Abstract
This review explores the potential of separating and recycling rare earth elements (REEs) from different energy conversion systems, such as wind turbines, electric vehicles batteries, or lighting devices. The REEs include 17 elements (with global production of 242 kilometric tons in 2020) that can be found abundantly in nature. However, they are expensive and complicated to extract and separate with many environmental challenges. The overall demand for REEs is continuously growing (with a 10% yearly increase) and it is quite clear that recycling has to be developed as a supply strategy in addition to conventional mining. However, the success of both mining and recycling depends on appropriate separation and processing technologies. The overall REE recycling situation today is very weak (only 2% of REEs are recovered by recycling processes compared with 90% for iron and steel). The biggest recycling potentials rely on the sectors of lamp phosphors (17%), permanent magnets (7%), and NiMH batteries (10%) mainly at the end-of-life stage of the products. The profitability of rare earth recycling mostly depends on the prices of the elements to accommodate the processing costs. Therefore, end-of-life REE recycling should focus on the most valuable and critical REEs. Thus, the relevant processes, feed, and economic viability warrant the detailed review as reported here.
1. Introduction
Rare earth elements (REEs) are key chemical raw materials in the development of low-carbon industrial processes and especially in green energy technologies [1]. The REEs include 17 elements that can be found in nature (15 lanthanides La-Lu, Sc, and Y). They are ironically quite well represented in the Earth’s crust, except for the radioactive promethium, which is very rare. However, they are rarely found alone and at economically attractive concentrations, which make them expensive and complicated to extract and separate in high purity with conventional separation techniques. The elemental form of REEs can be iron-gray to metal-silvery that are reactive at high temperatures, most commonly ductile and soft. Reserves of these elements are thought to be large, but some ores involve complications in mining because of the co-presence of radioactive components. This makes the valorization of secondary resources such as e-waste or end-of-life energy systems very attractive. REEs are especially used in the production of magnets, catalysts, alloys, electronics, glasses, and ceramics. They make electric and hybrid vehicles work [2]. Even though their name suggests that REEs are very rare and difficult to find, most of them are quite abundant in the Earth’s overall crust. They are nevertheless hard to extract from ores because they are often linked to other minerals and occur at low concentrations. They barely exist in pure form on earth. In addition, the processes required for their extraction and mutual separation use high amounts of energy and demand complex drilling technologies. Finally, the extractive separations of REEs have inevitable problems with radioactive compounds as by-products. The demand for these elements has been importantly increasing in past years.
Green energy, technology, and e-mobility strategy, now adopted by many countries are being strongly linked to the availability of REEs, and therefore the recycling of these elements is becoming increasingly important [2]. It is essential for the transition to a green and circular economy. Despite that, commercial recycling of REEs is still very low, mainly because of inefficient collection, technological separation challenges, and lack of incentives even though it has great potential [3,4].
Recycling could be an effective strategy to overcome the impact due to mining REEs. Targeting, the most sought metals such as neodymium (Nd) can help avoid the overproduction of low-value metals such as lanthanum (La) and cerium (Ce). In a way, it can also help to tackle the balance problem of surplus amounts of unwanted/less sought for REEs and their uneven pricing dynamics [3]. It is also important to determine what energy input is needed to develop this separation and recycling cycle and to see how difficult it will be to isolate the different materials products and by-products because they could also be recovered as mixed materials with less valuable purities. Finally, it is important to assess the economic feasibility of these recycling processes and rigorous separations required, as well as the availability of the feed if such processes are in place.
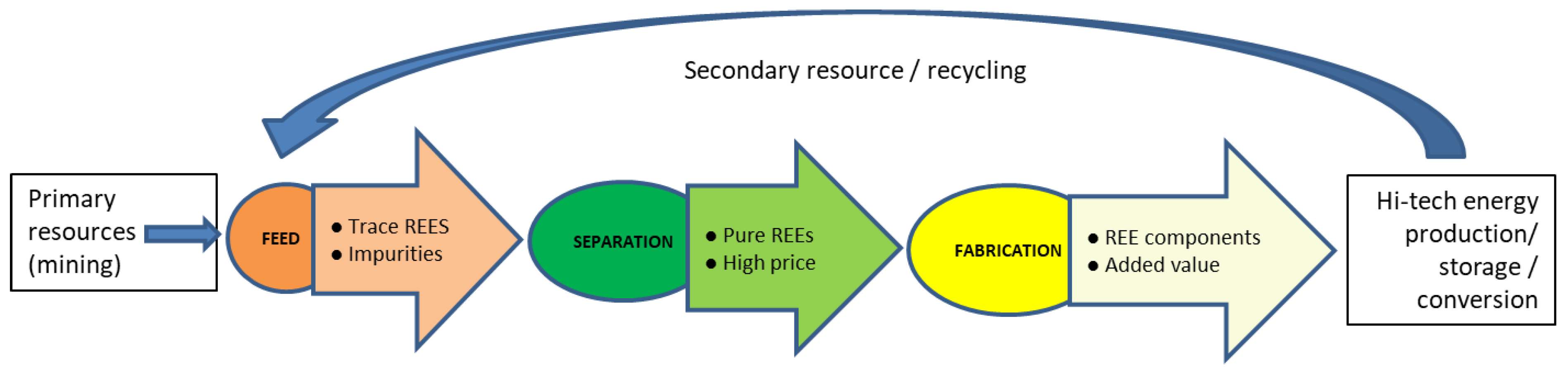
The focus area of the present review is shown in Figure 1. It is aiming to map the lifecycle of REEs in energy systems and the availability of the feedstock for the separation and recycling of rare earths and their economic viability. This is much needed as the techno-economic perspective of earlier reports and reviews has focused on the uses and the front-end material properties of the REEs [5]. Therefore, there remained the need to focus on back-end value chains, amount of feedstock availability, economic viability of available feedstock, and separation and recycling approaches. This can also serve as a concise summary of scattered details about the REE feed availability in different back-end energy systems.
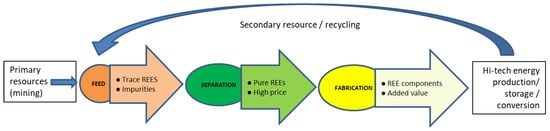
Figure 1.
Lifecycle of REE resources in energy production/storage/conversion systems and scope of the present review.
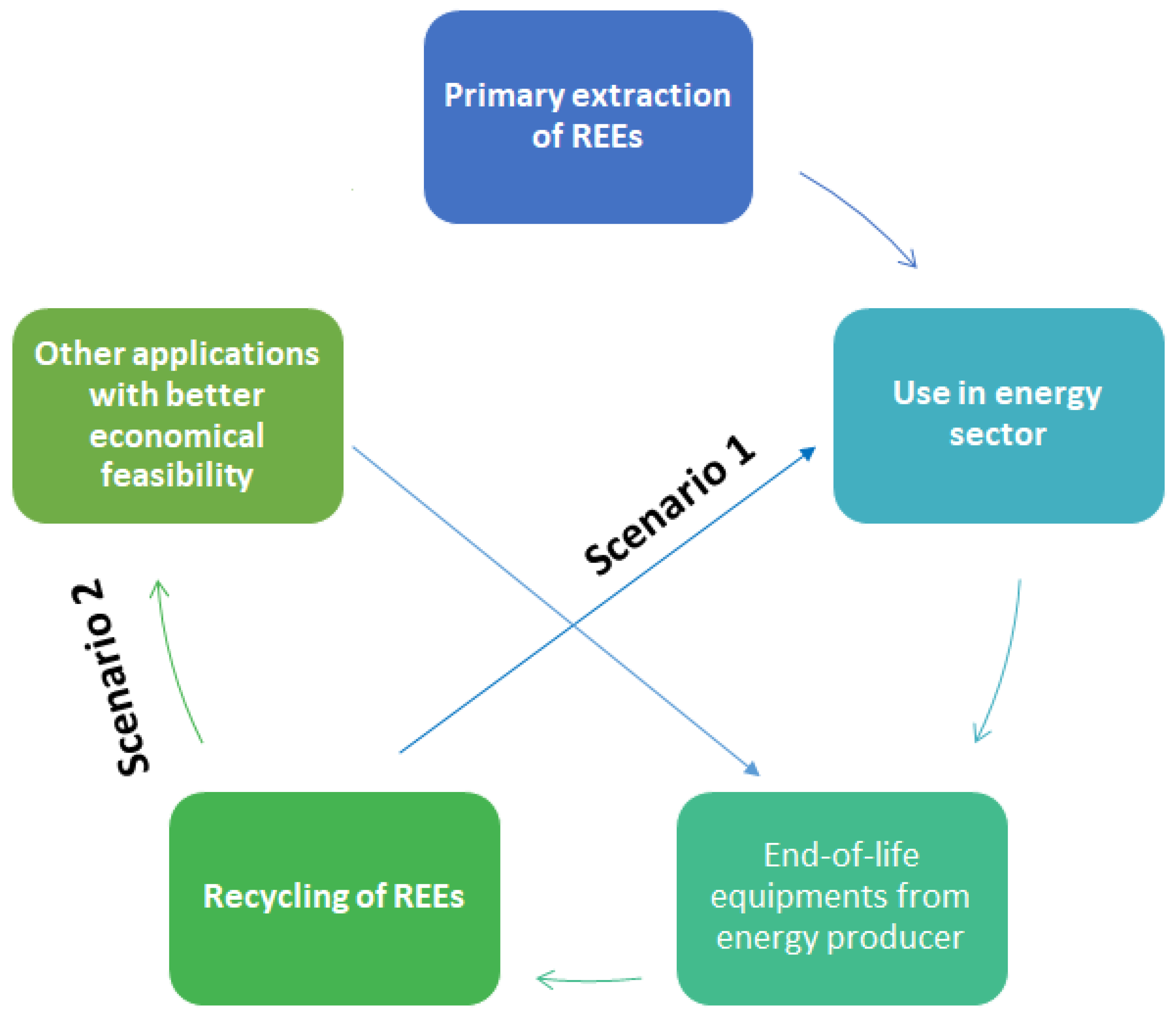
The resulting closed-loop economy of REEs could be defined as shown in Figure 2 below, by which recycled materials go back into the same energy system from which they came from (Scenario 1). A second possibility is to use recycled materials is to find other applications that require lower quality of the recovered materials. If there is an existing market with higher demand than the energy systems (Scenario 2). Therefore, there are two recycling streams of REEs possible from waste of a single energy sector [6].
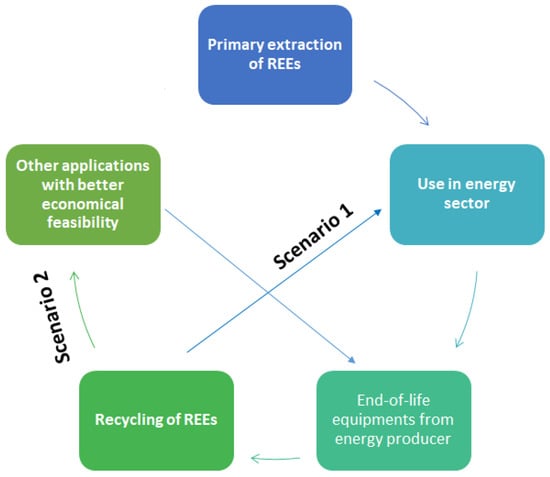
Figure 2.
Process cycle of the current study.
There is also material recovery potential with the primary production of REE-containing products at the initial manufacturing stage. They are usually referred as “recycling of production scrap”. It means that the waste is generated during the production phase. It can be directly collected and recovered at the production plants, for example, the waste from turbine magnets production or energy-saving lamps fabrication. The second step is conventionally understood as recycling and occurs at the end-of-life phase of a product as secondary production.
Therefore, this paper had the objective of reviewing and understanding the potential of recycling critical elements from different energy systems, such as wind turbines, electric vehicles, or lighting devices, for example. Different recycling pathways such as production waste and end-of-life waste in energy generation or lighting systems are compared in detail. It discusses the criticality of REEs, the number of feeds available for recycling, and the constraints in rolling out viable recycling strategies. The relevant processes, feed, and economic viability aspects warrant the detailed review as reported here.
2. Background and Methodology of Review
It is important to identify the different energy systems (including production, storage, and conversion) of interest for the recycling of REEs and to determine which REEs have the biggest re-use and recycling potential. In the present thematic review, quantitative and qualitative analyses were performed for the recoverable materials, assessing the following questions:
- -
- What quantity of the REEs can be recovered from the recycling process?
- -
- What quality in terms of purity of the element can be obtained?
- -
- In what chemical form could be the output element?
- -
- What market prospects do such elements have against mining supply?
The main energy sectors related to REEs are [5]:
- -
- Wind power generation (magnets);
- -
- Energy storage (NiMH batteries);
- -
- Energy-saving and conversion (lighting).
These energy systems were thus more precisely studied to assess in which parts of the devices the rare earths are used and can give information on the potential for recycling and the processes and economic boundary conditions required. The most common and critical REEs today are used for high-performance permanent magnets (neodymium, Nd, and dysprosium, Dy) and phosphor-based lighting (europium (Eu), yttrium (Y), and terbium (Tb)) [7]. The two most common REEs are lanthanum (La) and cerium (Ce) in the Earth’s crust, as well as in e-wastes. They are the two most produced and used rare earths as of today. The criticality of Eu, Y, and Tb may nevertheless change as new types of lighting (mainly LEDs) are gradually replacing phosphors [8].
REEs are part of many different technologies used in our everyday life. Their use in the development of green and other, traditional, technologies has been reviewed, e.g., by Zepf et al. and Goodenough et al. earlier in 2014, but they focused mainly on energy technologies [5,7]. However, comprehensive records combining the front-end use with the back-end recycling potential in the energy sector are still very scarce. The challenge is thus to understand the value chain and dynamics in terms of uses, amount of feedstock available, separation technologies, and economic boundary conditions. It is also imperative to find substitutes or ways to recover the materials from end-of-life products. This method has potential, even though it is quite clear that recycling will not be able to take care of exponentially growing REE demand alone. Recycling will likely be needed along with responsible primary mining.
Several investigations have been conducted in Europe to find REE ores. Europe has a wide range of REE occurrences and deposits that are mainly located in the northern part of the continent (Sweden and Norway). It seems that Europe has the potential deposits needed to address its supply of REEs at the moment [7,8,9,10,11]. The challenge today is to develop a sustainable exploitation model for these deposits [7]. Today, the production of REEs needs diversification with sustainable and environmentally friendly separation and process technologies to ensure the growing demands of our high-tech human society.
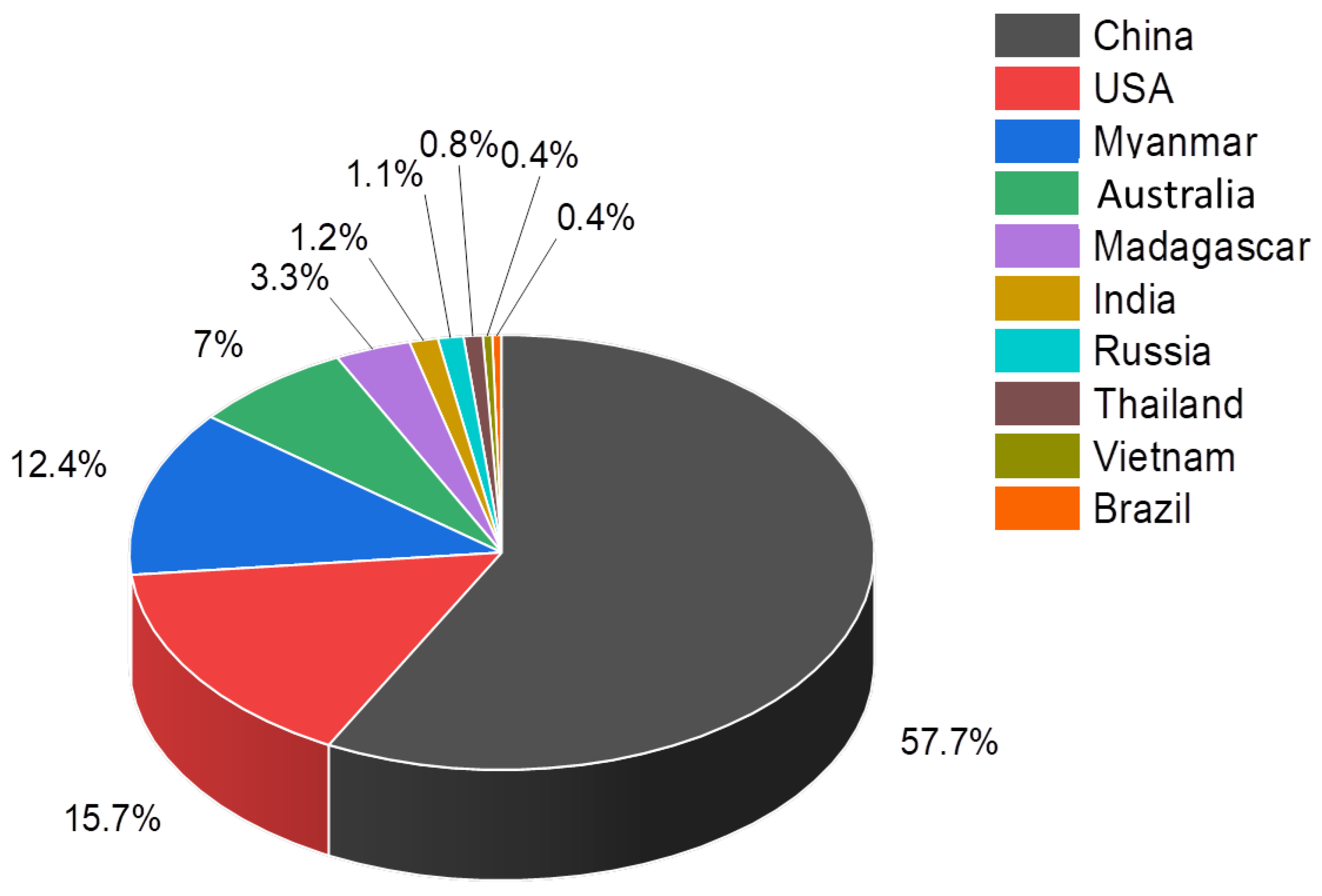
There has been already some evolution since many countries started exploring and developing mining activities around the world. The current key producers of REEs are shown in Figure 3. This may change in the future due to the growing consensus on critical raw materials that are rigorously studied and reported at the European Union (EU) level [9,10,11].
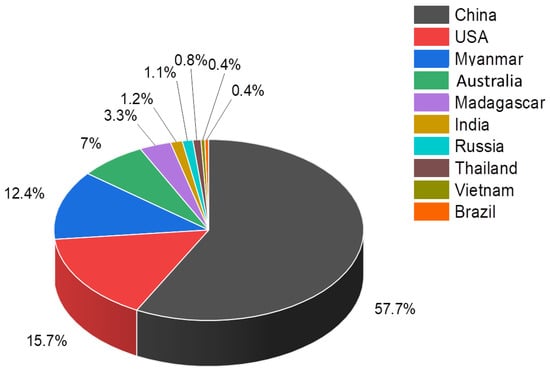
Figure 3.
Leading global producers of REEs in 2020 [12].
There are efforts ongoing in different EU projects to replace the REEs in magnets. However, given the best magnetic properties of REEs, it is difficult to eliminate them without compromising the price, performance, and size of such alternative magnets. However, the amounts of REEs used could be decreased with the optimization of technologies [2].
In 2020, the global production of REEs was 242 kilometric tons (kt). This is an inconsistent increase in comparison to the last two years, with a 10 and 15% increase, respectively [12]. A major issue in the rare earth element market is the uncertainty and lack of transparency between supply, demand, and use. In addition, the concerns about supply interruptions increase interest in recycling. There is an increasing demand for REEs since they are used in many new low-carbon energy technologies. This demand will most probably continue to grow with the increasing market of wind turbines, electric vehicles, compact fluorescent lamps, and LEDs. Thus far, there are no substitutes for REEs. However, research activities are aiming to find alternatives, especially in the magnet market.
3. Results
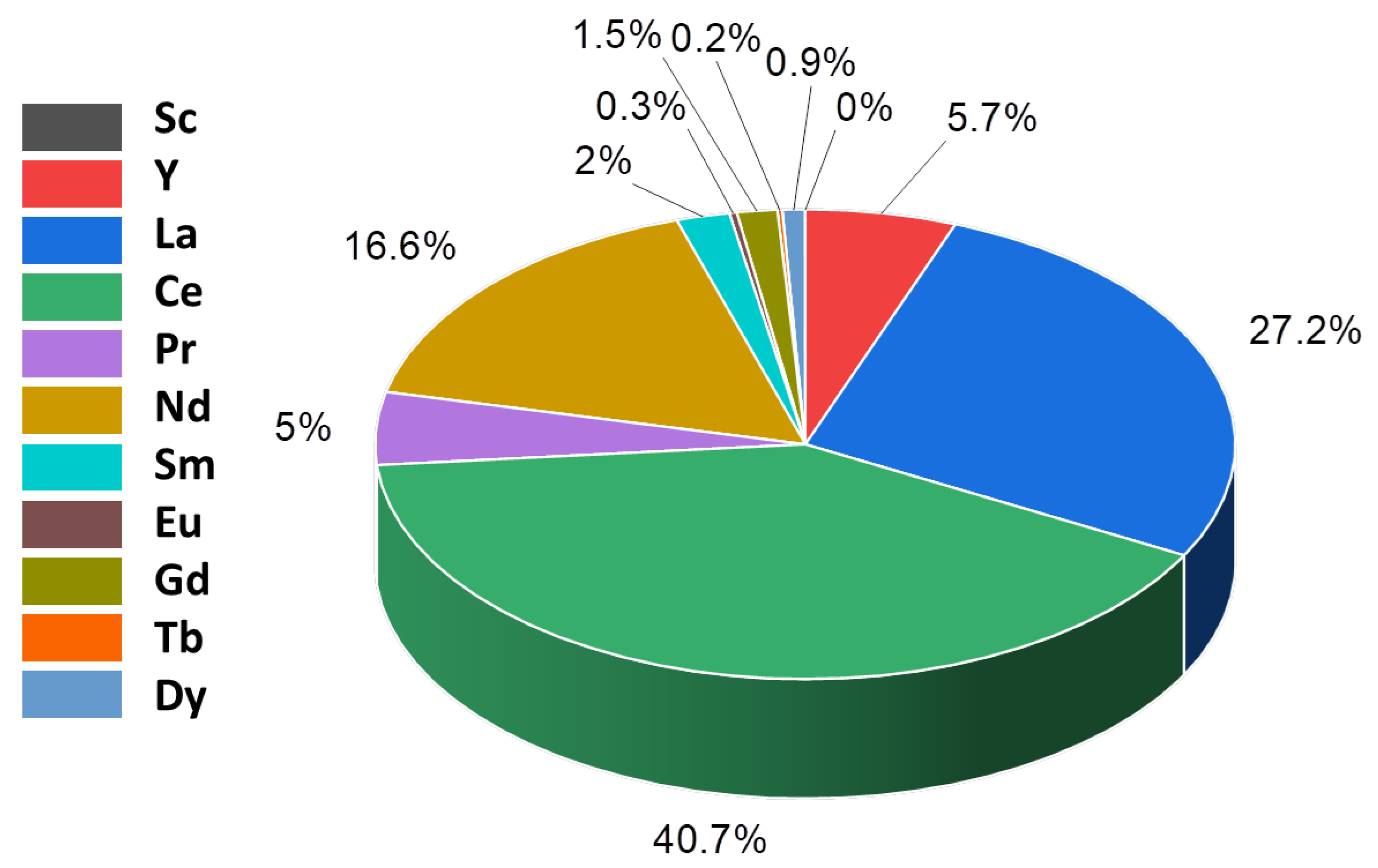
A global overview of the use of REEs was provided by Binnemans et al. in 2013 and by Royen and Fortkamp in 2016 [3,13]. The amounts of different REEs produced globally are uneven. Figure 4 shows the distribution of different REEs, and it is evident that the most expensive REEs such as Sc and Tb are produced in very fewer proportions compared to the production of light REEs (LREEs), such as La and Ce [13]. The unbalance is not only attributable to the geological distribution of the proportionally higher amount of LREEs versus heavy REEs (HREEs), but it is also governed by the fact that the minor quantities of HREEs are more difficult to separate than the LREEs using conventional separation technologies.
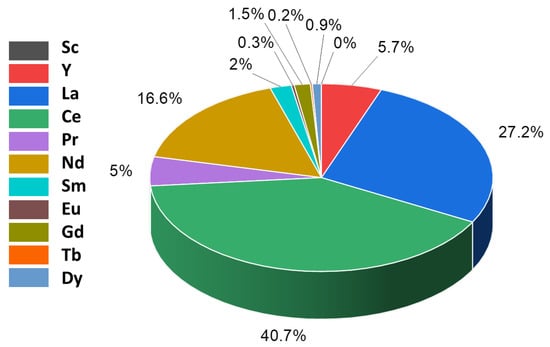
Figure 4.
Global distribution of REEs is uneven, resulting in unequal production and balance problems in 2018 [12,13].
Table 1 summarizes the different REEs used in energy technologies or allied scope.

Table 1.
Uses of different REEs in specific energy technologies [1,3,8,13].
It can be observed that La, Ce, Pr, Y, Dy, and Nd are rare earth elements that are most used in the specific energy-relevant applications described. It indicates that they are useful in many applications and that they will probably be more difficult to be substituted with other materials. It is also important to notice that La and Ce are the most commonly produced and used REEs. To extract one equivalent of Nd, two equivalents of Ce, and one equivalent of La are also inevitably removed from the mine as well [8]. This is due to the inherent abundance of the La and Ce as compared to Nd in the ores. In addition, they are lighter lanthanides and are difficult to separate from each other. Therefore, there is a surplus supply of La and Ce as compared to Nd that keeps their pricing lower. In addition, more processing and ore removal have an adverse impact on the environment in terms of the use of chemicals and the production of secondary wastes and tailings. It is negatively affecting the overall market, supply dynamics, and the environment. The applications relevant to the energy sector is discussed in more detail in the following sections.
3.1. Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
NiMH batteries are rechargeable batteries of importance mainly in electric and hybrid cars, electrical aircraft systems, and satellite pinpointing systems. These batteries have also a high energy density and have a wide operating temperature range (−30 to 70 °C) [14].
REE materials in the batteries provide adequate hydrogen storage and rapid desorption/re-absorption of this hydrogen for a quick recharge and high power. The batteries have a long life with a safe operation. Another characteristic of these batteries is their low maintenance requirement. However, in comparison to conventional Li batteries they can only store 66% energy capacity [14].
Hybrid and electric cars account for 57% of NiMH batteries in the world. As an example, every Toyota Prius car carries about 2.5 kg of REEs in the form of Misch-metal (Mm). Mm is a complex alloy of light REEs (La, Ce, Pr, Sm, and Nd). Therefore, electric and hybrid cars are a highly interesting market to study for the development of the recycling of rare earth metals even though it is still in an establishing phase. In the past, used NiMH batteries were exploited as cheap nickel sources without valorization of the 8 to 10% REEs (La, Ce, Pr, Sm, and Nd) [3,13].
Nevertheless, according to Binnemans et al., several active research groups in the field have now developed several chemical separation processes on the NiMH batteries that achieve a recovery rate of the REEs of up to 97.8% [3,4]. A first possibility (developed by Zhang et al. in 1998) is to use hydrometallurgical methods to recover nickel, cobalt, and REEs [15]. Another method (by Li et al. (2009)) consists of hydrometallurgical separation procedures including leaching by solvent extraction, evaporation of the strip liquor and the raffinate, and crystallization [16]. In pyrometallurgy, the metals are heated in a high-temperature furnace, and redox conditions are used to adjust the vapor pressure of different metals to separate them from each other. The pyrometallurgical operations can be automated easily; however, lack versatility in feed processing and require high investments in comparison to hydrometallurgy [1,2,3,4].
Guyonnet et al. [8] gave an overview of REE “flows into use” (e.g., Tb in lamps and Dy in magnets) and “in-use stocks” (average lifespans of products considered for the estimation of in-use stock) in Europe for the year 2010, showing a flow into the use of 120 (metric) tons for neodymium and 50 (metric) tons for praseodymium (Table 2). According to Guyonnet et al., the biggest potential for recycling from NiMH batteries is the recycling of Nd and Pr. This is probably because La and Ce are produced in excess and their prices are too low to be included in feasible recycling processes. Guyonnet et al. [8] also cited typical REE content data as a percentage concerning the entire NiMH battery weight. However, the weight percentage values for Pr (0.4%) and Nd (0.8%) did not agree well with the flow-in-use values (50 ton Pr and 120 ton Nd in Table 2). With Pr, the rare earth content (wt%) and flow into use-values reported by Guyonnet et al., either, the wt% value should be lower for the given flow into use value (viz., 0.33 instead of 0.4 wt%), or, the flow into use-value should be higher (viz., 60 metal ton instead of 50) for the given wt%-value. Also possible is that the reported values for Pr are inaccurate or were brought down to too little digits. Therefore, Table 2 shows rare earth usage (%) values with NiMH battery alloys from Curtis [17]. For many different applications, these and other values were originally presented by Curtis, and they are also shown and referred to by Binnemans et al. [3] and Royen et al. [13]. The flow in use amounts for La, Ce, and Sm were calculated here using the values for Nd (120-ton metal and 10% content) as a starting (reference) point.

Table 2.
Flow into use and content data for REEs with NiMH batteries in Europe for the year 2010 reported by Guyonnet et al. [8] (in bold script numbers) and Curtis [17] (in the normal script), respectively. The other flow in use-values are in italic script and were derived here (see text).
3.2. Permanent Magnets
Permanent magnets are used in automotive electric and hybrid motors, direct-drive wind turbine generators, and speakers. Magnets in automotive motors and wind power generator applications are directly linked to the energy sector and are thus of importance and interest for the present review. These permanent magnets usually consist of a neodymium-rich NdFeB alloy also containing Pr, Gd, Dy, and Tb in smaller amounts. The Nd fraction is the most important one, and with the literature consulted here takes about 65% to nearly 70% of the total REE share in permanent magnets.
Table 3 shows “flow in use” and “rare earths usage” (amount of REE used in defined application) values reported and estimated in this study for Nd, Pr, Dy, Gd, and Tb with magnets for the year 2010. The reported flow in use and the REE usage values are interrelated over a common REE content of the application under consideration. In Table 3, the flow into the use of the ton metal values for Europe (the year 2010) was taken from Guyonnet et al. [8], and they are written in bold script for clarity. The reported REE content values are from Curtis [17] and are also written in bold script. All other numbers are in italic bold script and estimated here as follows: Nd was most prominently present with magnets, and by considering 70% content associated with the 1230 ton metal into use flow (Table 3) as reference datasets, we were able to estimate the content for Pr and Dy from their flow into use values in proportion to the flow into use and the content value of Nd. Similarly, the flow into use-values estimated here for Gd and Tb followed from their reported content values relative to the Nd dataset. It must be mentioned that Curtis [17] also gave usage values for Pr and Dy of 23.4% and 5%, respectively. However, the latter values did not correspond well with the estimated 18% and 13% content values shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
REE mass flows and content in permanent magnets [8,17] (see text).
For the year 2020, Guyonnet et al. [8] estimated a recycling potential of 170 to 230 tons for neodymium—about 16% of the flow into use for Nd with permanent magnets in Europe in the year 2010 (Table 3). As a comparison, the study from Rademaker et al. (2013) presents potential recycling supply ratios (PRSR) for neodymium and dysprosium, as given in Table 4 [18]. The PRSR stands for the ratio between the REE in collected end-of-life flows and the total REE demand. The low PRSR value for Nd for the year 2020 in Table 4 suggests that the 16% recycling of Nd in 2020 forecasted by Guyonnet et al. [8] could probably be too optimistic. In addition, with the results in Table 4, it is also surprising to observe that the Nd recycling ratios are expected to decrease.

Table 4.
Global recycling potentials for neodymium and dysprosium including wind, automotive, and HDD magnets [18].
The recycling situation of magnets today is very weak. This is due to the following factors [14]:
- -
- Difficulty to decompose the chemical compounds (technological difficulties);
- -
- Low concentrations of REEs in the goods and location deep within consumer products;
- -
- Lack of financial incentives;
- -
- Inefficient collection of end-of-use objects.
This is true for all the different technologies used in the energy sector containing rare earth elements. The REEs are lost in shredded and melted fractions of e-waste not being focused by the existing separation processes [1,13]. On the other hand, Mueller et al. conducted an interesting analysis of the geological distribution data, the existing collection rates, the economic feasibility of recycling, and its environmental impact on Switzerland [19]. For permanent magnets, the situation seems to be quite promising since the collection rate is claimed to be close to 100%. This does not include the motors sent to developing countries where the materials are also reused as second-hand machinery or components. It is assumed that in 2017, 1.6 tons of magnets were available in 1 million electric cars. This number was assumed by Mueller et al. [19], and it did not represent a high confidence level. From these 1.6 tons, 2 wt% of Nd can be recovered, giving a total of 32 kg of neodymium recoverable in Switzerland.
The dismantling and processing of permanent magnets are expected to become feasible in the medium- or long-term future, and its impact on the environment has been observed to be rather small because the global warming potential of such recycling of Nd has been observed to be 14 kg CO2 equivalent per Nd2O3 according to kilogram mass allocation and without radioactive side products. This will make the motors manufactured using recycled REEs more sustainable in comparison to those dependent on mining resources [19]. According to this information, a fairly certain assumption can be made that there is a real potential for permanent magnet collection and the recycling of the contained REEs.
Different separation and recycling methods are proposed for REE magnets [3], ranging from (1) reuse in the original form up to (2) hydro- or (3) pyrometallurgical processing and processing using corrosive gases, such as (4) corrosive chlorine or (5) reducing hydrogen.
The first option (reuse) is of course the most economical way of recycling and does not generate any waste, but this only works for large and easily accessible magnets that can be found in large wind turbine generators and large electric or hybrid vehicle motors. This is not available in substantial quantities; therefore, other methods have been developed. The first option requires less energy than the hydro- or pyrometallurgical methods, and it does not produce any secondary waste either. This is particularly suited for hard disk drives, but it does not apply to mixed scrap feed or oxidized magnets. The second and third methods are equivalent to the recycling methods for NiMH batteries that were addressed in the last preceding section. Hydrometallurgical methods require many steps before obtaining a new recycled magnet and consuming many different chemicals. Pyrometallurgical methods require large energy inputs to bring enough heat to the material [1,3]. The fourth method (gas-phase extraction) consumes large amounts of chlorine gas, but it does not generate any wastewater and applies to every type of magnet composition; thus, it is easier to implement at a larger scale. However, the impact of gases has to be studied carefully, and the technology should not contradict the net zero-emission goals [3,20]. New approaches are being developed for direct reduction of the magnets in a hydrogen atmosphere (fifth method) under controlled conditions and sintering of the powdered metals in new magnet shapes again. This process needs a controlled and carefully designed safety concept due to the use of highly reductive hydrogen gas [21].
3.3. Lamp Phosphors
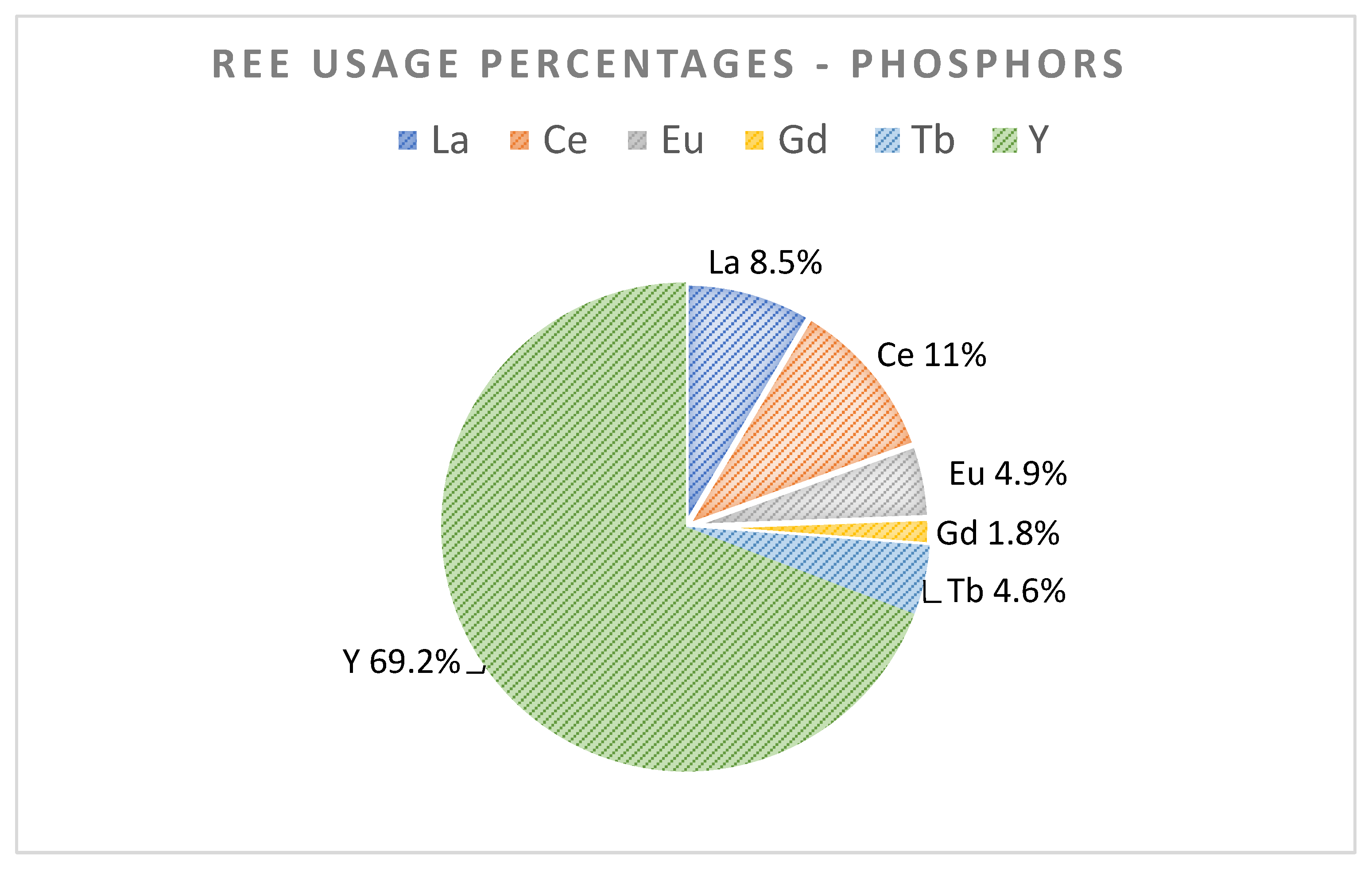
Phosphors are essential components of different fluorescent lamps (also known as low-energy lamps) and smartphone screens among other examples. Those phosphors include REEs, mainly Eu, Tb, Y, La, Ce, and Gd in smaller quantities. Television and LED phosphors are very attractive for REE recycling [1,13]. Lamps are composed of phosphors that can contain REEs (La, Ce, Eu, Gd, Tb, Y) up to 30% of their weight. At the moment, lamp phosphors are generally landfilled due to their toxic mercury (Hg) content. Figure 5 shows the different REE fractions present in phosphors.
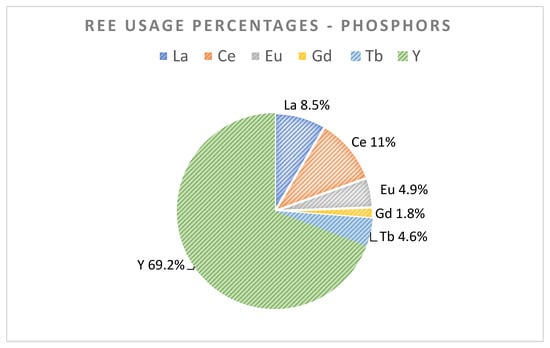
Figure 5.
REE usage percentages in phosphors [3,13] (Royen et al., 2016).
European feed for the important REE target in phosphors is estimated in the range of 140–2300 tons for Y, Tb, and Eu metals. In Table 5, in-use stock amounts for Y, Eu, and Tb for the year were reported by Guyonnet et al. [8]. Those of La, Ce, and Gd shown in Table 5 was calculated here, using the REE percentages in Figure 5, and linking these to the percentage and in-use stock numbers of yttrium (arbitrarily chosen base case).

Table 5.
REE-specific in-use stock of lamp phosphors in Europe [8].
Mueller et al. (2017) conducted the same analysis for phosphors and batteries in Switzerland for the year 2014 [19]. The available quantities of lamps were about 1169 tons with an REE mass fraction of 0.012 wt% per lamp. This gives a total mass of europium to be recovered in Switzerland in 2014 as 140 kg. A very high reverse supply collection and extractive yield of >80% was observed. The recycling of phosphors is nevertheless still uncommon. On the other hand, Guyonnet et al. estimated that 10 tons of Terbium will be recycled every year from phosphors, starting in 2020 [8]. Except for some piloting efforts in Switzerland, this has still become reality [1]. Notwithstanding these, Tb and Eu have a rather high potential for recycling from end-of-life lamp phosphors. Lamp collection costs could vary between 15 cents to a couple of Euros per unit kilogram. An important challenge linked to the recycling of phosphors from lamps is linked to mercury contamination. The treatment of Hg induces additional costs to ensure minimum human health impacts [1,13]. Lamp recycling is estimated to generate a greenhouse gas (GHG) impact of 23.5 kg per unit kilogram of metal oxides. Energy-saving lamps are part of electrical appliances. Moreover, worldwide, the stock of end-of-life lamp phosphors is large.
In Switzerland, retailers have to take back end-of-life electrical and electronic equipment free of charge by law. This type of waste cannot go into the municipal solid waste stream. Today, the dismantling of this equipment is done outside of Switzerland in countries belonging to the European Union or members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Sending waste to other countries is now forbidden according to new international regulations [6].
As with magnets, different recycling methods also exist for phosphors:
- Direct re-use of lamps (out phased due to technological change to LEDs);
- Separation of phosphor components or mixtures and reuse in lamp (or other) industry;
- Recovery of REE content on an individually high purity level.
In general, it is a challenge to recycle phosphors because of the contamination with mercury and the initiated replacement of lamps by other light-producing devices (LEDs). The first method can be to use still working electronics in spent and still active lamps in newer energy-to-light conversion devices. The second option is only applicable to one single type of lamp because different lamps use different types of phosphor mixtures. The advantage is that no chemical process is required, which makes this technique quite simple. The recycling technology may be a simple process, but it is difficult to reach pure phosphor fractions. The particle size of the phosphor may be changed to affect its light and energy conversion capabilities. The last method applies to all types of phosphors and the process is hydrometallurgical separation for the extraction of REEs. It produces high purity products that can be marketed irrespective of the application type. The disadvantage here is the production of high amounts of wastewater and the consumption of many chemicals [1].
Recycling lamp phosphors is particularly challenging because lamps are made of glass, metals, plastic, and REEs containing phosphor powder. This powder represents only 3% of the mass of the lamp. Since all the other materials can be more easily recycled, they have gained more interest for now. With the Solvay group, Rhodia has focused on recycling phosphors under wet conditions at the dedicated facility at La Rochelle [13,22]. According to Solvay, the process allowed treating and revalorizing more than 90% (1350 t/y) of fluorescent powders, thus recovering rare earths (Y, Eu, Tb, Gd, La, Ce) as oxides and nitrates, glass (to be valorized in the glass industry), and phosphates (valorized in the phosphates industry) [22]. Fluorescent lighting is also changing nowadays. There has been an inflection point in demand for REEs for lighting, i.e. fewer REEs are used in LEDs than in fluorescent lamps. LEDs are going to replace all fluorescent lamps in the future because they have higher energy efficiency, longer lifetimes, and require less packaging [23].
New phosphors are being developed at several U.S. national laboratories with the capacity to achieve the same efficiency and quality with much less amount of critical REE in use [24]. This jeopardized the investments in the recycling of rare earths coming from phosphors since there will be fewer REEs in this sector in future years. Nevertheless, being able to recover REEs present in current devices may be a real strength for a society to be less dependent on primary extraction ores. Therefore, the recycling of light phosphors is still advised, also from an environmental point of view [1]. As mentioned earlier, environmental impacts linked to the recycling of REEs are very low in comparison with the impact linked to mining.
4. Discussion
On the basis of our technology mapping and literature results, we herein discuss trends and perspectives that may be crucial for making REE separations and recycling processes viable. They are either supporting or contradicting factors for the research, development, and implementation of different separation technologies.
4.1. Criticality Assessment of Rare Earth Elements
As shown further up in the text in Figure 3, there are uneven REE production capacities between different countries, and REE value chains are reshaping due to changing global demands, consumption patterns, and difficult environmental and economic boundary conditions for the new mining possibilities.
In volatile and uncertain markets, Japan managed to double its consumption until 2007. In comparison, Chinese in-house consumption increased by 66% within the same years [25]. On the other hand, many geological sectors are being studied and there is potential for opening new mines, but such development processes are taking a long time because the ores are often associated with radioactivity and other environmentally relevant problems. It is thus quite straightforward that the growing demand is putting pressure on the global REE market, which increased prices considerably between 2008 and 2011 [14].
The prices of REEs are entirely determined by supply and demand from suppliers and manufacturers, respectively. They were falling since 2011 and became quite low until 2019, especially for La and Ce (around 150 USD/kg at their peak and less than 15 USD/kg in 2019) because they are largely supplied and extracted. This makes recycling less feasible economically than it used to be. However, the prices are increasing since mid-2020 at least for the heavy rare earths such as Nd, Dy, and Tb. Tb is the most expensive REE today with a price of 1450 USD/kg Tb oxide (in December 2021), followed by the then second highest price for scandium (Sc) oxide. However, its peak value was at about 2300 USD/kg in 2011. The pricing fluctuations are also attributed to the supply monopoly and additional dumping of some of the abundant REEs such as La and Ce. This scenario makes the REE pricing non-viable for the recycling industries.
Criticality assessment refers to the economic, environmental, and supply risk-related impact of REEs [19,25,26]. The EU Commission publishes the critical raw materials lists periodically. It is important to note that REEs were described as highly critical raw materials in all the versions of the list published thus far [11]. They have the highest supply risk of all studied elements while having medium-range economic importance. Shifting the lighting technology from fluorescent lamps to LEDs will decrease the criticality of Y, Eu, and Tb. However, magnet materials such as Dy, Pr, and Nd will continue to be critical in the near to long term [8]. Nd and Dy are often short in supply. Lighter REEs such as La can also see increased demand in the future due to their substance use in catalysts manufacturing [14]. The demand growth rate of REEs increases by 10% every year; therefore, the criticality assessment of the elements has to be considered seriously. Since Europe imports 90% of its REE consumption, the first objective would be to reduce its dependency on primary ore extraction. This will help to develop recycling-based sustainable value chains with a minimum environmental impact. However, this needs to be promoted as a state policy to ensure the development of such alternative value chains.
4.2. Challenges of Recycling
Recycling has substantial advantages in favor of the environment and human health due to natural protection and proper waste management. In the case of REE recycling, such advantages are even more pronounced due to the avoidance of radioactive by-products.
The profitability of REE recycling mostly depends on the prices of the elements. As seen in the earlier section, the prices of REEs have been falling since 2011 and are now increasing further. However, it is still making recycling non-viable [22].
Recycling of REEs can be promoted more by political will than by real economic activity, but decoupling the European REE market from minerals import may become important soon to develop healthy and competitive recycling and separation processes and their implementation [25]. Recycling has to compete, however, with primary mining prospects in the EU [8]. There is potential for opening REE mines in Sweden and Norway, which will reduce the need for recycling, but since the demand is growing, mining and recycling will both be needed. However, neither mining nor recycling will be able to satisfy the exponentially growing market on its own [27].
The separation technology for REEs is challenging due to complex and variable feeds from energy systems [1,3,28]. This is further complicated by the immature reverse supply chains and the dilute amounts of REEs present in complex product systems [1,2,3,4]. Such feed is usually lost with the EU states as it lands up as secondary use infrastructure in countries where after the end of use no collection or processing capabilities are in place [3].
4.3. Recycling Potentials
Recycling REEs can help in avoiding 1.5 times radioactive waste per ton of REE [29]. The governments have the power to decide whether they want to promote one technology or another by allowing subsidies or investing in specific research [26]. The profitability of REE recycling mainly depends on the price of these elements. Therefore, REE recycling from end-of-life e-waste should focus on the most valuable REEs [1,22].
Estimated amounts of Nd, Tb, and Dy recovery potential in the EU equivalent of 580, 10, and 70 tons, respectively, are impressive examples of recyclables feedstock in enhancing the alternative and secondary supply chain [8]. Recycling processes could be dedicated primarily to the most sought for critical REEs. This means that terbium would be recycled entirely from waste streams, which has seemed to be difficult to achieve thus far. Neodymium has a recovery rate of 40% following these results. As seen previously, this seems too high. A more realistic estimation would be around 10% of Nd recycling.
The global recycling potential for magnets, phosphors, and NiMH batteries in the EU of about 7.8% has been derived here on the basis of the data cited by Binnemans et al. [3] in 2013, showing, e.g., an estimated total amount of nearly 30,000 tons in old scrap (e-waste) and a total estimated available REE flow of nearly 375,000 tons in stocks for the year 2020. Out of different energy systems or applications, the three feedstocks presented in this table are commonly described as being the most feasible for REE recycling. The recycling rates as percentages, with respect to different types of energy applications of feedstock available, are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Expected mean lifetimes and global recycling potential for REEs estimated for 2020 [modified after Binnemans et al. 2013 [3]].
Recycling of phosphors seems to have a somewhat better recycling rate than other waste streams. This is because the average lifespan of such an application is much less (Table 6), and the amount of REEs available in the waste feedstock is substantially higher as compared to other energy applications related feedstocks.
The recycling potential for NdFeB magnets has recently been estimated for the years 2018–2040 by Maximilian V. Reimer et al. (2018). [30] Although several research projects have successfully been completed, most experts do not expect an industrial implementation in Europe within the next years. The main applications for NdFeB magnets are electric vehicles, electric and hybrid cars, industrial motors, wind turbines, MRIs, HDDs, and audio devices. However, the highest potential of NdFeB magnets is expected from mobility and wind turbines that are being designed for a service life of 20 years, yet the volumes above 1000 ton magnet/year considered necessary for an industrial recycling plant of these magnets is not expected before 2033 [20].
It is clear that the residence time of the goods is strongly influencing the current economic potential. As for the estimated average lifetimes of lamps, magnets, and batteries given by Binnemans et al. [3], it is not clear from the recent literature and the Internet whether they have changed (improved) substantially nowadays, partly because the performance, composition, and lifetime may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, as well as on how often and how long they are being stored, recharged (when applicable), and run by the consumer.
4.4. Existing Recycling Projects and Processes
Different examples of REE recycling in large companies exist. This section is presenting some of them in order to show that it can be an interesting activity at different levels and for different reasons [14].
Solvay S.A. is a company with a plant in La Rochelle (France) that is the only one in Europe that can purify rare earth elements. The project initially focused on the recycling of phosphorescent powders from used fluorescent lamps. Later on in a collaboration with Umicore, the focus was supplemented with the recycling of end-of-life NiMH batteries [1,22].
Rhodia S.A., SolarWorld Industries GmbH, and First Solar are three companies that have developed technologies for the recycling of REEs. Rhodia focuses on commercial magnet recycling processes, and the third company has obtained high recycling rates for glass (90%) [3].
The recovery of REEs from waste usually results in high costs. Therefore, some of the initiatives taken have been aborted in the EU and North America following the rapid lowering of market prices and consequent non-cost effectiveness. However, with increasing prices and better available process technologies, new initiatives are emerging [31,32].
Japanese companies such as Honda, Shōwa Denkō K.K., and Mitsubishi Motors have implemented recycling processes for batteries and magnets. The Chinese company Ganzhou Recycle Hi-Tech Co., Ltd. demonstrated swarf and magnet recycling capabilities on large scales. These are all large companies known worldwide. All these initiatives are located in Asia, where the use of REEs is especially important and significant. They may be more aware of the risks of potential supply shortages and tend to find solutions beforehand. In addition, they seem to understand the models of circular economy and the need for closing the loop [31].
5. Conclusions
Most studies dealing with the recycling of REEs state the same global situation for supply, demand, and end-of-life treatment issues in energy sectors (energy generation, use, and conversion). The current recycling of REEs is extremely low (only 2% of REEs are recovered by recycling processes against 90% for iron and steel). The lower prices of the elements today harm the development of recycling technologies as well as their economic feasibility. Moreover, there is a real challenge for recycling REEs because they are found at very low concentrations in end-of-life feedstocks, and they are located very deep in the energy-relevant equipment/gadgets and therefore their access is complex. Despite the low recycling rates, REEs are not expected to be used less in the upcoming years. On the contrary, their demand is growing rapidly, and the supply will have to adapt. Recycling of REEs is thus a real topic that will develop more and more rapidly with encouraging projects from large recycling companies located in Asia in the fields of NiMH batteries and lamp phosphors, for example. Such growth is often driven by the availability of appropriate and economically viable separation technologies for different metals. Europe has a few projects as well that are being developed that are quite promising but are not yet as large as the Asian projects. It would be beneficial to enhance the cooperation between the different REE recycling companies to gain more knowledge and accelerate the learning and implementation process.
Waste from energy technologies such as batteries, lamps, and magnets represent a powerful and futuristic opportunity for REE supply chain. Recycling will add up to mining to satisfy the future REE demand. It is found that about 7% of REEs in magnet use stocks, 10% in batteries, and 17% in phosphor lighting could be recovered through recycling processes. The biggest potential seems thus to come from lamp recycling, but this depends on viable separation process developments and its economic implementation and future demands of REEs present therein. Moreover, in Europe, 10 tons of terbium and 230 tons of neodymium are estimated to be recoverable from waste streams every year. Recycling of REEs should be prioritized for elements that are short in supply (dysprosium, neodymium, europium, yttrium, and terbium). Recycling should also be focused on the most valuable elements. Therefore, high-purity REE separation processes have to be developed from the complex energy system wastes.
However, it is inevitable and necessary for rare earths from energy-relevant appliances or end-of-life feedstocks to be recycled in order to implement green technologies hereby needed for the energy transition in a circular economy. Finally, it must also be noted that there are also theoretical, technical, economical, and environmental potentials to be elaborated on in more detail in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.B.P., V.P. and C.L.; data curation: A.B.P., V.P. and R.P.W.J.S.; formal analysis: A.B.P. and V.P.; funding acquisition: A.B.P., R.P.W.J.S. and C.L.; investigation: A.B.P., V.P. and C.L.; methodology: V.P.; project administration: A.B.P. and C.L.; supervision: A.B.P. and C.L.; validation: A.B.P., R.P.W.J.S. and C.L.; visualization: A.B.P., V.P. and R.P.W.J.S.; roles/writing—original draft: A.B.P. and V.P.; writing—review and editing: A.B.P., V.P., R.P.W.J.S. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) for the co-funding of the present work (project no.: UTF-1011-05300).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Co-author Ajay B. Patil thanks the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) for the co-funding of the present work (project no. UTF-1011-05300).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest associated with the work reported in the present paper. This work was a part of the master’s semester project of Viktoria Paetzel.
References
- Patil, A.B.; Tarik, M.; Struis, R.P.; Ludwig, C. Exploiting end-of-life lamps fluorescent powder e-waste as a secondary resource for critical rare earth metals. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rare Earth Element Metals Recycling: Is There Hope After All? (Part 1). (13 September 2016) and Rare Earth Element Metals Recycling: Is There Hope After All? (Part 2) (20 September 2016). Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/blog/metals/rare-earth-element-metals-recycling-is-there-hope-after-all-part-1/; https://www.thermofisher.com/blog/metals/rare-earth-element-metals-recycling-is-there-hope-after-all-part-2/ (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; McGuiness, P.; Jones, P.T. Rare-earth recycling needs market intervention. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepf, V.; Reller, A.; Rennie, C.; Ashfiled, M.; Simmons, B.P. Materials Critical to the Energy Industry. An Introduction. 2nd Edition. 2014. Available online: https://dokumen.tips/documents/materials-critical-to-the-energy-industry-an-introduction-a-materials-critical.html (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- FOEN, Federal Office for the Environment. Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Available online: https://www.bafu.admin.ch/bafu/en/home/themen/thema-abfall/abfallwegweiser--stichworte-a--z/elektrische-und-elektronische-geraete.html (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Goodenough, K.; Schilling, J.; Jonsson, E.; Kalvig, P.; Charles, N.; Tuduri, J.; Deady, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Schiellerup, H.; Müller, A.; et al. Europe’s rare earth element resource potential: An overview of REE metallogenetic provinces and their geodynamic setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyonnet, D.; Planchon, M.; Rollat, A.; Escalon, V.; Tuduri, J.; Charles, N.; Vaxelaire, S.; Dubois, D.; Fargier, H. Material flow analysis applied to rare earth elements in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Critical Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU—A Foresight Study. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/42881 (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Gauß, R.; Burkhardt, C.; Carencotte, F.; Gasparon, M.; Gutfleisch, O.; Higgins, I.; Karajić, M.; Klossek, A.; Mäkinen, M.; Schäfer, B.; et al. Rare Earth Magnets and Motors: A European Call for Action. In Rare Earth Magnets and Motors Cluster of the European Raw Materials Alliance; Berlin, Germany, 2021; Available online: https://eit.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2021_09-24_ree_cluster_report2.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- European Commission, Critical Raw Materials Resilience: Charting a Path towards Greater Security and Sustainability, Fourth Critical Raw Materials List. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/42849 (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Top 10 Countries for Rare Earths Production. 2021. Available online: https://investingnews.com/daily/resource-investing/critical-metals-investing/rare-earth-investing/rare-earth-producing-countries/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Royen, H.; Fortkamp, U. Rare Earth Elements-Purification, Separation and Recycling, Pubished by the IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute. Report Number C 211. 2016. Available online: https://www.ivl.se/download/18.76c6e08e1573302315f3b85/1480415049402/C211.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Lucas, J.; Lucas, P.; Mercier, T.L.; Rollat, A.; Davenport, W.G. Rare Earths Production, use and Price. In Rare Earths: Science, Technology, Production and Use; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Chapters 1–19; ISBN 978-0-444-62735-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yokoyama, T.; Itabashi, O.; Wakui, Y.; Suzuki, T.M.; Inoue, K. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent nickel-metal hydride secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 50, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, S.; Ju, Z.; Wu, F. Recovery of Ni, Co and rare earths from spent Ni–metal hydride batteries and preparation of spherical Ni(OH)2. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 100, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, N. Rare Earths, We Can Touch Them Everyday. In Lynas Presentation at the JP Morgan Australia Corporate Access Days; New York, NY, USA, 2010; Retrieved on 14 January 2022; Available online: https://www.asx.com.au/asxpdf/20100927/pdf/31sqqzmv0ng1tb.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Rademaker, J.H.; Kleijn, R.; Yang, Y. Recycling as a Strategy against Rare Earth Element Criticality: A Systemic Evaluation of the Potential Yield of NdFeB Magnet Recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10129–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.R.; Wäger, P.A.; Turner, D.A.; Shaw, P.J.; Williams, I.D. A framework for evaluating the accessibility of raw materials from end-of-life products and the Earth’s crust. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Net Zero by 2050: A Roadmap for the Global Energy Sector IEA (2021); OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Zakotnik, M.; Devlin, E.; Harris, I.; Williams, A. Hydrogen Decrepitation and Recycling of NdFeB-type Sintered Magnets. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2006, 13, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solvay (2015) SOLVAY Latest Developments in Rare Earth Recovery from Urban Mines. 2015. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/14043/attachments/1/translations/en/renditions/native (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Ku, A.Y.; Setlur, A.A.; Loudis, J. Impact of Light Emitting Diode Adoption on Rare Earth Element Use in Lighting: Implications for Yttrium, Europium, and Terbium Demand. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2015, 24, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambogi, J. 2015 Minerals Year Book. USGS. 2015. Available online: https://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/rare_earths/myb1-2015-raree.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Du, X.; Graedel, T. Uncovering the end uses of the rare earth elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wäger, P.; Widmer, R.; Stamp, A. Scarce Technology Metals—Applications, Criticalities and Intervention Options; Federal Office for the Environment: Bern, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Atwater, H.; Fromer, N.; Otten, V. Critical Materials for Sustainable Energy Applications; The Resnick Institute, 2011; Available online: https:/Authors.library.caltech.edu/32727/1/ri_criticalmaterials_report.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Patil, A.B.; Struis, R.P.W.J.; Testino, A.; Ludwig, C. Extraction of Rare Earth Metals: The New Thermodynamic Considerations Toward Process Hydrometallurgy. In Shape Casting; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- De Lima, I.B. Rare Earths Industry and Eco-management. Rare Earths Ind. 2016, 8, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, M.V.; Schenk-Mathes, H.Y.; Hoffmann, M.F.; Elwert, T. Recycling Decisions in 2020, 2030, and 2040—When Can Substantial NdFeB Extraction be Expected in the EU? Metals 2018, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global E-waste Monitor; United Nations University (UNU): Bonn, Germany; International Telecommunication Union (ITU): Geneva, Switzerland; International Solid Waste Association (ISWA): Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Salih, K.A.; Rabie, K.; Elwakeel, K.Z.; Zayed, Y.E.; Hamza, M.F.; Guibal, E. Development of phosphoryl-functionalized algal-PEI beads for the sorption of Nd(III) and Mo(VI) from aqueous solutions—Application for rare earth recovery from acid leachates. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 127399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).