Suppression for Phase Error of Fringe Projection Profilometry Using Outlier-Detection Model: Development of an Easy and Accurate Method for Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principles
2.1. Phase Calculation
2.2. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Model
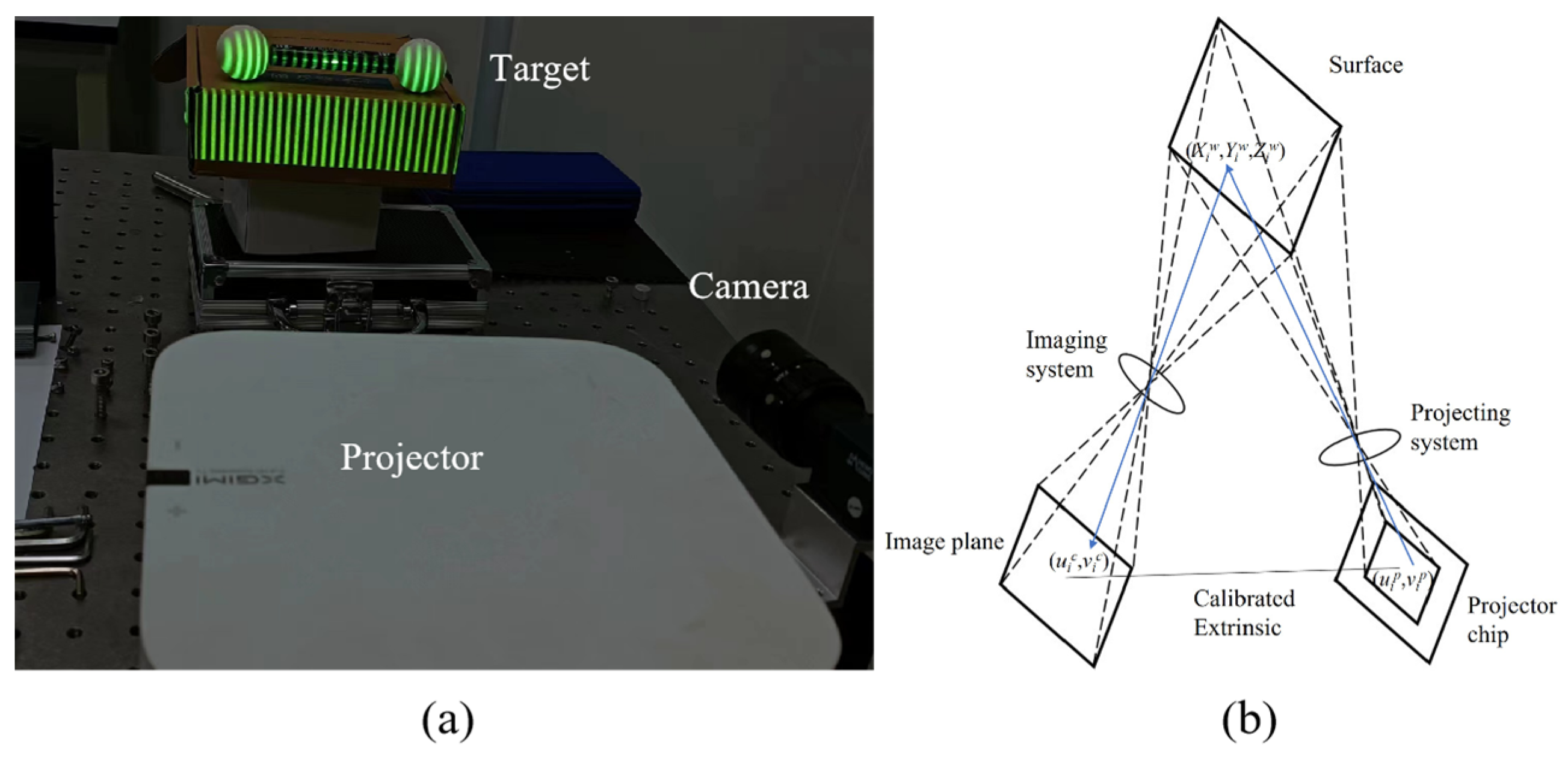
2.3. Absolute Phase to Projector Pixel Calibration
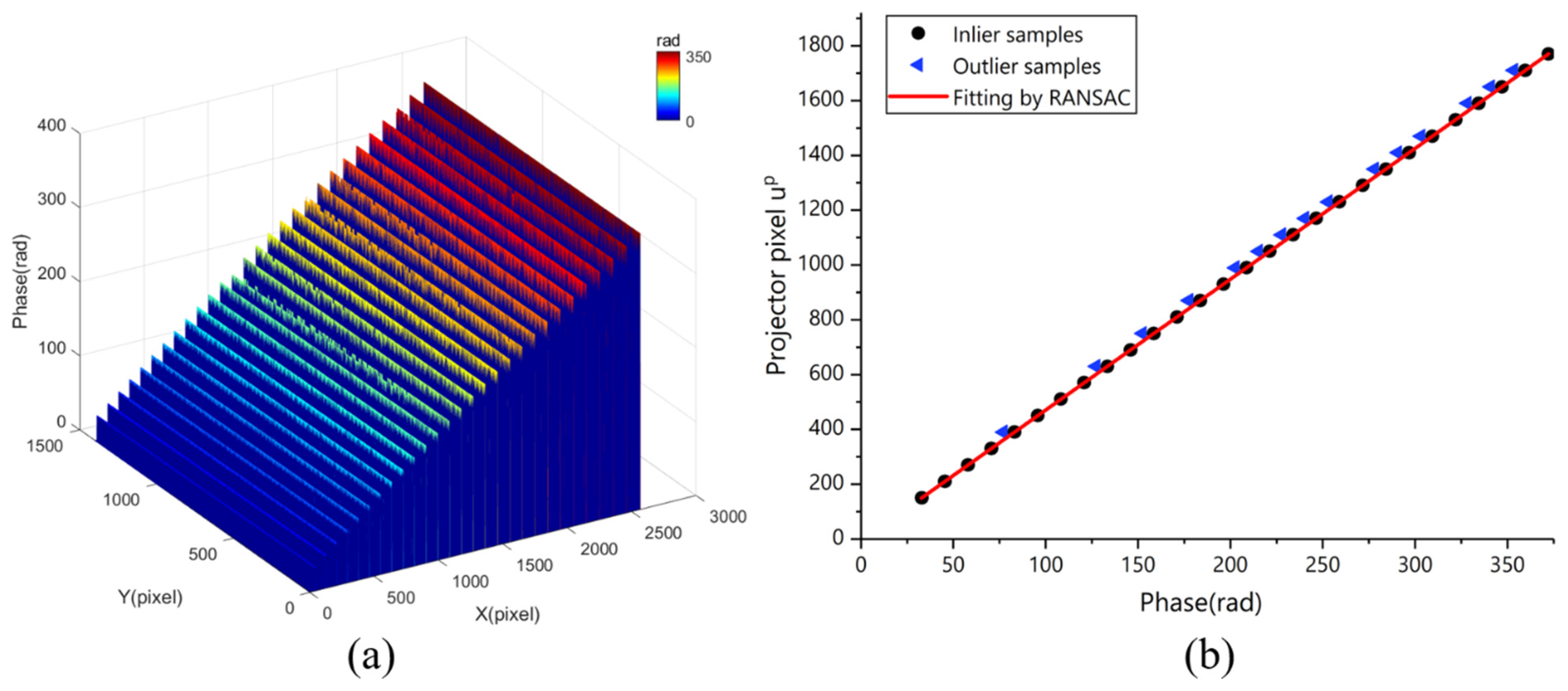
- Select the minimum dataset that can estimate the model, e.g., two points for straight line fitting,
- Use the minimum dataset to calculate the model;
- Insert all data into the model to determine the inliers, which remain within acceptable errors with the model. Meanwhile, the remaining data are outliers. Inliers follow the model well, while outliers reject it strongly.
- Compare the number of inliers between the current model and the best model previously calculated. The quality of a model is positively correlated with the number of inliers.
- Repeat steps 1–4 until the quality of the model meets the desired value (the number of inliers is greater than the desired number)
3. System Calibration
3.1. System Setup
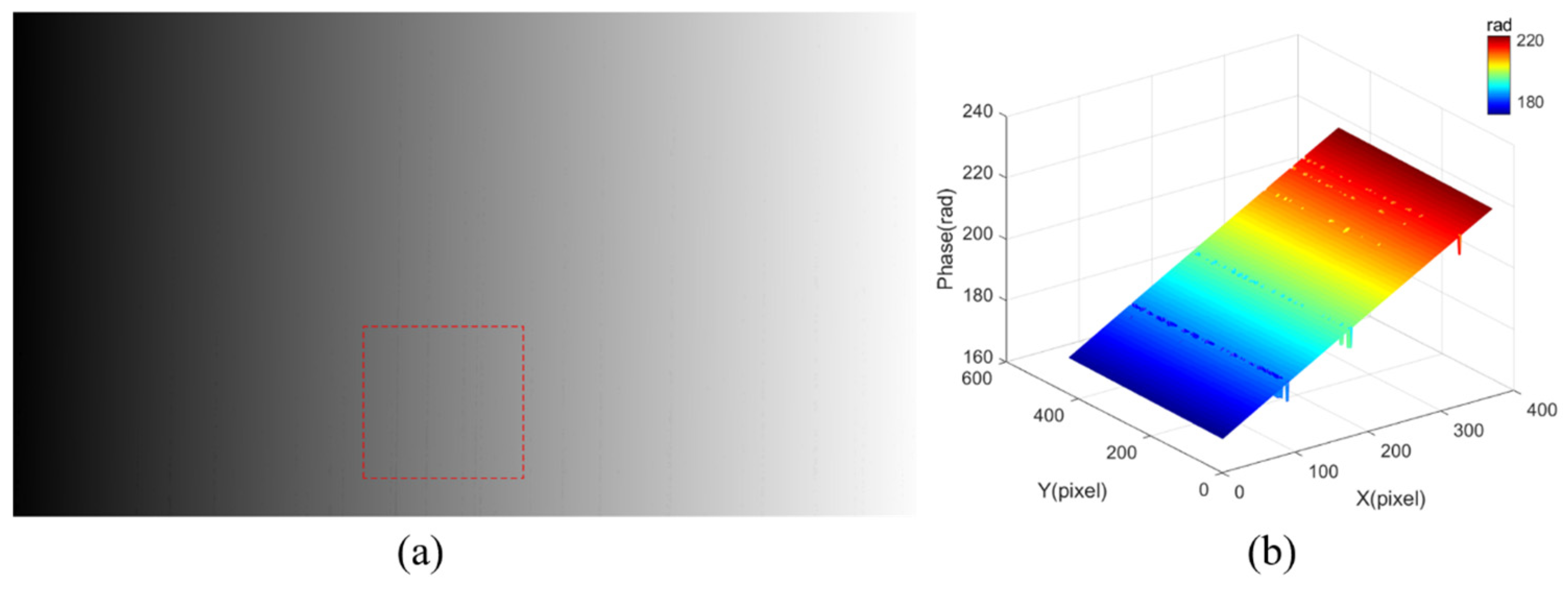
3.2. Gamma Correction
- (1)
- A series of full-frame grayscale map sets with uniformly increasing grayscale values are generated by the computer.
- (2)
- The projector projects the grayscale map and captures it sequentially using the camera.
- (3)
- The grayscale values of the captured images are calculated in turn.
- (4)
- Taking the actual gray value as the independent variable and the preset gray value as the dependent variable, the coefficients in Equation (9) are calculated using the fitting algorithm (such as the LMS method).
- (5)
- Taking Equation (9) as the inverse function of the nonlinear output of the system, the ideal sinusoidal fringe is pre-modulated, and the output at this time is the ideal sinusoidal fringe to complete the compensation.
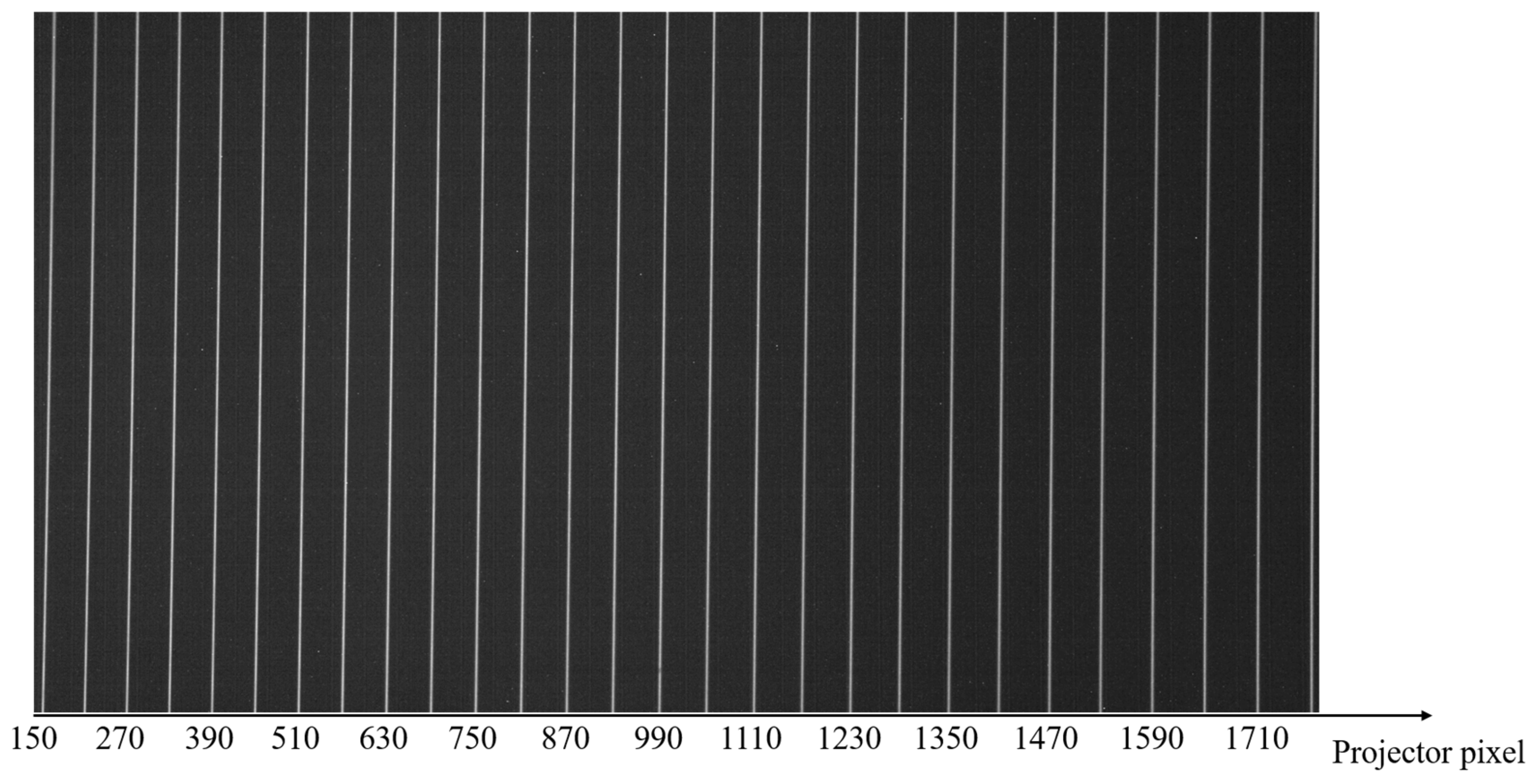
3.3. Fringe Recording
3.4. − Relation Calibration by RANSAC Method
4. Experiment of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, P.; Parks, R.E.; Wang, L.R.; Angel, R.P.; Burge, J.H. Software configurable optical test system: A computerized reverse Hartmann test. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 4404–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Wang, Y.H.; Burge, J.H.; Kaznatcheev, K.; Idir, M. Non-null full field X-ray mirror metrology using SCOTS: A reflection deflectometry approach. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 12393–12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Su, P.; Burge, J.H.; Huang, L.; Idir, M. High-accuracy aspheric x-ray mirror metrology using Software Configurable Optical Test System/deflectometry. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 084103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.S.; Zhang, S. Fast three-step phase-shifting algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 5086–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Royer, D.; Yau, S.T. High-resolution, real-time 3-D absolute coordinates measurement using a fast three-step phase-shifting algorithm. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Conference on Interferometry XIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 14 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, M.; Mutoh, K. Fourier-transform profilometry for the automatic-measurement of 3-D object shapes. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 3977–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Su, X.Y.; Guo, L.R. Improved Fourier-transform profilometry for the automatic-measurement of 3-dimensional object shapes. Opt. Eng. 1990, 29, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.J. Rainbow three-dimensional camera: New concept of high-speed three-dimensional vision systems. Opt. Eng. 1996, 35, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriu, E.M.; Sakr, Z.; Spoelder, H.J.W.; Monica, A. Object recognition using pseudo-random color encoded structured light. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–4 May 2000; pp. 1237–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Doi, K.; Tsuji, T. High-speed 3D image acquisition using coded structured light projection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 931–936. [Google Scholar]
- Sansoni, G.; Carocci, M.; Rodella, R. Three-dimesional vision based on a combination of gray-code and phase-shift light projection: Analysis and compensation of the systematic errors. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 6565–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Towers, C.E.; Towers, D.P. Time efficient color fringe projection system for 3D shape and color using optimum 3-frequency Selection. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 6444–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.J.; Chen, Q.; Zuo, C.; Sun, J.S.; Yu, S.L. High-speed real-time 3-D coordinates measurement based on fringe projection profilometry considering camera lens distortion. Opt. Commun. 2014, 329, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo, R.V.A.G.; Pineda, J.; Meneses, J.; Romero, A. Evaluating the influence of camera and projector lens distortion in 3D reconstruction quality for fringe projection profilometry. In Proceedings of the 3D Image Acquisition and Display: Technology, Perception and Applications, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–28 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.R.; Liu, M.; Song, J.H.; Yin, S.B.; Ren, Y.J.; Zhu, J.G.; Chen, S.Y. Projector distortion residual compensation in fringe projection system. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 114, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Kemao, Q.; Huang, L.; Asundil, A. Phase error analysis and compensation for nonsinusoidal waveforms in phase-shifting digital fringe projection profilometry. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gao, N.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H. Exponential fringe projection for alleviating phase error caused by gamma distortion based on principal component analysis. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 064105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Comparative study on passive and active projector nonlinear γ calibration. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3834–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, M.; Wang, Z.; Hoang, T.M.; Nguyen, D. Flexible calibration technique for fringe-projection-based three-dimensional imaging. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 3192–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chua, P.S.K.; Asundi, A. Least-squares calibration method for fringe projection profilometry considering camera lens distortion. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe, X.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Yang, Y.S.; Ren, M.J.; Zhu, M. Phase-to-Coordinates Calibration for Fringe Projection Profilometry Using Gaussian Process Regression. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Huang, S.J.; Meng, S.S.; Gao, F.; Jiang, Q. A simple, flexible and automatic 3D calibration method for a phase calculation-based fringe projection imaging system. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 12218–12227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.T.; Hyun, J.S.; Zhang, S. Pixel-wise absolute phase unwrapping using geometric constraints of structured light system. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 18445–18459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, P.S. Novel method for structured light system calibration. Opt. Eng. 2006, 45, 083601. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Asundi, A. Temporal phase unwrapping algorithms for fringe projection profilometry: A comparative review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 85, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, C.E.; Towers, D.P.; Jones, J.D.C. Absolute fringe order calculation using optimised multi-frequency selection in full-field profilometry. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2005, 43, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus—A paradigm for model-fitting with applications to image-analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R.; Wahl, R.; Klein, R. Efficient RANSAC for point-cloud shape detection. Comput. Graph. Forum 2007, 26, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetić, A.; Jurić, D.; Osmanković, D. The procedure of a camera calibration using Camera Calibration Toolbox for MATLAB. In Proceedings of the 35th International Convention MIPRO, Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2012; pp. 1752–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Falcao, G.; Hurtos, N.; Massich, J. Plane-based calibration of a projector-camera system. VIBOT Master 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]




| Diameter-Left (mm) | Diameter-Right (mm) | Spherical Center Distance (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30.0777 | 30.0327 | 100.0226 |
| 2 | 30.0124 | 30.0658 | 99.9937 |
| 3 | 30.0437 | 30.0112 | 99.9412 |
| 4 | 30.0057 | 30.0513 | 100.0352 |
| 5 | 30.0091 | 30.0144 | 100.1027 |
| 6 | 30.0107 | 30.0224 | 100.027 |
| Mean | 30.0266 | 30.0330 | 100.0204 |
| Reference | 29.9943 | 30.0093 | 100.1072 |
| Deviation | −0.0322 | −0.0237 | 0.0868 |
| Parameters | By RANSAC Method (mm) | By LSM (mm) | No Compensation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter-Left | 0.0322 | 0.0498 | 0.1591 |
| Diameter-Right | 0.0237 | 0.0423 | 0.1462 |
| Spherical center distance | 0.0868 | 0.1126 | 0.4674 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, G.; Sun, X.; Kong, L.; Peng, X. Suppression for Phase Error of Fringe Projection Profilometry Using Outlier-Detection Model: Development of an Easy and Accurate Method for Measurement. Photonics 2023, 10, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10111252
Dong G, Sun X, Kong L, Peng X. Suppression for Phase Error of Fringe Projection Profilometry Using Outlier-Detection Model: Development of an Easy and Accurate Method for Measurement. Photonics. 2023; 10(11):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10111252
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Guangxi, Xiang Sun, Lingbao Kong, and Xing Peng. 2023. "Suppression for Phase Error of Fringe Projection Profilometry Using Outlier-Detection Model: Development of an Easy and Accurate Method for Measurement" Photonics 10, no. 11: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10111252
APA StyleDong, G., Sun, X., Kong, L., & Peng, X. (2023). Suppression for Phase Error of Fringe Projection Profilometry Using Outlier-Detection Model: Development of an Easy and Accurate Method for Measurement. Photonics, 10(11), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10111252








