Abstract
Aflatoxin M1(AFM1), a major metabolite of Aflatoxin B1(AFB1), has been identified as a potential contaminant in dairy products. Because of its possible carcinogenicity, the legislation limits as set by Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 are very strict, namely 0.050 μg kg−1 in milk and 0.025 μg kg−1 in infant formulas. To meet these requirements, a sensitive and accurate method was developed, employing liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Ιmmunoaffinity columns (R-Biopharm) were used for sample purification and preconcentration of the analyte of interest. The quantification of AFM1 was conducted using fortified milk samples, while Aflatoxin B2 (AFB2) was used as an internal standard (IS). The method was validated in terms of linearity, precision, trueness, limits of detection and quantification and uncertainty. The performance criteria for the method were evaluated based on European Commission Regulation (EC) No. 401/2006 and its most recent amendment, as well as the suggested criteria for revision by the EU Reference Laboratory for Mycotoxins and Plant Toxins. The recovery was in the range of 77.9–81.0% for all fortification levels (0.025–0.050–0.075 μg kg−1), with RSDR values (Relative Standard Deviation of intermediate precision) ranging from 6.1% to 12%. The method’s detection and quantification limits were 0.0027 μg kg−1 and 0.0089 μg kg−1, respectively. The occurrence of AFM1 was investigated in 40 samples of different animal origin (cow, goat and sheep milk) provided by Greek producers.
1. Introduction
Aflatoxins are naturally occurring fungal secondary metabolites that belong to the class of mycotoxins [1]. AFB1 is typically produced by the Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus fungal strains [2], while AFM1 is its hydroxylated metabolite [3]. AFM1 is produced in the liver and is excreted in the milk of humans and other lactating animals fed an AFB1-contaminated diet [4]. The IARC classified this metabolite for its carcinogenicity to humans in IARC Monographs in the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans [5].
AFM1 residues remain stable even when heated to sterilization or pasteurization temperatures, or when stored at low temperatures [6,7]. The presence of AFM1 in milk and dairy products poses a significant risk to humans as these products are primarily consumed by children, including infants, who are thought to be more vulnerable to the adverse effects of AFM1 [8]. Due to its hepatotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity, the European Commission has set a maximum regulation limit of 0.050 and 0.025 μg kg−1 for milk and infant formulas, respectively (2006/1881/EC) [9].
For the determination of aflatoxins, several methods have been developed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) [10,11,12], thin-layer chromatography (TLC) [13,14], gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS) [15,16] and liquid chromatography (LC) coupled to Ultra-Violet (UV), fluorescence (FLD) and mass spectrometer (MS) detectors [17,18,19]. ELISA is preferred as a screening technique for routine analysis because it is a fast, simple and cost-effective method for the simultaneous analysis of numerous samples. However, it lacks reliability when the examined analytes are at trace levels (below 0.050 μg L−1) due to the cross-reaction interferences [16,20,21]. TLC was the first method used for the determination of AFM1, but it is not suitable for quantification purposes. Therefore, during the last decade, it has been replaced by LC techniques [22].
The LC-MS/MS methods have become an important tool, providing advantages in comparison to other techniques due to their good sensitivity and selectivity [16]. Moreover, the MS/MS methods offer complementary information in terms of identifying the analyte of interest and confirming the ambiguous positive results [23]. However, the strong matrix effect observed in the ESI source, which is used as an ionization source for AFM1, has an effect on the method’s accuracy and precision. Thus, more complex sample preparation protocols are required for a more thorough sample purification [22,23].
Several studies have been published on the determination of AFM1 using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in dairy products [24,25,26]. Τhe majority of the sample preparation procedures reported in the literature are complicated, expensive and time-consuming [10,15,16,27]. The extraction of aflatoxins was combined with a clean-up step using SPE cartridges or immunoaffinity columns (IAC) to remove the matrix interferences and preconcentrate the analyte of interest. Milk samples were defatted with chloroform and then purified using silica, IAC columns and C18 cartridges. In cases in which AFM1 was determined through a FLD detector, a derivatization step with trifluoroacetic acid or a post-column derivatization with pyridinium hydrobromide per-bromide was required [18,25,28].
The aim of this study was to develop a sensitive and accurate method for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples to monitor Greek milk samples of various origins. A sample preparation that includes the use of IAC columns for sample purification and analyte preconcentration in conjunction with an optimized UHPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated to meet the strict regulation limitations (0.050 μg kg−1). Performance characteristics were evaluated according to the Commission Regulation (EC) No. 401/2006, as well as the suggested amendments in the performance criteria of the European Union Reference Laboratory (EURL-MP guidance) [29,30]. This study incorporates all the suggestions given in the draft of the EURL-MP that have been revised since the paper’s publication. However, changes that may occur in the finalized official version in the future are not included.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
The purity of standards was greater than 99%. AFM1 and AFB2 were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany). Methanol (MeOH) LC-MS grade, acetonitrile (ACN) LC-MS grade, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) and potassium chloride (KCl) were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). ACN HPLC grade and ammonium formate (LC-MS grade) were provided from Fisher Scientific (Geel, Belgium), while formic acid (99%) and disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4, p.a. 99%) were acquired from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland). Hydrochloric acid (HCl) was obtained from Honeywell (Offenbach, Germany), while sodium chloride (NaCl) was acquired from Penta (Prague, Czech Republic). Furthermore, distilled water was provided by a Milli-Q purification apparatus (Millipore Direct-Q UV, Bedford, MA, USA). Aflaprep M immunoaffinity columns (1 mL) were obtained from R-Biopharm (Rhone Ltd., Glasgow, UK) (product code DP04/P04). Finally, regenerated cellulose syringe filters (RC filters, pore size 0.22 μm, diameter 15 mm) were acquired from Macherey-Nagel (Düren, Germany).
Standard stock solutions of AFM1 (10 mg L−1) and AFB2 (100 mg L−1) were prepared in ACN LC-MS grade and stored at −20 °C in amber glass vials. Intermediate working solutions of 0.05, 0.01 mg L−1 for AFM1 and 2 mg L−1 for AFB2 were prepared by subsequent dilutions of the stock solutions in ACN LC-MS grade. For the preparation of Phosphoric Buffer Solution (PBS), 0.05 g KCl, 2.0 g NaCl, 0.05 g KH2PO4 and 0.29 g Na2HPO4 were weighed and dissolved with ultrapure water in a 250 mL volumetric flask. The pH value was adjusted to 7.4 with the addition of HCl if needed, and the solution was diluted to volume with ultrapure water.
2.2. Instrumentation
The determination of AFM1 was performed through a Thermo TSQ Quantum Access triple quadrupole system, equipped with an ESI source, an UHPLC pump (Thermo Accela) and an Accela autosampler. The triple quadrupole mass spectrometer was operated in positive ionization mode and an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (1.7 μm, 100 × 2.1 mm) from Waters (Milford, MA, USA) equipped with a guard column was used for determination of the analyte. The column temperature was kept constant at 30 °C throughout the analysis, and the injection volume was set at 10 μL. The mobile phase was composed of (A) 5 mM ammonium formate acidified with 0.01% formic acid and (B) methanol. The elution program was gradient, starting with 25% solvent B and remaining constant for 3 min. Then, it increased to 75% in 0.1 min and kept increasing to 100% in the next 7 min. The initial conditions were restored within 0.1 min to reequilibrate the column for 3 min before the next injection. The flow rate was set to 0.1 mL min−1, and the total chromatogram was 13 min. Thermo Fisher Scientific’s Xcalibur software, Version 2.3 (Waltham, MA, USA) was used for instrument control and data acquisition.
Regarding the MS parameters, the precursor ion of the analyte and its corresponding products, the collision energy (CE), and the tube lens (TL) settings were obtained after direct infusion of 1 mg L−1 of individual standard solutions in 5 mM ammonium formate acidified with 0.01% formic acid: MeOH in a proportion of 20:80. Selected reaction monitoring (SRM) was used, and two transitions were selected for the analyte’s identification. Specifically, the most abundant product ion was selected as the quantification ion, while the second most abundant ion was set as the confirmation ion. These parameters are presented in Table 1. Following that, the ESI parameters were optimized using flow injection. The optimum ESI conditions acquired were: spray voltage, 4000 V; sheath gas, 40 a.u.; auxiliary gas, 10 a.u.; capillary temperature, 380 °C; probe position B, 0.5 mm.

Table 1.
Selected reaction monitoring (SRM) transitions of the aflatoxins M1 and B2.
2.3. Sample Preparation
A total of 40 milk samples were collected from Greek farmers from different locations and analyzed. The extraction of AFM1 from milk was carried out in accordance with the instruction sheet enclosed to the immunoaffinity columns, with a few modifications [31].
50 g of each sample were weighted in a 50 mL polypropylene tube, and AFB2, which was used as an internal standard, was added to every sample. Additionally, spike fortification was performed for quantification purposes. The samples (spiked and non-spiked) were left at room temperature for 30 min to allow the analytes to be absorbed onto the matrix. Subsequently, the samples were heated at 37 °C for 15 min before being centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 min. The fat-containing upper layer was then decanted, and the remaining sample was filtered through Whatman paper (No. 4). The filtrates were at least 45 mL in volume and were kept at 37 °C in a thermostated water bath to facilitate the loading to the Aflaprep M immunoaffinity columns. Consequently, the columns were washed by the addition of 20 mL of PBS solution. After that, 5 mL of ACN were added to the columns to elute the analytes. It is worth mentioning that ACN was applied to the columns in fractions (1 × 2 mL, 3 × 1 mL), and the solvent was allowed to contact the columns for three minutes after each application. The eluants were collected in glass tubes and evaporated to dryness at 40 °C under a gentle nitrogen stream. The residues were reconstituted by adding 0.3 mL of a 50:50 mixture of 5 mM ammonium formate acidified with 0.01% formic acid and methanol. The extracts were filtrated through RC syringe filters, transferred to glass vials and injected into the LC-MS/MS system.
2.4. Method Validation
The method was validated according the requirements outlined in Commission Decision 2006/401/EC and its amendments [29]. Performance criteria were also compared to the proposed ones of the draft version of the EURL-MP guidelines [30]. The following analytical parameters were evaluated: linearity, trueness (recovery), precision (repeatability and intermediate precision), specificity, decision limit (CCα), and the method’s limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ). All the validation experiments were conducted using the standard addition technique by spiking milk samples with the proper amounts of AFM1. Due to the lack of an internal standard for AFM1 in the laboratory, AFB2 was chosen as the internal standard [32]. As a result, the ratio of the AFM1 peak area to the AFB2 peak area was used for proper quantification.
Standard calibration and standard addition curves were constructed in six different concentration levels and linearity was evaluated based on the coefficients of determination (R2) and the relative back-calculation error. The maximum level (ML) for the AFM1 in milk corresponds to 0.05 μg kg−1. The concentration of AFM1 in the standard calibration curve ranged from 0.75 to 22.5 μg L−1, while in the standard addition curve, it was in the range of 0.005–0.1 μg kg−1. To investigate the matrix effect, a matrix-matched calibration curve was constructed. Repeatability and intermediate precision experiments were used to evaluate the method’s precision, expressed as the %RSD. Trueness was estimated through recovery studies. Milk samples were spiked in six duplicates at three different fortification levels (0.025, 0.050 and 0.075 μg kg−1) on two different laboratory days under the same conditions. The method’s LOQ was determined by spiking the analyte of interest in five duplicates at the instrument’s lowest detectable concentration level.
2.5. Method Assessment
2.5.1. Measurement of Uncertainty
The estimation of uncertainty was realized according to the Eurachem Guide for Quantifying Analytical Measurement Uncertainty [33] using the validation data. The uncertainty was calculated at three fortification levels. The sources of uncertainty with important contribution were taken into consideration for calculating the combined uncertainty. The expanded combined uncertainty was determined by multiplying with a coverage factor of 2, for a confidence level of 95% [33,34,35]. The estimated uncertainty was assessed with the maximum acceptable uncertainty (Uf), as defined in 2006/401/EC [29].
2.5.2. Application to Real Samples
The methods’ applicability was investigated by analyzing 40 samples of different animal origins provided by Greek producers. More specifically, 2 cow’s milk samples, 18 goat’s milk samples and 20 sheep’s milk samples were collected. All the samples were stored at 2–8 °C and left at room temperature before further analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Optimization
The method was optimized in terms of the MS parameters, as well as the sample preparation. Concerning the optimization of MS parameters, the spray voltage of the ion source (2500 V–4000 V), sheath gas (20–45 a.u.) and auxiliary gas (5–20 a.u.), as well as the capillary temperature (270 °C–400 °C), were investigated. It is noteworthy that the most critical parameter for the ionization efficiency of the analyte was the capillary temperature (380 °C), which attained a 10-fold greater intensity compared to the lowest examined temperature (270 °C). In the optimum MS conditions, the vertical position of the probe (B–D) and the horizontal one (0.5 mm–1.25 mm) were also tested. Therefore, the optimum ESI conditions obtained were: spray voltage, 4000 V; sheath gas, 40 a.u.; auxiliary gas, 10 a.u.; capillary temperature, 380 °C; probe position B, 0.5 mm.
Regarding the optimization of sample preparation, all the modifications to the procedure proposed by the IAC manufacturer were carried out to improve the analyte’s response. In particular, acetonitrile was selected as the eluant instead of the proposed one (MeOH: ACN 60:40): (H2O), 50:50 (v/v). Moreover, an evaporation step of the eluant was added to achieve the analyte’s preconcentration. As a reconstitution solution, the mobile phase (5 mM ammonium formate acidified with 0.01% formic acid: MeOH) was chosen to be compatible with the chromatographic system and its volume was set to 300 μL.
3.2. Method Validation
3.2.1. Matrix Effect
The matrix effect (ME) is a critical parameter that should be evaluated in the LC-MS/MS determination of analytes in food matrices, as it affects their ionization efficiency. Due to the increasing use of LC-MS/MS instrumentation, the calculation of this parameter has been included in the updated validation guidelines, such as SANTE guidelines and 2021/808/EC (replacing 2002/657/EC) [36,37]. Furthermore, the matrix effect is not specified in 2006/401/EC, whereas its evaluation is suggested in the EURL-MP guidelines [30].
The matrix effect was calculated by dividing the slopes of the matrix-matched curve (a) and the standard calibration curve (b) using the following equation.
In the case of positive ME, signal enhancement is observed, whereas in the case of negative ME, signal suppression is recorded. The matrix effect is considered acceptable when the %ME ranges from −20% to +20% [38]. The estimated %ME for AFM1 was −38.8%. This ME value indicates strong signal suppression, despite the contribution of SPE to the sample’s purification. Thus, standard addition calibration curve was used for the accurate quantification of AFM1 in the samples due to the observed matrix effect.
3.2.2. Linearity
To evaluate the linearity of the method, a six-point calibration curve was constructed by preparing working solutions of AFM1 in various concentrations in a mixture of 5 mM ammonium formate with 0.01% formic acid: MeOH (50:50, v/v), while AFB2, selected as an internal standard, was added at the same concentration (7.5 μg L−1) to each solution. The chosen AFB2 concentration was at the centroid of the AFM1 calibration curve. The linear region was ranged from 0.75 μg L−1 to 22.5 μg L−1. The linear regression coefficient of determination in the external calibration with AFB2 as an internal standard (R2 = 0.997) was satisfactory. Furthermore, the linearity of the standard addition calibration curve and the matrix-matched curve was investigated, and satisfactory coefficients of determination were obtained (R2 = 0.998 and 0.993 for the standard addition calibration curve and the matrix-matched curve, respectively).
AFM1 was quantified using a standard addition calibration curve with the internal standard in order to overcome the losses from the analytical procedure and the matrix effect. A sample that was certified to be free of AFM1 was used as the blank sample. AFM1 was added to blank samples at three different concentrations, while AFB2 was added in the same concentration to all the samples. The samples were prepared in accordance with the procedure outlined in Section 2.3.
Following that, the above-mentioned sample preparation was performed on six blank samples, and the extracts were used to construct the matrix-matched calibration curve, taking into account the samples’ preconcentration. Typical chromatograms of a standard solution, a real sample and a spiked sample for AFM1 and AFB2 are illustrated in Figure 1.
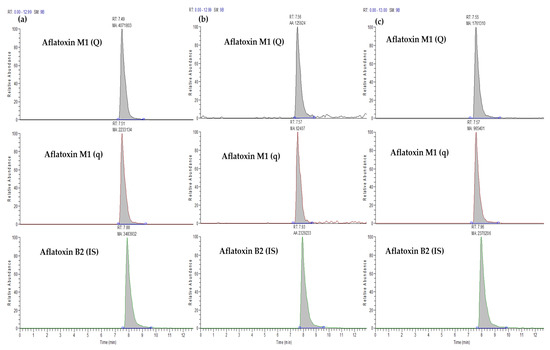
Figure 1.
Typical chromatograms of aflatoxins M1 and B2, where Aflatoxin M1 (Q) is the quantification ion for AFM1, Aflatoxin M1 (q) is the confirmation ion for AFM1 and Aflatoxin B2 (IS) is the most abundant ion for AFB2 used as an internal standard for (a) a standard solution (7.5 μg L−1) corresponding to 1 ML, (b) a real sample and (c) a spiked sample at the fortification level of 0.05 μg kg−1 corresponding to 1 ML.
The evaluation of linearity is more challenging than most validation guidelines describe for two reasons. Firstly, there is much discussion over the suitability of the coefficient of determination (R2) and the correlation coefficient (R) for evaluating linearity [39]. Furthermore, a weighting factor should be applied in many cases, especially in mass spectrometry techniques, even if the coefficients are within the acceptable limits. Hence, both SANTE pesticide guideline [36] and FDA bioanalytical technique guideline [40] utilize the back-calculation error as a criterion for evaluating linearity with a back-calculated concentration at a range of 20%. This calculation is also recommended in the draft guideline of EURL-MP [30]. The linearity results, the concentration range, the correlation coefficient and the relative back calculation range for each curve are demonstrated in Table 2. A 1/x2 weighting factor was utilized at each curve since it demonstrated the least relative back calculation error at every concentration level within the range of ±20%.

Table 2.
External standard calibration curve, matrix-matched curve and standard addition calibration curve, coefficient of determination and relative back-calculation error for AFM1.
3.2.3. Precision-Trueness
The method’s precision was estimated by calculating the intra-day precision (repeatability) and intermediate precision at three different fortification levels. The repeatability of the method was investigated by spiking 18 blank milk samples with AFM1 at concentrations of 0.025, 0.05 and 0.075 μg kg−1 (0.5–1–1.5 × ML) and AFB2 at a concentration of 0.05 μg kg−1 on the same working day. The method’s intermediate precision was evaluated by spiking 18 blank milk samples at the above-mentioned concentration levels on two different laboratory days, while keeping the laboratory, instrument and method constant. Precision experiments were conducted, and the %RSD values of three different concentration levels (0.5–1–1.5 × ML) were calculated. The method’s trueness was assessed by investigating the analytes’ recovery at three fortification levels (0.5–1–1.5 × ML), in six replicates at each level.
Based on the concentration of the examined analyte, 2006/401/EC set a range of acceptable recovery and precision values. For concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 0.05 μg kg−1, % recoveries should be in the range of 60–120%, and 70–110% for concentrations greater than 0.05 μg kg−1. The maximum acceptable relative standard deviation for intermediate precision (%RSDR) was calculated using the modified Horwitz equation, and the %RSDR value was multiplied by 0.66 to calculate the repeatability (%RSDr). More general limits are proposed in the draft EURL-MP guideline [30], with 70–120% recovery limits for AFM1 and a %RSD value of less than 20% for intermediate precision and repeatability. The results for each fortification level, as well as their acceptance limits, are presented in Table 3 and Table 4. According to the above-mentioned documentation, all concentration levels investigated are within the precision and trueness limits.

Table 3.
Precision (repeatability and intermediate precision) at every fortification level.

Table 4.
Trueness (recovery) results at every fortification level.
3.2.4. Selectivity
The method’s selectivity was tested by analyzing six blank milk samples to check for false-positive outcomes resulting from matrix interferences. The identification and the confirmation of AFM1 was conducted through the retention time and the ion ratio of SRM transitions. The ion ratios for AFM1 and AFB2, defined as the ratio of the peak area of the confirmatory ion to the quantification ion, were approximately 50% and 77%, respectively. As for the retention time, AFM1 was eluted at 7.49 min, whereas AFB2 was eluted at 7.88 min. No peaks were observed in blank samples for the SRM transitions at the same retention time as the analytes of interest. As a result, the method was found to be selective for the aflatoxins M1 and B2.
3.2.5. LODs and LOQs
LOD and LOQ are important parameters to consider, especially when determining contaminants with ML. The statistical approach for calculating LOD and LOQ is based either on the SD of blank samples, the SD of the regression line or the SD of the y-intercept. However, these approaches are not comparable, according to the literature [41]. A reliable estimation of LOQ is critical, especially for contaminants with ML, since many guidelines specify that LOQ should be consistently lower than ML. As a result, the “experimentally” determined LOQ can be defined as the lowest concentration at which the identification, trueness and precision criteria are fulfilled.
In this study, the instrumental LOD was calculated statistically using the SD of the y-intercept of the external calibration curve and was determined by multiplying, by 3.3 times, the SD of the ratio of the peak area of AFM1 to the peak area of AFB2 divided by the slope of its standard calibration curve. The instrumental LOQ was calculated by multiplying the LOD value three times. The method’s LOQ was first estimated statistically from the y-intercept SD of the standard addition curve and later confirmed by analyzing five blank samples spiked at 0.0089 μg kg−1. The instrumental and method LOD and LOQ are demonstrated in Table 5.

Table 5.
Instrumental and method limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantitation (LOQ).
In regulation 2006/401/EC, there are no criteria for the LOQ. However, a draft of the EURL-MP guideline was proposed in which it is stated that the LOQ should be lower than 0.5 × ML and, preferably, should be 0.2 × ML. The method’s LOD and LOQ were satisfactory, since the % recovery at the LOQ level was 71.1 ± 5.0% and the %RSD was 7.1% for five spiked samples. As a result, the criteria of trueness and precision were fulfilled according to the above-mentioned section.
3.2.6. CCα
According to 2006/401/EC, the calculation of method’s decision limit (CCα) is not required. However, following Commission Decision (EC) No. 2002/657, CCα can be employed as an alternative decision rule in the case of animal-derived foods. The CCα was calculated based on the following equation:
where the SDR corresponds to the standard deviation of the intermediate precision experiments at the ML level (fortification level B). The method’s CCα was 0.054 μg kg−1.
3.3. Method Assessment
3.3.1. Measurement of Uncertainty
The uncertainty of the measurement was estimated according to the Eurachem Guide for the comparison of the validation results and the evaluation of the method [33]. Τhe uncertainties, with their contributions to the measurement of the combined uncertainty of each concentration level, as well as the expanded combined uncertainty (U) are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Estimation of the uncertainty of aflatoxin M1 at three concentration levels.
The “fitness-for-purpose” approach was also followed to assess the suitability of the method in accordance with 2006/401/EC [29]. In this approach, the maximum standard measurement uncertainty (Uf) was calculated using the following equation and compared to the standard uncertainty of the method.
where:
- Uf: maximum standard measurement uncertainty (μg kg−1);
- LOD: method’s limit of detection (μg kg−1);
- α: a constant, numeric factor depending on the concentration C (in this case, α = 0.2 for all concentration levels);
- C: the concentration of interest (μg kg−1).
The parameters with significant impact on uncertainty were the uncertainty of random error, as the RSD of the intermediate precision (urandom) and the uncertainty of bias error, and as the relative standard error of recovery (ubias). Other parameters, such as the weighting uncertainty and the uncertainty of volumetric equipment, were excluded due to their minimum contributions. The uncertainty of the calibration curve was also not included because the standard addition curve is constructed on a daily basis, so its contribution had already been incorporated into the urandom. Taking into consideration the results demonstrated in Table 6, the method’s expanded combined uncertainty (U) was considerably lower than the Uf.
3.3.2. Application to Real Samples
A total of 40 milk samples of various animal origin (2 cow milk, 18 goat milk and 20 sheep milk samples) were provided by producers in Greece. All samples were subjected to the preparation procedure described in Section 2.3. AFM1 was found to be below the method’s LOD in 36 samples. Moreover, the AFM1 concentration in one sheep-origin sample was greater than the LOD but below the LOQ. Additionally, the determined concentrations, including their expanded uncertainty, in two cow-originated samples (0.0126 ± 0.0031 and 0.0258 ± 0.0063 μg kg−1) and one sheep-originated sample (0.0370 ± 0.0090 μg kg−1) were higher than the LOQ but lower than the regulatory limits (0.05 μg kg−1). In conclusion, all the investigated samples complied with the regulatory limits.
4. Conclusions
A sensitive and accurate LC-MS/MS method for determining AFM1 in milk samples was developed and fully validated. The method’s performance criteria were evaluated using 2006/401/EC and its most recent amendments, as well as the suggested criteria from EURL-MP. The analyte’s concentration was determined using the standard addition technique. A significant low LOD (0.0027 μg kg−1) was achieved, resulting in a reliable method for the monitoring of aflatoxin. Additionally, reproducible and accurate results were obtained with satisfactory %RSDR (2.9–12%) and % recovery values (77.4–81.0%) for all the fortification levels. Moreover, the method was assessed through the estimation of uncertainty and its comparison with the maximum standard measurement uncertainty (Uf). According to the obtained results, the method’s uncertainty was significantly lower than the Uf.
In comparison to other methods reported in the literature [2], it is a time-consuming method. However, a derivation step (as needed in HPLC-FLD methods) is not required with LC-MS instrumentation, balancing the time spent on sample pretreatment. The cost of analysis is high due to the IAC columns, as well as the instrumentation. The main advantage of these IAC columns is their specificity for aflatoxins attaining low LODs, while they are not suitable for the control of other contaminants. Thus, the developed methodology, which was used to analyze samples from Greek farmers, proved to be a valuable tool for the quality control of milk samples and can be utilized for the determination of AFM1 in routine analysis. As for the investigated samples, 36 samples were below the method’s LOD, one milk sample was above the LOD but below the LOQ of the method, whereas only three samples (two cow-origin milks and one sheep-origin milk) were determined in values above the method LOQ.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.T.; methodology, A.P.; validation, A.P., M.K. (Maria Katsa) and M.K. (Marios Kostakis); data curation, A.P., M.K. (Maria Katsa) and M.K. (Marios Kostakis); writing—original draft preparation, A.P., M.K. (Maria Katsa) and M.K. (Marios Kostakis); writing—review and editing, N.S.T. and E.B.; supervision, N.S.T.; project administration, N.S.T. and E.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund of the European Union and Greek national funds through the Operational Program Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation, under the call RESEARCH—CREATE—INNOVATE (project code: T2EDK-01934).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Asi, M.; Ariño, A. Aflatoxins. In Reference Module in Life Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z. Mycotoxins in food, recent development in food analysis and future challenges: A review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, A.A.; Jafari, T.; Fallah, A.; Rahnama, M. Determination of aflatoxin M1 levels in Iranian white and cream cheese. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1872–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbay, A.; Sabuncuoǧlu, S.A.; Girgin, G.; Şahin, G.; Yiǧit, Ş.; Yurdakök, M.; Tekinalp, G. Exposure of newborns to aflatoxin M1 and B1 from mothers’ breast milk in Ankara, Turkey. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Lyon Int. Agency Res. Cancer 2002, 82, 171–300. [Google Scholar]
- Prandini, A.; Tansini, G.; Sigolo, S.; Filippi, L.; Laporta, M.; Piva, G. On the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggira, M.; Ioannidou, M.; Sakaridis, I.; Samouris, G. Determination of aflatoxin m1 in raw milk using an hplc-fl method in comparison with commercial elisa kits—Application in raw milk samples from various regions of greece. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, A.; Jabbar, M.A.; Deng, Y.; Hussain, E.A.; Riffat, S.; Naveed, S.; Arif, M. A survey of aflatoxin M1 in milk and sweets of Punjab, Pakistan. Food Control. 2012, 26, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qiu, F.; Kong, W.; Wei, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, M. Development and validation of an accurate and rapid LC-ESI-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of aflatoxin B1, B2, G1 and G2 in lotus seeds. Food Control. 2013, 1, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, L.; Calderara, M.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Arletti, E.; Giraudi, G. Development and Application of Solvent-free Extraction for the Detection of Aflatoxin M 1 in Dairy Products by Enzyme Immunoassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumala-Devi, K.; Mayo, M.A.; Hall, A.J.; Craufurd, P.Q.; Wheeler, T.R.; Waliyar, F.; Subrahmanyam, A.; Reddy, D.V.R. Development and application of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunoassay for aflatoxin m(1) in milk and milk-based confectionery. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, F.; Fremy, J.M.; Bevis, S.; Dragacci, S. Joint IDF-IUPAC-IAEA(FAO) interlaboratory validation for determining aflatoxin M1 in milk by using immunoaffinity clean-up before thin-layer chromatography. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 21, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shundo, L.; Sabino, M. Aflatoxin M1 in milk by immunoaffinity column cleanup with TLC/HPLC determination. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, L.; Du, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin B1 and M1 in milk, fresh milk and milk powder by LC-MS/MS utilising online turbulent flow chromatography. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Yang, H.-M.; Guo, Q.-L. Simultaneous Determination of Chloramphenicol and Aflatoxin M 1 Residues in Milk by Triple Quadrupole Liquid ChromatographyÀTandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3532–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinto, M.; Spadaccino, G.; Palermo, C.; Centonze, D. Determination of aflatoxins in cereal flours by solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography and post-column photochemical derivatization-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8636–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetta, A.C.; Di Giuseppe, L.; Giammarco, M.; Fusaro, I.; Simonella, A.; Gramenzi, A.; Formigoni, A. High-performance liquid chromatography with post-column derivatisation and fluorescence detection for sensitive determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk and cheese. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1083, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirhan, A.Y.; Tan, G.H.; Wong, R.C.S. Determination of aflatoxins in food using liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS). Food Control. 2013, 31, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigić, I.K.; Prosen, H. An Overview of Conventional and Emerging Analytical Methods for the Determination of Mycotoxins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovic, S.; Spiric, D.; Petronijevic, R.; Trailovic, J.N.; Milicevic, D.; Nikolic, D.; Jankovic, S. Comparison of two Analytical Methods (ELISA and LC-MS/MS) for Determination of Aflatoxin B1 in Corn and Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Procedia Food Sci. 2015, 5, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yang, H.M.; Guo, Q.L. Food Additives and Contaminants Determination of aflatoxin M 1 in milk by triple quadrupole liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry Determination of aflatoxin M 1 in milk by triple quadrupole liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campone, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Celano, R.; Pagano, I.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Rapid and automated analysis of aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products by online solid phase extraction coupled to ultra-high-pressure-liquid-chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1428, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.K.; Elbæk, T.H. Determination of mycotoxins in bovine milk by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 820, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Li, W.J.; Peng, K.Y. Determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk powder using high-flow solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8474–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, J.; Hajnal, E.J.; Jajić, I.; Krstović, S.; Mastilović, J.; Šarić, B.; Jovanov, P. Comparison of ELISA, HPLC-FLD and HPLC-MS/MS methods for determination of aflatoxin M1 in natural contaminated milk samples. Acta Chim. Slov. 2016, 63, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, R.; Qiu, F.; Kong, W.; Wei, J.; Yang, M.; Luo, Z.; Qin, J.; Ma, X. Co-occurrence of aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, G2 and ochrotoxin A in Glycyrrhiza uralensis analyzed by HPLC-MS/MS. Food Control. 2013, 1, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Zheng, N.; Zheng, B.Q.; Wen, F.; Cheng, J.B.; Han, R.W.; Xu, X.M.; Li, S.L.; Wang, J.Q. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin M 1, ochratoxin A, zearalenone and a-zearalenol in milk by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Regulation (EC) No 401/2006 of 23 February 2006 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 70, 12–34.
- EURL-MP-Background doc_003 Guidance Document Performance Criteria v1.1 Draft 17.09.2021-WUR. Available online: https://www.wur.nl/en/show/EURL-MP-background-doc_003-Guidance-document-performance-criteria-v1.1-draft-17.09.2021.htm (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- R-Biopharm AG. AFLAPREP® M, Immunoaffinity Columns for Use in Conjunction with HPLC or LC-MS/MS. 2021. Available online: https://www.azmax.co.jp/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/AFLAPREP-M-IFU-P04V18.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Rosi, P.; Borsari, A.; Lasi, G.; Lodi, S.; Galanti, A.; Fava, A.; Girotti, S.; Ferri, E. Aflatoxin M1 in milk: Reliability of the immunoenzymatic assay. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, S.L.R.; Williams, A. (Eds.) Eurachem/CITAC Guide: Quantifying Uncertainty in Analytical Measurement, 3rd ed.; EURACHEM: Teddington, UK, 2012; Available online: https://www.eurachem.org (accessed on 25 January 2022)ISBN 978-0-948926-30-3.
- Taverniers, I.; De Loose, M.; Van Bockstaele, E. Trends in quality in the analytical laboratory. I. Traceability and measurement uncertainty of analytical results. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Estimating uncertainty in analytical procedures based on chromatographic techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SANTE/12682/2019 Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed; Accredia: Rome, Italy, 2019; pp. 1–48.
- 2021/808/EC Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/808 of 22 March 2021 on the performance of analytical methods for residues of pharmacologically active substances used in food-producing animals and on the interpretation of results as well as on the methods to. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, 180, 84–109.
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Bletsou, A.A.; Hanafi, A.H.; Thomaidis, N.S. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric methods for the determination of spinosad, thiacloprid and pyridalyl in spring onions and estimation of their pre-harvest interval values. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; Barceló, D. Assessment of goodness-of-fit for the main analytical calibration models: Guidelines and case studies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER); Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2018.
- Evard, H.; Kruve, A.; Leito, I. Tutorial on estimating the limit of detection using LC-MS analysis, part I: Theoretical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 942, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).