Pinus roxburghii and Nauplius graveolens Extracts Elevate Apoptotic Gene Markers in C26 Colon Carcinoma Cells Induced in a BALB/c Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Extract Preparation
2.3. Composition of Basal Diet
2.4. Determination of the Median Lethal Dose (LD50)
2.5. Animals
2.6. Induction of C26 Murine Cells in BALB/c Mice
2.7. Measurement of Body Wasting
2.8. Experimental Design
2.9. Changes in Body Weight (BW) and Feed Efficiency Ratio (FER)
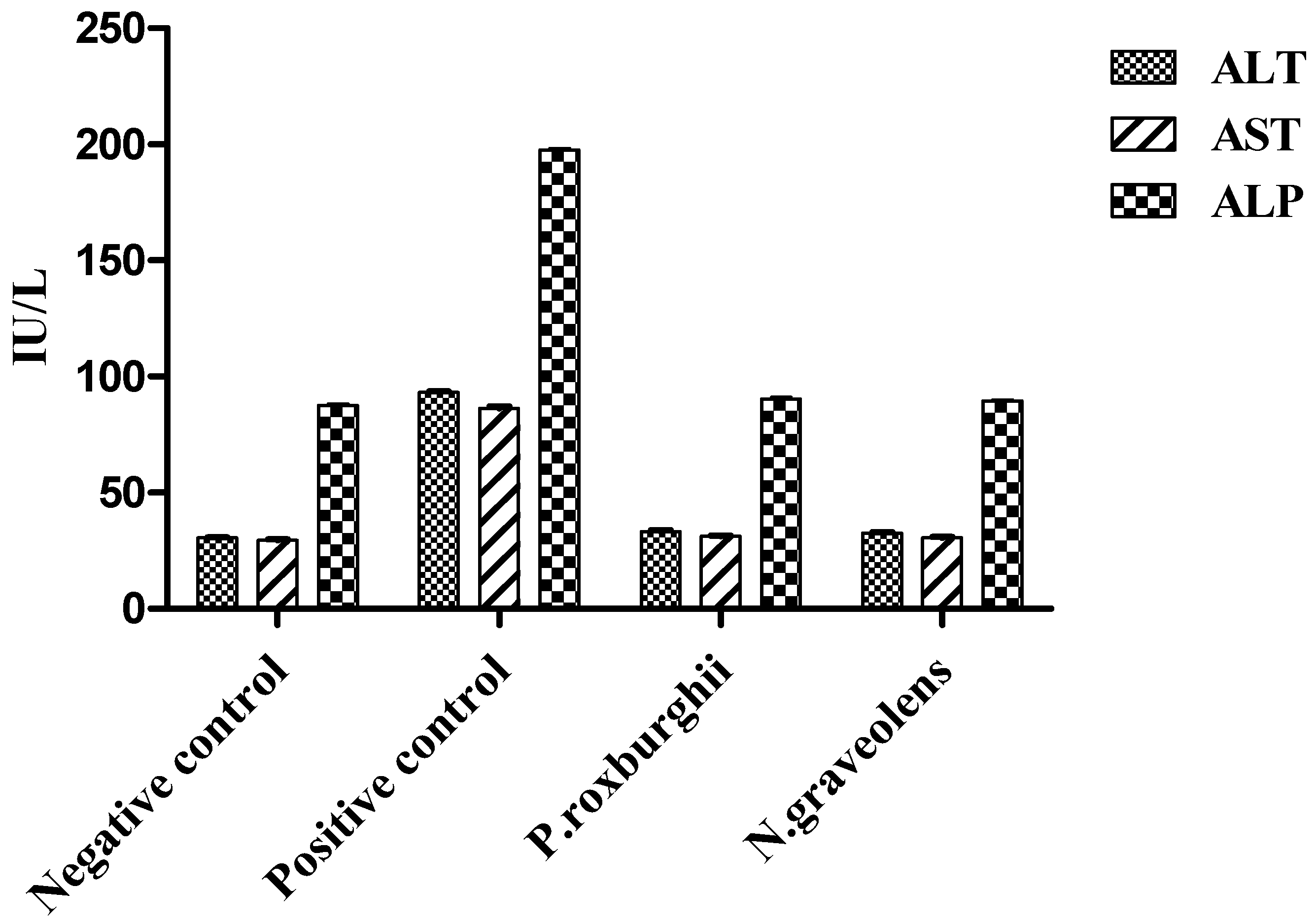
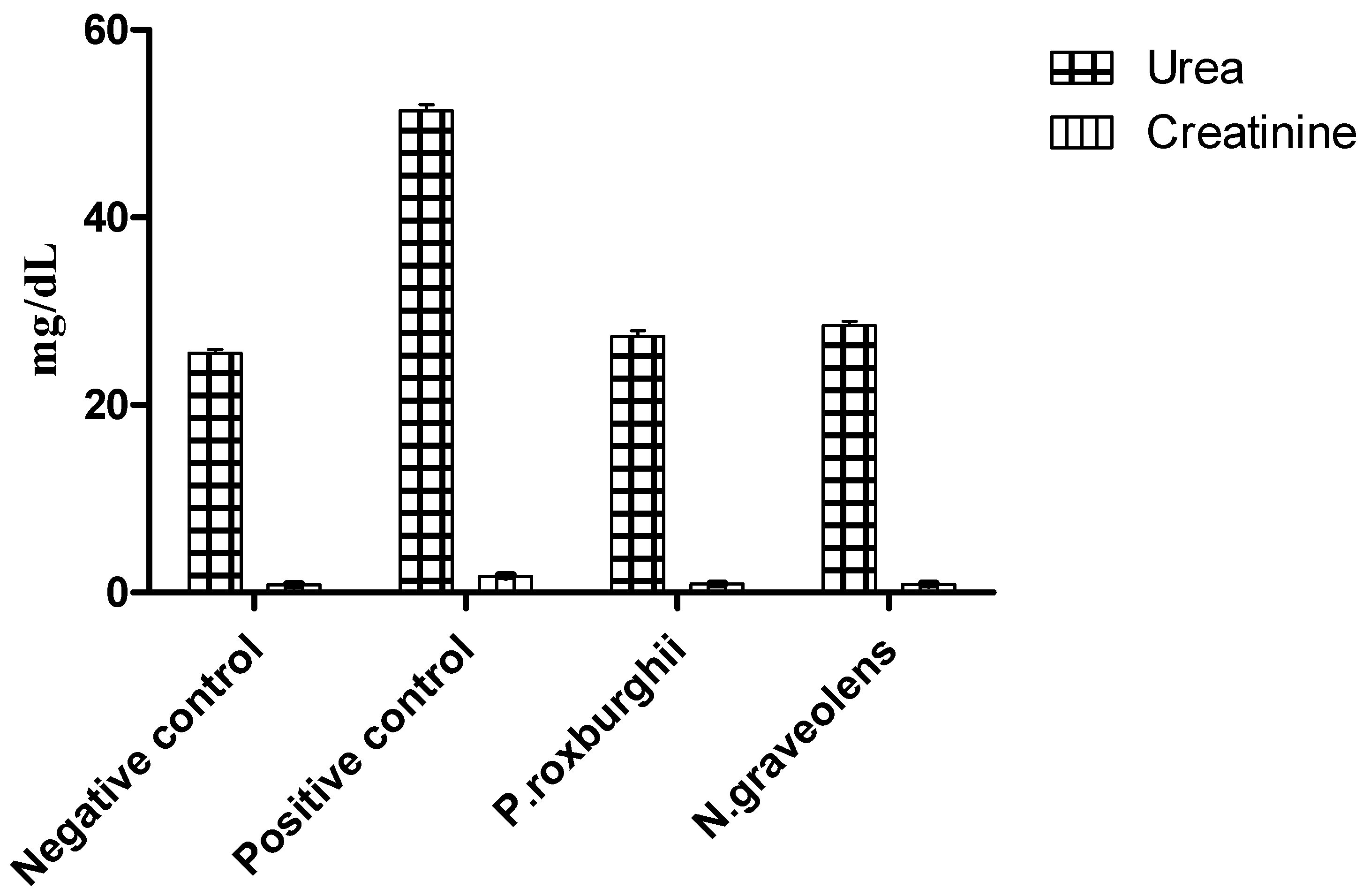
2.10. Biochemical Analyses
2.11. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.12. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.13. Histopathological Examination
2.14. Statistical Analyses
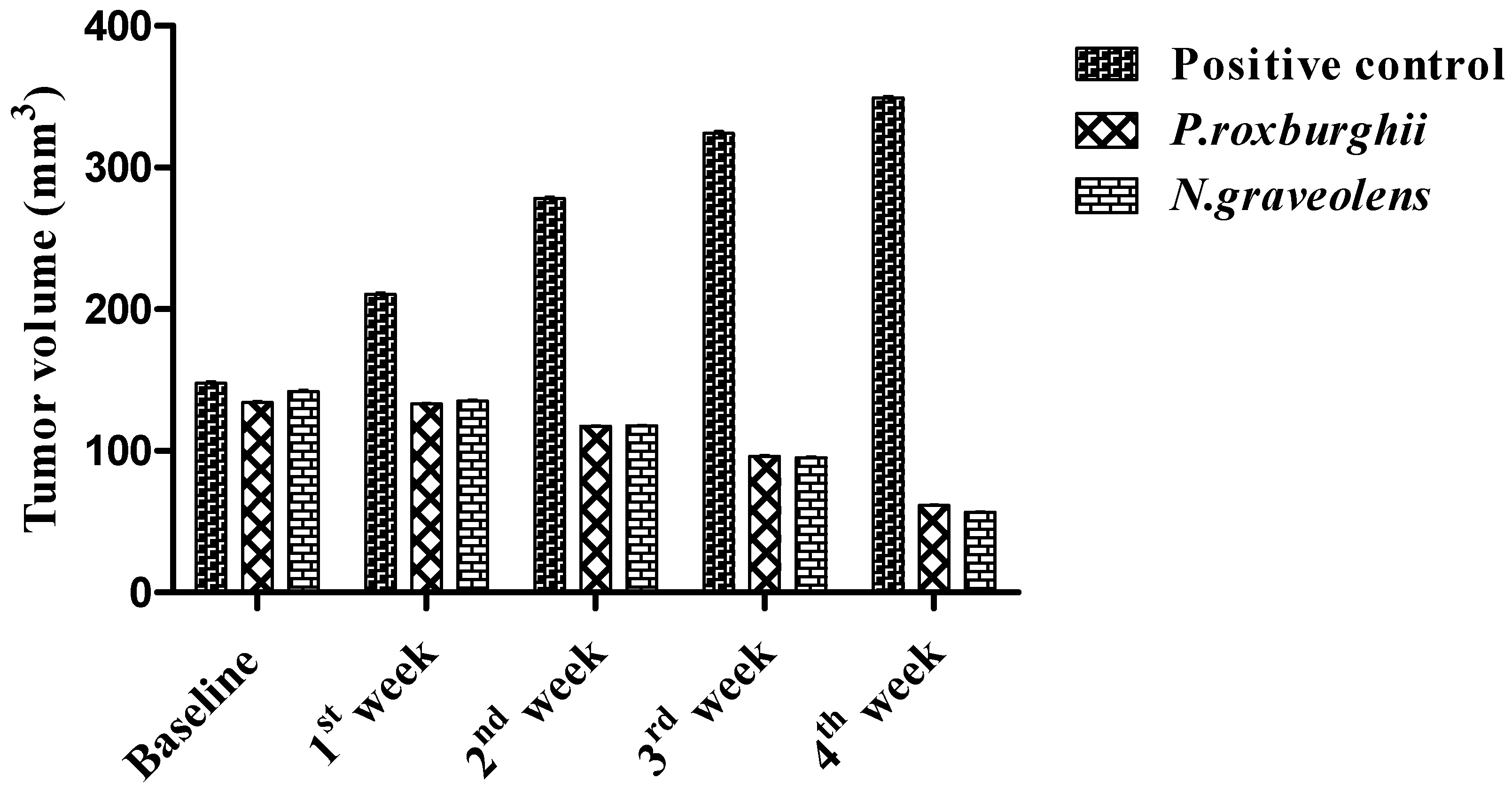
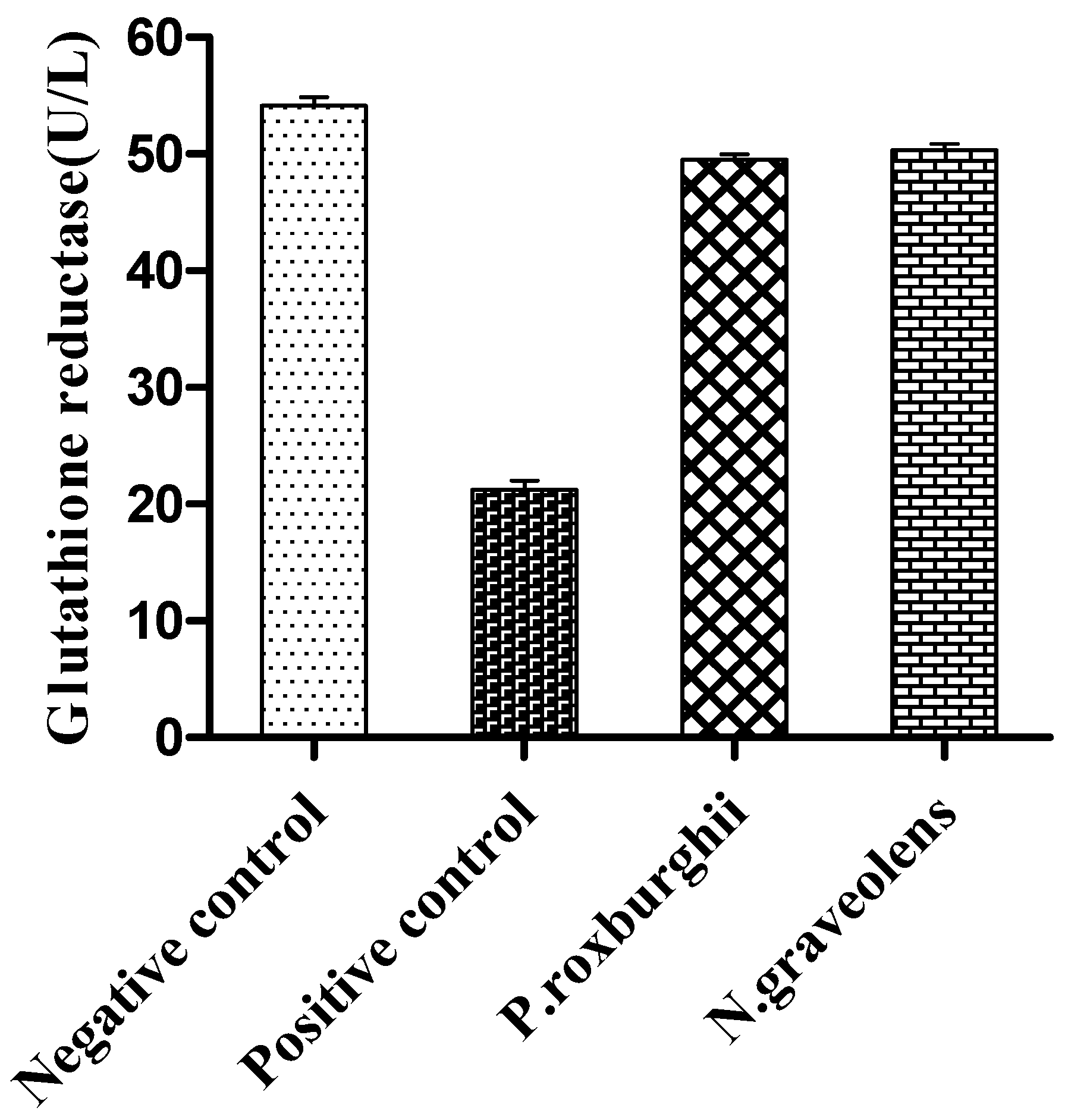
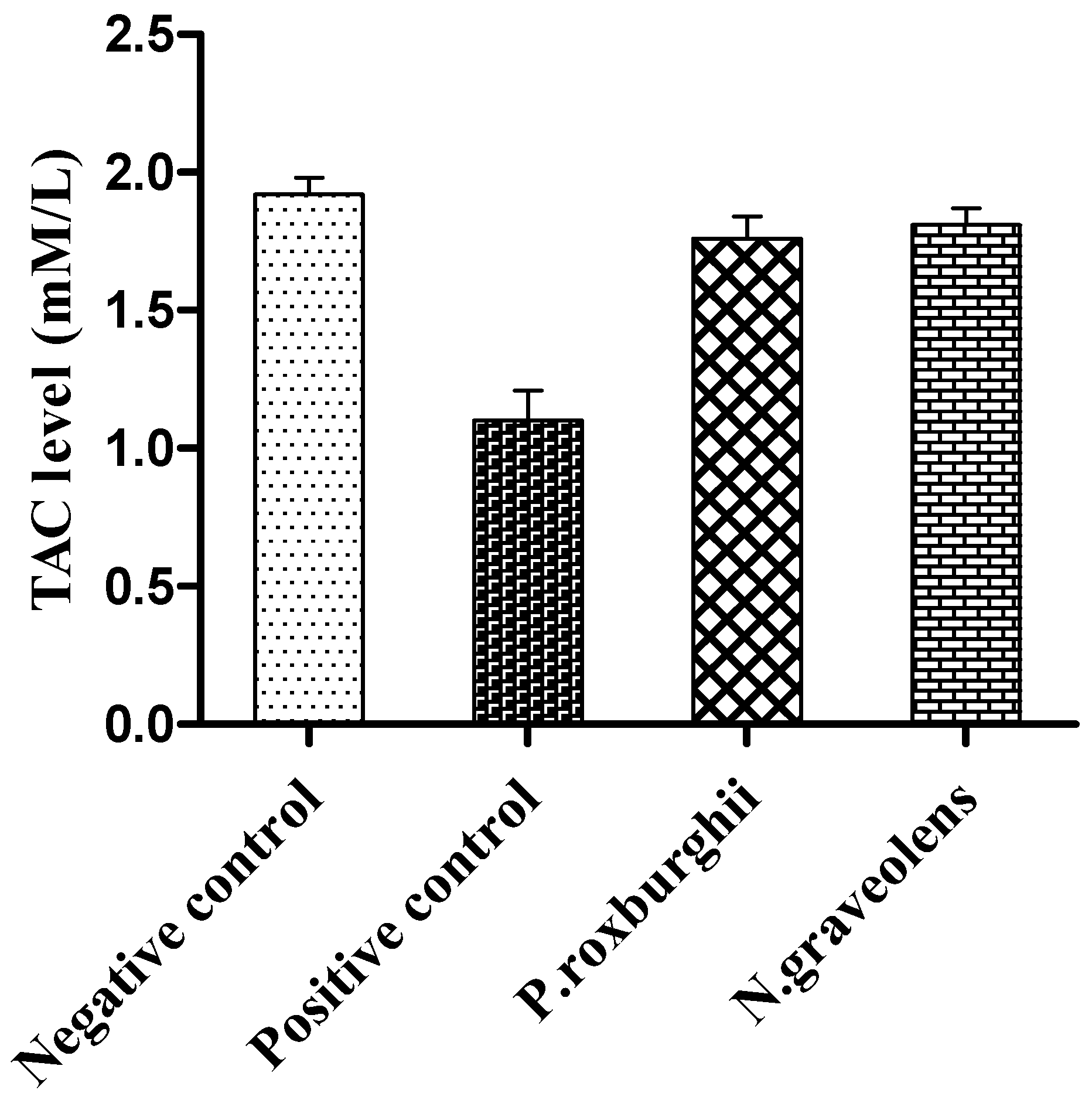
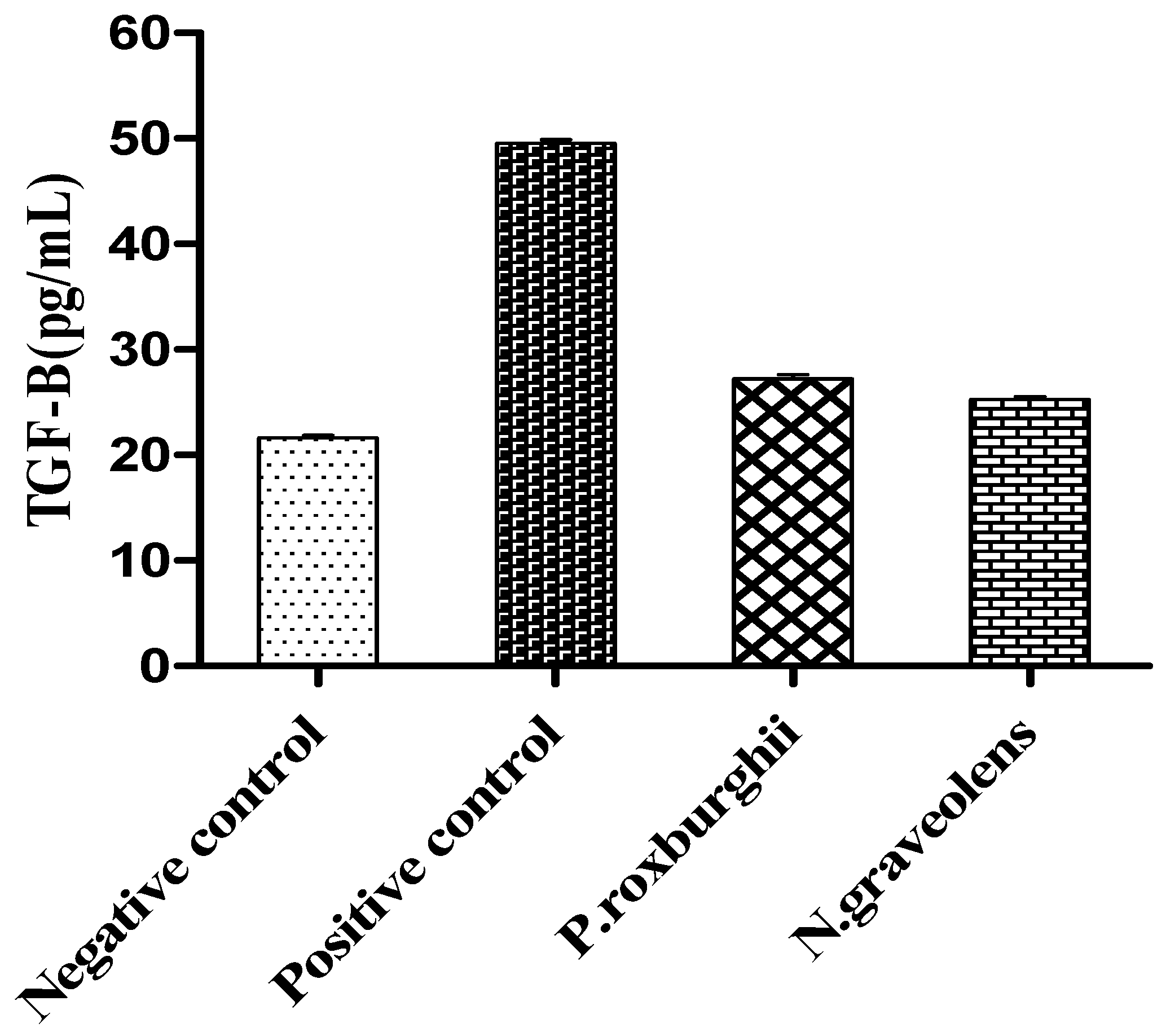
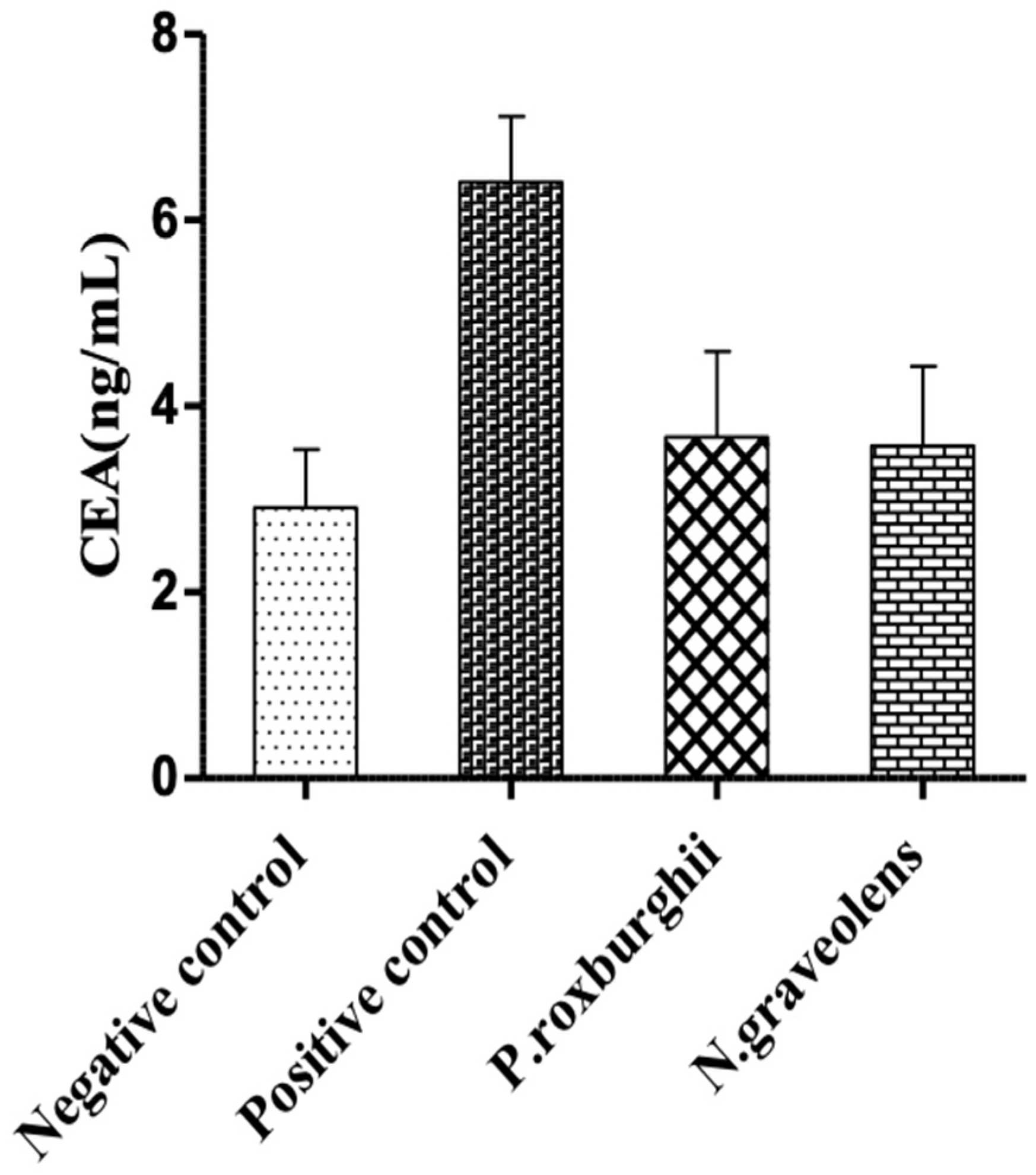
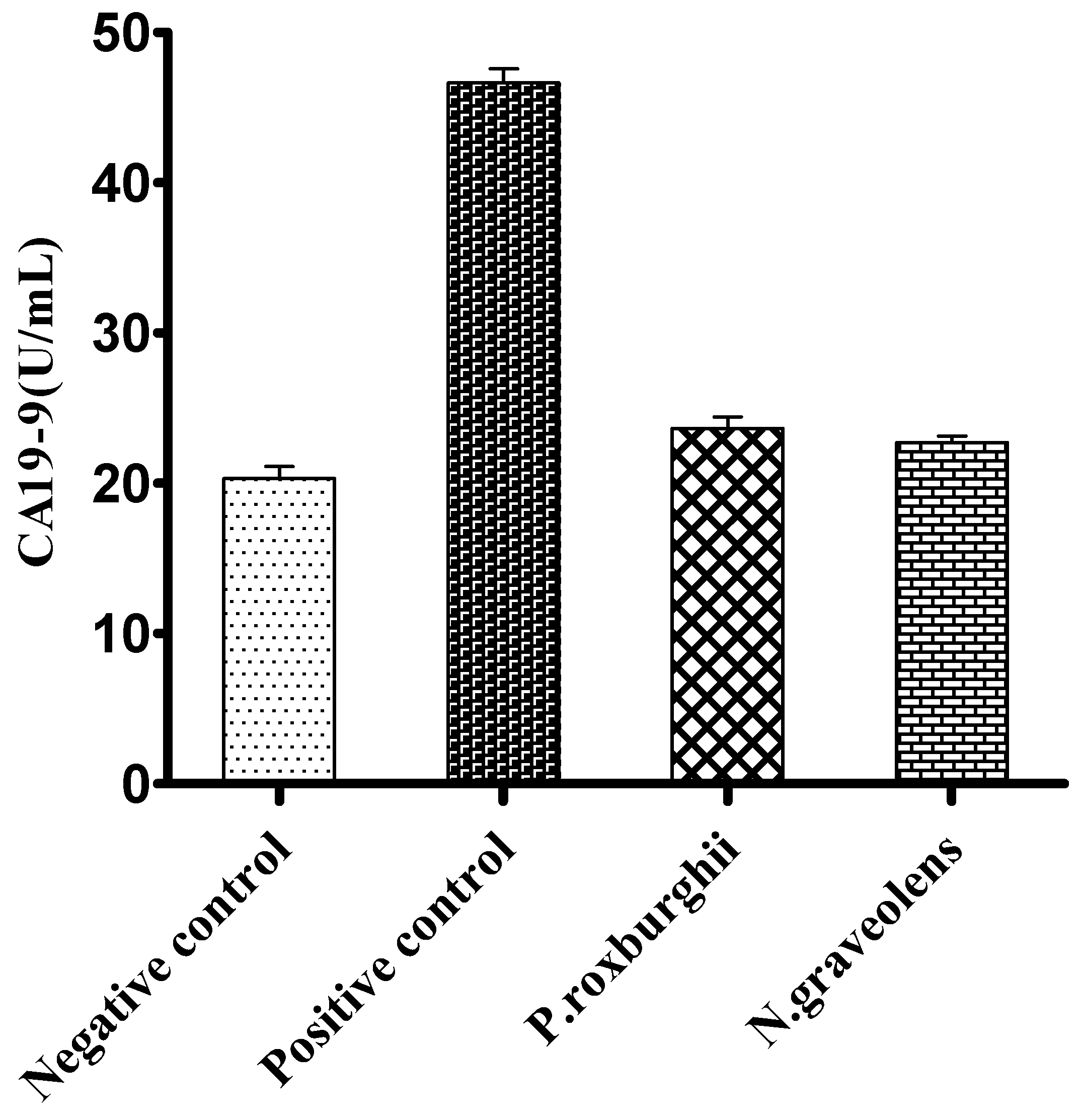
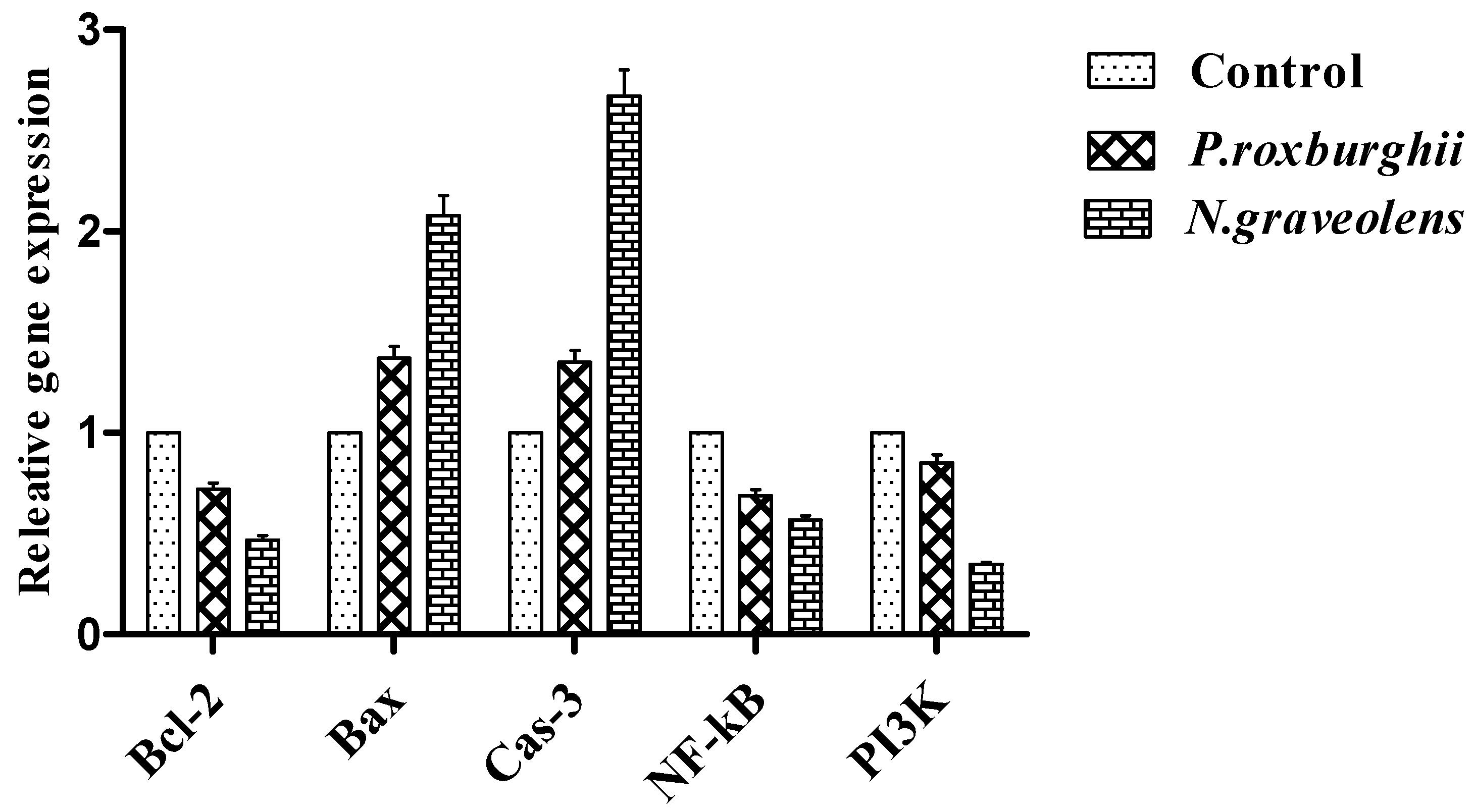
3. Results and Discussion
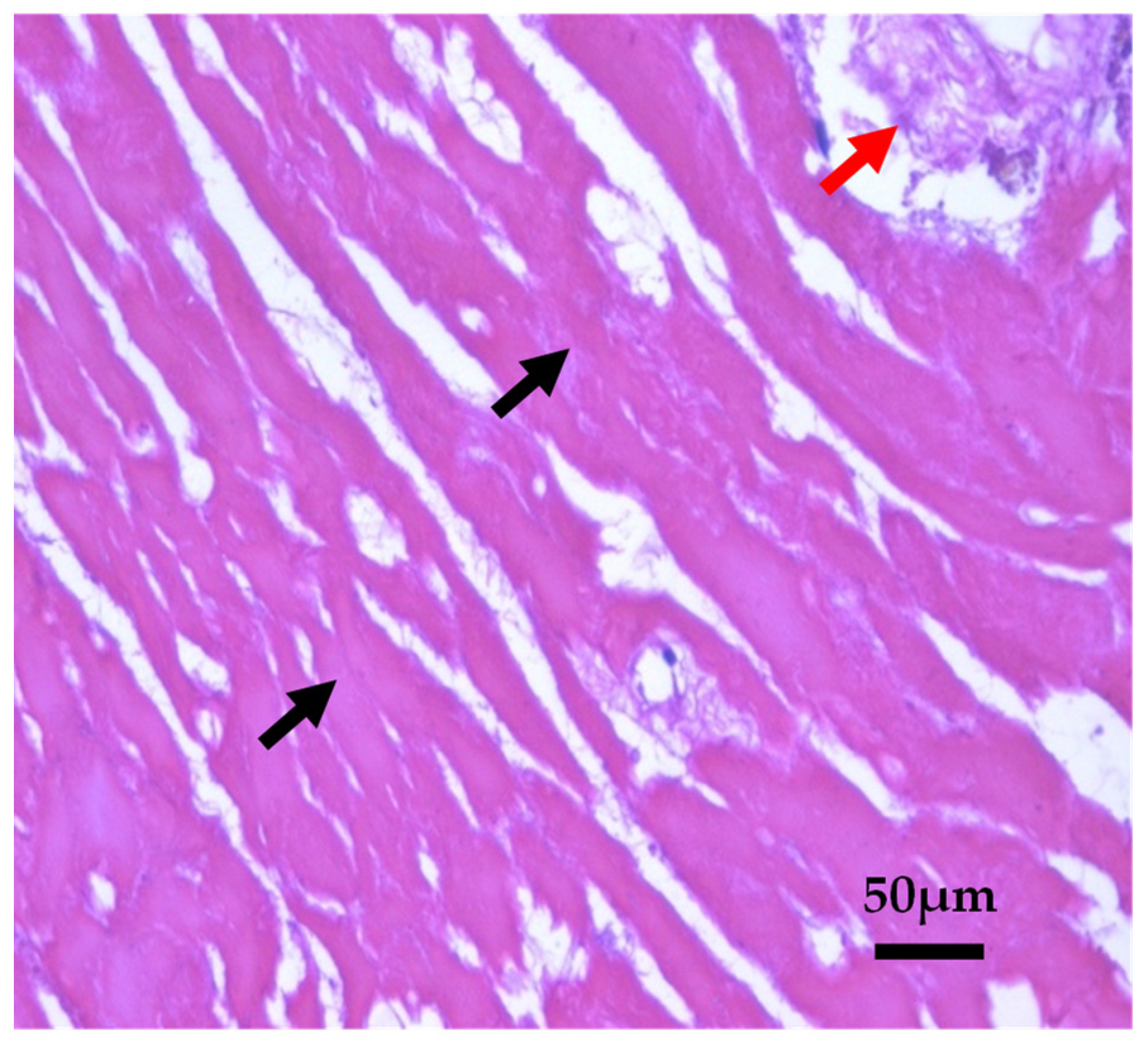
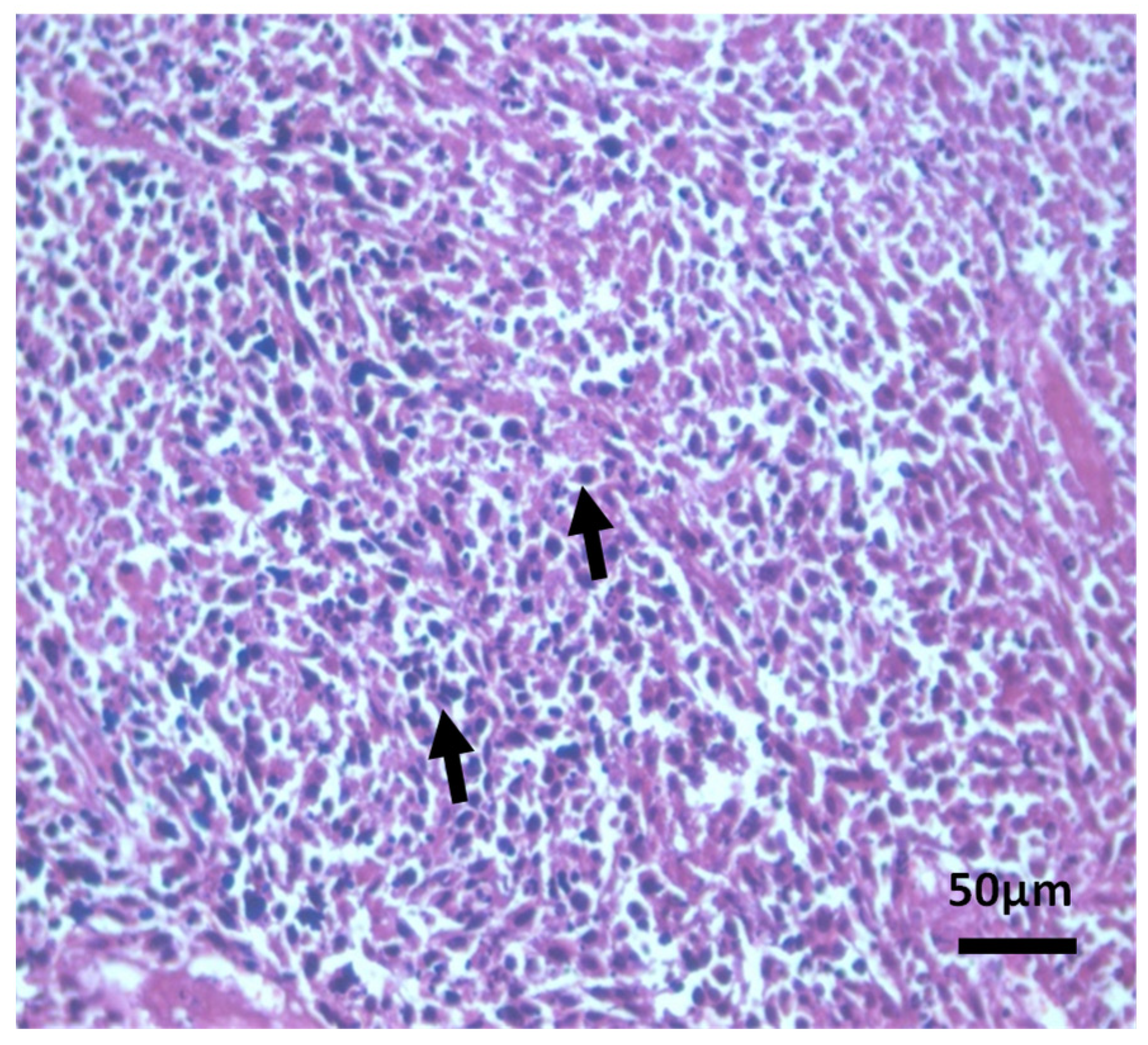
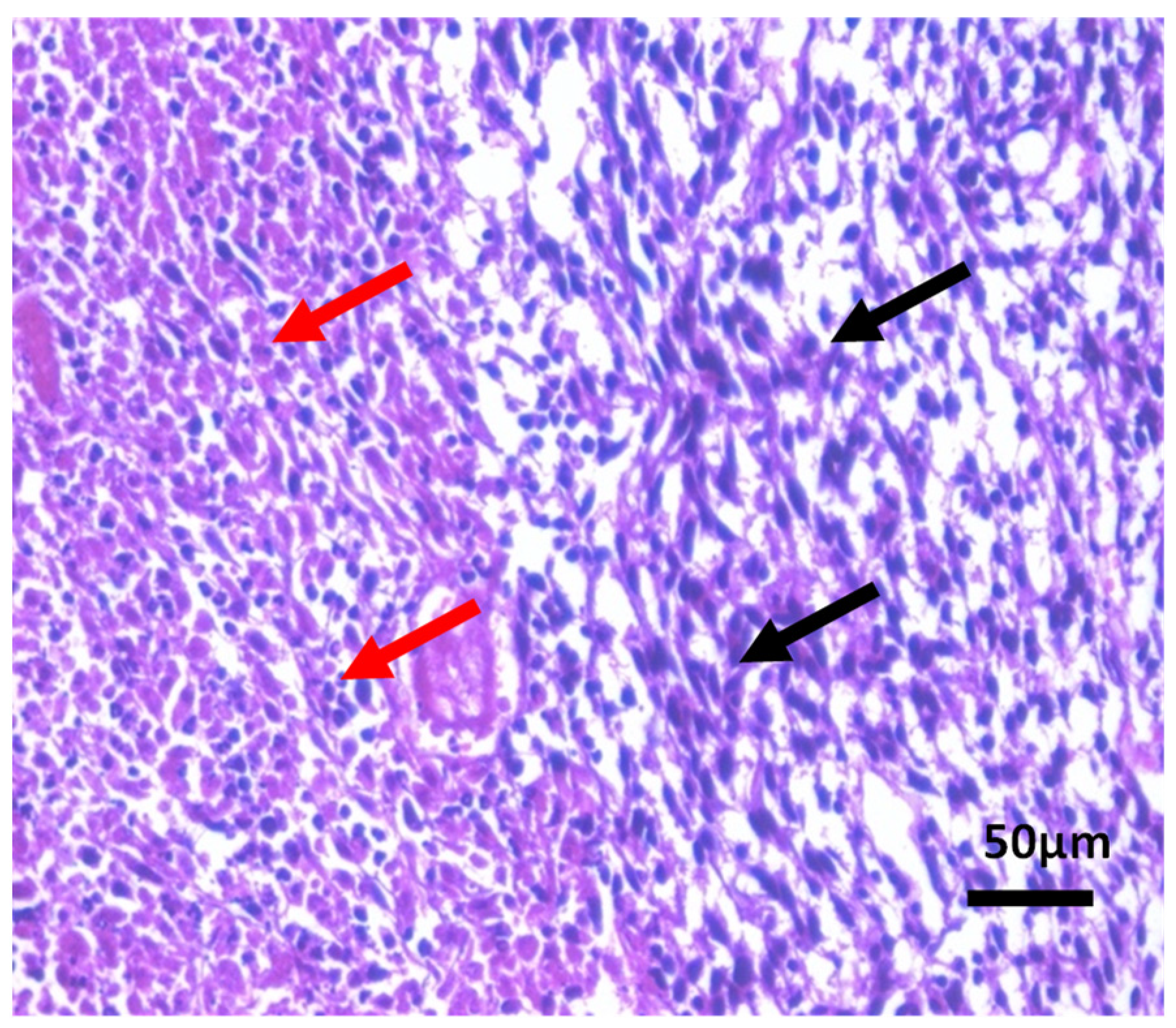
Histopathological Observations of Tissues
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Estimates 2020: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-estimates/ghe-leading-causes-of-death (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Wiseman, M. The second World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research expert report. Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: A global perspective. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2008, 67, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, A.S.; Edward, S.K.; Hong, W.K. Chemoprevention of cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2004, 54, 150–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, Y.J.; Na, H.K.; Lee, S.S. Transcription factors and mitogen-activated protein kinases as molecular targets for chemoprevention with anti-inflammatory phytochemicals. Biofactors 2004, 21, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez de Mejia, E.; Song, Y.S.; Ramirez-Mares, M.V.; Kobayashi, H. Effect of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) tea on topoisomerase inhibition and oral carcinoma cell proliferation. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2005, 53, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, H.; Mizoguchi, A.; Fukuda, K. The herbal medicine sho-saiko-to inhibits proliferation of cancer cell lines by inducing apoptosis and arrest at the G0/G1 phase. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 448–454. [Google Scholar]
- Oubre, A.Y.; Carlson, T.J.; King, S.R.; Reaven, G.M. From plant to patient: An ethnomedical approach to the identification of new drugs for the treatment of NIDDM. Diabetologia 1997, 40, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lamusta, J.; Zhang, W. F Tumor cell selective cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction by an herbal preparation from brucea javanica. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 4, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahri, S.; Razavi, S.M.; Niri, F.H.; Mohammadi, S. Induction of programmed cell death by Prangos uloptera, a medicinal plant. Biol. Res. 2009, 42, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Russo, M.; Spagnuolo, C.; Tedesco, I.; Bilotto, S.; Russo, G.L. The flavonoid quercetin in disease prevention and therapy: Facts and fancies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 83, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadi, M.Y.; Heidari, M.; Akbarpour, M.; Mirjalili, M.H.; Zeinali, A.; Parsa, M. In vitro cytotoxic activity of the essential oil of Dorema ammoniacum D. Don. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 7, 511–514. [Google Scholar]
- Tamimi, R.M.; Hankinson, S.E.; Campos, H.; Spiegelman, D.; Zhang, S.; Colditz, G.A. Plasma carotenoids, retinol, and tocopherols and risk of breast cancer. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 161, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Khor, S.C.; Zhou, F.; Duan, T.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.F. Chemoprevention by lipid-soluble tea polyphenols in diethylnitrosamine/phenobarbital-induced hepatic pre- cancerous lesions. Anticancer. Res. 2014, 34, 683–693. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, D.; Kumar, A.; Kaushik, P.; Rana, A.C. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of P. roxburghii Sarg. Advanc. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 2012, 245431. [Google Scholar]
- Anju, P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singhal, B.; Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, S.; Lakshmi, V. Antidyslipidemic and antioxidant activity of Pinus roxburghii needles. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Shah, W.A. GC-MS analysis, antibacterial, antioxidant and anticancer activity of essential oil of P. roxburghii from Kashmir, India. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Chem. 2014, 4, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Satyal, P.; Paudel, J.; Raut, A.; Noura, S.; Setzer, N. Volatile constituents of P. roxburghii from Nepal. Phcog. Res. 2013, 5, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Goyal, R.; Sharma, L. Potential biological efficacy of Pinus plant species against oxidative, inflammatory and microbial disorders. BMC Altern. Complement. Med. 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, U.; Srivastava, B.; Semwal, S.; Sati, O.P. Xanthones from Pinus roxburghii. J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 2009, 83, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriti, A.; Saad, A.; Belboukhari, N.; Ghezali, S. The essential oil composition of Bubonium graveolens (Forssk.) Maire from the Algerian Sahara. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2007, 22, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdane, F.; Essid, R.; Mkadmini, K.; Hammami, M.; Fares, N.; Mahammed, M.H.; El Ouassis, D.; Tabbene, O.; Limam, F.; Hadj, M.D. Phytochemical composition and biological activities of Asteriscus graveolens (Forssk) extracts. Process. Biochem. 2017, 56, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaib, F.; Allali, H.; Bennaceur, M.; Flamini, G. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from the aerial parts of Asteriscus graveolens (forssk.) less. and Pulicaria incisa (lam.) dc: Two asteraceae herbs growing wild in the hoggar. Chem. Biodiv. 2017, 14, 1700092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouissi, H.; Gourine, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.I.; Bombarda, I.; Boudjeniba, M.; Yousfi, M. Chemical composition, antioxidative, antimicrobial and anti-cancer activities of Asteriscus graveolens (Forssk) essential oil. Oriental. Pharm. Experim. Med. 2018, 18, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrín, G.; Eiroa, J.L.; Morales, M.; Triana, J.; Quintana, J.; Estévez, F. Naturally occurring asteriscunolide A induces apoptosis and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in human tumor cell lines. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 49, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Finger, L.R.; Yunis, J.; Nowell, P.C.; Croce, C.M. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14; 18) chromosome translocation. Science 1984, 226, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.C. Bcl-2 family proteins: Regulators of apoptosis and chemoresistance in haematologic malignancies. Semin. Haematol. 1997, 34, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Witzig, T.E.; Adjei, A.A. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, Y.J.; Peters, G.J.; Hull, W.E.; Punt, C.J.; Heerschap, A. Correlation between 5-fluorouracil metabolism and treatment response in two variants of C26 murine colon carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schastak, S.; Yafai, Y.; Geyer, W.; Kostenich, G.; Orenstein, A.; Wiedemann, P. Initiation of apoptosis by photodynamic therapy using a novel positively charged and water-soluble near infra-red photosensitizer and white light irradiation. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 30, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulino, P.; Berardi, E.; Cardillo, V.M.; Rizzuto, E.; Perniconi, B.; Ramina, C. Molecular, cellular and physiological characterization of the cancer cachexia-inducing C26 colon carcinoma in mouse. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt 3: Compositae-Verbenaceae; Al Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, M.; Hassouna, H.Z.; Mahmoud, K.; Abd-Rabou, A.A.; Abdel-Azeem, A.S.; Hegazy, A.H.; Adel-Lattife, M.S.; Ahmed, F.A. Preliminary study on the toxicological impacts of P. roxburghii and N. graveolens extracts on albino mice. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 purified diet for laboratory rodents: Final report of american institute of nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbrandt, W. Behrens methods for calculation of LD50. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1952, 2, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Eda, H.; Fujimoto, k.; Tanaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Ishitsuka, H. Anticachectic activity of 5′-Deoxy-5- fluorouridine in a murine tumor cachexia model, colon 26 adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 4528–4532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto-Ouchi, K.; Tamura, S.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishitsuka, H. Establishment and characterization of cachexia- inducing and -non-inducing clones of murine colon 26 carcinoma. Exper. Cancer 1995, 61, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euhus, D.M.; Hudd, C.; LaRegina, M.C.; Johnson, F.E. Tumor measurement in the nude mouse. J. Surg. Oncol. 1986, 31, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomayko, M.M.; Reynolds, C.P. Determination of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.W.; Sutton, N.E.; Banjo, M.O.; Satterlee, L.D.; Kendrick, J.G. The C-PER and assays for protein quality. J. Food Technol. 1978, 12, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Reitman, S.; Frankel, S.A. Colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Path. 1957, 28, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rec, G.S. Optimized standard colorimetric methods. Serum Alkaline phosphatase (DGKC). J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1972, 10, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, C.J.; Crouch, S.R. Spectrophotometric and kinetics investigations of the Berthelot reaction for the determination of ammonia. Analyti. Chem. 1977, 49, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, N.R.; King, J.W. Fundamental of Clinical Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Tietz, N.W., Ed.; Sannders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1976; pp. 994–998. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.M.; Spooner, R.J. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 3rd ed.; Bergmeyer, H.-U., Ed.; Verlog. Chem. Weinheim: Deerfield Beach, FL, USA, 1983; Volume 3, pp. 258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Koracevic, D.; Koracevic, G.; Djordjevic, V.; Andrejevic, S.; Cosic, V. Method for the measurement of antioxidant activity in human fluids. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K. Serum lipid peroxide in cerebrovascular disorders determined by a new colorimetric method. Clin. Chem. Acta 1978, 90, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, D.; Stevens, A.; Turner, R. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 4th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK; London, UK; Melbourne, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- International Union against Cancer. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 5th ed.; Sobin, L.H., Wittekind, C., Eds.; Wiley-Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tullie, L.G.; Sohn, H.M.; Zylstra, J. A role for tumor volume assessment in resectable esophageal cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.C.; Postow, M.A.; Orlowski, R.J. T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2017, 545, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.M.; Othus, M.; Caglar, H.B.; Allen, A.M. Tumor volume is a prognostic factor in non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, T. The role of tumor volume in radiotherapy of patients with head and neck cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; Newton, C.C.; Newcomb, P.A. Association between body mass index and mortality for colorectal cancer survivors: Overall and by tumor molecular phenotype. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baade, P.D.; Meng, X.; Youl, P.H. The impact of body mass index and physical activity on mortality among patients with colorectal cancer in Queensland, Australia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diculescu, M.; Iacob, R.; Iacob, S.; Croitoru, A.; Becheanu, G.; Popeneciu, V. The importance of histopathological and clinical variables in predicting the evolution of colon cancer. Rom. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 11, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, M.D.; Ross, J.A.; Fearon, K.C. Disordered metabolic response with cancer and its management. World J. Surg. 2000, 24, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.M.; Hebrant, A.; Dumont, J.E. Metabolic reprogramming of the tumor. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3999–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, M.; Li, K.; Beard, M.R. Mitochondrial injury, oxidative stress, and antioxidant gene expression are induced by hepatitis C virus core protein. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Meng, Q.H.; Ye, Y. Prognostic significance of pretreatment serum levels of albumin, LDH and total bilirubin in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer. J. Carcinog. 2015, 36, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Li, J.P.; Li, L.F. Elevated preoperative serum alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase (alt/ast) ratio is associated with better prognosis in patients undergoing curative treatment for gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, S.B.; Yun, M.R.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Kim, W.K. Alternative therapy and abnormal liver function during adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pfeiffer-Guglielmi, B.B.; Dombert, S.; Jablonka, V.; Hausherr, V.; Thriel, C.; Schobel, N.; Jansen, R.P. Axonal and dendritic localization of mRNAs for glycogen-metabolizing enzymes in cultured rodent neurons. BMC. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 15–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yasuda, Y.; Kawamura, K.; Ichikado, K.; Yoshioka, M. Alkaline phosphatase flare phenomenon following epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: Report of a case and case review. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 13, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lakshmi, A.; Subramanian, S. Chemotherapeutic effect of tangeretin, a poly methoxylated flavone studied in 7, 12-dimethylbenz (a) anthracene-induced mammary carcinoma in experimental rats. Biochimie 2014, 99, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.L.; De Azevedo, M.J.; Silveiro, S.P.; Canani, L.H.; Caramori, M.L.; Zelmanovitz, T. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faull, R. Prescribing in renal disease. Aust. Prescr. 2007, 30, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yener, Y.; Yerlikaya, F.H.; Toker, A. Evaluation of some renal function parameters in rats treated with acrylamide. AJAVS 2016, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, G.; Chidambaram, R.; Varunkumar, K.; Ravikumar, V.; Pandi, M. Chemopreventive potential of fungal taxol against 7,12-dimethylbenz [a] anthracene induced mammary gland carcinogenesis in Sprague Dawley rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 767, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Koji, K.; Shiro, H.; Mitsuo, T.; Hideyuki, A. Serum creatinine level for cervical cancer. J. Oncol. 1998, 28, 546–550. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, I.S.; Slater, C.; Ross, J.A.; Preston, T.; Fearon, K. Albumin synthetic rates, the acute phase response and cyrolanes in pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. 1995, 82, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Erel, O.A. A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perse, M.; Cerar, A. Morphological and molecular alterations in 1,2 dimethylhydrazine and azoxymethane induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 473964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, S.; Ortega, A.; Estrela, J.M. Oxidative stress in environmental-induced carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2009, 674, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Dupertuis, Y.M.; Pichard, C. Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids and lipid peroxidation on colorectal cancer risk and treatments. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab Care 2012, 15, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Lopez-Burillo, S.; Reiter, R.J. Oxidative damage to catalase induced by peroxyl radicals: Functional protection by melatonin and other antioxidants. Free Radic. Res. 2003, 37, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvorovic, J.; Tramer, F.; Granzotto, M.; Candussio, L.; Decorti, G.; Passamonti, S. Oxidative stress-based cytotoxicity of delphinidin and cyanidin in colon cancer cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.; Staudacher, J.J.; Beauchamp, D. Transforming growth factor beta superfamily signaling in development of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, D.R.; Doll, J.A.; Bauer, J.; Jung, B.; Munshi, H.G.; Bartholin, L.; Pasche, B.; Lee, C.; Grippo, P.J. TGF-β: Duality of Function Between Tumor Prevention and Carcinogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Cao, Z.; Jiao, S.B.; Pakala, D.N.; Sirigiri, R.; Li, W.; Kumar, R.; Mishra, L. Carcinoembryonic antigen interacts with TGF- receptor and inhibits TGF-ß signaling in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8159–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, R.C.P.; Ravdin, D.F.; Hayes, S.; Bates, H.J.R.; Fritsche, J.M.; Jessup, N.; Kemeny, G.Y.; Locker, R.G.; Mennel and Somerfield, M.R. Update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer: Clinical practice guidelines of the american society of clinical oncology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 19, 1865–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.; Saragovi, M.U.; Stanners, C.P. The adhesion and differentiation- inhibitory activities of the immunoglobulin superfamily member, carcinoembryonic antigen, can be independently blocked. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14632–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villano, B.C.; Brennan, S.; Brock, P.; Bucher, C.; Liu, V.; McClure, M.; Rake, B.; Space, S.; Westrick, B.; Schoemaker, H., Jr.; et al. Radio immunometric assay for a monoclonal antibody- defined tumor marker, CA 19-9. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, X.; Molina, R.; Grau, J.J.; Piqué, J.M.; Garcia-Valdecasas, J.C.; Astudillo, E.; Biete, A.; Bordas, J.M.; Novell, A.; Campo, E.; et al. Prognostic value of CA19-9 levels in colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 1992, 216, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Watanabe, M.; Teramoto, T.; Kitajima, M. CA19-9 as a predictor of recurrence in patients with colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 1997, 66, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbridge, A.R.D.; Valente, L.J.; Strasser, A. The role of the apoptotic machinery in tumor suppression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.X.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Jiang, D.; Lin, Y.J.; Jin, F.X.; Lee, S.K.; Jin, Y.H. P53-dependent Fas expression is critical for Gin- senoside Rh2 triggered caspase-8 activation in HeLa cells. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martin, M.A.; Goya, L. Time- course regulation of survival pathways by epicatechin on HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradzadeh, M.; Hosseini, A.; Erfanian, S.; Rezaei, H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallatepromotesapoptosisin human breast cancer T47D cells through down-regulation of PI3K/AKT and Telomerase. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, L.; Wu, P.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Gu, R.; Dan, X.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Xiao, Z. Gallic acid has anticancer activity and enhances the anticancer effects of cisplatin in non small cell lung cancer A549 cells via the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, A.; Manzoor, Q.; Iqbal, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Adil Sarfraz, R.; Sajid, A. Proxburghii essential oil anticancer activity and chemical composition evaluation. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Sghaier, M.; Pagano, A.; Mousslim, M.; Ammari, Y.; Kovacic, H.; Luis, J. Rutin inhibits proliferation, attenuates superoxide production and decreases adhesion and migration of human cancerous cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouthamchandra, K.; Sudeep, H.V.; Venkatesh, B.J.; Shyam Prasad, K. Chlorogenic acid complex (CGA7), standardized extract from green coffee beans exerts anticancer effects against cultured human colon cancer HCT-116 cells. Food. Sci. Hum. Wellness 2017, 6, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Shankar, E.; Fu, P.; MacLennan, G.T.; Gupta, S. Suppression of NF-κB and NF-κB-Regulated gene expression by apigenin through IκBα and IKK pathway in TRAMP mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmila, R.; Manoharan, S. Anti-tumor activity of rosmarinic acid in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) induced skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, E.; Zhuang, H.; Li, D.; Ni, F. Rosmarinic acid inhibits stem-like breast cancer through hedgehog and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways. Phcog Mag. 2019, 15, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelinson, L.P.; Assmann, C.E.; Palma, T.V.; da Cruz, I.B.M.; Pillat, M.M.; Manica, A.; Stefanello, N.; Weis, G.C.C.; de Oliveira Alves, A.; de Andrade, C.M. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of caffeic acid on SK-Mel-28 human melanoma cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaza, M.S.; Al-Attiyah, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Abbadi, G.; Koyippally, M.; Afzal, M. Syringic acid from Tamarix aucheriana possesses antimitogenic and chemo-sensitizing activities in human colorectal cancer cells. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S. Vanillic Acid Suppresses HIF-1alpha Expression via Inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K/4E- BP1 and Raf/MEK/ERK Pathways in Human Colon Cancer HCT-116 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.H.; Rajamanickam, V.; Nagarajan, S. Supplementation of p-coumaric acid exhibits chemopreventive effect via induction of Nrf2 in a short-term preclinical model of colon cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 28, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primers | Sequences |
|---|---|
| Bcl-2 | F: 5′TGGGATGCCTTTGTGGAAC 3′ R: 5′CATATTTGTTTGGGGCAGGTC3′ |
| Bax | F: 5′TGCTACAGGGTTTCATCCAG3′ R: 5′ATCCACATCAGCAATCATCC3′ |
| Cas-3 | F: 5′GCTGGACTGCGGTATTGAGA3′ R: 5′CCATGACCCGTCCCTTGA3′ |
| NF-kB | F: 5′GCAAAGGGAACATTCCGATAT3′ R: 5′GCGACATCACATGGAAATCTA3′ |
| PI3k | F: 5′GTGTCAGCGCTCTCCGCC3′ R: 5′CTGATAATTGATGTAGG3′ |
| GAPDH | F: 5′CATTCAAGACCGGACAGAGG3′ R: 5′ACATACTCAGCACCAGCATCACC3′ |
| Parameters Groups | Body Weight Gain (BWG) (g) | Food Intake (FI) (g) | Feed Efficiency Ratio (FER) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative control | 27.11 ± 0.37 a | 189.21 ± 0.53 a | 0.14 |
| Positive control | 19.36 ± 0.64 c | 177.54 ± 0.66 c | 0.10 |
| P. roxburghii | 24.52 ± 0.58 b | 184.37 ± 0.71 b | 0.13 |
| N. graveolens | 25.23 ± 0.45 b | 186.29 ± 0.49 b | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gad, M.; Hassouna, H.Z.; Mahmoud, K.; Abd-Rabou, A.A.; Abdel-Azeem, A.S.; Hegazy, A.M.; Abdel-Lattife, M.S.; Ahmed, F.A.; Oz, F.; Proestos, C.; et al. Pinus roxburghii and Nauplius graveolens Extracts Elevate Apoptotic Gene Markers in C26 Colon Carcinoma Cells Induced in a BALB/c Mouse Model. Separations 2022, 9, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100277
Gad M, Hassouna HZ, Mahmoud K, Abd-Rabou AA, Abdel-Azeem AS, Hegazy AM, Abdel-Lattife MS, Ahmed FA, Oz F, Proestos C, et al. Pinus roxburghii and Nauplius graveolens Extracts Elevate Apoptotic Gene Markers in C26 Colon Carcinoma Cells Induced in a BALB/c Mouse Model. Separations. 2022; 9(10):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100277
Chicago/Turabian StyleGad, Mosab, Hassan Z. Hassouna, Khaled Mahmoud, Ahmed A. Abd-Rabou, Amal S. Abdel-Azeem, Amany M. Hegazy, Mohamed S. Abdel-Lattife, Fouad A. Ahmed, Fatih Oz, Charalampos Proestos, and et al. 2022. "Pinus roxburghii and Nauplius graveolens Extracts Elevate Apoptotic Gene Markers in C26 Colon Carcinoma Cells Induced in a BALB/c Mouse Model" Separations 9, no. 10: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100277
APA StyleGad, M., Hassouna, H. Z., Mahmoud, K., Abd-Rabou, A. A., Abdel-Azeem, A. S., Hegazy, A. M., Abdel-Lattife, M. S., Ahmed, F. A., Oz, F., Proestos, C., & Zaky, A. A. (2022). Pinus roxburghii and Nauplius graveolens Extracts Elevate Apoptotic Gene Markers in C26 Colon Carcinoma Cells Induced in a BALB/c Mouse Model. Separations, 9(10), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100277










