An Optimized Pathway for Nitrate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Environmentally Friendly Calabash Gourd Shell Adsorbent Based on Experimental Design Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Characteriation of the Cationic Adsorbent
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Design of Statistical Experiments
3.2. Regression Models and Analytical Validation
- a linear polynomial model by FFD:
- a nonlinear polynomial model by CCD:
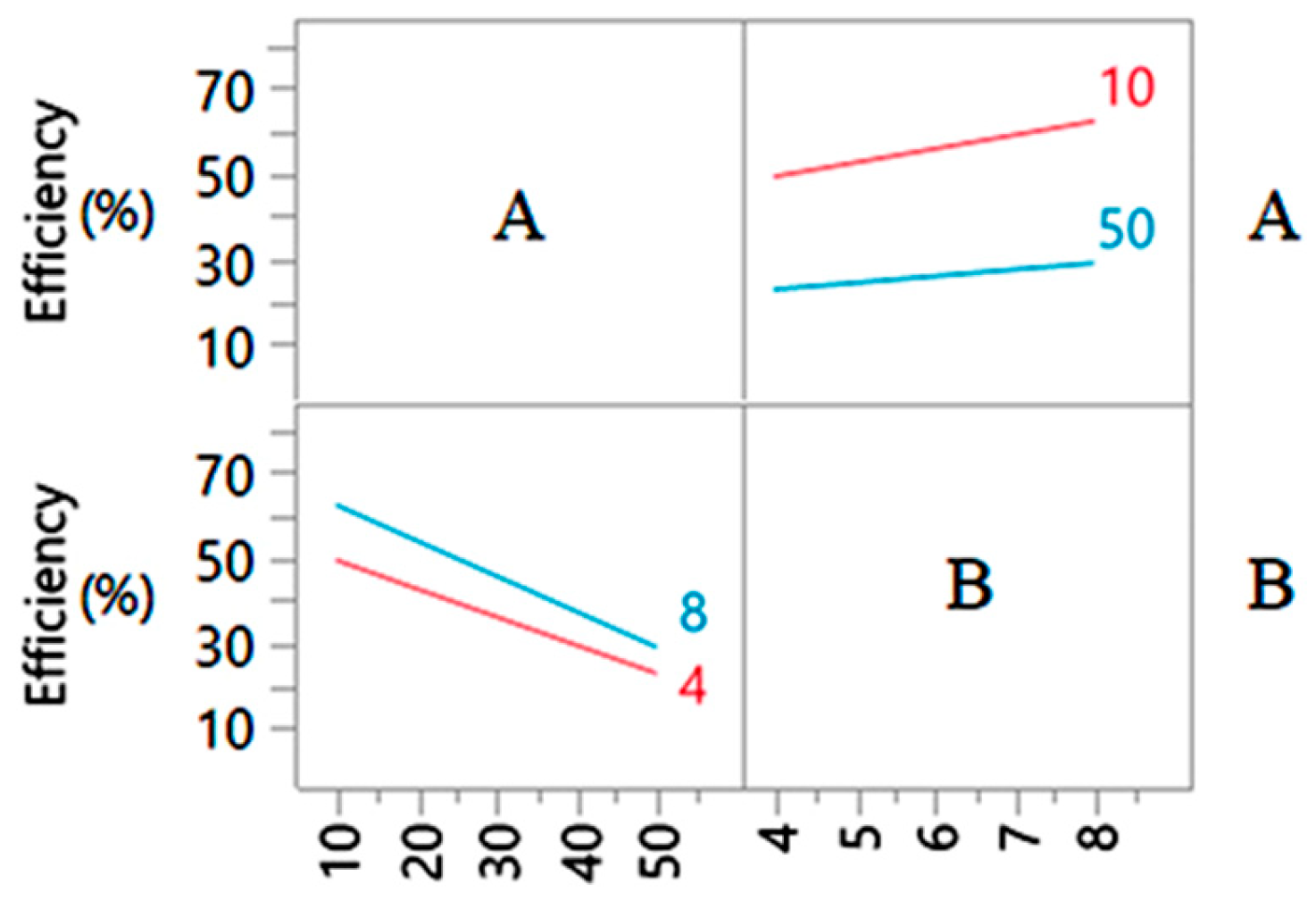
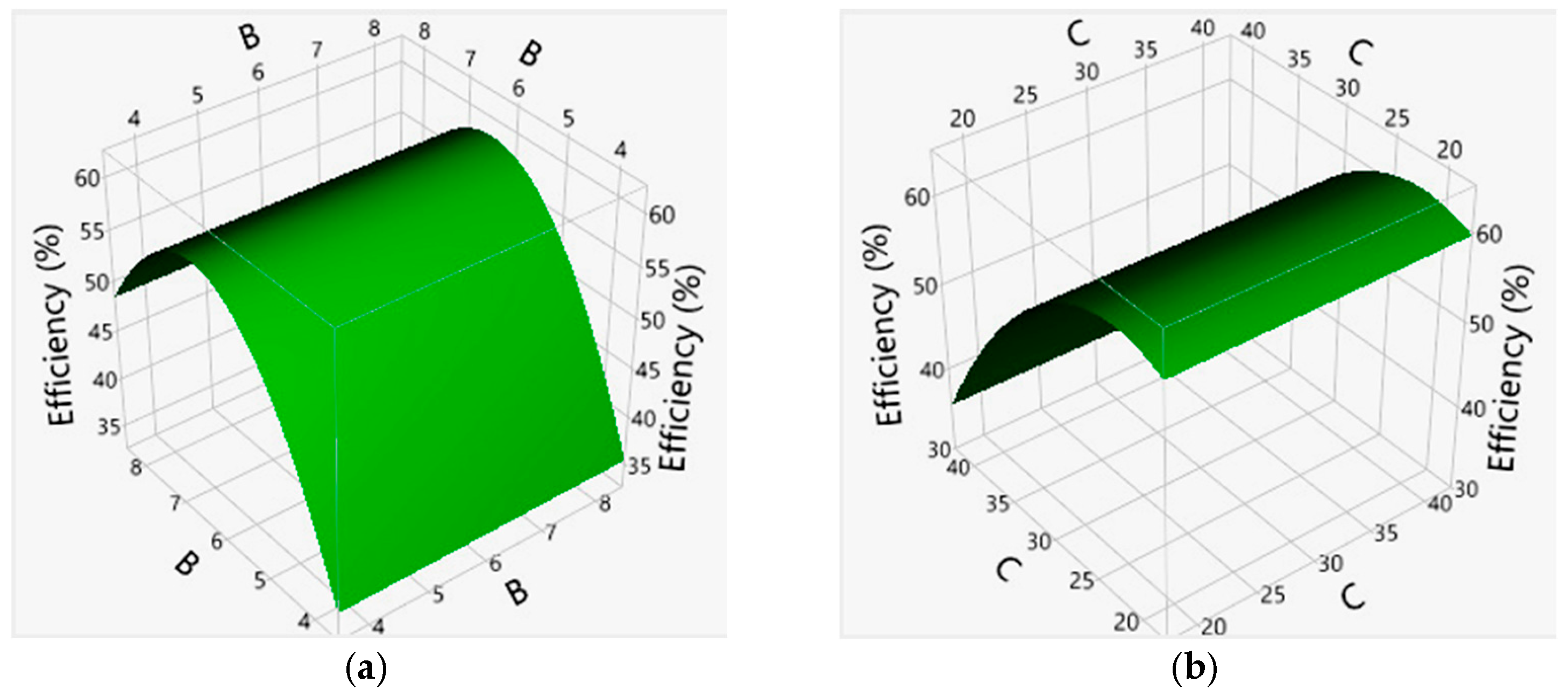
3.3. Effects of Main Factors and Their Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance test |
| CCD | Central Composite Design |
| CGS | Calabash gourd shell |
| CHTAC | N-(3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) trimethylammonium chloride |
| DF | Degrees of freedom |
| DoE | Design of Experiments |
| FFD | Full Factorial Design |
| pHpzc | pH value at the point of zero charge |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
References
- Valiente, N.; Gil-Márquez, J.M.; Gómez-Alday, J.J.; Andreo, B. Unraveling groundwater functioning and nitrate attenuation in evaporitic karst systems from southern Spain: An isotopic approach. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Xue, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y. Study on the influence of surface potential on the nitrate adsorption capacity of metal modified biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhu, Z. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution using cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) modified zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.I.M. Biological denitrification of groundwater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 123, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, J.J.; Steyn, A. Nitrate removal with reverse osmosis in a rural area in South Africa. Desalination 2003, 155, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Peng, C.; Bi, J.; Xu, H.; Juan Almeria, O. Recovery of Pb(II) and removal of NO3− from aqueous solutions using integrated electrodialysis, electrolysis, and adsorption process. Desalination 2012, 286, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieillard, J.; Bouazizi, N.; Nkuigue Fotsing, P.; Samir, B.; Raguillet, K.; Cosme, J.; Abou Serhal, C.; Mignot, M.; Sophie Bette, M.; Auger, P.; et al. Herbs carbonization and activation for fast sorption of nitrate ions: A new challenge for a full treatment of groundwater pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 82637–82646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Ribeiro Carrott, M.M.L.; Suhas, D. Low-cost adsorbents: Growing approach to wastewater treatment—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 783–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, A.; Leiviskä, T.; Hormi, O.; Tanskanen, J. Removal of nitrate by modified pine sawdust: Effects of temperature and co-existing anions. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliedeh, M.A.; Aljbour, S.H.; Al-Harahsheh, A.M.; Al-Zboon, K.; Al-Harahsheh, S. Implementing 24-1 fractional factorial design for filing the gaps in ovat sorption studies of nitrate ions onto Jordanian zeolitic tuff. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2021, 56, 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Karić, N.; Maia, A.S.; Teodorović, A.; Atanasova, N.; Langergraber, G.; Crini, G.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Đolić, M. Bio-waste valorisation: Agricultural wastes as biosorbents for removal of (in)organic pollutants in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, R.P.; Kalariya, M.; Parmar, S.K.; Sheth, N.R. Phytochemical and pharmacological review of Lagenaria sicereria. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2010, 1, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, D.L.; Smith, B.D.; Clarke, A.C.; Sandweiss, D.H.; Tuross, N. An Asian origin for a 10,000-year-old domesticated plant in the Americas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18315–18320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Bojić, A.; Bojić, D.; Nikolić, L.; Stanojević, L.; Durmišević, M.; Simonović, N.; Kostić, M. Bottle gourd (Lagenaria vulgaris) shell as a natural, biodegradable, highly available, cheap, agricultural by-product, miscellaneous biomass, ion exchanger, biosorbent and fertilizer. In Sorption-New Perspectives and Applications; Margeta, K., Farkaš, A., Eds.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2024; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, E.; Kumar, S.; Verma, C.; Sarkar, S.; Maji, P.K. A comprehensive review on technological advances of adsorption for removing nitrate and phosphate from waste water. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaruban, M.; Loganathan, P.; Shim, W.G.; Kandasamy, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Vigneswaran, S. Enhanced removal of nitrate from water using amine-grafted agricultural wastes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, J.; O’Sullivan, A.D.; Barker, D.; Tat Wai, K.; Basharat, S.; Bello-Mendoza, R. Novel quaternary ammonium functionalized cellulosic materials for nitrate adsorption from polluted waters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković Nikolić, D.Z.; Bojić, A.; Bojić, D.; Cvetković, D.; Cakić, M.; Nikolić, G.S. Preconcentration and immobilization of phosphate from aqueous solutions in environmental cleanup by a new bio-based anion exchanger. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.S.; Simonović, N.; Nikolić, L.; Durmišević, M.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Ristić, N.; Bojić, A. An integrated OVAT-RSM design to gaps-filling in the study of phosphate sorption process onto cationic modified bottle gourd shell. Adv. Technol. 2023, 12, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Kang, J.-K.; Jang, H.-Y.; Park, J.-A.; Kim, S.-B. Multi-parameter experiments and modeling for nitrate sorption to quaternary ammonium-functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimers in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11023–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafshejani, L.D.; Naserib, A.A.; Moradzadehc, M.; Daneshvard, E.; Bhatnagard, A. Applications of soft computing techniques for prediction of pollutant removal by environmentally friendly adsorbents (case study: The nitrate adsorption on modified hydrochar). Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, J. Design of Experiments for Engineers and Scientists, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-0-08-099417-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Befekadu, A.; Alemayehu, E. Optimization of indigenous natural coagulants process for nitrate and phosphate removal from wet coffee processing wastewater using response surface methodology: In the case of Jimma Zone Mana district. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baei, M.S.; Esfandian, H.; Nesheli, A.A. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions in batch systems using activated perlite: An application of response surface methodology. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 11, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.S.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Nikolić, T.; Stojadinović, D.; Andjelković, T.; Kostić, M.; Bojić, A. Nitrate removal by sorbent derived from waste lignocellulosic biomass of Lagenaria vulgaris: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 15, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković Nikolić, D.Z.; Bojić, A.L.; Savić, S.R.; Petrović, S.M.; Cvetković, D.J.; Cakić, M.D.; Nikolić, G.S. Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of anion exchanger based on green modified bottle gurd shell. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 2018, 1856109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J. 6—Full factorial designs. In Design of Experiments for Engineers and Scientists, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 65–87. ISBN 9780443151736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 233–292. ISBN 1118214714. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.T.; Makwana, A.R.; Ahammed, M.M. The use of response surface methodology for modelling and analysis of water and wastewater treatment processes: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Preparation, characterization of surfactants modified clay minerals and nitrate adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R.K. Use of agricultural waste for the removal of nitrate-nitrogen from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nujić, M.; Milinković, D.; Habuda-Stanić, M. Nitrate removal from water by ion exchange. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 9, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Höll, W.H. Quaternized biomass as an anion exchanger for the removal of nitrate and other anions from water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhang, P.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Development of iron-based biochar for enhancing nitrate adsorption: Effects of specific surface area, electrostatic force, and functional groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristek Janković, A.; Habuda-Stanić, M.; Dong, H.; Tutić, A.; Romić, Ž.; Ergović Ravančić, M.; Landeka Dragičević, T.; Šiljeg, M. Utilization of modified sunflower seed as novel adsorbent for nitrates removal from wastewater. Water 2024, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabani, M.; Amrane, A.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetic modelling of the adsorption of nitrates by ion exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 125, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Ren, B.; Xu, B.; Li, D.; Xia, Y.; Xu, C.; Hua, E. Bamboo chopstick biochar electrodes and enhanced nitrate removal from groundwater. Processes 2022, 10, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, A.; Godini, H.; Dehestani, S.; Khavanin, A. Application of impregnated almond shell activated carbon by zinc and zinc sulfate for nitrate removal from water. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2008, 5, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, U.S.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Preparation of agricultural residue anion exchangers and its nitrate maximum adsorption capacity. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, U.S.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. A new procedure to produce lignocellulosic anion exchangers from agricultural waste materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjepanović, M.; Velić, N.; Habuda-Stanić, M. Modified hazelnut shells as a novel adsorbent for the removal of nitrate from wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, B.-Y.; Yue, W.-W.; Yue, Q.-Y. Adsorption kinetics of nitrate from aqueous solutions onto modified wheat residue. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 308, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, S.; Saad, R.; Belkacemi, K. Adsorptive removal of phosphate and nitrate anions from aqueous solutions using ammonium-functionalized mesoporous silica. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 8806–8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sorption Parameters | Factors | 24 FFD | CCD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levels | Levels | |||||
| −1 | +1 | −1 | 0 | +1 | ||
| Initial nitrate concentration, C0 (mg/L) | A | 10 | 50 | 10 | 30 | 50 |
| pH value | B | 4 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| Temperature, T (°C) | C | 20 | 40 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Contact time, t (min) | D | 5 | 35 | 5 | 20 | 35 |
| Runs | Pattern | A | B | C | D | Efficiency Y (%) | Predicted Y1 (%) FFD | Predicted Y2 (%) CCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −−−− | 10 | 4 | 20 | 5 | 52.29 | 52.09 | 50.15 |
| 2 | +−−− | 10 | 4 | 20 | 5 | 22.86 | 25.67 | 22.56 |
| 3 | −+−− | 10 | 8 | 20 | 5 | 64.58 | 65.03 | 65.39 |
| 4 | −−+− | 50 | 4 | 40 | 5 | 32.74 | 33.62 | 32.76 |
| 5 | −−−+ | 50 | 4 | 20 | 35 | 67.12 | 65.41 | 67.42 |
| 6 | ++−− | 50 | 8 | 20 | 5 | 32.17 | 31.85 | 31.05 |
| 7 | +−+− | 10 | 4 | 40 | 5 | 10.93 | 7.19 | 7.20 |
| 8 | +−−+ | 50 | 4 | 20 | 35 | 36.71 | 38.98 | 39.27 |
| 9 | −++− | 30 | 8 | 40 | 5 | 47.12 | 46.55 | 44.83 |
| 10 | −+−+ | 30 | 8 | 20 | 35 | 78.93 | 78.35 | 82.92 |
| 11 | −−++ | 30 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 45.91 | 46.94 | 47.29 |
| 12 | +++− | 30 | 8 | 40 | 5 | 12.67 | 13.37 | 12.52 |
| 13 | ++−+ | 30 | 8 | 20 | 35 | 47.88 | 45.17 | 48.02 |
| 14 | +−++ | 30 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 21.84 | 20.51 | 21.18 |
| 15 | −+++ | 30 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 59.16 | 59.86 | 59.62 |
| 16 | ++++ | 30 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 24.35 | 26.69 | 26.75 |
| 17 | 0a00 | 30 | 4 | 30 | 20 | 39.42 | 41.96 | |
| 18 | 0A00 | 30 | 8 | 30 | 20 | 56.61 | 52.36 | |
| 19 | 00a0 | 10 | 6 | 20 | 20 | 64.72 | 60.46 | |
| 20 | 00A0 | 50 | 6 | 40 | 20 | 38.58 | 41.13 | |
| 21 | 000a | 10 | 6 | 30 | 5 | 38.17 | 47.06 | |
| 22 | 000A | 10 | 6 | 30 | 35 | 73.42 | 62.82 | |
| 23 | 0000 | 10 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 56.24 | 57.49 | |
| 24 | 0000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 55.71 | 57.49 | |
| 25 | 0000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 56.98 | 57.49 | |
| 26 | 0000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 55.96 | 57.49 | |
| 27 | a000 | 10 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 78.45 | 75.89 | |
| 28 | A000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 44.81 | 45.66 |
| Source of Variation | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | ||
| Model | 5 | 6 | 6039.3931 | 8879.7938 | 1207.88 | 1479.97 | 249.6024 | 74.9481 | |
| Error | 10 | 21 | 48.3921 | 414.6776 | 4.84 | 19.75 | Prob. > F | ||
| Corrected Total | 15 | 27 | 6087.7852 | 9294.4714 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| Determination coefficients | |||||||||
| Y1 (using FFD) | Y2 (using CCD) | ||||||||
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.960 | |||||||
| R2adjusted | 0.988 | 0.943 | |||||||
| R2predicted | 0.979 | 0.925 | |||||||
| Full Factorial Design | |||||
| Source | Nparm | DF | Sum of Squares | F Ratio | Prob. > F |
| A | 1 | 1 | 3553.3521 | 675.7728 | <0.0001 * |
| B | 1 | 1 | 365.3832 | 69.4882 | <0.0004 * |
| C | 1 | 1 | 1365.6720 | 259.7221 | <0.0001 * |
| D | 1 | 1 | 709.4232 | 134.9174 | <0.0001 * |
| A*B | 1 | 1 | 45.5625 | 8.6650 | <0.0321 * |
| A*C | 1 | 1 | 4.1616 | 0.7914 | 0.4144 |
| B*C | 1 | 1 | 10.0806 | 1.9171 | 0.2248 |
| A*D | 1 | 1 | 0.3136 | 0.0596 | 0.8168 |
| B*D | 1 | 1 | 0.0650 | 0.0124 | 0.9158 |
| C*D | 1 | 1 | 7.4802 | 1.4226 | 0.2865 |
| Central Composite Design | |||||
| Source | Nparm | DF | Sum of Squares | F Ratio | Prob. > F |
| A | 1 | 1 | 4112.6404 | 171.3500 | <0.0001 * |
| B | 1 | 1 | 487.2401 | 20.3005 | <0.0006 * |
| C | 1 | 1 | 1681.2268 | 70.0470 | <0.0001 * |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1116.9113 | 46.5353 | <0.0001 * |
| B*B | 1 | 1 | 275.5755 | 11.4816 | 0.0048 * |
| C*C | 1 | 1 | 115.8299 | 4.8260 | 0.0468 * |
| A*B | 1 | 1 | 45.5625 | 1.8983 | 0.1915 |
| A*C | 1 | 1 | 4.1616 | 0.1734 | 0.6839 |
| B*C | 1 | 1 | 10.0806 | 0.4200 | 0.5282 |
| A*D | 1 | 1 | 0.3136 | 0.0131 | 0.9107 |
| B*D | 1 | 1 | 0.0650 | 0.0027 | 0.9593 |
| C*D | 1 | 1 | 7.4802 | 0.3117 | 0.5862 |
| A*A | 1 | 1 | 27.7316 | 1.1554 | 0.3020 |
| D*D | 1 | 1 | 16.8535 | 0.7022 | 0.4172 |
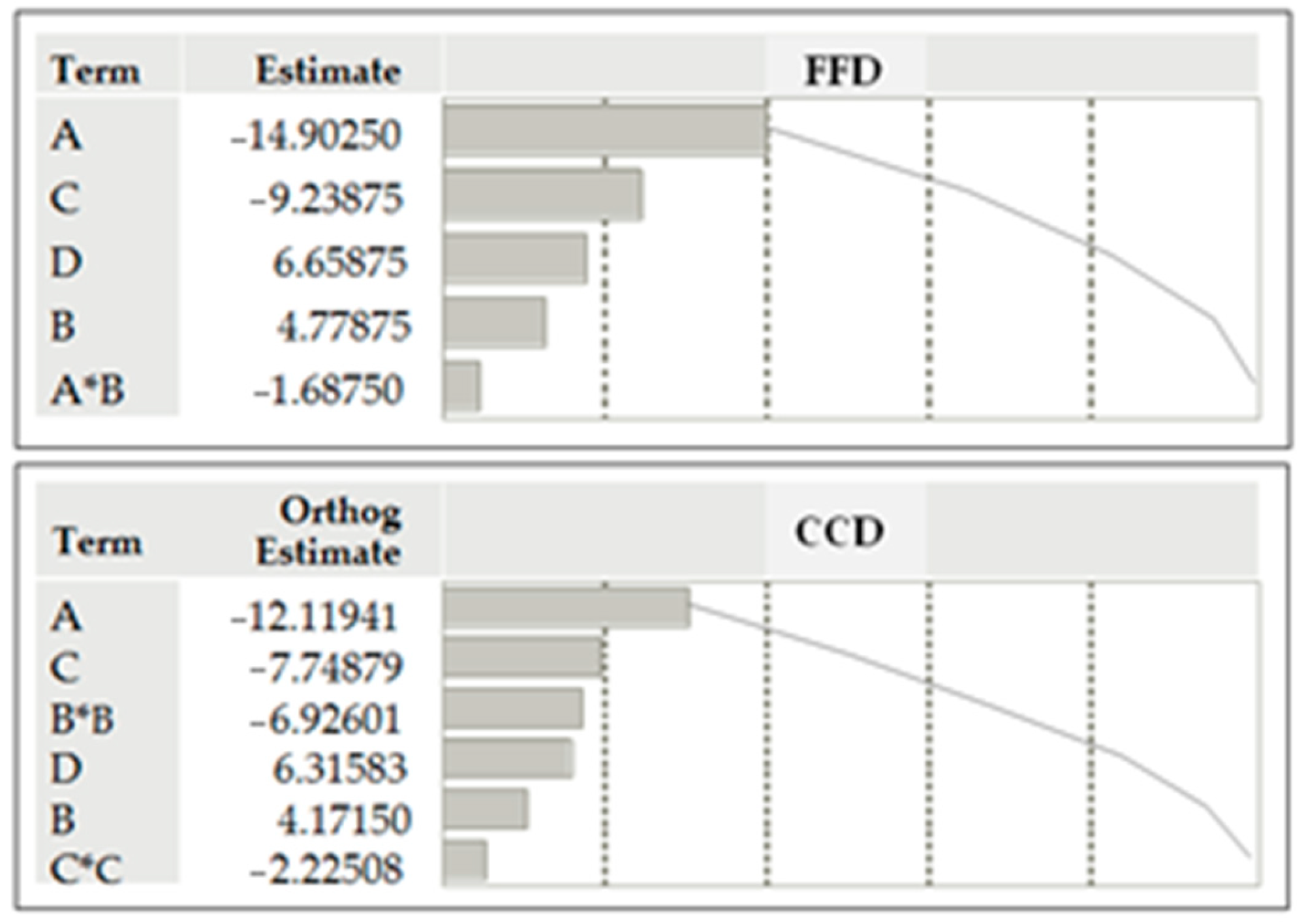
| Full Factorial Design | ||||
| Term | Estimate | Std. Error | t Ratio | Prob. > |t| |
| Intercept | 41.0787 | 0.549955 | 74.69 | <0.0001 * |
| A | −14.9025 | 0.549955 | −27.10 | <0.0001 * |
| B | 4.7787 | 0.549955 | 8.69 | <0.0001 * |
| C | −9.2387 | 0.549955 | −16.80 | <0.0001 * |
| D | 6.6587 | 0.549955 | 12.11 | <0.0001 * |
| A*B | −1.6875 | 0.549955 | −3.07 | 0.0119 * |
| Central Composite Design | ||||
| Term | Estimate | Std. Error | t Ratio | Prob. > |t| |
| Intercept | 57.5852 | 1.486101 | 38.75 | <0.0001 * |
| A | −15.1155 | 1.047392 | −14.43 | <0.0001 * |
| B | 5.2027 | 1.047392 | 4.97 | <0.0001 * |
| C | −9.6644 | 1.047392 | −9.23 | <0.0001 * |
| D | 7.8772 | 1.047392 | 7.52 | <0.0001 * |
| B*B | −10.0413 | 2.417854 | −4.15 | 0.0005 * |
| C*C | −6.4063 | 2.417854 | −2.65 | 0.0150 * |
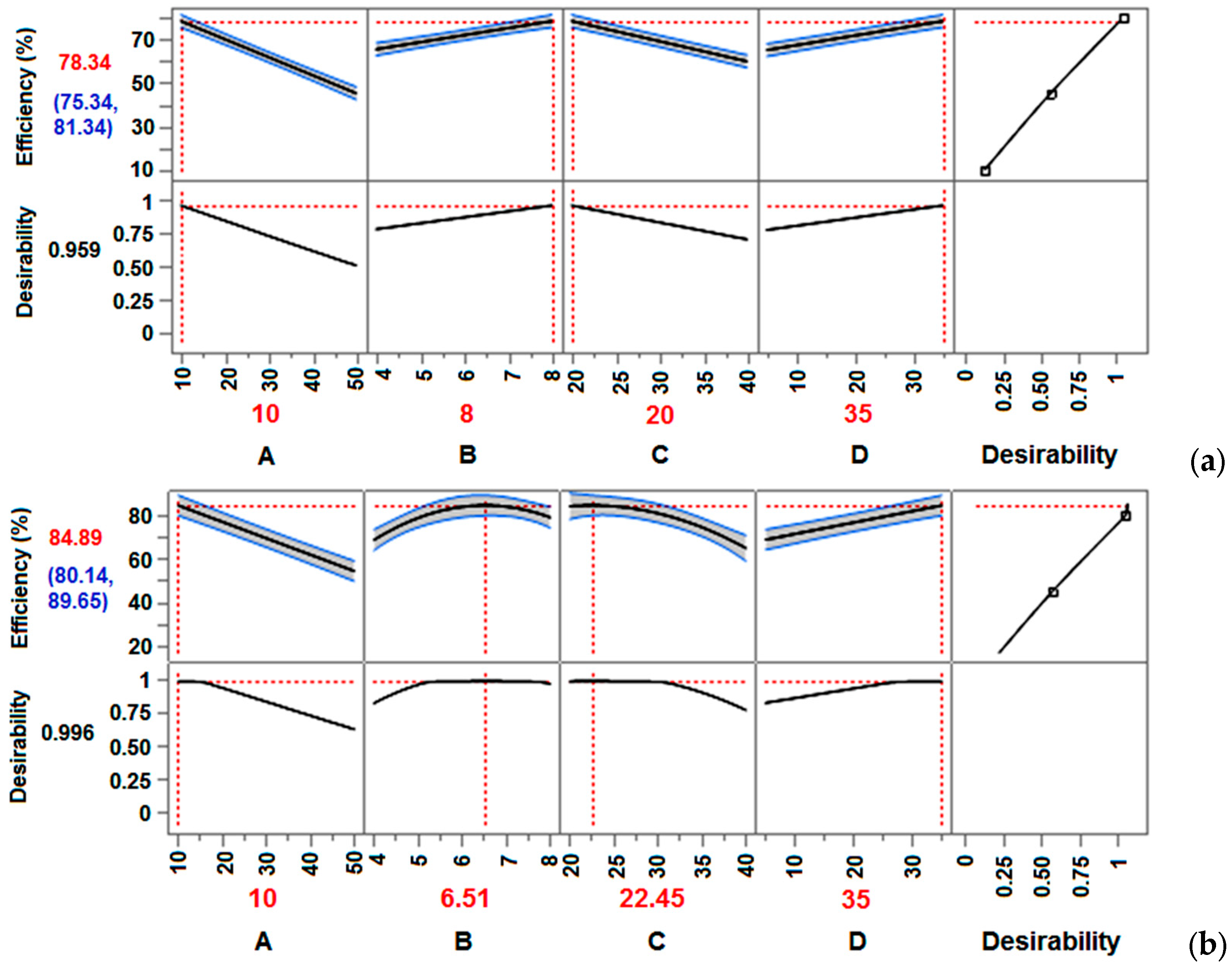
| DoE | A (C0) | B (pH) | C (T) | D (t) | Efficiency (%) | Efficiency (%) Lower CI | Efficiency (%) Upper CI | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFD | 10 | 8 | 20 | 35 | 78.345 | 75.343 | 81.347 | 0.9591 |
| CCD | 10 | 6.52 | 22.46 | 35 | 84.897 | 80.144 | 89.650 | 0.9962 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorpt. Capacity (mg/g) | Nitrate Solution (mg/L) | Temp. (°C) | pH | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halloysite | 0.54 | 100 | 17 h | Room | 5.4 | [31] |
| Wheat straw charcoal | 1.10 | 25 | 10 min | 15 | - | [32] |
| Commercial activated carbon | 1.22 | 25 | 10 min | 15 | - | [32] |
| Weak base anion exchanger Duolite A7 | 6.51 | 100 | 360 min | 25 | 5.4 | [33] |
| Cross-linked and quaternized chinese reed | 7.55 | 40 | 10 min | 25 | 5.8 | [34] |
| Modified corn-cob | 9.35 | - | - | - | - | [35] |
| Modified sunflower seed shells | 12.98 | 300 | 120 min | 25 | 7.5 | [36] |
| Strong base anion exchange resin Relite A490 | 13.02 | 100 | 360 min | 25 | 5.4 | [33] |
| Modified QLD-bentonite | 14.76 | 100 | 17 h | Room | 5.4 | [31] |
| Commercial anion exchanger Amberlite IRA-400 | 14.80 | - | - | - | - | [37] |
| Modified bambo chopstick | 16.39 | - | - | - | - | [38] |
| Impregnated almond shell activated carbon | 16–17 | 50 | 120 min | 20 | 6.2 | [39] |
| Modified CGS | 16.53 | 50 | 40 min | 23 | 6.5 | This study |
| Commercial anion exchanger Amberlite IRA-900 | 16.80 | - | - | - | - | [40] |
| Modified rice hull | 18.48 | 30 | 48 h | 30 | - | [41] |
| Modified sugarcane bagasse | 19.74 | 30 | 48 h | 30 | - | [41] |
| Modified hazelnut shells | 25.79 | - | - | - | - | [42] |
| Modified wheat residue | 29.12 | 500 | 150 min | 23 | 6.8 | [43] |
| Ammonium-functionalized mesoporous silica | 46.00 | 700 | 60 min | 5 | 8.0 | [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolić, G.S.; Simonović, N.; Durmišević, M.; Nikolić, N.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Nikolić, M.; Bogdanović, G.; Bojić, A. An Optimized Pathway for Nitrate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Environmentally Friendly Calabash Gourd Shell Adsorbent Based on Experimental Design Methodology. Separations 2025, 12, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12060139
Nikolić GS, Simonović N, Durmišević M, Nikolić N, Marković Nikolić D, Nikolić M, Bogdanović G, Bojić A. An Optimized Pathway for Nitrate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Environmentally Friendly Calabash Gourd Shell Adsorbent Based on Experimental Design Methodology. Separations. 2025; 12(6):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12060139
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolić, Goran S., Nataša Simonović, Miloš Durmišević, Nada Nikolić, Dragana Marković Nikolić, Milena Nikolić, Grozdanka Bogdanović, and Aleksandar Bojić. 2025. "An Optimized Pathway for Nitrate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Environmentally Friendly Calabash Gourd Shell Adsorbent Based on Experimental Design Methodology" Separations 12, no. 6: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12060139
APA StyleNikolić, G. S., Simonović, N., Durmišević, M., Nikolić, N., Marković Nikolić, D., Nikolić, M., Bogdanović, G., & Bojić, A. (2025). An Optimized Pathway for Nitrate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Environmentally Friendly Calabash Gourd Shell Adsorbent Based on Experimental Design Methodology. Separations, 12(6), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12060139








