A Novel Spinel High-Entropy Oxide (Cr0.2Mn0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)3O4 as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
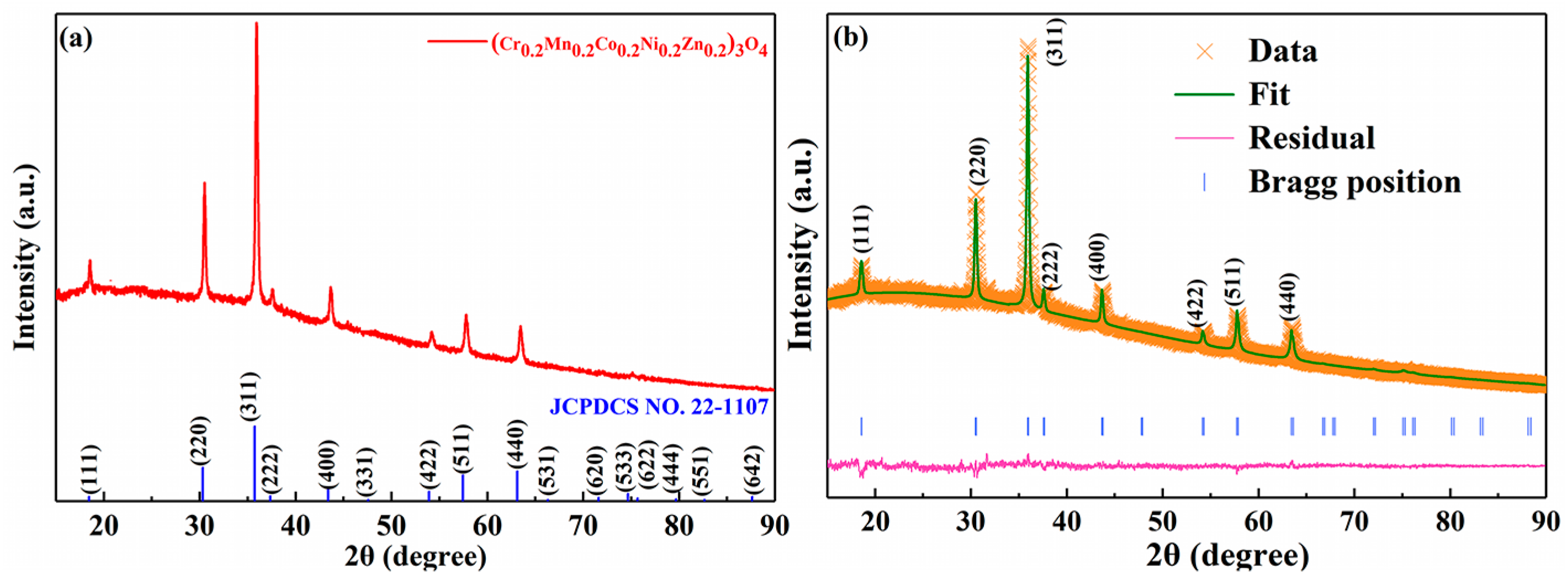
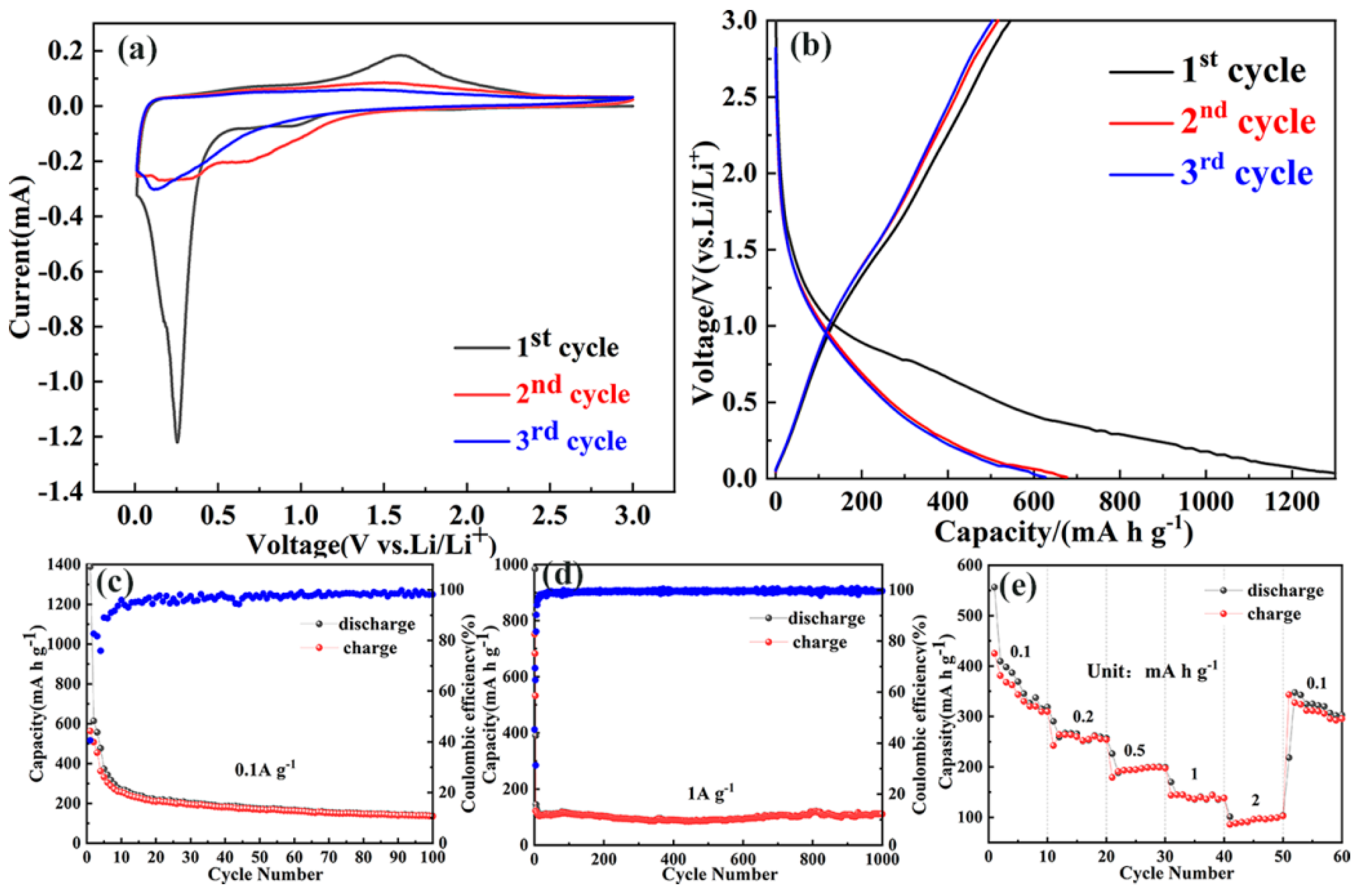
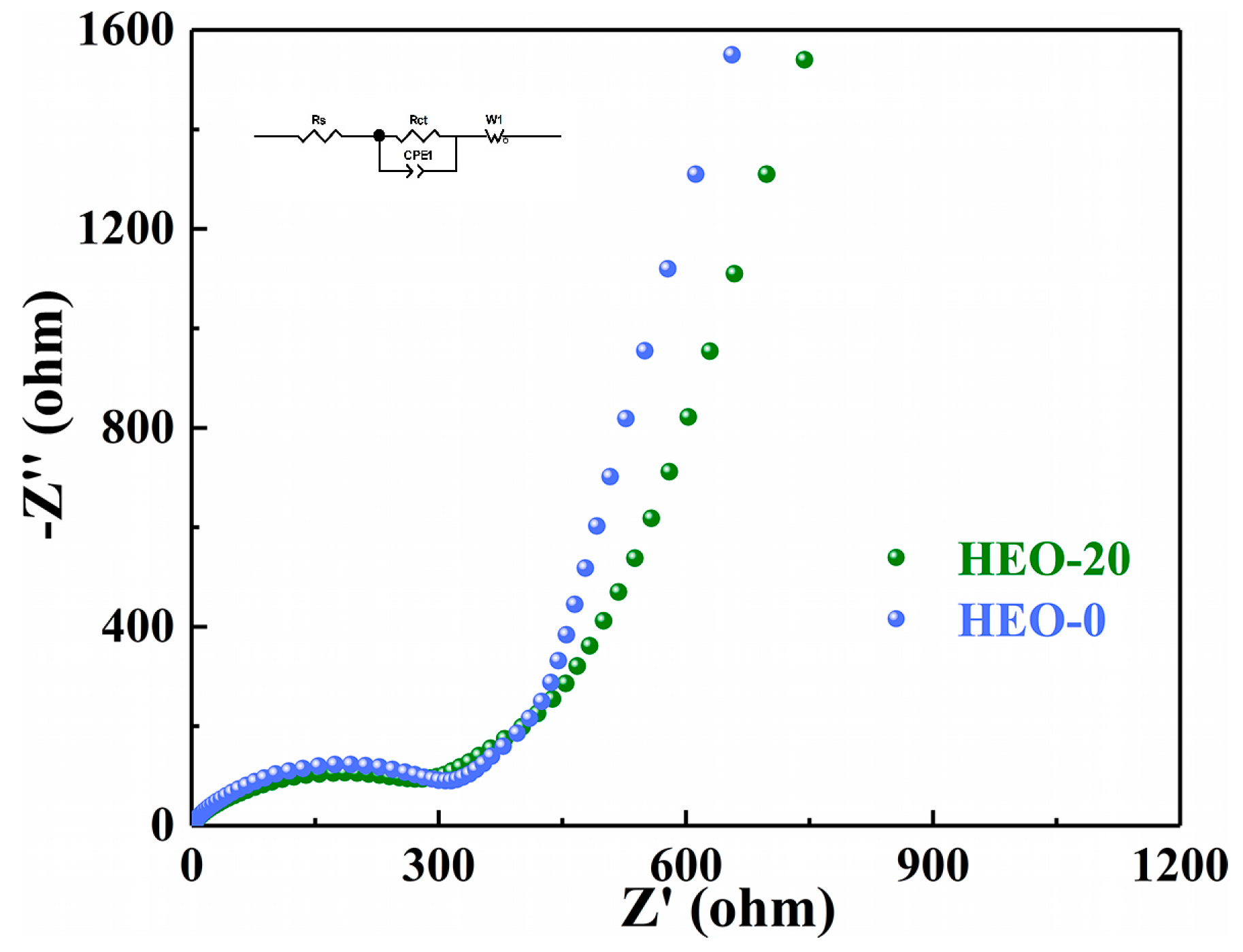
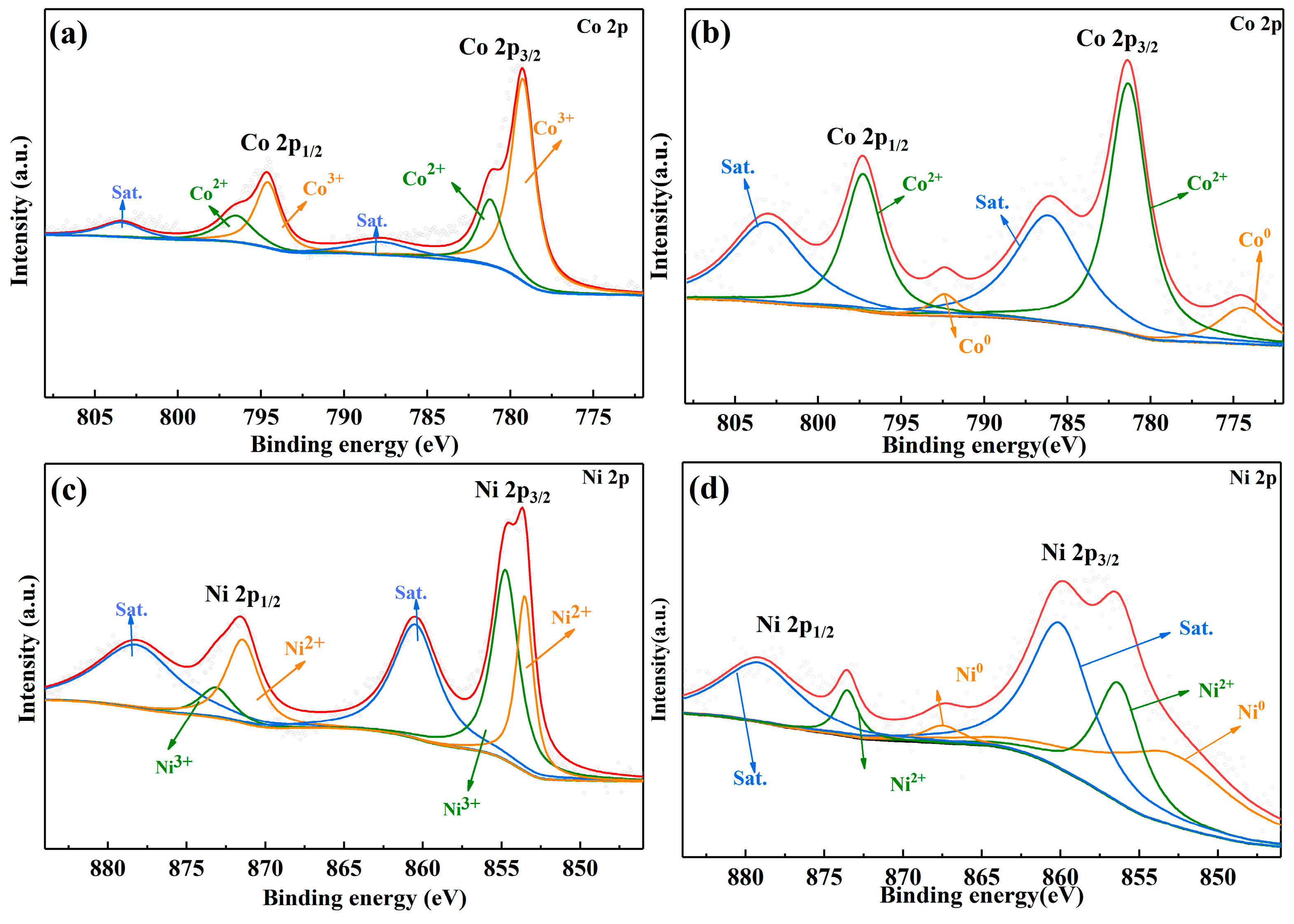
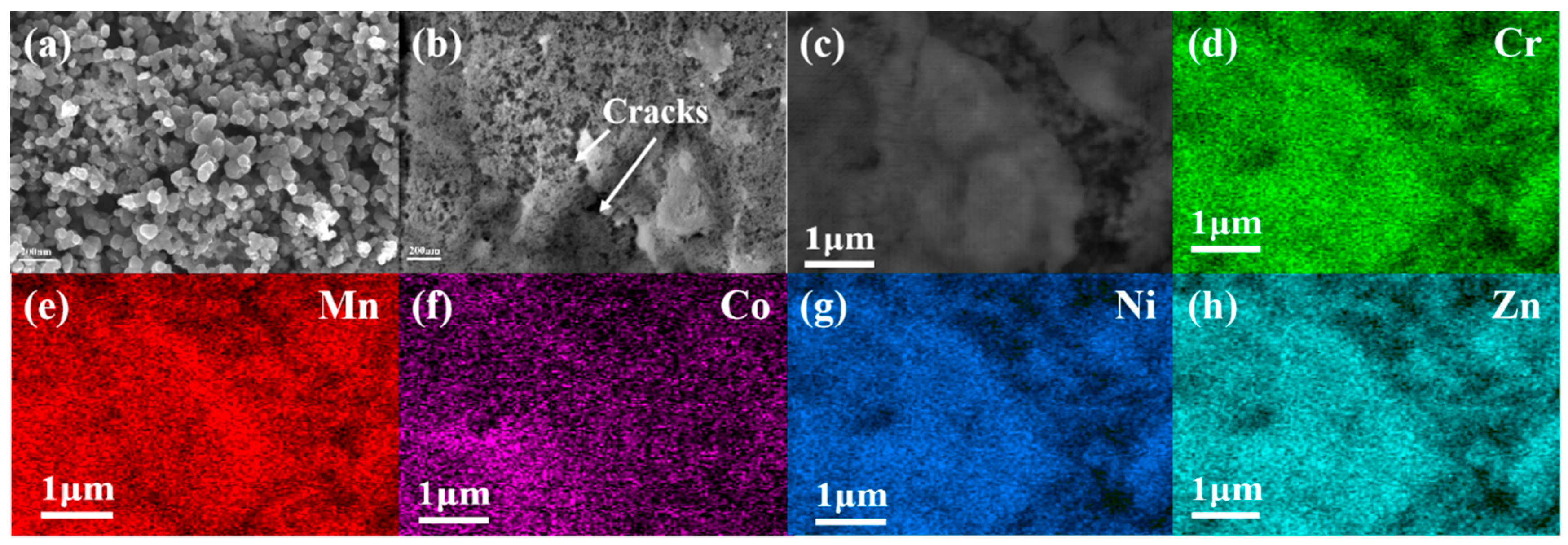
2. Results
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, C.; Xiong, B.; Xue, H.; Zhang, D.; Ge, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jing, L.Y.; Pan, S.Q. The role of new energy in carbon neutral. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freunberger, S.A. Batteries: Charging ahead rationally. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriparti, S.; Miele, E.; Angelis, F.D.; Fabrizio, E.D.; Zaccaria, R.P.; Capiglia, C. Review on recent progress of nanostructured anode materials for Lion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 257, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.W.; Lin, Z.; Alcoutlabia, M.; Zhang, X.W. Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2682–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.X.; Yushin, G. Conversion cathodes for rechargeable lithium and lithium-ion batteries. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 435–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cui, Y. Reviving the lithium metal anode for highenergy batteries. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, K.; Thakur, V.K.; Siwal, S.S. Synthesis and overview of carbon-based materials for high performance energy storage application: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 56, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.J.; Sung, Y.E.; Hyeon, T.W. Conversion reaction-based oxide nanomaterials for Lithium-ion battery anodes. Small 2016, 12, 2146–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Dominic, B.; Stefano, P. Transition metal oxide anodes for electrochemical energy storage in Lithium and sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 10, 1902485. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.M.; Lee, J.I.; Shin, M.S.; Park, S.J. Large-scale synthesis of interconnected Si/SiOx nanowire anodes for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oses, C.; Toher, C.; Curtarolo, S. High-entropy ceramics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, A.D.; Chellali, M.R.; Hahn, H.; Schoenung, J.M. Multiscale phase homogeneity in bulk nanocrystalline high entropy oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 4850–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, B.; Aparna, M.L.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Thomas, T. High entropy spinel metal oxide (CoCrFeMnNi)3O4 nanoparticles as a high-performance supercapacitor electrode material. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, C.M.; Sachet, E.; Borman, T.; Moballegh, A.; Dickey, E.C.; Hou, D.; Jones, J.L.; Curtarolo, S.; Maria, J.P. Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérardan, D.; Franger, S.; Meena, A.K.; Dragoe, N. Room temperature lithium superionic conductivity in high entropy oxides. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9536–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Djenadic, R.; Usharani, N.J.; Sanghvi, K.P.; Chakravadhanula, V.S.; Gandhi, A.S.; Hahn, H.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Nanocrystalline multicomponent entropy stabilised transition metal oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y. A high entropy oxide (Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2O) with superior lithium storage performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, S.; Duan, C.; Mao, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.; Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X. Spinel-structured high entropy oxide (FeCoNiCrMn) 3O4 as anode towards superior lithium storage performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Huang, S.C.; Lin, M.H.; Li, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Liao, Y.F.; Lin, C.C.; et al. In operando synchrotron X-ray studies of a novel spinel (Ni0.2Co0.2Mn0.2Fe0.2Ti0.2)3O4 high-entropy oxide for energy storage applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 21756–21770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Tian, K.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. New spinel high-entropy oxides (FeCoNiCrMnXLi)3O4 (X = Cu, Mg, Zn) as the anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32025–32032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Velasco, L.; Wang, D.I.; Wang, Q.; Talasila, G.; de Biasi, L.; Kübel, C.; Brezesinski, T.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Hahn, H.; et al. High entropy oxides for reversible energy storage. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, C.; Xu, W.; Petrovičovà, B.; Pinna, N.; Santangelo, S. Evaluation of entropy-stabilized (Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2)O oxides produced via solvothermal method or electrospinning as anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Huang, S.C.; Lin, M.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, H.Y. Operando synchrotron transmission X-ray microscopy study on (MgCoNiCuZn)O high-entropy oxide anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 274, 125105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, X.Y.; Paik, U. Etching-in-a-box: A novel strategy to synthesize unique yolk-shelled Fe3O4@ carbon with an ultralong cycling life for lithium storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osenciat, N.; Bérardan, D.; Dragoe, D.; Léridon, B.; Holé, S.; Meena, A.K.; Franger, S.; Dragoe, N. Charge compensation mechanisms in Li-substituted high-entropy oxides and influence on Li superionic conductivity. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 6156–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovičovà, B.; Xu, W.; Musolino, M.G.; Pantò, F.; Patanè, S.; Pinna, N.; Santangelo, S.; Triolo, C. High-entropy spinel oxides produced via sol-gel and electrospinning and their evaluation as anodes in Li-ion batteries. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.Z.; Jin, T.; Yang, L.; Jiao, L.F. Recent progress in conversion reaction metal oxide anodes for Li-ion batteries. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 2213–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.X.; Patra, J.; Chang, J.K.; Ting, J.M. High entropy spinel oxide nanoparticles for superior lithiation-delithiation performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 18963–18973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Z.; Tao, Z.L.; Mai, L.Q.; Kang, Y.M.; Chou, S.L.; Chen, J. Recent developments on and prospects for electrode materials with hierarchical structures for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.S.; Sarkar, A.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.; Velasco, L.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Brezesinski, T.; Hahn, H.; Breitung, B. High entropy oxides as anode material for Li-ion battery applications: A practical approach. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 100, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, O.J.; Walter, M.D.; Timofeeva, E.V.; Segre, C.U. Effect of initial structure on performance of high-entropy oxide anodes for li-ion batteries. Batteries 2023, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bi, J.; Xie, L.; Gao, X.; Meng, L. Preparation and electrochemical properties of two novel high entropy spinel oxides (MgTiZnNiFe)3O4 and (CoTiZnNiFe)3O4 by solid state reaction. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Lan, X.; Hu, R. A spinel (FeNiCrMnMgAl)3O4 high entropy oxide as a cycling stable anode material for Li-ion batteries. Processes 2021, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, C.; Maisuradze, M.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Ponti, A.; Pagot, G.; DiNoto, V.; Aquilanti, G.; Pinna, N.; Giorgetti, M.; et al. Charge Storage Mechanism in Electrospun Spinel-Structured High-Entropy (Mn0.2Fe0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)3O4 Oxide Nanofibers as Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Small 2023, 19, 2304585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bi, J.; Xie, L.; Gao, X.; Rong, J. High entropy spinel oxides (CrFeMnNiCox)3O4 (x = 2, 3, 4) nanoparticles as anode material towards electrochemical properties. J. Energy Storage 2023, 71, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Atomic Fraction (%) |
|---|---|
| O | 63.65 |
| Cr | 7.69 |
| Mn | 7.60 |
| Co | 7.08 |
| Ni | 7.29 |
| Zn | 6.69 |
| Materials | Method | Rate Capability/mAh·g−1 | Cyclic Performance (Cycles)/ mAh·g−1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MgFeCoNiZn)3O4 | Solid-state synthesis | 304 @ 0.5 A g−1 | 360(300) @ 0.1 A g−1 | [32] |
| (MgTiZnNiFe)3O4 | Solid-state reaction | 93.6 @ 1 A g−1 | 145(100) @ 0.1 A g−1; 100(800) @ 1 A g−1 | [33] |
| (CoTiZnNiFe)3O4 | Solid-state reaction | 150.3 @ 1 A g−1 | 290(100) @ 0.1 A g−1; 130(800) @ 1 A g−1 | [33] |
| (FeNiCrMnMgAl)3O4 | Solution combustion | 350 @ 4 A g−1 | 670(200) @ 0.2 A g−1 | [34] |
| (MnFeCoNiZn)3O4 | Electrospinning | 58 @ 2 A g−1 | 155(550) @ 0.5 A g−1 | [35] |
| (CrFeMnNiCo2)3O4 | Sol–gel | 147 @ 2 A g−1 | 520(100) @ 0.2 A g−1; 120(1000) @ 2 A g−1 | [36] |
| (CrFeMnNiCo3)3O4 | Sol–gel | 101 @ 2 A g−1 | 505(100) @ 0.2 A g−1; 118(1000) @ 2 A g−1 | [36] |
| (CrFeMnNiCo4)3O4 | Sol–gel | 97.2 @ 2 A g−1 | 510(100) @ 0.2 A g−1; 105(1000) @ 2 A g−1 | [36] |
| (CrMnCoNiZn)3O4 | Sol–gel | 96 @ 2 A g−1 | 132(100) @ 0.1 A g−1; 107(1000) @ 1 A g−1 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, H.; Wei, Y.; Nan, R.; Jian, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Q. A Novel Spinel High-Entropy Oxide (Cr0.2Mn0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)3O4 as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Inorganics 2024, 12, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070198
Jin C, Wang Y, Dong H, Wei Y, Nan R, Jian Z, Yang Z, Ding Q. A Novel Spinel High-Entropy Oxide (Cr0.2Mn0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)3O4 as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Inorganics. 2024; 12(7):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070198
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Changqing, Yulong Wang, Haobin Dong, Yongxing Wei, Ruihua Nan, Zengyun Jian, Zhong Yang, and Qingping Ding. 2024. "A Novel Spinel High-Entropy Oxide (Cr0.2Mn0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)3O4 as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Inorganics 12, no. 7: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070198
APA StyleJin, C., Wang, Y., Dong, H., Wei, Y., Nan, R., Jian, Z., Yang, Z., & Ding, Q. (2024). A Novel Spinel High-Entropy Oxide (Cr0.2Mn0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Zn0.2)3O4 as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Inorganics, 12(7), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12070198








