ± 2.81 ab | 14.16 ± 0.97 b |
| N-YM2 | 53.59 ± 0.07 a | 13.58 ± 0.65 ab | 17.54 ± 3.00 a | 15.29 ± 2.40 cb |
| W-HRM | 45.22 ± 2.98 b | 11.72 ± 2.77 ab | 13.49 ± 0.13 ab | 24.94 ± 0.32 a |
| W-BM | 44.47 ± 2.88 b | 14.27 ± 1.39 a | 12.33 ± 1.34 b | 22.94 ± 1.78 a |
| Samples | Td (°C) | ∆H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|
| N-HMM | 89.27 ± 0.31 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| N-YM2 | 89.73 ± 0.25 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| W-HRM | 87.26 ± 0.84 b | 0.03 ± 0 b |
| W-BM | 83.96 ± 1.42 c | 0.02 ± 0.01 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Ma, C.; Li, M.; Dang, Y.; Yu, X.; Du, S. Physicochemical, Structural Structural and Functional Properties of Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051116
Ren J, Ma C, Li M, Dang Y, Yu X, Du S. Physicochemical, Structural Structural and Functional Properties of Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Protein. Foods. 2023; 12(5):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051116
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jing, Chao Ma, Mengqing Li, Yueyi Dang, Xiuzhu Yu, and Shuangkui Du. 2023. "Physicochemical, Structural Structural and Functional Properties of Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Protein" Foods 12, no. 5: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051116
APA StyleRen, J., Ma, C., Li, M., Dang, Y., Yu, X., & Du, S. (2023). Physicochemical, Structural Structural and Functional Properties of Non-Waxy and Waxy Proso Millet Protein. Foods, 12(5), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051116






