Influence of Carbon Quantum Dots on the Biome
Abstract
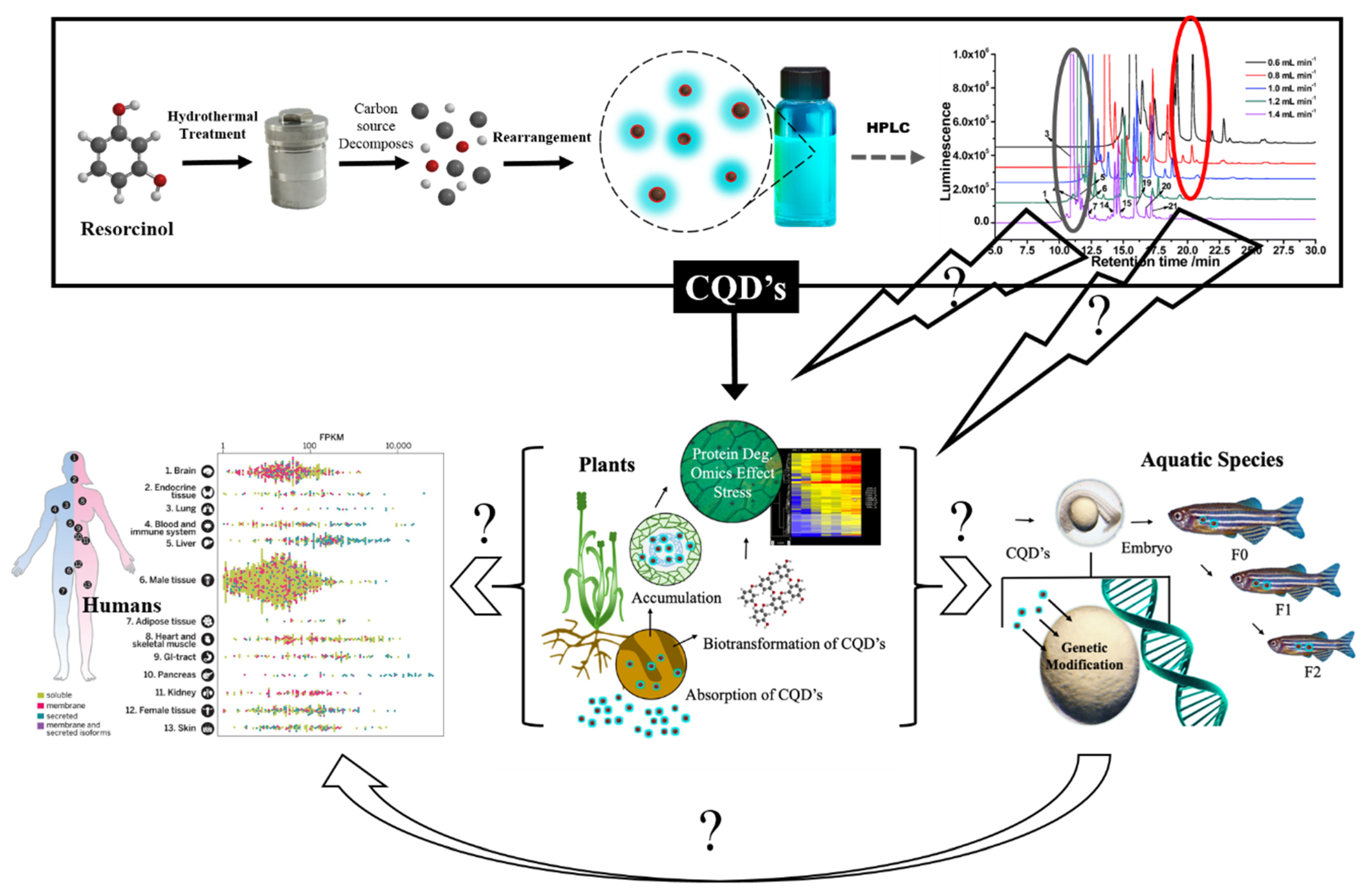
1. Introduction
2. CQDs in Plants
3. CQD Chemical Footprint and the Biome
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anmei, S.; Qingmei, Z.; Yuye, C.; Yilin, W. Preparation of carbon quantum dots from cigarette filters and its application for fluorescence detection of Sudan I. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1023, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandi, R.; Devulapalli, N.P.; Dadigala, R.; Gangapuram, B.R.; Guttena, V. Facile Conversion of Toxic Cigarette Butts to N,S-Codoped Carbon Dots and Their Application in Fluorescent Film, Security Ink, Bioimaging, Sensing and Logic Gate Operation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13454–13466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, S.W.; Adeleye, A.; Ji, Z.; Keller, A.A. Stability, metal leaching, photoactivity and toxicity in freshwater systems of commercial single wall carbon nanotubes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4074–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Meziani, M.J.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Luo, P.G.; Lin, Y.; Harruff, B.A.; Veca, L.M.; Murray, D. Carbon dots for multiphoton bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11318–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Yang, S.-T.; Wang, X.; Luo, P.G.; Liu, J.-H.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.-P. Competitive performance of carbon “quantum” dots in optical bioimaging. Theranostics 2012, 2, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.; Karak, N. A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8286–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, C.; Ribeiro, D.S.; Rodrigues, S.S.M.; Abreu, V.L.; Barbosa, J.A.; Prior, J.A.; Marques, K.L.; Santos, J.L. Application of quantum dots as analytical tools in automated chemical analysis: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 735, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R.H.; Monthioux, M.; Kane, A. Toxicology of carbon nanomaterials: Status, trends, and perspectives on the special issue. Carbon 2006, 44, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, G. Recent Advancements in Doped/Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Multi-Potential Applications. C—J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoo, J.M.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, M.J.; Lee, M.; Choi, S.; Kwon, S.H.; et al. Graphene quantum dots prevent α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Ou, C.-M.; Huang, C.-C.; Wu, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Lin, T.-E.; Ho, L.-C.; Wang, C.-W.; Shih, C.-C.; Zhou, H.-C.; et al. Carbon dots prepared from ginger exhibiting efficient inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4564–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, J.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Impacts of Carbon Dots on Rice Plants: Boosting the Growth and Improving the Disease Resistance. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Separation of carbon quantum dots on a C18 column by binary gradient elution via HPLC. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8124–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauter, M.S.; Elimelech, M. Environmental applications of carbon-based nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5843–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, M.J. Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6460–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Majumdar, S.; Servin, A.D.; Pagano, L.; Dhankher, O.P.; White, J.C. Carbon nanomaterials in agriculture: A critical review. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdari, P.; Negahdari, B.; Eatemadi, A. Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of carbon-based quantum dots: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Ma, C.; Xing, B. Distribution of different surface modified carbon dots in pumpkin seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. A biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water-soluble luminescent carbon nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12215–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.; Gopinath, P. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 2015, 140, 4260–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selck, H.; Handy, R.D.; Fernandes, T.F.; Klaine, S.J.; Petersen, E.J. Nanomaterials in the aquatic environment: A European Union-United States perspective on the status of ecotoxicity testing, research priorities, and challenges ahead. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servin, A.; Elmer, W.; Mukherjee, A.; De la Torre-Roche, R.; Hamdi, H.; White, J.C.; Bindraban, P.; Dimkpa, C. A review of the use of engineered nanomaterials to suppress plant disease and enhance crop yield. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, M.; Sharon, M. Carbon Nanoforms and Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, K.M.; Sonker, A.K.; Sonkar, S.K.; Sarkar, S. Pollutant soot of diesel engine exhaust transformed to carbon dots for multicoloured imaging of E. coli and sensing cholesterol. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30100–30107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xu, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Non-enzymatic-browning-reaction: A versatile route for production of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with tunable multicolor luminescent display. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, F.; Yi, X.; He, J.; Li, B. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Gynostemma for Bioimaging and Antioxidant in Zebrafish. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9832–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Cai, W.; Li, W.; Sreeprasad, T.S.; He, Z.; Ong, W.-J.; Li, N. Two-dimensional quantum dots: Fundamentals, photoluminescence mechanism and their energy and environmental applications. Mater. Today Energy 2018, 10, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Kuang, T.; Liu, Y.; Cai, L.; Peng, X.; Sreenivasan Sreeprasad, T.; Zhao, P.; Yu, Z.; Li, N. Heteroatom-doped carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization, properties, photoluminescence mechanism and biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7204–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Wei, J.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, C.; Sreeprasad, T.S.; Li, N.; Xia, Z. Synthesis, mechanistic investigation, and application of photoluminescent sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 9885–9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-T.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, G.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Luo, P.G.; Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M. Carbon dots as nontoxic and high-performance fluorescence imaging agents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18110–18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Lv, X.; Zheng, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z. Effects of Carbon Quantum Dots on Aquatic Environments: Comparison of Toxicity to Organisms at Different Trophic Levels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14445–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lan, M.; Zhu, X.; Xue, H.; Ng, T.-W.; Meng, X.; Lee, C.-S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Green Synthesis of Bifunctional Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Garlic for Cellular Imaging and Free Radical Scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Xie, G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, H.; Shan, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; et al. Bioimaging Application and Growth-Promoting Behavior of Carbon Dots from Pollen on Hydroponically Cultivated Rome Lettuce. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Sheng, Z.; Han, H.; Zou, M.; Li, C. Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots using watermelon peel as a carbon source. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, F.; Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X. The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: A review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peralta-Videa, J.; Sreenivasan, S.T.; Narayan, M. Influence of Carbon Quantum Dots on the Biome. Processes 2020, 8, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040445
Peralta-Videa J, Sreenivasan ST, Narayan M. Influence of Carbon Quantum Dots on the Biome. Processes. 2020; 8(4):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040445
Chicago/Turabian StylePeralta-Videa, Jose, Sreeprasad T Sreenivasan, and Mahesh Narayan. 2020. "Influence of Carbon Quantum Dots on the Biome" Processes 8, no. 4: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040445
APA StylePeralta-Videa, J., Sreenivasan, S. T., & Narayan, M. (2020). Influence of Carbon Quantum Dots on the Biome. Processes, 8(4), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040445






