Quantitative Determination of Bisphenol A and Its Congeners in Plant-Based Beverages by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Real Samples
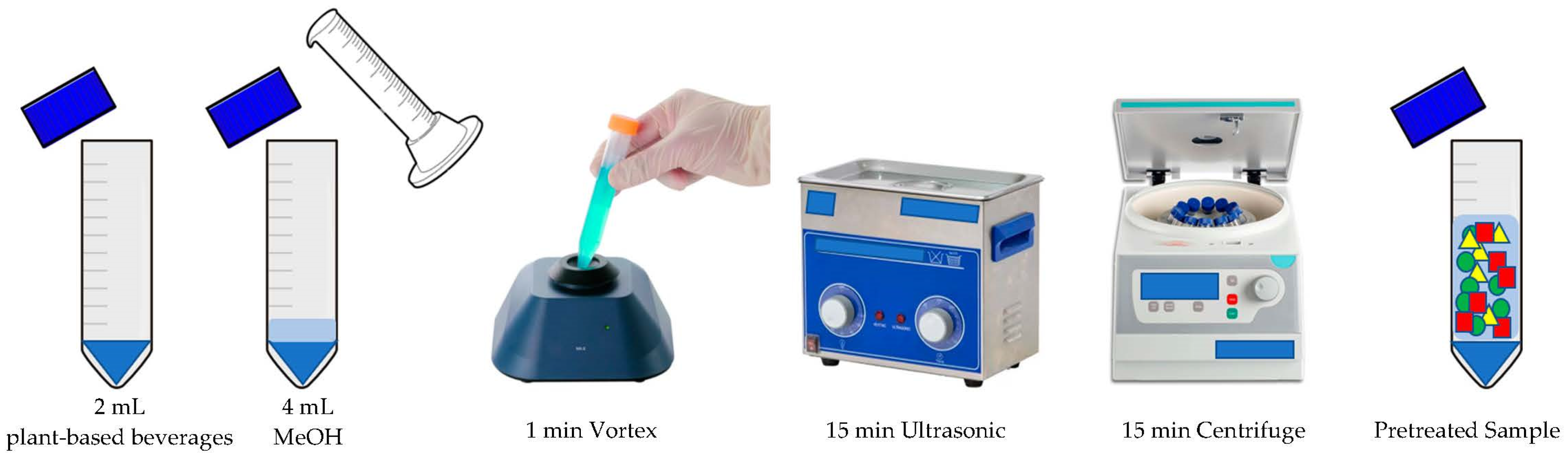
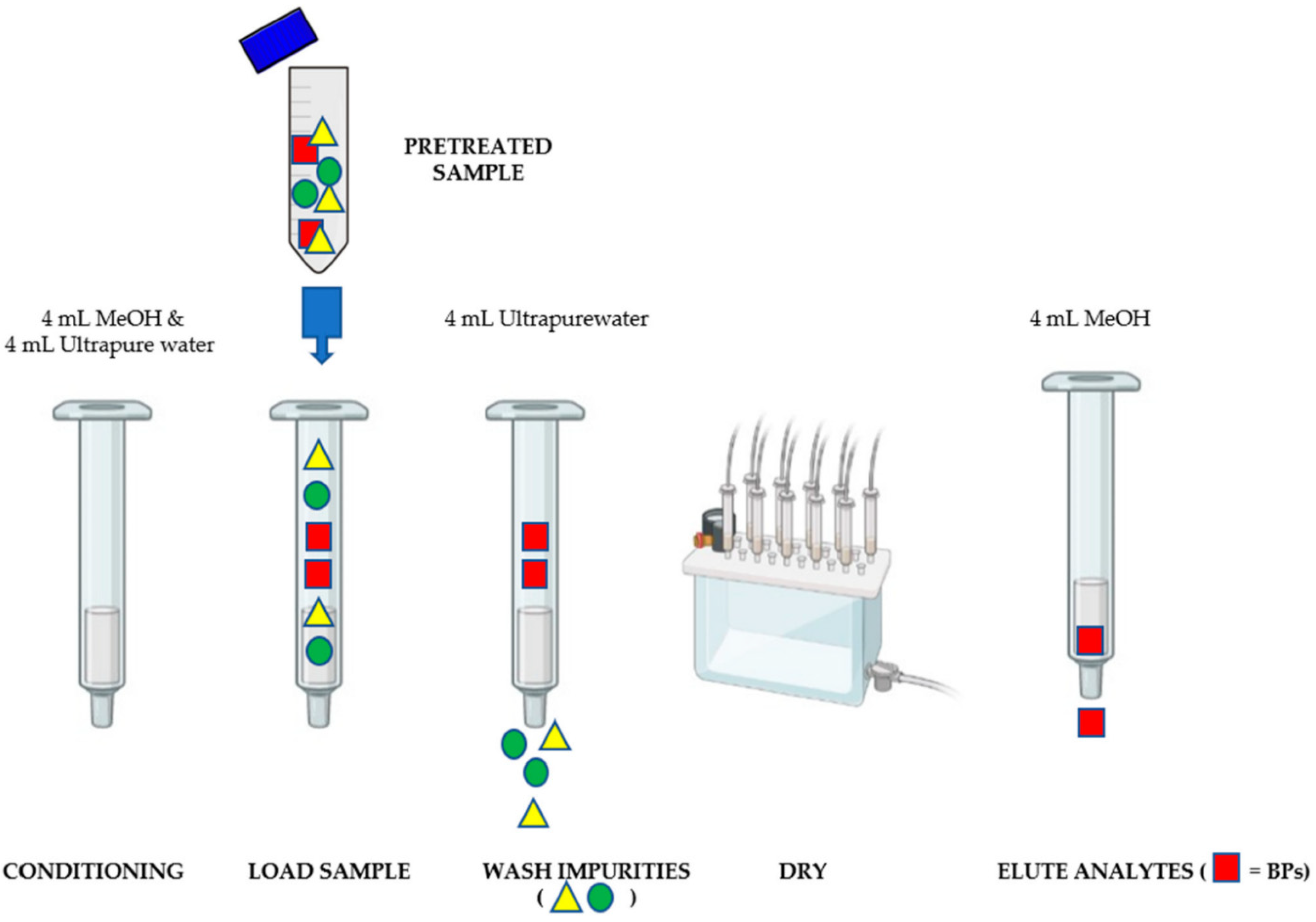
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.3.1. Sample Pretreatment
2.3.2. Sample Extraction Procedure by SPE
2.4. LC-ESI-QqQ-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Method Validation
- A = peak area obtained by adding the analytes to solvent consisted of ultrapure water and MeOH in the ratio of 50/50 (v/v).
- B = peak area obtained by spiking plant-based beverage extracts with the analytes.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Preparation and LC/ESI-QqQ MS/MS
3.2. Method Validation
3.3. BP Contamination in Plant-Based Beverages
3.4. Chronic Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zandona, L.; Lima, C.; Lannes, S. Plant-Based Milk Substitutes: Factors to Lead to Its Use and Benefits to Human Health. In Milk Substitutes—Selected Aspects, 1st ed.; Ziarno, M., Ed.; Intech Open, University of Life Sciences: Warsaw, Poland, 2021; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Astolfi, M.L.; Marconi, E.; Protano, C.; Canepari, S. Comparative elemental analysis of dairy milk and plant-based milk alternatives. Food Control 2020, 116, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Tyagi, S.K.; Anurag, R.K. Plant-based milk alternatives an emerging segment of functional beverages: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3408–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, H.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Alshahrani, S. Diet: A source of endocrine disruptors. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.; Chakraborty, P. A review on sources and health impacts of bisphenol A. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provvisiero, D.P.; Pivonello, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Negri, M.; De Angelis, C.; Simeoli, C.; Pivonello, R.; Colao, A. Influence of Bisphenol A on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 613, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M. Early life exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals and childhood obesity and neurodevelopment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wua, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P.W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The adverse health effects of bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575–108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Zou, J.; Li, Q.; Mai, H.; Su, D.; Ling, W.; Feng, X. Bisphenol A exposure induces gut microbiota dysbiosis and consequent activation of gut-liver axis leading to hepatic steatosis in CD-1 mice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114880–114891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predieri, B.; Bruzzi, P.; Bigi, E.; Cianci, S.; Made, S.E.; Lucaccioni, L.; Iughetti, L. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and type 1 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.B.; Bilenberg, N.; Timmermann, C.A.G.; Jensen, R.C.; Frederiksen, H.; Andersson, A.; Kyhl, H.B.; Jensen, T.K. Prenatal exposure to bisphenol A and autistic- and ADHD-related symptoms in children aged 2 and 5 years from the Odense Child Cohort. J. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, S. The politics of plastics: The making and unmaking of Bisphenol A safety. Am. J. Public Health 2019, 99, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wu, L.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol analogues other than BPA: Environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity—A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.; Wignall, J.A.; Goldstone, A.E.; Ross, P.K.; Blain, R.B.; Shapiro, A.J.; Holmgren, S.D.; Hsieh, J.H.; Svoboda, D.; Auerbach, S.S.; et al. A scoping review of the health and toxicological activity of bisphenol A (BPA) structural analogues and functional alternatives. Toxicology 2019, 424, 152235–152252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.; Ikhlas, S.; Ahmad, M. Occurrence, toxicity and endocrine disrupting potential of Bisphenol-B and Bisphenol-F: A mini-review. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 312, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, J.S.; Yina, L.; Measela, E.; Lianga, S.; Yu, X. Effects of bisphenol A and its analogs on reproductive health: A mini review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 79, 96–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Pirzada, M.; Jahan, S.; Ullah, H.; Shaheen, G.; Rehman, H.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Butt, M.A. Effect of bisphenol S exposure on male reproductive system of rats: A histological and biochemical study. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grumetto, L.; Gennari, O.; Montesano, D.; Ferracane, R.; Ritieni, A.; Albrizio, S.; Barbato, F. Determination of five bisphenols in commercial milk samples by liquid chromatography coupled to fluorescence detection. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattore, M.; Russo, G.; Barbato, F.; Grumetto, L.; Albrizio, S. Monitoring of bisphenols in canned tuna from Italian markets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, P.; Di Marco Pisciottano, I.; Fattore, M.; Rimoli, M.G.; Seccia, S.; Albrizio, S. A method to determine BPA, BPB, and BPF levels in fruit juices by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercogliano, R.; Santonicola, S.; Albrizio, S.; Ferrante, M.C. Occurrence of bisphenol A in the milk chain: A monitoring model for risk assessment at a dairy company. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 5125–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, C.; Castle, L.; Cravedi, J.P.; Engel, K.H.; Fowler, P.A.F.; Franz, R.; Grob, K.; Gürtler, R.; Husøy, T.; Mennes, W.; et al. Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs: Executive summary. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Gomez, A.; Rubio, S.; Pèrez-Bendito, D. Analytical methods for the determination of bisphenol A in food. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, P.; Di Marco Pisciottano, I.; Esposito, F.; Fasano, E.; Scognamiglio, G.; Mita, G.D.; Cirillo, T. Determination of BPA, BPB, BPF, BADGE and BFDGE in canned energy drinks by molecularly imprinted polymer cleaning up and UPLC with fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for evaluating the matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.; Harrison, S.M.; Monahan, F.J.; Cummins, E.; Brunton, N.P. Bisphenol A and metabolites in meat and meat products: Occurrence, toxicity, and recent development in analytical methods. Foods 2021, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco Pisciottano, I.; Albrizio, S.; Guadagnuolo, G.; Gallo, P. Development and validation of a method for determination of 17 endocrine disrupting chemicals in milk, water, blood serum and feed by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 1744–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürst, P.; Milana, M.R.; Pfaff, K.; Tlustos, C.; Vleminckx, C.; Arcella, D.; Barthélémy, E.; Colombo, P.; Goumperis, T.; Pasinato, L.; et al. Scientific technical assistance to RASFF on chemical contaminants: Risk evaluation of chemical contaminants in food in the context of RASFF notifications. EFSA Support. Publ. 2019, 16, 1–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Time | Ultrapure Water with 0.01% Acetic Acid | MeOH Water with 0.01% Acetic Acid |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 60.00 | 40.00 |
| 0.5 | 60.00 | 40.00 |
| 3.0 | 5.0 | 95.00 |
| 4.0 | 5.0 | 95.00 |
| Production | Q1  Q3 Q3m/z | Collision Energy | Fragmentor |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPA-Q | 227.2  133.0 133.0 | −20 | 162 |
| BPA-q | 227.2  211.8 211.8 | −28 | 162 |
| BPB-Q | 241.3  211.0 211.0 | −40 | 110 |
| BPB-q | 241.3  147.0 147.0 | −45 | 110 |
| BPS-Q | 249.3  156.1 156.1 | −30 | 130 |
| BPS-q | 249.3  108.1 108.1 | −30 | 130 |
| Compound | Spiking Level (ng/mL) | Mean Percentage Recovery (%) 1 | Repeatability (RSDr, %) 2 | Intermediate Precision (RSDR, %) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | 10.0 | 98.0 | 11.0 | 11.1 |
| 25.0 | 105.0 | 8.7 | 8.8 | |
| BPB | 10.0 25.0 | 98.0 101.3 | 6.4 12.1 | 8.1 12.3 |
| BPS | 10.0 25.0 | 85.3 78.0 | 13.2 10.2 | 14.1 10.3 |
| Sample | Taste | Brand * | BPA (ng/mL) | BPB (ng/mL) | BPS (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Almond | B1 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD |
| 2 | B2 | 1.15 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 3 | B3 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 4 | B5 | 7.25 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 5 | B6 | 1.14 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 6 | B7 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 7 | B10 | 2.6 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 8 | Oats | B1 | 3.75 | <LOD | <LOD |
| 9 | B2 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 10 | B3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 11 | B4 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 12 | B5 | 18.17 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 13 | B6 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 14 | B8 | 1.00 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 15 | B9 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 16 | Rice | B2 | 1.50 | <LOD | <LOD |
| 17 | B3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 18 | B4 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 19 | B7 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 20 | B8 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 21 | B9 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 22 | B10 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 23 | B11 | 1.85 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 24 | Soya | B1 | <LOD | 5.17 | <LOD |
| 25 | B2 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 26 | B3 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 27 | B4 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 28 | B6 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 29 | B7 | <LOQ | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 30 | B8 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 31 | B9 | 2.37 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 32 | B10 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| 33 | Coconut | B1 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| 34 | B7 | 3.7 | <LOD | <LOD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiano, M.E.; Sodano, F.; Cassiano, C.; Fiorino, F.; Seccia, S.; Rimoli, M.G.; Albrizio, S. Quantitative Determination of Bisphenol A and Its Congeners in Plant-Based Beverages by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2022, 11, 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233853
Schiano ME, Sodano F, Cassiano C, Fiorino F, Seccia S, Rimoli MG, Albrizio S. Quantitative Determination of Bisphenol A and Its Congeners in Plant-Based Beverages by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods. 2022; 11(23):3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233853
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiano, Marica Erminia, Federica Sodano, Chiara Cassiano, Ferdinando Fiorino, Serenella Seccia, Maria Grazia Rimoli, and Stefania Albrizio. 2022. "Quantitative Determination of Bisphenol A and Its Congeners in Plant-Based Beverages by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Foods 11, no. 23: 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233853
APA StyleSchiano, M. E., Sodano, F., Cassiano, C., Fiorino, F., Seccia, S., Rimoli, M. G., & Albrizio, S. (2022). Quantitative Determination of Bisphenol A and Its Congeners in Plant-Based Beverages by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 11(23), 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233853








