Mean Centered Kinetic—Spectrophotometric Data—Continuous Wavelet Transform for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid in Presence of Ascorbic Acid at Biological Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Apparatus and Reagents
2.2. Computational Software
2.3. General Procedure
2.4. Preparation of Real Samples
3. Result and Discussion
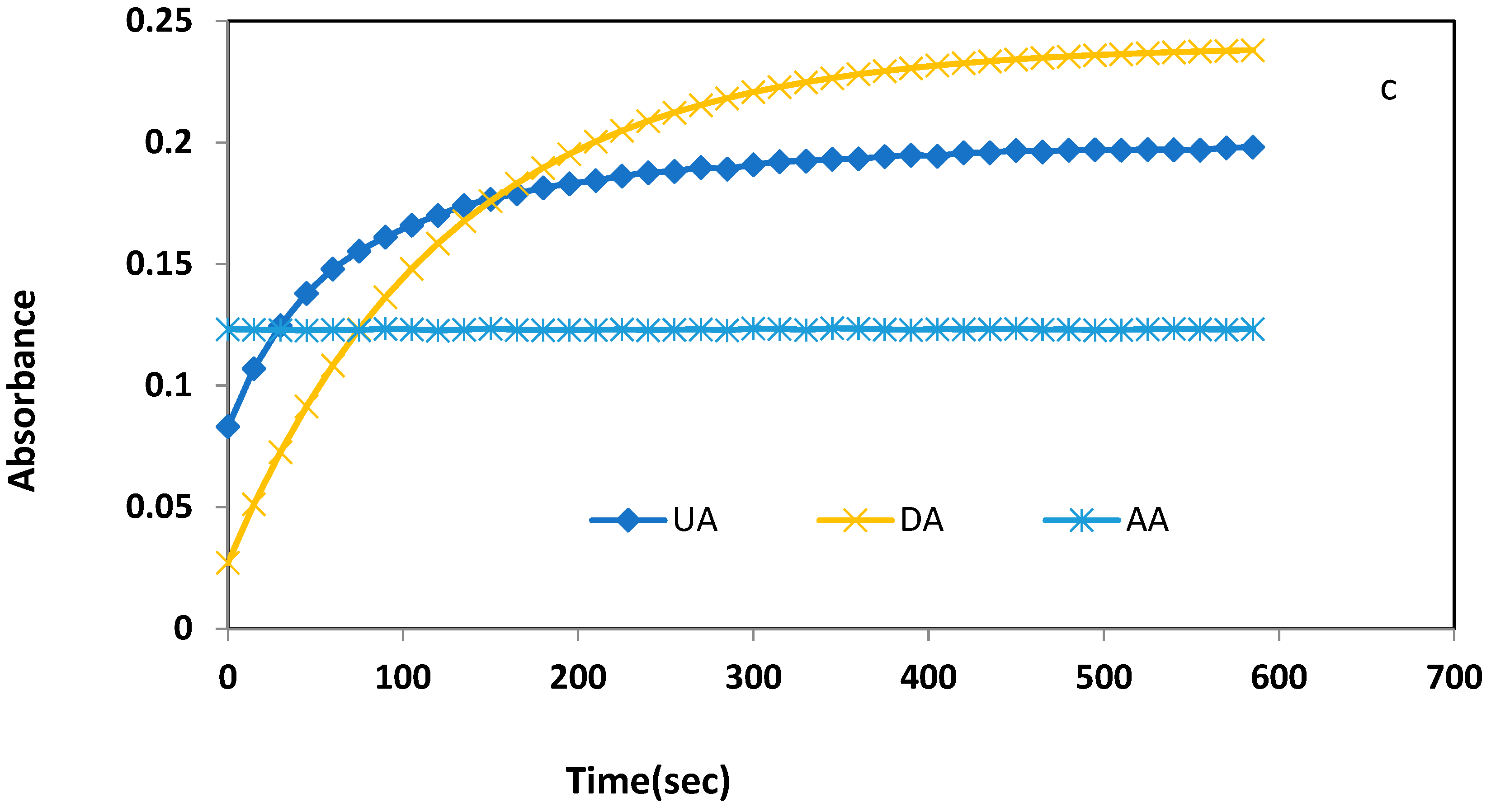
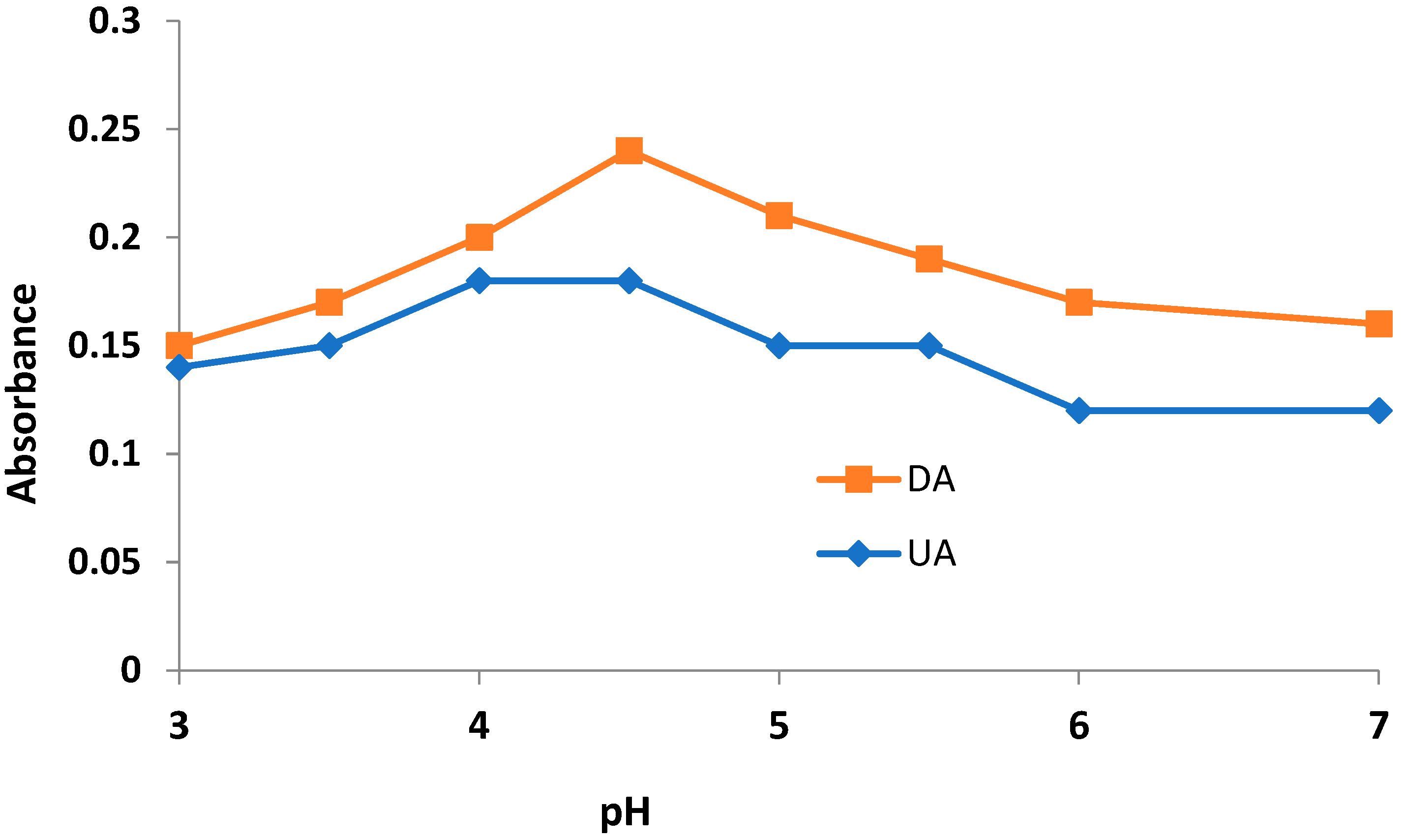
3.1. Preliminary Investigation
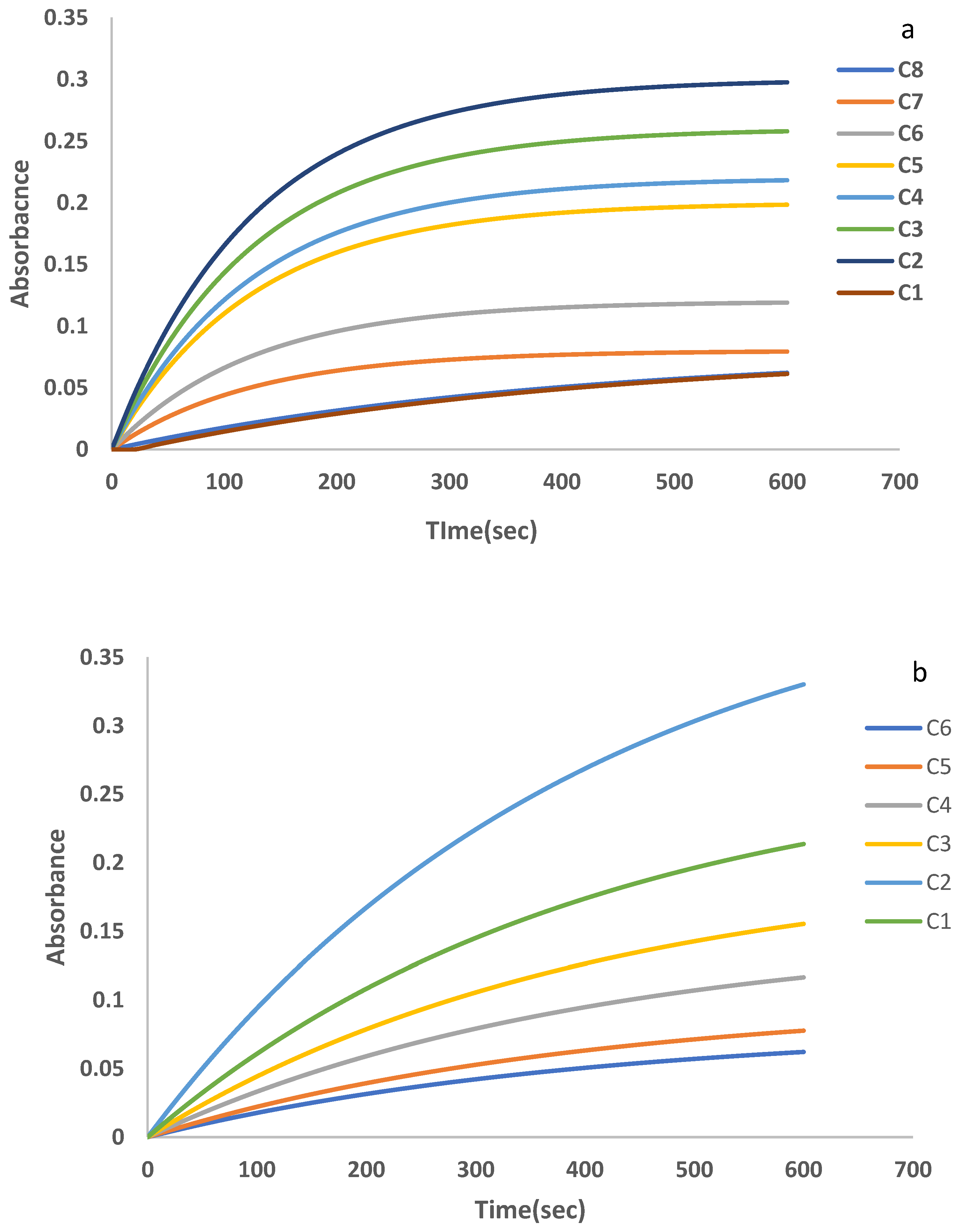
3.2. Individual Calibration Graphs of UA and DA
3.3. Chemometrics Analysis
Mean Centering of Data
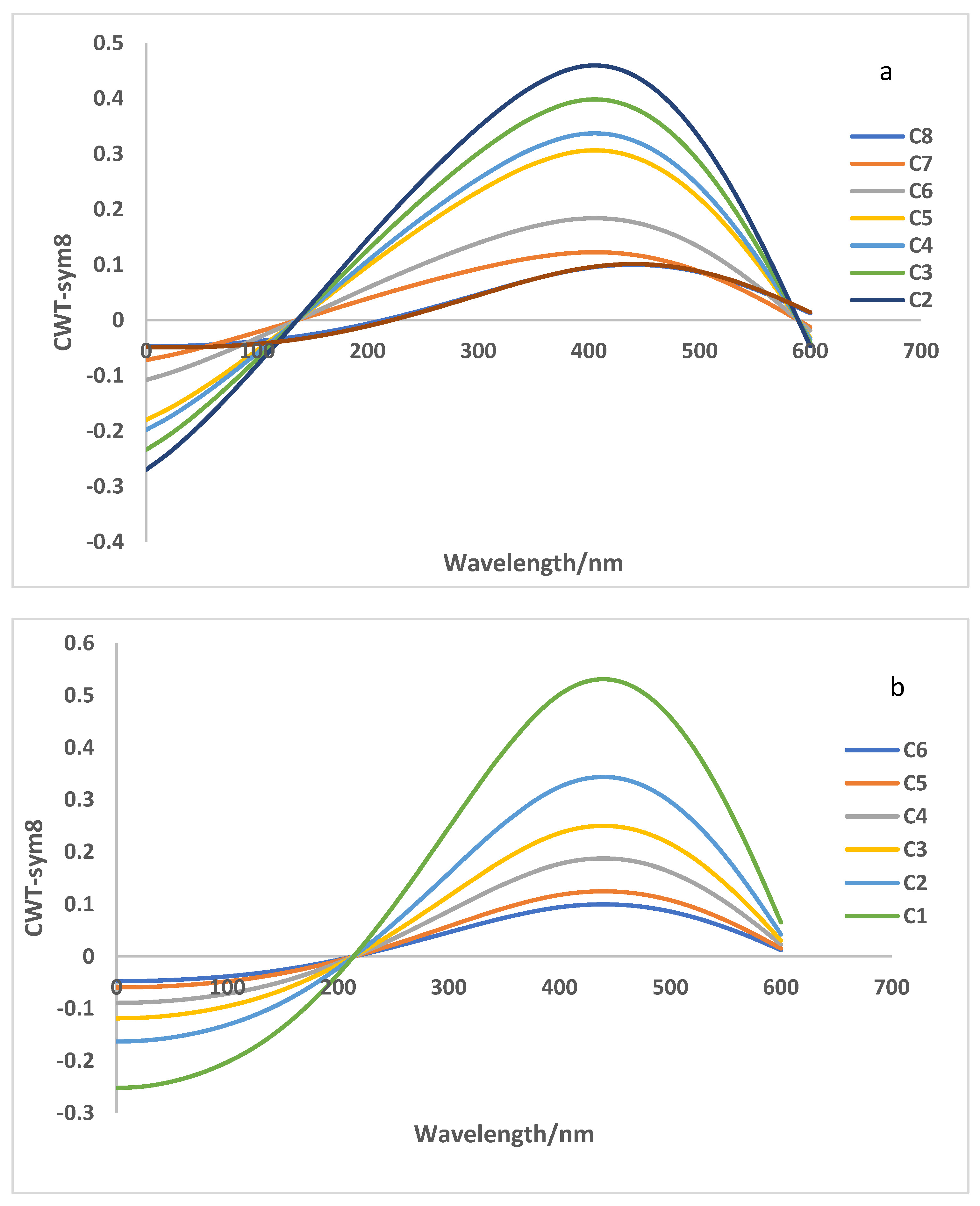
3.4. CWT Analysis
3.5. Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, T.E. Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations; Devlin, T.M., Ed.; Wiley/Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 929. [Google Scholar]
- Ulubay, S.; Dursun, Z. Cu nanoparticles incorporated polypyrrole modified GCE for sensitive simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Talanta 2010, 80, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiagarajan, S.; Chen, S.M. Preparation and characterization of PtAu hybrid film modified electrodes and their use in simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid. Talanta 2007, 74, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.H.; Moloudi, M. Flower-like ZnO decorated polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 512, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, H.; You, T. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid using palladium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, H.R.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Mazloum Ardakani, M. Electrochemical properties of a tetrabromo-p-benzoquinone modified carbon paste electrode Application to the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 577, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, C.; Yuan, H.; Du, J.; Xiao, D.; Xie, S.; Choi, M.M. Simultaneous determination of l-ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid with gold nanoparticles–β-cyclodextrin–graphene-modified electrode by square wave voltammetry. Talanta 2012, 93, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamford, J.A.; Justice, J.B. Probing brain chemistry: Voltammetry comes of age. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 359A–363A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani Moghadam, M.; Haji Shabani, A.M.; Shahbazikhah, P. Chemometric-assisted kinetic–spectrophotometric method for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, uric acid, and dopamine. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 410, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, N.F.; El-Kady, M.F.; Galal, A. Simultaneous determination of catecholamines, uric acid, and ascorbic acid at physiological levels using poly(N-methylpyrrole)/Pd–nanoclusterssensor. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 400, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakkthivel, P.; Chen, S.M. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid and dopamine in the presence of uric acid on ruthenium oxide modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.L.; Lee, H.H.; Yang, J.M.; Wu, C.C. The simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using graphene/size-selected Ptnanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3450–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.S.; Hou, H.Q.; You, T.Y. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid with electrospun carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1431–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, Z.; Gelmez, B. Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine and Uric Acid at Pt Nanoparticles Decorated Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Modified GCE. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Feng, Y.; Guo, H.; Hu, C.; Idris Mohmed, A.M.; Li, J.; Lu, X. A novel electrocatalytic platform for separation of the overlapping voltammetric responses of AA, DA and UA. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5849–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferin, R.; Pavão, M.L.; Baptista, J. Rapid, sensitive and simultaneous determination of ascorbic and uric acids in human plasma by ion-exclusion HPLC-UV. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martinoz-Perez, D.; Ferrer, M.L.; Mateo, C.R. A reagent less fluorescent sol–gel biosensor for uric acid detection in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 322, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooshki, M.; Shams, E. Selective response of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid on carbon paste electrode modified with titanium phosphated silica gel. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 587, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haloi, S.; Goswami, P.; Das, D.K. Differentiating response of 2,7-dichlorofluorescein intercalated CTAB modified Na-MMT clay matrix towards dopamine and ascorbic acid investigated by electronic, fluorescence spectroscopy and electrochemistry. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 77, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldawy, M.A.; Tawfik, A.S.; Elshiabouri, S.R. Rapid, sensitive spectrophotometric method for the determination of ascorbic acid. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, K.; Sozgen, K.; Tutem, E.; Ozyurek, M.; Apak, R. Spectrophotometric determination of ascorbic acid using copper(II)–neocuproine reagent in beverages and pharmaceuticals. Talanta 2005, 65, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Kamino, S.; Miyachi, K.; Tominaga, H.; Fujita, Y. Spectrophotometric determination of uric acid based on fading of ohydroxyhydroquinonephthalein–palladium(II)–hexadecyltrimethyl–ammonium complex. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Spectrophotometric determination of dopaminehydrochloride in pharmaceutical, banana, urine, and serum samples by potassium ferricyanide–Fe(III). Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afkhami, A.; Abbasi-Tarighat, M. Application of continuous wavelet transformation to the simultaneous kinetic determination of binary mixtures. Talanta 2009, 78, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, J.; Amini, R.; Niazi, A. Kinetic simultaneous determination of Fe (II) and Fe(III)using partial least squares (PLS) and principal component regression (PCR) calibration methods. Anal. Let. 2002, 35, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Sarlak, N.; Zarei, A.R. Simultaneous kinetic spectrophotometric determination of cyanide and thiocyanate using the partial least squares (PLS) regression. Talanta 2007, 71, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, A.; Abdollahi, H.; Nezhad, M.H. Artificial neural networks for simultaneous spectrophotometric differential kinetic determination of Co (II) and V (IV). Talanta 2003, 59, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Tarighat, M.; Afkhami, A. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of Cu(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) using ratio spectra-continuous wavelet transformation in some food and environmental samples. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Afkhami, A.; Abbasi-Tarighat, M.; Bahram, M. Artificial neural networks for determination of enantiomeric composition of α-phenylglycine using UV spectra of cyclodextrin host–guest complexes: Comparison of feed-forward and radial basis function networks. Talanta 2008, 75, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Madrakian, T.; Abbasi-Tarighat, M. Simultaneous determination of calcium, magnesium and zinc in different foodstuffs and pharmaceutical samples with continuous wavelet transforms. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Tarighat, M.; Nabavi, M.; Mohammdizadeh, M.R. Chemometrics-assisted spectrophotometric method for simultaneous determination of Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions in different foodstuffs, soil and water samples using 2-benzylspiro [isoindoline-1,5′-oxazolidine]-2′,3,4′-trione using continuous wavelet transformation and partial least squares–Calculation of pKf of complexes with rank annihilation factor analysis. Spectrochim. Acta 2015, 145, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Dinc, E.; Baleanu, D. Multidetermination of thiamine HCl and pyridoxine HCl in their mixture using continuous daubechies and biorthogonal wavelet analysis. Talanta 2003, 59, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, E.; Baleanu, D. A zero-crossing technique for the multidetermination of thiamine HCl and pyridoxine HCl in their mixture by using one-dimensional wavelet transform. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 31, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, E.; Baleanu, D. Application of the Wavelet Method for the Simultaneous Quantitative Determination of Benazepril and Hydrochlorothiazide in Their Mixtures. J. AOAC Int. 2004, 87, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi Tarighat, M. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of phosphate and silicate in different water and soil samples using chemometrics approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Tarighat, M.; Hasaninejad, A.; Abdi, G. Chemometrics-Enhanced Micelle-Mediated Extraction Spectrophotometric Method for Simultaneous Determination of Cu2+ and Zn2+ in Medicinal Plant, Rice and Water Samples Using Continuous Wavelet Transform. Food Anal. Met. 2016, 9, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Tarighat, M. Orthogonal projection approach and continuous wavelet transform-feed forward neural networks for simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of some heavy metals in diet samples. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Troutman, J.R.; Schmitz, T.L.; Ellis, J.D.; Tarbutton, J.A. Application of the continuous wavelet transform in periodic error compensation. Precis. Eng. 2016, 44, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslu, I.; Dinc, E.; Altinoz, S. An application of continuous wavelet transforms to electrochemical signals for the quantitative analysis. In Mathematical Methods in Engineering; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 303–313. [Google Scholar]
- Valizadeh, M.; Sohrabi, M.R.; Motiee, F. The application of continuous wavelet transform based on spectrophotometric method and high-performance liquid chromatography for simultaneous determination of anti-glaucoma drugs in eye drop, Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 242, 118777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.A.; Santos, L.S.; Prata, D.M. Optimal wavelet signal compression as an efficient alternative to investigate molecular dynamics simulations: Application to thermal and solvent effects of MRI probes. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2017, 136, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.A.; Júnior, A.M.; da Cunha, E.F.; Ramalho, T.C. Investigating an efficient and accurate protocol for sampling structures from molecular dynamics simulations: A close look by different wavelet families. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2021, 140, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Abbasi-Tarighat, M.; Bahram, M.; Abdollahi, H. A new strategy for solving matrix effect in multivariate calibration standard addition data using combination of H-point curve isolation and H-point standard addition methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 21, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seasholtz, M.B.; Kowalski, B.R. The effect of mean centering on prediction in multivariate calibration. J. Chemom. 1992, 6, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehsharifi, H.; Pourbasheer, E.; Tavallali, H.; Sarvi, S.; Sadeghi, M. The comparison of partial least squares and principal component regression in simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid in real samples. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3451–S3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, A.; Maleki, N.; Moradlou, O.; Tajabadi, F. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid using carbon ionic liquid electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 359, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Yo, T. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Zhang, D.; Fang, Y. Simultaneous Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid Using a Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Palladium Nanoparticles/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8812443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, P.; Tian, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; He, Q. Simultaneous and sensitive determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid via an electrochemical sensor based on PVP-graphene composite. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Deng, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; He, Q. MnO2 nanowires-decorated reduced graphene oxide modified glassy carbon electrode for sensitive determination of bisphenol A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 046514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | Time (s) | Dynamic Range | Regression Equation | R2 | LOD/μM | LOQ/μM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA | 220 | 2.0–50.0 | CWT = 0.0051CUA + 0.002 | 0.984 | 0.06 | 0.19 |
| DA | 140 | 2.0–40.0 | CWT = −0.002CDA − 0.028 | 0.998 | 0.3 | 0.96 |
| Analyte | Time (s) | Dynamic Range | Regression Equation | R2 | LOD | LOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA | 100 | 1.0–60.0 | CWT = 0.002CUA − 0.043 | 0.993 | 0.06 | 0.3 |
| DA | 500 | 7.0–40.0 | CWT = 0.004CDA − 0.001 | 0.995 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Concentration (μM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Value | Predicted Value | ||||
| Sym8 | Db4 | ||||
| UA | DA | UA | DA | UA | DA |
| 50 | 10 | 50.5 | 10.1 | 51 | 10.2 |
| 50 | 5 | 51.1 | 5.3 | 51 | 5.1 |
| 50 | 15 | 51.2 | 15.3 | 50.8 | 15.2 |
| 20 | 10 | 21.1 | 10.1 | 20.3 | 10.5 |
| 20 | 5 | 21 | 5.2 | 20.8 | 5.2 |
| 20 | 15 | 21.4 | 15.5 | 20.5 | 15.1 |
| R.S.E.% | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2 | 2.4 | |
| Sample | Analyte (μM) | Recovery% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Found | |||||
| DA | UA | DA | UA | DA | UA | |
| Urine | 0 | 0 | ND a | 8 | - | - |
| 10 | 10 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 18.2 ± 0.7 | 95 | 102 | |
| Urine | 0 | 0 | ND | 9.2 ± 0.8 | - | - |
| 10 | 10 | 9.8 ± 1.1 | 19.5 ± 1.1 | 98 | 103 | |
| Serum | 0 | 0 | ND | ND | - | - |
| 30 | 30 | 29.4 ± 0.8 | 31 ± 1.2 | 98 | 103.3 | |
| Modifier | Technique | Dynamic Range (μM) | R2 | LOD (μM) | LOQ (μM) | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA | UA | DA | UA | DA | UA | DA | UA | |||
| Kinetic-spectrophotometry | ANN a | 2–33 | 4.3–78.3 | - | - | 0.8 | 0.5 | - | - | [9] |
| Spectrophoometry | PLS b/PCR c | 0.57–22.76 | 1.68–28.58 | - | - | - | - | - | - | [45] |
| CILE d | DPV | 2–1500 | 2–220 | - | - | 0.1 | 0.1 | - | - | [46] |
| ERGO e | DPV | 0.5–60 | 0.5–60 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - | [47] |
| PdNPs/rGO/GC f | DVP | 15–42 | 0.3–1.4 | - | - | 1.0 | 16.67 | - | - | [48] |
| PVP-GR/GCE g | DPV | 0.02–0.2; 0.2–100 | 0.04–1.0; 1.0–100 | - | - | 0.002 | 0.02 | - | - | [49] |
| GR-Pt/GCE h | DPV | 0.03–8.13 | 0.05–11.85 | - | - | 0.03 | 0.05 | - | - | [50] |
| Kinetic-spectrophotometry | 10-phen i/Cu2+ | 1–60 | 7–40 | 0.995 | 0.998 | 0.06 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.75 | Current work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarighat, M.A.; Keshavarz, Z.; Abdi, G.; Proestos, C. Mean Centered Kinetic—Spectrophotometric Data—Continuous Wavelet Transform for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid in Presence of Ascorbic Acid at Biological Samples. Separations 2022, 9, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100282
Tarighat MA, Keshavarz Z, Abdi G, Proestos C. Mean Centered Kinetic—Spectrophotometric Data—Continuous Wavelet Transform for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid in Presence of Ascorbic Acid at Biological Samples. Separations. 2022; 9(10):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100282
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarighat, Maryam Abbasi, Zahara Keshavarz, Gholamreza Abdi, and Charalampos Proestos. 2022. "Mean Centered Kinetic—Spectrophotometric Data—Continuous Wavelet Transform for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid in Presence of Ascorbic Acid at Biological Samples" Separations 9, no. 10: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100282
APA StyleTarighat, M. A., Keshavarz, Z., Abdi, G., & Proestos, C. (2022). Mean Centered Kinetic—Spectrophotometric Data—Continuous Wavelet Transform for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid in Presence of Ascorbic Acid at Biological Samples. Separations, 9(10), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100282







