Headspace Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction Method Optimization and Evaluation for the Volatile Compound Extraction of Bronchoalveolar Lung Lavage Fluid Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects and Specimen Collection
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. HS-SPME Method Optimization
2.3.1. Optimization of Vial Size, Dilution Factor, Extraction Time, Extraction Temperature, and Salt Concentration
2.3.2. HS-SPME Method Evaluation
2.4. Sample Instrumental Analysis
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HS-SPME Method Optimization
3.1.1. Optimization of Vial Size
3.1.2. The Effect of Dilution
3.1.3. Optimization of Extraction Time and Temperature
3.1.4. The Effect of Salt Addition
3.2. Method Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lancioni, C.; Castells, C.; Candal, R.; Tascon, M. Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction: Fundamentals and Recent Advances. Adv. Sample Prep. 2022, 3, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid Phase Microextraction with Thermal Desorption Using Fused Silica Optical Fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risticevic, S.; Lord, H.; Górecki, T.; Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Protocol for Solid-Phase Microextraction Method Development. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalikas, C.; Fiamegos, Y.; Sakkas, V.; Albanis, T. Developments on Chemometric Approaches to Optimize and Evaluate Microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrubini, G.; Dugheri, S.; Cappelli, G.; Arcangeli, G.; Mucci, N.; Appelblad, P.; Melzi, C.; Speltini, A. Experimental Designs for Solid-Phase Microextraction Method Development in Bioanalysis: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1119, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risticevic, S.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-Phase Microextraction in Targeted and Nontargeted Analysis: Displacement and Desorption Effects. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8987–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.; Pawliszyn, J. SPME in Environmental Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Roszkowska, A.; Pawliszyn, J. In Vivo Solid-Phase Microextraction and Applications in Environmental Sciences. ACS Environ. Au 2022, 2, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkle, S.; Kleeberg, K.; Fritsche, J. Recent Developments and Applications of Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME) in Food and Environmental Analysis—A Review. Chromatography 2015, 2, 293–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Silva, É.A.; Gionfriddo, E.; Pawliszyn, J. A Critical Review of the State of the Art of Solid-Phase Microextraction of Complex Matrices II. Food Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojko, B.; Reyes-Garcés, N.; Bessonneau, V.; Goryński, K.; Mousavi, F.; Souza Silva, E.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-Phase Microextraction in Metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 61, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lin, S.; Huang, X.; Peng, S.; Shen, M.; Ouyang, S.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, G. Applications of in Vivo SPME Based on Mass Spectrometry for Environmental Pollutants Analysis and Non-Target Metabolomics: A Review. Green Anal. Chem. 2022, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X. Applications of Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction in Human Biological Matrix Analysis. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 41, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergiovanni, M.; Gosetti, F.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Termopoli, V. Aroma Determination in Alcoholic Beverages: Green MS-based Sample Preparation Approaches. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, e21802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; De La Guardia, M. Green Extraction Techniques in Green Analytical Chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytou, A.E.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Volatilomics for Food Quality and Authentication. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacy Costello, B.; Amann, A.; Al-Kateb, H.; Flynn, C.; Filipiak, W.; Khalid, T.; Osborne, D.; Ratcliffe, N.M. A Review of the Volatiles from the Healthy Human Body. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broza, Y.Y.; Zuri, L.; Haick, H. Combined Volatolomics for Monitoring of Human Body Chemistry. Sci Rep 2014, 4, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Metabolomics. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djago, F.; Lange, J.; Poinot, P. Induced Volatolomics of Pathologies. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabińska, N.; Flynn, C.; Ratcliffe, N.; Belluomo, I.; Myridakis, A.; Gould, O.; Fois, M.; Smart, A.; Devine, T.; Costello, B.D.L. A Literature Survey of All Volatiles from Healthy Human Breath and Bodily Fluids: The Human Volatilome. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, W.; Carr, L.; Cordell, R.; Wilde, M.J.; Salman, D.; Monks, P.S.; Thomas, P.; Brightling, C.E.; Siddiqui, S.; Greening, N.J. Breathomics for the Clinician: The Use of Volatile Organic Compounds in Respiratory Diseases. Thorax 2021, 76, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Y. Breath Biomarkers in Diagnosis of Pulmonary Diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijck, M.; Berkhout, D.J.C.; De Groot, E.F.J.; Benninga, M.A.; Van Der Schee, M.P.C.; Kneepkens, C.M.F.; De Boer, N.K.H.; De Meij, T.G.J. Sniffing Out Paediatric Gastrointestinal Diseases: The Potential of Volatile Organic Compounds as Biomarkers for Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondanelli, M.; Perdoni, F.; Infantino, V.; Faliva, M.A.; Peroni, G.; Iannello, G.; Nichetti, M.; Alalwan, T.A.; Perna, S.; Cocuzza, C. Volatile Organic Compounds as Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal Diseases and Nutritional Status. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 7247802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, K.; Fardindoost, S.; Ravishankara, A.; Tasnim, N.; Hoorfar, M. Exhaled Breath Analysis for Diabetes Diagnosis and Monitoring: Relevance, Challenges and Possibilities. Biosensors 2021, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.D.C.; Blake, D.R.; Galassetti, P.R. The Clinical Potential of Exhaled Breath Analysis for Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, E.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Lamote, K. Volatile Organic Compounds in Human Matrices as Lung Cancer Biomarkers: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 153, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Phillips, M.; Amann, A.; Haick, H. Volatile Organic Compounds of Lung Cancer and Possible Biochemical Pathways. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5949–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, M.; Simeon, A.; Vujić, D.; Giannoukos, S.; Brkić, B. Food and Lifestyle Impact on Breath VOCs Using Portable Mass Spectrometer—Pilot Study across European Countries. J. Breath Res. 2023, 17, 046004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H. Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Volatile Organic Compounds: A Perspective Review. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochalski, P.; King, J.; Klieber, M.; Unterkofler, K.; Hinterhuber, H.; Baumann, M.; Amann, A. Blood and Breath Levels of Selected Volatile Organic Compounds in Healthy Volunteers. Analyst 2013, 138, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kaneko, S.; Furuya, Y.; Asada, Y.; Ito, R.; Sugie, K.; Akutsu, M.; Yanagawa, Y. Confirmation of Synthetic Cannabinoids in Herb and Blood by HS-SPME-GC/MS. Forensic Chem. 2019, 13, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrogianni, O.; Theodoridis, G.; Spagou, K.; Violante, D.; Henriques, T.; Pouliopoulos, A.; Psaroulis, K.; Tsoukali, H.; Raikos, N. Determination of Venlafaxine in Post-Mortem Whole Blood by HS-SPME and GC-NPD. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 215, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, A.; Vitali, M.; Avino, P.; Manigrasso, M.; Protano, C. Sensitive Multiresidue Method by HS-SPME/GC-MS for 10 Volatile Organic Compounds in Urine Matrix: A New Tool for Biomonitoring Studies on Children. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5789–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligor, T.; Zawadzka, J.; Strączyński, G.; González Paredes, R.M.; Wenda-Piesik, A.; Ratiu, I.A.; Muszytowski, M. Searching for Potential Markers of Glomerulopathy in Urine by HS-SPME-GC×GC TOFMS. Molecules 2021, 26, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Mani-Varnosfaderani, A.; Poch, K.; Caceres, S.M.; Nick, J.A.; Hill, J.E. Volatile Sputum Biomarkers Can Monitor the Response to Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Disease: A Pilot Study. CMBES Proc. 2023, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.; Stephenson, D.; Sykes, H.E.; Perry, J.D.; Stanforth, S.P.; Dean, J.R. Detection of β-Alanyl Aminopeptidase as a Biomarker for Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in the Sputum of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Using Exogenous Volatile Organic Compound Evolution. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10634–10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Bean, H.D.; Smolinska, A.; Rees, C.A.; Zemanick, E.T.; Hill, J.E. Volatile Molecules from Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Can ‘Rule-in’ Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and ‘Rule-out’ Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.; Whiteson, K.; Davis, T.J.; Phan, J.; Sami, I.; Koumbourlis, A.C.; Freishtat, R.J.; Crandall, K.A.; Bean, H.D. Longitudinal Associations of the Cystic Fibrosis Airway Microbiome and Volatile Metabolites: A Case Study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins Keppler, E.A.; Van Dyke, M.C.C.; Mead, H.L.; Lake, D.F.; Magee, D.M.; Barker, B.M.; Bean, H.D. Volatile Metabolites in Lavage Fluid Are Correlated with Cytokine Production in a Valley Fever Murine Model. JoF 2023, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessonneau, V.; Bojko, B.; Azad, A.; Keshavjee, S.; Azad, S.; Pawliszyn, J. Determination of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Bile Acids by Solid Phase Microextraction Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Combination with Metabolite Profiling: Comparison with Enzymatic Assay. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1367, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanuto, P.-H.; Romano, R.; Rees, C.A.; Nasir, M.; Thakuria, L.; Simon, A.; Reed, A.K.; Marczin, N.; Hill, J.E. Volatile Organic Compound Profiling to Explore Primary Graft Dysfunction after Lung Transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins Keppler, E.A.; Jenkins, C.L.; Davis, T.J.; Bean, H.D. Advances in the Application of Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography in Metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinklein, T.J.; Cain, C.N.; Ochoa, G.S.; Schöneich, S.; Mikaliunaite, L.; Synovec, R.E. Recent Advances in GC×GC and Chemometrics to Address Emerging Challenges in Nontargeted Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspromonte, J.; Wolfs, K.; Adams, E. Current Application and Potential Use of GC × GC in the Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Field. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 176, 112817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemanick, E.T.; Wagner, B.D.; Robertson, C.E.; Ahrens, R.C.; Chmiel, J.F.; Clancy, J.P.; Gibson, R.L.; Harris, W.T.; Kurland, G.; Laguna, T.A.; et al. Airway Microbiota across Age and Disease Spectrum in Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcaro, G.; Stefanuto, P.-H.; Franchina, F.A.; Beccaria, M.; Wieland-Alter, W.F.; Wright, P.F.; Hill, J.E. SPME-GC×GC-TOF MS Fingerprint of Virally-Infected Cell Culture: Sample Preparation Optimization and Data Processing Evaluation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1027, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, H.D.; Hill, J.E.; Dimandja, J.-M.D. Improving the Quality of Biomarker Candidates in Untargeted Metabolomics via Peak Table-Based Alignment of Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1394, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, H.D.; Dimandja, J.-M.D.; Hill, J.E. Bacterial Volatile Discovery Using Solid Phase Microextraction and Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 901, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobak, C.A.; Kang, L.; Workman, L.; Bateman, L.; Khan, M.S.; Prins, M.; May, L.; Franchina, F.A.; Baard, C.; Nicol, M.P.; et al. Breath Can Discriminate Tuberculosis from Other Lower Respiratory Illness in Children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipler, A. An Introduction to headspace sampling in gas chromatography fundamentals and theory. Perkinelmer Rep. 2013, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pawliszyn, J. Theory of Solid-Phase Microextraction. In Handbook of Solid Phase Microextraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 13–59. ISBN 978-0-12-416017-0. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, P.; Baker, J.; Boyd, M.T.; Coyle, S.; Probert, C.; Chapman, E.A. Optimisation of Urine Sample Preparation for Headspace-Solid Phase Microextraction Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Altering Sample pH, Sulphuric Acid Concentration and Phase Ratio. Metabolites 2020, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalua, C.M.; Boss, P.K. Sample Preparation Optimization in Wine and Grapes. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1192, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Lu, J.; Gao, M.; Li, C.; Chen, S. Optimization and Validation of a Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction with Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometric Detection for Quantification of Trace Aroma Compounds in Chinese Liquor (Baijiu). Molecules 2021, 26, 6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Albanis, T.A. Headspace Solid Phase Microextraction Applied to the Analysis of Organophosphorus Insecticides in Strawberry and Cherry Juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3359–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godage, N.H.; Gionfriddo, E. Biocompatible SPME Coupled to GC/MS for Analysis of Xenobiotics in Blood Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1203, 123308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzel, F. Bronchoalveolar Lavage. In Principles and Practice of Interventional Pulmonology; Ernst, A., Herth, F.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 165–176. ISBN 978-1-4614-4291-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, G.A.; Walker, V. Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Procedures for Gas Chromatographic Analysis of Biological Fluids and Materials. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 902, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spietelun, A.; Marcinkowski, Ł.; Kloskowski, A.; Namieśnik, J. Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds in Water Samples Using Membrane-Solid Phase Microextraction (M-SPME) (Headspace Version). Analyst 2013, 138, 5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larreta, J.; Vallejo, A.; Bilbao, U.; Alonso, A.; Arana, G.; Zuloaga, O. Experimental Design to Optimise the Analysis of Organic Volatile Compounds in Cow Slurry by Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1136, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
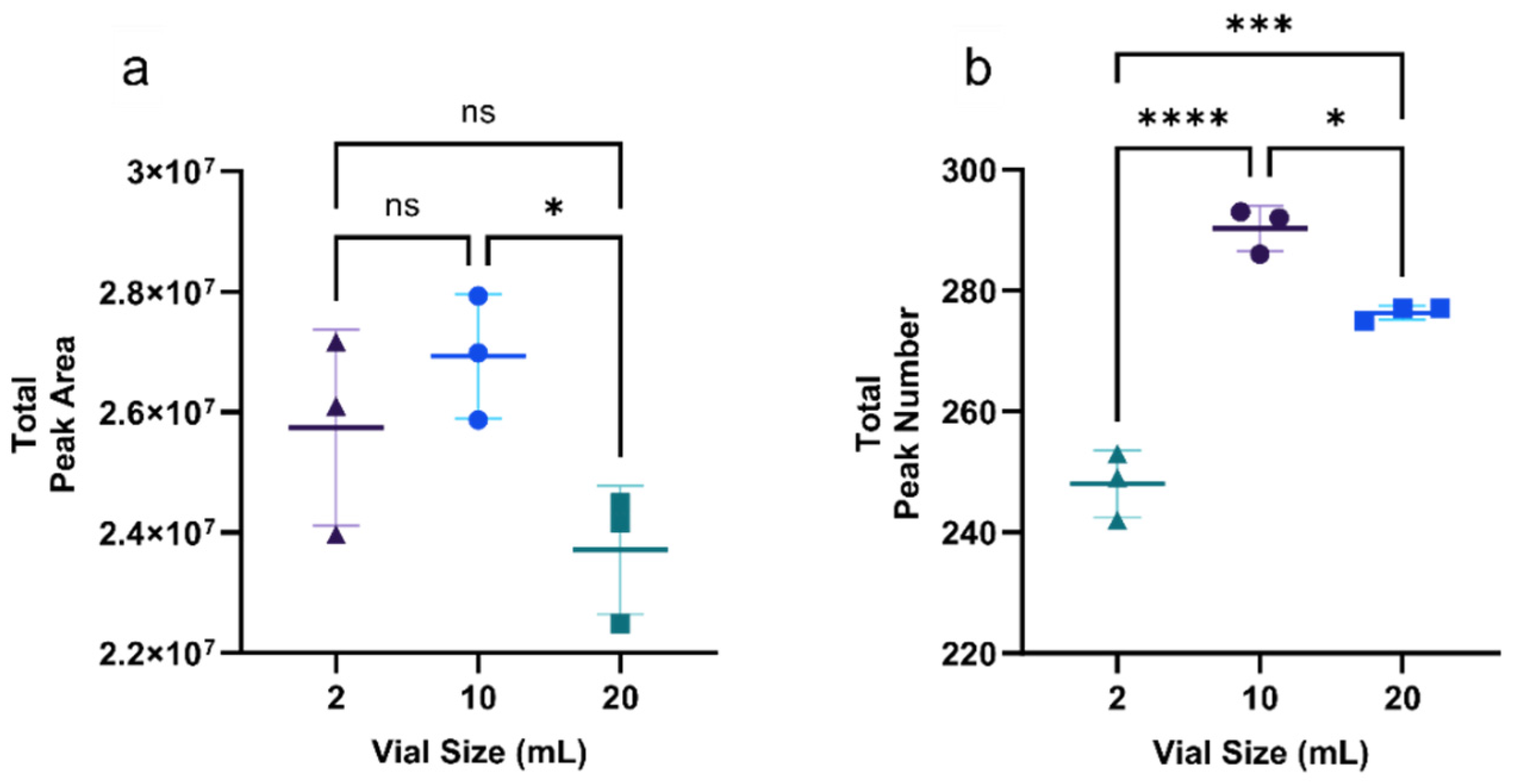
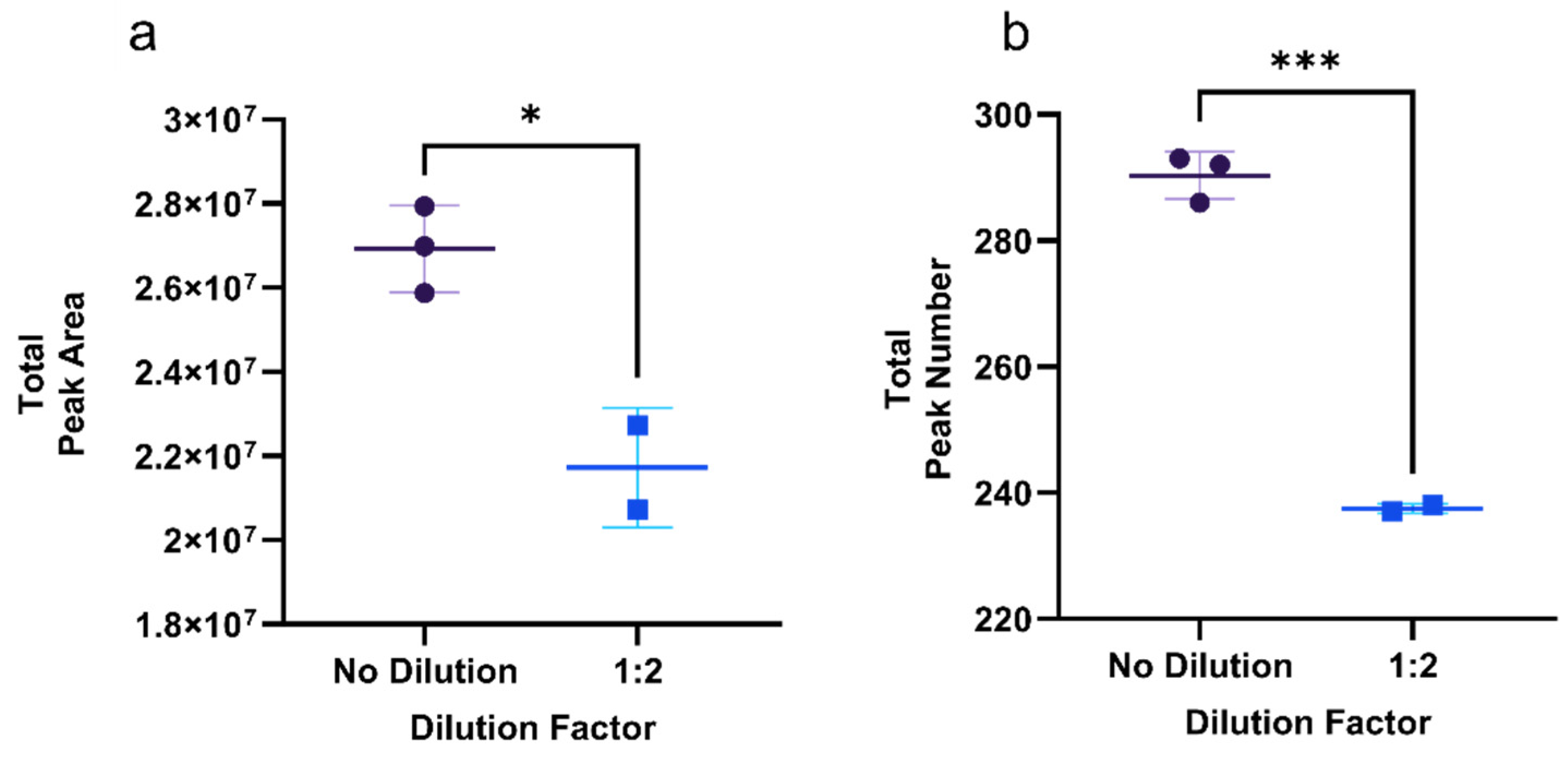
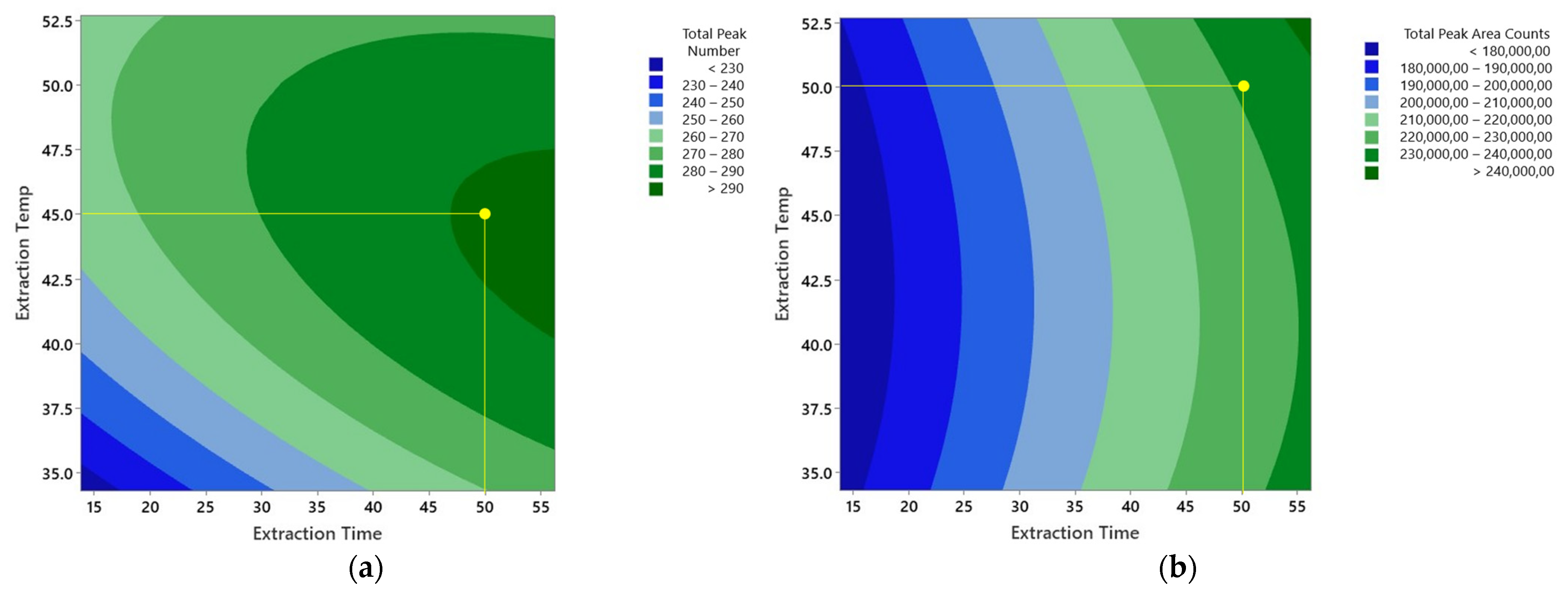

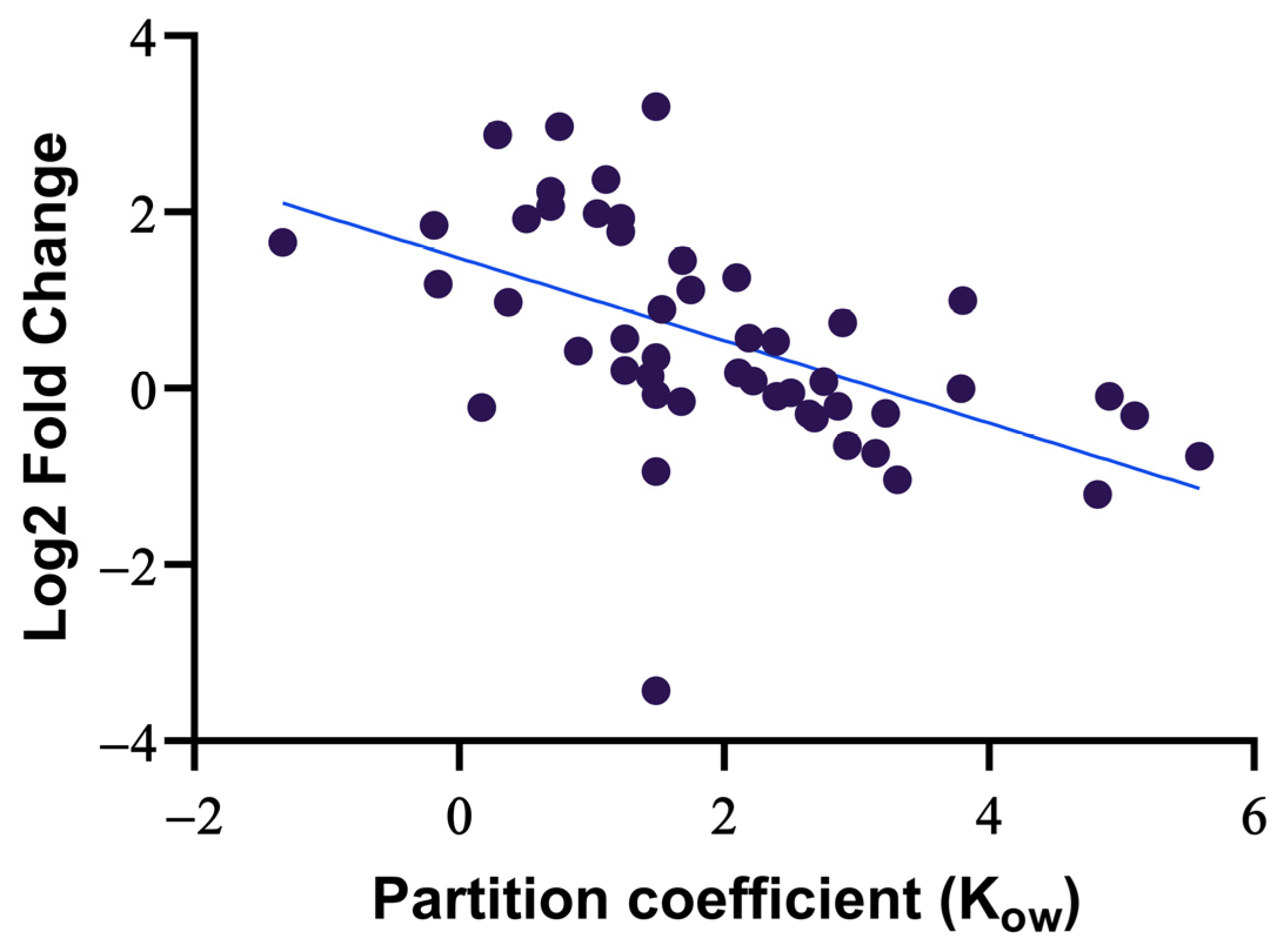

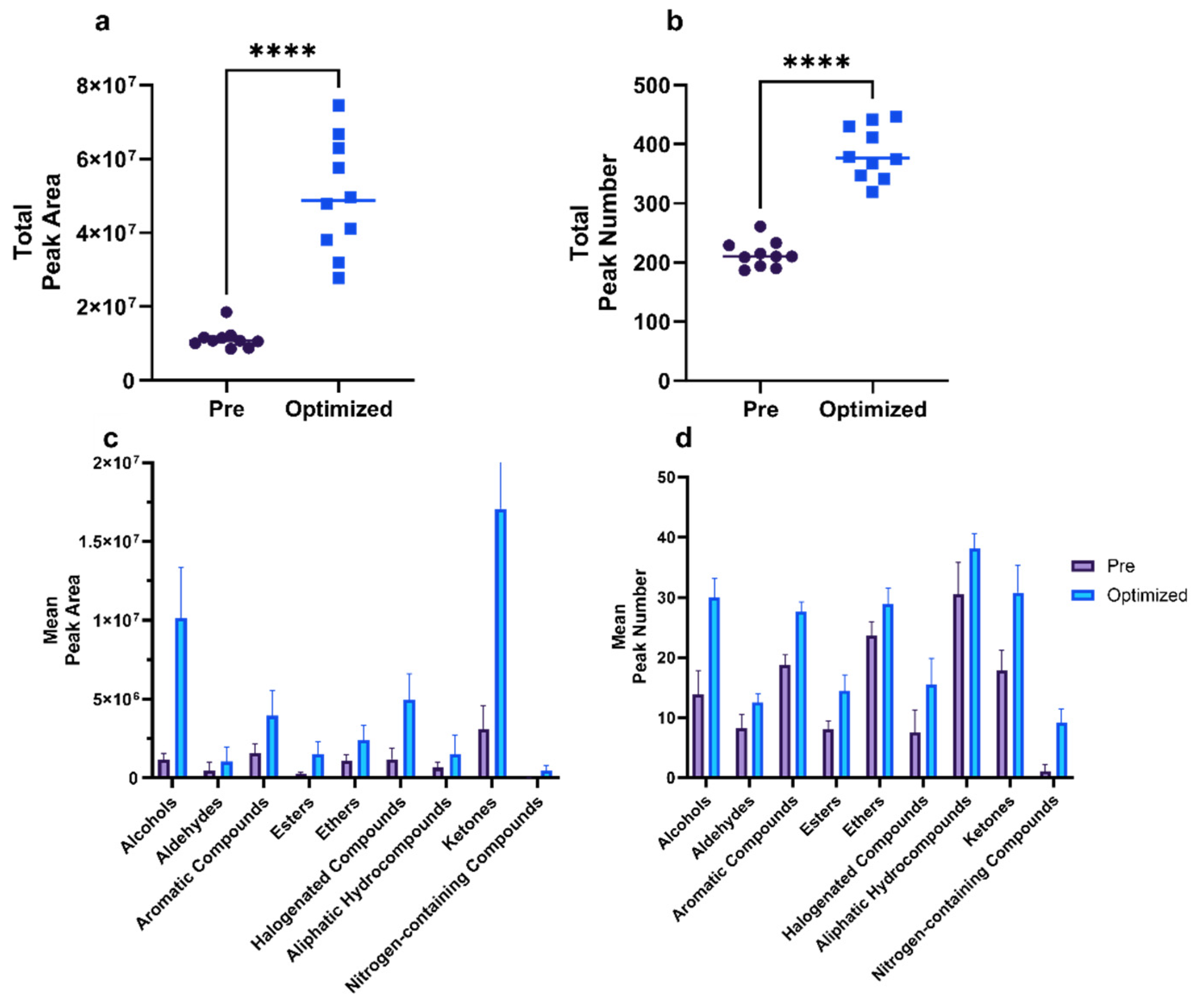
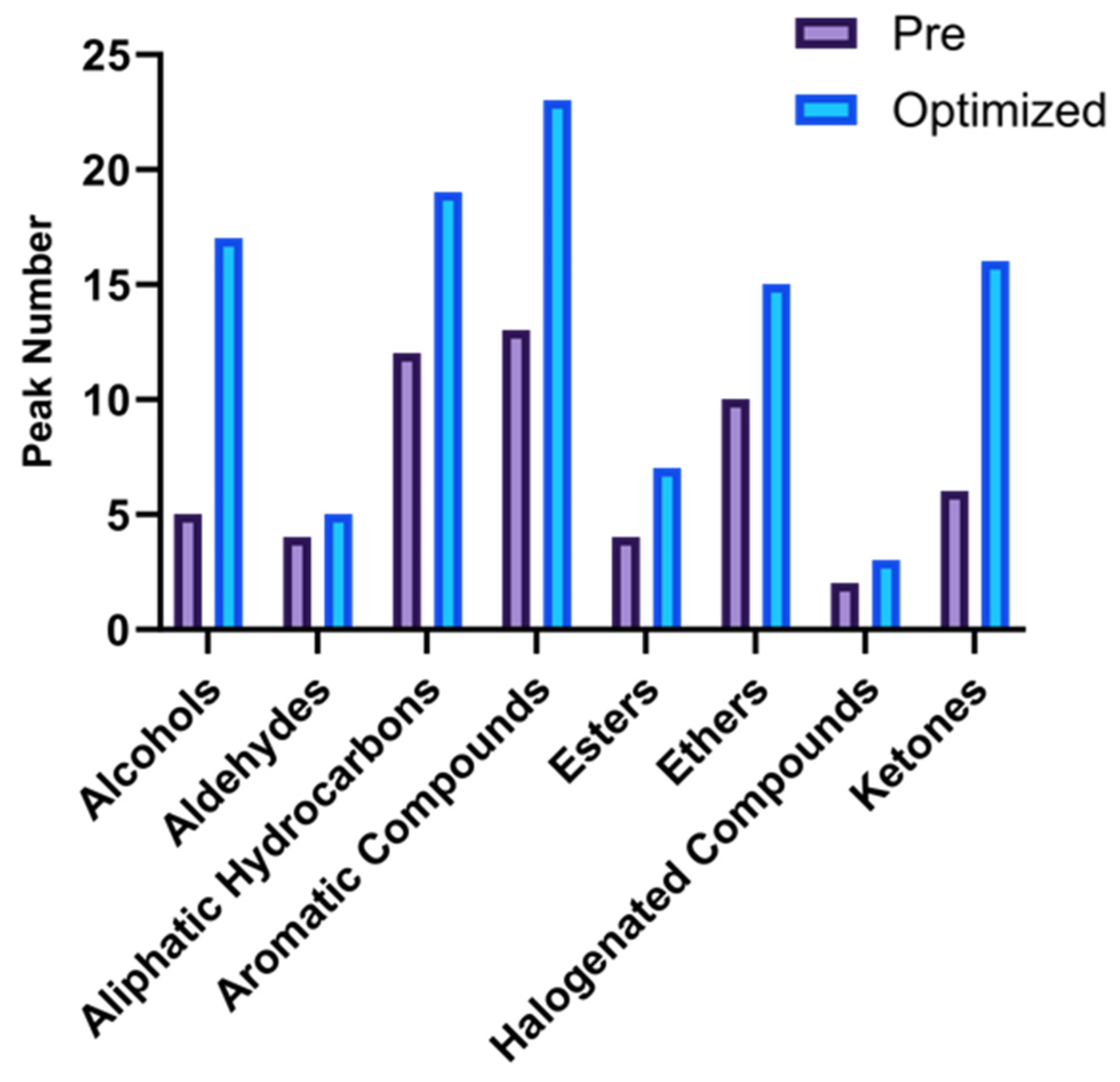
| Order | Extraction Temperature (°C) | Extraction Time (Min) | Order | Extraction Temperature (°C) | Extraction Time (Min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43.5 | 56 | 8 | 37.0 | 20 |
| 2 | 52.5 | 35 | 9 | 37.0 | 60 |
| 3 | 34.3 | 35 | 10 | 43.5 | 35 |
| 4 | 43.5 | 35 | 11 | 50.0 | 50 |
| 5 | 43.5 | 35 | 12 | 50.0 | 20 |
| 6 | 43.5 | 14 | 13 | 43.5 | 35 |
| 7 | 43.5 | 35 | 14 | 43.5 | 35 |
| Optimized Parameter | Pre-Optimization | Optimized |
|---|---|---|
| Vial Size | 20 mL | 10 mL |
| Dilution Factor | 1:2 Dilution | No Dilution |
| Extraction Time | 30 Minutes | 50 Minutes |
| Extraction Temperature | 43 °C | 45 °C |
| Salt Addition | No Salt | 40% (w/v) NaCl |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, A.; Nouri, N.; Stevenson, K.; Zemanick, E.T.; Nick, J.A.; Hill, J.E. Headspace Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction Method Optimization and Evaluation for the Volatile Compound Extraction of Bronchoalveolar Lung Lavage Fluid Samples. Separations 2024, 11, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010027
Gao A, Nouri N, Stevenson K, Zemanick ET, Nick JA, Hill JE. Headspace Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction Method Optimization and Evaluation for the Volatile Compound Extraction of Bronchoalveolar Lung Lavage Fluid Samples. Separations. 2024; 11(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Antao, Nina Nouri, Keisean Stevenson, Edith T. Zemanick, Jerry A. Nick, and Jane E. Hill. 2024. "Headspace Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction Method Optimization and Evaluation for the Volatile Compound Extraction of Bronchoalveolar Lung Lavage Fluid Samples" Separations 11, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010027
APA StyleGao, A., Nouri, N., Stevenson, K., Zemanick, E. T., Nick, J. A., & Hill, J. E. (2024). Headspace Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction Method Optimization and Evaluation for the Volatile Compound Extraction of Bronchoalveolar Lung Lavage Fluid Samples. Separations, 11(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010027






