Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Magnetized Hybrid Nanofluid with Joule Heating and Multiple Slip Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
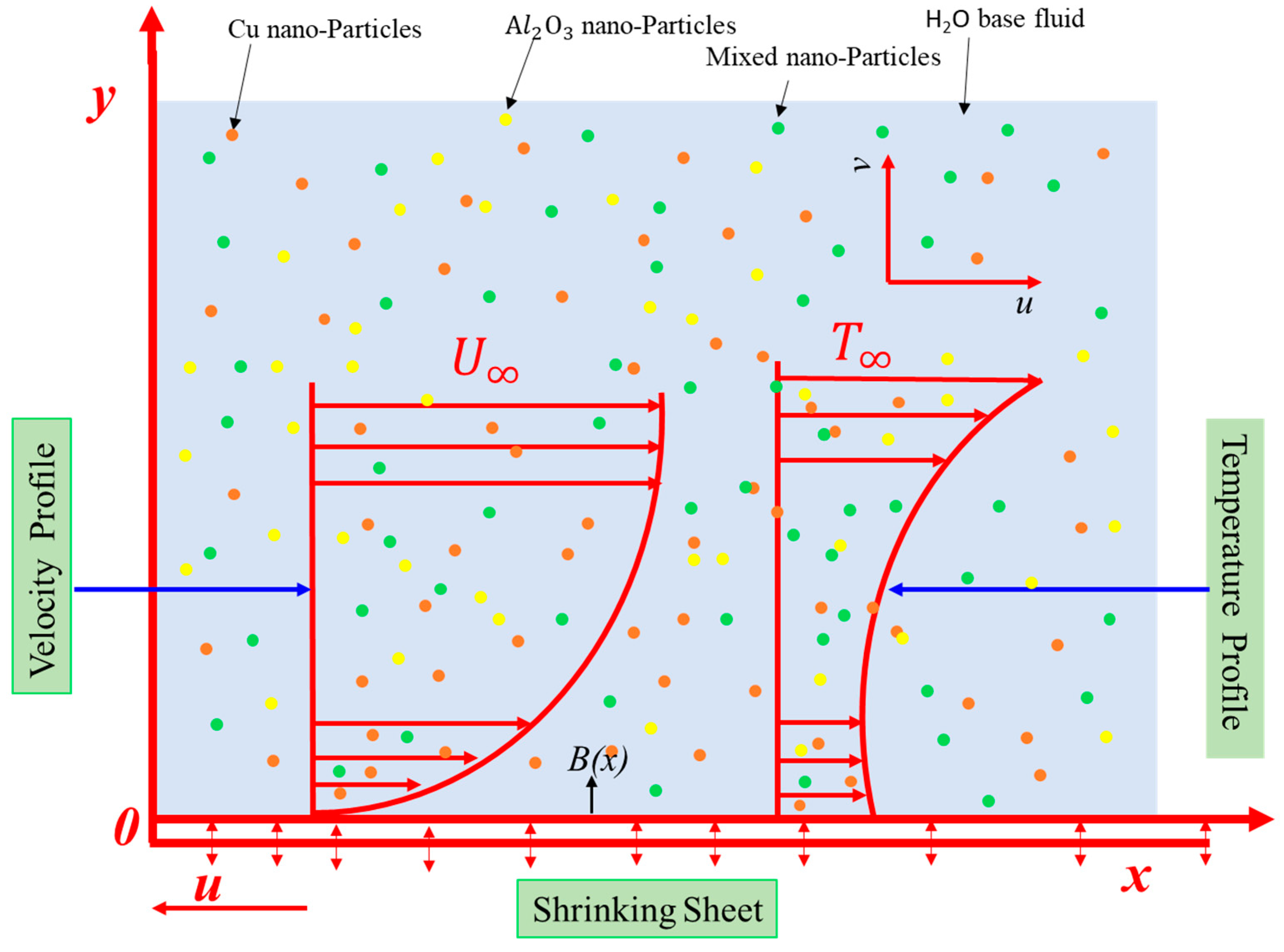
2. Mathematical Formulation
3. Stability Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- There exist two ranges of solution, namely dual solutions and no solution.
- Dual solutions do not exist beyond the critical values () of the parameters.
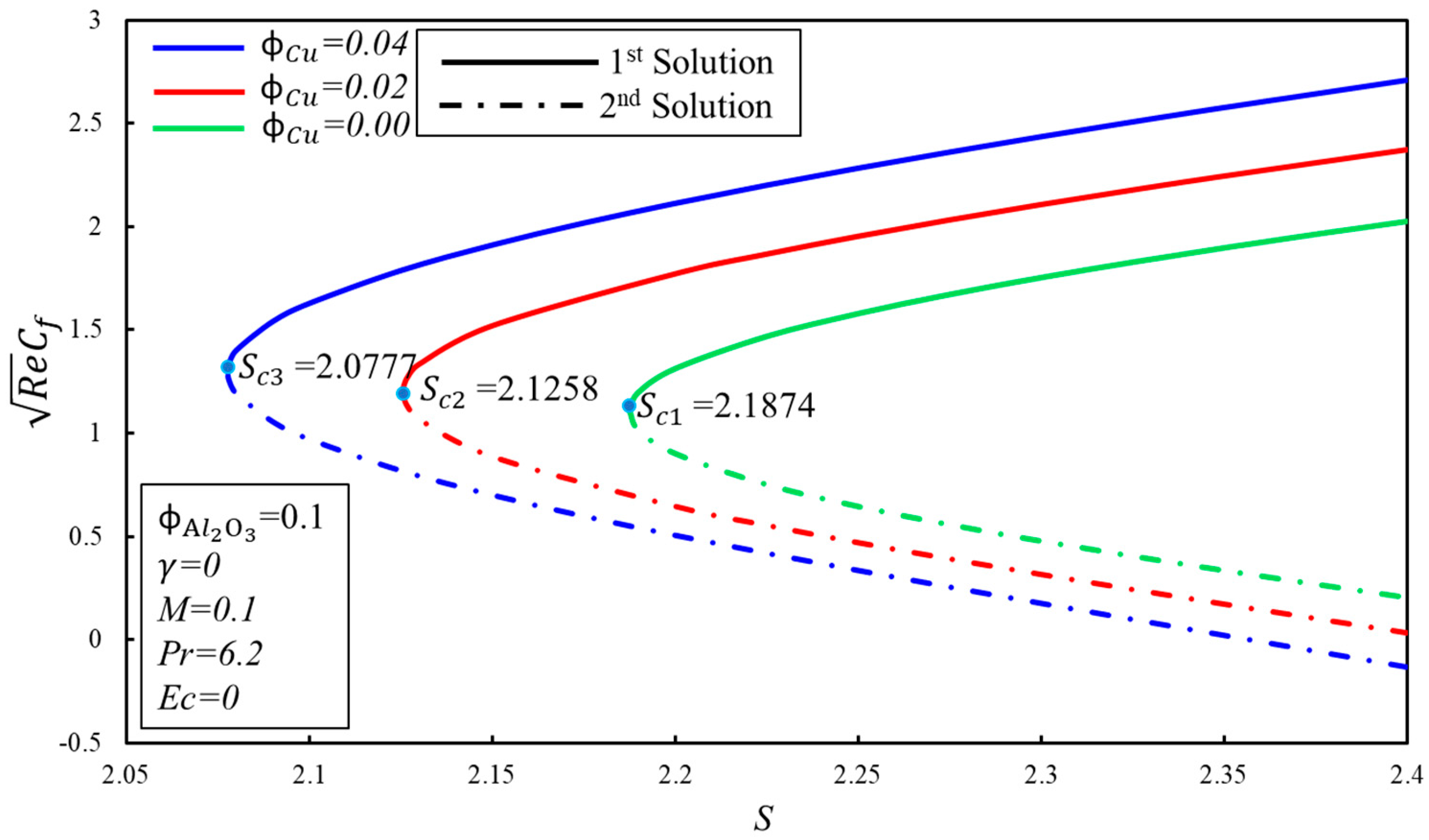
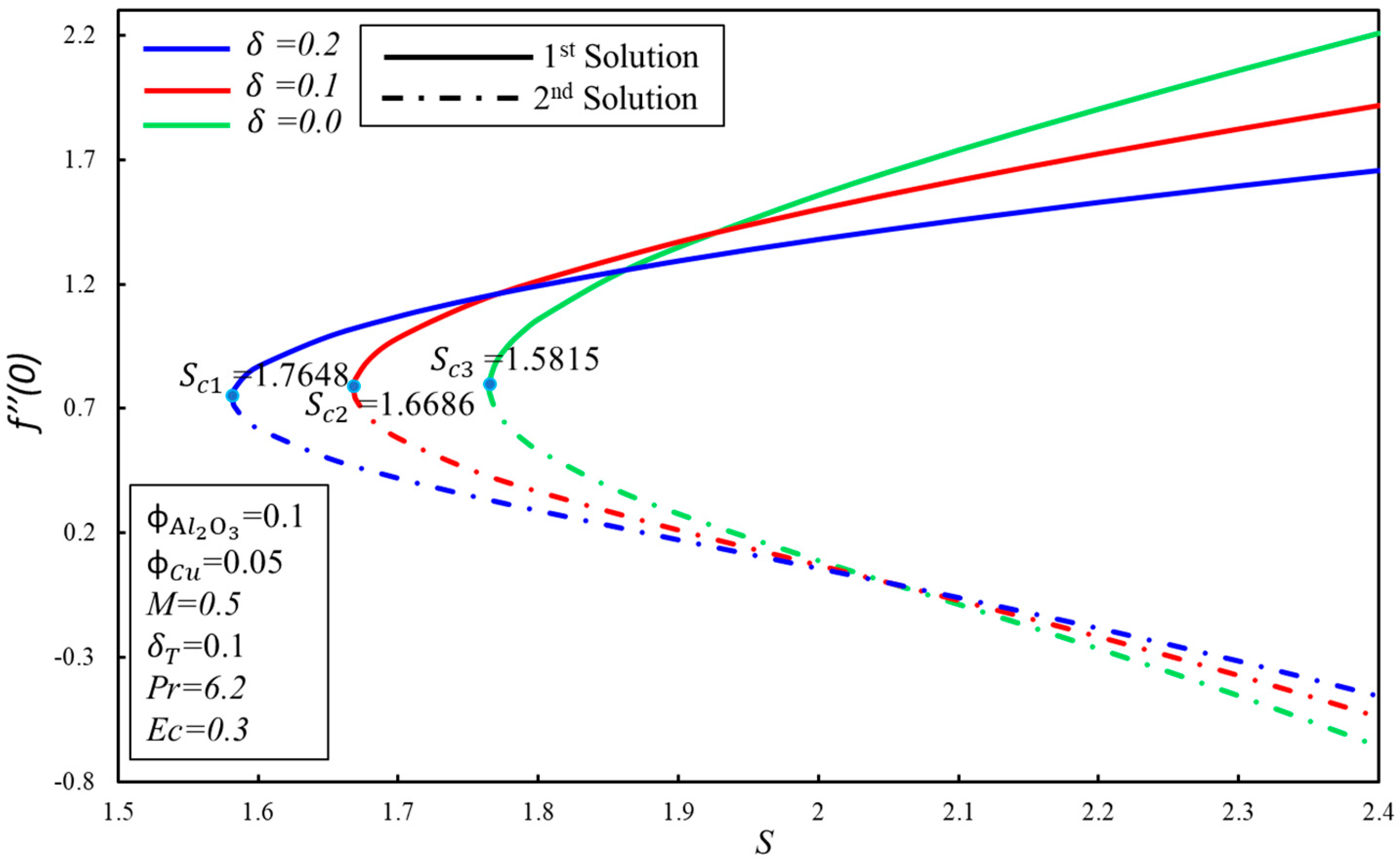
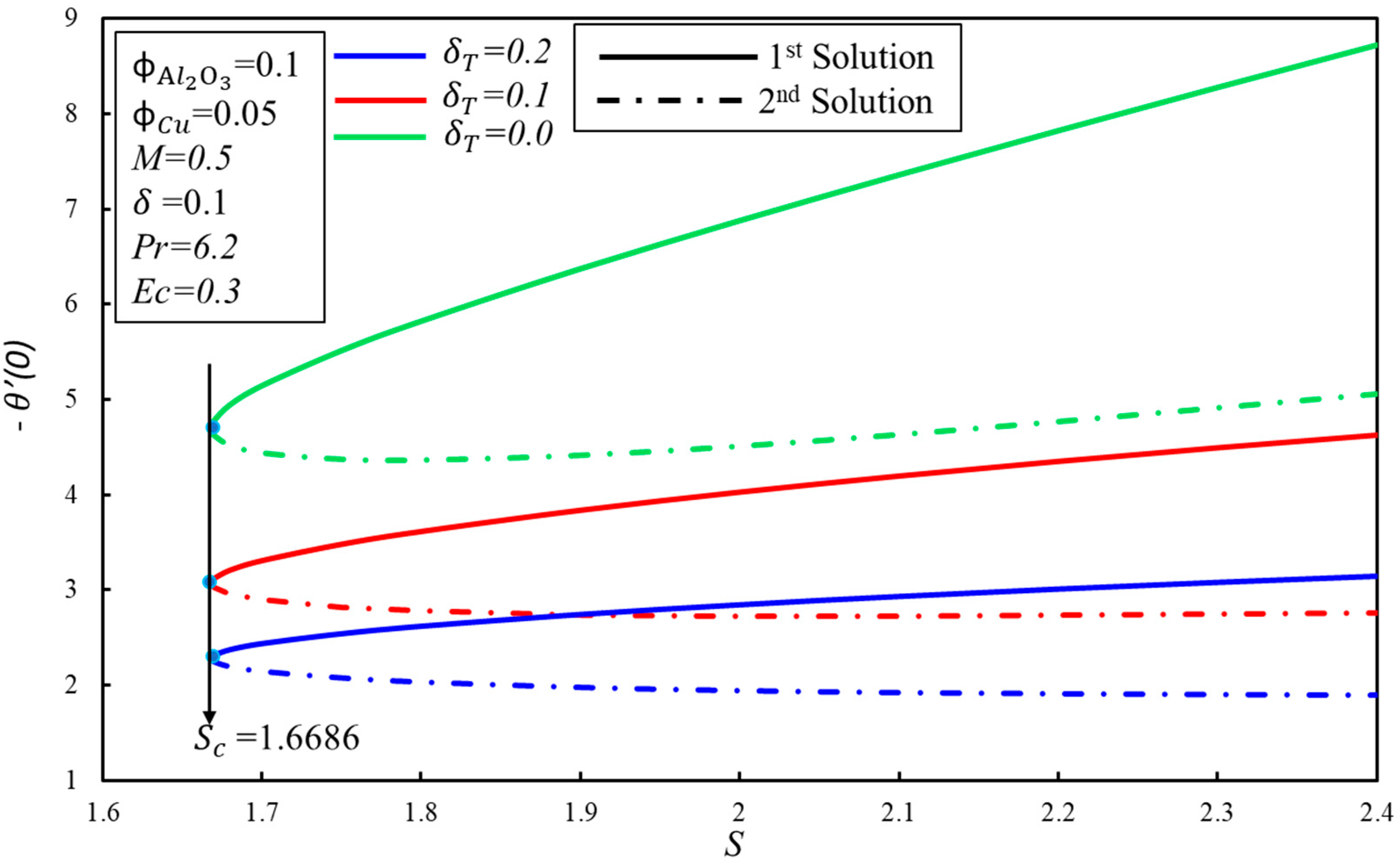
- The existence of dual solutions is possible in certain dimensions of the suction parameter .
- Due to the effect of Joule heating, the dual solutions also depend on certain ranges of the magnetic parameter, .
- The skin friction coefficient, , enhances for the first solution when the and parameters are increased, while reduces for the higher effect of the velocity slip factor, .
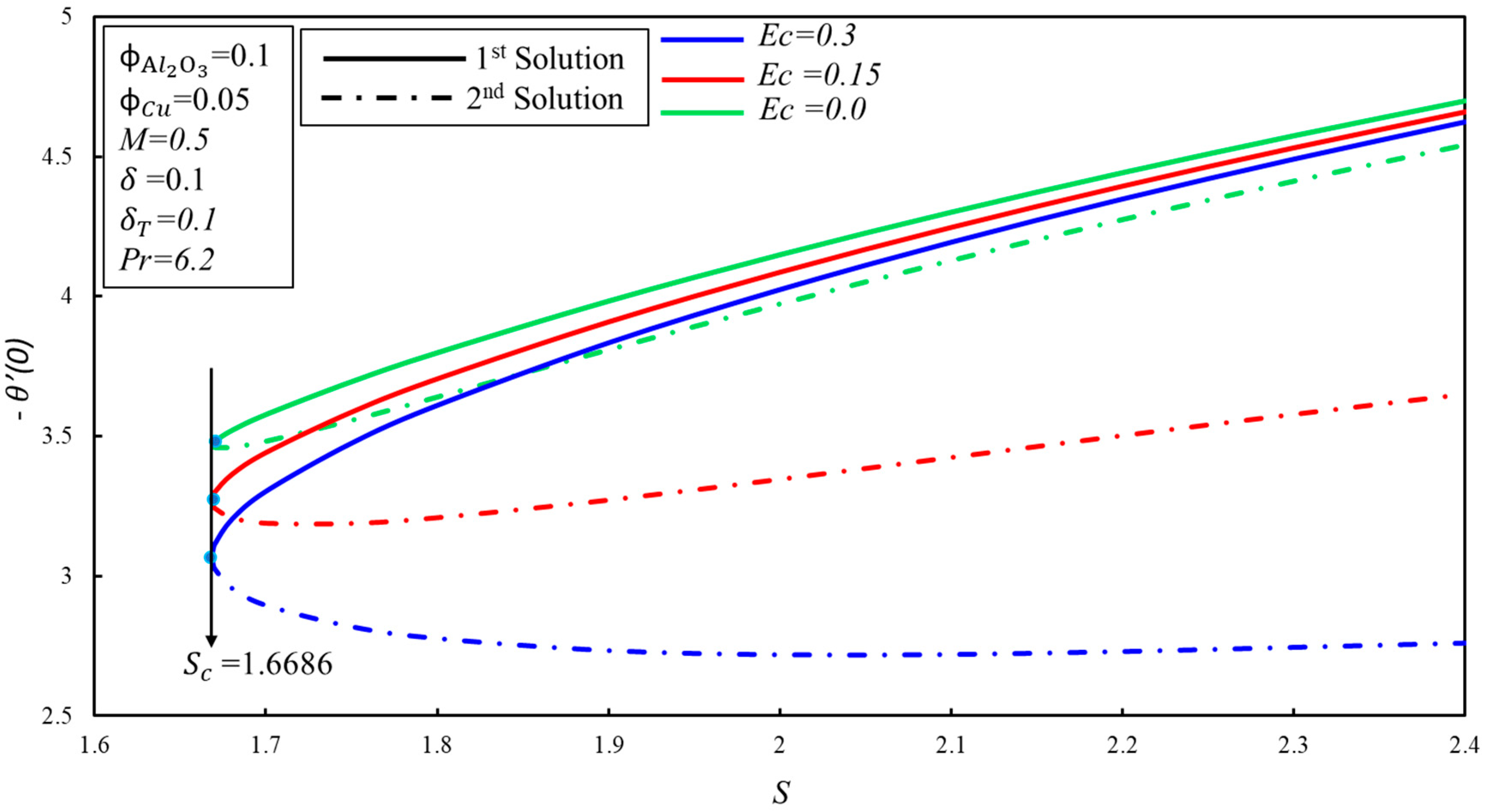
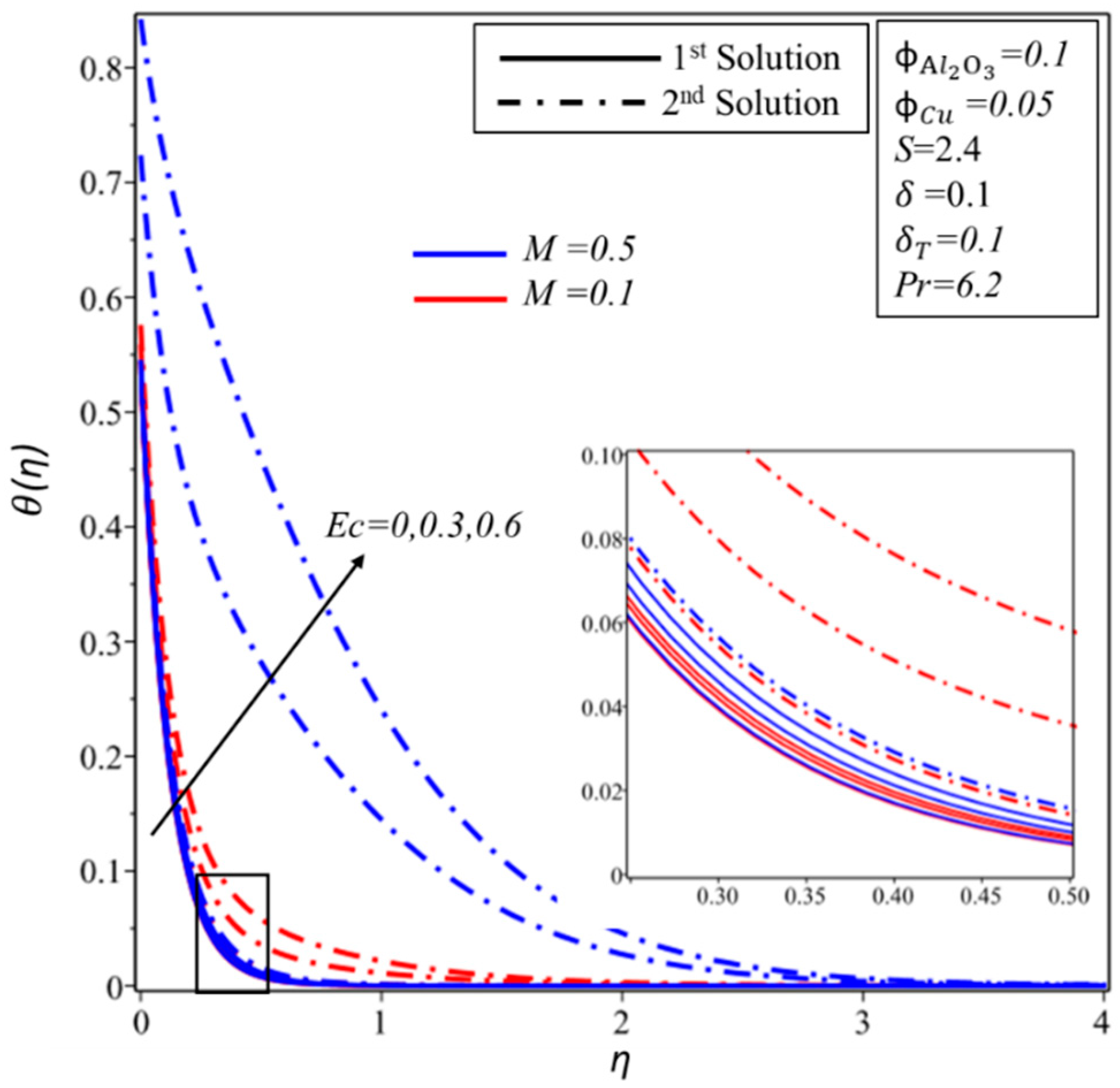
- The heat transfer rate, , reduces with increments in the Eckert number, , and the thermal slip parameter, ; however, Ec and do not affect the boundary layer separation.
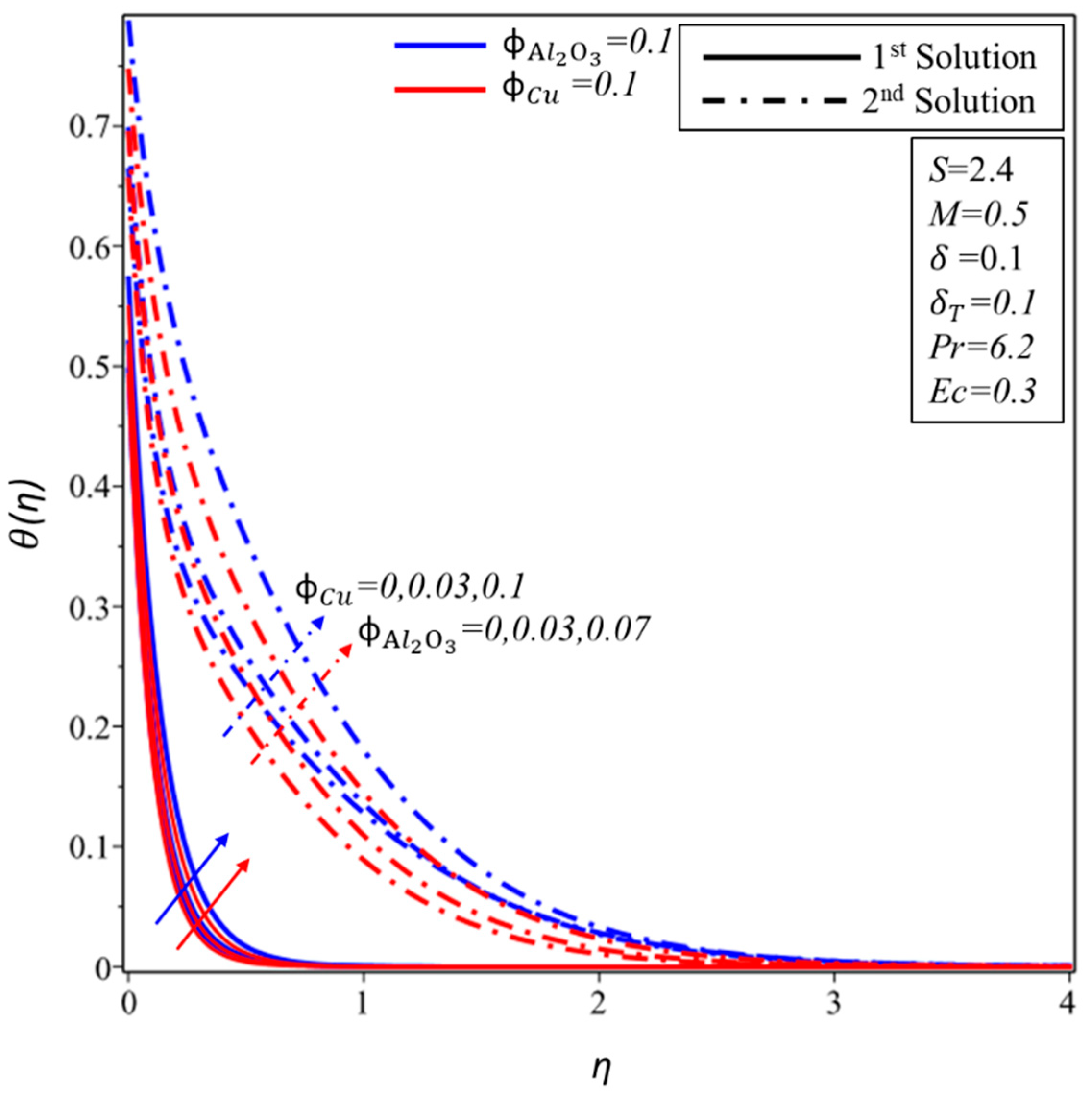
- The temperature and thermal boundary layer thickness have direct relationships with for both solutions.
- Positive smallest eigenvalues indicate the initial decay of the disturbance, and that the flow becomes the stable flow.
- The stability analysis indicates that the real solution is the first solution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.U.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; (No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135-29); Argonne National Lab.: Lemont, IL, USA, 1995.
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. Numerical study for external magnetic source influence on water based nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 106, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrajab, R.; Noghrehabadi, A.; Behbahani, M.; Hajidavalloo, E. An efficient enhancement in thermal conductivity of water-based hybrid nanofluid containing MWCNTs-COOH and Ag nanoparticles: Experimental study. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.S.; Raza, M.; Ellahi, R. Influence of induced magnetic field and heat flux with the suspension of carbon nanotubes for the peristaltic flow in a permeable channel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a moving surface in a flowing fluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.A.; Raza, M.; Mir, N.A.; Ellahi, R. Effects of different shapes of nanoparticles on peristaltic flow of MHD nanofluids filled in an asymmetric channel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Rohni, A.M. Stefan blowing and slip effects on unsteady nanofluid transport past a shrinking sheet: Multiple solutions. Heat Transf.—Asian Res. 2019, 48, 2047–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, U.; Khan, I.; Baleanu, D.; Nisar, K.S. Stability Analysis and Dual Solutions of Micropolar Nanofluid over the Inclined Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Convective Boundary Condition. Symmetry 2020, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Qasim, M.; Alderremy, A.A.; Noreen, S. Heat transfer enhancement using different shapes of Cu nanoparticles in the flow of water based nanofluid. Physica Scripta 2019, 95, 055209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Bhatti, M.M.; Ellahi, R.; Zeeshan, A.M.; Sait, S. Mathematical Analysis on an Asymmetrical Wavy Motion of Blood under the Influence Entropy Generation with Convective Boundary Conditions. Symmetry 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jaryani, P.; Amiri, A.; Rahimi, A.; Malekshah, E.H. Heat transfer and nanofluid flow of free convection in a quarter cylinder channel considering nanoparticle shape effect. Powder Technol. 2019, 346, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, J.; Moradikazerouni, A.; Shahsavar, A.; Afrand, M.; Salehipour, H.; Tran, M.D. Hydrothermal analysis of turbulent boehmite alumina nanofluid flow with different nanoparticle shapes in a minichannel heat exchanger using two-phase mixture model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 520, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Khan, I.; Rasool, G.; Sherif, E.S.M.; Sheikh, A.H. Influence of Single-and Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes on Magnetohydrodynamic Stagnation Point Nanofluid Flow over Variable Thicker Surface with Concave and Convex Effects. Mathematics 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Zhang, T.; Chamkha, A.J.; Shafiq, A.; Tlili, I.; Shahzadi, G. Entropy Generation and Consequences of Binary Chemical Reaction on MHD Darcy–Forchheimer Williamson Nanofluid Flow Over Non-Linearly Stretching Surface. Entropy 2020, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Synthesis of Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluids using two step method and its thermo physical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Effect of Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluid in heat transfer. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 38, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatundun, A.T.; Makinde, O.D. Analysis of Blasius flow of hybrid nanofluids over a convectively heated surface. In Defect and Diffusion Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 377, pp. 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattad, A.; Sarkar, J.; Ghosh, P. Hydrothermal performance of different alumina hybrid nanofluid types in plate heat exchanger. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhesh, D.; Kalaiselvam, S. Experimental analysis of hybrid nanofluid as a coolant. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, A.; Godini, A.; Sardari, P.T.; Toghraie, D.; Salehipour, H. Impact of variable fluid properties on forced convection of Fe3O4/CNT/water hybrid nanofluid in a double-pipe mini-channel heat exchanger. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Dixit, A.R.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, M. Novel uses of alumina/graphene hybrid nanoparticle additives for improved tribological properties of lubricant in turning operation. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.; Afrand, M.; Mehmandoust, B. Curve fitting on experimental data of a new hybrid nano-antifreeze viscosity: Presenting new correlations for non-Newtonian nanofluid. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 531, 120837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.A.; Devi, S.S.U. Numerical investigation of hydromagnetic hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with suction. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2016, 17, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.S.U.; Devi, S.A. Numerical investigation of three-dimensional hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with effecting Lorentz force subject to Newtonian heating. Can. J. Phys. 2016, 94, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Jana, R.N.; Makinde, O.D. MHD flow of Cu-Al2O3/Water hybrid nanofluid in porous channel: Analysis of entropy generation. In Defect and Diffusion Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 377, pp. 42–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mehryan, S.A.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Ghalambaz, M.; Chamkha, A.J. Free convection of hybrid Al2O3-Cu water nanofluid in a differentially heated porous cavity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Doostanidezfuli, A.; Izadpanahi, E.; Ghalambaz, M.J.A.P.T. Phase-change heat transfer of single/hybrid nanoparticles-enhanced phase-change materials over a heated horizontal cylinder confined in a square cavity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, A.U. Rotating flow of Ag-CuO/H2O hybrid nanofluid with radiation and partial slip boundary effects. Eur. Phys. J. E 2018, 41, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, F.; Ahmed, N.; Khan, U.; Waheed, A.; Rafiq, M.; Mohyud-Din, S.T. Thermophysical analysis of water based (Cu–Al2O3) hybrid nanofluid in an asymmetric channel with dilating/squeezing walls considering different shapes of nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sarkar, J. Particle ratio optimization of Al2O3 -MWCNT hybrid nanofluid in minichannel heat sink for best hydrothermal performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 165, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M. Experimental investigation of carbon dioxide cross-contamination in sorption energy recovery wheel in ventilation system. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2018, 39, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalambaz, M.; Roşca, N.C.; Roşca, A.V.; Pop, I. Mixed convection and stability analysis of stagnation-point boundary layer flow and heat transfer of hybrid nanofluids over a vertical plate. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Unsteady flow and heat transfer past a stretching/shrinking sheet in a hybrid nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 136, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Seikh, A.H.; Sherif, E.S.M.; Nisar, K.S. Stability analysis and multiple solution of Cu–Al2O3/H2O nanofluid contains hybrid nanomaterials over a shrinking surface in the presence of viscous dissipation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 9, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashi’ie, N.S.; Arifin, N.M.; Nazar, R.; Hafidzuddin, E.H.; Wahi, N.; Pop, I. Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Axisymmetric Flow and Heat Transfer of a Hybrid Nanofluid past a Radially Permeable Stretching/Shrinking Sheet with Joule Heating. Chin. J. Phys. 2019, 64, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H.; Pop, I. Stagnation-Point Flow and Heat Transfer Over an Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Sheet in Hybrid Nanofluid with Slip Velocity Effect: Stability Analysis. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 1366, p. 012002. [Google Scholar]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Hybrid nanofluid flow induced by an exponentially shrinking sheet. Chin. J. Phys. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Kadry, S.; Rho, S.; Mari, I.A.; Nisar, K.S. Effect of Viscous Dissipation in Heat Transfer of MHD Flow of Micropolar Fluid Partial Slip Conditions: Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavčič, M.; Wang, C. Viscous flow due to a shrinking sheet. Q. Appl. Math. 2006, 64, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Aziz, A. Viscous flow over a shrinking sheet with a second order slip flow model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Sakidin, H.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. Unsteady flow and heat transfer past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid: A revised model with stability and regression analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 261, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Transpiration effects on hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform shear flow. Alex. Eng. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S. Heat transfer enhancement with Ag-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M.; Simonson, C.J. Experimental effectiveness investigation of liquid-to-air membrane energy exchangers under low heat capacity rates conditions. Exp. Heat Transf. 2016, 29, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A. MHD micropolar nanofluid flow over an exponentially stretching/shrinking surface: Triple solutions. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2019, 56, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A.; Khan, I. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces. Energies 2019, 12, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Effect of Suction/Injection on Stagnation Point Flow of Hybrid Nanofluid over an Exponentially Shrinking Sheet with Stability Analysis. CDF Lett. 2019, 11, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, M.; Khan, N.A. Slip effects on fractional viscoelastic fluids. Int. J. Differ. Equ. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.I. Slip flow past a stretching surface. Acta Mech. 2002, 158, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Bég, O.A.; Ismail, A.I. Radiative convective nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking sheet with slip effects. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2015, 29, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.; Abbas, N. On both MHD and slip effect in Micropolar Hybrid nanofluid past a circular cylinder under stagnation point region. Can. J. Phys. 2019, 97, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, N.; Rehman, A.; Sadaf, H.; Iqbal, S. Study of Al2O3/copper–water nanoparticle shape, slip effects, and heat transfer on steady physiological delivery of MHD hybrid nanofluid. Can. J. Phys. 2019, 97, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Lund, L.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Raza, J.; Bakouri, M.; Tlili, I. Stability analysis of Darcy-Forchheimer flow of Casson type nanofluid over an exponential sheet: Investigation of critical points. Symmetry 2019, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Sherif, E.S.M. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of a Hybrid Nanofluid over a Stretching/Shrinking Sheet Executing MHD Flow. Symmetry 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1986, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I. Quadruple solutions of mixed convection flow of magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid over exponentially vertical shrinking and stretching surfaces: Stability analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 182, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidman, P.D.; Kubitschek, D.G.; Davis, A.M.J. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Properties | Hybrid Nanofluid |
|---|---|
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| Density | |
| Thermal conductivity | where |
| Heat capacity | |
| Electrical conductivity | where |
| Properties | Water (H2O) | Copper (Cu) | Alumina |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | S | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Solution | 2nd Solution | ||||
| 0.01 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2.48626 | −1.10767 |
| 0.05 | 2.81888 | −1.62610 | |||
| 0.1 | 3.07486 | −2.08072 | |||
| 0.1 | 3.11458 | −2.23019 | |||
| 0.3 | 3.19082 | −2.52303 | |||
| 0.5 | 3.26332 | −2.80767 | |||
| 2.75 | 2.91297 | −1.85553 | |||
| 2.5 | 2.54832 | −1.09550 | |||
| 2.25 | 2.15936 | −0.49407 | |||
| 0.1 | 1.89832 | −0.40155 | |||
| 0.2 | 1.64975 | −0.33685 | |||
| 0.3 | 1.44247 | −0.28945 |
| Pr | M | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Solution | 2nd Solution | ||||||
| 0.01 | 6.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.73018 | 12.53867 |
| 0.05 | 11.22377 | 10.95914 | |||||
| 0.1 | 9.63019 | 9.27579 | |||||
| 5 | 7.68933 | 7.24261 | |||||
| 3 | 4.48756 | 3.71706 | |||||
| 2 | 2.91926 | 1.84444 | |||||
| 6.2 | 0.1 | 9.63199 | 9.26130 | ||||
| 0.3 | 9.63543 | 9.23146 | |||||
| 0.5 | 9.63864 | 9.20009 | |||||
| 0.1 | 9.58876 | 7.37060 | |||||
| 0.2 | 9.53888 | 5.54111 | |||||
| 0.3 | 9.48900 | 3.71162 | |||||
| 0.1 | 4.83180 | 1.93313 | |||||
| 0.2 | 3.24108 | 1.30690 | |||||
| 0.3 | 2.43833 | 0.98712 | |||||
| 0.1 | 2.46617 | 1.01661 | |||||
| 0.2 | 2.47965 | 1.04232 | |||||
| 0.3 | 2.48722 | 1.06361 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, L.; Dero, S.; Khan, I.; Mari, I.A.; Baleanu, D.; Nisar, K.S.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Abdo, H.S. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Magnetized Hybrid Nanofluid with Joule Heating and Multiple Slip Conditions. Processes 2020, 8, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8030332
Yan L, Dero S, Khan I, Mari IA, Baleanu D, Nisar KS, Sherif E-SM, Abdo HS. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Magnetized Hybrid Nanofluid with Joule Heating and Multiple Slip Conditions. Processes. 2020; 8(3):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8030332
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Liang, Sumera Dero, Ilyas Khan, Irshad Ali Mari, Dumitru Baleanu, Kottakkaran Sooppy Nisar, El-Sayed M. Sherif, and Hany S. Abdo. 2020. "Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Magnetized Hybrid Nanofluid with Joule Heating and Multiple Slip Conditions" Processes 8, no. 3: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8030332
APA StyleYan, L., Dero, S., Khan, I., Mari, I. A., Baleanu, D., Nisar, K. S., Sherif, E.-S. M., & Abdo, H. S. (2020). Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Magnetized Hybrid Nanofluid with Joule Heating and Multiple Slip Conditions. Processes, 8(3), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8030332









