Abstract
The purpose of this study was to simultaneously develop anti-hyperuricemic and anti-wrinkle source using Camellia japonica leaf (CJ). CJ extract was prepared. Its contents of biomarkers and biological activities were then analyzed. First, we investigated the extraction efficiency. The extraction rate was 10% or less with hot water or 80% ethanol. HPLC analysis revealed that CJ extract contained rutin, hyperoside, isoquercitrin, chlorogenic acid (CGA), gallocatechin gallate (GCG), and phillygenin. As a result of measuring contents of biomarkers in the extract, CGA was detected in 20, 40, and 60% ethanol extracts. GCG showed the highest content in the hot water extract. Hyperoside and isoquercitrin showed the highest contents in the 80% ethanol extract. Philligenin showed an even content of 0.1% or more in all samples except for 40% ethanol extract. Rutin showed the highest content in 80% ethanol extract. Elastase inhibitory abilities of six extracts and PPRM were investigated at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. Results revealed that PPRM and 80% ethanol extract showed about 80% and 62% inhibition, respectively. As a result of comparing elastase inhibitory activities of biomarkers, hyperoside, isoquercitrin, and philligenin showed higher activities. Among six extracts, the extract that could be used as an anti-hyperuricemic source was 80% ethanol extract. When xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory activities of biomarkers were evaluated, rutin and hyperoside showed excellent activities. In particular, when XO activity was measured by mixing rutin and hyperoside with 80% ethanol extract, the same efficacy as 80% ethanol extract was obtained. It was predicted that 80% ethanol extract could be used simultaneously as an anti-hyperuricemic and anti-wrinkle source. Further studies are needed to determine anti-hyperuricemic activities of rutin and hyeproside in vivo.
1. Introduction
Camellia japonica L. (Theaceae, CJ) is known to possess antioxidant [1,2,3] and anti-inflammatory effects [4,5]. It has been used in traditional medicine, which has been described in Donguibogam (the Korean medical encyclopedia) [6]. According to recent reports, CJ oil has excellent anti-asthmatic effects. CJ oil can suppress asthma occurrence via GATA-3 and IL-4 pathway. In particular, oleic acid has been reported as the main effective substance of CJ oil [7]. The anti-hyperuricemic effect of CJ extract has been reported in an animal model of hyperuricemia. Rutin and chlorogenic acid have been identified as anti-hyperuricemic markers in CJ extract [8]. Recently, it has been reported that CJ extract can reduce skin diseases with whitening effects. CJ essential oil has been reported to possess a whitening effect by inhibiting α-MSH-induced melanin production. It also possesses tyrosinase inhibitory effect in B16F10 cells [9]. Camellioside A isolated from CJ flowers can regulate keratinocyte MMP-1 expression through MAPK pathway regulation [1,10]. Thus, CJ has potential as a source to develop cosmetic materials. In addition, CJ fruit and stem extracts have been reported to possess pluripotency and wound healing effects [1,10].
Studies on the optimization of CJ extract have been reported using by-products from CJ oil. Kim et al. have optimized the extraction through response surface methodology (RSM). An optimal extract made from CJ seed cake has been reported to possess about 19% of acetylcholinesterase (AchE) inhibitory activity with an extraction yield of 13%, indicating an excellent recycling potential of CJ seed cake [11,12]. Studies on the identification and analysis of active ingredients of CJ have revealed triterpenes, saponins, glycosylated flavonoids, and tannins as its constituents [13,14]. However, compared to reports on the efficacy and efficacy of CJ, there are few studies on the optimization of extraction and establishment of analysis methods for functional materials of CJ [12]. In particular, optimization of extraction of natural products is an essential process to improve material productivity. Establishment of analysis methods is important because it occupies an important part of product reliability.
From natural foods to functional foods and cosmetic materials, research begins with optimization of extraction. In general, hot water or organic solvent extract is used. Recently, supercritical CO2 extraction or subcritical extraction has been widely used [15,16]. Supercritical CO2 extraction or subcritical extraction is very useful in that it can extract various functional substances such as polyphenols and saponins. In the present study, the productivity of functional substances in hot water and ethanol extracts was investigated under the consideration of production cost.
Recently, the provincial governments of South Korea have made many efforts to industrialize C. japonica in the field of food and medicinal sources. Thus, we have investigated anti-hyperuricemic, anti-asthmatic, and antioxidant effects of CJ for the specialization of CJ and reported its biological constituents [8,9]. In addition, CJ leaf extract possesses antioxidant and skin protection effects [1,2,9,10,17,18]. We have identified biomarkers for anti-wrinkle effect of CJ extract and confirmed that CJ can be applied simultaneously as an anti-gout and wrinkle-improving source through optimization of CJ extract. In the present study, active substances and analysis methods related to the optimization of CJ leaf extract based on its anti-heperuricemic and anti-wrinkle effects are presented. The proposed biomarkers and analysis methods are considered to be appropriate for quality control of optimized extracts.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extraction Yields of Extracts and Analysis of Bioactive Markers
For CJ extract preparation, hot water and ethanolic extracts (20–100%) were prepared. The extraction yield of CJ was less than 10% with hot water or 80% ethanol. Other extracts showed yields of more than 10% (Table 1).

Table 1.
Extraction yields of Camellia japonica extracts.
Biomarkers such as rutin, hyperoside, isoquercitrin chlorogenic acid, gallocatechin gallate, and phillygenin in CJ extracts were analyzed by HPLC (Table 2). As a result of measuring contents of biomarkers in the extract, CGA was detected at 0.02% in 20, 40, and 60% ethanol extracts. GCG showed the highest content in the hot water extract (0.05 ± 0.004%). Hyperoside and isoquercitrin showed the highest contents in the 80% ethanol extract (0.65 ± 0.051 and 0.46 ± 0.042%, respectively). Philligenin showed an even content of 0.1% or more in all samples except for the 40% ethanol extract. Rutin showed the highest content (0.94 ± 0.078%) in 80% ethanol extract (Table 3).

Table 2.
HPLC analysis condition for CJ extract.

Table 3.
Content of biomarkers in hot water and ethanolic extracts from Camellia japonica leaf.
2.2. Evaluation of Elastase Inhibitory Effects of CJ Extracts
Elastase inhibitory effects of six extracts and phosphoramidon (PPRM), a control, at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL were evaluated. PPRM and 80% ethanolic extract showed about 80% and 62% of elastase inhibitory activity, respectively. In order to confirm correlations between analyzed biomarkers and elastase inhibition activities, elastase inhibitory activities of single markers were analyzed. Elastase inhibitory activities of hyperoside, isoquercitrin, and philligenin were 31.74 ± 0.57%, 17.98 ± 1.50%, and 13.70 ± 0.25%, respectively. They were thought to be main markers for anti-wrinkle substances. Inhibitory abilities of CGA, GCG, and rutin were 3.45 ± 0.21% and 4.57 ± 0.11%, 0.45 ± 0.003 respectively, showing weak activities (Table 4). Thus, they were considered as minor components of anti-wrinkle effect. Rutin was measured to be 0.45%. Therefore, it was determined that biomarkers for anti-wrinkle activities of CJ extract were hyperoside, isoquercitrin, and philligenin. Table 3 shows results of comparison of elastase inhibitory effects by preparing biomarkers under the same conditions as those contained in the 80% ethanolic extract. A mixture of the three biomarkers showed 50% elastase inhibition activity compared to the 80% ethanolic extract. According to this result, it is expected that hyperoside, soquercitrin, and philligenin are the main components of CJ extract. Other unknown biomarkers with elastase inhibitory effects need to be identified in the future.

Table 4.
Elastase inhibition of CJ extract and biomarkers.
2.3. Evaluation of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Effects of CJ Extracts
To standardize the anti-hyperuricemic source, xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities of six extracts were specified. The 80% ethanolic extract showed the best xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. As a result of relative comparison of xanthine oxidase activities of biomarkers, rutin showed the highest activity, followed by hyperoside, GCG, and CGA. Isoquercitrin and philligenin showed weak xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities. A mixture of rutin, hyperoside, GCG, and CGA was prepared with the same content as 80% ethanol extract and its xanthine oxidase inhibition activity was determined. Results showed that biomarkers for anti-hyperuriemic effects were rutin, hyperoside, GCG, and CGA (Table 5).

Table 5.
Xanthine oxidase inhibition of CJ extract and biomarkers.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Extract
Camellica. japonica leaves (CJ) were obtained from Jeollanamdo Wando Arboretum in Jeonnam, Korea. C. japonica leaves were collected from Joyag island, Korea (126°56′50.07″ E longitude and 34°22′31.27″ N latitude). A voucher specimen (MNUCSS-CJ-01) was deposited in Mokpo National University (Muan, Republic of Korea) [8]. Leaves were separated for the present study. Air-dried and powdered C. japonica leaf (100 g) was extracted twice with ethanol (500 mL) at room temperature for 3 days. C. japonica leaf (100 g) was extracted with hot water for 4 h. Since functional extracts are generally easy to use hot water or ethanol extract, we used hot water and ethanol as extraction solvents. The yield of the extract was calculated as the % of the extract based on the dried leaf (%, w/w). The resultant ethanol solution was evaporated, dried, and stored at −50° C. The sample was used for in vitro experiments and analysis of biomarkers.
3.2. Constituents Profiling by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
Constituent profiling of CJ extracts was performed with HPLC (Figure 1). All HPLC analyses were performed using an Alliance 2695 HPLC system (Waters; Milford, MA, USA) equipped with a photodiode array detector. Analysis method was described in Table 5. The biomarkers of our study were derived from prior studies.
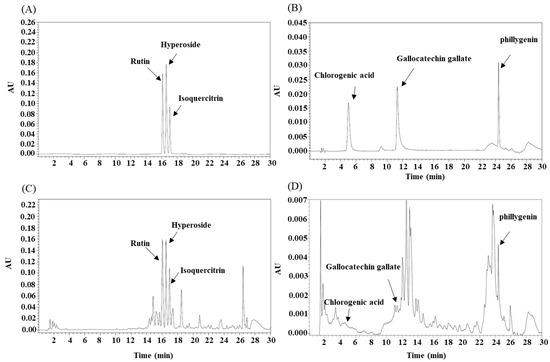
Figure 1.
Analysis of Camellia japonica extracts by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) (A,B): standard; (C,D): sample.
3.3. Determination of In Vitro Xanthine Oxidase (XO) Inhibitory Activity
First, each sample (200 μL) and 1 mM xanthine (200 μL) were mixed in 600 μL of 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) and reacted at room temperature for 5 min. After adding xanthine oxidase (0.1 unit/mL) (200 μL) to the reaction solution, the reaction was carried out at 37 °C for 15 min. Then, 1 N HCl (200 μL) was added to stop the reaction. Centrifugation was performed at 15,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was separated and measured at 292 nm. We calculated the enzyme activity as the ratio (%) of inhibitory activity compared to the control [8].
3.4. Determination of Elastase Inhibitory Activity
First, elastase 10 μL (10 μg/mL), 0.2 M Tris-HCl (90 μL), 2.5 mM N-succinyl-(Ala)3-p-nitroanilide (STANA, 100 μL), and sample (50 μL) were mixed at 37 °C for 30 min. The reaction solution was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 10 min and the absorbance of the supernatant was measured at 405 nm. We calculated the enzyme activity as the ratio (%) of inhibitory activity compared to the control [19].
4. Conclusions
The aim of the present study was to simultaneously develop an anti-hyperuricemic and anti-wrinkle source using Camellia japonica leaf (CJ). CJ extracts were prepared. Their contents of various biomarkers and biological activities were then evaluated. Biomarkers such as rutin, hyperoside, isoquercitrin, chlorogenic acid (CGA), gallocatechin gallate (GCG), and phillygenin were analyzed. Our results revealed that biomarkers for the anti-wrinkle activity of CJ extracts were hyperoside, isoquercitrin, and philligenin. The 80% ethanolic extract was optimal as an anti-wrinkle material. Among the six extracts, the extract that could be used as an anti-hyperuricemic source was the 80% ethanol extract. Rutin, hyperoside, GCG, and CGA were major components of CJ extract. Taken together, our results suggest that 80% ethanol extract could be used simultaneously as an anti-hyperuricemic and anti-wrinkle source. Anti-hyperuricemic and anti-wrinkle effects of different biomarkers need to be evaluated in vivo in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-S.C. and D.-H.P.; methodology, S.-Y.S., K.-W.A. investigation, S.-Y.S.; writing and editing, S.-S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2022R1A5A8033794). And this work was carried out with the support of the R&D program for forest science technology (project no. 2019148A00-1921-AB02) provided by the forest service (Korean Forestry Promotion Institute).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Onodera, K.; Hanashiro, K.; Yasumoto, T. Camellianoside, a novel antioxidant glycoside from the leaves of Camellia japonica. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, M.J.; Yoo, E.S.; Koh, Y.S.; Kang, H.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, H.H.; Hyun, J.W. Antioxidant effects of the ethanol extract from flower of Camellia japonica via scavenging of reactive oxygen species and induction of antioxidant enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2618–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yin, C.P.; Kong, L.C.; Jiang, D.H. Extraction optimisation, purification and major antioxidant component of red pigments extracted from Camellia japonica. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, E.; Shin, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Park, D. Anti-inflammatory activity of Camellia japonica oil. BMB Rep. 2012, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Choi, J.H.; Cui, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.M.; Yun, J.J.; Jung, J.E.; Choi, W.; Yoon, K.C. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidative Effects of Camellia japonica on Human Corneal Epithelial Cells and Experimental Dry Eye: In Vivo and In Vitro Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J. Donguibogam; Bubinmunhwasa: Seoul, Korea, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Bae, C.S.; Seo, N.S.; Na, C.S.; Yoo, H.Y.; Oh, D.S.; Bae, M.S.; Kwon, M.S.; Cho, S.S.; Park, D.H. Camellia japonica oil suppressed asthma occurrence via GATA-3 & IL-4 pathway and its effective and major component is oleic acid. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 57, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, I.S.; Park, D.H.; Kim, J.E.; Yoo, J.C.; Bae, M.S.; Oh, D.S.; Shim, J.H.; Choi, C.Y.; An, K.W.; Kim, E.I.; et al. Identification of the biologically active constituents of Camellia japonica leaf and anti-hyperuricemic effect in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Yang, J.K. Camellia japonica Essential Oil Inhibits α-MSH-Induced Melanin Production and Tyrosinase Activity in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2021, 2021, 6328767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadeniz, F.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, H.R.; Ko, J.; Kong, C.S. Camellioside A, isolated from Camellia japonica flowers, attenuates UVA-induced production of MMP-1 in HaCaT keratinocytes via suppression of MAPK activation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, C.R.; Lim, H.J.; Nam, S.H.; Joo, O.S.; Shin, D.H.; Shin, E.C. An optimized extraction technique for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the Camellia japonica seed cake by using response surface methodology. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, C.R.; Shin, D.H.; Shin, E.C. Responsive Surface Methodology Optimizes Extraction Conditions of Industrial by-products, Camellia japonica Seed Cake. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.N.; Sharma, G.; Yang, J.L.; Choi, H.S.; Lim, S.I.; Kang, K.W.; Oh, W.K. Oleanane triterpenes as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitors from Camellia japonica. Phytochemistry 2014, 103, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thao, N.T.; Hung, T.M.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, J.C.; Min, B.S.; Bae, K. Triterpenoids from Camellia japonica and their cytotoxic activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idham, Z.; Putra, N.R.; Aziz, A.H.A.; Zaini, A.S.; Rasidek, N.A.M.; Mili, N.; Yunus, M.A.C. Improvement of extraction and stability of anthocyanins, the natural red pigment from roselle calyces using supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 56, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, N.R.; Rizkiyah, D.N.; Idham, Z.; Veza, I.; Qomariyah, L.; Yunus, M.A.C. Optimization and modelling in flavonoid and phenolic compounds recovery from peanut skin by subcritical water. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.K.; Han, E.; Song, C.L.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.S. Effects of the Extracts from Fruit and Stem of Camellia japonica on Induced Pluripotency and Wound Healing. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Nam, G.B.; Karadeniz, F.; Kong, C.S.; Ko, J. Evaluation and enzyme-aided enhancement of anti-photoaging properties of Camellia japonica in UVA-irradiated keratinocytes. Z. Fur Naturforschung. C J. Biosci. 2022, 77, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.H.; Chae, J.I.; Cho, S.S. Identification and Extraction Optimization of Active Constituents in Citrus junos Seib ex TANAKA Peel and Its Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2019, 24, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).