High Heat Treatment of Goat Cheese Milk. The Effect on Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance and Microstructure of Cheese
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cheese Manufacture
2.2. Sensory Analysis
2.2.1. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
2.2.2. Consumer Testing
2.3. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Descriptive Data and PREFMAP
2.4.2. Consumer Data
2.4.3. Software
3. Results and Discussion
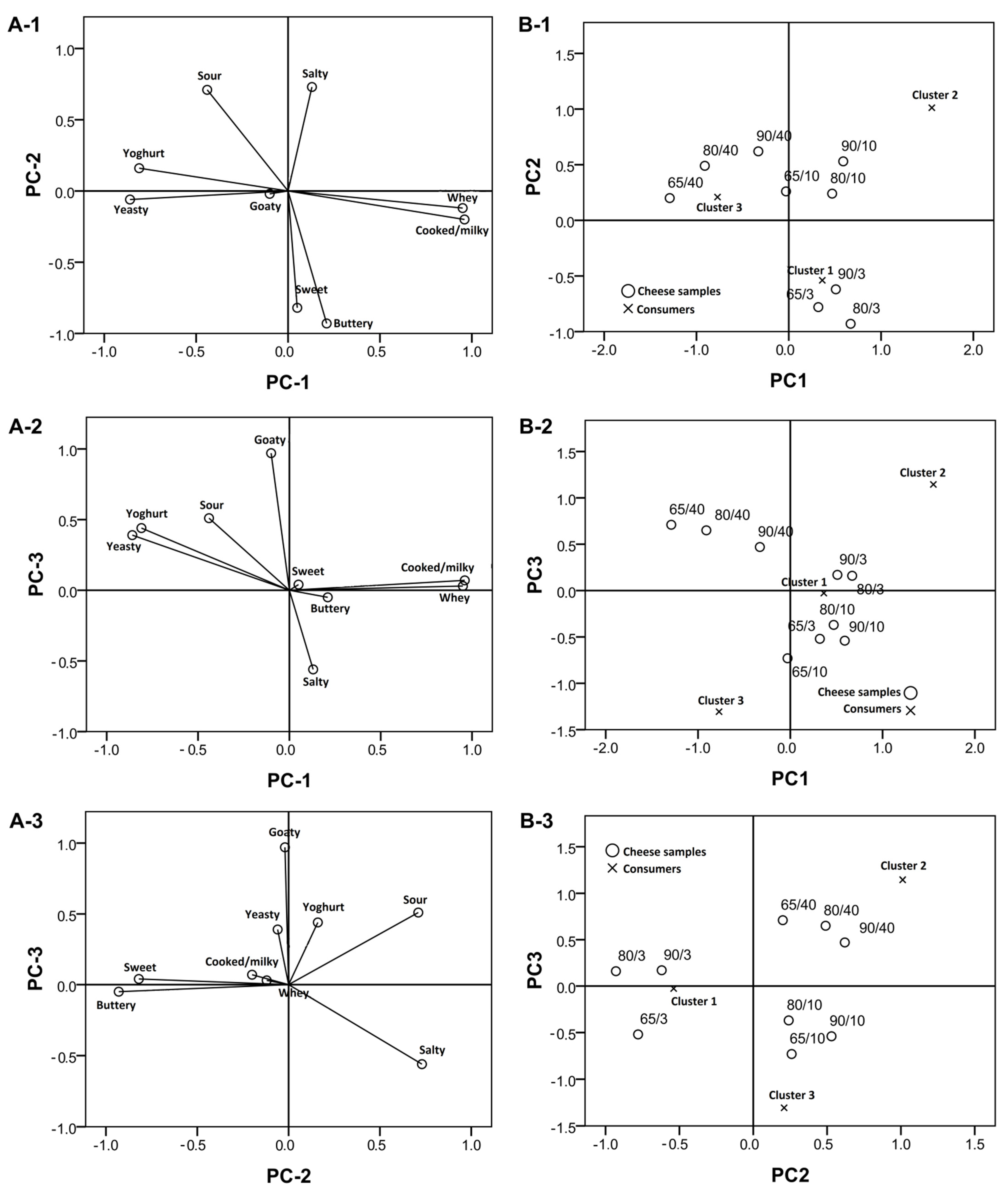
3.1. Descriptive Sensory Analysis and PREFMAP
3.2. Mean Drop Analysis
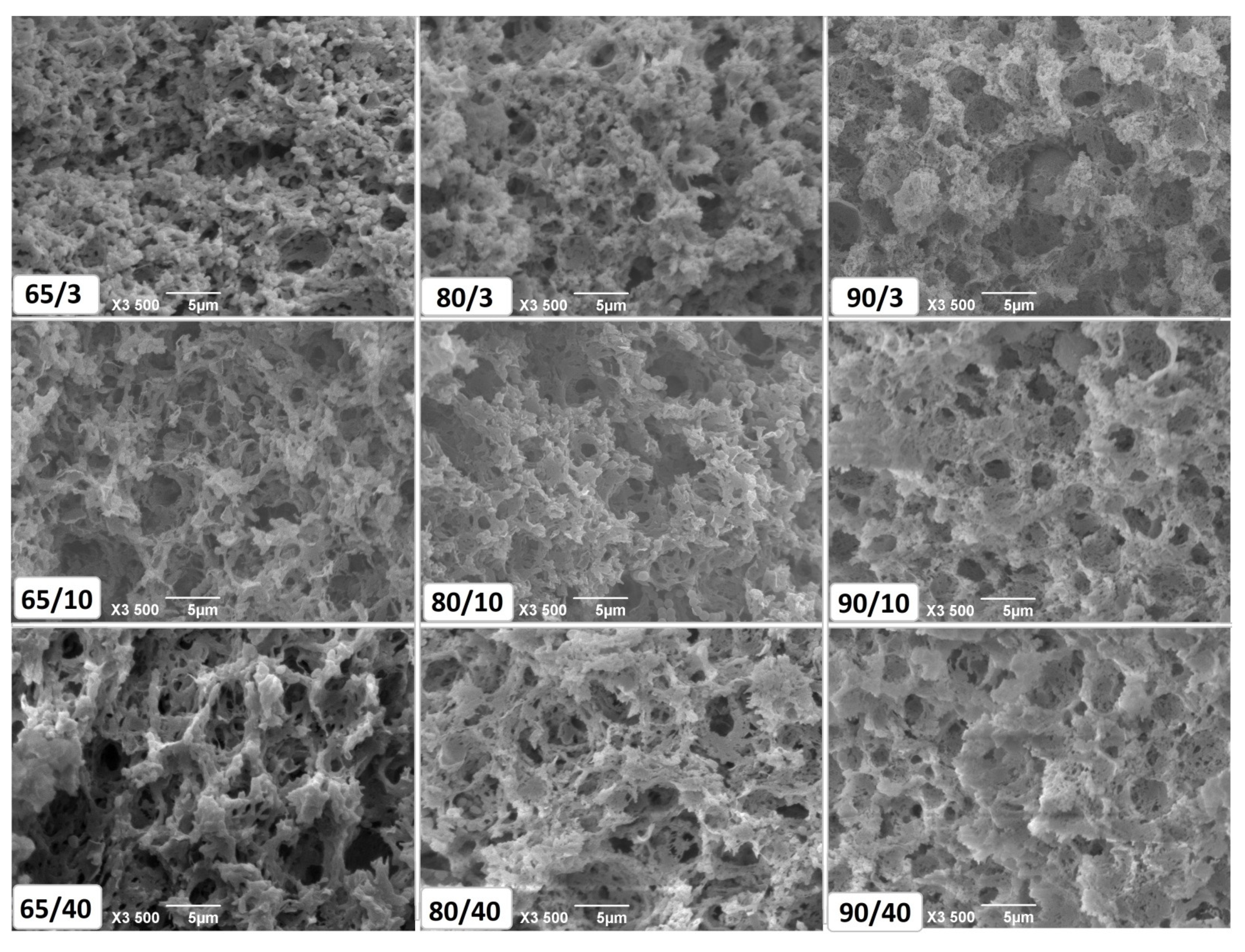
3.3. Microstructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryffel, S.; Piccinali, P.; Bütikofer, U. Sensory descriptive analysis and consumer acceptability of selected Swiss goat and sheep cheeses. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 79, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, L.; Argüello, A. Recent advances in dairy goat products. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.; García, M.B.M. A 100-Year Review: Advances in goat milk research. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10026–10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.C.; Souza, D.F.; Correia, R.T.P. Effect of incubation temperature, heat treatment and milk source on the yoghurt kinetic acidification. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Jana, A.H.; Chavan, R.S. Functionality of Milk Powders and Milk-Based Powders for End Use Applications—A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, S.; Dalgleish, D.G. The effect of ultra high-pressure homogenization (UHPH) on rennet coagulation properties of unheated and heated fresh skimmed milk. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chromik, C.; Partschefeld, C.; Jaros, D.; Henle, T.; Rohm, H. Adjustment of vat milk treatment to optimize whey protein transfer into semi-hard cheese: A case study. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.; Hinrichs, J. Rennet coagulation of heated milk concentrates. Lait 2000, 80, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Kljajevic, N.; Miocinovic, J.; Tomic, N.; Smiljanic, J.; Macej, O. High heat treatment of goat cheese milk. The effect on yield, composition, proteolysis, texture and sensory quality of cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Kljajevic, N.; Miocinovic, J.; Levic, S.; Pavlovic, V.B.; Blažić, M.; Pudja, P. Rheology and Microstructures of Rennet Gels from Differently Heated Goat Milk. Foods 2020, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świąder, K.; Marczewska, M. Trends of Using Sensory Evaluation in New Product Development in the Food Industry in Countries That Belong to the EIT Regional Innovation Scheme. Foods 2021, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H. Dimensions of sensory quality: A critique. Food Qual. Prefer. 1995, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polowsky, P.; Coude, B.; Jimenez-Maroto, L.A.; Johnson, M.; Park, Y.W. Flavor and Sensory Characteristics of Non-Bovine Species Milk and Their Dairy Products. In Handbook of Milk of Non-Bovine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Park, Y.W., Haenlein, G.F.W., Wendorff, W.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2017; pp. 595–625. [Google Scholar]
- Barrionuevo, C.A.; Bernat, E.E.; Velarde, I.J. We recovered food heritage, and then? Value enhancement and promotion of local agri-food products in Argentina and Spain. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 3168–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rivera, E.D.J.; Ramón-Canul, L.G.; Díaz-Rivera, P.; Juárez-Barrientos, J.M.; Herman-Lara, E.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Herrera-Corredor, J.A. Sensory profiles of artisan goat cheeses as influenced by the cultural context and the type of panel. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Florença, S.G.; Barroca, M.J.; Anjos, O. The Link between the Consumer and the Innovations in Food Product Development. Foods 2020, 9, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carunchiawhetstine, M.E.; Karagul-Yuceer, Y.; Avsar, Y.K.; Drake, M.A. Identification and Quantification of Character Aroma Components in Fresh Chevre-style Goat Cheese. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, N.; Dojnov, B.; Miocinovic, J.; Tomasevic, I.; Smigic, N.; Djekic, I.; Vujcic, Z. Enrichment of yoghurt with insoluble dietary fiber from triticale—A sensory perspective. LWT 2017, 80, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraidt, M. Appendix L: Penalty Analysis or Mean Drop Analysis. In ASTM Manual Series: MNL 63-Just-About-Right (JAR) Scales: Design, Usage, Benefits and Risks; Rotman, L., Parker, M.J., Eds.; ASTM International-American Society for Testing and Materials: Bridgeport, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Božanić, R.; Tratnik, L.; Drgalić, I. Goat’s milk: Characteristics and possibility. Mljekarstvo 2002, 52, 207–237. [Google Scholar]
- Çınar, Ç.; Karinen, A.K.; Tybur, J.M. The multidimensional nature of food neophobia. Appetite 2021, 162, 105177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystrand, B.T.; Olsen, S.O.; Tudoran, A.A. Individual differences in functional food consumption: The role of time perspective and the Big Five personality traits. Appetite 2021, 156, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenjuk, B.; Tešanović, D.; Gagić, S.; Erdeji, I.; Banjac, M. Offer of authentic food as a condition for gastronomic tourism development. Eur. J. Appl. Econ. 2015, 12, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Smigic, N.; Djekic, I.; Tomasevic, I.; Kljajevic, N.; Nedeljkovic, A.; Miocinovic, J. The influence of NaCl concentration of brine and different packaging on goat white brined cheese characteristics. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 79, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A. Formation, Structural Properties and Rheology of Acid-Coagulated Milk Gels. In Cheese Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press, Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 179–193. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, C. Focus on the supramolecular structure of milk fat in dairy products. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 45, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D.W.; Auty, M.A.E. Cheese Microstructure. In Cheese Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press, Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 547–564. [Google Scholar]

| Heat Treatment | Ripening Stage (Days) | Label | DM 1 (%) | TP 1(%) | MF 1(%) | pH | NaCl (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 °C/30 min | 3 | 65/3 | 42.38 ± 1.22 | 17.35 ± 0.44 | 18.41 ± 0.91 | 5.02 ± 0.11 | 1.96 ± 0.25 |
| 10 | 65/10 | 40.34 ± 1.31 | 16.35 ± 0.87 | 17.67 ± 1.53 | 4.94 ± 0.11 | 2.71 ± 0.37 | |
| 40 | 65/40 | 38.16 ± 3.82 | 16.03 ± 1.32 | 17.50 ± 2.64 | 5.00 ± 0.07 | 3.29 ± 0.53 | |
| 80 °C/5 min | 3 | 80/3 | 38.95 ± 1.12 | 15.25 ± 0.32 | 17.98 ± 0.86 | 4.71 ± 0.16 | 1.72 ± 0.32 |
| 10 | 80/10 | 39.93 ± 1.52 | 16.17 ± 0.96 | 18.00 ± 0.87 | 4.59 ± 0.04 | 2.58 ± 0.26 | |
| 40 | 80/40 | 39.84 ± 0.99 | 15.63 ± 0.90 | 18.58 ± 0.52 | 4.50 ± 0.08 | 3.09 ± 0.46 | |
| 90 °C/5 min | 3 | 90/3 | 38.05 ± 0.66 | 14.78 ± 1.36 | 18.20 ± 0.63 | 4.76 ± 0.06 | 1.75 ± 0.51 |
| 10 | 90/10 | 38.76 ± 0.43 | 14.94 ± 0.33 | 18.17 ± 0.28 | 4.47 ± 0.10 | 2.67 ± 0.45 | |
| 40 | 90/40 | 39.49 ± 1.38 | 15.86 ± 0.90 | 19.00 ± 1.73 | 4.49 ± 0.12 | 3.39 ± 0.92 |
| Term | Definition | Reference Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Buttery | Aromatics associated with butter | Butter “Meggle”, Kragujevac |
| Cooked/milky | Aromatics associated with cooked milk (mix of sweet and caramelized) | Pasteurized milk “Imlek”, Padinska Skela, 2.8% milk fat, cooked at 85 °C/10 min |
| Goaty | Aromatics associated with wet animal hair | Raw goat milk |
| Whey | Aromatics associated with cow’s whey | Fresh cow whey |
| Yeasty | Aromatics associated with baker’s yeast | Fresh yeast, “Vrenje”, Belgrade, dissolved in water (3%) |
| Yoghurt | Aromatics associated with yoghurt | Yoghurt, “Imlek”, Padinska Skela, 2.8% milk fat |
| Salty | Fundamental taste sensation elicited by salts | NaCl water solution (1%) |
| Sour | Fundamental taste sensation elicited by citric, acetic, apple acids | Citric acid, water solution(0,08%) |
| Sweet | Fundamental taste sensation elicited by saccharose | Saccharose, water solution (1%) |
| Ripening Stage | Heat Treatment | Hedonic Score | Consumers (n = 80) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 (47.5%) | Cluster 2 (32.5%) | Cluster 3 (20%) | |||
| 3 days | 65 °C/30 min | ODOUR | 7.25 ± 1.77 | 7.84 ± 1.41 | 7.28 ± 2.43 |
| (early) | TASTE | 6.95 ± 1.73 | 7.84 ± 1.14 | 7.43 ± 2.23 | |
| TEXTURE | 6.75 a ± 1.74 | 8.23 b ± 1.01 | 7.14 ab ± 1.86 | ||
| OVERALL | 6.85 a ± 1.35 | 8.38 b ± 0.87 | 8.00 ab ± 1.29 | ||
| 80 °C/5 min | ODOUR | 6.85 ± 2.23 | 7.30 ± 1.80 | 5.71 ± 2.81 | |
| TASTE | 7.25 ± 1.62 | 7.77 ± 1.36 | 6.43 ± 2.64 | ||
| TEXTURE | 6.60 ± 1.88 | 7.31 ± 1.80 | 6.28 ± 2.69 | ||
| OVERALL | 7.20 ± 1.58 | 7.61 ± 1.85 | 6.71 ± 1.25 | ||
| 90 °C/5 min | ODOUR | 7.85 b ± 2.13 | 7.92 b ± 1.12 | 5.57 a ± 1.51 | |
| TASTE | 8.00 b ± 1.52 | 8.46 b ± 0.97 | 5.86 a ± 1.86 | ||
| TEXTURE | 7.55 b ± 1.82 | 8.00 b ± 1.00 | 5.00 a ± 2.00 | ||
| OVERALL | 8.35 b ± 0.93 | 8.23 b ± 0.83 | 6.43 a ± 1.81 | ||
| 10 days | 65 °C/30 min | ODOUR | 7.45 ± 1.90 | 6.69 ± 2.18 | 7.28 ± 1.70 |
| (mid) | TASTE | 6.85 a ± 1.79 | 8.08 b ± 0.76 | 7.57 ab ± 1.81 | |
| TEXTURE | 6.90 ± 1.80 | 7.54 ± 1.51 | 7.57 ± 2.57 | ||
| OVERALL | 6.75 a ± 1.29 | 7.54 ab ± 1.33 | 8.57 b ± 0.79 | ||
| 80 °C/5 min | ODOUR | 7.35 ± 1.46 | 7.31 ± 1.55 | 8.00 ± 1.15 | |
| TASTE | 7.45 ± 1.54 | 7.61 ± 1.61 | 7.28 ± 1.50 | ||
| TEXTURE | 7.00 ab ± 1.81 | 8.15 a ± 0.90 | 6.14 b ± 3.08 | ||
| OVERALL | 7.25 ± 1.45 | 7.23 ± 1.69 | 7.71 ± 1.11 | ||
| 90 °C/5 min | ODOUR | 7.90 a ± 1.29 | 6.23 b ± 2.35 | 7.28 ab ± 1.25 | |
| TASTE | 8.35 a ± 0.99 | 7.23 b ± 2.01 | 7.71 ab ± 1.11 | ||
| TEXTURE | 7.95 ± 0.89 | 7.31 ± 1.60 | 6.86 ± 2.41 | ||
| OVERALL | 8.30 a ± 0.80 | 7.08 b ± 2.56 | 8.28 ab ± 0.95 | ||
| 40 days | 65 °C/30 min | ODOUR | 5.15 ± 2.78 | 4.92 ± 2.47 | 5.00 ± 2.16 |
| (late) | TASTE | 6.20 ± 2.04 | 6.61 ± 1.89 | 7.28 ± 0.95 | |
| TEXTURE | 6.00 ± 2.29 | 6.38 ± 1.71 | 7.28 ± 1.60 | ||
| OVERALL | 6.15 a ± 1.95 | 6.85 ab ± 1.21 | 7.71 b ± 1.11 | ||
| 80 °C/5 min | ODOUR | 6.05 ± 2.44 | 6.77 ± 1.54 | 5.71 ± 2.36 | |
| TASTE | 6.55 ± 2.04 | 7.23 ± 1.42 | 6.57 ± 2.23 | ||
| TEXTURE | 6.25 ± 2.20 | 6.69 ± 1.44 | 5.86 ± 2.61 | ||
| OVERALL | 6.80 ± 1.74 | 7.15 ± 1.57 | 7.28 ± 1.25 | ||
| 90 °C/5 min | ODOUR | 7.55 a ± 1.70 | 7.31 ab ± 1.75 | 5.57 b ± 2.44 | |
| TASTE | 8.40 ± 0.94 | 7.85 ± 1.28 | 7.86 ± 0.90 | ||
| TEXTURE | 7.85 ± 1.63 | 7.00 ± 1.68 | 7.28 ± 2.14 | ||
| OVERALL | 8.40 ± 0.82 | 7.69 ± 1.65 | 7.57 ± 0.98 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miloradovic, Z.; Tomic, N.; Kljajevic, N.; Levic, S.; Pavlovic, V.; Blazic, M.; Miocinovic, J. High Heat Treatment of Goat Cheese Milk. The Effect on Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance and Microstructure of Cheese. Foods 2021, 10, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051116
Miloradovic Z, Tomic N, Kljajevic N, Levic S, Pavlovic V, Blazic M, Miocinovic J. High Heat Treatment of Goat Cheese Milk. The Effect on Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance and Microstructure of Cheese. Foods. 2021; 10(5):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051116
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiloradovic, Zorana, Nikola Tomic, Nemanja Kljajevic, Steva Levic, Vladimir Pavlovic, Marijana Blazic, and Jelena Miocinovic. 2021. "High Heat Treatment of Goat Cheese Milk. The Effect on Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance and Microstructure of Cheese" Foods 10, no. 5: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051116
APA StyleMiloradovic, Z., Tomic, N., Kljajevic, N., Levic, S., Pavlovic, V., Blazic, M., & Miocinovic, J. (2021). High Heat Treatment of Goat Cheese Milk. The Effect on Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance and Microstructure of Cheese. Foods, 10(5), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051116






