Effects of Hydrolysis Condition and Detection Method on the Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Polysaccharides from Natural Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Extraction and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides
2.3. Chromogenic Method
2.4. Thin-Layer Chromatography
2.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.6. Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometer Method
2.7. Verification of Monosaccharide Quantitative Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Total Sugar and Sugar Acid Content by Chromogenic Method
3.2. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography
3.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.4. Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry
3.5. Evaluation of Monosaccharide Composition Determination Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.-F.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Han, Q.-B. Recent advances in qualitative and quantitative analysis of polysaccharides in natural medicines: A critical review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 220, 115016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, G.; Huang, H. Extraction, derivatization and antioxidant activities of onion polysaccharide. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 133000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Dong, N.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Cui, S.W.W.; Nie, S. Polysaccharides from natural Cordyceps sinensis attenuated dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Liang, L.; Huang, L.; Yu, G.; Li, Q. A novel low-molecular-mass pumpkin polysaccharide: Structural characterization, antioxidant activity, and hypoglycemic potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tang, W.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Monosaccharide composition analysis of polysaccharides from natural sources: Hydrolysis condition and detection method development. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedevi, P. Antioxidant and anticoagulant activity of crude polysaccharide and a-L-Rhamnose from Grateloupia lithophila. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, J.-D.; Zhang, W.; Guo, M.-F.; Kong, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, S.S.; Wu, C.-Y.; Li, S.L.; Mao, Q. Holistic quality evaluation of Callicarpae Formosanae Folium by multi-chromatography-based qualitative and quantitative analysis of polysaccharides and small molecules. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 227, 115282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Wen, X. Characterization and comparison of polysaccharides from Achyranthes bidentata, Cyathula officinalis and Achyranthes aspera by saccharides mapping. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 227, 115272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, L.-X.; Han, B.-X.; Wu, D.-T.; Cheong, K.-L.; Chen, N.-F.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.-P. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of specific polysaccharides in Dendrobium huoshanense by using saccharide mapping and chromatographic methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Niu, T.; Lu, X.; Liu, M. Effects of monosaccharide composition on quantitative analysis of total sugar content by phenol-sulfuric acid method. Front Nutr. 2022, 9, 963318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-C.; Zhao, X.; Pu, J.-H.; Luan, X.-H. Influences of acidic reaction and hydrolytic conditions on monosaccharide composition analysis of acidic, neutral and basic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 143, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Yang, F.-Q.; Li, S.-P. Evaluation of Carbohydrates in Natural and Cultured Cordyceps by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2010, 15, 4227–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhuang, D.; Meng, F.-C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Lv, G.-P. Structural characterization and immunoregulatory activity of two polysaccharides from the rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.-Y.; Ma, L.-Y.; Xie, M.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Wu, J.-Y. Molecular properties and gut health benefits of enzyme-hydrolyzed konjac glucomannans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wan, Y.; Li, O.; Zhang, X.; Xie, M.; Nie, S.; Yin, J. Two-step hydrolysis method for monosaccharide composition analysis of natural polysaccharides rich in uronic acids. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruiter, G.A.; Schols, H.A.; Voragen, A.G.; Rombouts, F.M. Carbohydrate analysis of water-soluble uronic acid-containing polysaccharides with high-performance anion-exchange chromatography using methanolysis combined with TFA hydrolysis is superior to four other methods. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 207, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Bera, K.; Ghosh, K.; Ali, I.; Khawas, S.; Ray, B.; Ray, S. Polysaccharides from Thymus vulgaris leaf: Structural features, antioxidant activity and interaction with bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Bai, X.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, L.; Min, X. Fractionation and antioxidant activities of the water-soluble polysaccharides from Lonicera japonica Thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Han, B.; Li, S.; Zhao, J. Fast saccharide mapping method for quality consistency evaluation of commercial xylooligosaccharides collected in China. J Pharm Anal. 2021, 11, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Hu, D.-J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.-D.; Lv, G.-P. Preparation, characterization and immunoregulatory activity of derivatives of polysaccharide from Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzyna-Szklarek, M.; Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A. Analysis of the chemical composition of natural carbohydrates—An overview of methods. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Yan, J.-K. Physicochemical, structural, and rheological characteristics of pectic polysaccharides from fresh passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa L.) peel. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kisara, K.; Danielsson, S.; Lindstrom, M.E.; Gellerstedt, G. An improved methodology for the quantification of uronic acid units in xylans and other polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanja, A.; Paikra, S.K.; Sutar, P.P.; Mishra, M. Characterization and identification of inulin from Pachyrhizus erosus and evaluation of its antioxidant and in-vitro prebiotic efficacy. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Cheng, X.; Qian, L.; Huo, A.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y. Extraction, Physicochemical Properties, Functional Activities and Applications of Inulin Polysaccharide: A Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensink, M.A.; Frijlink, H.W.; Maarschalk, K.V.D.V.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. Inulin, a flexible oligosaccharide I: Review of its physicochemical characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Shehzad, A.; Omar, M.; Rakha, A.; Raza, H.; Sharif, H.R.; Shakeel, A.; Ansari, A.; Niazi, S. Inulin: Properties, health benefits and food applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Cheng, G.; Yang, E.; Yi, C.; Ruenroengklin, N.; Lu, W.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Y. Modification of pectin polysaccharides during ripening of postharvest banana fruit. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohnen, D. Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vityazev, F.V.; Golovchenko, V.V.; Patova, O.A.; Khlopin, V.A.; Kosolapova, N.V.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Shashkov, A.S. Pectic polysaccharides of black radish taproots: Extraction, structural characterization. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, S.; Van Buggenhout, S.; Houben, K.; Kermani, Z.J.; Moelants, K.R.N.; Ngouemazong, E.D.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M.E.G. Process-Structure-Function Relations of Pectin in Food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Biological Functions of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masci, A.; Carradori, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Paolicelli, P.; Petralito, S.; Ragno, R.; Cesa, S. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, structural characterisation and evidence about hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic effects. A review. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.-T.; Guo, H.; Lin, S.; Lam, S.-C.; Zhao, L.; Lin, D.-R.; Qin, W. Review of the structural characterization, quality evaluation, and industrial application of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2018, 79, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-F.; Chen, X.-F.; Malterud, K.E.; Rise, F.; Barsett, H.; Inngjerdingen, K.T.; Michaelsen, T.E.; Paulsen, B.S. Structural features and complement fixing activity of polysaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. var. modesta L.T.Shen roots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Paulsen, B.S.; Fu, Y.-P.; Huang, C.; Feng, B.; Li, L.-X.; Chen, X.-F.; Jia, R.-Y.; Song, X.; et al. Prospects of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides: Structural features and bioactivities diversity. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2020, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; Ji, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, Q.; Cao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Zeng, N. Extraction, purification, structural characteristics and biological properties of the polysaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, W.; Mei, Y.; Cao, L.; Wei, X.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X. A review of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides: Health benefit, structure-activity relationship, modification, and nanoparticle encapsulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 243, 125199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Heleno, S.A.; Reis, F.S.; Stojkovic, D.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Helena Vasconcelo, M.; Sokovic, M. Chemical features of Ganoderma polysaccharides with antioxidant, antitumor and antimicrobial activities. Phytochemistry 2015, 114, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.; Zheng, F.; Beecher, L. Optimization of reactions between reducing sugars and 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-T.; Wang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Yang, W.-B. Structure determination of beta-glucans from Ganoderma lucidum with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry. Molecules 2008, 13, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Yao, J.; Li, J.; Ma, F.; Ding, K. A novel water-soluble beta-D-glucan isolated from the spores of Ganoderma lucidum. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 353, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, G.; Hu, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. Quality control of sweet medicines based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-L.; Li, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-S.; Zou, Y.-P. Comprehensive analysis of natural polysaccharides from TCMs: A generic approach based on UPLC-MS/MS. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Cai, Y.-Y.; Wang, Z.-C.; Alolga, R.N.; Qi, L.-W.; Li, B.; Huang, F.-Q. Paired Derivatization Approach with H/D-Labeled Hydroxylamine Reagents for Sensitive and Accurate Analysis of Monosaccharides by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Ma, S.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, G.; Zhao, Y. LC-MS/MS-based non-isotopically paired labeling (NIPL) strategy for the qualification and quantification of monosaccharides. Talanta 2021, 231, 122336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, G.; Luthria, D.L.; Chen, Y.; Bacalzo, N.P., Jr.; Tareq, F.S.; Harnly, J.; Phillips, K.M.; Pehrsson, P.R.; McKillop, K.; Fukagawa, N.K.; et al. Multi-Glycomic Characterization of Fiber from AOAC Methods Defines the Carbohydrate Structures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14559–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.-N.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Chai, J.-H.; Kuang, H.-X.; Xia, Y.-G. Direct acetylation for full analysis of polysaccharides in edible plants and fungi using reverse phase liquid chromatography-multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 222, 115083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, I.; Heiss, C.; Azadi, P. Comprehensive Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Insoluble Polysaccharides by Permethylation to Produce Methyl Alditol Derivatives for Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13787–13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.-Y.; Zhao, X.-H. Monosaccharide composition and in vivo immuno-stimulatory potential of soluble yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) polysaccharides in response to a covalent Se incorporation. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, G.; Alekseeva, A.; Bertini, S.; Gardini, C.; Paganini, D.; Fonseca, E.C.M.; Guerrini, M.; Naggi, A. Further advances in identification of pentosan polysulfate monosaccharide composition by NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 235, 115672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

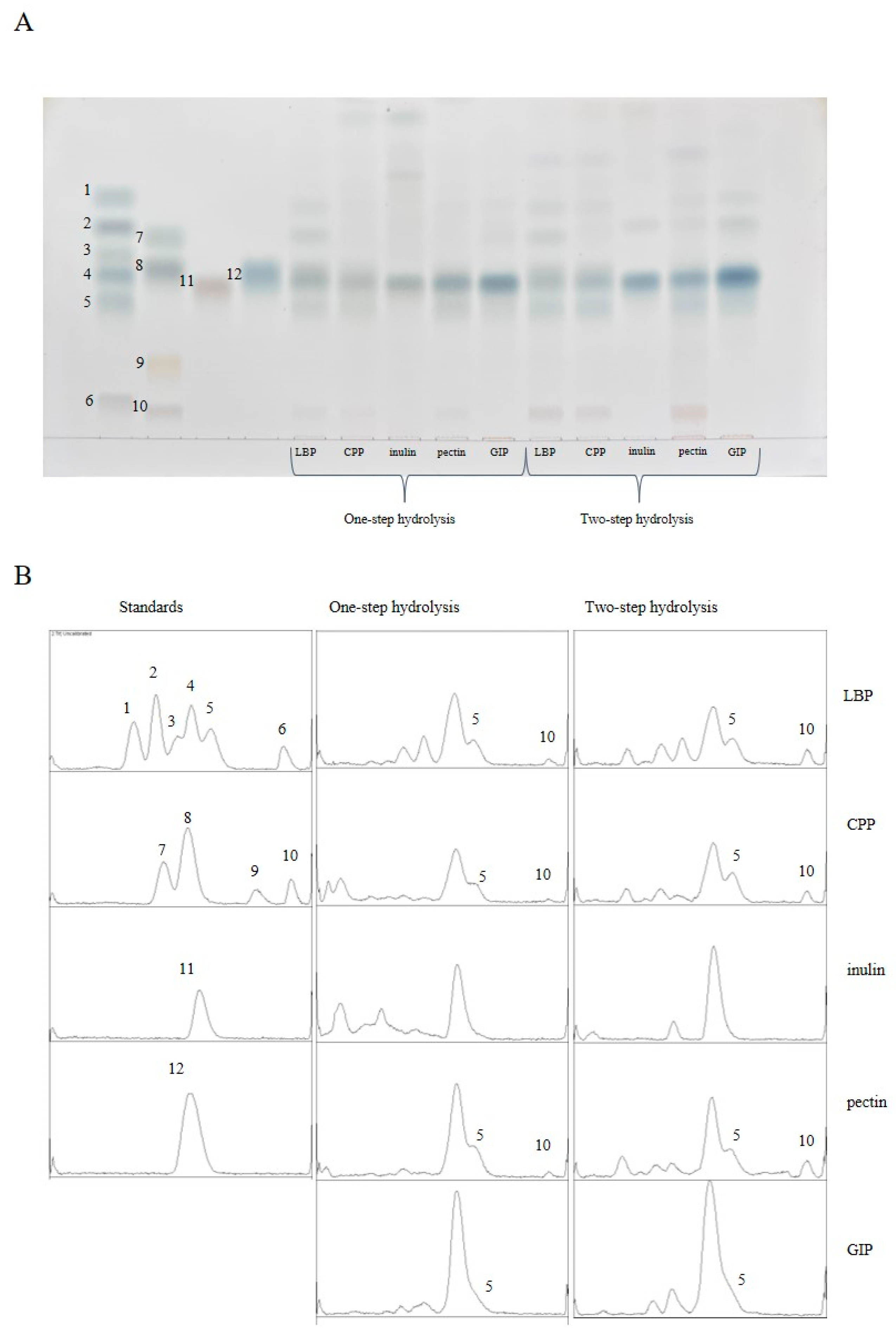
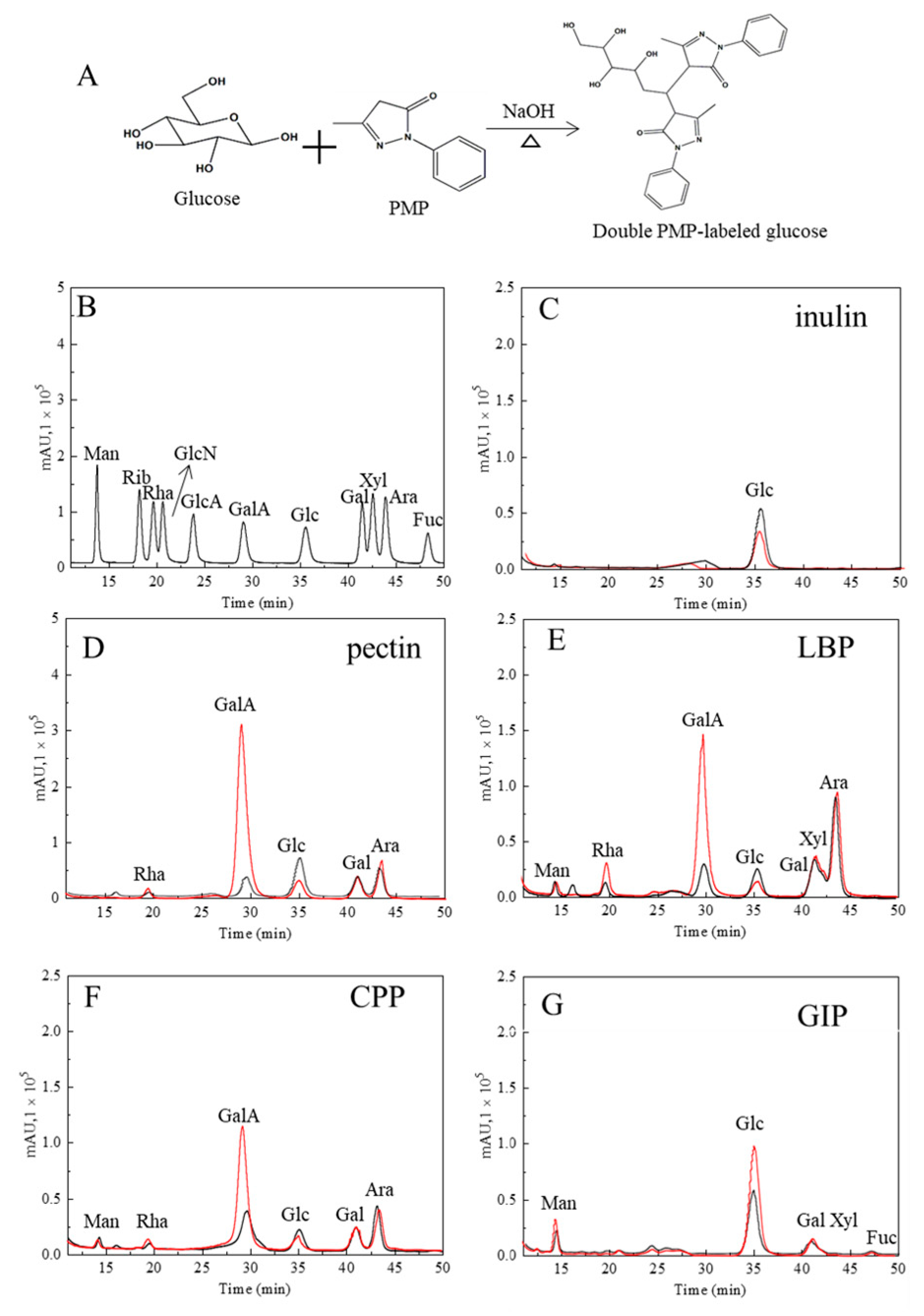
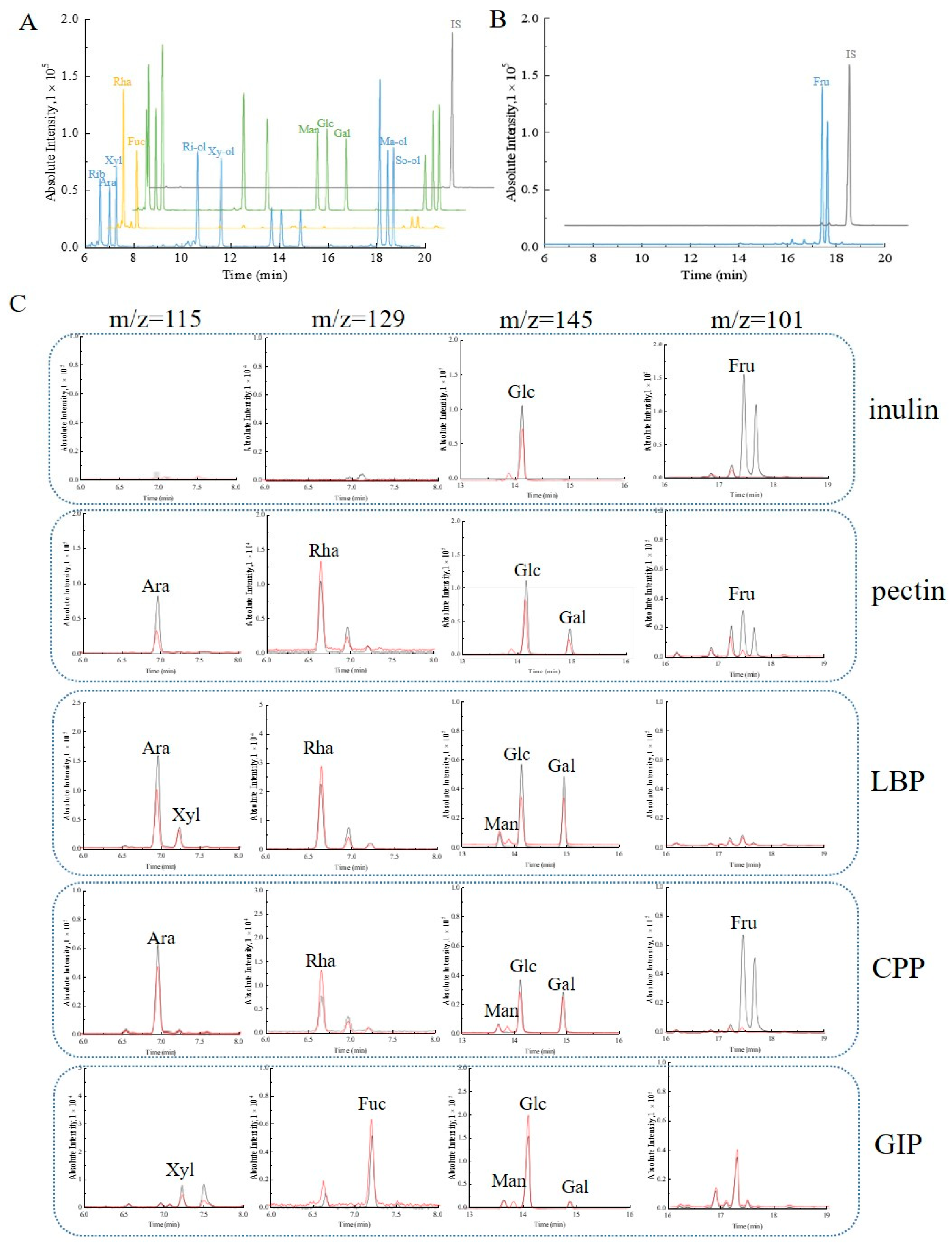
| Methods | Carbohydrates | Regression Equation | R2 | Linear Range (µg/mL) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenol–sulfuric acid method | Glc | Y = 0.0031X − 0.0037 | 0.9990 | 0–100 | 163.0 ± 2.9% |
| Fru | Y = 0.0045X − 0.0026 | 0.9991 | 111.5 ± 2.0% | ||
| Rha | Y = 0.0036X + 0.0056 | 0.9982 | 132.3 ± 2.5% | ||
| Carbazole sulfuric acid method | GalA | Y = 0.0039X + 0.0049 | 0.9991 | 0–80 | 150.6 ± 5.4% |
| GlcA | Y = 0.0023X + 0.0039 | 0.9993 | 205.3 ± 3.7% | ||
| M-hydroxybiphenyl method | GalA | Y = 0.0025X − 0.0055 | 0.9979 | 0–80 | 190.4 ± 6.2% |
| GlcA | Y = 0.0014X − 0.0054 | 0.9971 | 234.1 ± 3.0% |
| Chemical Composition | Methods | Reference Substance | Inulin (%) | Pectin (%) | LBP (%) | CPP (%) | GIP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total sugar | Phenol–sulfuric acid method | Glc | - | 46.5 ± 1.0 | 40.7 ± 0.9 | 71.7 ± 1.1 | 24.7 ± 0.5 |
| Fru | 89.5 ± 1.3 | 22.9 ± 0.5 | 19.9 ± 0.5 | 35.9 ± 0.6 | 11.7 ± 0.3 | ||
| Rha | - | 57.8 ± 1.2 | 50.5 ± 1.1 | 89.3 ± 1.4 | 30.6 ± 0.6 | ||
| Uronic acid | Carbazole sulfuric acid method | GalA | 18.3 ± 0.4 | 39.2 ± 0.2 | 23.0 ± 0.3 | 21.0 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.2 |
| GlcA | 28.5 ± 0.3 | 59.1 ± 0.1 | 35.3 ± 0.2 | 32.5 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | ||
| M-hydroxybiphenyl method | GalA | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 39.5 ± 0.1 | 19.7 ± 0.2 | 16.7 ± 0.1 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | |
| GlcA | 14.3 ± 0.4 | - | 50.3 ± 0.5 | 42.2 ± 0.3 | 8.4 ± 0.3 |
| Samples | Monosaccharide Composition (mg/g) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ara | Xyl | Rha | Fuc | Man | Glc | Gal | Fru | GalA | |||||||||||||
| HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | HPLC | - | HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | HPLC | GC | ||
| inulin | One-step | - a | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 77.0 ± 5.2 | 73.5 ± 4.7 | - | - | / b | 54.5 ± 2.2 | - | / | 77.0 | 128.0 |
| Two-step | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 50.4 ± 2.5 | 48.7 ± 3.9 | - | - | / | - | - | / | 50.7 | 48.7 | |
| pectin | One-step | 26.8 ± 2.7 | 28.8 ± 1.0 | - | - | 5.5 ± 0.9 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | - | - | - | - | 75.6 ± 9.8 | 74.4 ± 1.4 | 21.1 ± 3.4 | 21.3 ± 0.3 | / | - | 47.7 ± 10.8 | / | 176.7 | 130.0 |
| Two-step | 23.8 ± 5.3 | 21.2 ± 2.0 | - | - | 11.6 ± 2.6 | 10.3 ± 1.0 | - | - | - | - | 30.3 ± 5.0 | 28.5 ± 2.0 | 19.1 ± 0.9 | 17.2 ± 1.7 | / | - | 388.9 ± 33.6 | / | 473.8 | 77.3 | |
| LBP | One-step | 48.8 ± 0.1 | 46.9 ± 1.5 | 15.2 ± 2.3 | 14.3 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 2.2 | 9.5 ± 0.2 | - | - | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 4.4 ± 0.1 | 28.4 ± 1.4 | 26.2 ± 1.8 | 23.9 ± 8.3 | 21.5 ± 1.6 | / | - | 40.0 ± 1.7 | / | 169.9 | 122.7 |
| Two-step | 46.1 ± 1.6 | 44.7 ± 0.9 | 13.1 ± 3.8 | 11.8 ± 0.2 | 21.6 ± 4.0 | 20.5 ± 2.2 | - | - | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 12.9 ± 4.1 | 12.4 ± 0.1 | 21.7 ± 6.9 | 18.6 ± 1.6 | / | - | 184.9 ± 27.5 | / | 303.8 | 111.6 | |
| CPP | One-step | 22.4 ± 1.9 | 21.5 ± 0.2 | - | - | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | - | - | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 20.5 ± 5.0 | 17.4 ± 1.3 | 12.9 ± 5.9 | 13.7 ± 0.9 | / | 41.1 ± 2.4 | 70.4 ± 10.4 | / | 133.1 | 100.2 |
| Two-step | 18.3 ± 4.5 | 18.0 ± 0.2 | - | - | 7.0 ± 1.8 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | - | - | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 14.3 ± 0.4 | 14.0 ± 0.3 | 13.0 ± 3.1 | 12.5 ± 0.3 | / | - | 159.0 ± 11.5 | / | 213.8 | 53.4 | |
| GIP | One-step | - | - | 3.6 ± 5.1 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | - | - | 5.5 ± 4.4 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 12.8 ± 0.6 | 11.8 ± 0.3 | 88.4 ± 5.6 | 90.3 ± 2.8 | 8.9 ± 3.0 | 8.7 ± 0.4 | / | - | - | / | 119.1 | 119.8 |
| Two-step | - | - | 3.0 ± 2.3 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | - | - | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 15.0 ± 4.4 | 13.1 ± 0.4 | 141.8 ± 3.7 | 140.6 ± 3.9 | 11.8 ± 0.9 | 11.4 ± 0.3 | / | - | - | / | 178.1 | 175.0 | |
| Carbohydrates or Compare Content | Chromogenic Methods | HPTLC | HPLC-DAD | GC-MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rib | N | D | √ | √ |
| Ara | D | D | √ | |
| Xyl | D | D | √ | |
| Rha | √ | D | √ | |
| Fuc | D | √ | √ | |
| Man | D | √ | √ | |
| Glc | D | √ | √ | |
| Gal | √ | D | √ | |
| Fru | D | X | √ | |
| GlcA | √ | √ | X | |
| GalA | √ | √ | X | |
| GlcN | √ | D | X | |
| Ri-ol | X | X | √ | |
| Xy-ol | X | X | √ | |
| Ma-ol | X | X | √ | |
| So-ol | X | X | √ | |
| Derivatization time | - | - | 60 min | 60 or 120 min |
| Operation time | 20–30 min | 120 min | 30 min | 20 min |
| Instrument analysis time | 2 min | 2 min | 55 min | 30 min |
| Detection sensitivity | Low | Low | High, 0.19–0.42 μg/mL | High, 0.12–0.80 μg/mL |
| Quantification accuracy | Low | Low | High, 90.62–101.28% | High, 84.4–99.94% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Kuang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, G. Effects of Hydrolysis Condition and Detection Method on the Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Polysaccharides from Natural Sources. Separations 2024, 11, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010002
Zhao M, Kuang F, Zhang Y, Lv G. Effects of Hydrolysis Condition and Detection Method on the Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Polysaccharides from Natural Sources. Separations. 2024; 11(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Meijuan, Fengyan Kuang, Yingyue Zhang, and Guangping Lv. 2024. "Effects of Hydrolysis Condition and Detection Method on the Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Polysaccharides from Natural Sources" Separations 11, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010002
APA StyleZhao, M., Kuang, F., Zhang, Y., & Lv, G. (2024). Effects of Hydrolysis Condition and Detection Method on the Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Polysaccharides from Natural Sources. Separations, 11(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010002






