Study on the Flavor Compounds of Fo Tiao Qiang under Different Thawing Methods Based on GC–IMS and Electronic Tongue Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
- (1)
- Ultrasonic thawing: The Fo Tiao Qiang sample was placed into the ultrasonic device with a power of 200 W, frequency of 40 kHz, and temperature of 25 ± 1 °C for thawing.
- (2)
- Microwave thawing: The Fo Tiao Qiang sample was placed into a microwave tray and microwaved at a frequency of 500 W to defrost.
- (3)
- Water bath thawing: The Fo Tiao Qiang sample was placed in a water bath to thaw at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C.
- (4)
- Control group (natural thawing): The Fo Tiao Qiang samples were thawed in a ventilated room at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C in a natural environment.
2.2. GC–IMS Analysis
2.3. Electronic-Tongue Analysis
2.4. Free Amino Acid (FAA) Component Analysis
2.5. Taste Activity Value (TAV) Analysis
2.6. Measurement of Protein, Fat, Hydroxyproline, Total Sugar Content
2.7. Taste Nucleotide
2.8. Equivalent Umami Concentration (EUC)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protein, Fat, Hydroxyproline, and Total Sugar Content
3.2. FAA Component
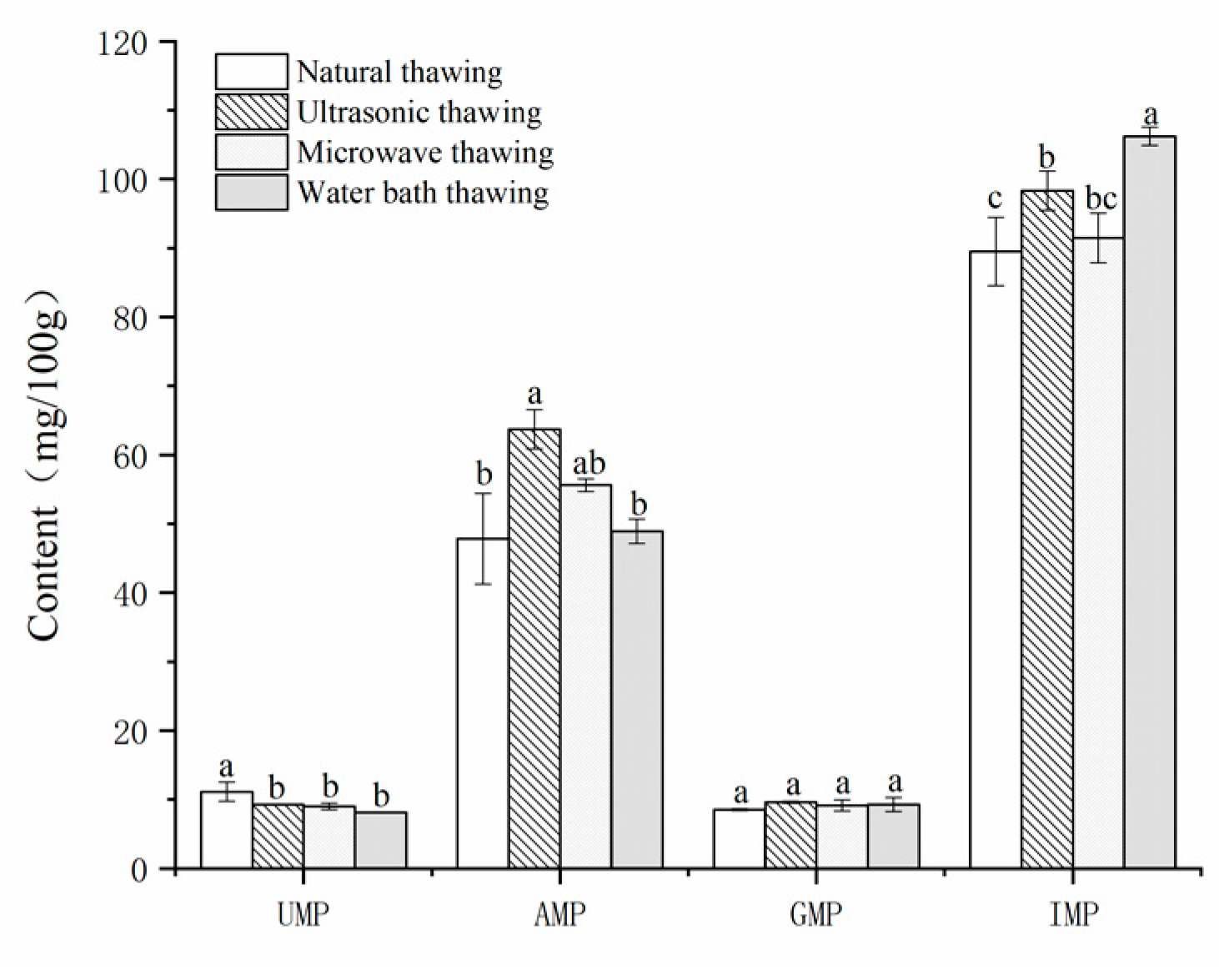
3.3. Taste Nucleotide
3.4. Electronic Tongue
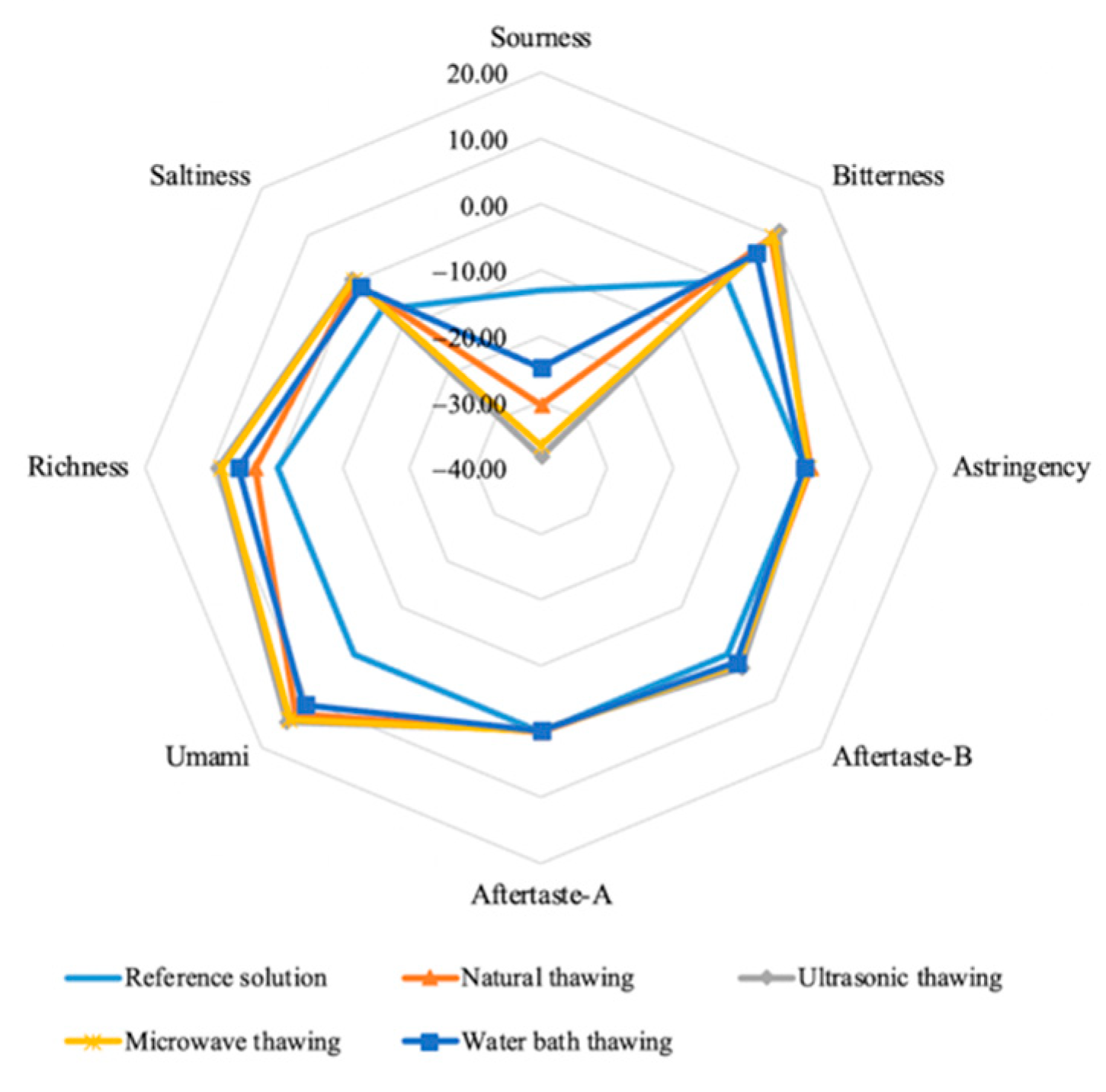
3.4.1. Flavor Profile
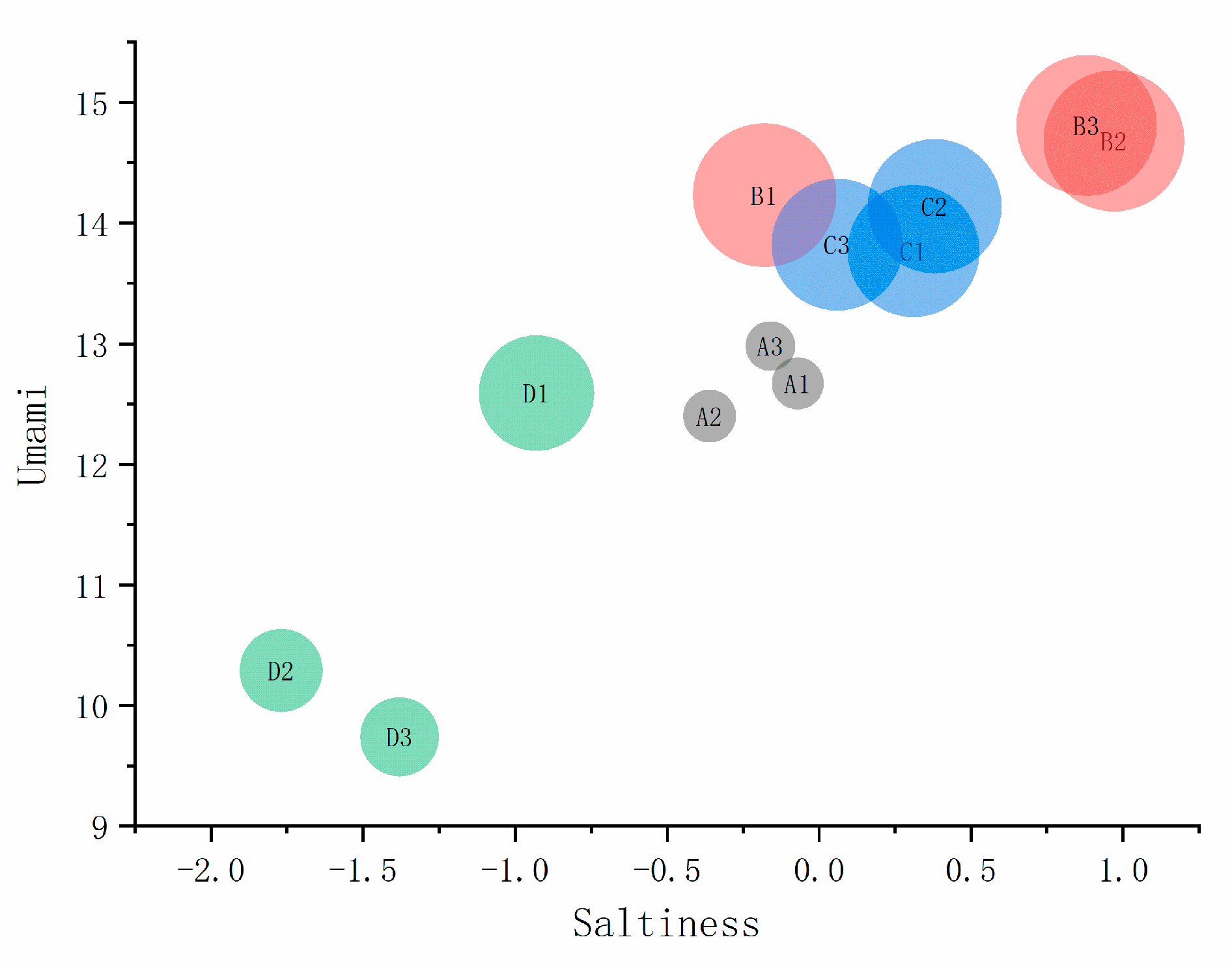
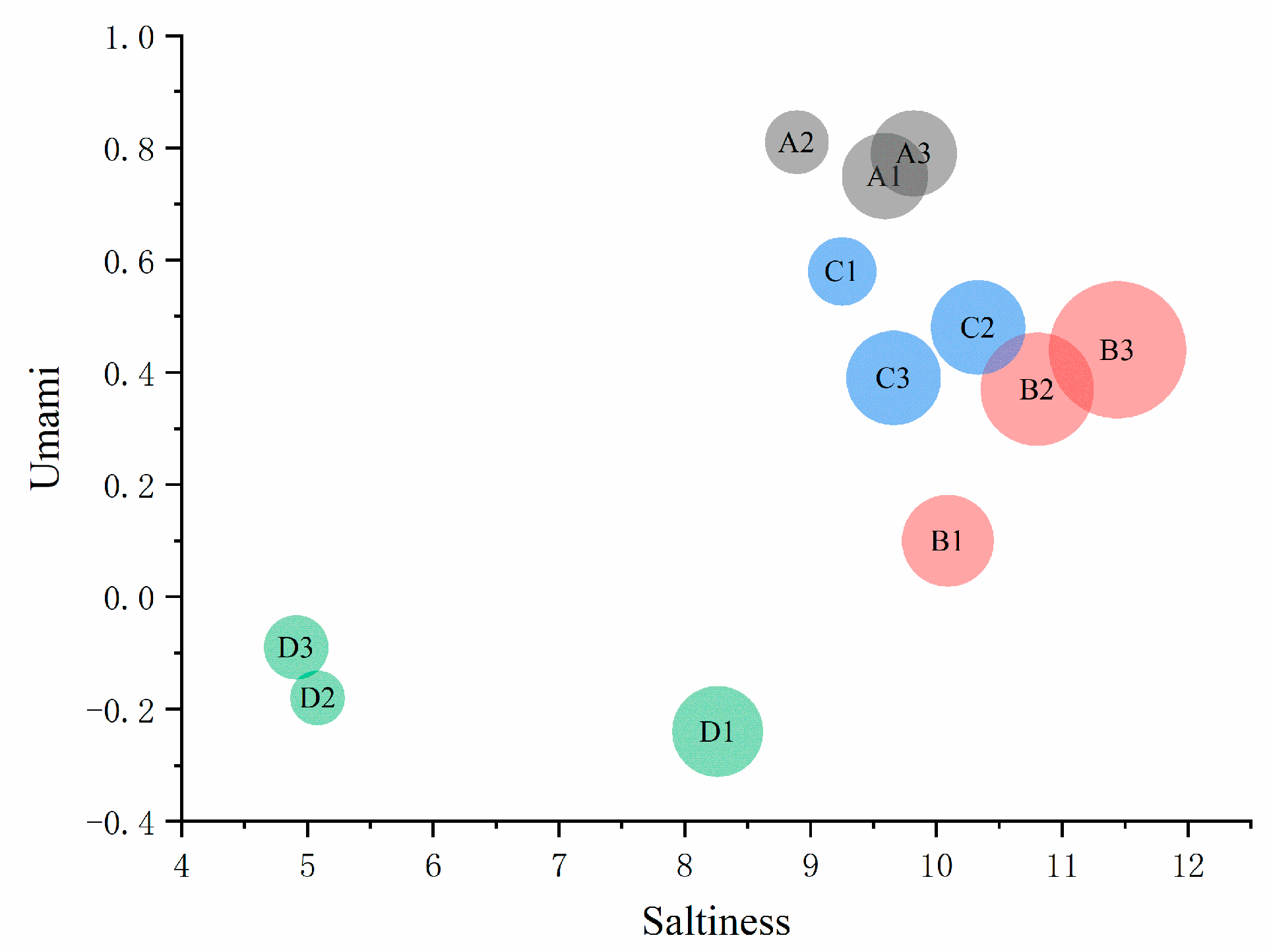
3.4.2. Umami, Saltiness, and Richness
3.4.3. Bitterness, Astringency, and Bitter Aftertaste
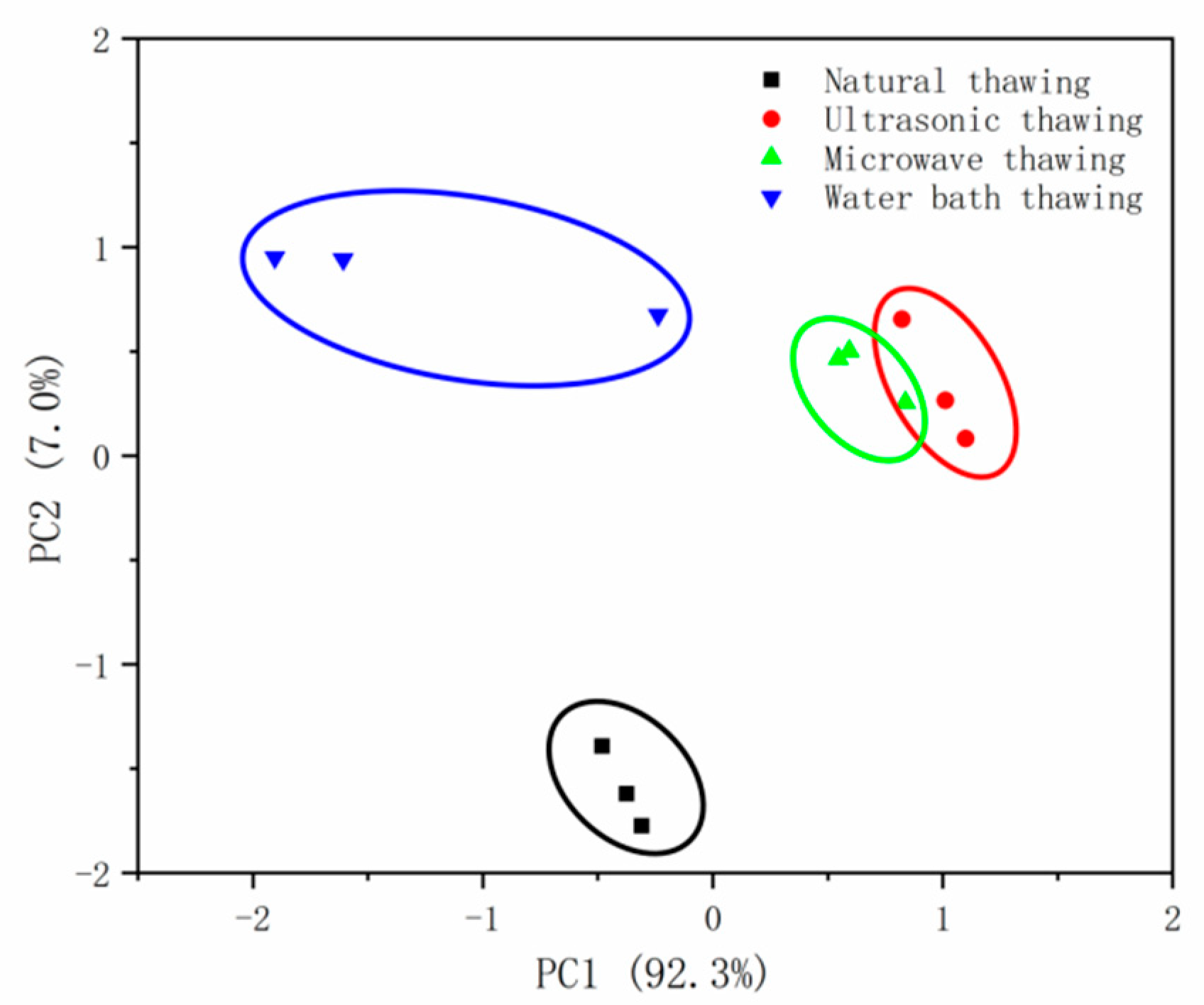
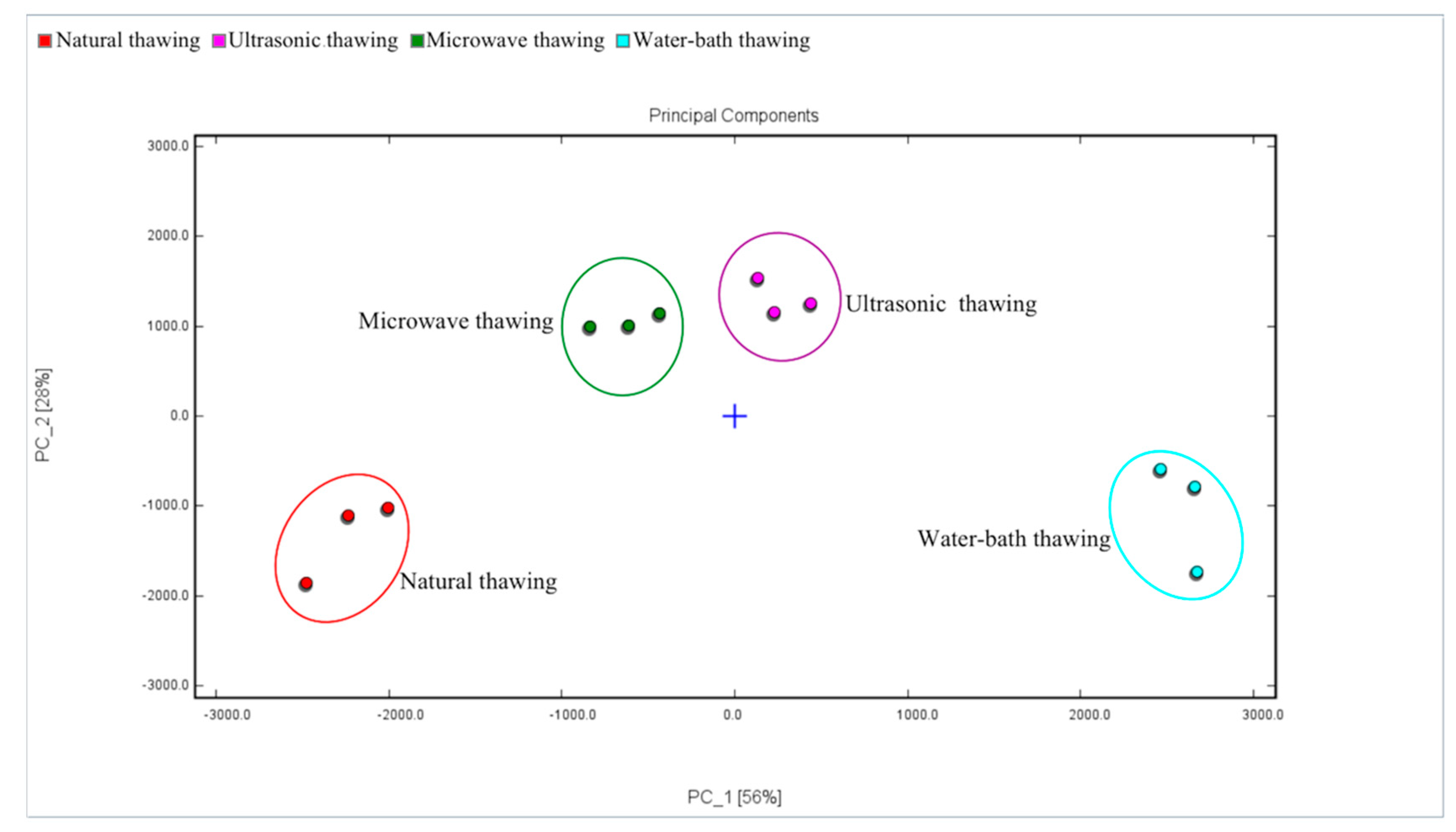
3.4.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.5. Volatile Substances
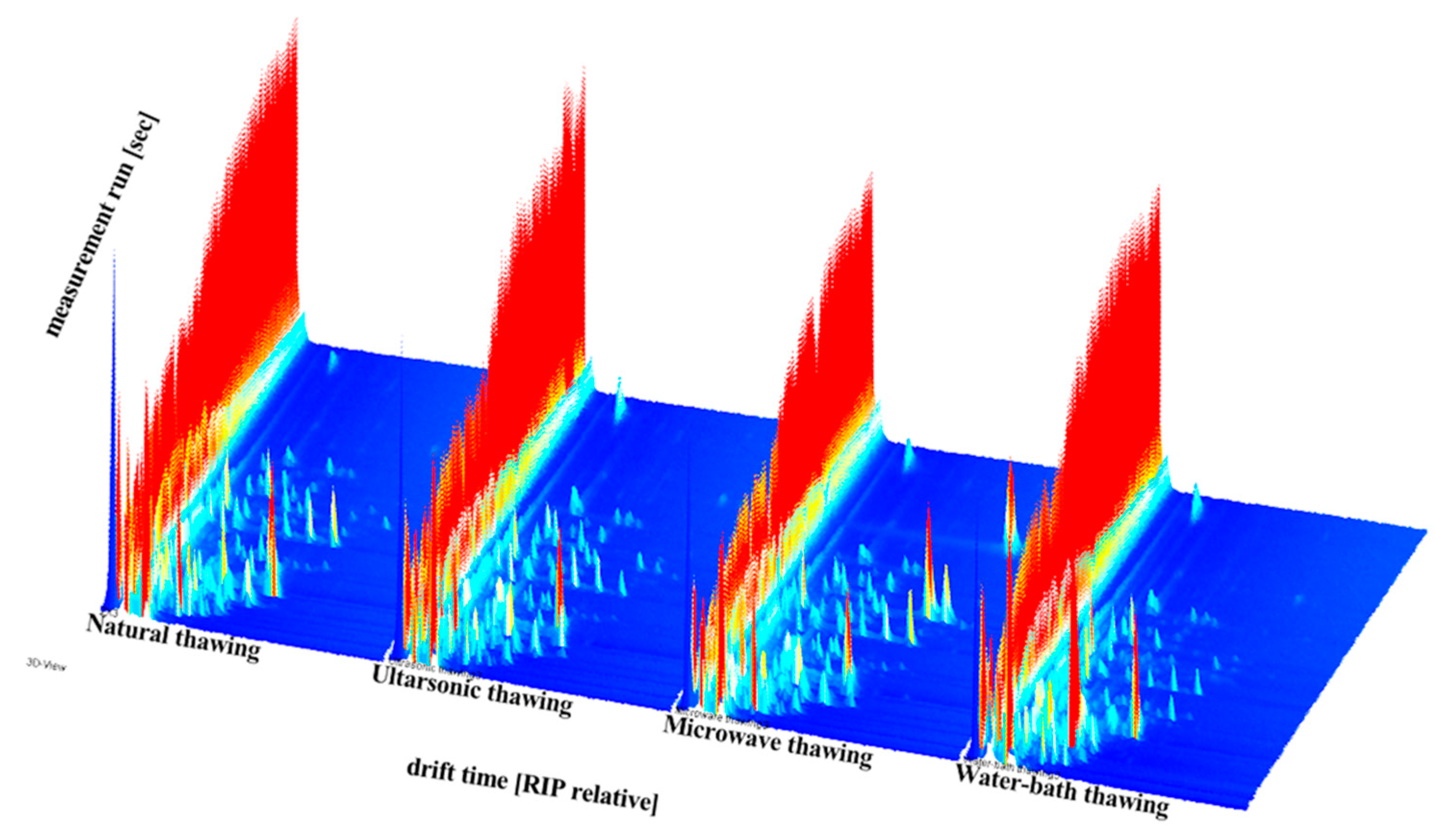
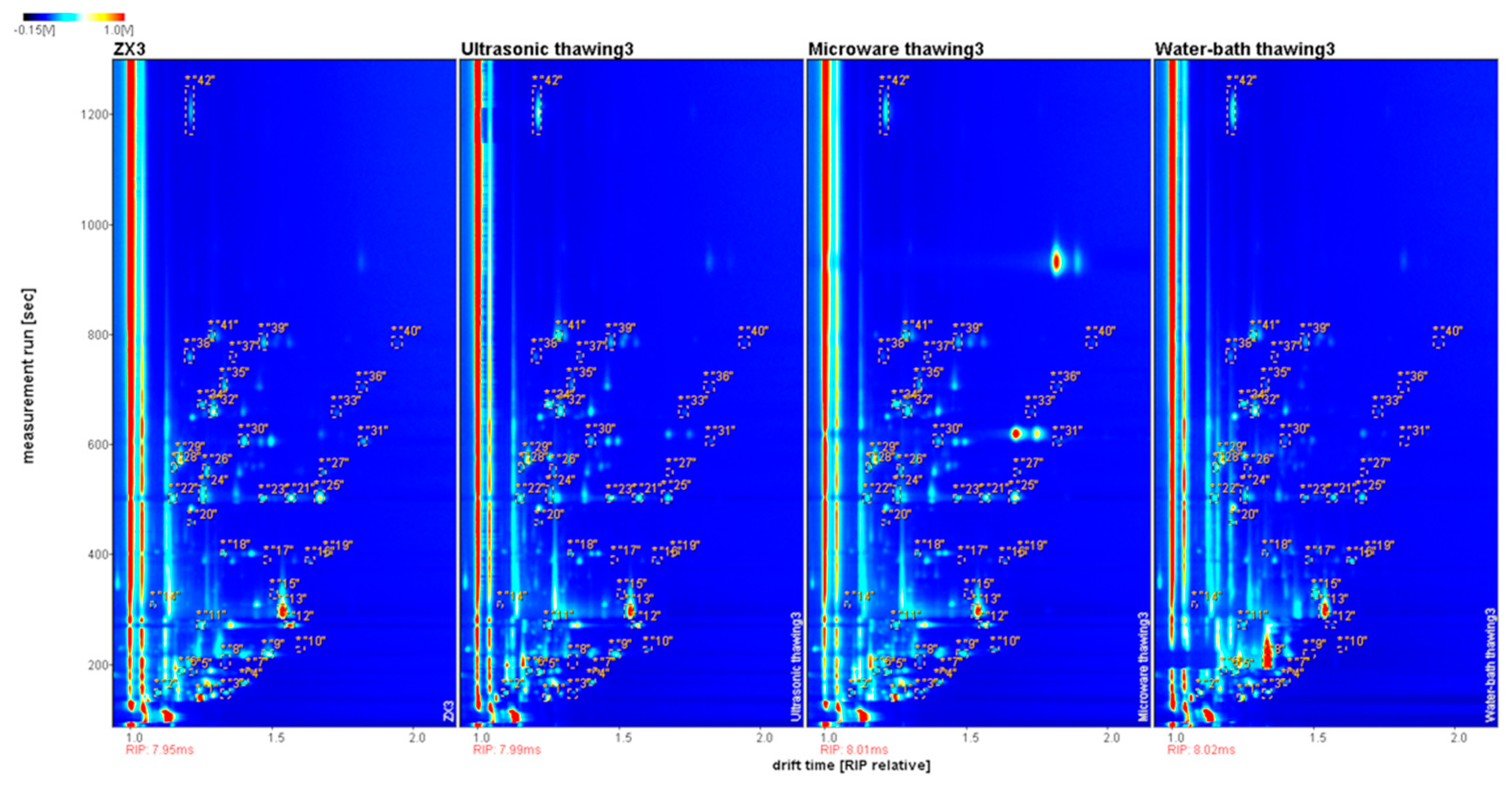
3.5.1. Comparative Analysis of GC–IMS Spectra
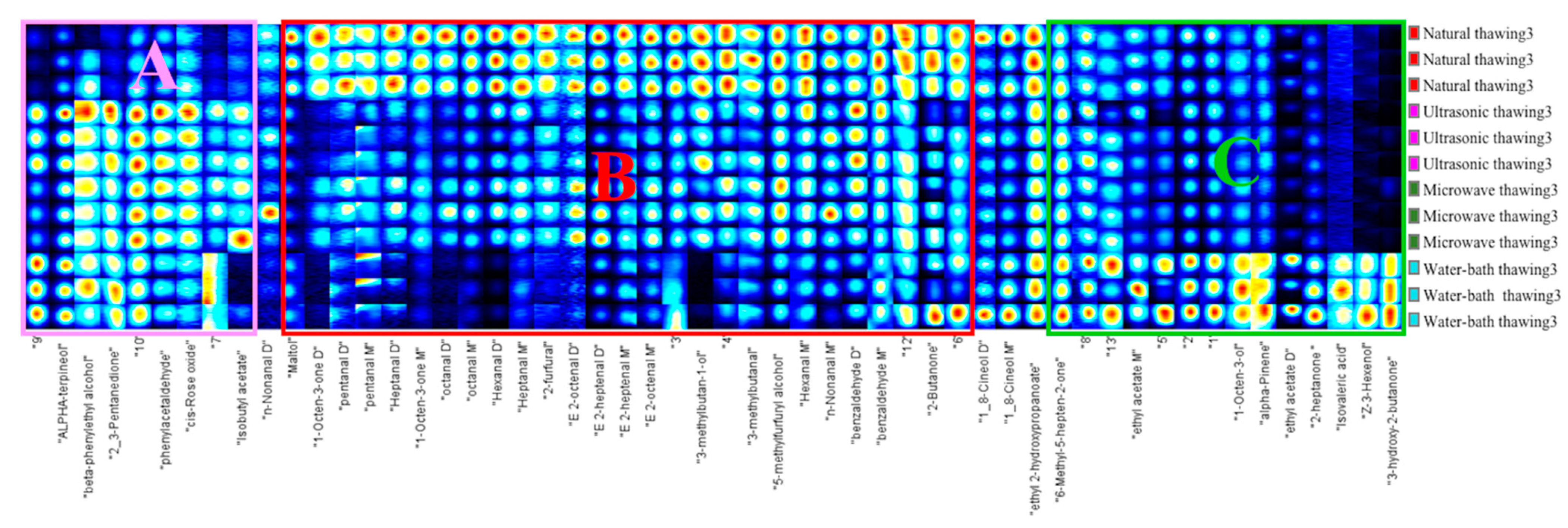
3.5.2. Qualitative Volatile Components
3.5.3. GC–IMS PCA
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Zhao, H.; Muhammad, A.I.; Song, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, D. The comparison of ultrasound-assisted thawing, air thawing and water immersion thawing on the quality of slow/fast freezing bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fillets. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevik, M.; Icier, F. Numerical simulation of temperature histories of frozen minced meat having different fat contents during ohmic thawing. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 165, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Nirasawa, S.; Ji, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, H. Physicochemical changes in myofibrillar proteins extracted from pork tenderloin thawed by a high-voltage electrostatic field. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Kou, X.; Liu, L.; Hou, L.; Li, R.; Wang, S. Effect of water, fat, and salt contents on heating uniformity and color of ground beef subjected to radio frequency thawing process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, A.; Cao, M.; Li, J. Effects of ultrasonics combined with far infrared or microwave thawing on protein denaturation and moisture migration of Sciaenops ocellatus (red drum). Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 55, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Ge, X.; Yang, L.; Ma, G.; Ma, J.; Yu, Q.-l.; Han, L. Ultrasound-assisted thawing of frozen white yak meat: Effects on thawing rate, meat quality, nutrients, and microstructure. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 70, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Kong, B.; Liu, S.; Zheng, O.; Zhang, C. Ultrasound-assisted thawing accelerates the thawing of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and improves its muscle quality. LWT 2021, 141, 111080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Ando, Y. Evaluation of heating uniformity and quality attributes during vacuum microwave thawing of frozen apples. LWT 2021, 150, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Dai, Y.; Cao, A.; Cao, M. The effects of CS@Fe3O4 nanoparticles combined with microwave or far infrared thawing on microbial diversity of red seabream (Pagrus major) fillets based on high-throughput sequencing. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Li, T.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Z. Estimation of Congou black tea quality by an electronic tongue technology combined with multivariate analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhao, F.; Chen, M.; Ye, N.; Lin, Q.; Ouyang, L.; Cai, X.; Meng, P.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y. Determination of 21 free amino acids in 5 types of tea by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) using a modified 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) method. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 81, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerdijk-Poortvliet, T.C.W.; de Jong, D.L.C.; Fremouw, R.; de Reu, S.; de Winter, J.M.; Timmermans, K.; Mol, G.; Reuter, N.; Derksen, G.C.H. Extraction and analysis of free amino acids and 5′-nucleotides, the key contributors to the umami taste of seaweed. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.Y.S.; Ikeda, T.S. NNinomiya. Measurement of the relative taste intensity of some l-α-amino acids and 5′-nucleotides. J. Food Sci. 1971, 36, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xia, X.; Kong, B. Changes in myofibrillar protein gel quality of porcine longissimus muscle induced by its stuctural modification under different thawing methods. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahnak, R.; Nourani, M.; Riahi, E. Ultrasound thawing of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus): Effects on thawing rate, protein denaturation and some physical properties. LWT 2021, 151, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xing, L.; Kang, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Effects of ultrasound-assisted vacuum tumbling on the oxidation and physicochemical properties of pork myofibrillar proteins. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 74, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-C.; Gao, X.-Q.; Ge, Q.-F.; Zhou, G.-H.; Zhang, W.-G. Effects of ultrasound on the beef structure and water distribution during curing through protein degradation and modification. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 38, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Niu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the quality, nutrients and volatile compounds of dry-cured yak meat. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 82, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xing, L.; Zhang, W. Influences of ultrasonic-assisted frying on the flavor characteristics of fried meatballs. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X. Enhancing the taste of raw soy sauce using low intensity ultrasound treatment during moromi fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Kang, D.; Liu, R.; Qi, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, W. Effects of ultrasonic assisted cooking on the chemical profiles of taste and flavor of spiced beef. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 46, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Gao, D.; Xu, E.; Guo, M.; Liu, D. Desorption of nutrients and flavor compounds formation during the cooking of bone soup. Food Control 2022, 132, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yi, S.; Zhu, W.; Mi, H.; Li, T.; Li, J. Combined ultrasound and heat pretreatment improve the enzymatic hydrolysis of clam (Aloididae aloidi) and the flavor of hydrolysates. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabikun, N.; Bakhsh, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Volatile and nonvolatile taste compounds and their correlation with umami and flavor characteristics of chicken nuggets added with milkfat and potato mash. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Pan, D.; Geng, F.; Cao, J.; Xia, Q. Kinetic response of conformational variation of duck liver globular protein to ultrasonic stimulation and its impact on the binding behavior of n-alkenals. LWT 2021, 150, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Protein (g/100 g) | Hydroxyproline (g/100 g) | Fat (g/100 g) | Total Sugar (g/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural thawing | 75.57 ± 1.57 a | 0.016 ± 0.00 a | 0.249 ± 0.02 a | 0.0162 ± 0.00 a |
| Ultrasonic thawing | 76.06 ± 4.18 a | 0.016 ± 0.00 a | 0.197 ± 0.03 ab | 0.0153 ± 0.00 a |
| Microwave thawing | 74.21 ± 1.67 a | 0.014 ± 0.00 a | 0.143 ± 0.00 b | 0.0162 ± 0.00 a |
| Water bath thawing | 74.35 ± 4.12 a | 0.015 ± 0.00 a | 0.175 ± 0.09 ab | 0.0154 ± 0.00 a |
| Amino Acid | Taste Contribution | Threshold (mg/100 g) | Natural Thawing | Ultrasonic Thawing | Microwave Thawing | Water bath Thawing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | |||
| Asp | fresh | 100 | 58.90 ± 3.88 b | 0.59 | 69.34 ± 1.97 a | 0.69 | 61.18 ± 0.74 ab | 0.61 | 69.20 ± 7.71 a | 0.69 |
| Glu | fresh | 30 | 332.84 ± 8.20 b | 11.09 | 371.00 ± 3.42 a | 11.43 | 318.91 ± 4.43 c | 10.63 | 342.84 ± 3.12 b | 11.43 |
| Ger | sweet | 150 | 62.25 ± 3.86 a | 0.41 | 72.52 ± 2.59 a | 0.41 | 64.80 ± 2.12 a | 0.43 | 62.24 ± 8.01 a | 0.41 |
| Gly | sweet | 130 | 104.06 ± 3.76 b | 0.80 | 96.74 ± 0.85 b | 0.48 | 121.61 ± 4.08 a | 0.94 | 130.12 ± 6.2 a | 1.00 |
| Thr | sweet | 260 | 42.67 ± 1.31 a | 0.16 | 44.77 ± 0.20 a | 0.50 | 41.82 ± 0.27 a | 0.16 | 42.66 ± 3.21 a | 0.16 |
| Ala | sweet | 60 | 108.89 ± 0.93 c | 1.81 | 119.26 ± 2.68 a | 0.71 | 110.57 ± 4.36 bc | 1.84 | 116.01 ± 2.18 ab | 1.93 |
| Pro | sweet | - | 66.05 ± 1.31 b | / | 68.50 ± 0.73 ab | / | 66.20 ± 0.51 b | / | 71.76 ± 4.37 a | / |
| Lys | sweet/bitter | 50 | 62.49 ± 1.84 a | 1.25 | 63.95 ± 0.20 a | 1.44 | 57.81 ± 0.64 b | 1.16 | 62.84 ± 3.67 a | 1.26 |
| Asn | sweet | - | 44.96 ± 0.82 a | / | 49.76 ± 2.66 a | / | 46.28 ± 2.29 a | / | 45.91 ± 3.24 a | / |
| Tyr | bitter | - | 41.45 ± 1.11 b | / | 46.93 ± 1.97 a | / | 41.09 ± 0.51 b | / | 41.51 ± 1.77 b | / |
| Val | bitter/sweet | 40 | 47.96 ± 0.41 b | 1.20 | 50.98 ± 2.96 a | 1.04 | 47.24 ± 0.28 b | 1.18 | 50.80 ± 1.31 a | 1.27 |
| Iel | bitter | 90 | 33.70 ± 2.50 a | 0.37 | 28.98 ± 2.20 b | 0.56 | 29.43 ± 2.62 ab | 0.33 | 27.96 ± 0.69 b | 0.31 |
| Leu | bitter | 190 | 67.08 ± 1.15 a | 0.35 | 64.05 ± 1.84 ab | 0.00 | 61.23 ± 1.52 b | 0.32 | 61.31 ± 2.51 b | 0.32 |
| Arg | bitter/sweet | 50 | 105.41 ± 5.86 a | 2.11 | 95.37 ± 5.91 a | 0.56 | 104.59 ± 0.06 a | 2.09 | 100.62 ± 1.0 a | 2.01 |
| His | bitter | 20 | 26.69 ± 0.10 b | 1.33 | 28.68 ± 0.19 a | 3.07 | 26.02 ± 0.52 b | 1.30 | 28.58 ± 0.56 a | 1.43 |
| Met | bitter | 30 | 12.03 ± 0.28 bc | 0.40 | 14.27 ± 0.62 a | 3.35 | 29.43 ± 2.62 ab | 0.33 | 11.17 ± 1.23 c | 0.37 |
| Trp | bitter | - | 6.98 ± 0.23 a | / | 5.71 ± 0.29 b | / | 13.55 ± 0.20 ab | / | 4.67 ± 0.95 b | / |
| Totol | 1224.40 ± 37.55 b | 1290.79 ± 31.28 a | 1217.67 ± 25.22 b | 1270.19 ± 53.98 ab | ||||||
| Nucleotide | Threshold (mg/100 g) | Natural Thawing | Ultrasonic Thawing | Microwave Thawing | Water Bath Thawing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | ||
| AMP Adenosine | 50 | 47.82 ± 6.58 b | 0.96 | 63.73 ± 2.87 a | 1.27 | 55.62 ± 0.91 ab | 1.11 | 48.90 ± 1.76 b | 0.98 |
| GMP Guanylic acid | 12.5 | 8.52 ± 0.14 a | 0.68 | 9.60 ± 0.14 a | 0.77 | 9.14 ± 0.80 a | 0.73 | 9.28 ± 0.99 a | 0.74 |
| IMP Inosinic acid | 25 | 89.53 ± 4.95 c | 3.58 | 98.34 ± 2.84 b | 3.93 | 91.48 ± 3.59 b | 3.66 | 106.23 ± 1.33 a | 4.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, R.; Yuan, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Z. Study on the Flavor Compounds of Fo Tiao Qiang under Different Thawing Methods Based on GC–IMS and Electronic Tongue Technology. Foods 2022, 11, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091330
Lin R, Yuan H, Wang C, Yang Q, Guo Z. Study on the Flavor Compounds of Fo Tiao Qiang under Different Thawing Methods Based on GC–IMS and Electronic Tongue Technology. Foods. 2022; 11(9):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091330
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ruirong, Hongfei Yuan, Changrong Wang, Qingyu Yang, and Zebin Guo. 2022. "Study on the Flavor Compounds of Fo Tiao Qiang under Different Thawing Methods Based on GC–IMS and Electronic Tongue Technology" Foods 11, no. 9: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091330
APA StyleLin, R., Yuan, H., Wang, C., Yang, Q., & Guo, Z. (2022). Study on the Flavor Compounds of Fo Tiao Qiang under Different Thawing Methods Based on GC–IMS and Electronic Tongue Technology. Foods, 11(9), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091330










