Hyphenated Techniques and NMR Methods for Possible Organochlorinated Pesticides Occurrence in Human and Animal Milk
Abstract
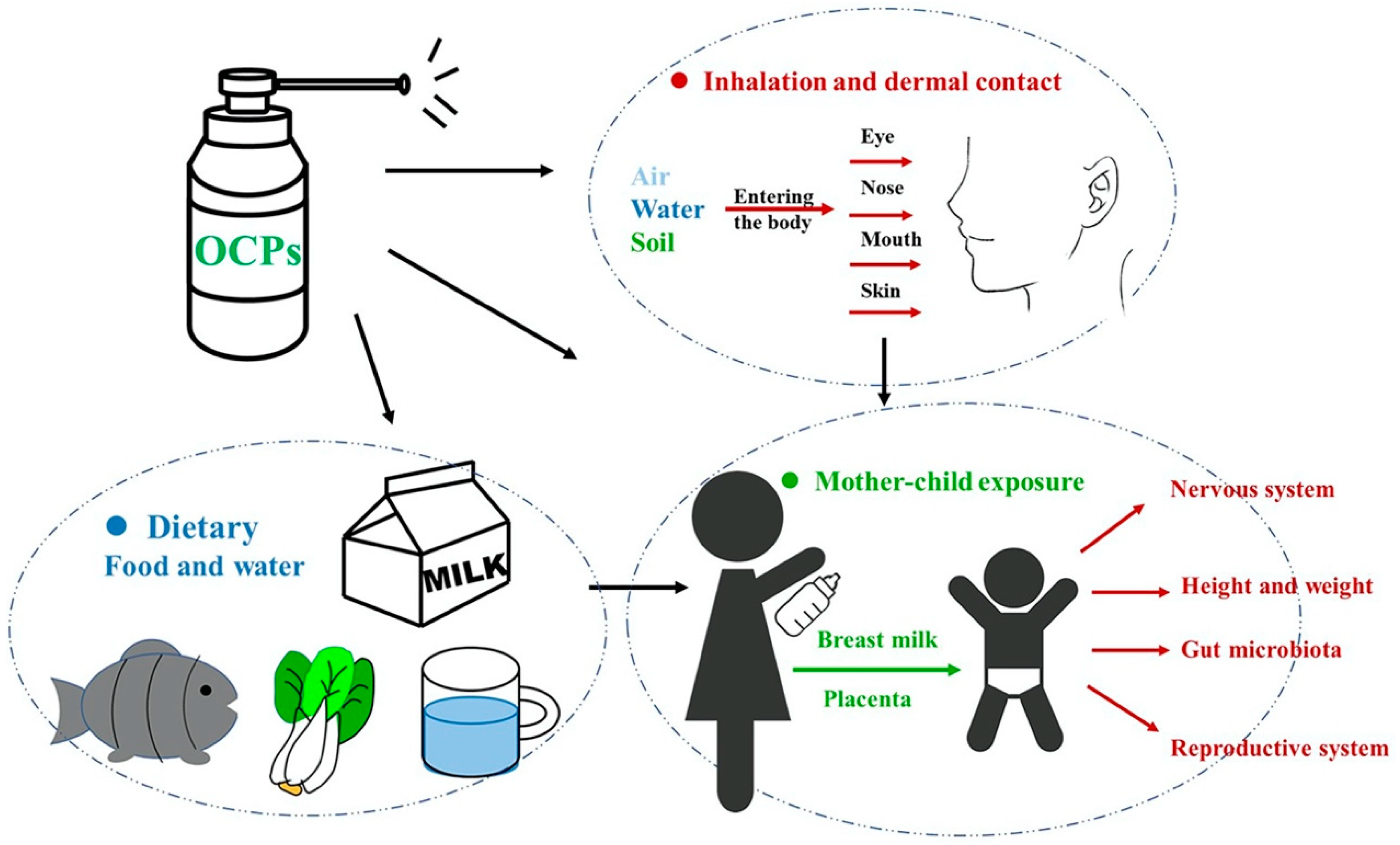
1. Introduction
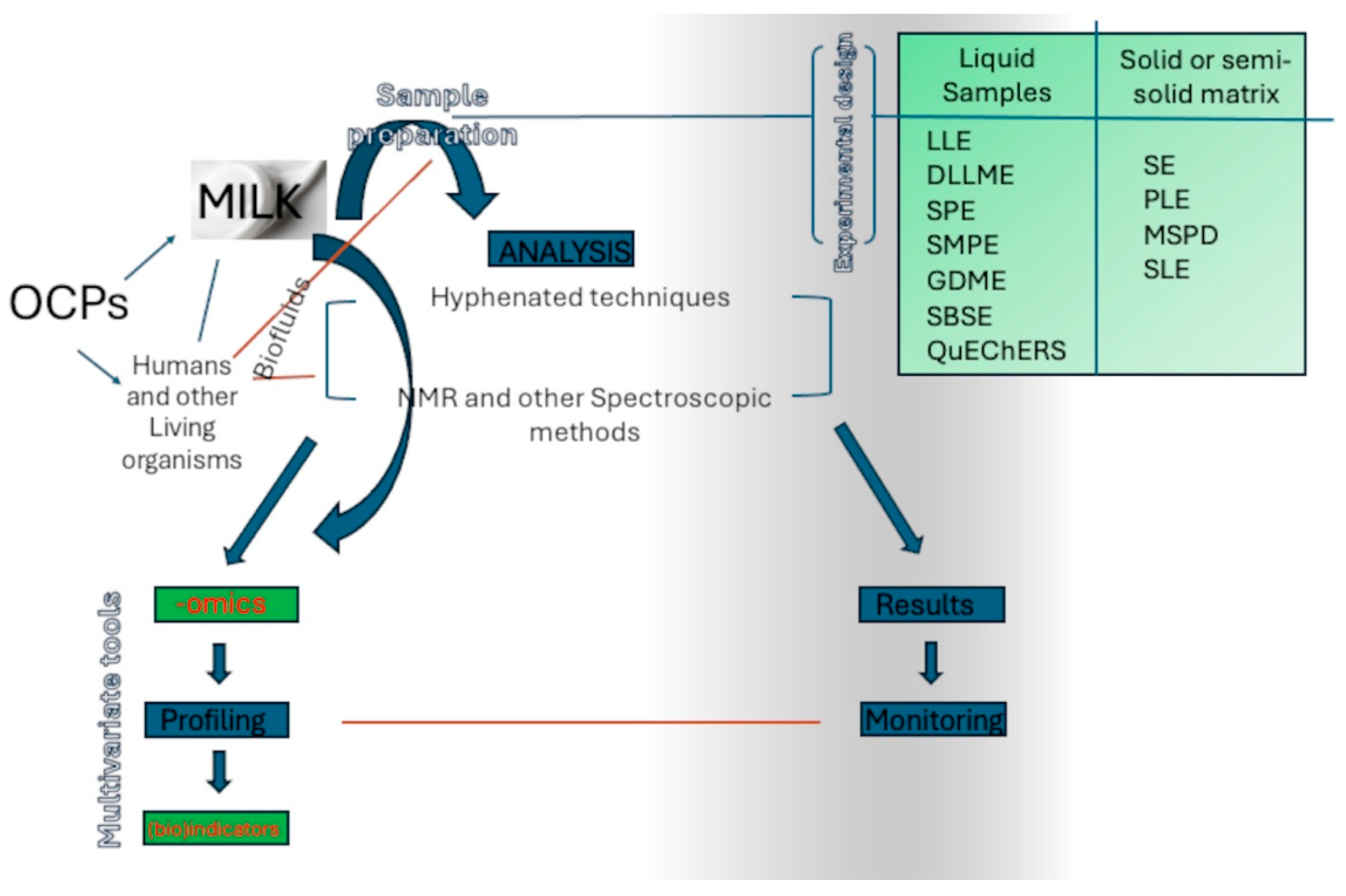
2. Overview of the Recent Studies for OCP in Both HM and AM
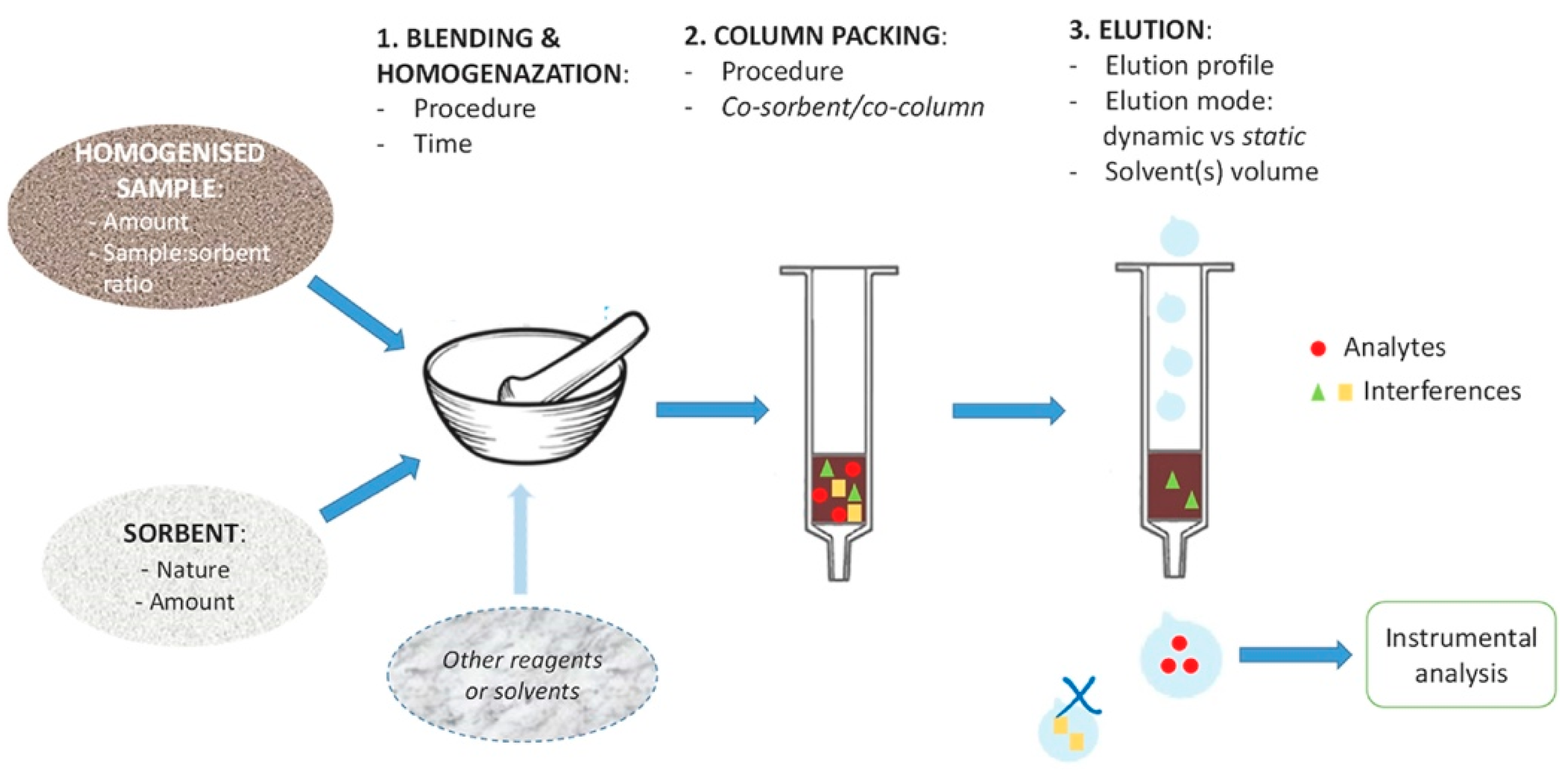
3. Methods for Sample Preparation
Method Selection Criteria for Sample Preparation
4. Extraction Methods
4.1. Liquid–Liquid Extraction (LLE)
4.2. Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction (DLLME)
4.3. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
4.4. Extraction Method Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME)
4.5. Gas-Diffusion MicroExtraction (GDME)
4.6. Stir-Bar-Sorptive Extraction (SBSE)
4.7. QuEChERS Method (QUick Easy ChEeap Robust Safe)
5. Solid or Semi-Solid Matrix
5.1. Soxhlet Extraction (SE)
5.2. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
5.3. Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion (MSPD)
5.4. Solid–Liquid Extraction (SLE)
5.5. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
6. Commenting on the Methods
Application for the Determination of OCPs in AM and HM
7. The NMR Approach—NMR and MS Metabolomics
7.1. NMR-Based Metabolomics
7.2. MS Metabolomics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saeid, M.H.; Hassanin, A.S.; Bazeyad, A.Y. Levels of pesticide residues in breast milk and the associated risk assessment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3741–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.A.; Slorach, S.A. Chemical Contaminants in Human Milk; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Tsygankov, V.Y.; Gumovskaya, Y.P.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Donets, M.M.; Koval, I.P.; Boyarova, M.D. Bioaccumulation of POPs in human breast milk from south of the Russian Far East and exposure risk to breastfed infants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5951–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.-Y.; Xu, X.-L.; Ma, W.-Z.; Deng, S.-L.; Lian, Z.-X.; Yu, K. Effects of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Maternal Body on Infants. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 890307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witczak, A.; Pohoryło, A.; Abdel-Gawad, H. Endocrine-Disrupting Organochlorine Pesticides in Human Breast Milk: Changes during Lactation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, N.; Mahdi, A.A.; Deo, S. Assessment of endocrine disrupting chemicals in breast milk: Association with dietary habits and duration of lactation. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Moreno, A.C.; Mejia-Grau, K.; Puente-DelaCruz, L.; Codling, G.; Villa, A.L.; Ríos-Marquez, O.; Patequiva-Chauta, L.; Cobo, M.; Johnson-Restrepo, B. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in human breast milk from Colombia: A probabilistic risk assessment approach. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, P.; Jain, V.; Gupta, P.; Banerjee, B.D. Organochlorine pesticide residues in maternal blood, cord blood, placenta, and breastmilk and their relation to birth size. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarne-Durán, L.; Castillero-Rosales, I.; Peinado, F.; Artacho-Cordón, F.; Molina-Molina, J.; Medianero, E.; Nicolás-Delgado, S.; Sánchez-Pinzón, L.; Núñez-Samudio, V.; Vela-Soria, F.; et al. Placental concentrations of xenoestrogenic organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls and assessment of their xenoestrogenicity in the PA-MAMI mother-child cohort. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadevosyan, N.S.; Guloyan, H.A.; Wallis, A.B.; Tadevosyan, A.E. Maternal exposure to organochlorine pesticides and anthropometrics of newborns—A hospital-based cross-sectional study in rural and urban settings in Armenia. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2023, 58, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, P.M.; La Merrill, M.A.; Krigbaum, N.Y.; Cohn, B.A. Grandmaternal Perinatal Serum DDT in Relation to Granddaughter Early Menarche and Adult Obesity: Three Generations in the Child Health and Development Studies Cohort. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prev. 2021, 30, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashnagar, A.; Naseri, N.G.; Farmad, M.C. Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in cow’s milk marketed in Ahwaz city of Iran. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2009, 1, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Helou, K.; Harmouche-Karaki, M.; Karake, S.; Narbonne, J.-F. A review of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in Lebanon: Environmental and human contaminants. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blus, L.J. Organochlorine pesticides. In Handbook of Ecotoxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 337–364. [Google Scholar]
- Tue, N.M.; Sudaryanto, A.; Minh, T.B.; Nhat, B.H.; Isobe, T.; Takahashi, S.; Viet, P.H.; Tanabe, S. Kinetic differences of legacy organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in Vietnamese human breast milk. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, A.M.; Javed, I.; Ayaz, M.; Abdullah, M.; Imran, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Gondal, T.A.; Ali, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Salehi, B.; et al. Organochlorine pesticide residues in raw milk samples collected from dairy farms and urban areas of Lahore district, Pakistan. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/163 of 18 January 2023 Amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Maximum Residue Levels for DDT and Oxathiapiprolin in or on Certain Products (Text with EEA Relevance). COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2023/163. 2023. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/163/oj (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Park, J.-W.; Jang, L.-W.; Jensen, E.C.; Stockton, A.; Kim, J. Sensing Techniques for Organochlorides through Intermolecular Interaction with Bicyclic Amidines. Biosensors 2021, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Han, A.; Hao, S.; Li, X.; Luo, X.; Fang, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. Fluorescent methylammonium lead halide perovskite quantum dots as a sensing material for the detection of polar organochlorine pesticide residues. Anal. 2020, 145, 6683–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Papaemmanouil, C.; Alivertis, D.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Miltiadou, D.; Balayssac, S.; Malet-Martino, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P. NMR-Based Μetabolomics of the Lipid Fraction of Organic and Conventional Bovine Milk. Molecules 2019, 24, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Liaggou, C.; Garoufis, A.; Magiatis, P.; Roussis, I.G. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of extra virgin olive oil: Classification through secoiridoids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1992–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, D.; Miao, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Teng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Discrepant effects of α-endosulfan, β-endosulfan, and endosulfan sulfate on oxidative stress and energy metabolism in the livers and kidneys of mice. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canlet, C.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Gautier, R.; Molina, J.; Métais, B.; Estrada, F.B.-Y.; Gamet-Payrastre, L. Specific Metabolic Fingerprint of a Dietary Exposure to a Very Low Dose of Endosulfan. J. Toxicol. 2013, 2013, 545802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ye, X.; Lei, H.; Cao, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Multiomics analyses reveal dose-dependent effects of dicofol exposure on host metabolic homeostasis and the gut microbiota in mice. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Jung, Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Hwang, G.-S. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of human plasma to examine the effect of exposure to persistent organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 307 Pt 4, 135963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, L.; Robinson, O.; Martinez, D.; Toledano, M.B.; Ibarluzea, J.; Marina, L.S.; Sunyer, J.; Villanueva, C.M.; Keun, H.C.; Vrijheid, M.; et al. Urine Metabolic Signatures of Multiple Environmental Pollutants in Pregnant Women: An Exposome Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13469–13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, E.K.; Donets, M.M.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Gumovskaya, Y.P.; Boyarova, M.D.; Anisimova, I.Y.; Koval, I.P.; Tsygankov, V.Y. Organochlorine Pollutants in Human Breast Milk from North of the Far Eastern Region of Russia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 110, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizek, O.; Gramblicka, T.; Parizkova, D.; Polachova, A.; Bechynska, K.; Dvorakova, D.; Stupak, M.; Dusek, J.; Pavlikova, J.; Topinka, J.; et al. Assessment of organohalogenated pollutants in breast milk from the Czech Republic. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 871, 161938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.L.L.; Freitas-Costa, N.; Freire, S.d.S.R.; Figueiredo, A.C.C.; Padilha, M.; Alves-Santos, N.H.; Kac, G. Association of pre-pregnancy maternal overweight/obesity and dietary intake during pregnancy with the concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in the human milk of women from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 44999–45014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.S.E.; Moreira, J.C.; Rosa, A.C.S.; Câmara, V.M.; Azeredo, A.; Asmus, C.I.R.F.; Meyer, A. Persistent Organic Pollutant Levels in Maternal and Cord Blood Plasma and Breast Milk: Results from the Rio Birth Cohort Pilot Study of Environmental Exposure and Childhood Development (PIPA Study). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguos, C.L.; Suárez, O.L.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; Couce, M.L. Postnatal exposure to organic pollutants in maternal milk in north-western Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonen, S.; Ambelu, A.; Wondafrash, M.; Kolsteren, P.; Spanoghe, P. Exposure of infants to organochlorine pesticides from breast milk consumption in southwestern Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, S.; Akkaya, H.; Daglioglu, N.; Eyuboglu, S.; Atasayan, O.; Mete, F.; Colak, C.; Sandal, S.; Yilmaz, B. Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in breast milk samples and their correlation with dietary and reproductive factors in lactating mothers in Istanbul. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, L.; Hou, Y.; Huang, F.; Guo, A.; Deng, W.; Sun, H.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Hong, H. Pesticides in human milk collected from Jinhua, China: Levels, influencing factors and health risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhaj, F.A.; Elhamri, H.; Lhaj, Z.A.; Malisch, R.; Kypke, K.; Kabriti, M.; El Hajjaji, S.; Bellaouchou, A. First WHO/UNEP survey of the current concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in human milk in Morocco. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2023, 40, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardebusch, B.; Polley, J.; Dambacher, B.; Kypke, K.; Lippold, R. Analysis and Quality Control of WHO- and UNEP-Coordinated Human Milk Studies 2000–2019: Organochlorine Pesticides and Industrial Contaminants. In Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Milk; Fürst, P., Malisch, R., Šebková, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 109–144. [Google Scholar]
- Malisch, R.; Kypke, K.; Dambacher, B.; Hardebusch, B.; Lippold, R.; van Leeuwen, F.X.R.; Moy, G.; Tritscher, A. WHO- and UNEP-Coordinated Exposure Studies 2000–2019: Findings of Organochlorine Pesticides and Industrial Chemicals. In Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Milk; Malisch, R., Fürst, P., Šebková, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 249–297. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, R.C.; Portella, R.B.; Almeida, P.V.N.B.; Pinto, C.O.; Gubert, P.; da Silva, J.D.S.; Nakamura, T.C.; Rego, E.L.D. Human milk contamination by nine organochlorine pesticide residues (OCPs). J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Luo, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Mei, S.; Zhang, G. Levels and profiles of persistent organic pollutants in breast milk in China and their potential health risks to breastfed infants: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 753, 142028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olisah, C.; Okoh, O.O.; Okoh, A.I. Occurrence of organochlorine pesticide residues in biological and environmental matrices in Africa: A two-decade review. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-C.; Que, D.E.; Bongo, S.J.; Tayo, L.L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Lin, S.-L.; Gou, Y.-Y.; Hsu, W.-L.; Shy, C.-G.; et al. Residue Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Breast Milk and Its Associations with Cord Blood Thyroid Hormones and the Offspring’s Neurodevelopment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, S.; Mahdavi, V.; Gordan, H.; Rezadoost, H.; Conti, G.O.; Khaneghah, A.M. Determination of multi-class pesticides residues of cow and human milk samples from Iran using UHPLC-MS/MS and GC-ECD: A probabilistic health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, S.; Qadir, A.; Mumtaz, M.; Evans, N.P.; Ahmad, S.R. Spatial trends and human health risks of organochlorinated pesticides from bovine milk; a case study from a developing country, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnolo, A.; Clausi, M.; Mercogliano, R.; Fusco, G.; Fiorentino, M.; Buono, F.; Lama, A.; Ferrante, M. Levels of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in donkey milk: Correlation with the infection level by intestinal strongyles. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, M.E.; Beduk, F.; Ulvi, A. Organohalogenated pollutants in raw and UHT cow’s milk from Turkey: A risk assessment of dietary intake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12788–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, S.; Akkaya, L.; Gök, V.; Konuk, M. Organochlorine pesticide (OCP) residues in cow’s, buffalo’s, and sheep’s milk from Afyonkarahisar region, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 181, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadevosyan, A.; Reynolds, S.J.; Kelly, K.M.; Fuortes, L.; Mairapetyan, A.; Tadevosyan, N.; Petrosyan, M.; Beglaryan, S. Organochlorine pesticide residues in breast milk in Armenia. J. Pre-Clin. Clin. Res. 2007, 1, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Keswani, C.; Dilnashin, H.; Birla, H.; Roy, P.; Tyagi, R.K.; Singh, D.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Singh, S.P. Global footprints of organochlorine pesticides: A pan-global survey. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.G.; Chávez, A.A.; Waliszewski, S.M.; Cruz, A.C.; Fabila, M.M.G. Extraction and clean-up methods for organochlorine pesticides determination in milk. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Chang, G.; Sun, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Post-synthetic modification of covalent organic framework for efficient adsorption of organochlorine pesticides from cattle’s milk. Food Chem. 2023, 439, 138182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Gómez, A.S. Rubio, and D. Pérez-Bendito, Analytical methods for the determination of bisphenol A in food. J. Chrom. A 2009, 1216, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert-López, B.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Sample treatment and determination of pesticide residues in fatty vegetable matrices: A review. Talanta 2009, 79, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Maštovská, K.; Yun, S.J. Evaluation of Two Fast and Easy Methods for Pesticide Residue Analysis in Fatty Food Matrixes. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, A.; Cummins, W.; Connolly, D. Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction in the Analysis of Milk and Dairy Products: A Review. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4040165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Pawliszyn, J. Analysis of Environmental Air Samples by Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography/Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanfar, N.; Yamini, Y.; Ghambarian, M. Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Water and Fruit Samples. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, E.C.P.D.; Guimarães, E.d.F.; dos Santos, A.L.M.; Mothé, E.d.S.M.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Netto, A.D.P. The validation of a new high throughput method for determination of chloramphenicol in milk using liquid–liquid extraction with low temperature partitioning (LLE-LTP) and isotope-dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (ID-LC-MS/MS). Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.J. Principles of Extraction and the Extraction of Semivolatile Organics from Liquids. In Sample Preparation Techniques in Analytical Chemistry; Mitra, S., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 37–138. [Google Scholar]
- Oyekunle, J.A.O.; Adekunle, A.S.; Adewole, A.M.; Elugoke, S.E.; Durodola, S.S.; Oyebode, B.A. Determination of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Some Evaporated Milk Samples in Nigeria Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Afr. 2021, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinčić, D.; Romanić, S.H.; Sarić, M.M.; Grzunov, J.; Dukić, B. Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in human milk samples from two regions in Croatia. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoli-Diva, M.; Taherimaslak, Z.; Allahyari, M.; Pourghazi, K.; Manafi, M.H. Application of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with vortex-assisted hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticles based solid-phase extraction for determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples by sensitive micelle enhanced spectrofluorimetry. Talanta 2015, 134, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Albanis, T.A. Liquid-phase micro-extraction techniques in pesticide residue analysis. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 195–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, L.; He, X.; Wang, S. Analysis of Additives in Milk Powders with SPE-HPLC or 2D-HPLC Method. In Milk Production, Processing and Marketing; Khalid, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y. Multiresidue analysis of 30 organochlorine pesticides in milk and milk powder by gel permeation chromatography-solid phase extraction-gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6016–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Pawliszyn, J. A critical review in calibration methods for solid-phase microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Panigrahi, S. Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) Techniques for Quality Characterization of Food Products: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risticevic, S.; Vuckovic, D.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-Phase Microextraction. In Handbook of Sample Preparation; Pawliszyn, J., Lord, H.L., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 81–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Ortega, A.; Sampedro, M.; Unceta, N.; Goicolea, M.; Barrio, R. Solid-phase microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography using on-line diode-array and electrochemical detection for the determination of fenitrothion and its main metabolites in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1094, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsi, C.S.; Albanis, T.A. Optimization of headspace solid-phase microextraction conditions for the determination of organophosphorus insecticides in olive oil. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2004, 84, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsi, C.; Konstantinou, I.; Hela, D.; Albanis, T. Screening method for organophosphorus insecticides and their metabolites in olive oil samples based on headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573–574, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.Y.; Recepoğlu, Y.K.; Khataee, A. Chapter 4—Language of response surface methodology as an experimental strategy for electrochemical wastewater treatment process optimization. In Artificial Intelligence and Data Science in Environmental Sensing; Asadnia, M., Razmjou, A., Beheshti, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 57–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hanrahan, G.; Zhu, J.; Gibani, S.; Patil, D.G. Chemometrics and Statistics|experimental Design. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed.; Worsfold, P., Townshend, A., Poole, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Merib, J.; Nardini, G.; Carasek, E. Use of Doehlert design in the optimization of extraction conditions in the determination of organochlorine pesticides in bovine milk samples by HS-SPME. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3254–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tağaç, A.A.; Erdem, P.; Bozkurt, S.S.; Merdivan, M. Utilization of montmorillonite nanocomposite incorporated with natural biopolymers and benzyl functionalized dicationic imidazolium based ionic liquid coated fiber for solid-phase microextraction of organochlorine pesticides prior to GC/MS and GC/ECD. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1185, 339075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Alvarez, M.; Llompart, M.; Lamas, J.P.; Lores, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Cela, R.; Dagnac, T. Development of a solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography with microelectron-capture detection method for a multiresidue analysis of pesticides in bovine milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 617, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.M.; Magalhães, P.J.; Valente, I.M.; Pacheco, J.G.; Dostálek, P.; Sýkora, D.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Barros, A.A. Analysis of aldehydes in beer by gas-diffusion microextraction: Characterization by high-performance liquid chromatography–diode-array detection–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3717–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, J.G.; Valente, I.M.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Barros, A.A. Gas-diffusion microextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, A.; Fernandes, V.C.; Pacheco, J.G.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Gonçalves, L.M. Organochlorine pesticide analysis in milk by gas-diffusion microextraction with gas chromatography-electron capture detection and confirmation by mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1636, 461797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, European. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 839/2008. 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32008R0839 (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- David, F.; Sandra, P. Stir bar sorptive extraction for trace analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.-J.; Wang, Y.-B.; Su, Q.; Wu, L. Hollow Fiber–Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry for Determination of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Environmental and Food Matrices. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Štajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.-S.; Kwak, B.-M.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H. Determination of pesticide residues in milk using a QuEChERS-based method developed by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Gridneva, Z.; Gay, M.C.; Trengove, R.D.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T. Pesticides in human milk of Western Australian women and their influence on infant growth outcomes: A cross-sectional study. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, K.; Kalenik, T.K.; Piekoszewski, W. Sample preparation and determination of pesticides in fat-containing foods. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bascón, M.A.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Chapter 11—Soxhlet Extraction. In Liquid-Phase Extraction; Poole, C.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 327–354. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro, L.; Priego-Capote, F. Soxhlet extraction: Past and present panacea. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.L.; del Nozal, M.J.; Jiménez, J.J. Use of a high-pressure Soxhlet extractor for the determination of organochlorine residues by gas chromatography. Chromatographia 1992, 34, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak, A.; Abdel-Gawad, H. Assessment of health risk from organochlorine pesticides residues in high-fat spreadable foods produced in Poland. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2014, 49, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, V.; Dell’oRo, D.; Palermo, C.; Centonze, D. Multi-residue method for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in fish feed based on a cleanup approach followed by gas chromatography–triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4996–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetto, R.; León, A.; Burguera, J.; Burguera, M. Levels of DDT residues in human milk of Venezuelan women from various rural populations. Sci. Total. Environ. 1996, 186, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, G.; González, G.D.; Tolentino, R.G.; León, S.V.; Pérez, M.N.; García, E.C. Residuos de plaguicidas organoclorados en leche de cabra de Querétaro, Querétaro, México. Vet. México 2007, 28, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Wu, Y.; Yin, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, X. National survey of the levels of persistent organochlorine pesticides in the breast milk of mothers in China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, Y.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Pressurized liquid extraction of organic contaminants in environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Rivera, G.; Bueno, M.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E. Pressurized Liquid Extraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barp, L.; Višnjevec, A.M.; Moret, S. Pressurized Liquid Extraction: A Powerful Tool to Implement Extraction and Purification of Food Contaminants. Foods 2023, 12, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.W.; Chen, B.L. Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in fatty foods: A critical review on the analytical methods and their testing capabilities. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5555–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezcua, M.; Repetti, M.R.; Agüera, A.; Ferrer, C.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Determination of pesticides in milk-based infant formulas by pressurized liquid extraction followed by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Pressurized liquid extraction of organic contaminants in environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchan, P.; Pulkrabová, J.; Hajšlová, J.; Kocourek, V. Pressurized liquid extraction in determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in fish samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 520, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.A.; Long, A.R.; Short, C.R. Isolation of drug residues from tissues by solid phase dispersion. J. Chromatogr. A 1989, 475, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe, C.; Bayarri, S.; Lázaro, R.; Conchello, P.; Ariño, A.; Herrera, A. Multiresidue Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Milk by Gas Chromatography with Electron-Capture Detection after Extraction by Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion. J. AOAC Int. 2001, 84, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.A. Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD). J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Du, W.; Zheng, P.; Guo, P.; Wu, N.; Tang, W.; Zeng, A.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Molecularly imprinted polymer cartridges coupled to liquid chromatography for simple and selective analysis of penicilloic acid and penilloic acid in milk by matrix solid-phase dispersion. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.; Chen, W. A Review on the Recent Progress in Matrix Solid Phase Dispersion. Molecules 2018, 23, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, L. Current trends in the determination of organic compounds in foodstuffs using matrix solid phase dispersion. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 172, 117601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L. Use of new tailored and engineered materials for matrix solid-phase dispersion. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, N. A toxic reagent-free method for normal-phase matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and reversed-phase liquid chromatographic determination of aldrin, dieldrin, and DDTs in animal fats. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 2004–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, F.J.; Wagner, R. Screening procedure for organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticide residues in milk using matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD) extraction and gas chromatographic determination. Food Addit. Contam. 1995, 12, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.M.; Torres, M.J.; Frenich, A.G.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Olea, N. Determination of organochlorine compounds in human biological samples by GC-MS/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzler, K.; Salgó, A.; Valkó, K. Microwave extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 1986, 371, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, D.; Beccaria, M.; Cordero, C.E.; Purcaro, G. Microwave-assisted extraction in closed vessel in food analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2300390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Ren, N. Recent advances in microwave-assisted extraction of trace organic pollutants from food and environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 75, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro-Gonzalez, E.; Gonzalez-Castro, M.J.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Lopez-Mahia, P.; Prada-Rodriguez, D. Analytical methodology for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in vegetation. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1291–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, A.C.; Ruiz-Aceituno, L.; Ramos, L.; Sanz, L.M. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Polysaccharides. In Polysaccharides: Bioactivity and Biotechnology; Ramawat, K.G., Mérillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Eskilsson, C.S.; Björklund, E. Analytical-scale microwave-assisted extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 902, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummert, K.; Vetter, W.; Luckas, B. Fast and effective sample preparation for determination of organochlorine compounds in fatty tissue of marine mammals using microwave extraction. Chromatographia 1996, 42, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichbrodt, M.; Vetter, W.; Luckas, B. Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Accelerated Solvent Extraction with Ethyl Acetate–Cyclohexane before Determination of Organochlorines in Fish Tissue by Gas Chromatography with Electron-Capture Detection. J. AOAC Int. 2000, 83, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.d.A.; Lopes, A.S.d.C.; de Souza, L.C.; Lima, M.d.O.; Santos, L.d.S. DDT concentration in fish from the Tapajós River in the Amazon region, Brazil. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paré, J.J.; Matni, G.; Bélanger, J.M.; Li, K.; Rule, C.; Thibert, B.; Yaylayan, V.; Liu, Z.; Mathé, D.; Jacquault, P. Use of the Microwave-Assisted Process in Extraction of Fat from Meat, Dairy, and Egg Products under Atmospheric Pressure Conditions. J. AOAC Int. 1997, 80, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, E.-N.; Kyrgidou, A.; Vryzas, Z.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Development of a Microwave-Assisted Extraction Method for the Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Mussel Tissue. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkowska, A.M.; Biziuk, M. Rapid Method for the Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and PCBs in Fish Muscle Samples by Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Analysis of Extracts by GC-ECD. J. AOAC Int. 2010, 93, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriada-Pereira, M.; Iglesias-García, I.; Gonzlez-Castro, M.J.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; López-Maha, P.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Microwave-Assisted Extraction in the Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Fish Muscle Samples. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, N.; Su, S.; Shen, G.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, W.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Freeze drying reduces the extractability of organochlorine pesticides in fish muscle tissue by microwave-assisted method. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 191, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvoršćak, M.; Jagić, K.; Besednik, L.; Šimić, I.; Klinčić, D. First application of microwave-assisted extraction in the analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human milk. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Lau, H.F.; Law, W.S.; Li, S.F.Y. Systematic optimisation of coupled microwave-assisted extraction-solid phase extraction for the determination of pesticides in infant milk formula via LC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Powers, R.; Raftery, D.; Wishart, D.S. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Everett, J.R. NMR Spectroscopy of Biofluids. In Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy; Webb, G.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bingol, K.; Brüschweiler, R. Knowns and unknowns in metabolomics identified by multidimensional NMR and hybrid MS/NMR methods. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingol, K.; Brüschweiler, R. Two elephants in the room: New hybrid nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry approaches for metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Q.; Miao, X.; Fan, T.; Meng, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W. Study on toxicity effects of environmental pollutants based on metabolomics: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erich, S.; Schill, S.; Annweiler, E.; Waiblinger, H.-U.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Monakhova, Y.B. Combined chemometric analysis of 1H NMR, 13C NMR and stable isotope data to differentiate organic and conventional milk. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Meng, X.; Pang, X.; Liu, Y.; Frew, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, G. The application of NMR-based milk metabolite analysis in milk authenticity identification. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girelli, C.R.; Del Coco, L.; Zelasco, S.; Salimonti, A.; Conforti, F.L.; Biagianti, A.; Barbini, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. Traceability of “Tuscan PGI” Extra Virgin Olive Oils by 1H NMR Metabolic Profiles Collection and Analysis. Metabolites 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostara, C.E.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Bairaktari, E.T.; Tsimihodimos, V. Altered RBC membrane lipidome: A possible etiopathogenic link for the microvascular impairment in Type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lolli, V.; Caligiani, A. How NMR contributes to food authentication: Current trends and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2024, 58, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, B.; Righetti, L.; Caligiani, A.; Tedeschi, T.; Cirlini, M.; Galaverna, G.; Sforza, S. Chapter Six—Assessing food authenticity through protein and metabolic markers. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Toldrá, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 233–274. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, P.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, H. Recent advances in the application of metabolomics for food safety control and food quality analyses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1448–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Li, X.; Petriello, M.C.; Wang, C.; Morris, A.J.; Hennig, B. Application of metabolomics to characterize environmental pollutant toxicity and disease risks. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.H.; Amri, I.N.; Rahmat, C.M.C.; Nu’MAn, A.H.; Hasliyanti, A.; Rohaya, M.H. Potential of nuclear magnetic resonance for the determination of organochlorine in edible oils. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 122, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, T.; Campas, M.; Matta, K.; Ouzia, S.; Guitton, Y.; Duval, G.; Ploteau, S.; Marchand, P.; Le Bizec, B.; Freour, T.; et al. A comprehensive multiplatform metabolomic analysis reveals alterations of 2-hydroxybutyric acid among women with deep endometriosis related to the pesticide trans-nonachlor. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 918, 170678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Giannetto, A.; Parrino, V.; De Marco, G.; Mauceri, A.; Maisano, M.; Cappello, T.; Giannetto, A.; Parrino, V.; De Marco, G.; et al. Food safety using NMR-based metabolomics: Assessment of the Atlantic bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus, from the Mediterranean Sea. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, T.; Chen, S.; Sun, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Sun, R.; Hang, B.; et al. Metabolomics study and meta-analysis on the association between maternal pesticide exposome and birth outcomes. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fang, S.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, C.; Ouyang, G. Combined effect of microplastics and DDT on microbial growth: A bacteriological and metabolomics investigation in Escherichia coli. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolmarans, N.J.; Bervoets, L.; Meire, P.; Wepener, V. Sub-lethal exposure to malaria vector control pesticides causes alterations in liver metabolomics and behaviour of the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 251, 109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihovic, S.; Ganna, A.; Fall, T.; Broeckling, C.D.; Prenni, J.E.; van Bavel, B.; Lind, P.M.; Ingelsson, E.; Lind, L. The metabolic fingerprint of p,p′-DDE and HCB exposure in humans. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Extraction Method | Pros | Cons | Type of Milk 1 | Selected Citations for Application for OCPs in Milk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid matrix | ||||
| LLE |
|
| AΜ | [61] |
| SPE |
|
| AΜ | [66] |
| SPME |
|
| HM AM | [34] [77] |
| GDME |
|
| HM | [80] |
| SBSE |
|
| RM | [83] |
| QuEChERS |
|
| HM | [34] |
| Solid or semi-solid matrix | ||||
| SE |
|
| HM | [95] |
| PLE |
|
| ||
| MSPD |
|
| ||
| SLE |
|
| ||
| MAE |
|
| ||
| Technique(s) Used † | MS Apparatus and/or Ionization Mode | Sample Preparation †† | Matrix | OCP Used for Method Development/Application | LOD/LOQ (mg kg−1) | Monitoring/Measurement in Milk Samples (Number of Samples/Number of OCPs above LOD) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC-MS | (a) | LLE | HM | -HCH, β-HCH, γ-HCH, d-HCH, Heptachlor, Heptachlor epoxide, Aldrin, Dieldrin, Endosulfan I, Endosulfan II, Endosulfan sulfate, p,p′-DDD, p,p′-DDE, p,p′-DDT, Endrin, Endrin aldehyde | Six samples/eighteen OCPs for method/three major classes of OCPs detected | [61] | |
| UHPLC-MS/MS and GC-ECD | triple quadrupole mass analyzer | QuEChERS and SPE | HM and AM | Fifteen OCPs for method development/ p,p′-DDT, and p,p′-DDD, p,p′-DDE | 0.00015–0.0009/0.0005–0.001 | Thirty-five commercial and fifteen raw milk samples/p,p′ DDE above MRL (FAO and WHO) in three human milk samples, other two OCPs below MRL | [44] |
| GC-ECD | SPE | M and PM | Sixteen OCPs and metabolites (α-chlordane, methoxychlor, γ-chlordane, endrin ketone, aldrin, α-lindane, β-lindane, γ-lindane, δ-lindane, 4,4′- DDD, 4,4′-DDE, 4,4′-DDT, dieldrin, endosulfan I, endosulfan II, endosulfan sulfate, endrin, heptachlor, heptachlor epoxide isomer B). | 0.010–0.52/0.003–0.16 ng mL−1 | Thirty-five raw milk samples/chlordane at 1 ng mL−1 at one sample | [77] | |
| GC-ECD and GC-MS | Ion Trap Mass Detector in SIM and MS/MS mode | GDME | HM | α- and β-hexachlorocyclohexane, lindane, hexachlorobenzene, p,p-DDE, aldrin, dieldrin, and α-endosulfan | LODs: from 3.7 to 4.8 μg L−1 | Six milk samples /Aldrin in one sample below the LOD | [80] |
| GC-MS | Electron Ionization/SIM mode | HF-SBSE | RM | α-BHC β-BHC γ-BHC δ-BHC p,p′-DDE p,p′-DDD o,p′-DDT p,p′-DDΤ | LOD: 0.0003 to 0.0030 (μg mL−1 )/LOQ: 0.0010 to 0.0090 (μg mL−1 ) | (b)/p,p′-DDE detected, but could not be quantified, p,p′-DDD and p,p′-DDΤ at 0.100 mg kg−1 (each of them) | [83] |
| GC-ECD | QuEChERS followed by dispersed SPE | HM | DDT, p,p′-DDE, p,p-DDD, o,p-DDT, p,p′-DDT, aldrin, dieldrin, endosulfan α, hexachlorobenzene | LOD: 0.018–0.078 µg g−1 milk fat /LOQ: 0.062 to 2.38 µg g−1 milk fat | 447 (at three sampling times)/only DDT and its metabolites were detected, total DDT concentrations at baseline (1st month), midline (6th month), and end line (12th months) were 2.25, 1.68 and 1.32 μg g−1 milk fat, respectively. | [34] | |
| GC-NCI-MS | negative chemical ionization-mass spectrometry | SE | HM | α-HCH, β-HCH, γ-HCH (lindane), δ-HCH, p,p′-DDT, o,p′-DDT, p,p′-DDE, o,p′-DDE, p,p′-DDD, o,p′-DDD, HCB, aldrin, di eldrin, endrin, trans-chlordane, trans-nonachlor, cis-nonachlor oxychlordane, heptachlor, trans-heptachlor epoxide, cis-heptachlor epoxide, mirex | LOD: 0.00 to 1660 ng g−1 lipid | Twenty-four pooled samples (from 1237 milk samples)/DDTs (from 153.6 ng g−1 to 1756.3 ng g−1 lipid), HCHs (from 55.8 ng g−1 to 536.4 ng g−1 lipid) and HCB (from 18.4 ng g−1 to 56.8 ng g−1 lipid) detectable in every pooled sample; CHLs (from 6.1 ng g−1 to 25.2 ng g−1 lipid), drins (from 7.9 ng g−1 to 21.8 ng g−1 lipid), and mirex (from not detected to 21.8 ng g−1 lipid) detected in 75.0%, 29.2% and 20.8% of samples, respectively | [95] |
| GC/MS and LC/MS/MS | EI/SIM mode (mainly) LC/MS: triple quadrupole using electrospray ionization. | QuEChERS and MSPD | M | Chlordane, DDE, dieldrin, endosulfan sulfate, heptachlor epoxide and lindane | (b) | [55] | |
| GC-ECD | MSPD | UHTM | 22 OCPs (HCB, α-HCH, β-HCH, γ-HCH, aldrin, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, heptachlor epoxide, α-chlordane, γ- chlordane, α-chlordene, trans-nonachlor, α-endosulfan, β- endosulfan, endosulfan sulfate, o,p′-DDD, p,p′-DDD, o,p′-DDE, p,p′-DDE, o,p′-DDT, p,p′-DDT | Detection limit: from 0.02 to 0.1 μg L−1/LOQs: from 0.02 μg L−1 to 0.58 μg L−1 | Twenty-five milk samples/HCB at 0.6 μg L−1 | [104] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thanou, E.D.; Tsiafoulis, C.G. Hyphenated Techniques and NMR Methods for Possible Organochlorinated Pesticides Occurrence in Human and Animal Milk. Separations 2024, 11, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100282
Thanou ED, Tsiafoulis CG. Hyphenated Techniques and NMR Methods for Possible Organochlorinated Pesticides Occurrence in Human and Animal Milk. Separations. 2024; 11(10):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100282
Chicago/Turabian StyleThanou, Eleni D., and Constantinos G. Tsiafoulis. 2024. "Hyphenated Techniques and NMR Methods for Possible Organochlorinated Pesticides Occurrence in Human and Animal Milk" Separations 11, no. 10: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100282
APA StyleThanou, E. D., & Tsiafoulis, C. G. (2024). Hyphenated Techniques and NMR Methods for Possible Organochlorinated Pesticides Occurrence in Human and Animal Milk. Separations, 11(10), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100282






